1. Introduction
In its essence, nanotechnology can be defined as the study of particles at the size range of 1–100 nm [
1]. Nanoscience is the study of particles and atoms on this scale. Since all matter is made of atoms and molecules, it can be stated that nanoscience relates to any scientific discipline continues to connect disciplines at the fundamental sciences to related fields [
2,
3].
Nanoscience is the most knowledge-intensive area the field of topics and is the foundation for amazing technical applications. When it involves the adjustment of product residential or commercial properties based on the exploration of exactly how they influence the performance of other systems, it is referred to as nanotechnology [
3]. Nanoscience is the study of materials and structures of the size of 1-100 nanometers, of the quantal properties of such structures, and of disciplines that have access to or use such structures. On the other hand, is the level at which such materials and structure are in the neighborhood of 20 to 15,000 atoms and fit in a domain which straddles quantum and Newtonian physics [
2,
4]. Nanoscience is about the unique chemical and physical properties of materials that are determined by their size [
4].
In order to generate new materials with particular characteristics, nanotechnology allows the control and manipulation of objects at the nanoscale scale [
3]. Because there are fewer crystal flaws in nanocrystalline substances than in their bulk counterparts, they have higher rigidity [
5]. The optical and electromagnetic properties of materials at the nanoscale can be substantially altered by the quantum size effect, which is the outcome of quantum limitation, making them very different from their bulk counterparts [
6]. The prime objectives of nanoscience are to modify matter at the nanoscale level to produce useful materials, tools, and structures, and to harness the unique physical and biochemical phenomena and characteristics [
7,
8,
9].
The ongoing rise in antibiotic resistance in human disease-causing pathogenic bacteria leads to the resurgence of multi drug resistant (MDR) bacteria [
10,
11]. Since the ancient time, silver metal, and silver nitrate have been used for the treatment of burn-associated wound, oral healthcare procedures, medical devices for urinary drainage, and measures to prevent the spread of bacterial infections [
12]. The utilization of silver against bacterial contaminations got to be unpopular after the discovery of penicillin in the 1940s [
13]. The later rise of antibiotic-resistant microscopic organisms and the constrained viability of antibiotics Revived the practicality of using silver, particularly in wound dressings [
14]. Thus, by manipulating the nanoscale, increasing the surface-area-to-volume proportion, and altering the physical and chemical characteristics, one might enhance the antibacterial viability of silver [
9,
15,
16].
Yamanaka et al. (2005) have analyzed the bactericidal mechanism of silver containing salt on the
E. coli as model organism using electron microscopic, and gel electrophoresis combined with mass spectrometric method. The research revealed that the silver nanoparticles subsequently infiltrate into the bacterial cells and bind to a key ribosomal subunit protein as well as an enzyme they believe is glyoxalase 1, which supports dozens of essential cellular processes in vivo [
10].
In 2007, Kim et al. had already researched the bacteriostatic effect of silver nanoparticles sized between 1 and 100 nm on
E. coli, a Gram-negative bacterium. To explore the interaction of silver nanoparticles with bacteria, the authors cultured the bacterial cells until they reached the mid-log stage, recorded OD at 595 nm, determined the effect of different silver concentrations on bacterial growth and found medium with a silver content 3.3 nM to 6.6 nM to be bacteriostatic [
11].
By listing out the antibacterial activity of nineteen different antibiotics when used in combination with a solution containing dispersed silver in water, Souza et al. (2006) showed that multi drug resistant bacteria like
E. coli,
Sh. flexneri,
S. typhi,
B. subtilis,
S. aureus are sensitive to both amoxicillin and clindamycin. In a second, quite similar type of experiment, the dispersion of silver in water with amoxicillin or clindamycin acted additively against
S. typhi,
S. aureus,
Sh. flexneri, and
B. subtilis, whereas they revealed antagonistic interactions with the methicillin-resistant
S. aureus strain (MRSA) [
12].
Duran et al. (2007) utilize
Fusarium oxysporum, a fungus, to prepare silver nanoparticle. They then tested how well the nanoparticles killed bacteria by putting them on fabric and confirmed their findings using high resolution microscopic and spectroscopic methods. The researchers found that cotton apparel that had been treated with silver nanoparticles possessed effective bactericidal activity [
13].
Jia et al. (2007) proposed and tested the strong and effective antibacterial potential of polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers infused with silver nanoparticles against
S. aureus and
E. coli in wound dressings [
14]. Baker et al. (2005) manufactured silver nanoparticles using the condensation and co-condensation methods of idle gas, and they conducted a study to assess the ability of nanoparticles to inhibit the growth of
E. coli in solid as well as liquid environments and concluded that the nanoparticles demonstrated bactericidal activity against
E. coli [
15].
