Preprint
Article
Simulated Annealing Driven by the Free-Energy: The SAFE Algorithm
Altmetrics
Downloads
102
Views
96
Comments
0
This version is not peer-reviewed
Submitted:
16 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
Optimization techniques are pivotal across various scientific domains, typically involving solving problems among feasible alternatives based on specific goals, alternatives, or constraints. In mathematical optimization, traditional methods like Simulated Annealing (SA) do not guarantee finding global minima/optima, especially in cases that contain high dimensions in objective functions. This paper introduces a novel approach where a free-energy driven self-adaptive SA algorithm is designed to handle such cases by incorporating free-energy costs within the Metropolis-Hastings framework. This algorithm not only dynamically adjusts to the changing dimensions of the objective function, but it also enhances a faster optimization process. Furthermore, as examples we demonstrate its capability on a convex unimodal function and the non-convex Rastrigin function, revealing faster convergence to search global minima compared to standard SA algorithm. At last, parameter estimation of noisy exponential data has been executed by our Simulated Annealing driven by the Free-Energy (SAFE) algorithm. Our results suggest that this novel approach may significantly improve optimization speed and accuracy, providing a robust tool for complex multidimensional optimization problems.
Keywords:
Subject: Computer Science and Mathematics - Computational Mathematics
1. Introduction
Optimization is one of the fundamental tools in natural sciences (from biological sciences to physical sciences, from economics to engineering sciences) [1,2,3]. It concerns how certain problems can be solved among a set of feasible alternatives based on certain goals or constraints. Mathematically an optimization problem can be formulated as an objective function that could represent a desired outcome to be maximized, such as profit or utility, or minimized, such as cost or error [4,5] and/or finding an optimal solution, that is, a feasible solution for which the optimal value of the objective function is achieved. The nature of the optimization problem mostly depends on the specific characteristics of the problem, such as the nature of the objective function, the constraints, and the required precision. Usually, the optimizer is either local or global, thus there are different kinds of optimization algorithm techniques (e.g., deterministic, stochastic, hybrid, etc.) [6,7,8]. Now, to find global minima researchers use mostly stochastic or genetic algorithms, ranging from Simulated annealing (SA) [9,10,11] to particle swarm optimization [12] and from Differential evolution [13] to stochastic ranking [14]). The question is if the dimension of any objective function becomes too large and symmetric, can we optimize the problem in a faster time? In other words, can we search for a global minimum for this kind of cost function in a faster manner? To solve this we propose a free-energy driven self-adaptive simulated annealing algorithm (SAFE algorithm). This algorithm can help us to minimize the dimension of the problem by choosing the random dimension given a minimum length of the multidimensional objective function and it calculates and compares the free energy cost of the solution and its previous solution. As free energy has two components, on one hand, the energy part minimizes the cost function or reduces the objective function over iterations. On the other hand, the entropy difference minimizes the dimension of the problem. Based on these it later uses the infamous Metropolis-Hastings algorithm [15]. Later, we apply our algorithm in two examples where in the first case, we choose (i) Convex unimodal function and (ii) Rastrigin function (Non-convex Multimodal function). Furthermore, we ask if the optimization speed is better than standard simulated annealing. Interestingly, we investigated these questions and found that free-energy-driven self-adaptive SA is much faster than standard SA. This distinctive approach underpins our algorithm’s enhanced performance, providing a novel perspective on integrating information theory into optimization. At last, we estimate the parameter set of a stochastic exponential equation.
This article is arranged in the following way. In Section 2 we formalize the free-energy-driven self-adaptive SA algorithms. After that, in Section 3 we choose two examples one from the convex function and one from the non-convex function, and search the global minimum values and optimization speed. Furthermore, we showed parameter estimation of a simple exponential decay stochastic equation as an application. At last, we discussed our results in Section 4.
2. Methods
In this section, we shall describe our Free energy-driven Stochastic-Annealing algorithm. So, first, we shall talk about the statistical physics of Free energy.
