Submitted:
16 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. The Magnetically Induced Isotropically Averaged Lorentz Force Density
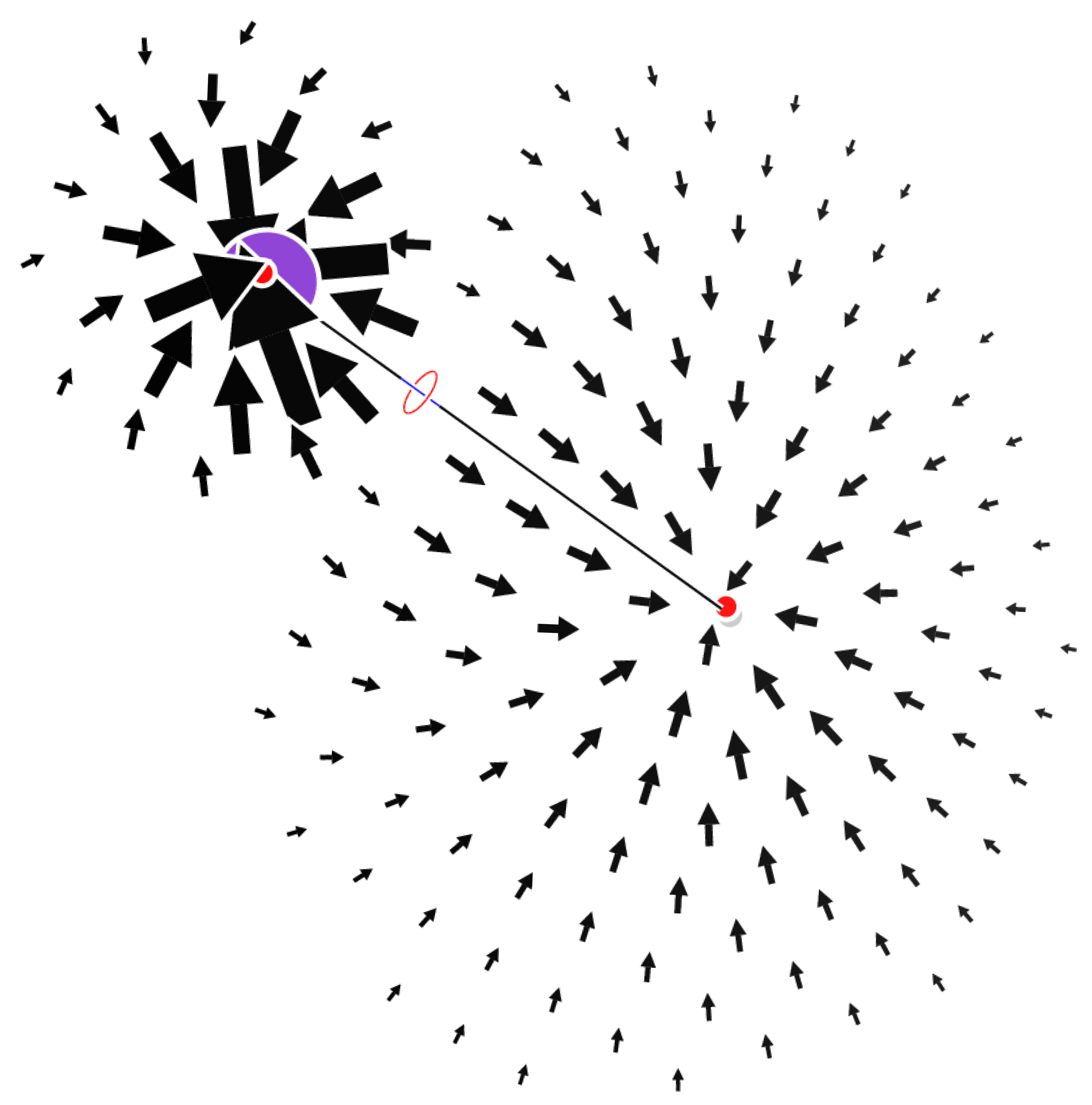
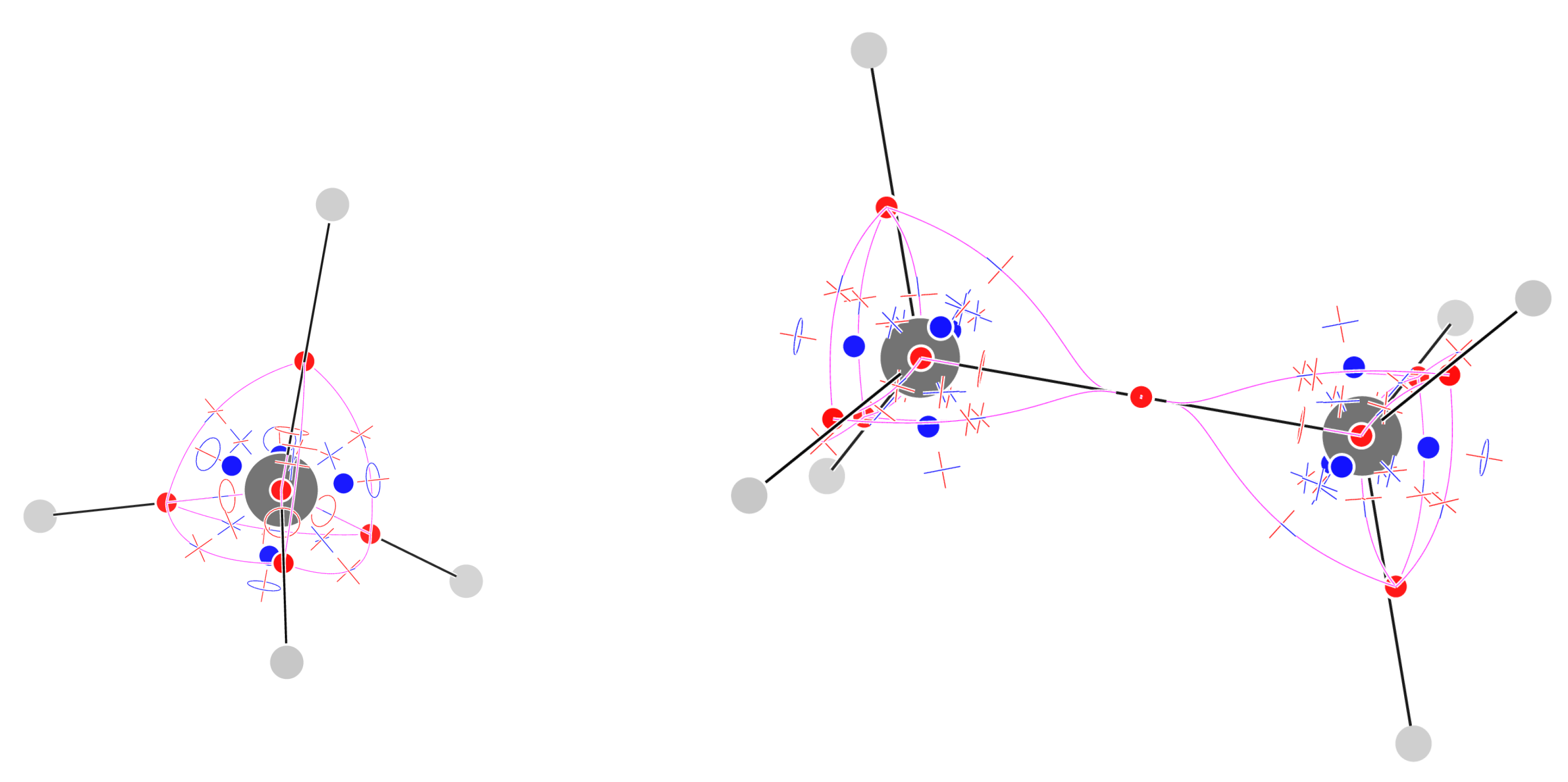
