1. Introduction
Optimizing funding for in-patient care has been crucial for the Greek healthcare system [
1]. In 2011, Greece launched a new hospital reimbursement system, KEN, inspired by the DRG (Diagnosis Related Groups) concept. However, limitations arose due to absence of: i) proper medical classifications suited for a case mix system, ii) an automated DRG grouping tool, and iii) a process for cost adjustments. These limitations resulted in the KEN-system proving initially inadequate to provide fair and objective budget allocation among hospitals within the health system [
2,
3,
4].
Established by 2014 legislation the Greek DRG Institute, known as the National Center for Documentation and Costing of Hospital Services, hereinafter referred to as “KETEKNY”, and initially known as ESAN S.A, is an independent, self-governing body with a core mission to implement a fair and transparent system for hospital service costing and reimbursement. KETEKNY's central goal is to create an integrated system for scientifically-based costing and compensation of hospital care in Greece. This approach aims at promoting an evidence-based healthcare system, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. KETEKNY initially signed a License Agreement with the German limited liability company InEK GmbH to secure the rights to implement a DRG system in Greece, modelled after the German system. Since then, the Greek DRG system has been updated in two major revisions in 2019 and 2021. KETEKNY, drawing on best practices from around the world, focuses on developing, implementing, monitoring, and updating a Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) patient classification system.
In January 2021, the University General Hospital of Heraklion (PAGNI) was selected by KETEKNY to be the first to adopt the Greek DRG system because it covers a vast majority of hospital specialties and services. A Joint Ministerial Decision rendered by the Ministries of Health, Finance and Labor & Social Affairs was signed on 07/04/2021, which enabled PAGNI to apply the Greek DRG system coding guidelines on all inpatient cases and initiate the adaptation and/or provision of financial data. After another Joint Ministerial Decision on December 24, 2021, the rest of the hospitals in the healthcare region of Crete began applying the Greek DRG system coding guidelines to all inpatient cases. Subsequently, all the hospitals within the health region of Macedonia, as well as eight other hospitals throughout Greece, began applying the Greek DRG system following one more Joint Ministerial Decision on November 28, 2022. The remaining public hospitals, and three non-profit, private law legal entity (Papageorgiou General Hospital, Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center and Santorini General Hospital) applied the Greek DRG system after a final Joint Ministerial Decision December 21, 2023.
The implementation of a DRG system in a country raise concerns about the accuracy of medical coding [
5]. Since the quality of hospital discharge data has a significant impact on the allocation of cases to the DRG system, it is crucial to understand the relationship between case mix and accurate medical coding [
6]. Personnel training, monitoring quality standards, and setting clear standards and practical guidelines are aspects that should be taken into consideration at this stage of implementation. Countries like France addressed this challenge by further developing DRGs to control hospital activity and ensure medically appropriate care [
7]. This study aims at highlighting and illustrating alternative actions which can be implemented for achieving and/or improving reliable medical coding.
2. Materials and Methods
The concerns for medical coding accuracy, in parallel to the installation and reinforcement of medical coding control mechanisms in the phase of full implementation of the new DRG system, forced KETEKNY to develop a special digital platform to support a previously conducted audit project for medical coding, which was co-funded by the EU & the Greek Government, and was expected to highlight any problems in the coding of an incident, capturing the medical information contained in the patient's medical file, based on the Greek Coding Guidelines.
Τhe implementation of the project included current situation analysis, assessment of needs, development of a platform, auditing, analysis of results and training of healthcare professionals in the Clinical Coding of incidents by the DRG coding system.
During the project, the already grouped DRG cases from the first year of implementation in the region of Crete were examined. A sample of 133,922 cases, out of a total of 200,000, were analyzed and audited. The audit process consisted of the following stages:
Digitalization: The Greek DRG Institute developed a digital platform to support auditing, which resulted in the establishment and strengthening of medical coding control mechanisms. This intervention aimed to identify and address any discrepancies between the coding of a patient's medical record and the allocated DRG coding, based on the Greek Coding Guidelines. The platform boasts a highly sophisticated architecture. Data flows seamlessly directly from hospitals, and through secure connections, to KETEKNY's specialized grouper software and. On a single, user-friendly interface, the platform presents two key data sources:
Data from the grouper software which analyzes and classifies hospital medical coding data collected directly from hospitals' coders.
Individual patient medical files which provide comprehensive patient information for a holistic view.
This consolidated view empowers auditors to efficiently conduct controls by having all relevant information readily available on a single screen. Furthermore, the platform offers a range of user-friendly functionalities surrounding this core function:
Easy-to-use browsing menus for efficient navigation
Ability to make corrections and add notes for improved clarity
Feature to assign statuses to cases for better organization
Option to schedule meetings with therapists or physicians for further clarifications
These features streamline the auditing process and facilitate effective communication with medical personnel, all while maintaining the highest standards of data privacy. The platform is built upon a foundation of data anonymization and strict adherence to GDPR regulations.