2.1. The Free Energy in Statistical Physics
In Statistical Physics, free energy is a crucial concept that quantifies the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. It provides insights into the equilibrium properties and spontaneous processes within the system. The free energy combines the system’s internal energy and entropy, reflecting both the energy available and the degree of disorder.
The Helmholtz free energy, F, is particularly important in systems at constant temperature and volume. It is defined as:
where U is the internal energy, T is the absolute temperature, and S is the entropy of the system. The Helmholtz free energy is minimized at equilibrium, making it a useful function for determining the stability and spontaneity of processes.
Alternatively, the Gibbs free energy, G, is used for systems at constant temperature and pressure. It is given by:
where is the enthalpy, with P being the pressure and V the volume of the system. The Gibbs free energy is minimized at equilibrium under these conditions, and it is particularly relevant for chemical reactions and phase transitions.
2.2. Simulated Annealing Driven by the Free-Energy: The SAFE Algorithm
Mathematical optimization problems are pretty diverse. It guides us to choose a set of best solutions out of feasible ones based on some inherent goals or constraints, and/or the target can be to make faster optimization time or convergence time. Optimization problems can be discrete or continuous. Depending on the problem we choose optimizers which can be local or global in nature. Simulated Annealing is one of the algorithms or an optimizer that is typically used to search the global minima of a function. It’s based on the probabilistic thermodynamic approach motivated by a metal cooling or annealing process. In this article, we develop a free-energy driven self-adaptive Simulated Annealing (SA) which can search the global minima of a function where the dimension of the function is completely random over time t. To do this, we explore the effectiveness of a modified SA algorithm incorporating entropy as an additional factor. Initially, we need to formulate the problem mathematically. Let us assume a multidimensional function defined as , where vector of size k. Interestingly, the dimension k can change over time or in each iteration n. The initialization of this problem can be written as
After initializing the problem, we iterate this multidimensional function using an SA algorithm where first it perturbs the candidate solution i.e., using a uniform distribution that follows the range . After that, it evaluates the objective function (or the energy and calculates the corresponding numerical entropy of the function followed by the free-energy function . Here is defined as a joint entropy of multivariate distributions as
where is the joint probability. We use intrinsic temperature which is a parameter that tells precisely that it will not change during the comparison stage of choosing the solution. Furthermore, we assess the cost of free energy as the optimization cost as . Based on this Monte-Carlo criterion we use the free energy difference criterion to accept the new solution or the best solution. At last, we updated the temperature as the standard SA and used it in the Free energy relation as
The process terminates after iterations or when the temperature and cost function reach predefined minimum values. The pseudocode of the algorithm is presented below in Algorithm (1).
| Algorithm 1: The SAFE algorithm |
|
Here is the random number generator taken from uniform distribution lies between . The performance of this modified algorithm was compared with a standard simulated annealing algorithm.
3. Results
As we know optimization algorithms often help us to figure out the minima (i.e., local or global) of any function based on an optimization time or a convergence time. This optimization/convergence time is crucial because it helps us to find the nature of the full landscape of a cost function. So, in this section, we shall test some multidimensional functions and try to compare them with standard Simulated Annealing (SA) to see which can reach the global minimum in a shorter time.
3.1. Convex Unimodal Function
Convex unimodal functions are the simplest class of multidimensional functions with a single minima in a multidimensional space. These functions can be seen diversely. For example in physics from the prospect of potential energy landscapes of a harmonic trap to any parameter estimation problem of a mathematical model to calculate the cost function, we find these. Here we write the function as
where A is a constant or the point where the minima is located. This objective function we use in our algorithm and found that the results are pretty close to A. We initialize our solution from a uniform random distribution of array size 100 with lower and upper bounds following as . As the array size changes in each iteration with a minimum length set at 2, we find the optimizer reduces its dimension from 100 to 2 after the end of the simulation. For target A set to 5 and for each number of simulations, we get the following results in Table 1. Here simulate the function 10 times to reach minima. After that, we plot energy, entropy, and cost function change over each iteration as in this Figure 1, we have compared the energy function over different iteration values for standard SA. This tells us that, the optimization time is faster for free-energy-driven self-adaptive SA than standard SA, which eventually takes a longer time to reach the minima. The self-adaptivity can be seen through the evolution of the temperature parameter (T). Interestingly, the convergence time of the standard SA increases with the initial dimension of the problem.
