Introduction
Heterogeneous photocatalyst are extensively used for wastewater treatment because of its higher effectiveness in the removal of recalcitrant pollutants and harmful bacteria during the UV-Solar irradiation [
1]. The process is based on the photo-activation of semiconductor nanoparticles (TiO₂, SiO₂, Al₂O₃, ZnS) through visible light irradiation. The photo-catalytic oxidation lead to the generation of reactive oxidizing species (commonly OH radical) which can cause the degradation of organic pollutants and denaturation of microbes [
2]. The photo-activation of nanomaterials is the transition at ambient temperature of an electron (e
−) from the valence band (VB) to the conduction band (CB) due to the absorption of photons having equal or higher energy than the bandgap energy [
3]. This absorption generates oxidizing sites known as holes (h
+) in the valence band that may react directly with the pollutants. This process can lead to the total degradation of toxic pollutants to harmless species such as carbon dioxide and water [
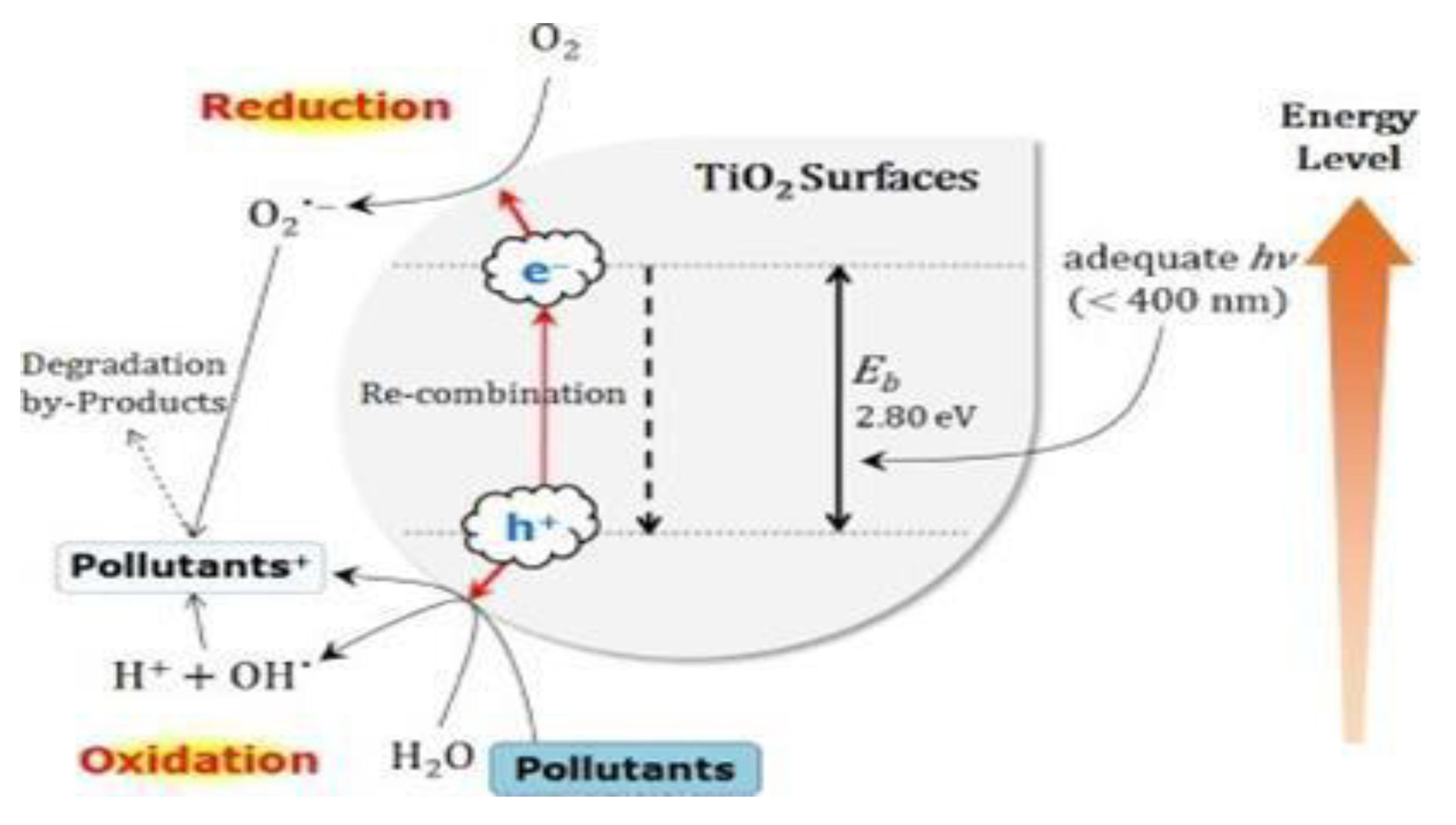
4]. The mechanism of photocatalytic activation in the TiO₂ was as demonstrate [
5].
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of photo-catalytic activation in the TiO2 on removal of pollutants.
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of photo-catalytic activation in the TiO2 on removal of pollutants.
Titanium dioxide, TiO₂ is the ideal semi-conductor nanoparticle used in the photo-catalytic processes due to its thermochemical stability, cost effectiveness, availability, high reactivity under light irradiation and low toxicity [
6]. The high chemical stability of TiO₂ is one of its major advantages over other common heterogenous photocatalysts [
7]. However, TiO₂ shows photo-physical limitations due to its large energy bandgap (3.0 - 3.20 eV) which limits its activity to only the UV range (5%) of electromagnetic spectrum [
8]. Reductions in the energy band gap of TiO₂ will facilitate its application as a photo-catalyst and enhances the photo-physical utilization of larger percentage of natural solar light. This can be achieved by modifying the TiO₂ with compounds such as metal and non-metal [
9].
Titanium (IV) Oxide (Tio2) Modifications of Enhanced Solar Activities
The principal objective of TiO₂ modifications is to reduce its energy bandgap thus moving its optical response from the UV to the visible region and reducing the electron-hole pair recombination. Several modifications techniques including doping with metals and non-metals, dye sensitization, deposition with noble metals, and coupled semiconductor have been applied. However, studies show that doping has a positive effect on TiO₂ because it introduces elements such as metal and non-metal in the titania structure that lead to the increase of its photo-activity by changing the functional properties of the TiO₂ [
10,
11]. The impact of doping in the photo-catalytic is regulated by factors, such as the nature of the dopants, the synthesis process, and physicochemical properties of the photo-catalyst [
2,
12].