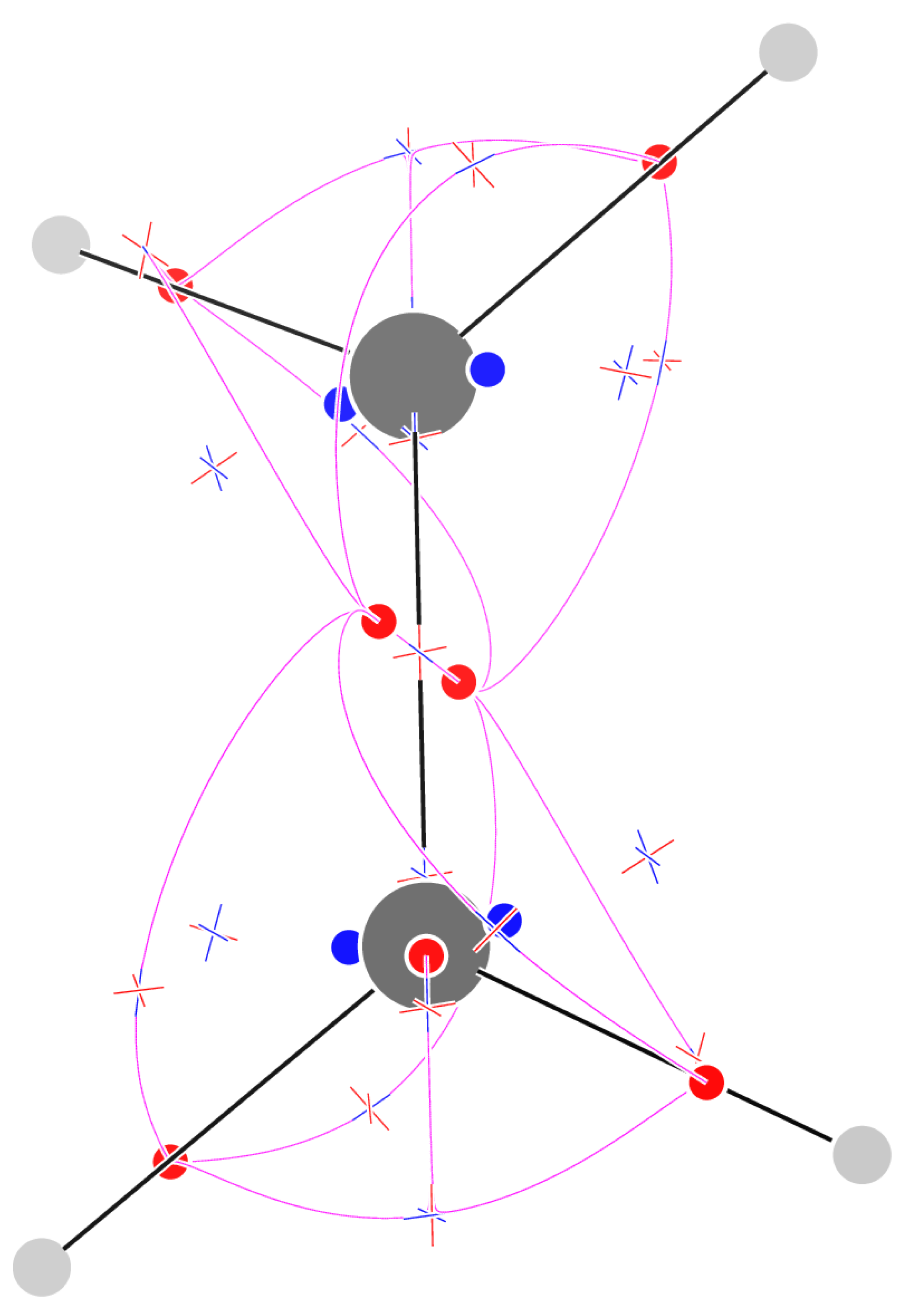
2.2. Topological Analysis of the Critical Points
3. Computational Methods
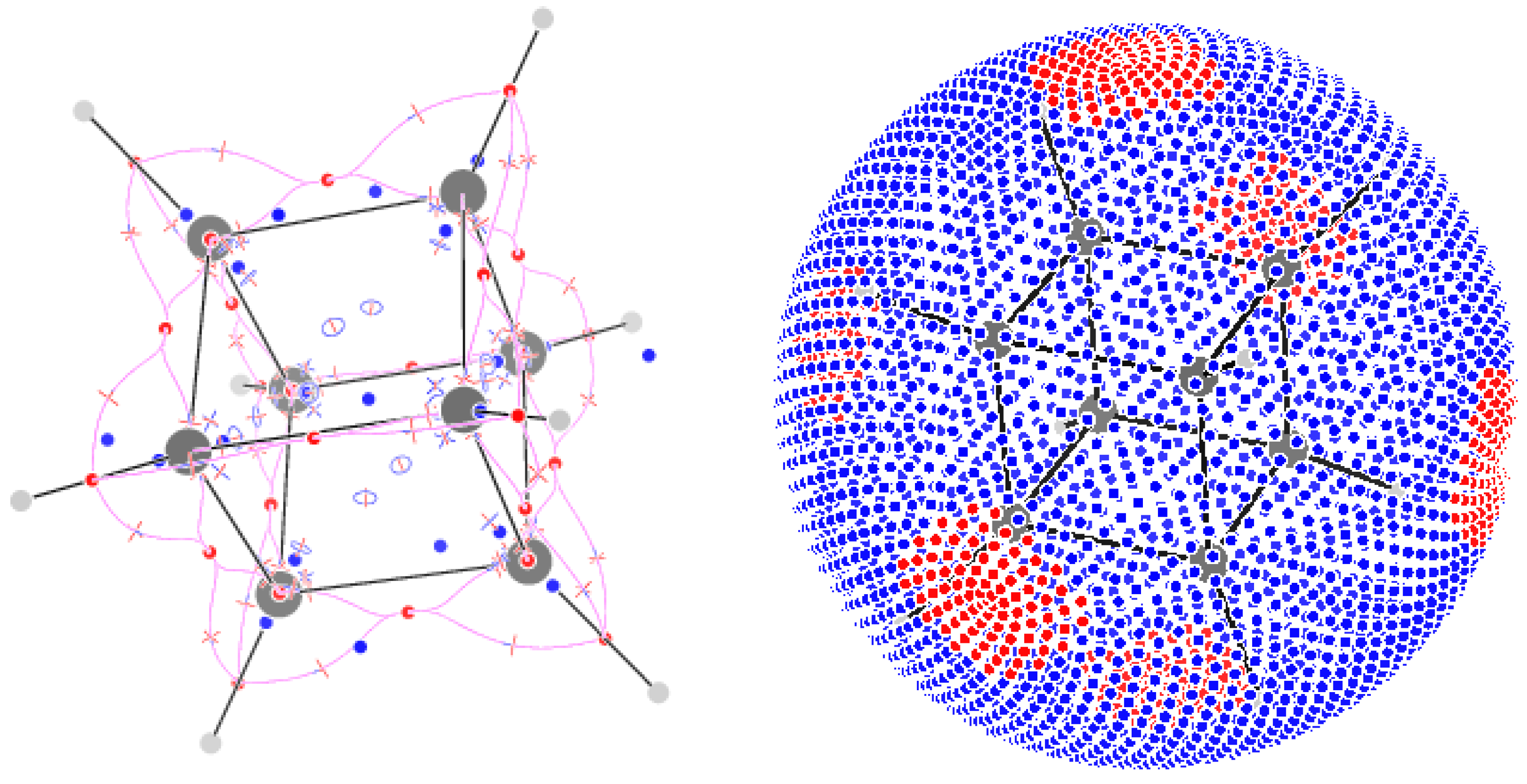
4. Results
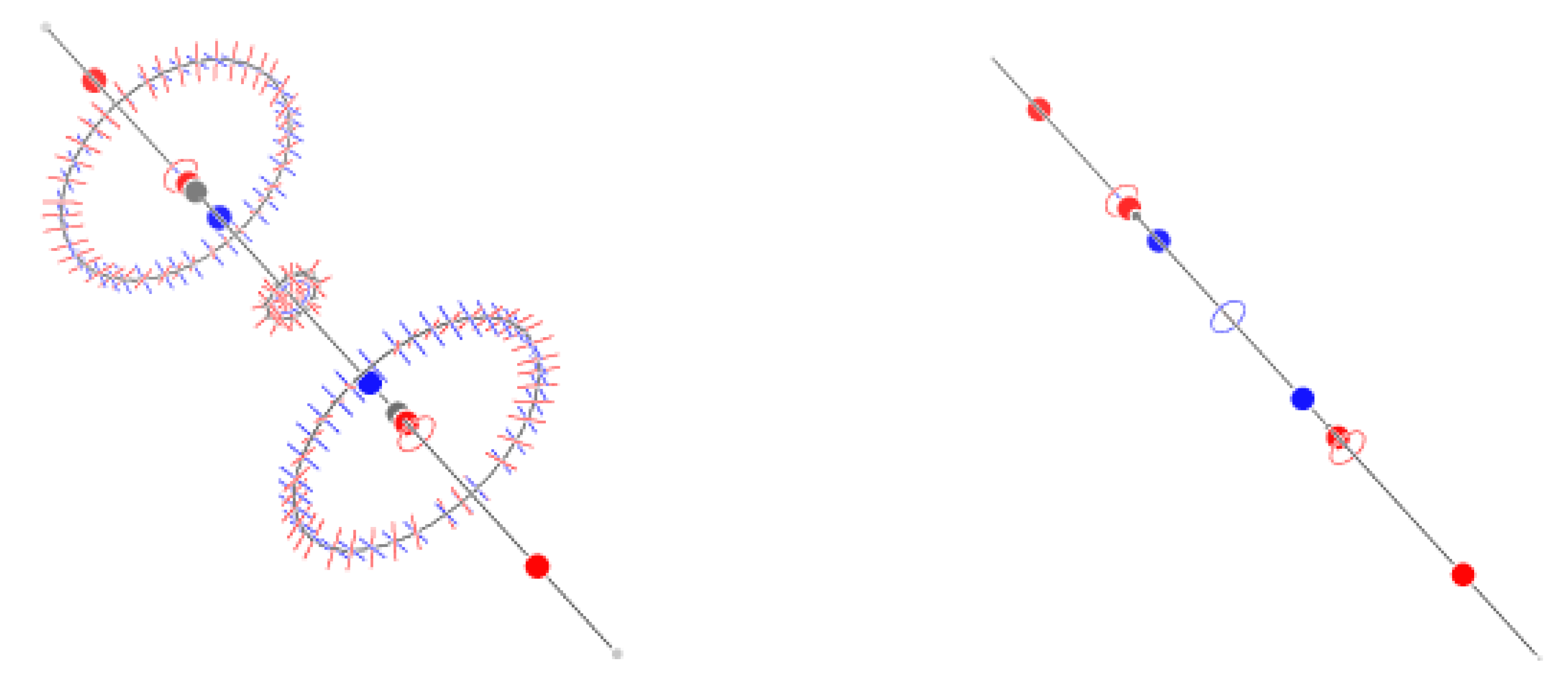
4.1. Lithium Hydride