Shahverdi et al. (2007) studied the combined antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles and common antibiotics such as ampicillin, amoxicillin, vancomycin, clindamycin, and erythromycin against
E. coli and
S. aureus. The study findings suggest that the combination of silver nanoparticles and certain antibiotics could function together as a potential antibacterial agent showing synergy, and this new hybrid approach would provide a hopeful strategy to fight the multi drug-resistant bacteria [
16]. They concluded that, silver nanoparticles of 10 to 100 nm size have a very high toxicity against wide spectra of bacteria including the multi-drug resistant strain of
P. aeruginosa and
S. aureus (MRSA) as well as the ampicillin-resistant strain of
E. coli, vancomycin-resistant strain of
S. aureus (VRSA), erythromycin-resistant strain of
S. pyogenes [
16].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Silver nitrate (AgNO3) was collected from Honeywell Fulka, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP 40000), Polyethylene glycol, and sodium borohydride from Sigma-Aldrich. In addition, hydrogen peroxide. Trisodium citrate was purchased from Roth, whereas ethanol and ammonium hydroxide were purchased from Merck. All chemicals and reagents were used as received without further purification. Water used in all procedures was obtained from a water purification system (Purelab from ELGA) and had a measured resistivity of 18.2 MΩ cm−1.
2.2. Instruments
Experiments were conducted using various instruments like UV–vis double beam spectrophotometer (PG Instrument, UK T60 U), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) (Model Joel JSM-7600FE, Japan). In addition, Ultra Sonicator (Power-Sonic, Korea), Hotplate Stirrer (Stuart), Micro Centrifuge Machine (Tomy, MX-305), Orbital shaker Incubator (JSR) and Laboratory incubator (Incucell), Particle Size Analyzer (Malvern), Freeze Dryer, TGA (Hitachi instrument—TG/DTA 7200) are also used as per manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3. Methods
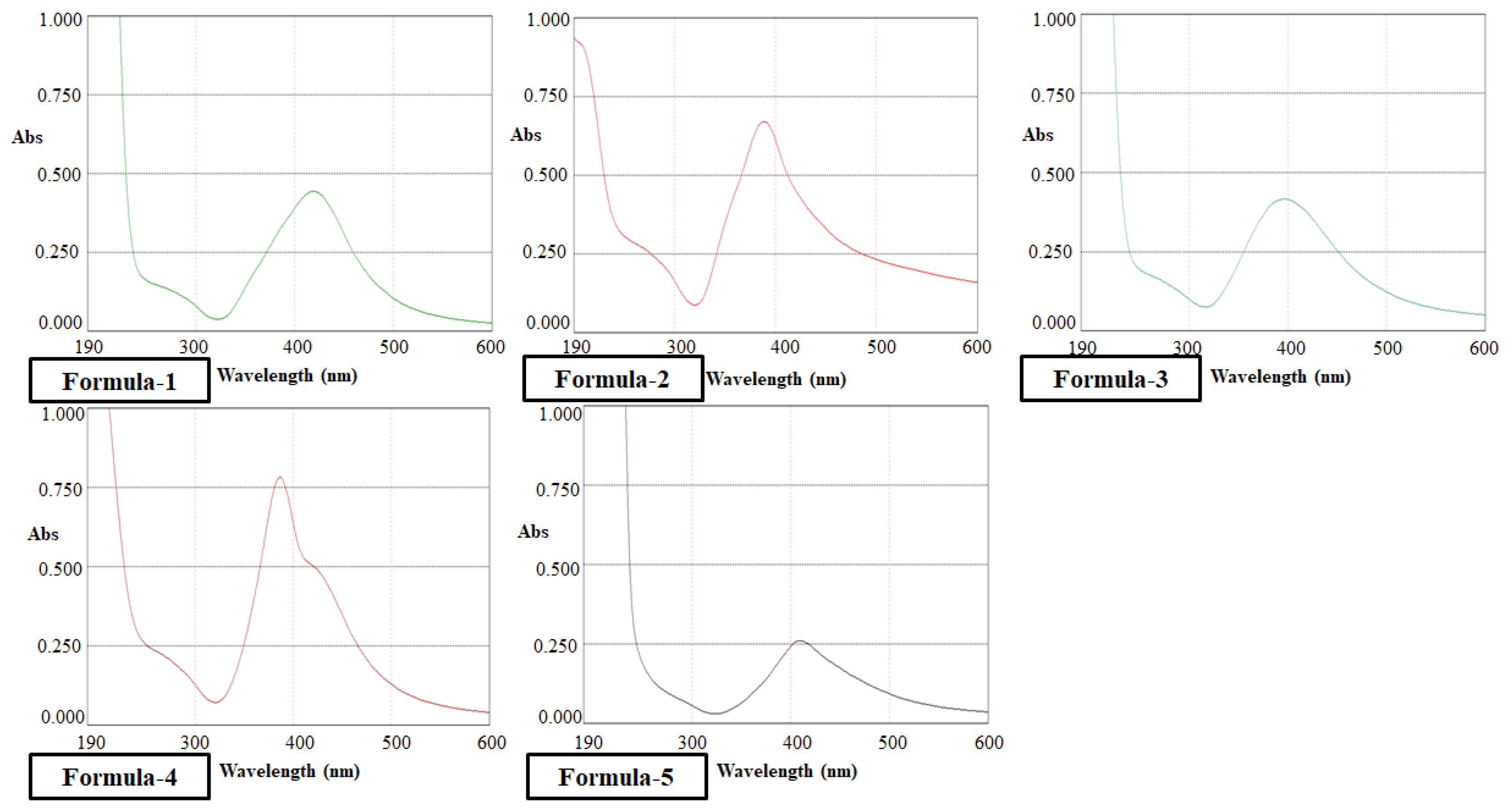
2.3.1. Formula One (F1). AgNP Synthesis Using Trisodium Citrate as a Reducing Agent
150 ml of 7 mM Trisodium Citrate solution was prepared in a beaker at room temperature and placed on a magnetic stirrer. The solution was first brought to boil while being stirred and then 1.5 ml of 0.1 M aqueous silver nitrate was added to start the reaction. The color of the reaction was observed to change slowly from colorless to yellow, then turbid. At last, no more change took place indicating that the reaction was completed [
17].
