1. Definition of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Leukemias are characterized by the inhibition of proper blood cell differentiation. Leukemic cells exhibit rapid growth and increasing aggressiveness [
1]. If the inhibition in maturation in blood cells occurs at the level of Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs), or subsequent early myeloid progenitors like myeloblasts, the disease's progression will be faster than leukemias occurring in more mature progenitors and becomes clinically categorized as Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) once there are 20% of AML blasts in the peripheral blood. Similarly, if there is a block at the lymphoid progenitors, leukemias are categorized as Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) using similar criteria. ALL is one of the most common types of leukemia in young children [
2]. Acute leukemias are characterized by the rapid increase of immature blood cells, often leading to a rapid progression of the disease, whereas chronic leukemias progress more slowly and allow for the accumulation of more mature and functional cells of the granulocyte lineage (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils and their precursors) [
3,
4]. Conversely, AML is a common type of leukemia that is more prevalent in elderly adults than in children [
5].
AML accounts for approximately 80% of all leukemias in adults and eventually leads to aberrant hematopoiesis caused by bone marrow failure that become full of AML blasts as well as blast crisis caused by global dissemination of AML blasts throughout the body. More recent treatments have improved cure rates to around 15% in 60-year-old patients and approximately 40% in patients under 60 [
6]. The global cancer surveillance system (GLOBOCAN), that tracks worldwide cancer trends, has reported a significant global incidence of 474,519 cases, among which 67,784 have been identified in the North American region. The Age-Standardized Rates (ASRs) are consistently registering at approximately 11 cases per 100,000 population, reflecting the prevalence of this malignancy [
7].
2. Classifications of AML
AML was initially classified into various subtypes ranging from M0 to M7 based on the French-American-British (FAB) system, which emphasizes morphological and immunological characteristics [
8]. These subtypes include M0 with minimal differentiation [
9], and M1 with a higher proportion of mature myeloid forms [
8]. M2 shows more advanced stages of cell maturation, for example, leukemias harboring the AML1:ETO and ETO:AML1 fusion proteins [
9,
10]. M3, known as Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL), accounts for approximately 10% of all AML cases and presents the characteristic PML-RARα fusion protein due to the t(15;17) translocation. M3 is known to have favorable prognosis since these leukemias can be effectively treated with the use of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (ATO) [
11,
12,
13,
14]. M4 represents acute myelomonocytic leukemia [
15,
16], and M5 denotes monocytic leukemia, commonly associated with a poor prognosis, extramedullary disease, and abnormalities in the long arm of chromosome 11 (11q) [
17], resulting for example in the MLLT3:KMT2A (MLL-AF9) fusion protein [
18,
19,
20]. Subtype M6, also known as erythroleukemia, is a rare form of AML (comprising less than 5% of AML cases) [
21,
22,
23]. Lastly, the rare subtype M7 (around 1% of AML cases), also known as megakaryocytic/megakaryoblastic leukemia, exhibits poor megakaryocytic differentiation, characterized by scant cytoplasm and nuclei with dense chromatin [
24,
25].
The advent of flow cytometry and next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has significantly deepened our understanding of the molecular and genetic factors that contribute to the development and progression of AML. These advancements have highlighted the complex genetic landscape of AML, revealing a diversity of mutations and chromosomal abnormalities that drive the disease. Consequently, the need for a more comprehensive and accurate classification system became evident to better stratify patients according to their genetic profiles, which can influence treatment decisions and prognostic outcomes [
26,
27,
28].
3. Genetic Variability of AML
The International Consensus Classification (ICC) of 2022 and the WHO's fifth edition have introduced new categories and redefined existing ones to better align with genetic data and clinical outcomes. For instance, the ICC has established a new category for AML with mutated TP53, which requires at least 20% of blasts and any somatic TP53 mutation with a variant allele fraction greater than 10%. This category is particularly noted for its poor prognosis and complex karyotype abnormalities, underscoring the unique biology of TP53 mutations in AML patients [
29,
30]. Additionally, the ICC has reclassified some previous categories to incorporate genetic abnormalities more comprehensively. For example, the former category of AML with myelodysplasia-related changes has been split into two: AML with myelodysplasia-related gene mutations and AML with myelodysplasia-related cytogenetic abnormalities, each requiring a blast count of at least 20% [
29,
30]. In line with the latter, the recent advancements in the classification of AML incorporate significant updates from the WHO-ICC 2022 and the European Leukemia Net guidelines of 2022 [
31,
32]. These updates emphasize the importance of genetic and molecular information in the diagnosis and management of AML, reflecting the shift towards precision medicine in oncology.
The European LeukemiaNet (ELN) 2022 recommendations have also updated their guidelines to incorporate hierarchical genetic abnormalities for defining AML. This includes the introduction of a category for MDS/AML with 10%-19% blasts if specific genomic abnormalities are present, prioritizing genetic markers over purely morphological assessments. These guidelines emphasize the diagnostic significance of genetic mutations such as NPM1, FLT3-ITD, and CEBPA, which are associated with different risk classifications and treatment responses [
32].
The following table summarizes the findings of the WHO 2022 and European LeukemiaNet 2022 guidelines alongside additional literature, detailing the impact of genetic variations on the prognosis of different AML subtypes. It categorizes AML subtypes based on specific genetic abnormalities and their corresponding blast percentage requirements, highlighting how these factors influence ELN risk classification.
Table 1.
Overview of AML Subtypes Based on Genetic Abnormalities and Blast Requirement combining ELN risk category and WHO guidelines of 2022, respectively.
Table 1.
Overview of AML Subtypes Based on Genetic Abnormalities and Blast Requirement combining ELN risk category and WHO guidelines of 2022, respectively.
| AML Type |
Blast % |
Genetics |
ELN Risk Class (2022) |
Literature (2024) |
Refs. |
| APL with t(15;17)/PML::RARA |
>10% |
PML: RARA |
- |
Favorable |
[33,34] |
| APL with other RARA rearrangements |
>10% |
Various RARA rearrangements |
- |
Variable, depends of the rearrangement |
[35,36] |
| AML with t(8;21)/RUNX1::RUNX1T1 |
>10% |
RUNX1:RUNX1T1 |
Favorable |
Favorable |
[37] |
| AML with inv(16) or t(16;16)/CBFB::MYH11 |
>10% |
CBFB:MYH11 |
Favorable |
Favorable |
[38,39] |
| AML with t(9;11)/MLLT3::KMT2A |
>10% |
MLLT3:KMT2A |
Intermediate |
Intermediate |
[40,41] |
| AML with other KMT2A rearrangements |
>10% |
Various KMT2A rearrangements |
- |
Variable, depends of the rearrangement |
[40] |
| AML with t(6;9)/DEK::NUP214 |
>10% |
DEK:NUP214 |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[42] |
| AML with inv(3) or t(3;3)/GATA2; MECOM |
>10% |
GATA2; MECOM |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[43] |
| AML with other MECOM rearrangements |
>10% |
Various MECOM rearrangements |
- |
Adverse |
[44] |
| AML with other rare recurring translocations |
>10% |
Rare recurring translocations |
- |
Adverse |
[45] |
| AML with t(9;22)/BCR::ABL1 |
>10% |
BCR:ABL1 |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[46] |
| AML with mutated NPM1 |
>10% |
Mutated NPM1 |
Favorable |
Favorable |
[47] |
| AML with bZIP CEBPA mutations |
>10% |
bZIP CEBPA mutations |
Favorable |
Favorable |
[48] |
| AML/MDS with mutated TP53 |
10-19% / >20% |
Mutated TP53 |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[49] |
| AML/MDS with myelodysplasia-related gene mutations |
10-19% / >20% |
Myelodysplasia-related gene mutations |
- |
Adverse |
[50] |
| AML with myelodysplasia-related cytogenetic abnormalities |
10-19% / >20% |
Myelodysplasia-related cytogenetic abnormalities |
- |
Intermediate |
[51] |
| AML not otherwise specified (NOS) |
10-19% / >20% |
- |
- |
- |
[52] |
| Myeloid sarcoma |
Not specified |
- |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[53] |
| MDS with mutated TP53 |
0-9% |
Multi-hit TP53 mutation or TP53 mutation (VAF > 10%) and complex karyotype often with loss of 17p |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[29,30] |
| MDS/AML with mutated TP53 |
10-19% |
Any somatic TP53 mutation (VAF > 10%) |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[29,30] |
| AML with mutated TP53 |
>20% |
Any somatic TP53 mutation (VAF > 10%) |
Adverse |
Adverse |
[29,30] |
Next, we will explore one of the well-studied genetic aberrations in AML, specifically within the M5 subtype—the MLL-AF9 fusion. We will review the molecular mechanisms underlying its pathogenicity and its significant role in therapy-related AML (t-AML), understanding how these genetic fusion influences disease progression and impacts treatment strategies.
4. MLL-AF9 Fusion Protein Oncogenic Mechanisms and Incidence in AML
MLL, a large protein weighing 431 kDa, is encoded by the KMT2A gene located on chromosome 11q23 [
54,
55]. This protein undergoes intracytoplasmic cleavage by the enzyme Taspase 1, resulting in two functional subunits, MLL-N and MLL-C, which are essential for its role in the MLL complex along with WDR5, RbBP5, and ASH2L [
56]. This complex is integral to maintaining proper chromatin structure and facilitates the efficient transcription of critical developmental genes, including those involved in hematopoiesis [
57,
58,
59,
60]. One of the crucial functions of the MLL complex is the methylation of lysine 4 on histone H3 (H3K4), an epigenetic mark that is vital for the activation of HOX genes. These genes are essential for developmental processes and are particularly notable for their roles in maintaining the properties of hematopoietic stem or progenitor cells [
61,
62]. The epidemiology of MLL rearrangements indicates a high incidence in infant leukemias and a significant presence in adult AML, often leading to monocytic differentiation corresponding to FAB classifications AML-M4 or AML-M5. These rearrangements, particularly the MLL-AF9 fusion resulting from the t(9;11)(p22;q23) translocation, are associated with a poorer prognosis in AML patients, highlighting the clinical importance of recognizing this genetic alteration for targeted treatment strategies [
63,
64,
65,
66,
67,
68,
69].
AF9, encoded by the MLLT3 gene, is a protein varying in molecular weight between 63 and 88 kDa. Part of the YEATS family, it features intrinsically disordered proteins and is characterized by its distinctive YEATS domain. AF9 is pivotal in hematopoiesis, primarily tasked with maintaining the population of Hematopoietic Stem or Progenitor Cells (HSPCs), essential for the generation and regulation of blood cells [
70,
71]. AF9 also plays a critical role in gene expression regulation through its interaction with acetylated lysine 27 on histone H3. This interaction is important for enhancing the recruitment of the Like Histone Lysine Methyltransferase (DOT1L). Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies have shown that DOT1L binds to AF9 across three of its domains, facilitating this process [
72] and through this interaction, DOT1L specifically targets lysine 79 residues on histone H3 for methylation. This mark plays a pivotal role in chromatin remodeling, leading to decompaction of the chromatin structure, facilitating the transition from a more condensed heterochromatin state to a more relaxed euchromatin state, promoting gene expression [
73].
In the context of AML, the interaction between AF9 and MLL is crucial for the regulation of gene expression, specifically facilitating the binding of the MLL enzyme complex to gene promoters in an active transcriptional state [
74]. This interaction significantly promotes the activation of HOX genes, which are key transcription factors regulating the development of the anteroposterior axis across various organisms. Their continuous expression is vital for maintaining the undifferentiated state of progenitor cells, similar to blast cells in AML [
74].
HOX genes, organized into four clusters (HOXA, HOXB, HOXC, HOXD), play crucial roles in development and disease. In early vertebrate development, their expression is regulated by chromosomal positioning, with specific clusters being condensed and inaccessible to transcription machinery, thereby inhibiting expression during early phases [
75,
76,
77,
78]. Typically down-regulated post-embryogenesis, these genes can become aberrantly reactivated in neoplastic conditions, potentially leading to states that favor uncontrolled cellular proliferation [
79]. Humans possess 39 HOX genes across seven families, with specific genes like HOXB3, HOXB4, and HOXA7 to HOXA11 linked to adverse outcomes in diseases such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) [
80,
81,
82,
83,
84].