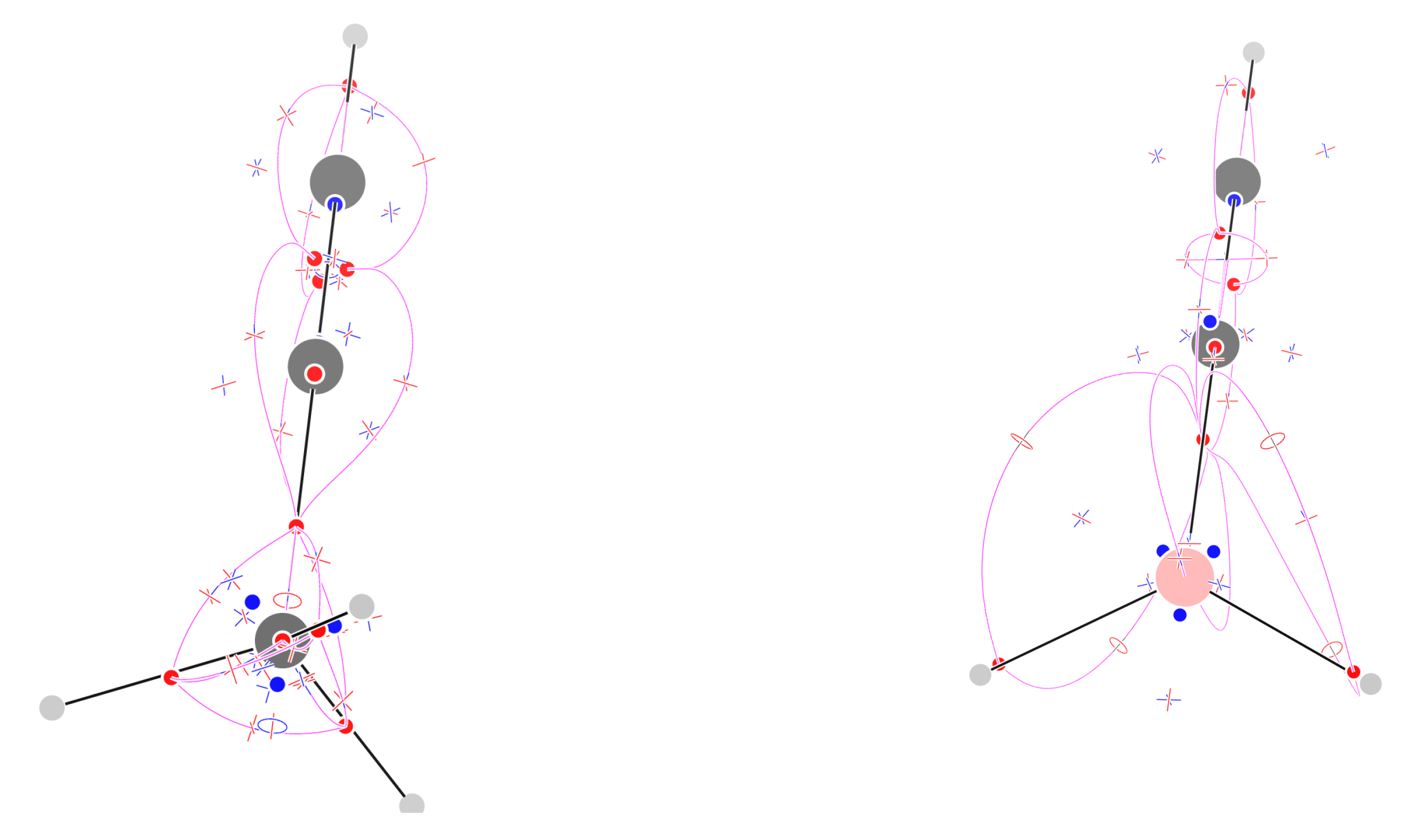
4.2. Methane
4.3. Ethane
4.4. Ethylene
4.5. Acetylene
4.6. Propyne
4.7. 3-Borapropyne
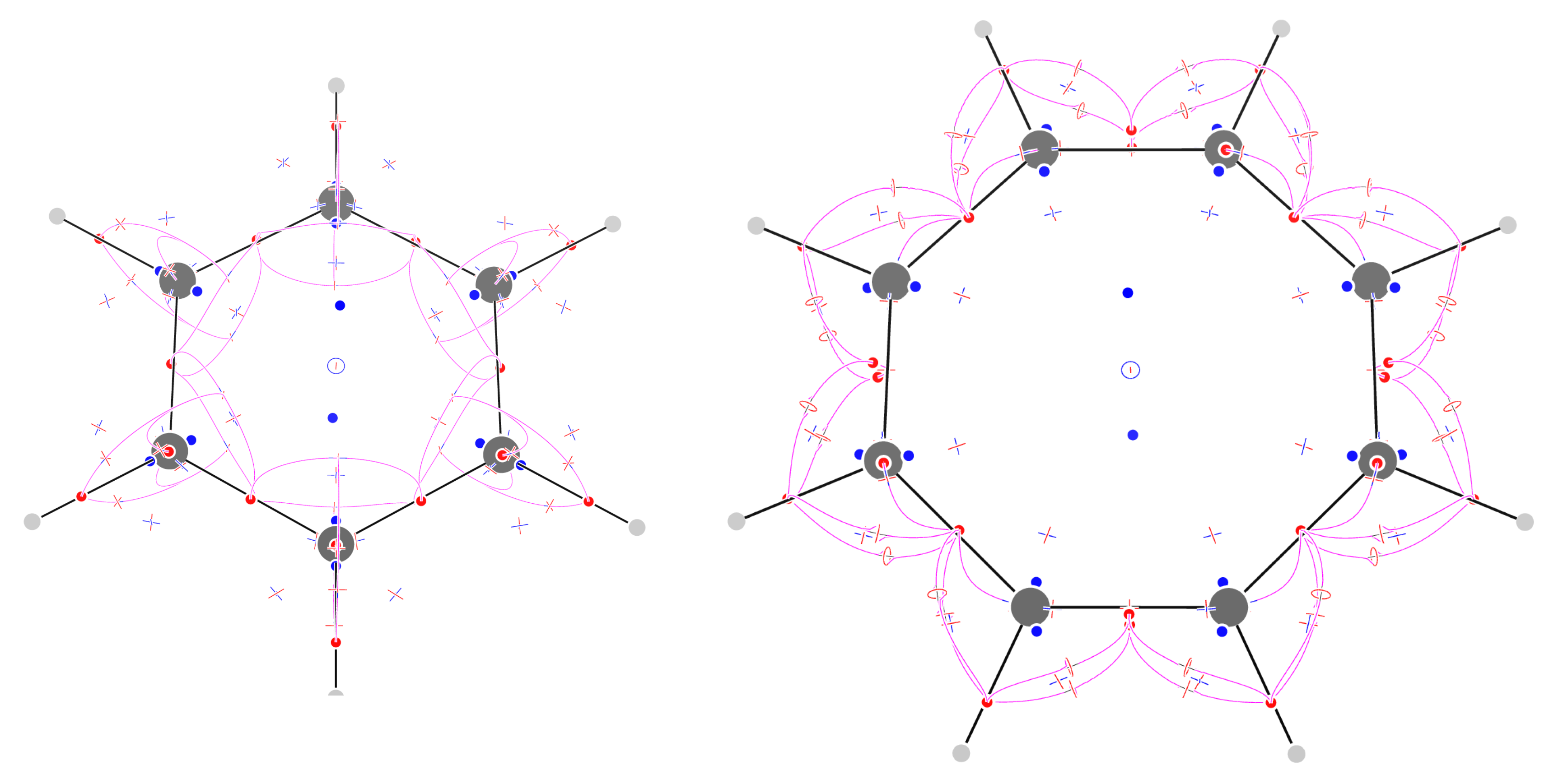
4.8. Benzene
4.9. Cyclooctatetraene
4.10. Borazine
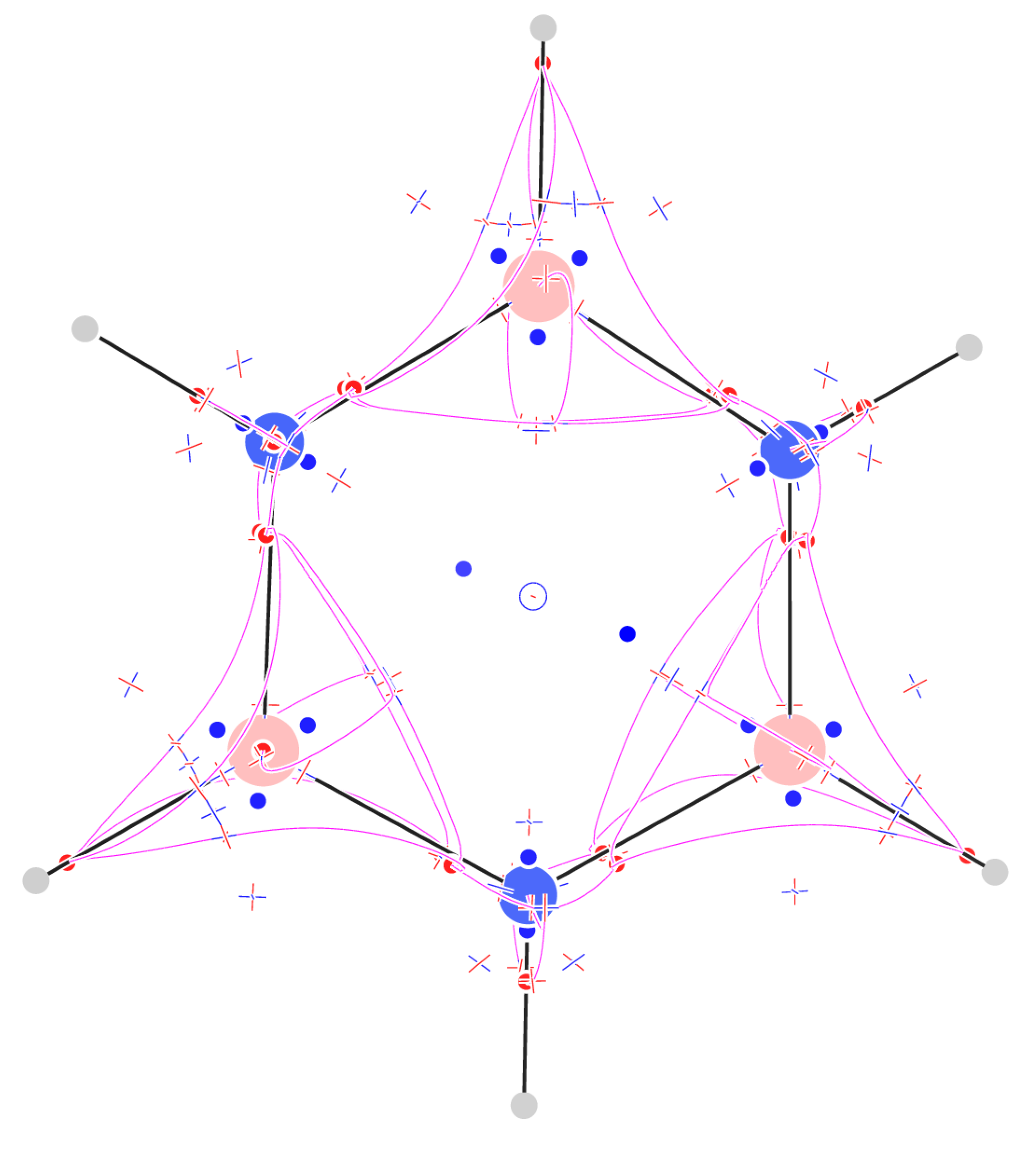
4.11. Cubane
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCP | Bond Critical Point |
| CP | Critical Point |
| DIAL | Divergence of the Isotropically Averaged Lorentz force density |
| QCT | Quantum Chemical Topology |
References
- Popelier, P.L.A. The QTAIM Perspective of Chemical Bonding. In The Chemical Bond; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2014; pp. 271–308. [CrossRef]
- Popelier, P.L.A. On Quantum Chemical Topology. In Applications of Topological Methods in Molecular Chemistry; Springer International Publishing, 2016; pp. 23–52. [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory (International Series of Monographs on Chemistry); Clarendon Press, 1994.
- Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J. (Eds.) The quantum theory of atoms in molecules: from solid state to DNA and drug design; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Gatti, C.; MacDougall, P.; Bader, R. On the Presence of Non-Nuclear Attractors in the Charge Distributions of Li and Na Clusters. Chem Phys Lett 1987, 141, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, G.K.H.; Gatti, C.; Iversen, B.B.; Damjanovic, L.; Stucky, G.D.; Srdanov, V.I. F center in sodium electrosodalite as a physical manifestation of a non-nuclear attractor in the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 12359–12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendás, A.M.; Blanco, M.A.; Costales, A.; Sánchez, P.M.; Luaña, V. Non-nuclear Maxima of the Electron Density. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, C.F.; Hernández-Trujillo, J.; Tang, T.H.; Bader, R.F. Hydrogen-Hydrogen Bonding: A Stabilizing Interaction in Molecules and Crystals. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, J.; Solà, M.; Bickelhaupt, F.M. Hydrogen-Hydrogen Bonding in Planar Biphenyl, Predicted by Atoms-In-Molecules Theory, Does Not Exist. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Mück-Lichtenfeld, C.; Erker, G.; Kehr, G.; Wang, H.; Beckers, H.; Willner, H. When Do Interacting Atoms Form a Chemical Bond? Spectroscopic Measurements and Theoretical Analyses of Dideuteriophenanthrene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2592–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Bond Paths Are Not Chemical Bonds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 10391–10396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrowski, I.; de Lange, J.H.; Adeyinka, A.S.; Mangondo, P. Evaluating common QTAIM and NCI interpretations of the electron density concentration through IQA interaction energies and 1D cross-sections of the electron and deformation density distributions. Comput Theor Chem 2014, 0000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, P.; Zanasi, R.; Monaco, G. Hydrogen-Hydrogen Bonding: The Current Density Perspective. J Comput Chem, 36, 707–716. [CrossRef]
- Popelier, P.L.A.; Maxwell, P.I.; Thacker, J.C.R.; Alkorta, I. A relative energy gradient (REG) study of the planar and perpendicular torsional energy barriers in biphenyl. Theor Chem Acc 2019, 138, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplaza, R.; Boto, R.A.; Contreras-García, J.; Montero-Campillo, M.M. Steric Clash in Real Space: Biphenyl Revisited. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 21251–21256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeros-Rivera, B.; Hernández-Trujillo, J. Control of Molecular Conformation and Crystal Packing of Biphenyl Derivatives. ChemPlusChem 2022, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, T.A.; Bader, R.F.W.; Aray, Y. Structural homeomorphism between the electron density and the virial field. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1996, 57, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. A Bond Path: A Universal Indicator of Bonded Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 7314–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendás, A.; Francisco, E.; Blanco, M.; Gatti, C. Bond Paths as Privileged Exchange Channels. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 9362–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín Pendás, A.; Francisco, E.; Gallo Bueno, A.; Guevara Vela, J.M.; Costales, A. Emergent Scalar and Vector Fields in Quantum Chemical Topology. In Applications of Topological Methods in Molecular Chemistry; Chauvin, R., Lepetit, C., Silvi, B., Alikhani, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, G.; Zanasi, R. The Molecular Electronic Structure Revealed by the Magnetically Induced Lorentz Force Density. J. Chem. Phys., 153, 104–114. [CrossRef]
- Popelier, P.L.A.; Burke, J.; Malcolm, N.O.J. Functional Groups Expressed as Graphs Extracted from the Laplacian of the Electron Density. Int J Quantum Chem 2003, 92, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeretti, P. Handbook of Molecular Physics and Quantum Chemistry, Wilson, S., Ed. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, S.P.A. Molecular electromagnetism: a computational chemistry approach; Oxford graduate texts, Oxford University Press: Oxford ; New York, 2011. OCLC: ocn753655526.
- Jameson, C.J.; Buckingham, A.D. Molecular Electronic Property Density Functions: The Nuclear Magnetic Shielding Density. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 73, 5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, G.; Zanasi, R. Magnetically Induced Current Density Spatial Domains. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, G.; Summa, F.F.; Zanasi, R.; Lazzeretti, P. Electronic Current Density Induced by UniformMagnetic Fields in Clarenes. Chemistry – A European Journal 2024, e202401167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquera-Lozada, J.E. Vorticity: Simplifying the Analysis of the Current Density. J Comput Chem 2019, 40, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricoche, X.; Garth, C. Topological Methods for Visualizing Vortical Flows. In Mathematical Foundations of Scientific Visualization, Computer Graphics, and Massive Data Exploration; Möller, T., Hamann, B., Russell, R.D., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; pp. 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboeuf, M.; Köster, A.M.; Jug, K.; Salahub, D.R. Topological analysis of the molecular electrostatic potential. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 4893–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, A. Algebraic topology, 14th printing 2015 ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Milnor, J.W.; Weaver, D.W. Topology from the Differentiable Viewpoint, rev. ed ed.; Princeton Landmarks in Mathematics and Physics, Princeton university press: Princeton (N. J.), 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brasselet, J.P.; Seade, J.; Suwa, T. Vector fields on singular varieties; Number 1987 in Lecture notes in mathematics, Springer: Heidelberg London, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Revision C.01, 2016. Gaussian Inc. Wallingford CT.