Titanium-Oxide Supported Carbon Composites in Photocatalysis
Extensive studies have been done on the photocatalytic activity of TiO₂ supported carbon in the degradation of organic pollutants [
21,
22,
23]. Singh et al., (2016) studied the degradation of Direct Blue 199 dye using activated carbon-based TiO₂ nanocomposites under 196 W mini lamps. They also studied the reaction kinetic modeling of the photocatalytic, sonocatalytic, and sono-photocatalytic processes. Their result showed that the sono-photocatalytic process showed maximum degradation. However photocatalytic reactor was more efficient as it consumed less energy. They also demonstrated that the degradation reactions of Direct blue 199 followed the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model. Rashed et al., (2017) studied the adsorption and photocatalysis of methyl orange and Cd removal from wastewater using TiO₂/sewage sludge-based activated carbon nanocomposites under (15 W) UV irradiation lamps. They also investigated the factors influencing photocatalysis such as amount of TiO₂, initial pollutant concentrations, solution pH, nanocomposite dosage, and UV irradiation time. Their results revealed that these factors have a direct effect on photocatalysis efficiency. Nguyen et al., (2020) studied the kinetics of adsorption and photocatalysis in the removal of phenol, naphthol blue-black, and reactive black 5 under UV lamps. Their kinetic analysis revealed that the adsorption-assisted photocatalysis performance depended on the similarity of the initial rates of adsorption and degradation determined by the properties of the photocatalyst and the dye. Mondol et al., (2021) synthesised Activated Carbon/ TiO₂ nanohybrids by hydrothermal technique. They studied the photocatalytic activity by photodegradation of Reactive Red-35 dye using solar irradiation in open-air. Their report showed that the photodegradation was mainly controlled by the radicals •OH and •O₂‾. The photo-catalytic performance was significant due to the synergistic effect of adsorption and photodegradation activity of the nanohybrids. Despite the research effort in the synthesis of Activated Carbon/TiO₂ nanocomposite, there are challenges in the preparation process time-line, calcination temperatures and chemical reagents. Therefore, there is a need to apply energy efficient and simple preparation method which will ensure fast production process and depend on cost effective and low energy. Hydrothermal synthesis is a well-known for its tremendous advantages. It has potential for reduced in-process reduction and continuous catalyst activation as well as potential for industrial-scale production. It is also important to consider the sources and economic advantages when chosen the carbon material for the production of bio-char. The various sources of carbon have been investigated for their benefits in the biochar production. However, most trials have supported the use end-of-life biomass (ELB) such as sewage sludge, animal manure and agricultural residues as a feedstock [
27]. The use invasive plants can play an important role in reduction of carbon sequestration and unprofitable application of weedicide. The fast production and strong environmental adaptability of invasive plants make them harmful to the environment. Valorisation of this lant therefore aid their control and management.
Port Jackson Willow (Acacia saligna)
The Port Jackson willow (PJ) is a flexible tree that grows rapidly in semi-desert regions (including South Africa) as windscreens and as an ornamental tree. It has become an invasive species outside of its natural range, threatening biological diversity and categorized as an Invasive Alien Plant (IAP) [
27]. IAP has a negative impact on the ecosystem by consuming more water than local plants, exhausting valuable water resources, and also providing material for wildfires, making them exceptionally hot, which destroys the soil structure and sterilise the soil for up to three years . This results into negatives ecological, social, and economic impacts.
Chemical Reagents and Materials
The chemical used in the current investigations include; Hydrochloric acid (≥ 37 %), Nitric acid (65 %), ethanol (≥ 99 %), Titanium (III) trichoride solution (≥ 12%), and orange II sodium salt (≥ 85 %). They were purchased from Sigma Aldrich. Port Jackson Willow leaves were obtained from the Cape flats forest and identified at the Department of Botany, University of Cape Town.
Preparation of Biochar
Biochar was prepared by pyrolysis of the port Jackson willow leaves. The collected leaves were washed several times with deionized water to remove dust and other impurities, then dried and grinded into powder form. The 10.0 g of the dried powdered leaves were put in a Teflon crucible and place in the oven at 250 oC for 2 hours (with limited air supply) obtain biochar.
Synthesis of the Photocatalyst
Titanium dioxide TiO₂ was prepared using TiCl₃ precursor. Firstly, TiCl₃ (7 ml) was added to 1.5 ml HCl and mixture was diluted in distilled water (9 ml) and stirred for 15 minutes. The obtained solution was put in a water bath at 80°C for 10 minutes before slowly adding 6 ml of concentrated HNO₃ as the reaction is highly exothermic. The heating was then continued for 10 hours. The resultant titanium solution was washed with deionized water and recovered through centrifugation.
Synthesis of Biochar Supported-TiO2 Nanocomposite
TiO2 supported biochar nanoparticles were obtained by mixing the 200 mg synthesised TiO2 with 50 mg biochar and dissolve the mixture in ethanol (10 ml). The mixture was then sonicated for about 1 hour at room temperature. The solution was dried in the oven for 2 hours at 80oC. The resulting samples were calcinated under N2 stream at 500oC for 3 hours. The obtained powder was washed 50 mL ethanol (30%) and dried in a desiccator. The procedure was repeated at varied ratio of biochar to TiO2 (2:1, 2:2, 2:3 and 2:4).
TAUC Method for Energy Band Gap Determination
Energy band gap of a semiconductor is the needed energy for the excitement of its electron to move from the valence band to the conduction band. This is important in predicting photophysical and photochemical properties of semiconductors. The method is based on the assumption that the energy-dependent absorption coefficient.
Table 1.
The Energy bandgap of the synthesized TiO2 as calculated from TAUC plots.
Table 1.
The Energy bandgap of the synthesized TiO2 as calculated from TAUC plots.
| Weight TiO₂ (mg) |
Weight biochar (mg) |
Ratio |
Energy band gap(eV) |
| 200 |
50 |
4 : 1 |
2.52 |
| 200 |
100 |
2 : 1 |
2.50 |
| 200 |
200 |
1 : 1 |
2.49 |
| 200 |
300 |
2 : 3 |
1.96 |
| 200 |
400 |
1 : 2 |
2.12 |
| 200 |
500 |
2 : 5 |
2.33 |
It was discovered that Biochar/ TiO2 (2:3) ratio gave the smallest Energy band gap (1.96 eV). This ratio Biochar/ TiO2 was considered as the optimum for the synthesis of Biochar Supported-TiO2 photocatalyst and it was used for further characterizations and application.
Characterisation of Biochar Obtained from PJW Leaf
The obtained yield of Biochar after the carbonization of the PJW leafs is as presented in
Table 2. Increased pyrolysis period (from 1 to 3 hours) lead the reduction in Biochar yield from 70.58 to 68.90 %. The declined yield of biochar at an increased temperature may be attributed to combustion of the retained organic materials and the elimination of retained volatile organic compounds.
Functional Group Identification
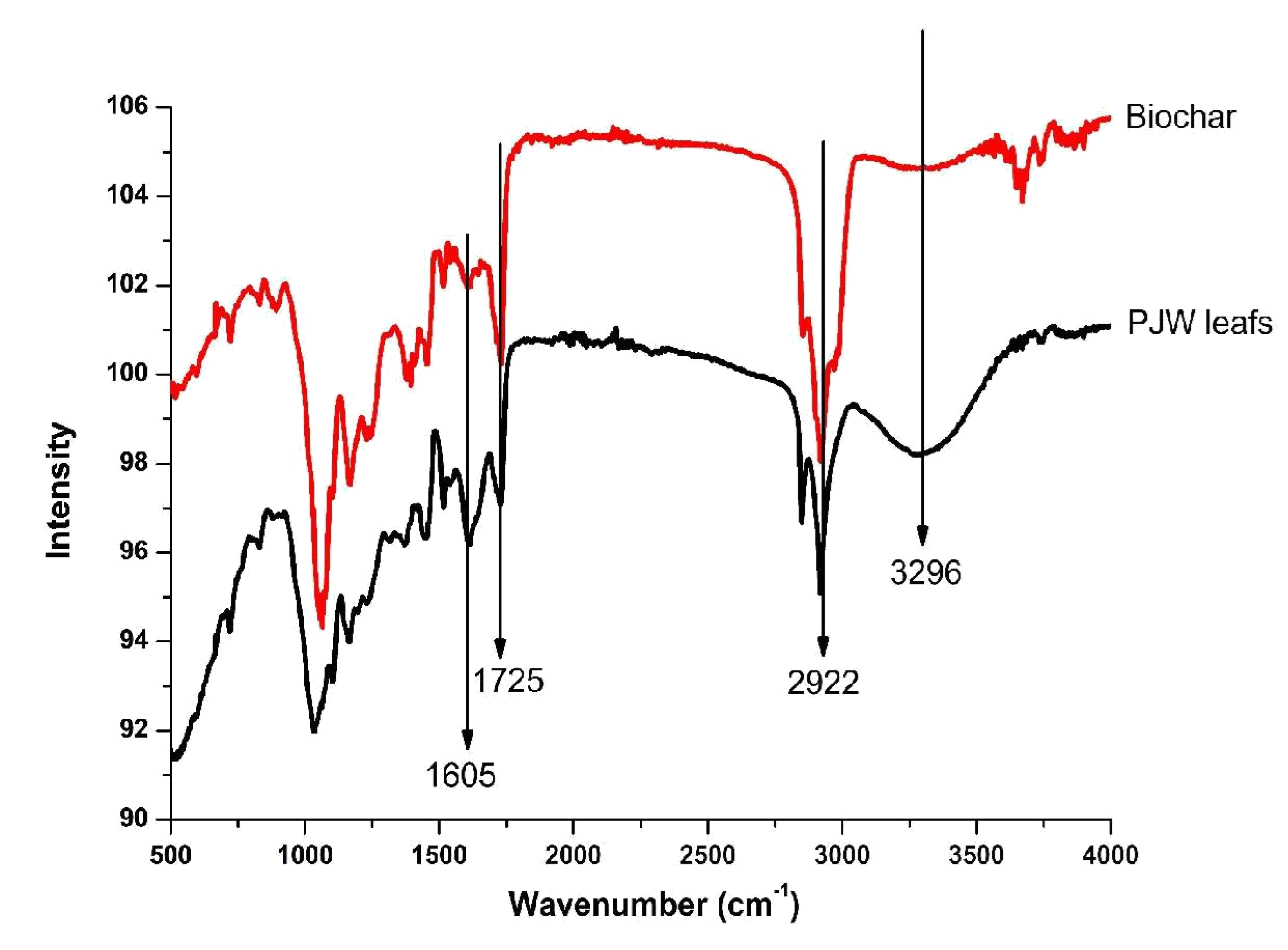
The Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra of the PJW leafs and the prepared Biochar is as presented in
Figure 2. The band at 3296 cm
-¹ is attributed to the –OH stretching vibration due to the surface adsorbed moisture or hydroxyl group is observed in PJW sample but less pronounced in Biochar. The -CH₂- symmetric stretch peaks of an alkyl at 2992 cm
-¹ was also observed on the FT-IR spectra of both PJW leafs and the prepared Biochar. Meanwhile, the C=O stretching vibration at 1725 cm
-¹ and the C=C stretching variation aromatic ring were present in the both PJW leafs and the prepared Biochar.