In leukemia, specific HOX genes like HOXA1, HOXA9, HOXB4, and HOXB7 influence various regulatory pathways that affect prognosis. For instance, HOXA1 modulates TGFβ2 and BFGF, enhancing apoptosis in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), while HOXA9 promotes cell growth by upregulating c-myb transcription and IGF-IR surface expression. Conversely, HOXB4's inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway and HOXB7's downregulation of p27 are linked to the progression of diseases like ALL [
85].
Specifically, the RUNX1 and MLL-AF9 interaction disrupts normal hematopoietic gene expression, highlighting the significance of the NPM1 gene in AML pathology. NPM1 mutations, present in about 30% of AML cases, correlate with HOX gene expression and impact leukemogenesis through pathways like the CEBPα pathway, activating CTBP transcriptional regulators and affecting the expression of HOXA5, HOXB5, and HOXA10 in NPM1 mutant AMLs [
86,
87,
88,
89,
90].
Therefore, the recognition of the presence of the MLL-AF9 fusion gene in AML is clinically significant, as this genetic alteration can influence treatment selection and therapeutic response monitoring. Patients with this gene fusion may require more aggressive therapeutic approaches and combined treatment strategies to enhance outcomes and overcome resistance to conventional treatments [
91].
5. First Line Treatments for AML May Cause T(9;11), a Mechanistic Perspective
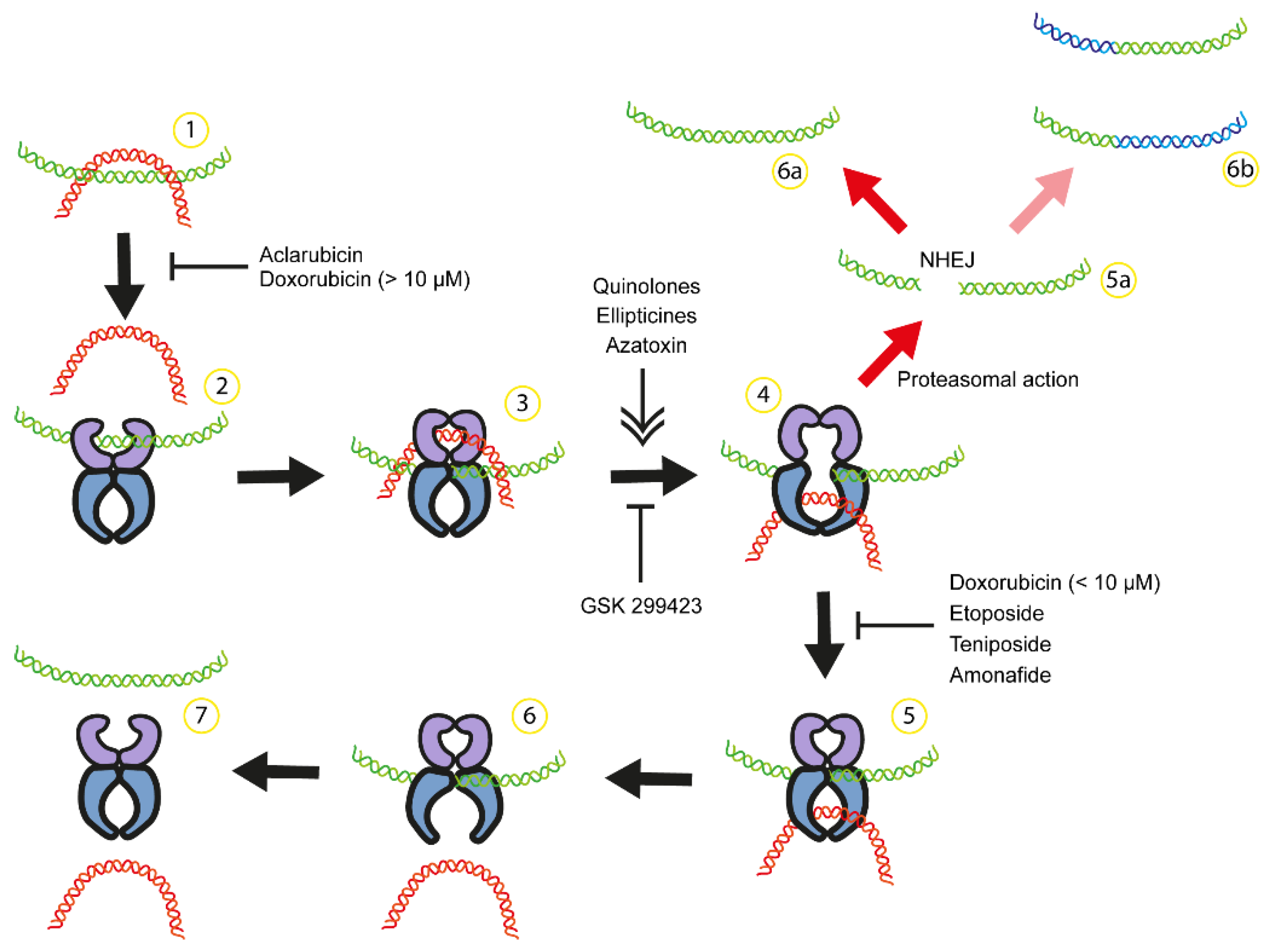
A range of anticancer agents specifically target topoisomerase II (Top2), an essential enzyme in DNA replication, to combat malignant neoplasms. These drugs disrupt the Top2 catalytic cycle in various steps (
Figure 1), leading to an acomulation of Top2-DNA cleavage complexes and double-strand break (DSB), culminating with cell death. Top2 poisons such as etoposide, teniposide, and doxorubicin inhibit the re-ligation of DNA following Top2-induced cleavage, while other compounds like quinolone CP-115,953 and azatoxins initiate DNA break formation [
92,
93]. Notably, doxorubicin, a well-known anthracycline, acts as an inhibitor of DNA re-ligation at lower concentrations (<1 μM) but may interfere with Top2's DNA binding at higher concentrations (>10 μM) [
93]. Despite their effectiveness, these Top2 poisons, which remain in clinical use, are linked to severe adverse effects, including the emergence of secondary malignancies [
94,
95,
96]. Notably, therapy-related Acute Leukemias (t-AL), often following treatment-related Myelodysplastic Syndromes (t-MDS), culminate in therapy-related Acute Myelocytic Leukemia (t-AML), presenting significant clinical challenges [
97,
98]. Etoposide, a chemotherapy drug, is linked to an increased risk of t-AML and t-MDS, particularly when used in cumulative doses exceeding 2000 mg/m2 in the treatment of testicular and extragonadal germ cell tumors [
99,
100]. The risk is notably higher within the first five years post-treatment, although cases of t-AML/MDS have been reported even two decades after initial treatment with this drug [
101]. Systematic reviews reported that in the context of germ cell tumor treatment, the incidence rates of t-AML/MDS far surpass those of spontaneously occurring AML/MDS, underscoring the significant risk increase attributable to etoposide-based chemotherapy regimens [
102,
103].
Comparing de novo AML/MDS to t-AML/MDS showcases a significant risk increase, with t-AML/MDS being 13 to 200 times more likely. This heightened risk, notably following etoposide and anthracycline treatments, extends to other chemotherapies for various cancers [
101,
103,
104]. A common feature in t-AML is chromosomal translocations, particularly involving the MLL gene on chromosome 11q23, with translocations such as MLL-AF9 being pivotal in leukemia development [
105,
106,
107,
108]. The MLL gene frequently translocate with partners such as ENL (MLLT1), AF4 (MLLT2), and AF9 (MLLT3), among over a hundred identified partner genes [
20,
109,
110]. These translocations play a crucial role in leukemia development; for instance, MLL-AF9 can transform hematopoietic precursors and induce leukemia in animal models [
111,
112,
113].
The most frequently translocation partners for MLL gene are AF4 (MLLT2), AF9 (MLLT3), ENL (MLLT1), AF10 (MLLT10), and ELL, respectively [
20,
109,
110]. However, in the case of therapy-induced leukemia, the most frequently translocation partners are AF9, ELL, AF4, and ENL, respectively. Interestingly, AF9 is very common in pediatric AML cases with most of the MLL translocation at intron 9; however, in adult AML cases with MLL-AF9 fusion protein, MLL translocations occur more frequently at intron 11 [
109], probably caused by poison-induced DNA cleavage [
19,
109].
Taken together, first line treatments for AML, and other malignancies, use drugs against Top2 due to their ability to disrupt DNA replication processes. However, their use is associated with significant adverse effects, notably the increased risk of therapy-related malignancies like t-AML and t-MDS, largely due to the induction of chromosomal translocations involving the MLL gene, among others. These insights underscore the need for a delicate balance in cancer therapy, weighing the benefits of effective cancer treatment against the potential for long-term genetic consequences and the development of secondary malignancies. The fact that in t-AML the most frequently translocation is MLL-AF9 and patients with this fusion protein have an aggressive AML with bad prognosis. Also, as previously described, once MLL-AF9 has been formed, different target genes and cellular processes will be affected by this fusion protein. This leads to patients to have an aggressive AML with bad prognosis, which urges to have a better understanding of the mechanism downstream and upstream this fusion protein.
Figure 1.
Anticancer drugs can interfere with catalytic cycle of Top2 causing chromosomal translocation. 1) DNA supercoiling and catenation. 2) Top2 dimer binds to one DNA double helix (green) and some compounds can inhibit Top2 binding to DNA ([
93,
114]). 3-4) Top2 generate a double strand break of green DNA in the presence of Mg+2 and Top2 remains attached to both DNA ends. A second DNA double helix (red) passes through the break in an ATP-dependent process. Some compounds can stimulate or inhibit DNA break formation ([
92,
114,
115]). 5-7) After red DNA passage is completed, green DNA is religated and both DNA are released from the enzyme. 5a) Etoposide and doxorubicin can inhibit DNA religation ([
92,
114]) resulting in the accumulation of TOP2 attached to DNA ends. After proteasomal action, DNA with double strand breaks is repaired by non-homologous end-joining NHEJ and potentially leading to mutation (6a, ) or chromosome translocation (6b, [
19].
Figure 1.
Anticancer drugs can interfere with catalytic cycle of Top2 causing chromosomal translocation. 1) DNA supercoiling and catenation. 2) Top2 dimer binds to one DNA double helix (green) and some compounds can inhibit Top2 binding to DNA ([
93,
114]). 3-4) Top2 generate a double strand break of green DNA in the presence of Mg+2 and Top2 remains attached to both DNA ends. A second DNA double helix (red) passes through the break in an ATP-dependent process. Some compounds can stimulate or inhibit DNA break formation ([
92,
114,
115]). 5-7) After red DNA passage is completed, green DNA is religated and both DNA are released from the enzyme. 5a) Etoposide and doxorubicin can inhibit DNA religation ([
92,
114]) resulting in the accumulation of TOP2 attached to DNA ends. After proteasomal action, DNA with double strand breaks is repaired by non-homologous end-joining NHEJ and potentially leading to mutation (6a, ) or chromosome translocation (6b, [
19].
6. Emergence of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Factors in the Risk and Progression of AML: Role of ZEB Transcription Factors
The acknowledgment of increased t-AML incidence following first-line treatments for AML underscores a critical need for innovative therapeutic strategies that mitigate the risk of secondary malignancies while effectively combating primary disease states. As research progresses, a promising area of exploration involves the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) factors, known for their pivotal roles in cell differentiation and migration. In the context of AML, EMT factors contribute to the plasticity of leukemic cells, influencing their ability to resist apoptosis and evade the immune system, thus presenting a dual challenge and opportunity in leukemia treatment. By targeting these EMT factors, new treatments could potentially disrupt the cellular mechanisms that contribute to the aggressiveness and poor prognosis often observed in MLL-AF9 mediated AML.