- Summa, F.F.; Monaco, G.; Lazzeretti, P.; Zanasi, R. Assessment of the Performance of DFT Functionals in the Fulfillment of Off-Diagonal Hypervirial Relationships. Phys Chem Chem Phys, p. 10.1039/D1CP01298C. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F. Segmented Contracted Basis Sets Optimized for Nuclear Magnetic Shielding. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, G.; Summa, F.F.; Zanasi, R. Program Package for the Calculation of Origin-Independent Electron Current Density and Derived Magnetic Properties in Molecular Systems. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 61, 270–283. [CrossRef]
- Kuck, D.; Schuster, A. Centrohexaindan, The First Hydrocarbon with Topologically Non-Planar Molecular Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1988, 27, 1192–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C.; Meringer, M. How Many Organic Compounds Are Graph–Theoretically Nonplanar? MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry 2002, 45, 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zanasi, R.; Fowler, P. Ring Currents and Magnetisability in C60. Chem Phys Lett 1995, 238, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J. An Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules. In The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules, 1 ed.; Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J., Eds.; Wiley, 2007; pp. 1–34. [CrossRef]
- Silvi, B.; Savin, A. Classification of Chemical Bonds Based on Topological Analysis of Electron Localization Functions. Nature 1994, 371, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncini, A.; Fowler, P.W.; Jenneskens, L.W. Angular Momentum and Spectral Decomposition of Ring Currents: Aromaticity and the Annulene Model. In Intermolecular Forces and Clusters I; Wales, D.J., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, G.; Zanasi, R.; Pelloni, S.; Lazzeretti, P. Relative Weights of σ and π Ring Currents in a Few Simple Monocycles. J Chem Theory Comput, 6, 3343–3351. [CrossRef]
- Báez-Grez, R.; Pino-Rios, R. The Hidden Aromaticity in Borazine. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7906–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
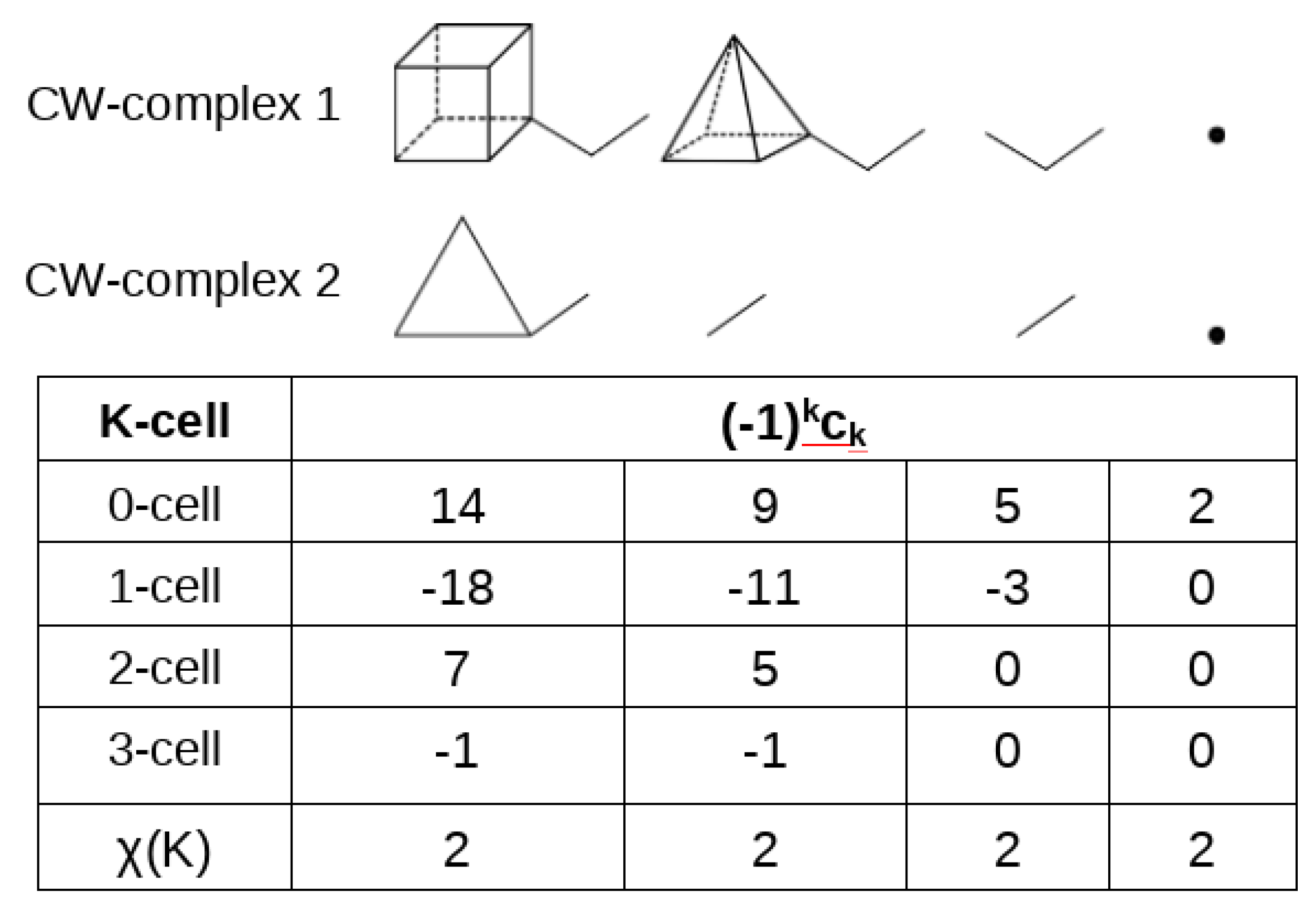
| r | s | n | cell | cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | -3 | 3 | -1 | 3-cell | 0-cell |
| 3 | -1 | 2 | 1 | 2-cell | 1-cell |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1-cell | 2-cell |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0-cell | 3-cell |
| 1 | -1 |
| Molecule | Formula | - | + | - | + | = | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium hydride | LiH | - | 2 | + | 1 | - | 0 | + | 0 | = | |
| Methane | CH4 | - | 5 | + | 10 | - | 10 | + | 4 | = | |
| Ethane | C2H6 | - | 9 | + | 20 | - | 20 | + | 8 | = | |
| Ethene | C2H4 | - | 8 | + | 11 | - | 8 | + | 4 | = | |
| Acetylene | C2H2 | - | 4 | + | 2 | - | 1 | + | 2 | = | |
| Propyne | C3H4 | - | 11 | + | 21 | - | 17 | + | 6 | = | |
| 3-Borapropyne | BC2H3 | - | 9 | + | 15 | - | 13 | + | 6 | = | |
| Benzene | C6H6 | - | 18 | + | 36 | - | 31 | + | 14 | = | |
| Cyclooctateraene | C8H8 | - | 28 | + | 44 | - | 33 | + | 18 | = | |
| Borazine | B3N3H6 | - | 24 | + | 48 | - | 40 | + | 17 | = | |
| Cubane | C8H8 | - | 28 | + | 48 | - | 38 | + | 23 | = |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