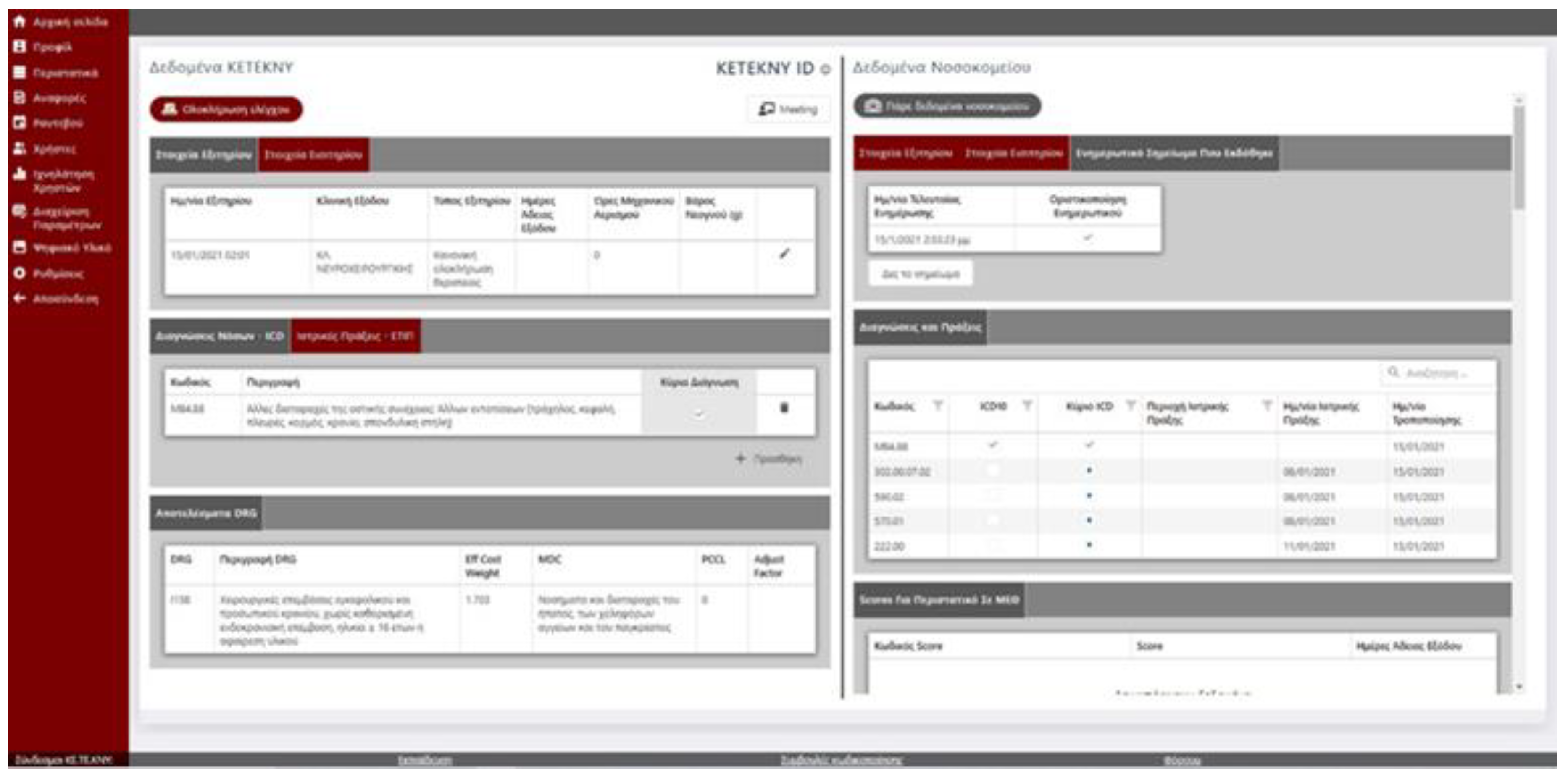
Figure 1.
Print screen from the digital platform.
Figure 1.
Print screen from the digital platform.
Auditors training: A team of highly skilled auditors underwent specialized training in medical coding according to the DRG classification system, conducted by experts from the Greek DRG Institute.
Control & consultation: Performed by specialized auditors, on a randomly selected sample of cases. The objectives of this processes were:
to verify the accuracy of the classification of incidents in DRG,
to ensure completeness, in accordance with the information obtained from the patient's medical file,
to assess whether coding adheres to the Greek Coding Guidelines,
to promptly address phenomena of under- and overcoding, which are identified in the international literature and are addressed through ongoing training for coders,
to enhance and streamline the process of medical recordkeeping, objectively showcasing the work performed by each hospital, to promote fair resource allocation within the healthcare system.
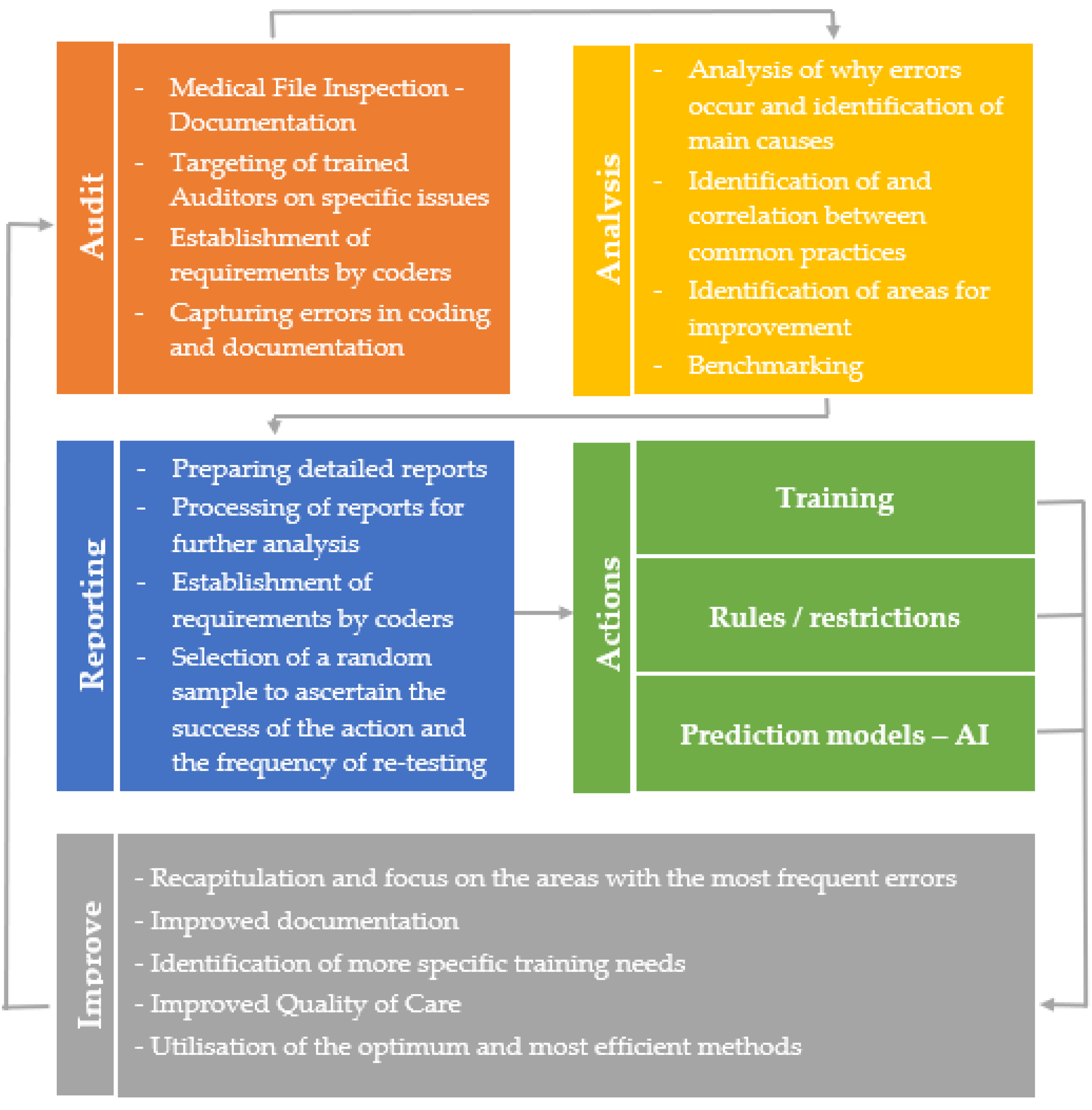
Ultimately, this shortens the coding learning curve, from four years typically reported in the international literature, to a more efficient duration of two years, leading to rational and documented clinical and financial management of hospitals. The audit platform and the results of the provision of medical coding control and consulting services will be used for the correct implementation of the DRG system by ensuring the quality of medical coding and the