Based on the work of Prange et al. [
116] and Stavropoulou et al [
117], it is increasingly clear that ZEB1 and ZEB2 may act as transcriptional targets of MLL fusion proteins. Prange et al. highlighted the genome-wide binding of MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 fusion proteins in AML cell lines, revealing both shared and unique target genes marked by specific epigenetic signatures. This study demonstrated how MLL fusions, alongside subsets of transcription factors, can deregulate critical gene programs in AML, suggesting a role for ZEB1 and ZEB2 within this framework. Similarly, Stavropoulou et al. underscored the impact of cellular origin on AML aggressiveness and identified EMT-related genes, including ZEB1, associated with poor outcomes in AML patients. Their work emphasizes the complex interplay between MLL fusion proteins and cellular origin in determining AML characteristics, where ZEB1 and ZEB2 emerge as potential mediators in the MLL-driven leukemic processes. These findings offer a refined perspective on the molecular mechanisms underpinning MLL-associated leukemia, highlighting the potential of ZEB1 and ZEB2 as EMT factors to be as critical components within this oncogenic network in AML.
7. Role of ZEB Transcription Factors
ZEB1/2 transcription factors dysregulation has previously been demonstrated to play pathological roles in the EMT processes involved in: 1) the malignant dissemination (metastasis) of epithelial derived tumour cells [
118,
119] 2) the acquisition of cancer or tumour stem cell properties [
120,
121], and 3) the development of treatment resistance [
122,
123]. The ZEB transcription factors are large multidomain proteins that contain both amino terminal as well as carboxy terminal Zinc Finger DNA binding domains that bind to bi-partite E-box binding sites (CACCT(G), sometimes CACANNT(G)) [
124] in the promoter/enhancer regions of target genes. These proteins can either suppress transcription by recruiting corepressor complexes such as the Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylase (NuRD) complex that contain Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) 1/2 resulting in chromatin closure and gene repression, or enhance transcription by attracting additional transcription complexes containing p300 acetylation factor that opens chromatin, allowing access to transcription factors [
125,
126] and the basic transcriptional machinery.
ZEB2 [
127,
128] and more recently ZEB1 [
129,
130] have been demonstrated to play important roles in regulating murine hematopoiesis as well as immune cell differentiation and function [
131,
132,
133] distinct from its roles in EMT. In Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells (HSPCs) ZEB2, and to a lesser degree ZEB1, limits inappropriate expression of innate and adaptive immune cell programs [
129,
130]. Upon lineage commitment, ZEB2 maintains distinct immune programs to produce defined populations of functional macrophage, dendritic, natural killer, and T cells [
131,
132,
133,
134]. Not only does ZEB2 ensure immune cell lineage fidelity that is unique to a given lineage, but it does so with very little overlap in terms of common gene expression programs it regulates. To exemplify this point, ZEB2 interacts with signals from the tissue environment to specify macrophage identity that is unique to the host organ (lung vs colon, etc.) with very little overlap of common Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) between organs that is associated with Zeb2 loss [
134]. Given the importance of these unique genetic programs in controlling lineage fate/function it is perhaps not surprising that ZEB protein dysregulation can lead to various different forms of leukemia via lineage-specific mechanisms including myeloid lineage transformation leading to AML [
135]. Recently, it has been described the role of ZEB1 in macrophage differentiation [
186], dendritic cell homeostasis [
187], pointing out that oncogenic ZEB1 can alter these processed during leukemogenesis.
Within the AML context ZEB1 and ZEB2 may become dysregulated though direct transcriptional control of the MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 oncofusion proteins [
116,
117]. Additionally, ZEB1/2 are known to be negatively regulated by the miR200 family of miRNAs [
136] and in their absence, ZEB proteins levels may accumulate to oncogenic levels. Within AML, the miR200 family of miRNAs has been found to be methylated and repressed, associated with increased ZEB2 levels [
137,
138]. Additional AML oncofusions including AML-ETO and PML-RARα have also been demonstrated to transcriptionally upregulate Zeb2 [
139] implying that ZEB2 upregulation may be a common driver of AML progression.
In terms of the importance of ZEB proteins in driving AML development/progression ZEB2 plays an oncogenic role. In two separate and unrelated genetic screening approaches ZEB2 was found to be involved in myeloid and lymphoid leukemic transformation and as being a novel genetic dependency in murine and human AML[
120,
137]. In the first instance, ZEB2 was overexpressed from the ROSA26 (R26) safe-harbor locus in Tie2-Cre lineage marked cells that includes the endothelium and entire hematopoietic system that is derived from the hemogenic endothelium of the Aorta-Gonad-Mesonephros (AGM) region [
120]. Tie2-Cre, R26Tg/Tg mice develop spontaneous T cell transformation around 6 months of age that genetically and phenotypically resembles Early Thymic Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ETP-ALL). ETP-ALL is characterized by transformed early T cell progenitors that express HSPC as well as myeloid cell markers. On a sensitized p53 null background Tie-Cre, R26Tg/Tg mice also developed AML and B-ALL but at lower frequencies. These results imply that ZEB2 may play oncogenic roles in myeloid and B cells, but additional genetic hits may be required for ZEB2-mediated leukemic transformation. In line with the latter, genetic alterations frequently implicate ZEB2 in various translocations and mutations within T-lymphoid leukemia and AML, with 14q32 rearrangements involving BCL11B marking a distinct subgroup. These genetic rearrangements form a unique expression profile that significantly affects leukemia biology and patient prognosis [
140].
In a separate unbiased CRISPR/Cas9 based screening approach, ZEB2 was found to be a top genetic dependency involved in in both human AML cell lines and MLL-AF9 murine AML proliferation [
137]. Knock-down of ZEB2 in human AML cell lines resulted in enhanced morphological differentiation as assayed by May-Grunwald-Giemsa staining analysis and increased mature CD11B myeloid marker expression in flow cytometry analysis [
137]. Genetic deletion of ZEB2 using a tamoxifen-inducible Cre-based approach in established murine MLL-AF9 model was found to significantly increase overall survival [
130]. Moreover, several studies support the oncogenic role of ZEB2 in human AML. Mechanistically, it has been shown that miR-454-3p targets ZEB2, playing a critical role in AML progression. Overexpression of miR-454-3p induces apoptosis and autophagy in AML cells by downregulating ZEB2 expression, which concurrently inhibits the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway [
141]. Additionally, the overexpression of the ZEB2-AS1 lncRNA, which leads to increased ZEB2 levels, has been associated with poorer clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia [
142]. These findings highlight the necessity of maintaining tight regulation of ZEB2 to prevent its upregulation to oncogenic levels.
The oncogenic role of ZEB1 in AML is more controversial as Almotiri et al., have recently postulated that ZEB1 may act as a tumor suppressor in that Zeb1 deletion in MLL-AF9 models can accelerate AML progression [
129]. Bioinformatically, evidence was provided that ZEB1 levels may be lower in certain subtypes of AML [
129]. However, simultaneous deletion of both Zeb2 and Zeb1 in murine MLL-AF9 AML settings was not found to alter overall survival. This is even though R26 locus-based expression of either Zeb1 or Zeb2 can both drive extramedullary hematopoiesis and monocyte lineage skewing [
130]. Separate bioinformatic analysis demonstrated that both ZEB1 and ZEB2 in human AML are significantly higher in the leukemic blast population than in the bulk tumor population analysed by Almotiri et al., suggesting that these transcription factors may be diluted in the bulk RNA-sample analysis as well as in overall levels of expression used in the Kaplan–Meier survival curves [
130]. Consistent with an oncogenic role of ZEB1 in AML, Stavropoulou et al., identified Zeb1 as an essential target of MLL-AF9 in HSC-like leukemic AML blast populations that play an important role of leukemic blast invasion to extramedullary sites [
117]. ZEB1 was also found to play an oncogenic role in human AML cell lines by increasing PI3K/AKT signaling [
143] that relies upon p53-PTEN pathway modulation. In the latter study, it was demonstrated that ZEB1 expression is negatively correlated with tumor suppressor P53 expression, and ZEB1 can directly bind to P53 as a molecular mechanism to exert oncogenesis.
The complex role of ZEB1 within AML extends to its effect on the immunological landscape, where it downregulates CD8 T cell activity and promotes the expansion of Th17 cells, enhancing the survival and proliferative capabilities of leukemia cells in the AML niche. Recently, Bassani et al. has been demonstrated that high levels of ZEB1 correlate with increased Th17 cell development and a pro-invasive phenotype associated with poor patient outcomes [
144,
145]. The analysis of ZEB1 expression in larger datasets of AML identifies two distinct groups, ZEB1high and ZEB1low, each with specific immunological and gene expression signatures. Importantly, ZEB1high patients exhibit increased expression of IL-17, SOCS2, and TGF-β pathways and a negative association with overall survival.
The role of ZEB1 is beyond protein level. It has been described that mutations in the splicing factor 3b subunit 1 (SF3B1) gene are frequent in myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS). In this context, is has been reported a strong upregulation of circRNAs processed from the ZEB1 locus, which may impact mitochondrial function and cellular metabolism in Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) [
146]. Moreover, ZEB1 interacts with long non-coding RNA MALAT-1, influencing its activity and stability through m6A modification, thereby modulating the aggressiveness of AML [
147]. Taken together this evidence highly suggests that ZEB1 serves as an oncogene at various levels of AML.
In summary, ZEB1 and ZEB2 transcription factors play important roles in the progression and aggressiveness of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by influencing epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stem cell characteristics, and therapy resistance. These factors are often dysregulated due to transcriptional control by MLL fusion proteins or repression by the miR200 family of miRNAs, leading to enhanced oncogenic activity. Specifically, ZEB2 has been linked to both myeloid and lymphoid leukemic transformations, affecting hematopoietic differentiation and immune modulation, while ZEB1 impacts the immune system by regulating T cell activities and promoting Th17 cell expansion, which correlates with poor clinical outcomes. Given their significant roles, targeting ZEB proteins offers a promising therapeutic approach to potentially improve treatment efficacy and reduce the incidence of secondary malignancies like therapy-related AML (t-AML).
8. Role of SNAI Transcription Factors
The SNAI family (SNAI1-3) of transcription factors have also been demonstrated to play essential roles in EMT [
148] as well as acquisition of cancer stemness properties [
149] and drug resistance [
150]. SNAI proteins have conserved carboxy terminal Zinc Finger DNA binding domains that are also capable of binding to E-box elements (5’-CAGGTG-3’) in the promoter of epithelial genes such as E-cadherin, where is involved in its transcriptional repression. Regarding the miR200-SNAI1 relationship, studies have shown that SNAI1 plays a key role in facilitating EMT and mesoderm differentiation during a particular phase of embryonic stem cell differentiation, which aligns with the early epiblast stage. In this period, Snai1 modifies the levels of various miRNAs, notably those within the miR200 family, but it is unclear if this relationship occurs in hematopoiesis [
151]. The SNAI proteins all have an amino terminal SNAI-GFI (SNAG) binding domain that is responsible for recruitment and promoter binding of epigenetic factors such as Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) that is responsible for histone 3 lysine 4 demethylation (H3K4me1/2) and gene repression [
152]. This SNAG domain as its name implies is shared with other proteins including the GFI1/1B transcription factors that play important roles in hematopoiesis [
153]. The SNAI proteins have as well been demonstrated to play roles in hematopoiesis. SNAI2 has been demonstrated to act downstream of the c-Kit signaling pathway in HSPC [
154] and SNAI2/3 have been demonstrated to play functionally redundant roles in B and T cell development [
155].
From an AML perspective SNAI1 has been found to be overexpressed broadly in both primary AML samples and cell lines irrespective of the driver mutations [
156] present. ShRNA-mediated knock-down (KD) of SNAI1 in human AML cell lines was found to lead to enhanced morphological differentiation as assayed by May-Grunwald-Giemsa staining analysis and increased mature CD11B myeloid marker expression in flow cytometry analysis [
156] similar to the effects associated with ZEB2 KD [
137]. As well, tamoxifen-mediated knock out of Snai1 significantly improved the survival of mice transplanted with MLL-AF9 as well as AML-ETO/N-RAS models of AML [
156], also similar to ZEB2 knockouts [
130].