2.3.2. Formula Two (F2). AgNP Synthesis Using Sodium Borohydride as Reducing Agent
About 30 ml of 2 mM Sodium Borohydride solution was prepared and chilled at 4°C for 20 minutes. The solution was poured into a beaker and placed on a magnetic stirrer. A 2.5 ml solution of 0.01M Silver Nitrate was added dropwise to the beaker while the mixture was continuously stirred. The solution turned pale yellow after only a few drops and brighter yellow after all the solution had been poured, following which stirring was stopped [
18].
2.3.3. Formula Three (F3). AgNP Synthesis by a Combined Method Using Sodium Borohydride as Primary Reductant and Trisodium Citrate as Secondary Reductant
A mixture of 72 mL of distilled water, 2 mL of 0.01M trisodium citrate, and 2 mL of 0.01 M silver nitrate was stirred for 3 minutes at 10°C. Then, 3 mL of 0.002 M sodium borohydride was added to the mixture, and immediately after the addition, stirring was stopped. Following that, the color of the solution turned golden yellow, indicating the formation of nanoparticles [
19].
2.3.4. Formula Four (F4). AgNP Synthesis by a Combined Method Using Trisodium Citrate and Sodium Borohydride as Reducing Agent in the Presence of Hydrogen Peroxide
At first, an aqueous solution combining 0.05 M, 50 μL silver nitrate, 0.075 M, 0.5 mL trisodium citrate, and 30% (v/v) 20 μL H
2O
2, each prepared separately, was stirred vigorously at room temperature to allow homogenous mixing. Then 100 mM, 250 μL sodium borohydride was injected into the solution mixture to initiate the reaction. Initially, the color of the solution was light yellow, which gradually became deep reddish yellow after 3-4 minutes under continuous stirring [
20].
2.3.5. Formula Five (F5). AgNP Synthesis Using Polyethylene Glycol as a Reducing Agent
0.5 g of polyethene glycol (PEG) was completely dissolved in 60 mL of distilled water under magnetic stirring by heating at 120°C. Then, 1.5 g of Polyvinyl pyrrolidine (PVP) and 0.05 g AgNO3 were added to the solution and stirred for 1 hour, continuing heating. The solution’s color slowly changed from light to brighter yellow, and the stirring was stopped [
21].
2.4. Purification
The previously synthesized silver nanoparticle has been purified using centrifugation at 14000 rpm for 15 minutes. For all methods where NaBH4 was used as a reducing agent, the nanoparticle formulation was freeze-dried before centrifugation to reduce two-thirds of the volume. After centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was resuspended in 80 ml ethanol and centrifuged again at 14000 rpm for another 15 minutes. Finally, the pellet was collected.
In the formula where PEG was used as a reducing agent, the pellet obtained after the first centrifugation was suspended in 150 ml acetone and centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 15 minutes. After that, a small amount of orange floating pellet appeared at the bottom of the falcon tube, carefully collected by discarding the supernatant from the top. Then, 20 ml of ethanol was added to the pellet and centrifuged under the same parameters, and the final pellet was collected.