It was noted that all the functional groups prominent in the PJW leafs were retained in Biochar after the carbonization. However, the FT-IR of the fingerprint region in both PJW leafs and the prepared Biochar was not similar. There is an obvious improvement in the acidic functional groups on the produced biochar surface in comparison with the PJW. This is an indication that the PJW leafs have been converted to entirely new product by its carbonization [
28].
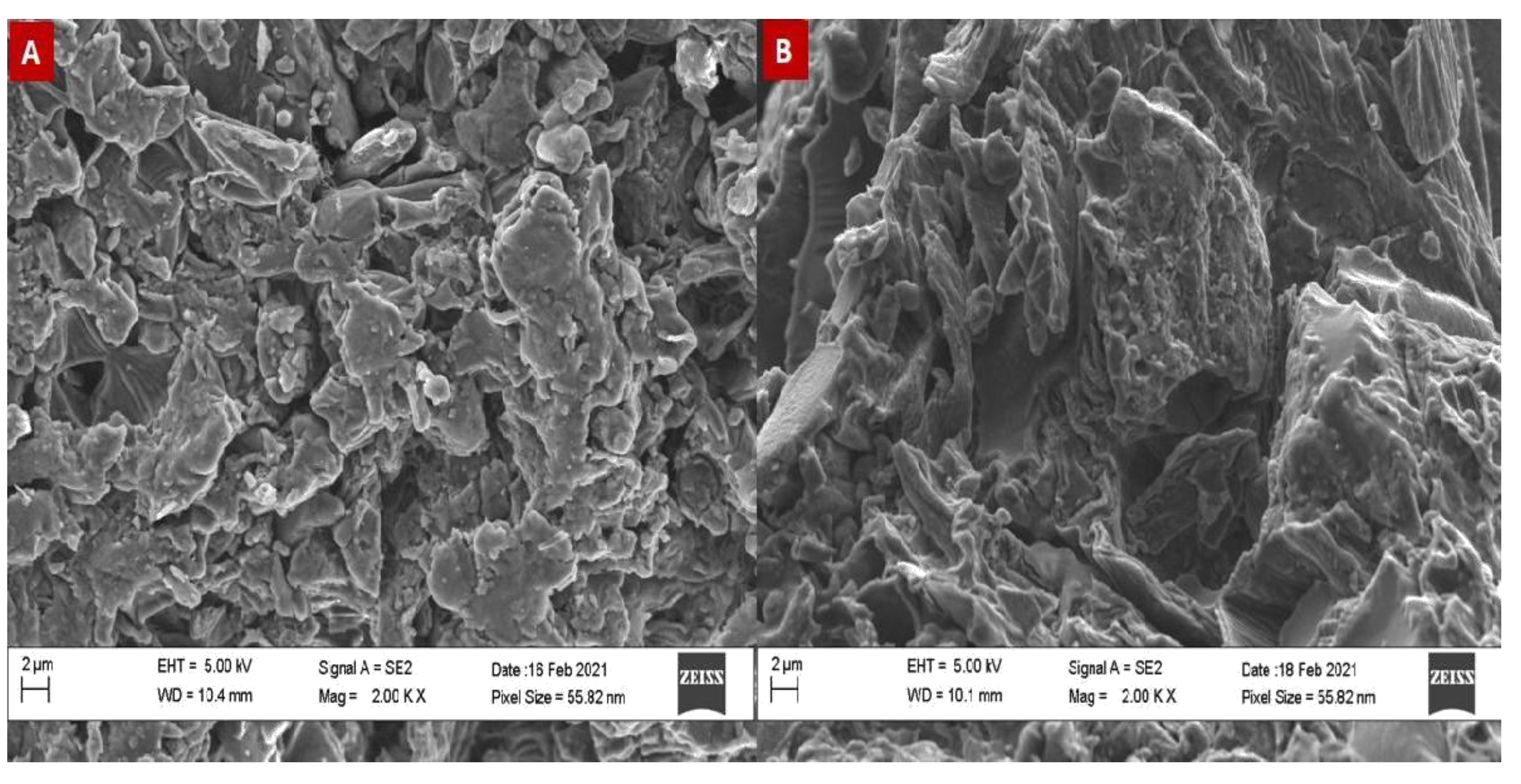
Surface Morphology of the Prepared Biochar
The produced Biochar from carbonization of PJW has a significantly oxygenated functional groups on its surface as presented by the Scan Electron Microscope (SEM) (
Figure 3). There is a clear reduction in the surface porosity of the produced Biochar. The superiority of the surface oxidized Biochar in term its hydrophilicity was reported by Singh et al., (2016). The high hydrophilicity and wettability of the biochar surface will lead to an enhanced binding with metals.
Energy Band-Gap of Biochar Supported-TiO₂
The energy band gap of TiO₂ and Biochar Supported- TiO₂ photocatalyst were measured using the Tauc plots. It was observed that the energy band gap of the synthesised TiO₂ nanoparticle and that of the Biochar Supported- TiO₂ were 2.81 eV and 2.11 eV respectively. The significant reduction in the energy band gap of Biochar Supported-TiO₂ photocatalyst was as a result of Ti-O-C bonds. The carbon
2p interacts with oxygen
2p atomic orbitals in an inert reaction environment (nitrogen) to produce a sub-band levels between the valence band (VB) and conduction (CB) [
30]. The observed increases in the edge of the valence band, consequently caused the reduction in energy band gap [
18]. In the current investigation, application of PJW biochar as a support for TiO
2 lead to a significant modification in the morphological structure and reduction in the energy band gap. The Biochar supported-TiO₂ photocatalyst showed greater promise as a solar active photocatalyst.