documented distribution of available resources in hospitals. These implemented actions can include highly targeted training sessions, for example focusing on the most frequent mistakes or errors. Additionally, interventions can be made that address both user experience and the medical file itself, potentially including the adoption of new, sophisticated rules or restrictions. Finally, prediction models can be adopted to suggest more accurate codes and schedule periodic controls. The flowchart in
Figure 2 illustrates the flow of the total process.
3. Results
The final report included a comprehensive analysis of the data obtained from the digital audit platform. This analysis occurred in two phases: the main audit project phase and a second phase focused on re-controlling a subset of cases for verification. The audit results were analyzed based on the following main categories of findings reflected in the digital audit platform:
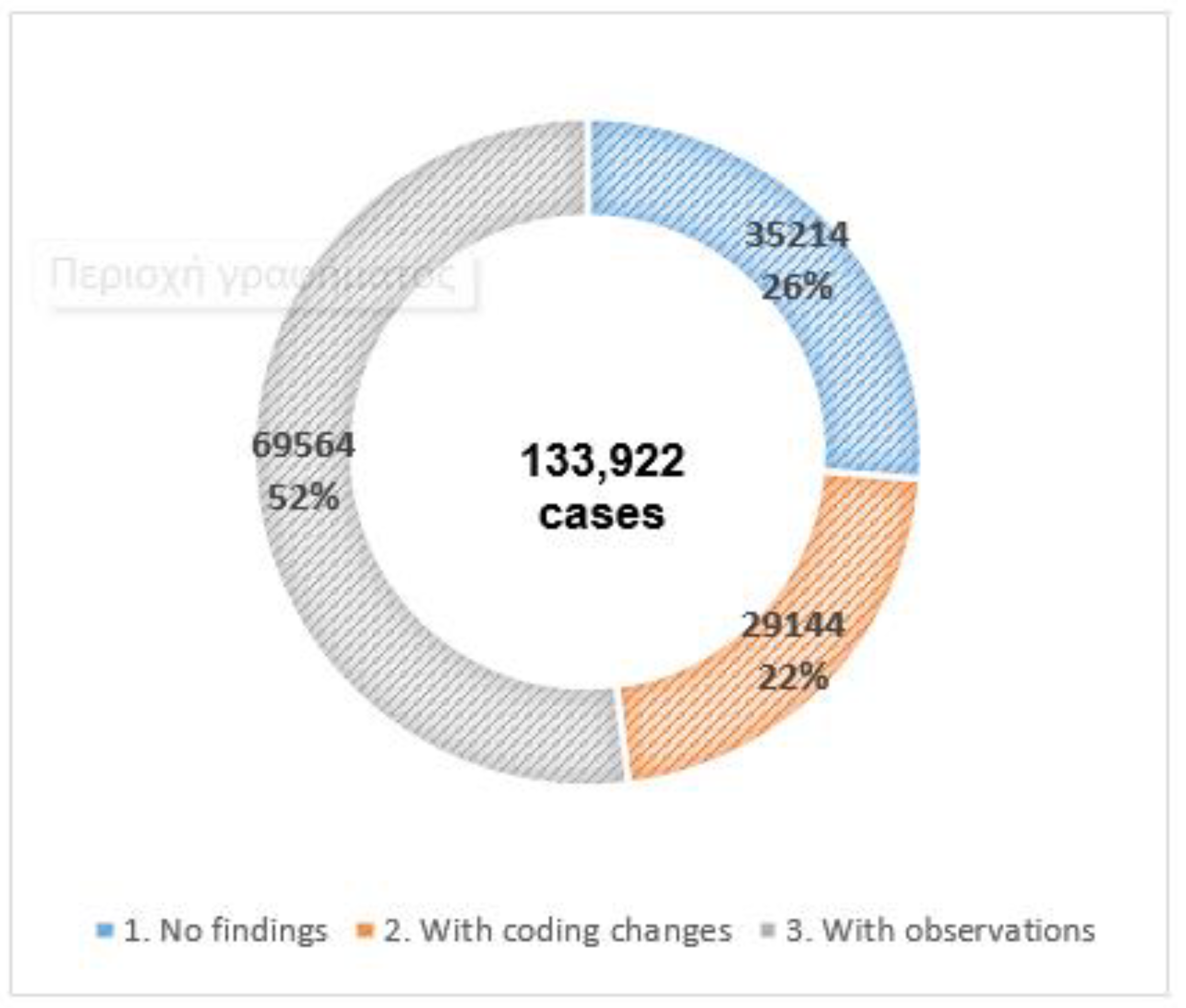
A complete analysis of a sample coded by the coders of the Hospitals of the Crete Healthcare Region indicated that 26.29% of the sample had no coding errors and was fully correct. 51.94% of the cases had observations and 21.76% of the overall sample required coding changes in the initial phase of the audit (Figure 1). An interesting finding was that only 6.7% of the 9,022 cases had their DRG code changed. The remaining cases (93.3%) had their original DRG codes unchanged. Of the cases changed, 13.91% remained within the same DRG group, but were assigned a code for more complex cases.