3.2. Rastrigin Function
To test the global minima of a more complicated function, we choose the Rastrigin function [16]. This function was first characterized by Rastrigin in 1974. The nature of the function is non-convex and it contains multiple local minima and the global minima lies at the value 0. The Rastrigin function is written as
Here B is a constant. In our simulation, we set the B value to . Our results show that the global minima are situated around 0 can be seen in Table 2. Similar to the convex unimodal function, we record for the whole optimization time the energy function, entropy, and cost function over different iterations. Interestingly, we observe similar trends. As we know, this Rastrigin function can take a longer time to search global minima for any optimizing algorithm but our free-energy driven self-adaptive SA can search this global minimum in a shorter time which can be seen in Figure 2.
In Figure 1 and Figure 2 we try to understand how entropy optimization can play a key role in the SAFE algorithm. In the plot, the dimension or the length of the function can be seen in terms of the iterations. Interestingly, we can see that the dimension reduction happens for the SAFE algorithm over the iterations (which can be seen in Figure 1 and Figure 2) while in the case of the standard SA, it is not changing over the iterations. Even if we try with dynamic array size in standard SA over each iteration. So, the dimension of SA is constant.
3.3. Parameter Estimation in a Noisy Process
Parameter estimation [17] is a process where the parameters are estimated based on the observed data. This estimation is important from engineering to systems biology as it helps us to figure out a more realistic state of the system. As an application of our algorithm, we use this to estimate the parameters of an exponential fit as
here noise is Gaussian in nature which has a mean 0 and standard deviation set to . This equation includes rigorous applications from Physics (e.g., radioactive decay, the waiting time distribution, etc.) to biology (e.g., protein degradation, inhibition processes, etc.). Here is a parameter that will be estimated by our free-energy-driven self-adaptive SA algorithm. We choose a 100 dimensional initial value of and We shall fit the average true value of and the fitted average value of . so the objective function can be defined as
Now, using this convex unimodal objective function we have fit the exponential stochastic equation after averaging 10 simulations, where the mean value of is , and the true value of the parameters are (i.e., ) are , 2 and 1. So, the fit is really close to the original one and we got a decay nature of the entropy, energy, and cost function over time. Also, this method can play a crucial if one has a high dimensional parameter set and initial conditions are completely unknown. So, this algorithm can be used in those scenarios using the difference between the average parameters of the true value and the average parameters which we shall estimate as an objective function or the cost function.
Figure 3.
Fit of the exponential solution and corresponding energy, entropy, and cost function over iteration after averaging 10 simulations using SAFE optimization.
Figure 3.
Fit of the exponential solution and corresponding energy, entropy, and cost function over iteration after averaging 10 simulations using SAFE optimization.