SEM-EDS of the Synthesized TiO2 Photocatalyst
The SEM-EDS of TiO₂ showed Oxygen (41.10 %) and Titanium (43.45 %) were presented in a near similar ratio, indicates the formation of Titanium oxide nanocomposite in its pure form (
Table 3). Meanwhile, the SEM-EDS result for the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ showed the Oxygen (39.71 %), Titanium (24.29 %) and Carbon (34.49 %) as the main elements in the nanocomposite. The increased in % composition of carbon is a direct effect and indication of successful incorporation of Titanium within the Biochar. Likewise, an observed increased oxygen-titanium ration was due to formation of new oxygen bond. The resultant oxygen vacancy is responsible for lower energy gap and consequently reduction in electron recombination associated with the titanium oxide photocatalyst.
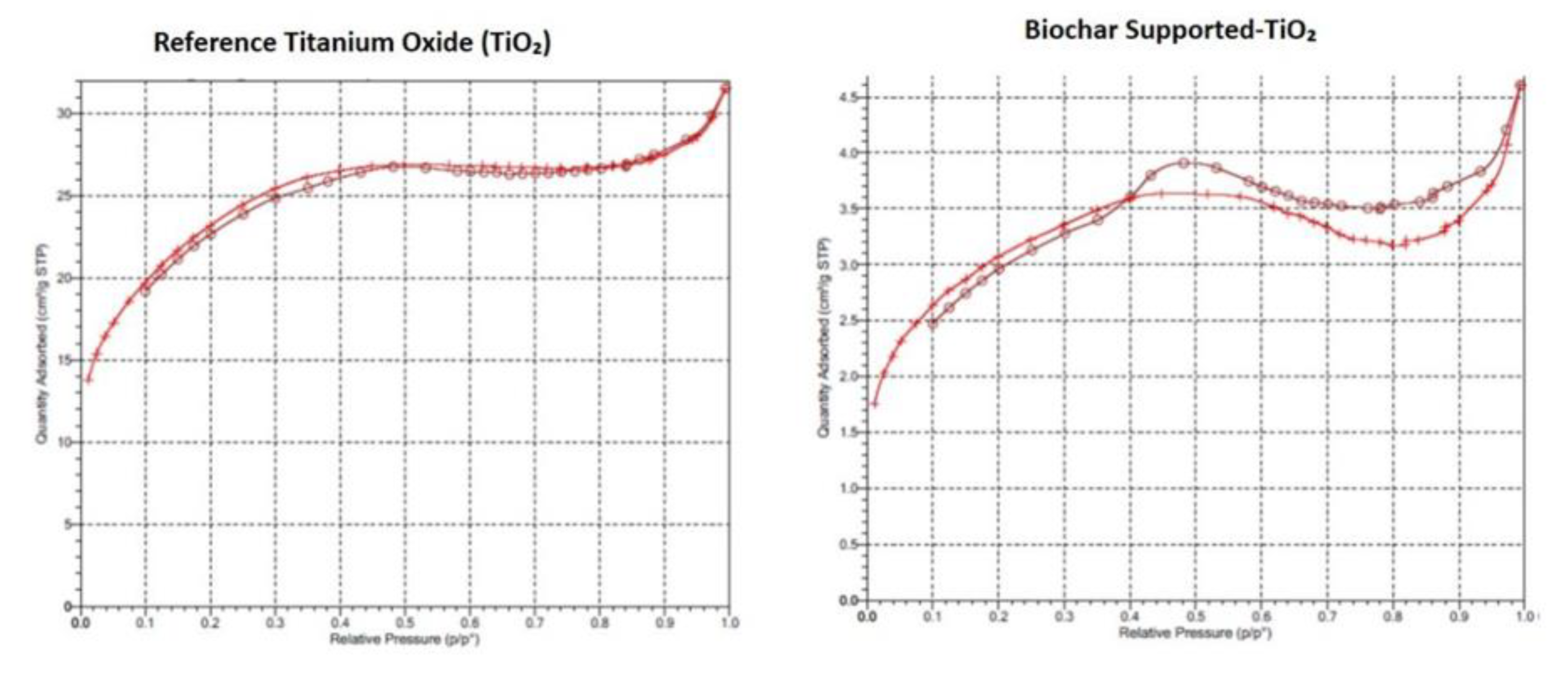
Brunauer Emmet Teller (BET) Surface Area Analysis
The N
2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of the synthesized TiO
2 and Biochar Supported-TiO
2 was presented (
Figure 4). The adsorption-desorption isotherms exhibits a characteristics of mesopores solids resulting with type IV adsorption isotherm undergoing capillary condensation and hysteresis during desorption [
31].. Different parameters were obtained for the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method surface area and Barrett-Joyner-Helanda (BJH) method poresize distribution. The BET surface area and adsorption average pore diameter of synthesized TiO
2 were 11.11 m2/g, 9.793 Å respectively. And for the Biochar Supported-TiO
2, the BET surface area and adsorption average pore diameter were 84.45 m2/g, 10.12 Å respectively.
The increased BET surface area and average pore diameter indicates that there is a reduction on the surface of titanium oxide as a result of the presence of biochar. The higher surface area and adsorption pore diameter in Biochar Supported-TiO2 ensure higher contact time, enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic efficiency [
32].
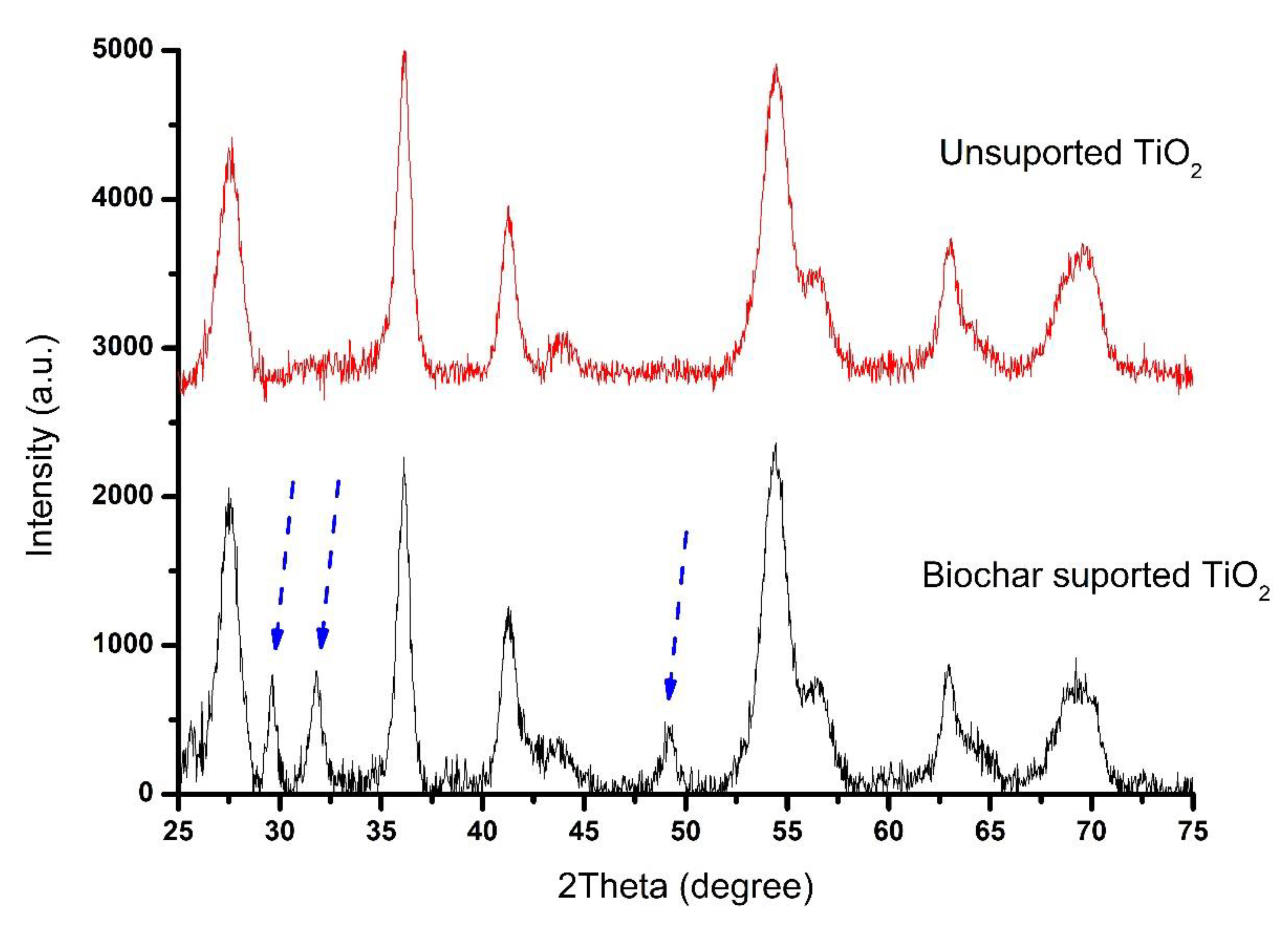
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The x-ray diffraction patterns of TiO₂ and Biochar Supported-TiO₂ were provided in
Figure 5. In this pattern, all lines can be indexed using the ICDD no. 00-001-1292. The position of 2θ corresponds to Miller indices of (110), (101), (111), (211), (220), (002), and (301) crystalline planes. The distinctive peaks at 2θ angles in the synthesized TiO₂ are corresponding to the rutile phase. Meanwhile, the distinct peaks in Biochar Supported-TiO₂ at (220), (301), and (200) crystalline planes showed the characteristic anatase phase. Therefore, there is a mixture of rutile and anatase crystalline phase in the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ due to the influence of Biochar. According to Zhang, (2017), photocatalysts with anatase and rutile phases are more efficient than those with only one crystalline phase.