Figure 3.
Audit results of all cases based on three main categories of findings.
Figure 3.
Audit results of all cases based on three main categories of findings.
The analysis revealed discrepancies in various coding categories across cases. In more detail, 6.61% of the cases had a different primary diagnosis, 27.63% had a different secondary diagnosis, 17.62% had a different medical procedure and 0.75% had a different category regarding the pathological and surgical sector. Finally, 29.19% of the incidents reviewed were labelled as "Incomplete File" whereas 30.70% had absence of medical notice and practical surgery.
Regarding the re-checks phase, out of 46,762 re-checks reviewed by the project team's medical examiners, it was found that in 21.8% of the sample there were no findings and the coding was deemed correct, whereas 52.1% of the incidences resulted in observations, and 26.1% resulted in coding changes. Furthermore, 6.8% of the cases had a different primary diagnosis, 23.2% had a different secondary diagnosis, and 18.3% had a different medical procedure. Finally, 32.47% of the incidents reviewed were labelled as "Incomplete File", while 39.27% of the cases had absence of medical notice and practical surgery.
DRG-based payment systems can potentially reduce the LOS [
8]. Technological advancements also contribute to shorter LOS, as exemplified by minimally invasive procedures leading to faster healing and discharge times [
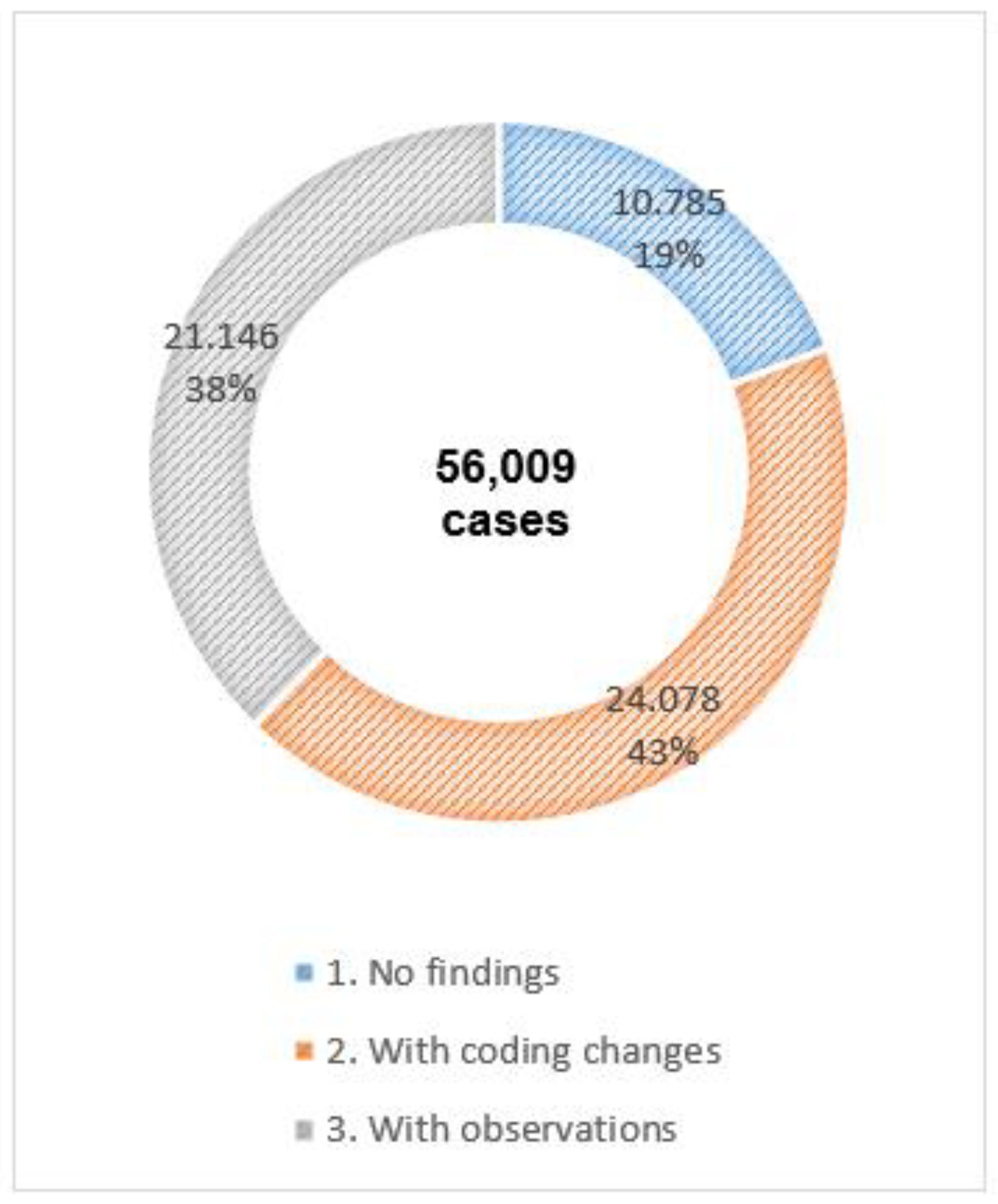
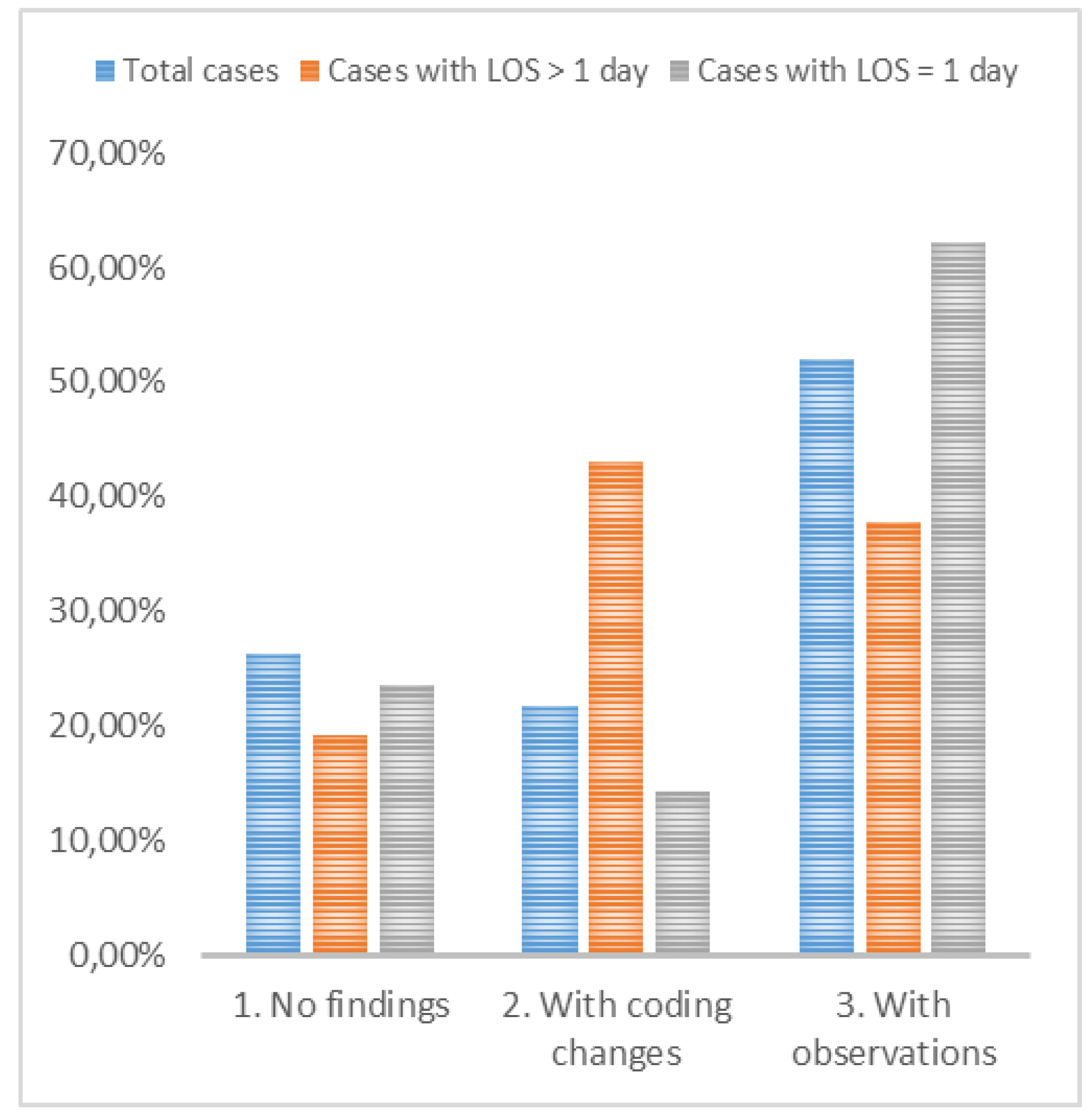
9]. However, the analysis excluded cases with a one-day LOS, which are typically less complex, simplifying medical coding for primary, secondary diagnoses and medical procedures. A second analysis was conducted for cases with a Los longer than one day. Among these cases, which represent 41.82% (56,009) of the total sample, 19.26% had no coding errors, 37.75% had some observations requiring further investigation, and the remaining 42.99% required coding changes (
Figure 4).
The analysis revealed that cases with a LoS exceeding one day were nearly twice as likely to require coding changes, compared to total cases and three times more than the ones with LOS equal to one (
Figure 5). The analysis revealed that 12.35% of DRG codes required changes. This is a significant finding, as it represents a nearly two-fold increase compared to the overall case analysis. Among the changed codes, 16.72% remained within the same DRG group, possibly due to minor coding adjustments. More significantly, 90.92% of the DRGs which remained in the group resulted in upgrades to higher-valued DRGs, suggesting increased resource utilization or case complexity. The remaining 9.75% of changes involved downgrades to lower-valued DRGs, which may indicate coding errors that initially attributed a higher acuity level than was accurate.