Mechanistically, increased mouse Snai1 was demonstrated to alter myeloid development and lead to enhanced self-renewal of myeloid progenitors [
156]. Vav-iCre, R26-Snai1Tg mice go on to develop a myeloproliferative disorder that progresses to full AML transformation with 50% of these mice succumbing to AML by 400 days [
156]. These effects on myeloid differentiation were demonstrated to be due to binding to LSD1 as point mutants in the SNAG domain that ablated LSD1 binding while still preserving protein stability did not alter myeloid development [
156]. As well, RNA-seq and ChIP-seq experiments demonstrated that increased SNAI1 expression lead to enhanced recruitment of LSD1 to repress SNAI1 target genes, potentially at the expense of other key transcriptional regulators that require LSD1 for ensuring normal hematopoiesis such as GFI-1 proteins [
156,
157].
9. ZEB2-LSD1 Axis and Other Potential Therapeutic Targets
The ability of EMT transcription factors to alter LSD1 function is an emerging theme in AML and other leukemias such as ETP-ALL, as ZEB2 has previously been demonstrated to interact with LSD1 [
137,
158] in both of these settings. Within the ETP-ALL context increasing levels of ZEB2 were shown to be associated with increased susceptibility to LSD1 inhibitors [
158]. The same likely holds true for the levels of SNAI1 and ZEB2 in human AML. LSD1 inhibitor therapy is an emerging promising new cancer therapy not only in AML [
159] but other solid forms of cancer including Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and childhood sarcomas [
160]. Whether or not EMT-TF levels also drives LSD1 inhibitor sensitivity in solid tumour settings also remains to be determined.
Like other monotherapies, resistance mechanisms to LSD1 inhibition is likely to occur. As an example, ZEB2 has been demonstrated to upregulate IL-7R expression that may be part of its ability to transform T cells [
120,
161]. Enhanced IL-7 signaling has recently emerged as a resistance mechanism for developing LSD1 inhibitor resistance [
162] as the IL-7R pathway drives increased JAK/STAT signaling that increases the amount of the pro-survival BCL2 protein. ZEB2-LSD1 complexes in ETP-ALL were shown to repress pro-apoptotic BIM protein levels. Therefore, combination therapies using LSD1i with JAK/BCL2 inhibition were demonstrated to be synergistic in treating ETP-ALL in vitro and in vivo patient derived xenotransplant settings [
162] as this combination was demonstrated to shift the balance of survival factors towards pro-apoptotic programs.
IL-7 is not known to be expressed in AML, however ZEB2 has been demonstrated to modulate other myeloid relevant cytokines such as IL-6 and G-CSF [
128] and SNAI1 may enhance TNF/NF signaling [
156] that may activate similar pro-survival pathways in AML.
Overall, the ability of ZEB and SNAI family members to influence key epigenetic modulators such as LSD1 and control key cytokine signaling pathways may offer new therapeutic options for treating AML the more we understand this crosstalk. The roles of SNAI and ZEB proteins are summarized in
Table 2. In addition to the ability of ZEB and SNAI proteins to control genes involved in adhesion and migration may also offer new therapeutic avenues in AML that are discussed below.
10. Role of SNAI2 in AML
It has been shown that SNAI2, like SNAI1 is closely linked with the progression and treatment response of leukemia. SNAI2 promotes leukemogenesis, and its loss or pharmacological inhibition impairs Leukemic Stem Cells (LSCs) self-renewal and delays leukemia progression. At the transcriptional level, Slc13a3, a direct target of SNAI2 in LSCs, restricts the self-renewal of LSCs and significantly prolongs recipient survival, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target [
163]. Furthermore, SNAI2's involvement in chemoresistance complicates treatment strategies; its expression is associated with robust resistance to conventional chemotherapy in LSCs, underscoring the need for targeted therapies that can overcome this barrier [
164]. Taken together, these studies underscore SNAI2's oncogenic role in leukemia biology, influencing stem cell dynamics and conferring drug resistance, each aspect offering potential opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
11. Role of TWIST1 in AML
TWIST1, a transcription factor, is central to the pathophysiology of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), affecting multiple biological processes that govern disease progression and treatment response. TWIST1 promotes cell growth, drug resistance, and progenitor clonogenic capacities in myeloid leukemia, and it is linked to poor prognostic factors [
165]. In line with this, a recent study demonstrated Twist1 expression and promoter methylation level were significantly upregulated in AML tissues and cell lines, and its expression was further downregulated by using the demethylating agent 5'-azacitidine (5-Aza)-treated cells, leading to apoptosis [
166]. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was positively regulated by Twist1, suggesting that Twist1 serves as an oncogene in AML.
Moreover, TWIST1 is notably involved in the extramedullary manifestations of AML, where it significantly promotes tissue invasion and metastasis. Treatments with TWIST1-siRNA or metformin downregulate TWIST1, including SNAI2, which is associated with significant impairment of migration and invasion processes [
167]. TWIST1 is also essential for the viability and self-renewal of leukemia stem cells (LSCs), especially in MLL-AF9 leukemia, thus promoting disease initiation and maintenance [
168]. The role of TWIST1 is not only restricted to LSCs, since it has been demonstrated that TWIST1 influences bone marrow microenvironment interactions by modulating mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, which in turn promotes leukemia expansion [
169]. In line with the latter, the role of TWIST1 in promoting AML are also seen in the recruitment of regulatory T cells within the tumor microenvironment, potentially providing new targets for immunotherapeutic approaches [
170].
TWIST1's role extends to chemoresistance, where it interacts with DNA methyltransferase 3a (DNMT3a) to regulate resistance to decitabine, a key therapeutic agent in treating AML [
171]. This interaction underscores the potential for targeting TWIST1 in therapeutic strategies aimed at overcoming chemoresistance.
In summary, the extensive involvement of TWIST1 in AML suggests its utility not only as a biomarker for disease progression and treatment response but also as a promising target for therapeutic intervention. This could lead to the development of more personalized and effective treatment strategies for AML, transforming current paradigms and improving patient outcomes [
165].
Table 2.
Comparative Overview of EMT Factors and Their Roles in AML:.
Table 2.
Comparative Overview of EMT Factors and Their Roles in AML:.
| Feature |
ZEB1 |
ZEB2 |
SNAI1 |
SNAI2 |
TWIST1 |
| Roles in EMT Processes |
Involved in malignant dissemination and metastasis [116,117] |
Plays a role in cancer or tumor stem cell properties, development, and treatment resistance [118,119] |
Essential for EMT, cancer stemness, and drug resistance [148,149,150] |
Promotes leukemogenesis and influences chemotherapy resistance [163,164] |
Central to AML pathophysiology, affects growth, and drug resistance [165] |
| Roles in Hematopoiesis |
Lesser degree of influence compared to ZEB2
[129,130] |
Limits inappropriate expression of immune cell programs [131,132,133,134] |
Influences stem and progenitor cell functions [151] |
Impairs LSCs self-renewal, restricts LSC self-renewal via Slc13a3 [163] |
Impacts progenitor clonogenic capacities [168] |
| Regulation by MiR200 Family of miRNAs |
Negatively regulated, lower levels in certain AML subtypes [136] |
Negatively regulated, absence leads to oncogenic levels [136,137,138] |
Relationship in hematopoiesis unclear [151] |
Not specified |
Not specified |
| Influence on AML Patient Outcomes |
Associated with poor outcomes, essential for leukemic blast invasion [117,130] |
Upregulation associated with leukemic blasts [130] |
Overexpression contributes to impaired differentiation and enhanced self-renewal [156] |
Associated with poor clinical outcomes [164] |
Linked to poor prognostic factors, promotes tissue invasion [165,167] |
| Oncofusion Protein Interactions |
Upregulated by MLL-AF9, MLL-AF4 [117] |
Upregulated Upregulated by AML-ETO, MLL-AF9, MLL-AF4, and PML-RARα [116,117] |
Not clear |
Not specified |
Notably involved in extramedullary manifestations [167] |
| Genetic Screening Findings |
Deletion may accelerate AML progression
[129,130] |
Involved in myeloid and lymphoid leukemic transformation
[120,137] |
Knockdown enhances morphological differentiation and improves survival [156] |
Not specified |
Essential for viability and self-renewal of LSCs [168] |
| Functional Roles in Immune Cell Differentiation |
Plays a role in macrophage differentiation [172], dendritic cell homeostasis [173] |
Ensures immune cell lineage fidelity
[131,132,133,134] |
Implicated in myeloid development and self-renewal of progenitors [154,155]
|
Not specified |
Influences bone marrow microenvironment interactions [169] |
| Contribution to Leukemic Transformation |
Potentially oncogenic, may act as a tumor suppressor [129,130] |
Involved in myeloid leukemia transformation [135] |
Leads to myeloproliferative disorders and AML transformation [155,156]
|
Promotes leukemogenesis [163] |
Promotes disease initiation and maintenance [168] |
| Potential Therapeutic Targets |
Could offer novel approaches for AML treatment if targeted [143,144,145] |
Inhibition may improve outcomes [137,138,139,162] |
Knockout or inhibition improves survival [156] |
Targeting could impair LSCs self-renewal and chemoresistance [164] |
Targeting TWIST1 could overcome chemoresistance and influence treatment [171] |
12. Spread of AML Cells
In this section we review some of the most studied molecular components of microenvironments responsible for AML spread and extramedullary hematopoiesis. AML, as a liquid tumor, inherently possesses greater mobility and penetration capabilities than solid tumors. Still, AML cells require robust molecular mechanisms for invading other bone marrow sites or establishing ExtraMedullary Engraftment (hereafter referred to as EME) [
174]. Certain molecular factors involved in AML-EME can hinder immunotherapy effectiveness and protect AML cells within the bone marrow [
175]. Others enhance engraftment properties, facilitate cell motility, and enable the transition of AML cells between the bone marrow and bloodstream, contributing to EME [
176,
177].
A critical area of focus is the role of EMT factors in AML-EME, which may elucidate aspects of the disease's aggressive progression. A recent study using RNA-seq analyses to compare gene expression between AML patients with and without relapse have identified EMT-related genes such as CDH2 [
178], LOX [
179], and COL3A1 [
180,
181,
182] as strong correlates of AML prognosis and EME. CDH2, also known as N-cadherin, plays a pivotal role in cell adhesion and motility, thereby enhancing the potential for leukemic cells to invade distant tissues. Similarly, LOX and COL3A1, which are crucial to Extracellular Matrix (ECM) functionality, support the structural dynamics necessary for tumor metastasis and invasion. [
181].
13. Intravasation and Extravasation Mechanisms of AML
The mechanism by which AML cells gain the ability to extravasate from the bone marrow and into the bloodstream marks the beginning of AML-EME. A key component in this process is the formation of invadosomes, cellular structures in cancer cells that degrade the ECM and facilitate entry into the bloodstream [
183]. These structures are also crucial during extravasation, where AML cells must breach the endothelial cell barrier to exit the vasculature and invade surrounding tissues. The transformation of AML cell structures into invadopodia, actin-based membrane protrusions capable of degrading the ECM, is critical for penetration through the vasculature endothelium. Invadopodia also recruit ECM proteases, aiding this process [
184,
185]. These actin-based membrane protrusion structures can degrade the ECM and make cell penetration through the endothelium of vasculature and in addition, invadopodia can recruit ECM proteases that contribute to this process [
186].
Proteins commonly found in invadopodia include cortactin [
187], actin filament nucleating proteins like N-WASP [
188], scaffold proteins such as Tks4 [
189] and Tks5 [
189,
190], and metalloproteases [
191]. These proteins work together to facilitate cell motility and ECM degradation, enabling intravasation and extravasation in metastatic AML, including other leukemias [
192,
193]. The Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) produced by AML cells induces bone marrow degradation, specifically targeting laminin and type IV collagen, and promoting vessel sprouting [
194]. This process creates thin ECM 'hotspots,' making these sites more susceptible to invasion by AML cells [
195], Once relocated to other bone marrow sites, AML cells can grow by re-establishing their initial niche microenvironments.