Application of the Biochar Supported-TiO2 as a Photocatalyst in the Degradation of Orange II Sodium Azo-Dye
The ability of the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ to act as a photocatalyst at various reaction conditions was investigated through the photochemical degradation (Visible light) of an orange II sodium (OR2) Azo-dye in simulated textile wastewater. A quantity of OR2 equal to 100mL in a 250 mL glass container was subjected to degradation (100 rpm, 30 degree Celsius) by exposure to a 160 W Mega-Ray irradiation lamps light with UV filter (450 nm). The solution was initially set-up in the dark for 20 minutes to allow the adsorption-desorption equilibrium between the photocatalyst (TiO₂) and OR2 molecules. The reaction setup was subjected to the various condition as presented in
Table 4. Thereafter, the samples were centrifuged and then analysed with the aid of UV-Visible Spectrophotometer to determine the % degradation.
The calibration curve for the absorption spectra of Orange II Sodium salt (OR2) for concentrations ranging from 2 ppm to 10 ppm was obtained by measuring the respective absorbance of the prepared OR2 concentration (λmax = 483 nm). This was done in other to be able to determine the concentrations of OR2 during the batch photodegradation experiments.
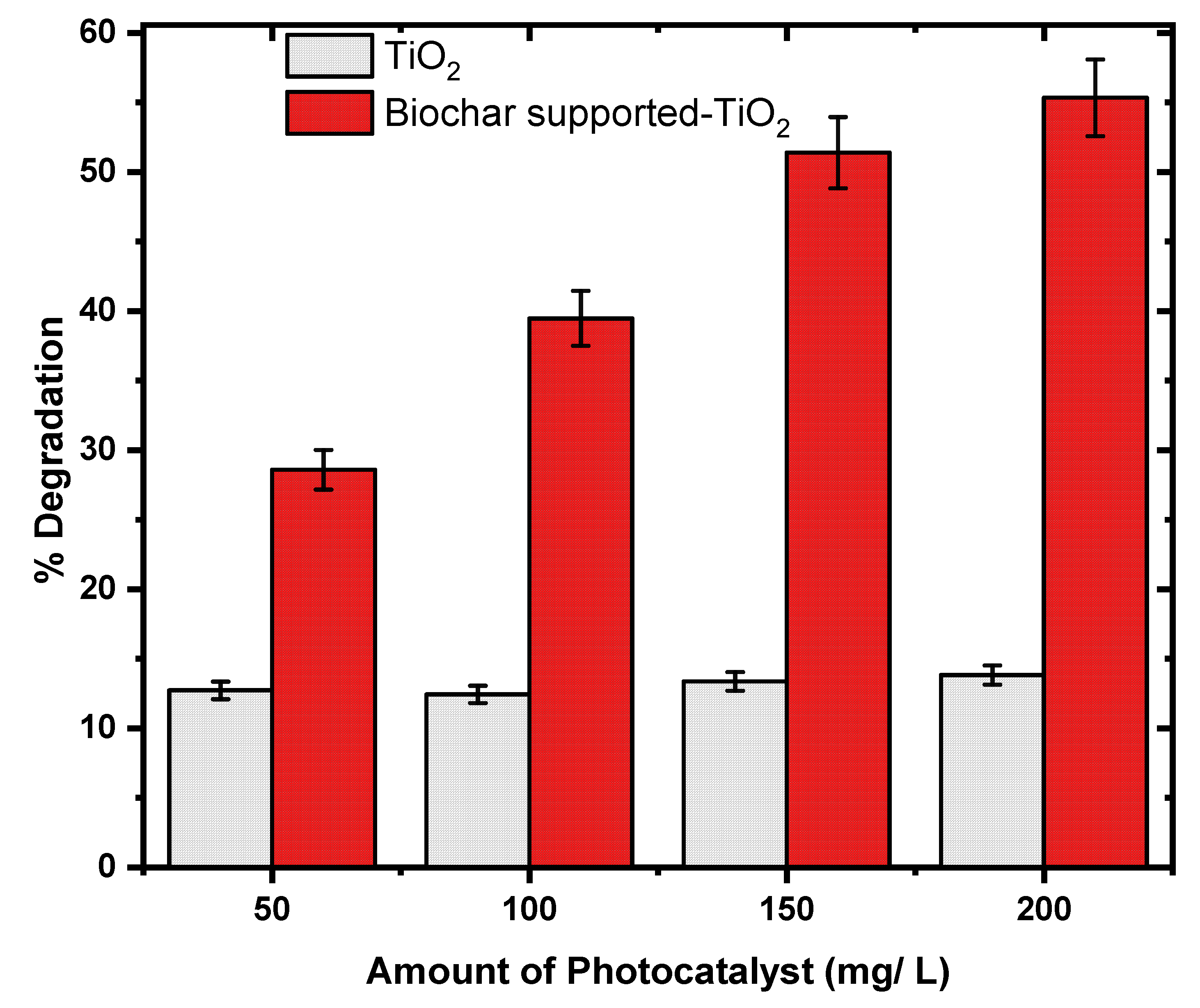
Effect of Photo-Catalyst Loading
An amount of the synthesized TiO₂ and Biochar Supported-TiO₂ between 50 mg/L and 200 mg/L were applied in a reaction chamber for the photodegradation reaction of OR2. The OR2 photo-degradation was very poor (12.47 %) when the synthesized TiO₂ was applied and there was no significant improvement in the OR2 photodegradation despite the increased in the TiO₂ photocatalyst dosage. Meanwhile, Biochar Supported-TiO₂ on application, gave a relatively higher % photodegradation (28.58 %) with increased degradation efficiency (55.34 %) as the amount of the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ increased (
Figure 6).
The photo-degradation efficiency of OR2 during the application of Biochar Supported-TiO₂ was directly proportional to the catalyst loading. This indicated a true catalytic regime that can be attributed to the increased photo reactive sites on the surface of Biochar. The photo-reactive is capable of enhanced photocatalytic activity in the TiO₂ nanocomposite [
33]. The noticed reduction of photo-degradation efficiencies maybe due to increased turbidity of OR2 solution and the consequential low light penetration [
8].