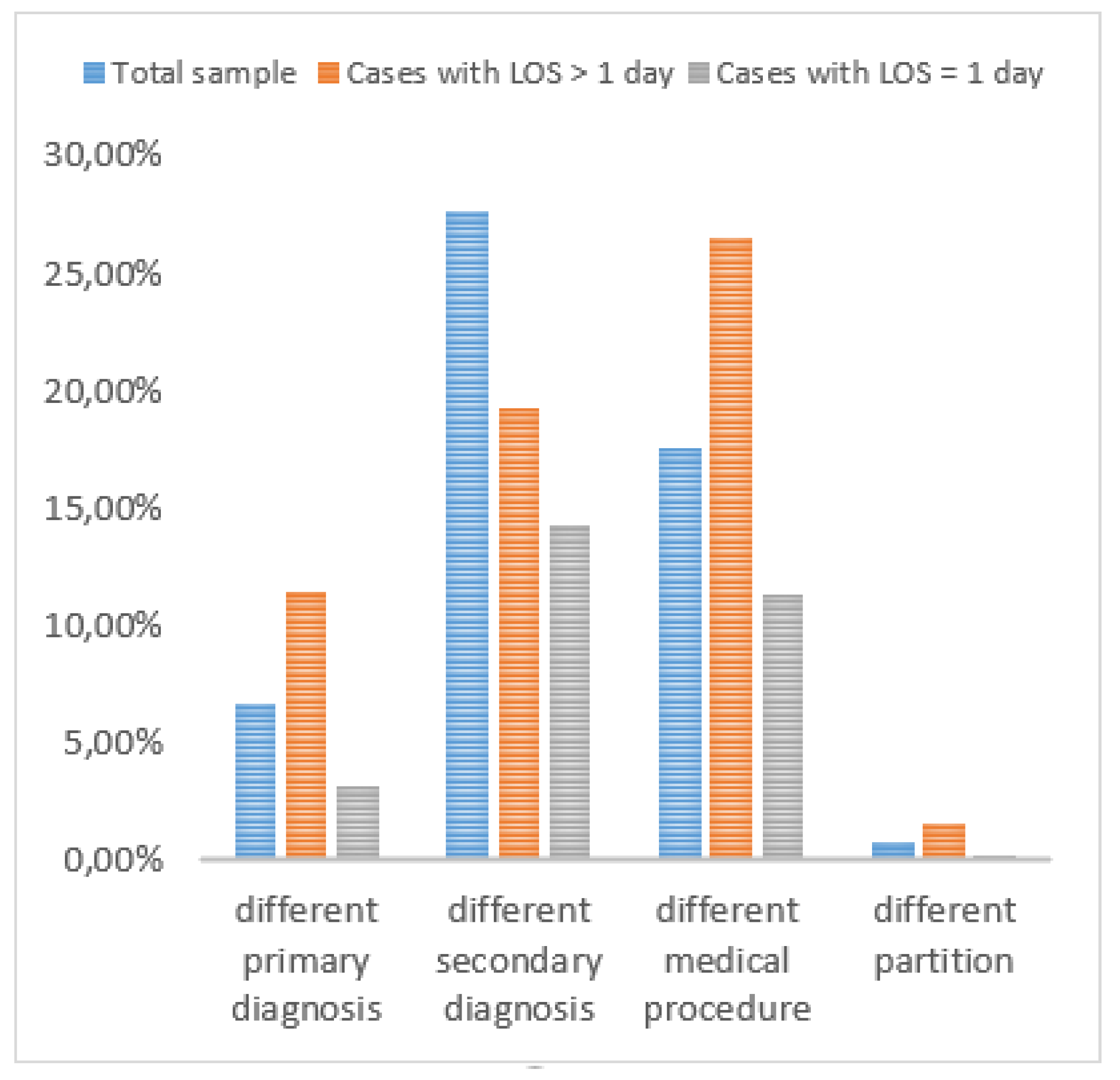
A significant analysis finding is the presence of discrepancies in coding categories across cases in comparison with the total sample (
Figure 6). Notably, 11.40% of cases had a different primary diagnosis, 19.26% had a different secondary diagnosis, and a substantial 26.54% involved a different medical procedure code. Interestingly, discrepancies within the pathological and surgical partition category were much lower at only 1.60%. The above finding highlights the importance of auditing the primary diagnosis and the medical procedure of the cases that have LOS longer than one day.
To further support the findings regarding the relationship between DRG codes requiring changes, and a LoS exceeding one day, a chi-square test of independence was performed to assess the significance of the association between these two categorical variables. Crosstabulation was used to visualize this relationship (
Table 1).
To test the hypothesis that LoS influences medical coding, resulting in cases requiring DRG code changes. The Pearson chi-square test was yielded a chi-square value of 4824.574 and a p-value of <0.001 (
Table 2), which suggests that DRG code changes is likely dependent on LoS, particularly for stays equal to one day and exceeding one day.
Taking the analysis a step further, the relationship between LoS exceeding one day and DRG code changes across different hospitals was examined (
Table 3). It can be concluded that there is a statistically significant association between hospitals and DRG code changes (
Table 4), which suggests a need for more targeted and tailored actions to be implemented at hospital level.
Results also indicated that a significant proportion of DRGs were reclassified by the auditors into different DRGs, with most being recoded to higher cost weighted DRGs. This reclassification could lead to a substantial increase in hospital revenue. To investigate how hospital revenue was affected, we examined whether the DRG assignment after the audit improved or worsened revenue to the same extent for all hospitals. The ordinal DRG change data (unchanged, improved, worsened) was categorized for each hospital and compared using non-parametric tests.