2.5. Characterization
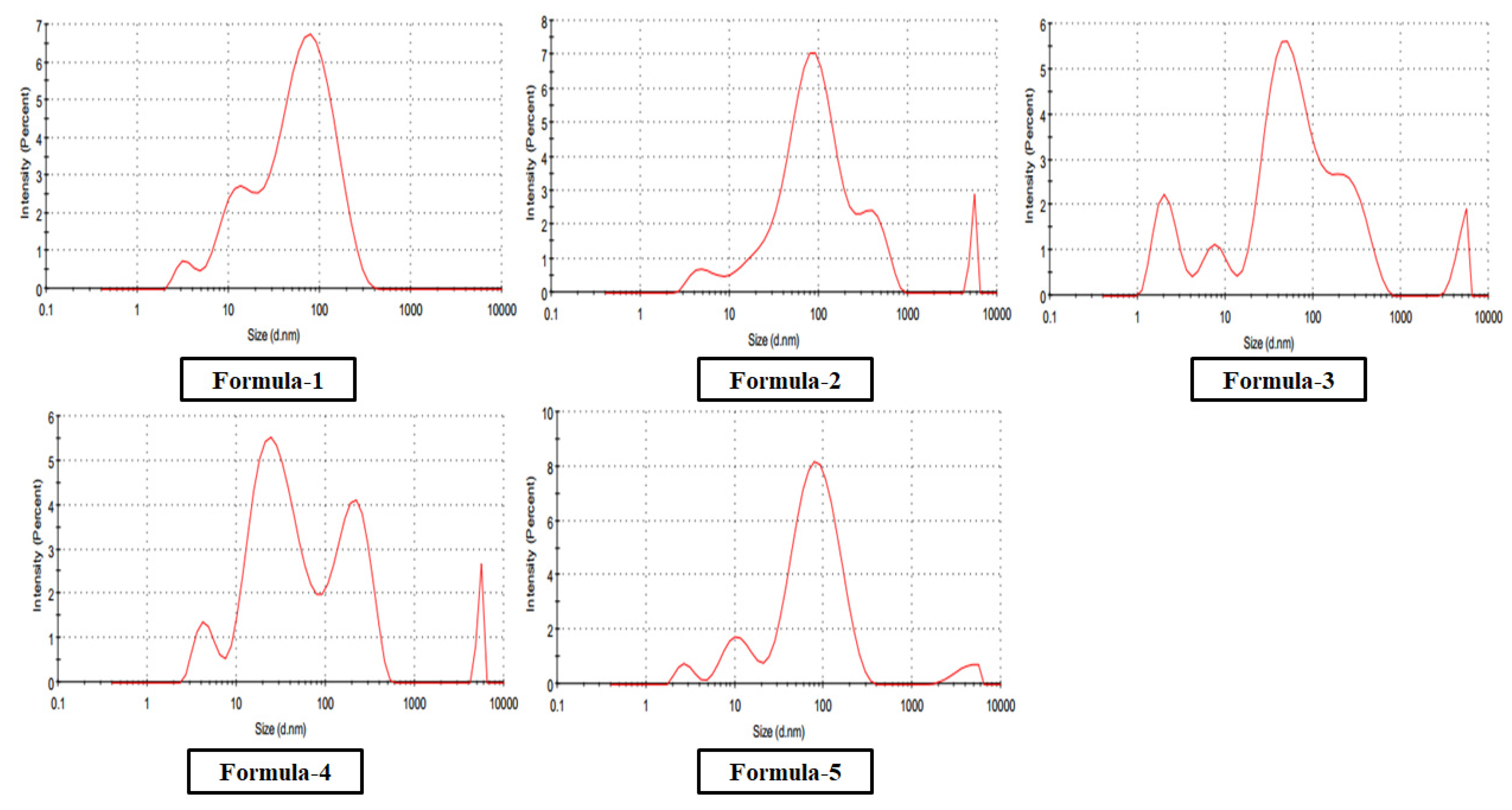
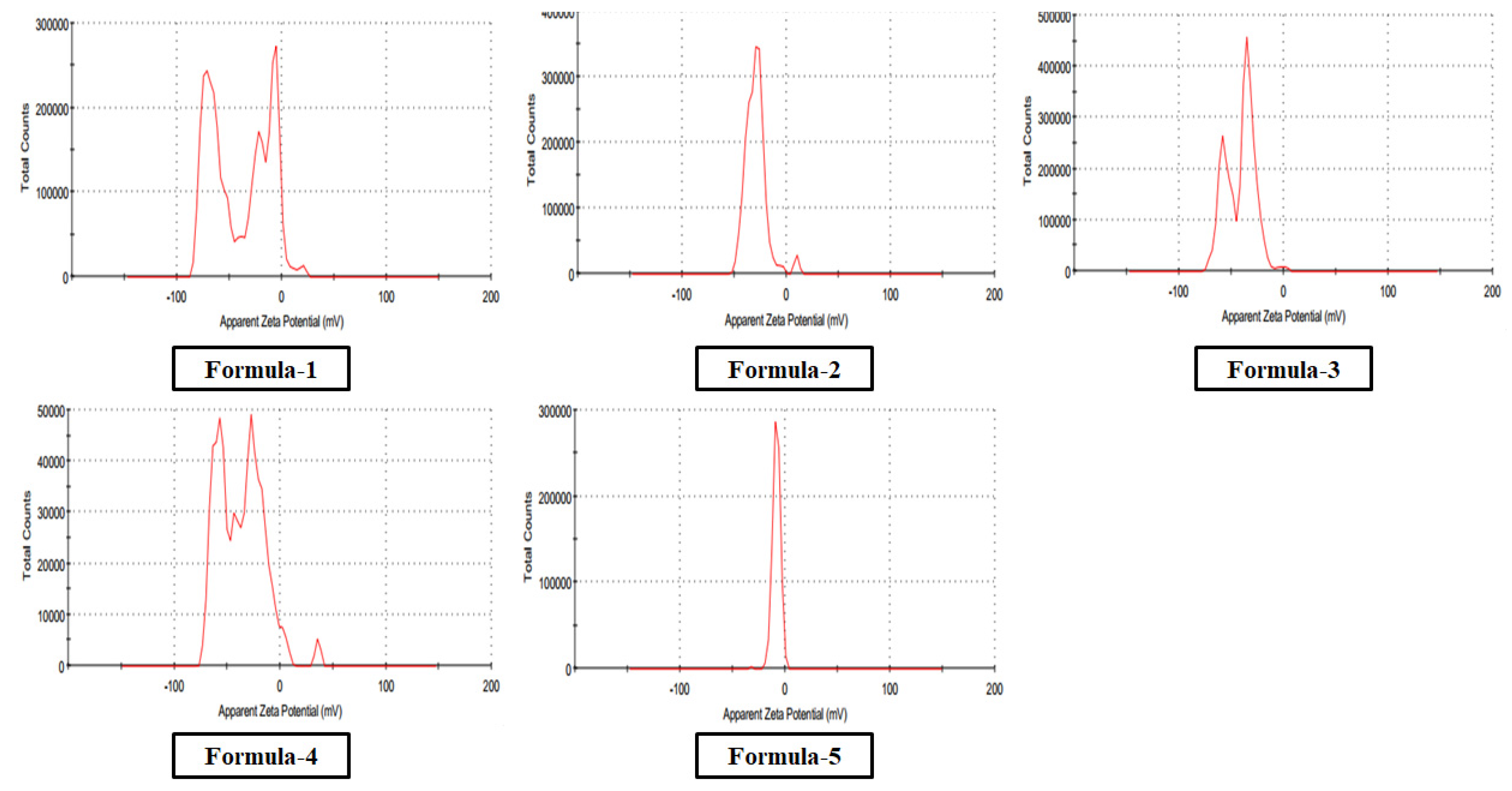
The optical absorption spectra for nanoparticles in colloidal preparation were recorded using a double beam PG UV-Visible spectrophotometer, UK-T60 U. Rectangular quartz cells of path length 1 cm were used throughout the investigation. The Malvern DLS measurement Instrument measured the size and size distribution