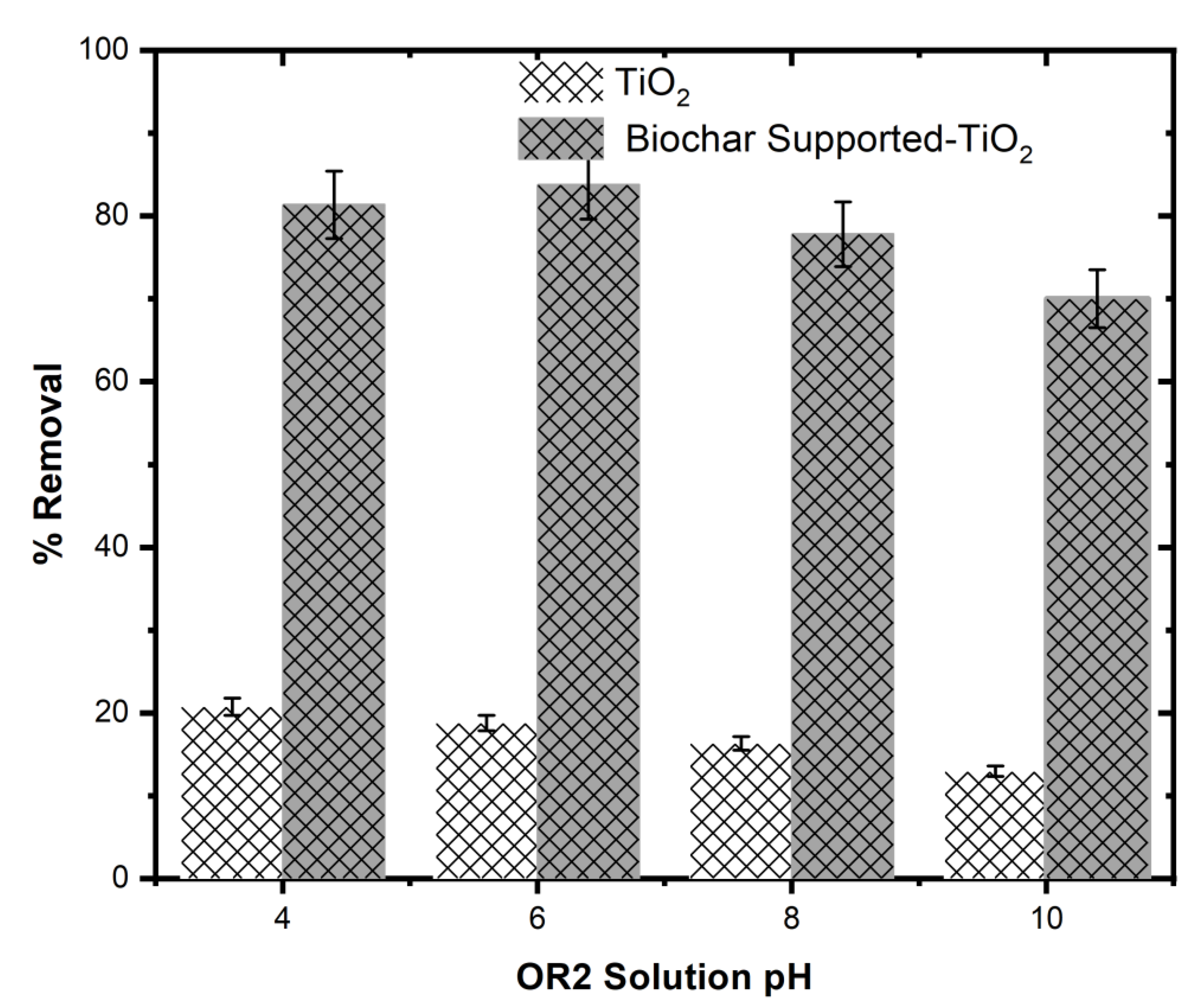
Impact of Solution pH on Photodegradation of OR2
The photocatalytic efficiency of the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ was strongly affected by the OR2 solution pH. Highest photocatalytic efficiency of OR2 was recorded for the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ (83.48 %) at pH 6 while the lowest (73.08 %) was attained at pH 10 (
Figure 7). The results showed that the influence of solution pH at an acidic and neutral pH conditions were more favourable than that of the basic conditions. This suggests that the photophysical generation of free radical oxidants such as hydroxyl radical was more intense in an acidic and neutral OR2 solution [
34].
A higher photocatalytic efficiency was observed in a neutral medium due to the non-dissociative nature of the dye which lead to a strong adsorption onto the catalyst surface. The noticed decrease in photo-degradation efficiency was a resultant effect of the negatively charged nature of the photocatalyst surface and the resultant poor surface activity in a basic medium [
35].
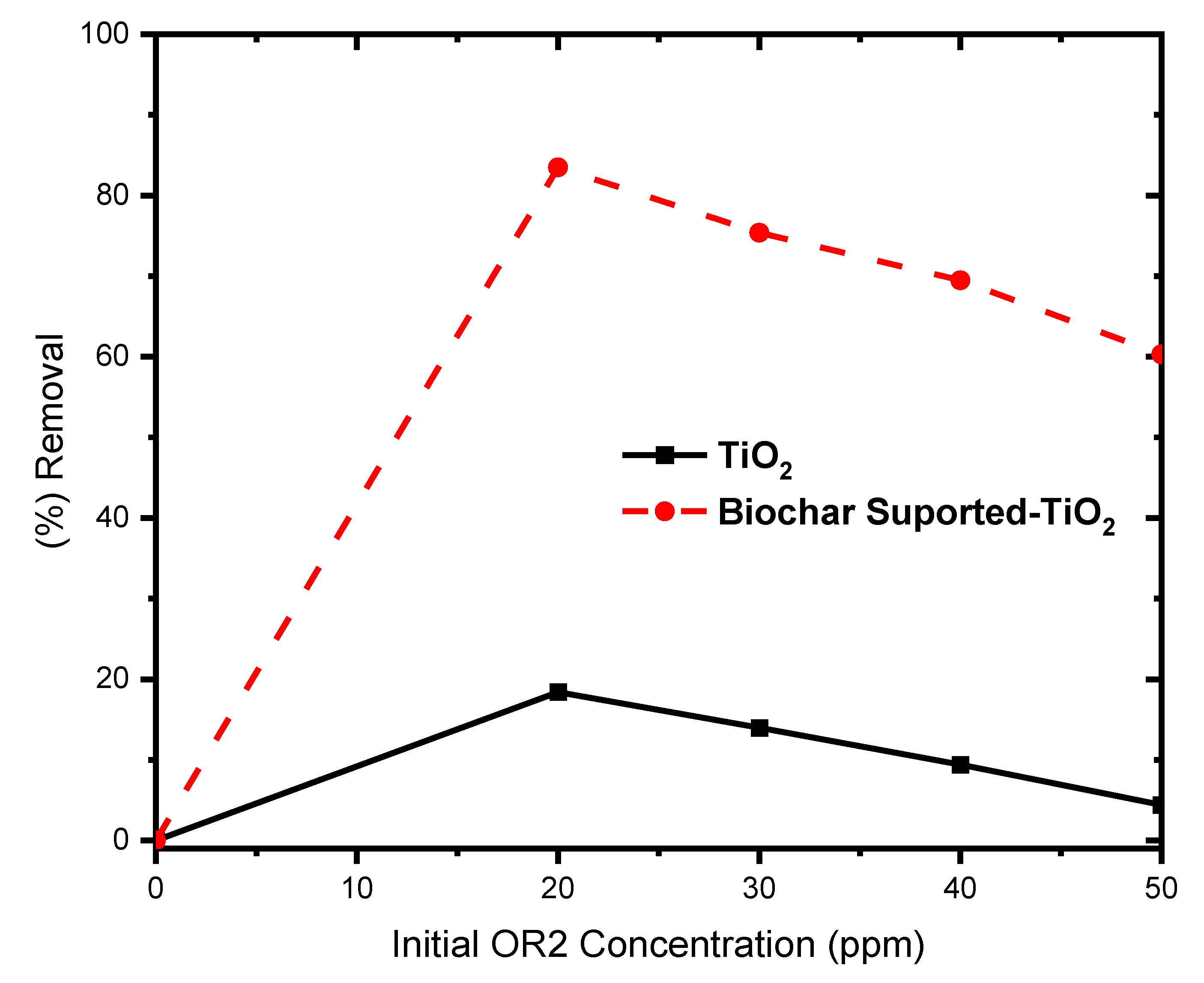
Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
A decreased photo-degradation efficiency was noticed as the concentration of ORS exceeded 20 ppm (
Figure 8). This can be accounted for by the opacity nature of the concentrated OR2 which prevented the photo-degradation by blocking the light penetration. This implies that a well diluted textile wastewater is required for the photocatalytic treatment. Besides, the photo-degradation is more efficient in the tertiary stages of water treatment [
36].