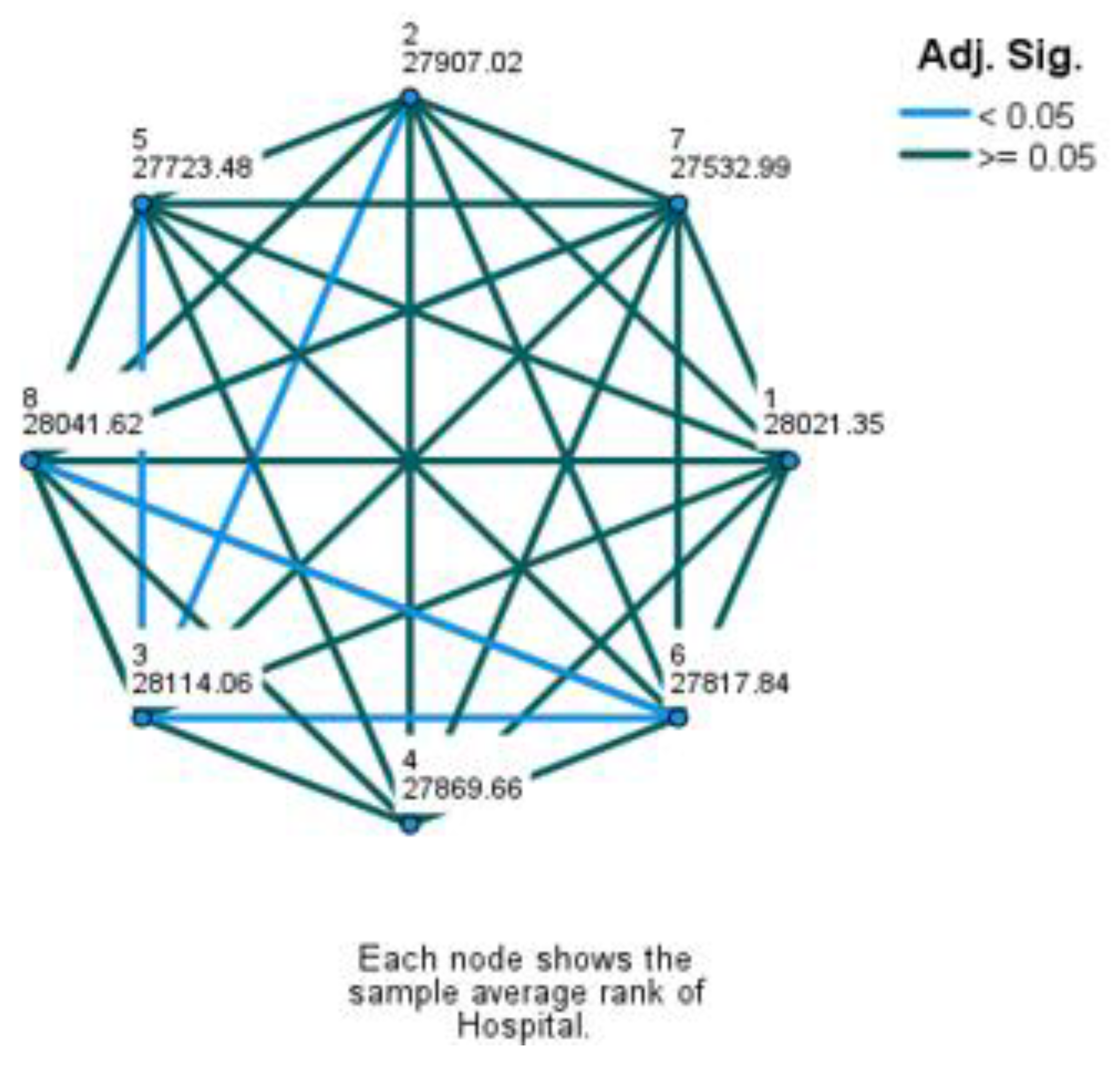
The Kruskal-Wallis H test revealed a statistically significant difference (χ2(2) = 40.005, p < .001) in how DRG changes impacted revenue across hospitals. The mean rank scores were: Hospital 1 (28021.35), Hospital 2 (27907.02), Hospital 3 (28114.06), Hospital 4 (27869.66), Hospital 5 (27723.48), Hospital 6 (27817.84), Hospital 7 (27532.99), and Hospital 8 (28041.62). Since the null hypothesis of the Kruskal-Wallis test was rejected, indicating an overall difference, it was proceeded with Dunn's test for non-parametric pairwise multiple comparisons to identify which hospitals have statistically different outcomes in revenue change (results are illustrated on
Figure 7).
Considering cases with a LoS exceeding one day, the primary errors stemmed from various coding issues. These issues included omitting secondary diagnoses and medical procedures that should have been coded, and using overly general codes. Analyzing and comparing cases with a LOS exceeding one day underscores the importance of targeted analysis and action based on different patient segments. This is because the results can vary significantly when examined from different perspectives. Beyond LOS, analysis could be further conducted by hospital, clinic, major diagnostic category, admission type, and other relevant factors.
4. Discussion
These findings form this study indicate that the provision of medical coding control and consulting services can be instrumental in the proper implementation of the DRG classification system, by fostering accurate medical coding and ensuring transparent allocation of resources within hospitals. The main actions that can be regulated and adopted for the proper implementation of the DRG system might include correct and complete entry of all medical data into the electronic medical record to ultimately retrieve correct information, as well as correct coding of all necessary medical information. By classifying patients into DRGs based on their condition, hospitals can improve the accuracy of medical records and ensure they are receiving appropriate reimbursement, ultimately leading to higher quality healthcare [
10].
In Greece, the DRG system has been connected to the majority of public hospitals' digital patient files. This in itself is an opportunity for the coding software to be further developed to do more than suggest codes or prevent coder errors through pre-programmed rules and edits based on official coding manuals. It can also be developed to check the assigned diagnosis and procedure codes for accuracy [
5]. Initial rules and restrictions have been implemented, such as preventing coders from making errors based on age/sex, and prohibiting assistance in the coding process using "balloons" (which likely refers to prompts or suggestions). It can also be further developed to identify potential coding errors. This could involve a coding and validation process that checks for missing codes or incorrect code combinations.
Additionally, by applying coding logic, the software could highlight cases where a certain procedure wouldn't typically be performed for a specific diagnosis, prompting the coder to review the case in real-time. A coding system like this could be implemented by checking the medical materials used during a hospitalization and the invasive medical procedures performed. For example, if medical materials are used, but no corresponding medical procedure is coded, the software would prevent the case submission until the medical procedure is documented. Furthermore, analyzing the data can lead to more sophisticated methods for adding value to coding quality. This includes filtering data, adding rules and improving user experience of medical data records. For instance, adding DRG information to the home page of medical records can provide a solid foundation for both a comprehensive evaluation of DRG effectiveness and improvements in overall medical quality [
11].
Deep learning and artificial intelligence techniques can also be used to develop DRG prediction models for accurate identification of primary diagnosis, secondary diagnosis, and medical procedures. The platform serves as a core component of the data analysis architecture for DRG prediction. Utilizing deep supervised learning approaches, it can assess the quality and completeness of the database. Additionally, the platform can enforce the creation of labeled datasets for both training and testing phases. These deep learning models measure their accuracy using a loss function and adjust their weights until the error is minimized sufficiently [
12,
13]. Studies have shown that deep learning models can achieve high accuracy in predicting DRGs' primary diagnosis. Implementing an automated DRG coding system based on these models could help reduce incorrect coding, leading to increased hospital revenue, fairer allocation of medical resources, and improved hospital performance [
14,
15].