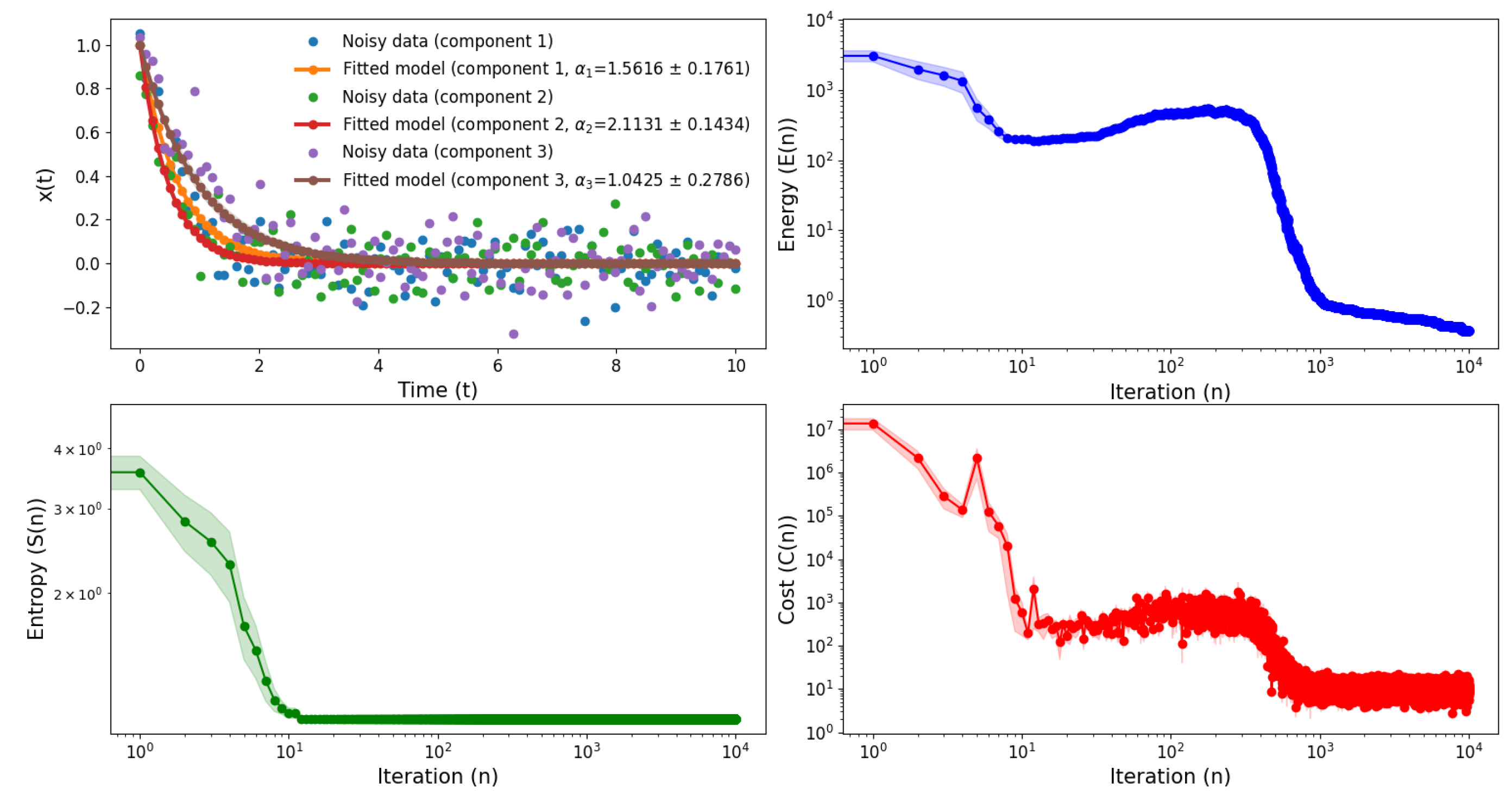
4. Discussion
In this article, we developed a free-energy-driven self-adaptive SA algorithm to search for the global minima of a multidimensional function, where the lengths of the variables are random over the iterations. As examples, we used both a convex function and a non-convex function. In both cases, our algorithm not only searched the global minima but also did so in a much shorter time than standard SA. Interestingly, the global minima of the two examples provided above do not depend on the dimension size. This suggests that entropy-driven self-adaptive SA can be employed in scenarios where dimensionality reduction can help to search global minima and can create faster convergence times. Finally, we demonstrated how this algorithm can be used for parameter estimation.