of the nanoparticles synthesized in the colloidal solution. The same equipment was used to determine zeta potential (ζ) for a surface charge of Ag nanoparticles. The cuvette used in this experiment was the universal dip cell. The Huckel equation was used to calculate the electrophoretic mobilities of silver nanoparticles.
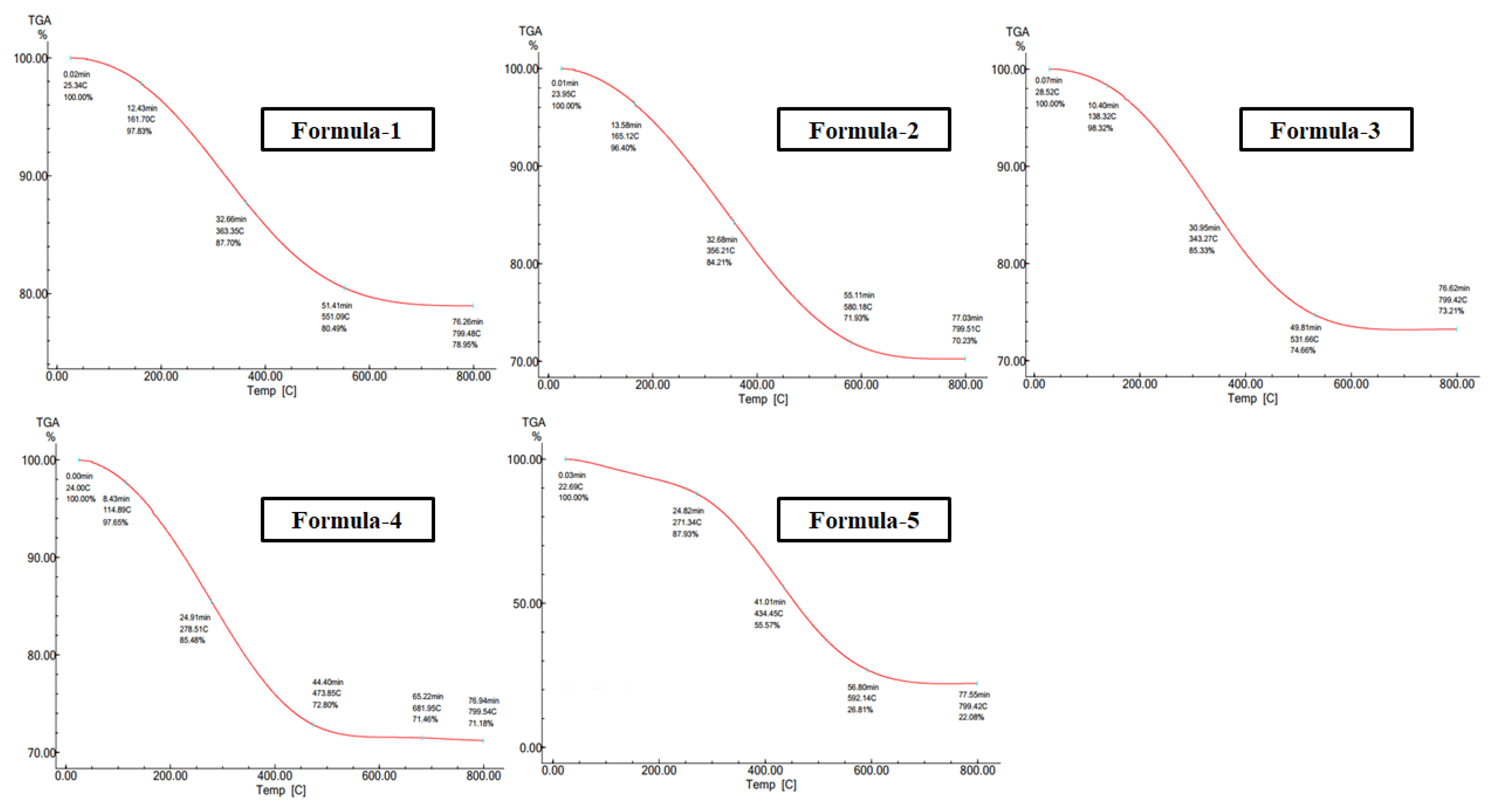
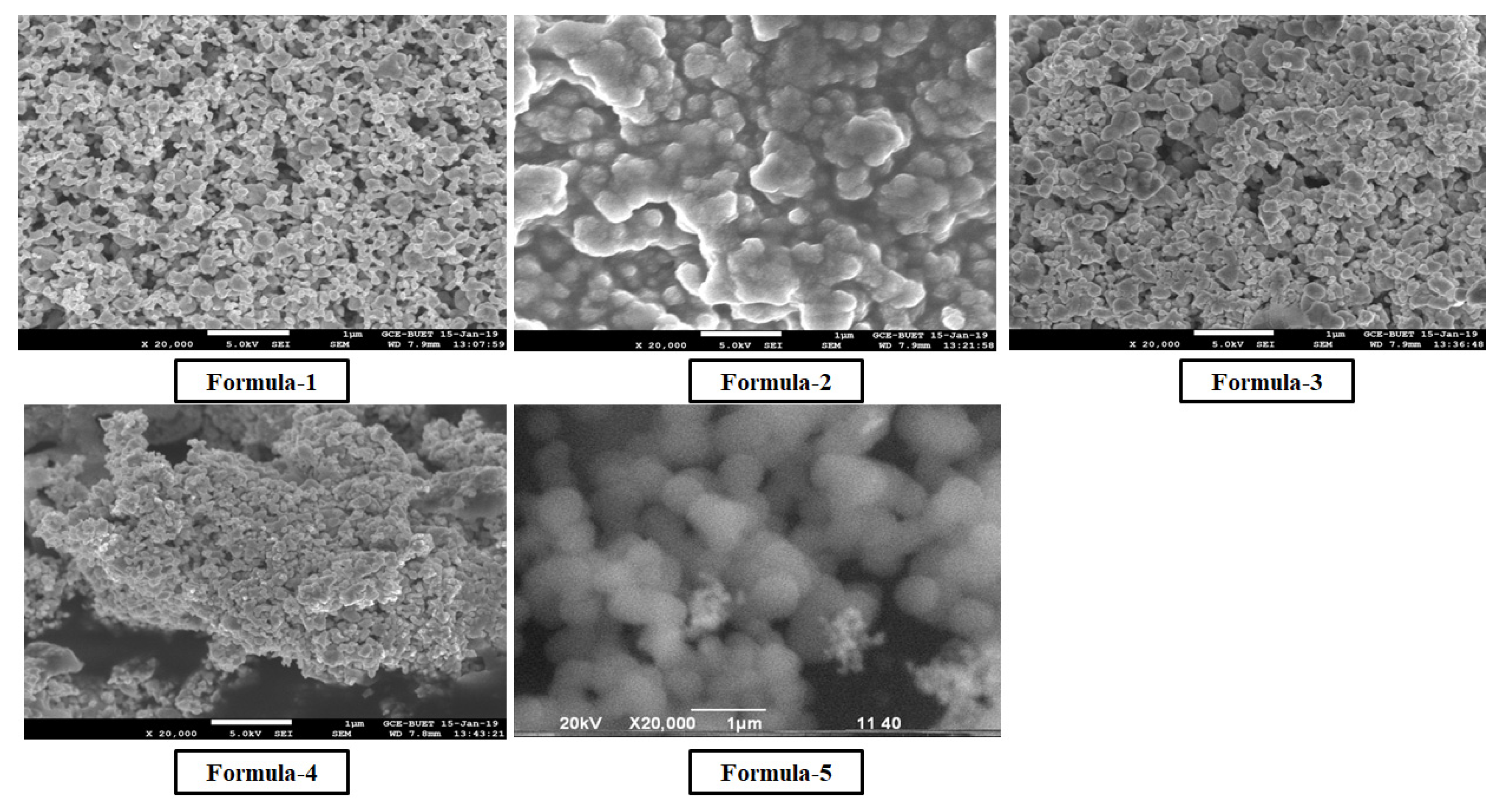
Morphological analyses of nanoparticles were carried out using the JEOL analytical scanning electron microscope (SEM) model JSM-7600FE. Dried purified nanosilver powder was spread on the carbon-coated aluminum stubs for the measurements at an acceleration voltage of 20 kV. TGA was studied by a Hitachi instrument (TG/DTA 7200) in the 20–800°C temperature range under a Nitrogen gas atmosphere at a per-minute heating rate of 10°C.