From a mechanistic perspective, the Myocardin-Related Transcription Factors and Serum-Response Factor (MRTF-SRF) pathway mediates some migration properties of AML cells and is notably present in the MLL-AF9 model [
196]. E-selectin, a surface glycoprotein expressed by the vasculature [
197], binds to ligands on both normal immune and AML cells. Activated endothelial cells expressing E-selectin may signal AML cell attachment and facilitate intravasation, working in conjunction with motility strategies [
195]. While in the bloodstream, AML cells require additional molecular tools to evade immune detection. SETDB1, a lysine methyltransferase key in epigenetic regulation, helps AML cells escape immune response by methylating retrotransposons [
198]. While SETDB1 can repress tumorigenic genes, it also enables AML cells to evade immune detection [
198,
199]. Similarly, CD36, a multifunctional scavenger receptor, is linked to EME dissemination and increased relapse risk post-chemotherapy. Blocking CD36 delays AML relapse, while binding of thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) to CD36 promotes AML migration [
200]. Altogether, these findings suggest that a balance is required between molecular properties for migration and those that improve homing and treatment resistance.
During extramedullary invasion, AML cells may adhere to microenvironments near critical organs during their journey through the bloodstream, initiating extramedullary colonization [
201]. The survival of AML cells within the bone marrow depends on the chemokine Stromal Cell-Derived Factor (SDF-1), also known as CXCL12, which acts as a survival and attachment factor within the bone [
202]. SDF-1 is produced by stromal cells in the spleen, bone marrow, and extramedullary sites like the skin and central nervous system, facilitating AML cell attachment outside the bone marrow [
203]. This aspect of AML is less studied than in ALL.
Interestingly, CXCR4, the receptor for SDF-1, is expressed variably among AML cells [
204]. AML cells show lower CXCR4 expression compared to normal bone marrow cells [
205], suggesting that reduced CXCR4 expression is linked to loss of bone marrow attachment. Blocking CXCR4 increases AML cell migration, indicating CXCR4's role in regulating bone marrow niche adherence [
188]. Additionally, poor prognosis in AML patients is associated with the expression of CXCR4 or E-selectin [
206]. ZEB2, a regulator of CXCR4, therefore emerges as a potential target in the EME process [
127,
137].
Regarding the extravasation process, there is opportunity for targeted therapies. Extravasation by E-selectin is reduced by the action of Uproleselan, an E-selectin antagonist that also induces AML cell mobilization from the bone marrow into the bloodstream, making them more vulnerable to chemotherapy [
207] On the other hand, Integrin β2, expressed by AML cells, binds to Matrix Metalloprotease 2 (MMP-2), responsible for extramedullary cell invasion and metastasis by degrading the ECM [
183]. Altogether these findings highlight the complexity of AML metastasis and suggest novel potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Table 3.
An analysis of various molecular factors that significantly impact the behavior of AML cells, particularly in the context of metastasis.
Table 3.
An analysis of various molecular factors that significantly impact the behavior of AML cells, particularly in the context of metastasis.
| Factor |
Survival |
Motility |
Adherence |
| SDF-1 |
✓ [202] |
|
✓ [203] |
| METTL-3 |
✓ [208] |
|
|
| Integrin β |
|
✓ [183] |
✓ [183] |
| N-WASP |
|
✓ [188] |
|
| Tks4, Tks5 |
|
✓ [189,190] |
|
| E-selectin |
|
✓ [197] |
✓ [197] |
AML-EME can manifest as sarcomas, which are solid myeloblasts proliferating outside the bone marrow. This occurs in approximately 2.5-9.1% of adults with AML [
212]. However, certain AML subtypes, such as those involving the t(8;21) translocation, show a higher incidence of AML-EME, reported in 18-24% of cases [
213]. Locations reported include soft tissues, ovary, intestines, testis, breast, lymph nodes, renal mass and eye, but the most common ones are soft tissue and lymph nodes [
213]. CD56, a Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule (N-CAM) commonly expressed in the brain, has been consistently linked to poor prognosis in AML [
214,
215,
216]. The brain, considered a sanctuary tissue, is often associated with a poor leukemia prognosis [
217].
The infiltration of AML-EME cells into the Central Nervous System (CNS), including the skull, meninges, and the brain, is considered rare, though its incidence may be underestimated due to infrequent diagnostic procedures [
218]. The most documented cases involve cranial bone marrow infiltration by AML cells. For example, a patient case report indicated bone marrow replacement disorder in the skull's bone marrow, leading to an AML diagnosis [
218]. Notably, CNS involvement is more common in pediatric AML than in adult cases [
219]. Key risk factors for CNS involvement in AML include complex karyotypes, AML relapse, FAB M5 classification, high LDH levels, the presence of other extramedullary AML manifestations, and FLT3-ITD mutations [
220]. In contrast, CNS involvement in APL typically presents as meningeal leukemia and is more frequently observed [
212].
In summary, the role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) factors is particularly notable in AML-EME, impacting prognosis and disease progression. Genes like CDH2, LOX, and COL3A1 have been identified as key correlates of AML-EME. Also, intravasation and extravasation mechanisms, including the formation of invadosomes and invadopodia, are crucial in the spread of AML cells. These mechanisms are supported by proteins such as cortactin, N-WASP, Tks4, Tks5, and metalloproteases, which facilitate cell motility and degrade the extracellular matrix. Adaptation to new tissue environments requires AML cells to evade immune detection, by various discussed mechanisms. In conclusion, understanding the molecular mechanisms behind AML's EME ability is crucial. This knowledge provides insight into potential therapeutic targets and strategies to combat the spread of AML, particularly in challenging cases involving extramedullary sites including CNS involvement.
The overall roles of EMT-TFs in normal hematopoiesis, AML transformation and EME is summarized in
Figure 2.
14. Overall Conclusions and Future Directions
AML, with its profound genetic, molecular, and clinical heterogeneity, continues to pose significant challenges in oncology. This review has explored the complex landscape of AML, considering the current disease classification, molecular characteristics, and the dynamic mechanisms that drive its aggressive progression and spread. The presence of genetic aberrations, such as FLT3, NPM1 mutations, and the MLL-AF9 gene fusion, are pivotal in predicting the prognosis, relapse, and therapeutic responses in AML, emphasizing the crucial role of personalized medicine in its management.
The exploration of EMT factors, particularly the ZEB, SNAI and TWIST gene families, reveals promising avenues for new therapeutic targets. Their significant roles in regulating hematopoiesis and influencing AML's aggressive EME behaviors highlight potential innovative treatment strategies that could target these pathways. Furthermore, understanding the molecular mechanisms that facilitate AML-EME—including the adaptation of AML cells to various microenvironments and their ability to evade immune surveillance—is essential. This knowledge opens new avenues for research and therapeutic interventions, which are crucial for developing novel strategies to manage and potentially overcome the aggressive nature of this malignancy.
The need to enhance the precision of genetic and molecular diagnostics is crucial for accurately categorizing AML subtypes and predicting treatment responses. Current strategies for stratifying AML increasingly rely on Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and other genomic technologies. These methods, including targeted gene panels and low-coverage whole genome sequencing, provide a more efficient classification of leukemia, pushing the boundaries of precision medicine. Such advancements not only improve diagnostic accuracy but also facilitate the development of targeted therapeutic strategies in AML.
Additionally, the development of targeted therapies that address the unique molecular aberrations of each AML subtype is critical. This approach may include novel drug combinations, advanced immunotherapies, including novel gene-editing technologies. Given the significant role of the bone marrow microenvironment in the progression of AML, targeting this niche presents a promising strategy to combat the disease. The exploration of EME and CNS involvement in AML also require further investigation to develop effective treatments for these particularly challenging manifestations of the disease.
Lastly, AML's management requires a multifaceted approach that integrates genetics, molecular biology, and innovative therapeutic strategies. Future research and clinical approaches should aim to incorporate these elements, moving towards more personalized and effective treatment modalities for patients afflicted with this complex form of leukemia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, DC, RA, AA, AAH, ARB, CF, JH. and TC.; investigation, DC, RA, ARB, AA, AAH, ARB, CF, JH. and TC.; writing—original draft preparation, DC, RA, AA, AAH, ARB, CG, VGP, CF, JH. and TC.; writing—review and editing, ARB, CF, JH , TC, VGP, CG.; visualization, CF, RA, JH, AR; funding acquisition, CF. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ANID SIA/PAI program code SA77210106 “Estudio de los factores de transcripción ZEB1 y ZEB2 en el desarrollo de células madre leucémicas para descubrir nuevos blancos terapéuticos contra la leucemia mieloide aguda (LMA).”
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Arber DA, O.A., Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M, Vardiman JW., The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. 19 ed. Vol. 127. 2016, blood.
- Chennamadhavuni A, L.V., Mukkamalla SKR, Shimanovsky A. , Leukemia. 2023, StatPearls.
- Clarkson, B., et al., Chronic myelogenous leukemia as a paradigm of early cancer and possible curative strategies. Leukemia, 2003. 17(7): p. 1211-62. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternak, G., et al., Chronic myelogenous leukemia: molecular and cellular aspects. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 1998. 124(12): p. 643-60. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis AS, V.A., Mead MD., Leukemia: an overview for primary care. . Am Fam Physician, 2014. 1;89(9): p. 731-8.
- Mewawalla1., A.V.P., Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 2023, StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- GLOBOCAN, estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. 2018: , CA Cancer J Clin: Erratum: Global cancer statistics 2018.
- Dohner, H., D.J. Weisdorf, and C.D. Bloomfield, Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med, 2015. 373(12): p. 1136-52.
- Reikvam, H., et al., Acute myeloid leukemia with the t(8;21) translocation: clinical consequences and biological implications. J Biomed Biotechnol, 2011. 2011: p. 104631. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallman MS, K.H., Paietta E, Bennett JM, Dewald G, Cassileth PA, Wiernik PH, Rowe JM; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group., Acute monocytic leukemia (French-American-British classification M5) does not have a worse prognosis than other subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2004, 2004. 1;22(7): p. 1276-86. [CrossRef]
- De Rossi G, A.G., Coluzzi S, Fenu S, LoCoco F, Lopez M, Nanni M, Pasqualetti D, Mandelli F., Immunological definition of acute promyelocytic leukemia (FAB M3): a study of 39 cases. Eur J Haematol., 1990. 45(3): p. 168-71. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TR., R., cute promyelocytic leukemia (AML-M3)--Part 1: Pathophysiology, clinical diagnosis, and differentiation therapy. Clin Lab Sci Spring, 2000. 13(2): p. 98-105.
- TR., R., Acute promyelocytic leukemia (AML-M3)--Part 2: Molecular defect, DNA diagnosis, and proposed models of leukemogenesis and differentiation therapy. Clin Lab Sci 2000 Spring, 2000. 13(2): p. 106-16.
- Saeed, S., et al., Genome-wide functions of PML-RARalpha in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Br J Cancer, 2011. 104(4): p. 554-8.
- Delaunay, J., et al., Prognosis of inv(16)/t(16;16) acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a survey of 110 cases from the French AML Intergroup. Blood, 2003. 102(2): p. 462-9.
- Plantier, I., et al., Inv(16) may be one of the only 'favorable' factors in acute myeloid leukemia: a report on 19 cases with prolonged follow-up. Leuk Res, 1994. 18(12): p. 885-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varotto E, M.E., Stefanachi F, Della Torre F, Buldini B., Diagnostic challenges in acute monoblastic/monocytic leukemia in children. Front Pediatr., 2022. 29;10.
- de Boer, J., V. Walf-Vorderwulbecke, and O. Williams, In focus: MLL-rearranged leukemia. Leukemia, 2013. 27(6): p. 1224-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, I.G. and C.A. Austin, DNA fragility at the KMT2A/MLL locus: insights from old and new technologies. Open Biol, 2023. 13(1): p. 220232.
- Meyer, C., et al., The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia, 2013. 27(11): p. 2165-76. [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z., et al., Acute erythroid leukemia. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2010. 134(9): p. 1261-70. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera N, L.A., Adélaïde J, Guille A, Murati A, Mozziconacci MJ, Vey N, Birnbaum D, Gelsi-Boyer V., Acute erythroid leukemias have a distinct molecular hierarchy from non-erythroid acute myeloid leukemias. Haematologica., 2020. 105(7): p. 340-342.