Free energy is a superposition of the system’s dynamics, quantified by the energy term, and information content of the system, quantified by the corresponding entropy. Here, we will use the concept of Helmholtz Free Energy to improve SA performance. Interestingly, one can visualize this aspect from Information thermodynamics [18] as a change in free energy due to the extraction of work after performing optimization. So, if one considers an initial solution of the optimization problem is prepared (and it follows a probability and at the end of the optimization task ( or by a Maxwell’s Demon [19]) it reaches to global minima and has a final probability distribution. In this way, one can write the fluctuations theorem [20] in the solution space and can define heat and work properties which can be translated further to the infamous Jarzynski’s inequality [21] if we consider the initial state prepared in an equilibrium condition and the terminal stage after optimization is in equilibrium as the free energy does not change over time.
There exist different kinds of modified versions of SA, where the temperature schemes are mainly varied [10] such that it can circumvent the local minima and eventually better search the global minima in a faster manner while bypassing the local minima. However, for higher dimensions, it appears to lack the dynamism required for escaping local minima effectively. On the other hand, our SAFE algorithm minimizes the dimension while minimizing the entropy to give liberty to the optimizer such that it can search the global minima more efficiently and conveniently concerning time. To check it, we compared furthermore our model with the modified SA where the temperature update or the scheme follows as: where [22]. Interestingly, we did not find a rapid change in the energy landscape for the modified SA which can be comparable to the SAFE algorithm. Instead, we observed that the SAFE algorithm consistently outperformed the modified SA in terms of finding lower energy solutions within a given computational budget. So, this SAFE algorithm can give us efficient robust solutions for a high-dimensional case.
Although SAFE shows promise as an optimization technique, some drawbacks can limit its effectiveness and applicability. First, the parameters depend on the symmetry of the problem. So, the global optimum is problem-specific. Free-energy-driven algorithms extend beyond SA and can be applied to genetic or evolutionary algorithms. The main goal is to find optimal solutions and/or global minima with high convergence rates while searching a broader space. One potential application of free-energy driven algorithms is the food foraging problem [23], where the agent or decision-maker optimizes its time to search for more food while foraging. In decision-making or game theory, when a decision-maker has to choose among multiple options within a constrained time or when decisions depend on the choices of other decision-makers, this algorithm can guide the decision-making process. Another example of a multidimensional objective function is a path optimization problem in network theory [24] . When dealing with a large set of paths in a network and trying to find the least path in a network among any set of points is challenging in nature due to the network topology. It will be interesting to observe how this algorithm can reduce convergence time in such network configurations.
The potential applications of this algorithm are vast, ranging from machine learning and complex system modeling to real-time optimization problems in various scientific and engineering domains. The scalability, robustness, and flexibility of our approach make it suitable for a wide range of challenging optimization problems, promising significant advancements in the field.
Acknowledgments and Funding
AB and HH want to acknowledge Prof. Dr. Adriana Gabor for her useful comments. AB thanks TIFR Hyderabad for the support and acknowledges the support of the Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India, under Project Identification No. RTI4007. HH would like to thank Volkswagenstiftung for its support of the "Life?" program (96732). HH has received funding from the Bundes Ministeriums für Bildung und Forschung under grant agreement No. 031L0237C (MiEDGE project/ ERACOSYSMED). Finally, HH acknowledges the support of the RIG-2023-051 grant from Khalifa University and the UAE-NIH Collaborative Research grant AJF-NIH-25-KU.