2.6. Microbiological Studies
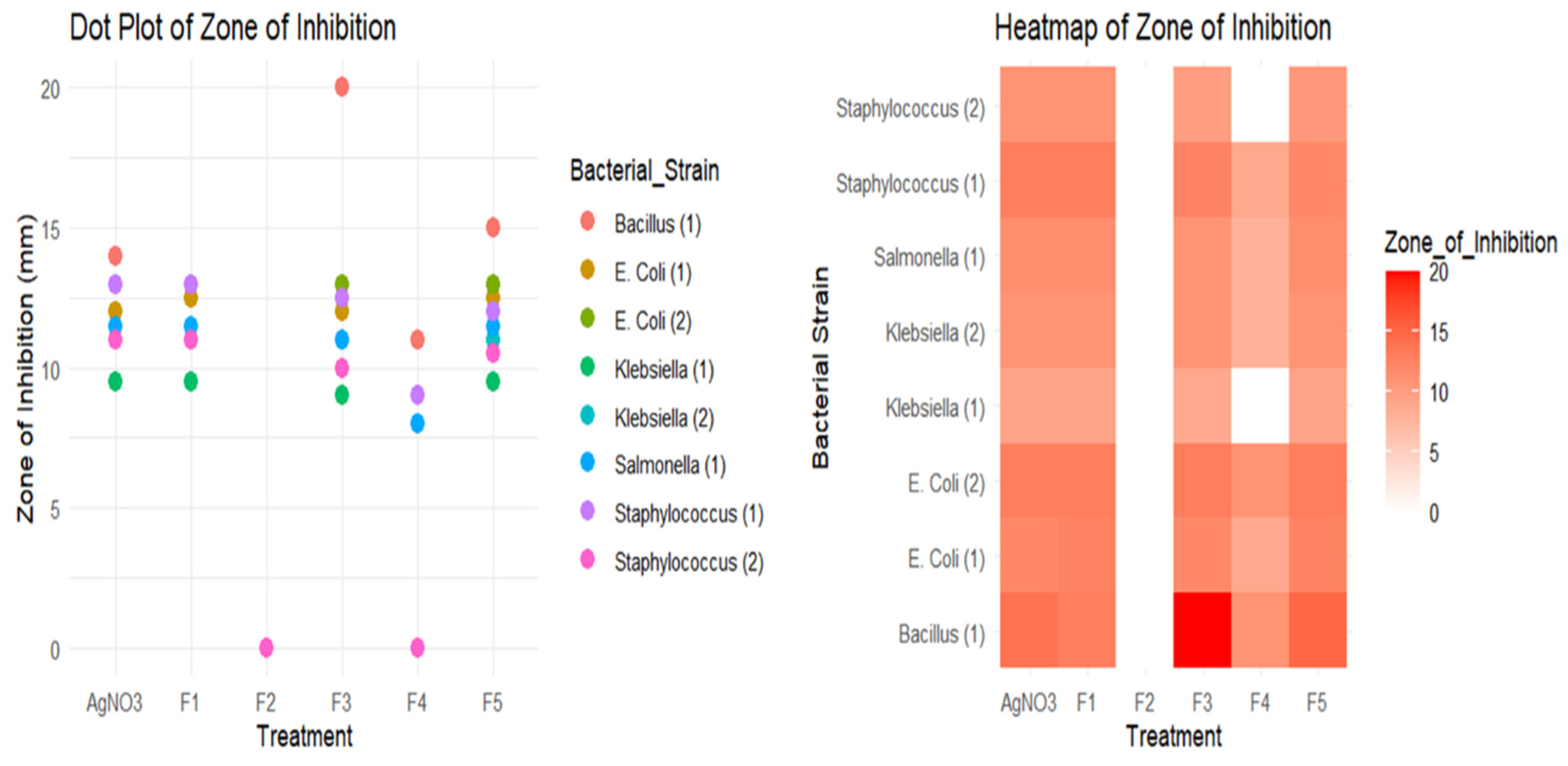
The antimicrobial studies of this research were carried out in the laboratory of Microbiology of the Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of BRAC University. The antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized by five methods were observed and compared through the Well Diffusion Method. The efficiency of the same concentration of silver nitrate was also measured, as silver nitrate was the basis of silver nanoparticle synthesis in all five methods. Apart from that, the Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) of five nanoparticles was determined against an E. coli isolate.
2.6.1. Bacterial Strains Collection
Klebsiella spp. was collected from Mohakhali TB Hospital, and a few sample strains of E. coli were collected at Uttara Adhunik Medical College Hospital. Salmonella Typhi, Staphylococcus spp., and Bacillus spp. were also collected from BRAC University Microbiology laboratory. These strains were subcultured in Nutrient Agar Media every week without fail, ensuring their viability and preventing contamination. The freshly cultured colonies were then used in the procedure, providing reliable and consistent results.