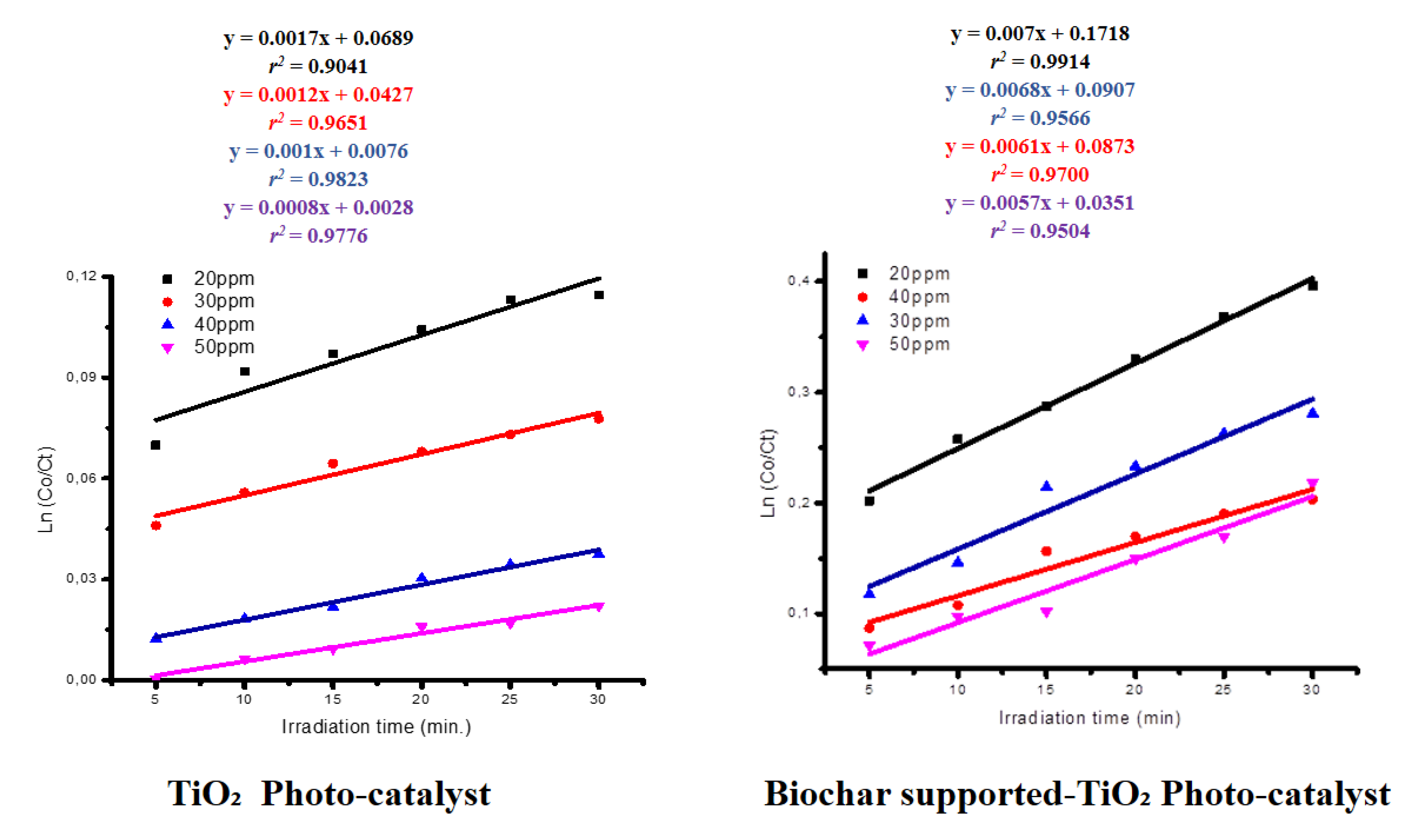
Kinetics of the Photodegradation of Orange II Sodium Dye
The kinetic studies for OR2 photo-degradation using both TiO₂ and Biochar supported- TiO₂ were as presented (
Figure 9). The photo-degradation of OR2 by the photocatalyst followed pseudo-first-order and aligned with the Langmuir-Hinshelwood kinetic model.
The high values of coefficient of determination (r
2;) obtained for TiO₂ and Biochar Supported-TiO₂ kinetic plots in the current investigations implies a good correlations values in the linear regression models. This showed that the photo-degradation processes of OR2 in the presence of the TiO₂ and Biochar Supported-TiO₂ were governed by Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model [
35,
37]. The K values for TiO₂ and Biochar Supported-TiO₂ were compared (
Table 5). It became apparent that the prepared TiO₂ had a lower photocatalytic activity under visible light in comparison with Biochar Supported-TiO₂.
Electrical Energy Efficiency per Order (EEo) of the Photocatalytic Degradation of OR2
The lowest value of EEo of 136.49 kWh/m3; was obtained using Biochar Supported-TiO₂ at pH 6.8. The results confirm that photocatalytic degradation is affected by the solution pH. Besides, it can observed that the Biochar Supported-TiO₂ offered a better energy efficiency at all tested pH (136.49 KWh/m3; at pH 6.8) compared to the unsupported TiO₂ (1182.19 KWh/m3; at pH 6.8)
Conclusion
The reported limitations in the photophysical application of TiO₂ under the solar radiation are caused by its large energy bandgap (3.0 - 3.20 eV) and electron recombination. Overcoming these issues has been achieved by modification through the synthesis of Biochar Supported-TiO₂. The biochar which was produced from leafs of an invasive plant (Acacia Saligna) was subsequently applied as a support during the synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticle. A massive reduction in the energy band gap (1.96 eV) was achieved in the mixed anatase/ rutile Biochar Supported-TiO₂ photocatalyst. The characterization of TiO2 doped biochar using methods such as SEM-EDS, FTIR, XRD and BET have showed that the TiO₂ was successfully immobilized on the Biochar external surface. The synthesized Biochar Supported-TiO₂ nanoparticles exhibiting small hysteresis phenomenon which represent a typical type IV adsorption isotherm attributed to mesosoporous material with a low porosity.