Data Availability Statement
All the codes and figures will be available soon on the GitHub page.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sreedhar, M.; Reddy, S.A.N.; Chakra, S.A.; Kumar, T.S.; Reddy, S.S.; Kumar, B.V. A Review on Advanced Optimization Algorithms in Multidisciplinary Applications. Recent Trends in Mechanical Engineering; Narasimham, G.S.V.L., Babu, A.V., Reddy, S.S., Dhanasekaran, R., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 745–755. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L.; Curtis, F.E.; Nocedal, J. Optimization Methods for Large-Scale Machine Learning. SIAM Review 2018, 60, 223–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Tobar, A.; Massi Pavan, A.; Petrone, G.; Spagnuolo, G. A Review of the Optimization and Control Techniques in the Presence of Uncertainties for the Energy Management of Microgrids. Energies 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter,G.,ReviewofOptimizationTechniques.In Encyclopedia ofAerospaceEngineering; JohnWiley&Sons, Ltd, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Gunantara, N. A review of multi-objective optimization: Methods and its applications. Cogent Engineering 2018, 5, 1502242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, M.S.; Shehab, M.; Al-Mimi, H.M.; Abualigah, L.; Zitar, R.A.; Shambour, M.K.Y. Gradient-Based Optimizer (GBO): A Review, Theory, Variants, and Applications. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 2023, 30, 2431–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, J.S.; Elwakeil, O.A.; Chahande, A.I.; Hsieh, C.C. Global optimization methods for engineering applications: A review. Structural optimization 1995, 9, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: past, present, and future. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetterling, W.T., Ed. Numerical recipes example book (C), 2nd ed ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge ; New York, 1992.
- Guilmeau, T.; Chouzenoux, E.; Elvira, V. Simulated Annealing: a Review and a New Scheme. 2021 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), 2021, pp. 101–105. [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Adeli, H. Simulated Annealing, Its Variants and Engineering Applications. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools 2016, 25, 1630001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonyadi, M.R.; Michalewicz, Z. Particle Swarm Optimization for Single Objective Continuous Space Problems: A Review. Evolutionary Computation 2017, 25, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential Evolution – A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. Journal of Global Optimization 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runarsson, T.; Yao, X. Stochastic ranking for constrained evolutionary optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 2000, 4, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chib, S.; Greenberg, E. Understanding the Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm. The American Statistician 1995, 49, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A., R.L. Systems of extremal control. Nauka 1974.
- Godfrey, K. Identification of parametric models from experimental data [Book Review]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 1999, 44, 2321–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, J.M.R.; Horowitz, J.M.; Sagawa, T. Thermodynamics of information. Nature Physics 2015, 11, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sorting Demon of Maxwell1. Nature 1879, 20, 126–126. [CrossRef]
- Sevick, E.; Prabhakar, R.; Williams, S.R.; Searles, D.J. Fluctuation Theorems. Annual Review of Physical Chemistry 2008, 59, 603–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarzynski, C. Nonequilibrium Equality for Free Energy Differences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2690–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundy, M.; Mees, A. Convergence of an annealing algorithm. Mathematical Programming 1986, 34, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoi, E.N.; Dafinescu, V. Review of Metaheuristics Inspired from the Animal Kingdom, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Networks: an introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford; New York, 2010.
Figure 1.
Plot of the energy function, entropy, solution length, and cost function of the convex unimodal function over the iterations averaged across 10 simulations. is fixed to .
Figure 1.
Plot of the energy function, entropy, solution length, and cost function of the convex unimodal function over the iterations averaged across 10 simulations. is fixed to .