Another important action that can be adopted is the organization of post-audit training of coders (physicians) who must know what findings were made, be aware of miscoding, and adhere to the rules of DRG coding. KETEKNY has already organized the first presentation of this finding and plans to further adapt it. In the Greek DRG system, physicians currently handle the coding of cases. While this allows them to describe each incident in greater detail and more consistently, surveys indicate that many hospitals are hesitant to transition entirely to specialist coders [
16]. Customized and targeted training is suggested, with material that is enriched by the results of the audits with coding quality [
17]. These trainings can be highly targeted and adaptive to small group training when necessary - Sometimes post-test training is effective at a large group level, but sometimes it still needs to be one-on-one to maximize effectiveness.
This project should be viewed as groundwork for future activities such as implementation of a permanent sample control process through the KETEKNY platform, with a selection of cases under medical and other criteria from cases of all Greek hospitals, in order to ensure to the greatest extent possible, correct recording of hospitalization data both in the medical file and in Grouper, ensuring the matching of the cases to the correct DRG. One strategy that could be adopted is to scale audit frequency based on past performance in medical coding. Hospitals with a strong track record would undergo fewer audits, while those with lower performance would be subject to more frequent audits. Currently, the KETEKNY platform connects directly with the hospitals' electronic patient files. It complies with GDPR regulations and aims to expand this direct connection to the rest of the Greek healthcare region. Concurrent implementation of all the above actions, alongside with the already assignment of responsibility for the Gr-DRG system to an independent, self-governing body, can achieve a clear strategic objective: optimal resource allocation among all hospital care providers in Greece. This approach would also support the establishment of clear standards and practical guidelines, with all the necessary legal and policy support.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.P. and L.P.; methodology, K.C.; software, P.S.; validation, L.P., C.P. and N.K.; formal analysis, L.P.; investigation, C.P.; resources, P.M.; data curation, P.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.P.; writing—review and editing, N.K..; visualization, K.C.; supervision, L.P.; project administration, P.M.; funding acquisition, K.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
EU & Greek Government.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Polyzos, N.; Karanikas, H.; Thireos, E.; Kastanioti, C.; Kontodimopoulos, N. Reforming reimbursement of public hospitals in Greece during the economic crisis: Implementation of a DRG system. Health Policy 2012, 109, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotopoulos, P.; Maniadakis, N.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Petkasidis, D. An evaluation of Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) implementation focused on cancer DRGs in Greek public hospitals. PharmacoEconomics 2020, 4, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigas, C.; Theodorou, P.; Karagianni, R.; Psomiadi, ME.; Platis, C. Exploring the perception of medical personnel regarding DRGs Implementation in Greek public hospitals. Int. J. Caring Sci. 2022, 15, 332. [Google Scholar]
- Rodosthenous, M.; Roumeliotis, E. Adjusting the costing/pricing systems of public health units in times of emergency health crises: The case of Greece. KnE Soc. Sci. 2021, 5, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongpirul, K.; Walker, DG.; Winch, PJ.; Robinson, C. A qualitative study of DRG coding practice in hospitals under the Thai universal coverage scheme. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2011, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Calderón, V.; Figueiras Huante, I.A.; Carbajal Martínez, M.; Yacaman Handal, R.E.; Palami Antunez, D.; Soto, M.-E.; Gabriela Koretzky, S. The impact of improving the quality of coding in the utilities of Diagnosis Related Groups system in a private healthcare institution. 14-year experience. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 129, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, F.; Sabahi, A.; Ramezanghorbani, N.; Emami, H. Challenges of implementing diagnostic-related groups and healthcare promotion in Iran: A strategic applied research. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yan, J.Q.; Xue-Tang; Qian, M. C.; Ying, X.H. Impact of Diagnosis-Related Groups on inpatient quality of health care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inquiry 2023, 60, 469580231167011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scheller-Kreinsen, D.; Quentin, W.; Busse, R. DRG-based hospital payment systems and technological innovation in 12 European countries, Value Health 2011, 14, 1166–1172. 14.
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Application of DRGs in hospital medical record management and its impact on service quality. Int J Qual Health Care 2022, 34, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaohua, C.; Wang, J.; Su, Z. Impact of improving the quality of medical coding on comprehensive evaluation of DRG performance on the home page of medical records. Hosp. Adm. Med. Pract. 2023, 2, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Talaei Khoei, T.; Ould Slimane, H.; Kaabouch, N. Deep learning: systematic review, models, challenges, and research directions. Neural Comput & Applic 2023, 35, 23103–23124. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Hasan, M.; Van Essen, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.S.; Asari, V.K. A state-of-the-art survey on deep learning theory and architectures. Electronics 2019, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, MM.; Li, GH.; Poly, TN.; Li, YJ. DeepDRG: Performance of artificial intelligence model for real-time prediction of Diagnosis-Related Groups. Healthcare (Basel) 2021, 9, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alowais, SA.; Alghamdi, SS.; Alsuhebany, N.; et al. Revolutionizing healthcare: the role of artificial intelligence in clinical practice. BMC Med Educ 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, F.; Walgenbach, M.; Göbel, P.; Parbs, S.; Neugebauer, E. Ist die Kodierung im Krankenhaus zu wichtig, um sie Ärzten zu überlassen? – Evaluation der betriebswirtschaftlichen Effizienz von Gesundheitsökonomen an einem Zentrum der Maximalversorgung [Is DRG Coding too Important to be Left to Physicians? - Evaluation of economic efficiency by health economists in a university medical centre]. Z. Orthop. Unfall, 2017; 155, 177–783. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Quan, L. Comprehensive evaluation of disease coding quality in gastroenterology and its impact on the diagnosis-related group system: a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).