References
- F. Zeribi et al., “ Dependence of the Physical Properties of Titanium Dioxide (TiO 2 ) Thin Films Grown by Sol-Gel (Spin-Coating) Process on Thickness,” ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol., vol. 11, no. 2, p. 023003, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Pelaez et al., “A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications,” Appl. Catal. B Environ., vol. 125, pp. 331–349, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Hofierka and J. Kaňuk, “Assessment of photovoltaic potential in urban areas using open-source solar radiation tools,” Renew. Energy, vol. 34, no. 10, pp. 2206–2214, 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Rashed, M. A. Eltaher, and A. N. A. Abdou, “Adsorption and photocatalysis for methyl orange and Cd removal from wastewater using TiO2/sewage sludge-based activated carbon nanocomposites,” R. Soc. Open Sci., vol. 4, no. 12, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Q. Guo, C. Zhou, Z. Ma, and X. Yang, “Fundamentals of TiO2 Photocatalysis: Concepts, Mechanisms, and Challenges,” Adv. Mater., vol. 31, no. 50, pp. 1–26, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Chang, Q. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. Shi, and Z. Qin, “Preparation of Fe3O4/TiO2 magnetic photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of phenol,” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., vol. 29, no. 10, pp. 8258–8266, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Hengerer, B. Bolliger, M. Erbudak, and M. Grätzel, “Structure and stability of the anatase TiO2 (101) and (001) surfaces,” Surf. Sci., vol. 460, no. 1–3, pp. 162–169, 2000. [CrossRef]
- X. Luo, S. Zhu, J. Wang, C. Wang, and M. Wu, “Characterization and computation of Yb/TiO2 and its photocatalytic degradation with benzohydroxamic acid,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 14, no. 12, 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. de Oliveira Pereira, I. Marques Sales, L. Pereira Zampiere, S. Silveira Vieira, I. do Rosário Guimarães, and F. Magalhães, “Preparation of magnetic photocatalysts from TiO2, activated carbon and iron nitrate for environmental remediation,” J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem., vol. 382, no. April, p. 111907, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Mo, “Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titania by,” 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Wong, “ScienceDirect Smog induces oxidative stress and microbiota disruption,” J. Food Drug Anal., vol. 477, no. March, pp. 1–10, 2017. [CrossRef]
- W. Jiang, M. Pelaez, D. D. Dionysiou, M. H. Entezari, D. Tsoutsou, and K. O’Shea, “Chromium(VI) removal by maghemite nanoparticles,” Chem. Eng. J., vol. 222, pp. 527–533, Apr. 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Mahlambi, C. J. Ngila, and B. B. Mamba, “Recent Developments in Environmental Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants: The Case of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles-A Review,” J. Nanomater., vol. 2015, no. October, 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. O. Badmus, F. Wewers, M. Al-Abri, M. Shahbaaz, and L. F. Petrik, “Synthesis of oxygen deficient tio2 for improved photocatalytic efficiency in solar radiation,” Catalysts, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 1–15, 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Bourquard, Y. Bleu, A. Loir, B. Caja-Munoz, J. A.- Materials, and undefined 2019, “Electroanalytical performance of nitrogen-doped graphene films processed in one step by pulsed laser deposition directly coupled with thermal annealing,” Materials (Basel)., vol. 12, p. 666, 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. M. Mohammadi and N. Ghasemi, “Influence of temperature and concentration on biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using cherry extract,” J. Nanostructure Chem., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 93–102, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Z. Hejri, M. Hejri, M. Omidvar, and S. Morshedi, “Synthesis of TiO2/nZVI nanocomposite for nitrate removal from aqueous solution,” Int. J. Ind. Chem., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 225–236, 2019. [CrossRef]
- X. Kang, S. Liu, Z. Dai, Y. He, X. Song, and Z. Tan, “Titanium dioxide: From engineering to applications,” Catalysts, vol. 9, no. 2, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Yanhui, K. Wang, P. Wang, C. Wang, and J. Hou, “Synthesis of novel 2D-2D p-n heterojunction BiOBr/La2Ti2O7 composite photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic performance under both UV and visible light irradiation,” Appl. Catal. B Environ., vol. 194, pp. 157–168, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Abel et al., “Application of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-Gel Methods in Wastewater Treatment,” J. Nanomater., vol. 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Castro, I. Lopes, and T. Rocha-santos, “applied sciences Evaluation of the Potential Toxicity of E ffl uents from the Textile Industry before and after Treatment,” Appl. Sci., vol. 9, no. 18, p. 384, 2019.
- Y. H. Chiu, T. F. M. Chang, C. Y. Chen, M. Sone, and Y. J. Hsu, “Mechanistic insights into photodegradation of organic dyes using heterostructure photocatalysts,” Catalysts, vol. 9, no. 5, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A.K. Subramani, K. Byrappa, S. Ananda, K. M. Lokanatha Rai, C. Ranganathaiah, and M. Yoshimura, “Photocatalytic degradation of indigo carmine dye using TiO2 impregnated activated carbon,” Bull. Mater. Sci., vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 37–41, 2007. [CrossRef]
- P. Singh et al., “Comparative study of dye degradation using TiO2-activated carbon nanocomposites as catalysts in photocatalytic, sonocatalytic, and photosonocatalytic reactor,” Desalin. Water Treat., vol. 57, no. 43, pp. 20552–20564, 2016. [CrossRef]
- C. H. Nguyen, H. N. Tran, C. C. Fu, Y. T. Lu, and R. S. Juang, “Roles of adsorption and photocatalysis in removing organic pollutants from water by activated carbon–supported titania composites: Kinetic aspects,” J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., vol. 109, pp. 51–61, 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. Mondol et al., “Preparation of Activated Carbon/TiO2 Nanohybrids for Photodegradation of Reactive Red-35 Dye Using Sunlight,” Photochem, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 54–66, 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Lian et al., “Utilization of biochar produced from invasive plant species to efficiently adsorb Cd (II) and Pb (II),” Bioresour. Technol., vol. 317, no. August, p. 124011, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Y. Pudza, Z. Z. Abidin, S. A. Rashid, F. M. Yasin, A. S. M. Noor, and M. A. Issa, “Eco-friendly sustainable fluorescent carbon dots for the adsorption of heavy metal ions in aqueous environment,” Nanomaterials, vol. 10, no. 2, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. K. Singh, R. Kumar, and D. P. Singh, “Graphene oxide: strategies for synthesis, reduction and frontier applications,” RSC Adv., vol. 6, no. 69, pp. 64993–65011, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Eppa, K. Durgam, M. V. Ramana;, S. R. Reddy, and J. Sivakumar, “Structural, Optical and Photocatalytic Properties of Anatase/Rutile Tio2 Nanoparticles,” i-manager’s J. Mater. Sci., vol. 6, no. 3, p. 43, 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, W. Cai, Y. Lin, G. Wang, and C. Liang, “Mass production of micro/nanostructured porous ZnO plates and their strong structurally enhanced and selective adsorption performance for environmental remediation,” J. Mater. Chem., vol. 20, no. 39, pp. 8582–8590, Sep. 2010. [CrossRef]
- F. Zhang, “Grand Challenges for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology in Energy and Health,” Front. Chem., vol. 5, no. October, pp. 1–6, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tong et al., “Photo-catalyzed TiO2 inactivates pathogenic viruses by attacking viral genome,” Chem. Eng. J., vol. 414, no. February, p. 128788, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Kumari, C. U. Pittman, and D. Mohan, “Heavy metals [chromium (VI) and lead (II)] removal from water using mesoporous magnetite (Fe3O4) nanospheres,” J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 442, pp. 120–132, Mar. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ali, M. Mehmood, J. Ahmed, and M. N. Nizam, “Synthesis of graphitic nanofibers and carbon nanotubes by catalytic chemical vapor deposition method on nickel chloride alcogel for high oxygen evolution reaction activity in alkaline media,” Nano-Structures and Nano-Objects, vol. 24, p. 100574, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Bhati and R. Rai, “Nanotechnology and water purification: Indian know-how and challenges,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., vol. 24, no. 30, pp. 23423–23435, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Madhvi, L. Singh, S. Saroj, Y. Lee, and S. V. Singh, “Facile synthesis of nano-crystalline anatase TiO2 and their applications in degradation of Direct blue 199,” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 2581–2588, 2016. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).