- Santos FP, F.S., Garcia-Manero G, Koller C, Beran M, O'Brien S, Pierce S, Freireich EJ, Huang X, Borthakur G, Bueso-Ramos C, de Lima M, Keating M, Cortes J, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F. Adult acute erythroleukemia: an analysis of 91 patients treated at a single institution. Leukemia. 2009 Dec;23(12):2275-80. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.181. Epub 2009 Sep 10. PMID: 19741728; PMCID: PMC4217206., Adult acute erythroleukemia: an analysis of 91 patients treated at a single institution. . Leukemia, 2009. 23(12): p. 2275-80. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gassmann W, L.H., Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma., 1995. 18(1): p. 69-73. [CrossRef]
- Dima D, O.L., Rosu AM, Trifa A, Selicean C, Moisoiu V, Frinc I, Zdrenghea M, Tomuleasa C. , Adult acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: rare association with cytopenias of undetermined significance and p210 and p190 BCR-ABL transcripts. Onco Targets Ther, 2017. 19;10: p. 5047-5051.
- SM., H., Classification of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Res. 2020, 2020. 31;55(S1): p. S1-S4.
- DA., A., The 2016 WHO classification of acute myeloid leukemia: What the practicing clinician needs to know. Hematol. 2019. 56(2): p. 90-95.
- Vardiman JW, T.J., Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM, Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A, Bloomfield CD., The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. . Blood., 2009. 39;114(5): p. 937-51.
- Marks, J.A., et al., TP53 in AML and MDS: The new (old) kid on the block. Blood Rev, 2023. 60: p. 101055. [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.G., et al., Treatment outcomes for newly diagnosed, treatment-naive TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hematol Oncol, 2023. 16(1): p. 19.
- Shimony, S., M. Stahl, and R.M. Stone, Acute myeloid leukemia: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol, 2023. 98(3): p. 502-526. [CrossRef]
- Huber, S., et al., AML classification in the year 2023: How to avoid a Babylonian confusion of languages. Leukemia, 2023. 37(7): p. 1413-1420. [CrossRef]
- Cicconi, L., et al., Long-term results of all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide in non-high-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia: update of the APL0406 Italian-German randomized trial. Leukemia, 2020. 34(3): p. 914-918. [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.A. and P. Montesinos, Risk-adapted treatment for low- and intermediate-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk, 2010. 10 Suppl 3: p. S130-4. [CrossRef]
- Cicconi, L., et al., Characteristics and outcome of acute myeloid leukemia with uncommon retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RARA) fusion variants. Blood Cancer J, 2021. 11(10): p. 167. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnera, L., et al., Atypical Rearrangements in APL-Like Acute Myeloid Leukemias: Molecular Characterization and Prognosis. Front Oncol, 2022. 12: p. 871590. [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.L., P.J. Jiang, and M. Yuan, [Clinical Prognostic Factors Analysis of Initially Treated AML Children with t(8;21)/RUNX1-RUNX1T1()]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2020. 28(5): p. 1510-1515.
- Schnittger, S., et al., Rare CBFB-MYH11 fusion transcripts in AML with inv(16)/t(16;16) are associated with therapy-related AML M4eo, atypical cytomorphology, atypical immunophenotype, atypical additional chromosomal rearrangements and low white blood cell count: a study on 162 patients. Leukemia, 2007. 21(4): p. 725-31.
- Ye, Y., et al., Lower relapse incidence with haploidentical versus matched sibling or unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation for core-binding factor AML patients in CR2: A study from the Global Committee and the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Am J Hematol, 2024. [CrossRef]
- van Weelderen, R.E., et al., Optimized Cytogenetic Risk-Group Stratification of KMT2A-Rearranged Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Adv, 2024.
- Krauter, J., et al., Prognostic factors in adult patients up to 60 years old with acute myeloid leukemia and translocations of chromosome band 11q23: individual patient data-based meta-analysis of the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Intergroup. J Clin Oncol, 2009. 27(18): p. 3000-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiriches, C., et al., Understanding a high-risk acute myeloid leukemia by analyzing the interactome of its major driver mutation. PLoS Genet, 2022. 18(10): p. e1010463. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.Y., et al., Validation of the prognostic significance of the 2022 European LeukemiaNet risk stratification system in intensive chemotherapy treated aged 18 to 65 years patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol, 2023. 98(5): p. 760-769. [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, D., et al., Molecular Classification and Overcoming Therapy Resistance for Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Adverse Genetic Factors. Int J Mol Sci, 2022. 23(11). [CrossRef]
- Rorvik, S.D., et al., Acute myeloid leukemia with rare recurring translocations-an overview of the entities included in the international consensus classification. Ann Hematol, 2024. 103(4): p. 1103-1119. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branford, S., et al., Prognosis for patients with CML and >10% BCR-ABL1 after 3 months of imatinib depends on the rate of BCR-ABL1 decline. Blood, 2014. 124(4): p. 511-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, J., et al., Molecular, clinical and therapeutic determinants of outcome in NPM1 mutated AML. Blood, 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, F.M. and H.A. Hou, CEBPA mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: implications in risk stratification and treatment. Int J Hematol, 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.L., et al., [Efficacy and prognostic factors of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of secondary acute myeloid leukemia]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2024. 45(1): p. 41-47. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, X.C., et al., Poor prognostic implications of myelodysplasia-related mutations in both older and younger patients with de novo AML. Blood Cancer J, 2023. 13(1): p. 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawankar, N. and B.R. Vundinti, Cytogenetic abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndrome: an overview. Hematology, 2011. 16(3): p. 131-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, I., et al., AML, NOS and AML-MRC as defined by multilineage dysplasia share a common mutation pattern which is distinct from AML-MRC as defined by MDS-related cytogenetics. Leukemia, 2022. 36(7): p. 1939-1942. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H., et al., Clinical characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of 118 cases of myeloid sarcoma. Sci Rep, 2022. 12(1): p. 6752. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi S, Y.A., he molecular functions of common and atypical MLL fusion protein complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020, 2020. 1863(7): p. 194548. [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci I, M.C., KMT2A-rearranged leukemia: the shapeshifter. blood, 2022. 27;140(17): p. 1833-1835. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H., The complex activities of the SET1/MLL complex core subunits in development and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2020. 1863(7): p. 194560. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel AT, B.P., Zou T, Feather D, Wu X, Yan J, Zhang H, Liu Z, Ernst P, Koretzky GA, Hua X., MLL-AF9-induced leukemogenesis requires coexpression of the wild-type Mll allele. Cancer Cell. 2010 2010. 17;17(2).
- Slany., R.K., The molecular biology of mixed lineage leukemia. Haematologica 2009, 2009. 94(7): p. 984-993. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedadi M, B.L., Eram MS, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Arrowsmith CH, Hajian T., Targeting human SET1/MLL family of proteins. Protein Sci. 2017, 2017 26(4): p. 662-676.
- Yang, W., Ernst, P., SET/MLL family proteins in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Int J Hematol 2017. 105: p. 7–16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove MS, P.A., Mixed lineage leukemia: a structure-function perspective of the MLL1 protein. . FEBS J. 2010, 2010. 277(8): p. 1832-42. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RK., S., he molecular biology of mixed lineage leukemia. Haematologica. 2009, 2009. 94(7): p. 984-93.
- Winters, A.C. and K.M. Bernt, MLL-Rearranged Leukemias-An Update on Science and Clinical Approaches. Front Pediatr, 2017. 5: p. 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X. and Y. Song, Structure, function and inhibition of critical protein-protein interactions involving mixed lineage leukemia 1 and its fusion oncoproteins. J Hematol Oncol, 2021. 14(1): p. 56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuts, B.M.H.A.-A., S.; Alkema, S.G.; Tijchon, E.; Jussen, L.; Bergevoet, S.M.; van der Reijden, B.A.; Martens, J.H.A, Inducible MLL-AF9 Expression Drives an AML Program during Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hematopoietic Differentiation. Cells 2023, 2023. 12: p. 1195. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoch C, S.S., Klaus M, Kern W, Hiddemann W, Haferlach T., AML with 11q23/MLL abnormalities as defined by the WHO classification: incidence, partner chromosomes, FAB subtype, age distribution, and prognostic impact in an unselected series of 1897 cytogenetically analyzed AML cases. blood 2003, 2003. 1;102(7): p. 2395-402.
- Hagag AA, S.S., El-Fadaly NH., Frequency of 11q23/MLL gene rearrangement in Egyptian childhood acute myeloblastic leukemia: Biologic and clinical significance. South Asian J Cancer. 2014, 2014. 3(4): p. 206-8.
- Heuts, B.M.H., et al., Inducible MLL-AF9 Expression Drives an AML Program during Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hematopoietic Differentiation. Cells, 2023. 12(8). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschalek, R., MLL. Elsevier, 2017.
- Kabra A, B.J., The Intrinsically Disordered Proteins MLLT3 (AF9) and MLLT1 (ENL) - Multimodal Transcriptional Switches With Roles in Normal Hematopoiesis, MLL Fusion Leukemia, and Kidney Cancer. J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan, 2022. 15;434(1): p. 167117. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GeneCards., MLLT3 Gene. GeneCards. 2023.
- Yi, Y., Ge, S. , Targeting the histone H3 lysine 79 methyltransferase DOT1L in MLL-rearranged leukemias. J Hematol Oncol, 2022. 15: p. 35. [CrossRef]
- Olsen SN, G.L., Healy JP, Choi YA, Kai Y, Hatton C, Perner F, Haarer EL, Nabet B, Yuan GC, Armstrong SA. , MLL::AF9 degradation induces rapid changes in transcriptional elongation and subsequent loss of an active chromatin landscape. Mol Cell. 2022, 2022. 17;82(6): p. 1140-1155.
- Stavropoulou V, P.A., Schwaller J. , Aggressive leukemia driven by MLL-AF9. Mol Cell Oncol. 2017, 2017. 23;5(3): p. 1241854.
- Francis, J.C., Gardiner, J.R., Renaud, Y. et al., HOX genes promote cell proliferation and are potential therapeutic targets in adrenocortical tumours. Br J Cancer, 2021. 124: p. 805–816. [CrossRef]
- Ikeda D, C.S., Uchiyama S, Nakamura H, Guo YM, Yamauchi N, Yuda J, Minami Y., Molecular Classification and Overcoming Therapy Resistance for Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Adverse Genetic Factors. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 2022. 25;23(11): p. 5950.
- Myers, P.H.g.i.d.T.H.c.N.E., http://scienceblogs.com/pharyngula/2007/09/the_hox_code.php Hox genes in development: The Hox code. . Nature Education, 2008. 1(1): p. 2.
- Hubert KA, W.D., Hox genes in development and beyond. . Development. 2023, 2023. 1;150(1): p. 192476. [CrossRef]
- Lappin TR, G.D., Thompson A, Halliday HL. HOX genes: seductive science, mysterious mechanisms., HOX genes: seductive science, mysterious mechanisms. Ulster Med J. 2006, 2006. 75(1): p.:23-31.
- Luo Z, R.S., Farnham PJ., The Enigmatic HOX Genes: Can We Crack Their Code? Cancers (Basel). 2019, 2019. 7;11(3): p. 323.
- Alharbi RA, P.R., Pandha HS, Morgan R., The role of HOX genes in normal hematopoiesis and acute leukemia. Leukemia. 2013 2013. 27(5): p. 1000-8.
- Nagy Á, Ő.Á., Budczies J, Krizsán S, Szombath G, Demeter J, Bödör C, Győrffy B., Elevated HOX gene expression in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with NPM1 mutations and poor survival. J Adv Res. 2019 Jun, 2019. 11;20: p. 105-116.
- Aryal S, Z.Y., Wren S, Li C, Lu R., Molecular regulators of HOXA9 in acute myeloid leukemia. FEBS J. 2023 2021. 290(2): p. 321-339.