2.6.2. Well Diffusion Test
For well diffusion method, two isolates of Klebsiella species, two isolates of E. coli, one isolate of Bacillus species, one isolate of Salmonella species, and two isolates of Staphylococcus were used. Muller Hilton agar was used as culture media for the well diffusion procedure. Each isolate was cultured on separate petri dishes. In each petri dish, six wells were made to observe the antimicrobial efficiency of five nanoparticles and silver nitrate of the same concentration. It must be mentioned that the same amount of silver nitrate was used in each formula of silver nanoparticle synthesis. Thus, the assumed concentration of silver nanoparticles is supposed to be constant in each procedure if the total amount of silver nitrate is evenly transformed into a nanoparticle state. The approximate nanoparticle concentration for each method was adjusted to 80 ppm, and a solution of silver nitrate was prepared to measure the same concentration. 40 μl of nanoparticle solution was applied per well from each type of nanoparticle alongside the same amount of silver nitrate in the last well. After overnight incubation, the zone of inhibition was measured for each nanoparticle and silver nitrate.
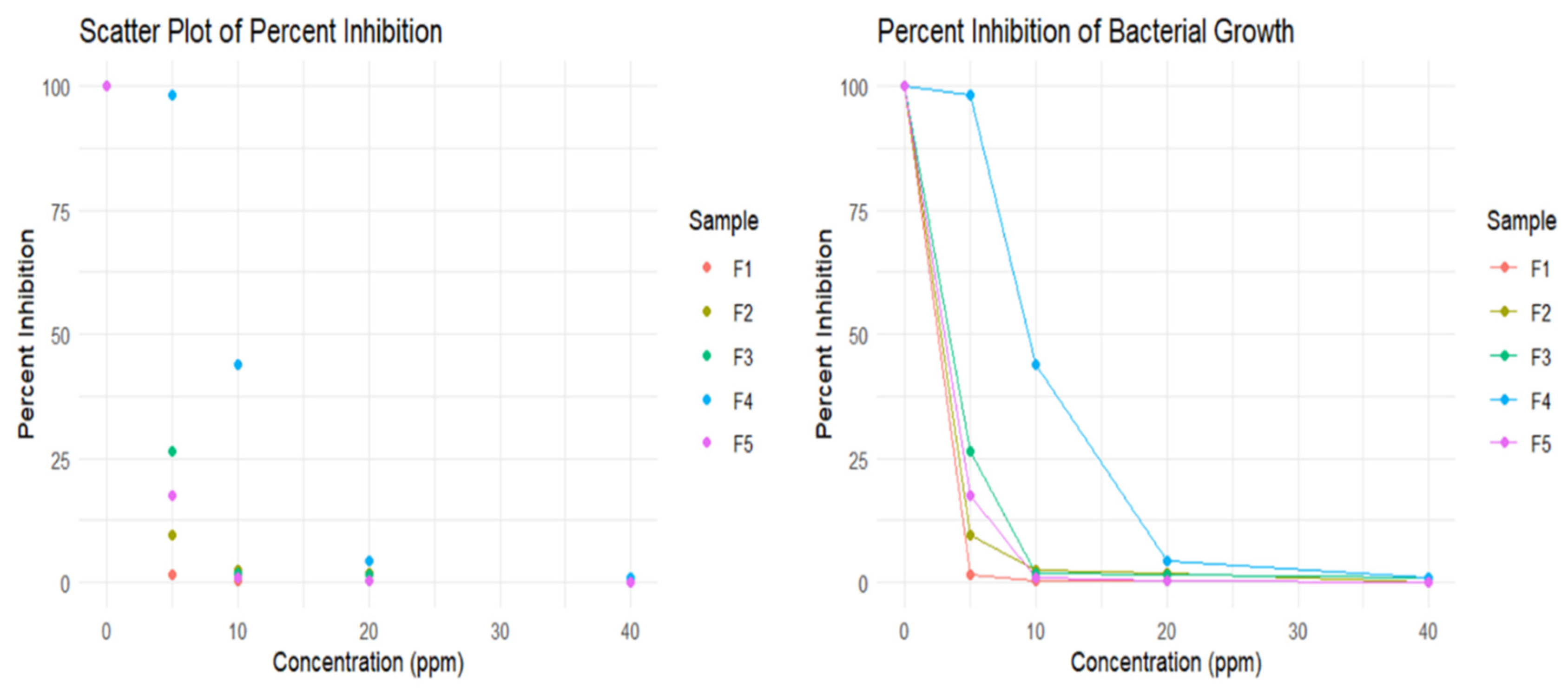
2.6.3. Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
E. coli was used to determine each formula’s MBC of silver nanoparticles. E. coli culture was grown on Luria Bertani broth till the desired range of Optical Density was reached. 1 ml of culture was diluted ten times before using the organism in a series of test tubes containing different concentrations of silver nanoparticles. For each type of silver nanoparticle formulation, a series of test tubes containing Luria Bertani broth was prepared using the serial dilution method. Five test tubes contained 0 ppm, 5 ppm, 10 ppm, 20 ppm, 40 ppm of silver nanoparticle, and an additional test tube contained only LB broth. 50 μl of the cell from the diluted culture was applied to each test tube except the last one, which contains LB broth only. After 2 hours of incubation, 5 μl from each test tube were spread into separate petri dishes containing nutrient agar. This step was followed by overnight incubation before counting the colonies per petri dish. The LB broth was cultured to ensure a contamination-free procedure in determining MBC for each type of AgNP.