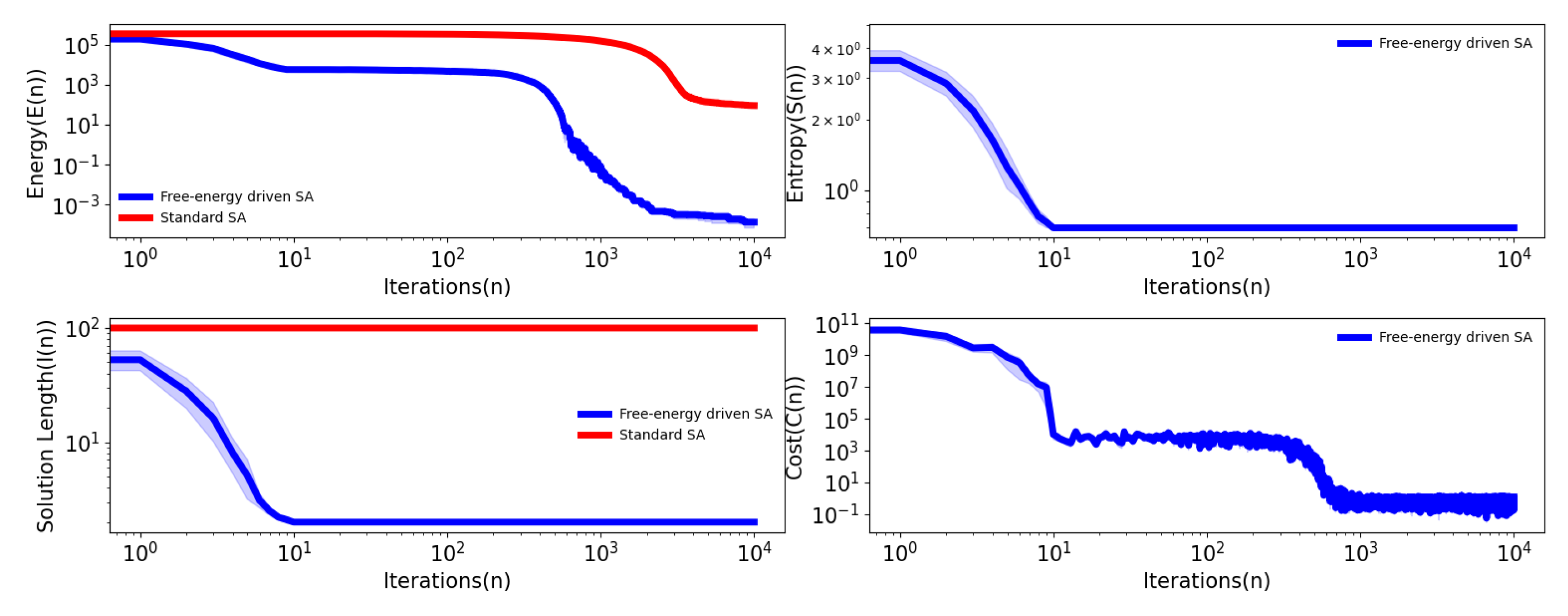
Figure 2.
Plot of the energy, entropy, solution length, and cost function of Rastrigin function over the iterations averaged across 10 simulations. is fixed to .
Figure 2.
Plot of the energy, entropy, solution length, and cost function of Rastrigin function over the iterations averaged across 10 simulations. is fixed to .
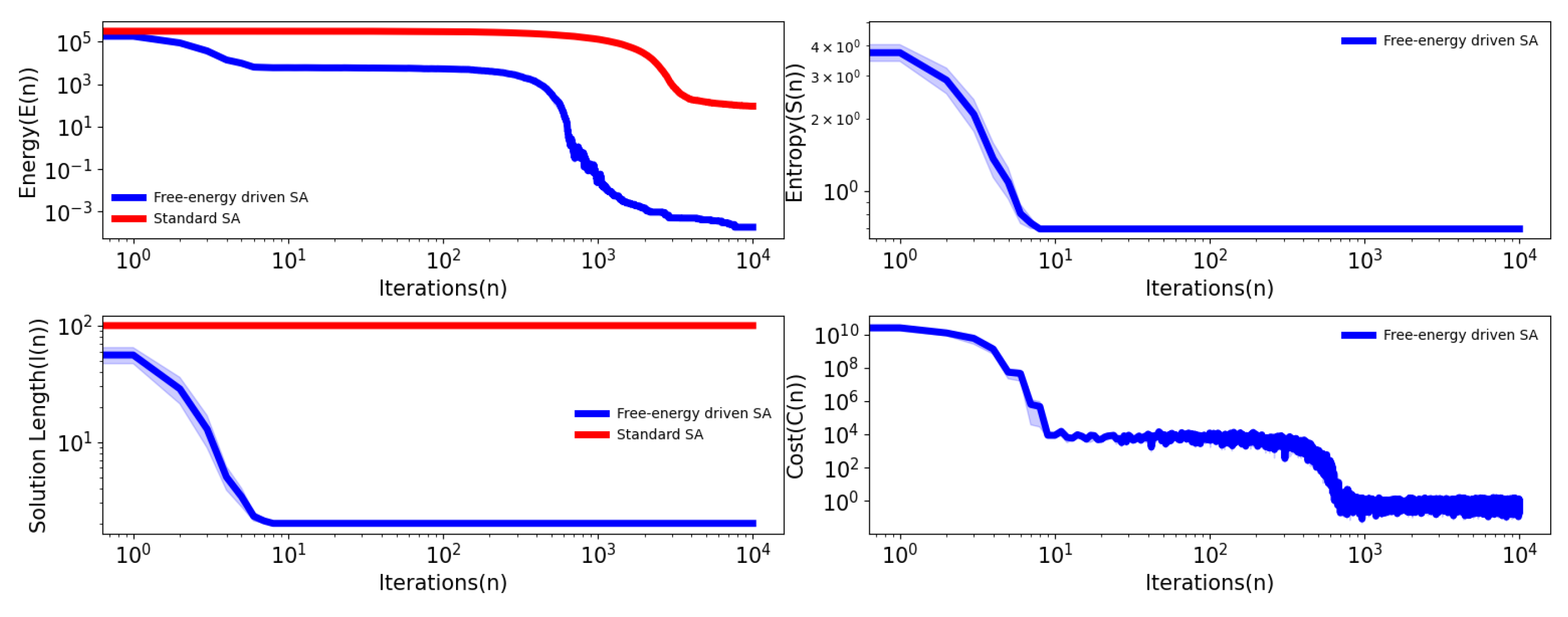
Table 1.
Minima values of the convex unimodal function for 10 different simulations using SAFE algorithm after iterations.
Table 1.
Minima values of the convex unimodal function for 10 different simulations using SAFE algorithm after iterations.
| Simulation No. | Minima values | Average minima |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [5.00877628, 4.99931244] | 5.00404436 |
| 2 | [4.99290482, 5.00108504] | 4.99699493 |
| 3 | [4.99307059, 5.00878274] | 5.00092667 |
| 4 | [5.00493791, 5.00035783] | 5.00264787 |
| 5 | [4.98592684, 5.00017079] | 4.99304882 |
| 6 | [5.01441376, 5.00885234] | 5.01163305 |