- Chen, S.-L.Q., Z.-Y.; Hu, F.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.-J.; Liang, Y., The Role of the HOXA Gene Family in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes 2019, 2019. 10: p. 621.
- Yu, M., J. Zhan, and H. Zhang, HOX family transcription factors: Related signaling pathways and post-translational modifications in cancer. Cell Signal, 2020. 66: p. 109469. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prange, K., Mandoli, A., Kuznetsova, . MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 oncofusion proteins bind a distinct enhancer repertoire and target the RUNX1 program in 11q23 acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 36, 3346–3356 (2017). MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 oncofusion proteins bind a distinct enhancer repertoire and target the RUNX1 program in 11q23 acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene, 2017. 36: p. 3346–3356. [CrossRef]
- Nagy A, O.A.B.J.K.S.S.G.D.J.B.C.G.B., Elevated HOX gene expression in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with NPM1 mutations and poor survival. Adv Res. 2019 2019. 20: p. 105-116. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- anieri, R., Pianigiani, G., Sciabolacci, S. , Current status and future perspectives in targeted therapy of NPM1-mutated AML. Leukemia, 2022. 36: p. 2351–2367. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma N, L.J., NPM 1 Mutations in AML-The Landscape in 2023. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 2023. 15(4): p. 1177. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C., Song, CM., Liu, S. et al. , ZFX-mediated upregulation of CEBPA-AS1 contributes to acute myeloid leukemia progression through miR-24-3p/CTBP2 axis. Cell Biol Toxicol (2023), 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen X, B.D., Hartman AA, Hu X, Eastman AE, Sun C, Wang X, Zhong M, Krishnaswamy S, Guo S., MLL-AF9 initiates transformation from fast-proliferating myeloid progenitors. Nat Commun. 2019, 2019. 18;10(1): p. 5767.
- Fortune, J.M. and N. Osheroff, Topoisomerase II as a target for anticancer drugs: when enzymes stop being nice. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol, 2000. 64: p. 221-53.
- Pommier, Y., et al., DNA topoisomerases and their poisoning by anticancer and antibacterial drugs. Chem Biol, 2010. 17(5): p. 421-33. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, U., et al., Cancer chemotherapy and beyond: Current status, drug candidates, associated risks and progress in targeted therapeutics. Genes Dis, 2023. 10(4): p. 1367-1401. [CrossRef]
- Dohner, H., et al., Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood, 2022. 140(12): p. 1345-1377. [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A.J., et al., Adjuvant and neoadjuvant breast cancer treatments: A systematic review of their effects on mortality. Cancer Treat Rev, 2022. 105: p. 102375. [CrossRef]
- Cowell, I.G. and C.A. Austin, Do transcription factories and TOP2B provide a recipe for chromosome translocations in therapy-related leukemia? Cell Cycle, 2012. 11(17): p. 3143-4.
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, J., et al., Genetic pathways in therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, 2002. 99(6): p. 1909-12. [CrossRef]
- Kollmannsberger, C., et al., Secondary leukemia following high cumulative doses of etoposide in patients treated for advanced germ cell tumors. J Clin Oncol, 1998. 16(10): p. 3386-91. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, J., et al., Increased risk of myelodysplasia and leukaemia after etoposide, cisplatin, and bleomycin for germ-cell tumours. Lancet, 1991. 338(8763): p. 359-63. [CrossRef]
- Howard, R., et al., Risk of leukemia among survivors of testicular cancer: a population-based study of 42,722 patients. Ann Epidemiol, 2008. 18(5): p. 416-21. [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y., et al., Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome among refractory germ cell tumor patients. Int J Urol, 2018. 25(7): p. 678-683. [CrossRef]
- Richiardi, L., et al., Second malignancies among survivors of germ-cell testicular cancer: a pooled analysis between 13 cancer registries. Int J Cancer, 2007. 120(3): p. 623-31. [CrossRef]
- Travis, L.B., et al., Treatment-associated leukemia following testicular cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2000. 92(14): p. 1165-71. [CrossRef]
- Winick, N.J., et al., Secondary acute myeloid leukemia in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with etoposide. J Clin Oncol, 1993. 11(2): p. 209-17. [CrossRef]
- Ratain, M.J., et al., Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia following etoposide and cisplatin combination chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell carcinoma of the lung. Blood, 1987. 70(5): p. 1412-7.
- Kushner, B.H., et al., Reduced risk of secondary leukemia with fewer cycles of dose-intensive induction chemotherapy in patients with neuroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2009. 53(1): p. 17-22. [CrossRef]
- Le Deley, M.C., et al., High cumulative rate of secondary leukemia after continuous etoposide treatment for solid tumors in children and young adults. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2005. 45(1): p. 25-31. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C., et al., The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2017. Leukemia, 2018. 32(2): p. 273-284. [CrossRef]
- Rowley, J.D. and H.J. Olney, International workshop on the relationship of prior therapy to balanced chromosome aberrations in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes and acute leukemia: overview report. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2002. 33(4): p. 331-45. [CrossRef]
- Dobson, C.L., et al., The mll-AF9 gene fusion in mice controls myeloproliferation and specifies acute myeloid leukaemogenesis. EMBO J, 1999. 18(13): p. 3564-74. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisi, M., et al., Id2 and E Proteins Orchestrate the Initiation and Maintenance of MLL-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell, 2016. 30(1): p. 59-74. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivtsov, A.V., et al., Transformation from committed progenitor to leukaemia stem cell initiated by MLL-AF9. Nature, 2006. 442(7104): p. 818-22. [CrossRef]
- Nitiss, J.L., Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer, 2009. 9(5): p. 338-50. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, B.D., et al., Type IIA topoisomerase inhibition by a new class of antibacterial agents. Nature, 2010. 466(7309): p. 935-40. [CrossRef]
- Prange, K.H.M., et al., MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 oncofusion proteins bind a distinct enhancer repertoire and target the RUNX1 program in 11q23 acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene, 2017. 36(23): p. 3346-3356. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulou, V., et al., MLL-AF9 Expression in Hematopoietic Stem Cells Drives a Highly Invasive AML Expressing EMT-Related Genes Linked to Poor Outcome. Cancer Cell, 2016. 30(1): p. 43-58. [CrossRef]
- Krebs, A.M., et al., The EMT-activator Zeb1 is a key factor for cell plasticity and promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Nat Cell Biol, 2017. 19(5): p. 518-529. [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, N., et al., The EMT Transcription Factor ZEB2 Promotes Proliferation of Primary and Metastatic Melanoma While Suppressing an Invasive, Mesenchymal-Like Phenotype. Cancer Res, 2020. 80(14): p. 2983-2995. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, S., et al., ZEB2 drives immature T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia development via enhanced tumour-initiating potential and IL-7 receptor signalling. Nat Commun, 2015. 6: p. 5794. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellner, U., et al., The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol, 2009. 11(12): p. 1487-95. [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T., et al., Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res, 2009. 69(14): p. 5820-8.
- Sayan, A.E., et al., SIP1 protein protects cells from DNA damage-induced apoptosis and has independent prognostic value in bladder cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009. 106(35): p. 14884-9. [CrossRef]
- Verschueren, K., et al., SIP1, a novel zinc finger/homeodomain repressor, interacts with Smad proteins and binds to 5'-CACCT sequences in candidate target genes. J Biol Chem, 1999. 274(29): p. 20489-98.
- Postigo AA, D.D., ZEB represses transcription through interaction with the corepressor CtBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999, 1999. 96(12): p. 6683-8. [CrossRef]
- Stanislav Drápela1, 3 Jan Bouchal4 Mohit Kumar Jolly5 Zoran Culig2,6 Karel Souček1,2,3*, ZEB1: A Critical Regulator of Cell Plasticity, DNA Damage Response, and Therapy Resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci., 19 March 2020.
- Sec. Molecular Diagnostics and Therapeutics, 2020. 7.
- Goossens, S., et al., The EMT regulator Zeb2/Sip1 is essential for murine embryonic hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell differentiation and mobilization. Blood, 2011. 117(21): p. 5620-30.
- Li, J., et al., The EMT transcription factor Zeb2 controls adult murine hematopoietic differentiation by regulating cytokine signaling. Blood, 2017. 129(4): p. 460-472. [CrossRef]
- Almotiri, A., et al., Zeb1 modulates hematopoietic stem cell fates required for suppressing acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest, 2021. 131(1). [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., et al., Interplay between the EMT transcription factors ZEB1 and ZEB2 regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell differentiation and hematopoietic lineage fidelity. PLoS Biol, 2021. 19(9): p. e3001394. [CrossRef]
- Omilusik, K.D., et al., Transcriptional repressor ZEB2 promotes terminal differentiation of CD8+ effector and memory T cell populations during infection. J Exp Med, 2015. 212(12): p. 2027-39. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.L., et al., The transcription factor Zeb2 regulates development of conventional and plasmacytoid DCs by repressing Id2. J Exp Med, 2016. 213(6): p. 897-911. [CrossRef]
- van Helden, M.J., et al., Terminal NK cell maturation is controlled by concerted actions of T-bet and Zeb2 and is essential for melanoma rejection. J Exp Med, 2015. 212(12): p. 2015-25.
- Scott, C.L., et al., The Transcription Factor ZEB2 Is Required to Maintain the Tissue-Specific Identities of Macrophages. Immunity, 2018. 49(2): p. 312-325 e5.
- Soen, B., et al., ZEB Proteins in Leukemia: Friends, Foes, or Friendly Foes? Hemasphere, 2018. 2(3): p. e43. [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, S. and T. Brabletz, The ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop--a motor of cellular plasticity in development and cancer? EMBO Rep, 2010. 11(9): p. 670-7.
- Li, H., et al., The EMT regulator ZEB2 is a novel dependency of human and murine acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, 2017. 129(4): p. 497-508. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.D., et al., Dysregulation of miR-200s clusters as potential prognostic biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. J Transl Med, 2018. 16(1): p. 135. [CrossRef]
- De Conti, G., et al., A Novel Platform to Test In Vivo Single Gene Dependencies in t(8,21) and t(15,17) AML Confirms Zeb2 as Leukemia Target. Cancers (Basel), 2020. 12(12).
- Di Giacomo, D., et al., 14q32 rearrangements deregulating BCL11B mark a distinct subgroup of T-lymphoid and myeloid immature acute leukemia. Blood, 2021. 138(9): p. 773-784.
- Wang, X., et al., MiR-454-3p promotes apoptosis and autophagy of AML cells by targeting ZEB2 and regulating AKT/mTOR pathway. Hematology, 2023. 28(1): p. 2223874. [CrossRef]
- Shi, X., et al., Overexpression of ZEB2-AS1 lncRNA is associated with poor clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol Lett, 2019. 17(6): p. 4935-4947. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., et al., ZEB1 serves as an oncogene in acute myeloid leukaemia via regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway by combining with P53. J Cell Mol Med, 2021. 25(11): p. 5295-5304. [CrossRef]
- Bassani, B., et al., ZEB1 shapes AML immunological niches, suppressing CD8 T cell activity while fostering Th17 cell expansion. Cell Rep, 2024. 43(2): p. 113794. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y., et al., Th17 cells and interleukin-17 increase with poor prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Sci, 2014. 105(8): p. 933-42. [CrossRef]
- Trsova, I., et al., Expression of circular RNAs in myelodysplastic neoplasms and their association with mutations in the splicing factor gene SF3B1. Mol Oncol, 2023. 17(12): p. 2565-2583. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J., et al., MALAT-1 regulates the AML progression by promoting the m6A modification of ZEB1. Acta Biochim Pol, 2023. 70(1): p. 37-43. [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, U.D., J.V. Joseph, and F.A.E. Kruyt, EMT- and MET-related processes in nonepithelial tumors: importance for disease progression, prognosis, and therapeutic opportunities. Mol Oncol, 2017. 11(7): p. 860-877.
- Wilson, M.M., et al., Emerging Mechanisms by which EMT Programs Control Stemness. Trends Cancer, 2020. 6(9): p. 775-780. [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, P.G., G. Moreno-Bueno, and A. Cano, Contribution of Epithelial Plasticity to Therapy Resistance. J Clin Med, 2019. 8(5). [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.G., et al., Snail and the microRNA-200 family act in opposition to regulate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and germ layer fate restriction in differentiating ESCs. Stem Cells, 2011. 29(5): p. 764-76. [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C. and K. Ayyanathan, Snail/Gfi-1 (SNAG) family zinc finger proteins in transcription regulation, chromatin dynamics, cell signaling, development, and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2013. 24(2): p. 123-31. [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, H. and T. Moroy, Multifaceted Actions of GFI1 and GFI1B in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Lineage Commitment. Front Genet, 2020. 11: p. 591099. [CrossRef]
- Pioli, P.D. and J.H. Weis, Snail transcription factors in hematopoietic cell development: a model of functional redundancy. Exp Hematol, 2014. 42(6): p. 425-30. [CrossRef]
- Pioli, P.D., et al., Snai2 and Snai3 transcriptionally regulate cellular fitness and functionality of T cell lineages through distinct gene programs. Immunobiology, 2016. 221(5): p. 618-33. [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, C.L., et al., The EMT modulator SNAI1 contributes to AML pathogenesis via its interaction with LSD1. Blood, 2020. 136(8): p. 957-973. [CrossRef]
- Malinge, S., SNAIL trail in myeloid malignancies. Blood, 2020. 136(8): p. 920-921. [CrossRef]
- Goossens, S., et al., Oncogenic ZEB2 activation drives sensitivity toward KDM1A inhibition in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood, 2017. 129(8): p. 981-990. [CrossRef]
- Hartung, E.E., K. Singh, and T. Berg, LSD1 inhibition modulates transcription factor networks in myeloid malignancies. Front Oncol, 2023. 13: p. 1149754. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noce, B., et al., LSD1 inhibitors for cancer treatment: Focus on multi-target agents and compounds in clinical trials. Front Pharmacol, 2023. 14: p. 1120911. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, S., et al., ZEB2 and LMO2 drive immature T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia via distinct oncogenic mechanisms. Haematologica, 2019. 104(8): p. 1608-1616. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyoucef, A., et al., JAK/BCL2 inhibition acts synergistically with LSD1 inhibitors to selectively target ETP-ALL. Leukemia, 2022. 36(12): p. 2802-2816. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z., et al., Inhibition of Slug effectively targets leukemia stem cells via the Slc13a3/ROS signaling pathway. Leukemia, 2020. 34(2): p. 380-390.
- Dorn, D.C., et al., The effect of cantharidins on leukemic stem cells. Int J Cancer, 2009. 124(9): p. 2186-99. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N., et al., TWIST-1 promotes cell growth, drug resistance and progenitor clonogenic capacities in myeloid leukemia and is a novel poor prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(25): p. 20977-92. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, A., et al., Twist1 Promoter Methylation Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via PI3K/AKT Pathway. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus, 2023. 39(1): p. 25-32. [CrossRef]
- Ottone, T., et al., Expression profiling of extramedullary acute myeloid leukemia suggests involvement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways. Leukemia, 2023. 37(12): p. 2383-2394. [CrossRef]
- Wang, N., et al., Twist family BHLH transcription factor 1 is required for the maintenance of leukemia stem cell in MLL-AF9(+) acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica, 2024. 109(1): p. 84-97. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., et al., Clonal MDS/AML cells with enhanced TWIST1 expression reprogram the differentiation of bone marrow MSCs. Redox Biol, 2023. 67: p. 102900. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C., et al., Increased NFATC4 Correlates With Poor Prognosis of AML Through Recruiting Regulatory T Cells. Front Genet, 2020. 11: p. 573124. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H., et al., Reciprocal regulation of TWIST1 and OGT determines the decitabine efficacy in MDS/AML. Cell Commun Signal, 2023. 21(1): p. 255.
- Jiang, H., et al., Zeb1-induced metabolic reprogramming of glycolysis is essential for macrophage polarization in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis, 2022. 13(3): p. 206. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y., et al., The transcription factor Zeb1 controls homeostasis and function of type 1 conventional dendritic cells. Nat Commun, 2023. 14(1): p. 6639.
- Eckardt, J.N., et al., Molecular profiling and clinical implications of patients with acute myeloid leukemia and extramedullary manifestations. J Hematol Oncol, 2022. 15(1): p. 60. [CrossRef]
- Tettamanti, S., et al., Catch me if you can: how AML and its niche escape immunotherapy. Leukemia, 2022. 36(1): p. 13-22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancilla, D., M.P. Rettig, and J.F. DiPersio, Targeting CXCR4 in AML and ALL. Front Oncol, 2020. 10: p. 1672. [CrossRef]
- Hanoun, M., et al., Acute myelogenous leukemia-induced sympathetic neuropathy promotes malignancy in an altered hematopoietic stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell, 2014. 15(3): p. 365-375. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J., et al., Targeting N-cadherin (CDH2) and the malignant bone marrow microenvironment in acute leukaemia. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2023. 25: p. e16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunadt, D., et al., Lysyl oxidase expression is associated with inferior outcome and Extramedullary disease of acute myeloid leukemia. Biomark Res, 2020. 8: p. 20. [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, R.J., et al., Phenotypic, genotypic, and functional characterization of normal and acute myeloid leukemia-derived marrow endothelial cells. Exp Hematol, 2016. 44(5): p. 378-89. [CrossRef]
- Qu, S., et al., Metastasis Related Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Signature Predicts Prognosis and Response to Chemotherapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2023. 17: p. 1651-1663. [CrossRef]
- Li, G., et al., Genomic analysis of biomarkers related to the prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol Lett, 2020. 20(2): p. 1824-1834. [CrossRef]
- Stefanidakis, M., et al., Role of leukemia cell invadosome in extramedullary infiltration. Blood, 2009. 114(14): p. 3008-17. [CrossRef]
- Paz, H., N. Pathak, and J. Yang, Invading one step at a time: the role of invadopodia in tumor metastasis. Oncogene, 2014. 33(33): p. 4193-202. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, A.E., et al., Leukaemia: a model metastatic disease. Nat Rev Cancer, 2021. 21(7): p. 461-475. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augoff, K., A. Hryniewicz-Jankowska, and R. Tabola, Invadopodia: clearing the way for cancer cell invasion. Ann Transl Med, 2020. 8(14): p. 902. [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.L., et al., Cortactin recruits FMNL2 to promote actin polymerization and endosome motility in invadopodia formation. Cancer Lett, 2018. 419: p. 245-256. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gligorijevic, B., et al., N-WASP-mediated invadopodium formation is involved in intravasation and lung metastasis of mammary tumors. J Cell Sci, 2012. 125(Pt 3): p. 724-34. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, S., et al., The role of Tks adaptor proteins in invadopodia formation, growth and metastasis of melanoma. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(48): p. 78473-78486. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C., et al., TKS5-positive invadopodia-like structures in human tumor surgical specimens. Exp Mol Pathol, 2019. 106: p. 17-26. [CrossRef]
- Kudlik, G., et al., Advances in Understanding TKS4 and TKS5: Molecular Scaffolds Regulating Cellular Processes from Podosome and Invadopodium Formation to Differentiation and Tissue Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2020. 21(21). [CrossRef]
- Daubon, T., et al., Invadopodia and rolling-type motility are specific features of highly invasive p190(bcr-abl) leukemic cells. Eur J Cell Biol, 2012. 91(11-12): p. 978-87.
- Poincloux, R., et al., Re-arrangements of podosome structures are observed when Hck is activated in myeloid cells. Eur J Cell Biol, 2006. 85(3-4): p. 327-32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukwaya, A., L. Jensen, and N. Lagali, Relapse of pathological angiogenesis: functional role of the basement membrane and potential treatment strategies. Exp Mol Med, 2021. 53(2): p. 189-201. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seano, G. and L. Primo, Podosomes and invadopodia: tools to breach vascular basement membrane. Cell Cycle, 2015. 14(9): p. 1370-4. [CrossRef]
- Morimatsu, M., et al., Migration arrest of chemoresistant leukemia cells mediated by MRTF-SRF pathway. Inflamm Regen, 2020. 40: p. 15. [CrossRef]
- Auvinen, K., S. Jalkanen, and M. Salmi, Expression and function of endothelial selectins during human development. Immunology, 2014. 143(3): p. 406-15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar, T.L., et al., Silencing of retrotransposons by SETDB1 inhibits the interferon response in acute myeloid leukemia. J Cell Biol, 2017. 216(11): p. 3535-3549. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E., K. Salari, and S. Yang, SETDB1: A perspective into immune cell function and cancer immunotherapy. Immunology, 2023. 169(1): p. 3-12. [CrossRef]
- Farge, T., et al., CD36 Drives Metastasis and Relapse in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Res, 2023. 83(17): p. 2824-2838. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J., et al., DNMT3A mutation leads to leukemic extramedullary infiltration mediated by TWIST1. J Hematol Oncol, 2016. 9(1): p. 106. [CrossRef]
- Ponomaryov, T., et al., Induction of the chemokine stromal-derived factor-1 following DNA damage improves human stem cell function. J Clin Invest, 2000. 106(11): p. 1331-9. [CrossRef]
- Voermans, C., et al., Migratory behavior of leukemic cells from acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia, 2002. 16(4): p. 650-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Targeting primary acute myeloid leukemia with a new CXCR4 antagonist IgG1 antibody (PF-06747143). Sci Rep, 2017. 7(1): p. 7305. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavor, S., et al., CXCR4 regulates migration and development of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells in transplanted NOD/SCID mice. Cancer Res, 2004. 64(8): p. 2817-24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoplev, S., et al., Overexpression of CXCR4 predicts adverse overall and event-free survival in patients with unmutated FLT3 acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Cancer, 2007. 109(6): p. 1152-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B., et al., Targeting E-selectin to Tackle Cancer Using Uproleselan. Cancers (Basel), 2021. 13(2). [CrossRef]
- Li, M., et al., METTL3 mediates chemoresistance by enhancing AML homing and engraftment via ITGA4. Leukemia, 2022. 36(11): p. 2586-2595.
- Shi, Y., et al., Reduced Expression of METTL3 Promotes Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by m6A Methylation-Mediated COL3A1 Up-Regulation. Front Oncol, 2020. 10: p. 1126. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X., et al., Deletion of Mettl3 in mesenchymal stem cells promotes acute myeloid leukemia resistance to chemotherapy. Cell Death Dis, 2023. 14(12): p. 796. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipkins, D.A., et al., In vivo imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for tumour engraftment. Nature, 2005. 435(7044): p. 969-73. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakst, R.L., et al., How I treat extramedullary acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, 2011. 118(14): p. 3785-93. [CrossRef]
- Paydas, S., S. Zorludemir, and M. Ergin, Granulocytic sarcoma: 32 cases and review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma, 2006. 47(12): p. 2527-41. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H., et al., Extramedullary infiltrates of AML are associated with CD56 expression, 11q23 abnormalities and inferior clinical outcome. Leuk Res, 2004. 28(10): p. 1007-11. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, J.R., H. Nuckel, and U. Duhrsen, Correlation between expression of CD56/NCAM and severe leukostasis in hyperleukocytic acute myelomonocytic leukaemia. Eur J Haematol, 2006. 76(4): p. 299-308.
- Alegretti, A.P., et al., The expression of CD56 antigen is associated with poor prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter, 2011. 33(3): p. 202-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, E.M., The expression of the CD56 antigen is associated with poor prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter, 2011. 33(3): p. 176-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaad, M., et al., Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Central Nervous System Involvement Following Routine Surgical Procedures: A Bridge Between Surgical, Medical, and Neurological Critical Care. Cureus, 2022. 14(1): p. e21245. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.L., et al., Clinical significance of central nervous system involvement at diagnosis of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: a single institution's experience. Leukemia, 2003. 17(11): p. 2090-6.
- Alakel, N., et al., Symptomatic central nervous system involvement in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Manag Res, 2017. 9: p. 97-102. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).