| 7 | [4.98497483, 5.0057631 ] | 4.99536897 |
| 8 | [4.98334158, 4.9984179 ] | 4.99087974 |
| 9 | [4.99803777, 4.9836407 ] | 4.99083924 |
| 10 | [5.00153187, 4.98777709] | 4.99465448 |
Table 2.
Minima values of the Rastrigin function for 10 different simulations using SAFE algorithm after iterations.
Table 2.
Minima values of the Rastrigin function for 10 different simulations using SAFE algorithm after iterations.
| Simulation No. | Minima values | Average minima |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [0.00809873, 0.00861702] | 0.00835788 |
| 2 | [-0.00794215, -0.00571157] | -0.00682686 |
| 3 | [-0.01599466, -0.01036956] | -0.01318211 |
| 4 | [-0.01365662, -0.00456229] | -0.00910946 |
| 5 | [0.01600855, -0.00308025] | 0.00646415 |
| 6 | [0.00527557, -0.00856973] | -0.00164708 |
| 7 | [-0.00066081, 0.00897958] | 0.00415939 |
| 8 | [0.00025436, 0.00287327] | 0.00156382 |
| 9 | [-0.000922, 0.01212199] | 0.00559900 |
| 10 | [-0.00444366, 0.00968743] | 0.00262189 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated







