1. Introduction
In recent years, the advancement of mobile sensing technology and the widespread popularity of mobile social media have provided a rich resource for a variety of emerging researches due to the massive amount of data generated by people using these services. Diverse location-based services can be provided using a variety of shared data sources, such as GPS tracks of taxis, geotagging and reviews on social media, etc. Among them, travel planning services have become a hot area of research. With more and more travelers choosing to travel alone, travel planning has become one of the most critical and time-consuming preparations before traveling. Before heading to their destination, travelers need to have an in-depth understanding of all the attractions in their destination, filter out the best combination of attractions, and plan an efficient travel route [
1]. In doing so, they need to consider the type of attraction, rating, duration of visit, and the order in which they visit different attractions. In addition, the traffic conditions of the route and the overall time required need to be considered to ensure that the planned route meets the time requirements of the trip. Only after taking all these factors into account can tourists determine the most suitable travel route for themselves.
In recent years, travel route planning has received extensive attention as a new type of path search problem. Travel route planning is more complex than traditional path search problems, such as the well-known Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). In traditional path searching methods, the problem is usually limited to considering the weights of each segment of edges in the path, with the goal of finding a set of edges with the minimum or maximum total weights [
2]. However, in travel planning, route search faces more complex needs and challenges. It is necessary to consider not only the efficiency of the route, but also the comprehensive evaluation of various factors, such as the attractiveness of the scenic spots, the individual needs of tourists, and the actual conditions during the journey, so that the solution of the problem becomes more multi-dimensional and dynamic [
3].
Travel Route Planning Optimization involves a complex set of decision-making issues designed to provide travelers with the best route options from one location to another. This includes not only the calculation of the shortest journey time and lowest cost, but also the ability to tailor travel routes based on visitor preferences, attraction characteristics, seasonal events, and real-time traffic [
4]. With the advancement of technology, especially in the field of mobile perception technology, big data analysis and artificial intelligence, modern travel route planning is facing unprecedented development opportunities. With these technologies improvement, massive amounts of data, including user behavior, traffic flow, and geolocation data, can be processed and analyzed to enable more accurate and personalized travel route planning.
In traditional travel planning applications, there are a number of significant problems. First of all, most apps only provide basic information about attractions, and the actual travel planning needs to connect each attraction into a complete route, and only a few apps currently consider recommending specific travel routes. Secondly, the existing route recommendations are often too uniform, usually covering only a few well-known attractions and simply connecting them [
5]. This approach results in each user getting the same travel route, ignoring the individual needs of tourists and not meeting the specific preferences of all travelers. Different tourists have different preferences for attractions, and travel planning should provide a customized combination of attractions for different tourists. Finally, traditional travel planning often only considers time efficiency and ignores the quality of points of interest, which is an important factor when it comes to travelers' choices [
6]. In addition, traditional travel planning relies on static data, while information such as transportation and attractions that need to be considered in actual travel is often in flux, and relying on static data for travel planning can lead to inaccurate planning.
In current travel planning research, researchers are mainly focused on developing the most appropriate travel itinerary according to the specific needs of tourists. Since travel path planning is essentially an NP-hard problem, i.e., it is computationally non-polynomial complex, and it is not practical to find the optimal solution by exhaustive method in the case of a large number of scenic spots. In addition, unlike traditional route planning, which pursues the shortest travel time, travel route planning needs to consider factors such as the type of attraction, the time of visit, the popularity, and the order of visits between each attraction [
7]. In view of these characteristics, researchers need to develop new algorithms for the special needs of travel route planning, so that the best travel route can be efficiently planned according to the individual needs of tourists when there are many attractions.
However, travel route planning also faces a series of challenges, such as how to deal with complex multi-objective optimization problems, how to respond in real time to changes in environmental and traffic conditions, and how to meet the individual needs of different travelers. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the latest research progress in travel route planning, and introduce the current challenges and future development directions, especially how to use large language models and other advanced technologies to improve the efficiency and accuracy of route search. Through a detailed analysis of different optimization strategies and algorithms, this paper hopes to provide new ideas and solutions for travel route planning.
2. Related Work
The field of study on the issue of itineraries is quite broad, and the studies cover many aspects of the field. In this series of studies, Cheng et al. [
8] introduced a novel path search method called Trip Planning Query (TPQ) for the first time. This method considers information including a starting point, an end point, a set of points of interest, and their categories. Its core research goal is to find an optimal path that starts from a specified starting point, passes through one or more points of interest in each category, and finally reaches a predetermined endpoint. Unlike traditional route planning based on point of interest selection, TPQ focuses on selecting from a preset set set of points of interest categories, making route planning more focused on the type of point of interest rather than the individual points of interest itself.
In addition, the Optimal Sequenced Route (OSR) search approach, proposed by Sharifzadeh et al. [
9] focuses on a unique aspect of path search. Unlike traditional planning methods, the OSR approach is to conduct line searches when the type of point of interest is determined and ordered. This approach provides a new solution for how to effectively arrange the order of visits to fixed types of points of interest, breaking through the limitations of traditional planning methods. The premise of a path search is usually based on a category of points of interest. This approach differs from the traditional point-of-interest-focused search by using route planning based on the type of interest. Through this search strategy, the route planning problem can be effectively solved when tourists fail to determine the specific points of interest, which provides new possibilities for the flexible configuration of travel routes.
Further, Chen et al. [
10] explored a method to optimize travel routes based on the quality of points of interest and the distance between them. In the TripPlanner system they developed, points of interest were selected not only based on travel time, but also on the quality of the points of interest and the degree of preference of the tourists. While itineraries planned through TripPlanner may result in a slight increase in travel time, these routes are more tailored to the individual needs of travelers. Immediately afterward, Dai et al. [
11] also valued the quality of points of interest in their research. During the itinerary planning process, they proposed that the average quality of the points of interest they passed through should meet certain standards. By implementing their proposed ETOTP method, travelers are able to get a travel itinerary that is optimized in time and meets the quality of points of interest.
At present, there are several challenges in the search for travel planning routes, including how to use efficient planning algorithms and how to ensure that the algorithmically planned travel routes meet the diverse needs of tourists [
12]. The efficiency of the travel path search algorithm is the key, because the travel path search problem belongs to the NP-hard problem. Traditional path search algorithms, such as linear programming and dynamic programming, can only provide exact solutions when the number of points of interest is low. However, when it comes to selecting based on all points of interest in a city, these traditional algorithms often spend a lot of time judging the validity of all candidate sets and comparing their advantages and disadvantages, and their efficiency is difficult to accept in practical applications [
13]. Therefore, when solving NP-hard problems, heuristic algorithms or approximate algorithms are often considered to improve the practical feasibility and efficiency of problem solving.
3. Methodologies
In this study, a large language model (LLM)-based optimization method for travel route planning was proposed. This method uses the deep learning ability of the language model to parse the natural language input and combine it with the Geographic Information System (GIS) to intelligently generate personalized travel itineraries. The model not only takes route optimization into account, but also incorporates user preferences and real-time data to provide travel recommendations that are practical and meet the user's needs.
A. Notions and Preprocessing
Above all, we summarize primary parameters and functions in following
Table 1.
Following items describe the processing for the collected data.
Input data: Inputs typically include a starting point, end point, point of interest, travel date and time limit, and so on. Users can express their queries through natural language. Geographic and traffic data includes road networks, traffic conditions, historical travel data, etc., and is usually derived from publicly available GIS databases or proprietary datasets.
Data Cleansing: Standardization: Convert data from different formats or sources into a unified format, such as a unified address format and time representation. Correct errors in input data, such as spelling mistakes, place ambiguity, etc. Data fusion integrates data from disparate sources to improve data integrity and accuracy.
B. Large Language Model
Large language models (LLMs) are used to perform semantic analysis of user input to parse travel-related needs and parameters. This step can be mathematized as an optimization problem in which the model tries to maximize the accuracy of information extraction from the input statement. Specifically, it can be expressed as the following optimization problem, which is described as Equation 1.
Where
is the natural language text entered by the user,
is the parsed parameter (e.g., travel preference, time window, budget, etc.), and
is the model parameter.
is the probability of correctly resolving
given the input
and the model parameter
.
The parsed information is used to define the search parameters. This can be represented by a conditional probabilistic model, whose goal is to determine the most likely set of travel parameters
, based on the extracted information
. Following Equation 2 describes the calculation process.
Note that the parameter includes the start and end points of the route, important transit points, time constraints, etc., which are determined by the output condition of semantic parsing.
Graph search techniques use the Dijkstra algorithm to search for the shortest path in a weighted graph. Let
be a graph where
is the set of vertices (places) and
is the set of edges (segments), and each edge
has a weight
(such as time or distance). The cost of a path can be expressed as following Equation 3.
Where
is the path from the start point to the end point. The Dijkstra algorithm optimizes the search through the heuristic function
, which estimates the cost from node
to the target node. The path is chosen to minimize the total cost.
The scoring system is based on user reviews and historical data by a given point of interest
, and its score
can be based on user reviews and the historical data. When our model selects a point of interest, the system calculates a score to decide whether to include the point of interest in the path. The scoring system mathematical calculation is expressed as following Equation 4.
Where
is a score based on historical data,
is a score based on user reviews, and
is the weight that balances these two factors.
Selection mechanism is based on the point of interest score and user preference
, select the set of points of interest that meets the needs of the user. The selection process is expressed as Equation 5.
This selection criterion ensures that only points of interest that score above the user's preference threshold are selected, where is a user-defined threshold parameter that adjusts the rigor of the selection.
Through above formulas and steps provide a framework that makes the process of quantification and optimization from user input to the recommendation of the final travel itinerary, increasing the accuracy and personalization of route planning for different users.
C. Optimization Process
The cost function is the core of the travel route planning optimization problem, which is used to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different routes. This function takes into account the time cost of the route
, the distance cost
and the satisfaction
to find the ideal path that is fast and economical, and at the same time meets the preferences of tourists. The time cost
reflects the total time required for the travel route, including travel time and dwell time. The cost of time is usually related to the length of the journey and the traffic situation, such as the level of congestion. The time cost function is expressed as Equation 5.
Where
represents the time it takes to traverse each leg of road
on path
.
Distance cost
calculates the total mileage for the entire trip, and long distances usually mean higher fuel consumption and wear and tear. The calculation process is expressed as following Equation 6.
Where
represents the distance of each leg
on route
.
Satisfaction
is a measure of how well a route matches a user's preferences. It can be based on factors such as the traveler's evaluation of the point of interest, the comfort of the route, or the aesthetics of the landscape. The satisfaction function is expressed as Equation 7.
Where
is the satisfaction score for each point of interest
in the path. Weight factor
parameters are set by the user to balance the importance of time, distance, and satisfaction. Adjusting these weights can meet the specific needs of different users, such as preferring fast arrival or prioritizing cost and experience.
The task of the optimization algorithm is to find the path that minimizes the cost function in the set of possible paths. This model adopts a heuristic optimization method, that is, a genetic algorithm to simulate the selection, crossover, and mutation processes in natural evolution. Initialize a set of path populations, and generate a new generation of paths by selecting the optimal path, crossing and mutating in each generation, and iterate until the lowest cost path is found.
Additionally, our proposed model utilizes the feedback adjustments to adjust the parameters in training process, which is described as following items.
User feedback: Collect feedback from visitors on their actual experience with the travel route, such as overall satisfaction with the route, ratings of specific points of interest, etc.
Parameter update: Based on the feedback collected, adjust the weights in the cost function to better reflect the actual preferences of users.
Algorithm fine-tuning: Optimize path search and generation algorithms based on user feedback and path performance. This may include adjusting the crossover rate and mutation rate of the genetic algorithm, or improving the cooling plan and acceptance guidelines of the simulated annealing algorithm.
Through this detailed mathematical model and optimization process, the travel planning system is able to provide highly personalized and optimized travel itineraries, greatly improving traveler satisfaction and travel efficiency.
4. Experiments
A. Experimental setups
The purpose of this study was to construct a detailed map model of points of interest to optimize multi-day travel route planning, systematically classify all points of interest and select them based on type, while ensuring that the shortest route time between points of interest is accurately calculated. The experiment was conducted using Eclipse software using the Windows 10 operating system, an Intel Core i7-6700HQ processor, and 8GB of memory, and covered three different route planning algorithms: rule-based algorithms, heuristic search algorithms, and optimization algorithms combined with large language models.
Additionally, the evaluation focuses on the time efficiency, route optimization and resource consumption of the algorithms, so as to compare and verify the performance and efficiency of each algorithm in practical applications, so as to provide a scientific basis and improvement direction for the development of future travel planning technology.
B. Experimental analysis
User satisfaction is a key indicator to measure the performance of travel planning algorithms, which mainly reflects the effectiveness of the algorithm in meeting users' personalized needs and expectations. It covers core elements such as compliance, comfort, quality of experience, and efficiency.
Evaluation methods include questionnaires, real-time feedback, follow-up interviews, and data analysis, with the aim of optimizing algorithms and service processes through direct feedback from users. In the study of travel planning algorithms, the specific calculation of user satisfaction usually relies on the comprehensive evaluation of multiple dimensions. The exact formula may vary from study to study, using a weighted scoring system to combine scores across dimensions. The satisfaction is expressed as Equation 8.
Where
stands for the score of compliance,
stands for the score of comfort,
stands for the score of quality of experience, and
stands for the score of efficiency.
is the weight of these dimensions and may vary depending on the focus of the study
These evaluation results are not only used for algorithm tuning and service improvement, but also influencing product decisions to continuously improve service quality and user experience. Through effective user satisfaction evaluation, travel planning services can be more customer-oriented and enhance their market competitiveness. Following
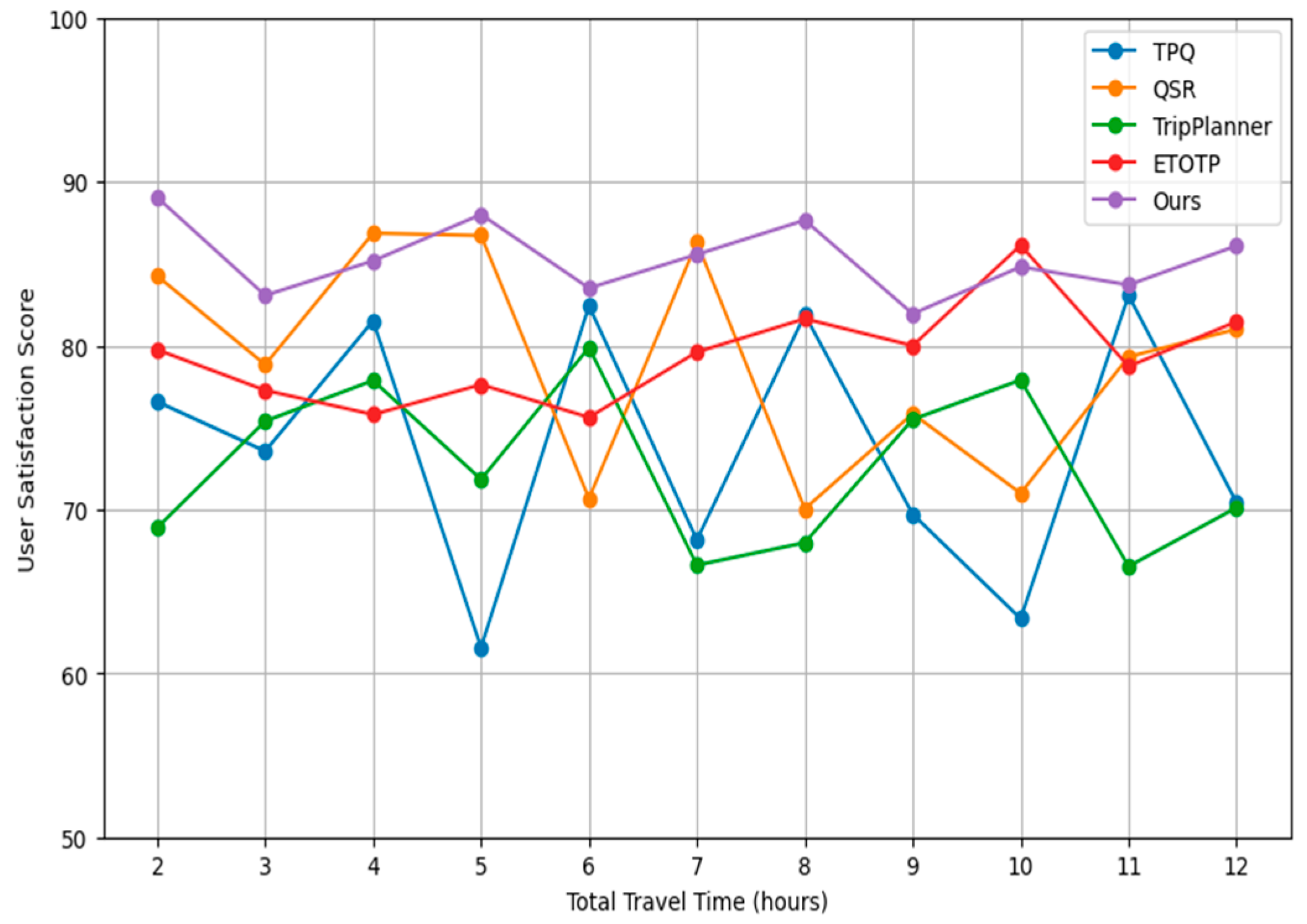
Figure 1 demonstrates the comparison of user satisfaction through increasing the total travel time for simulated users in the path planning model.
From above
Figure 1 displays the comparison of user satisfaction scores across different travel planning methods, as the total travel time increases from 2 to 12 hours. The methods compared include TPQ, QSR, TripPlanner, ETOTP, and our method (Ours). Each line represents the satisfaction trends associated with each method, providing a visual insight into which methods may offer higher satisfaction levels under varying travel durations.
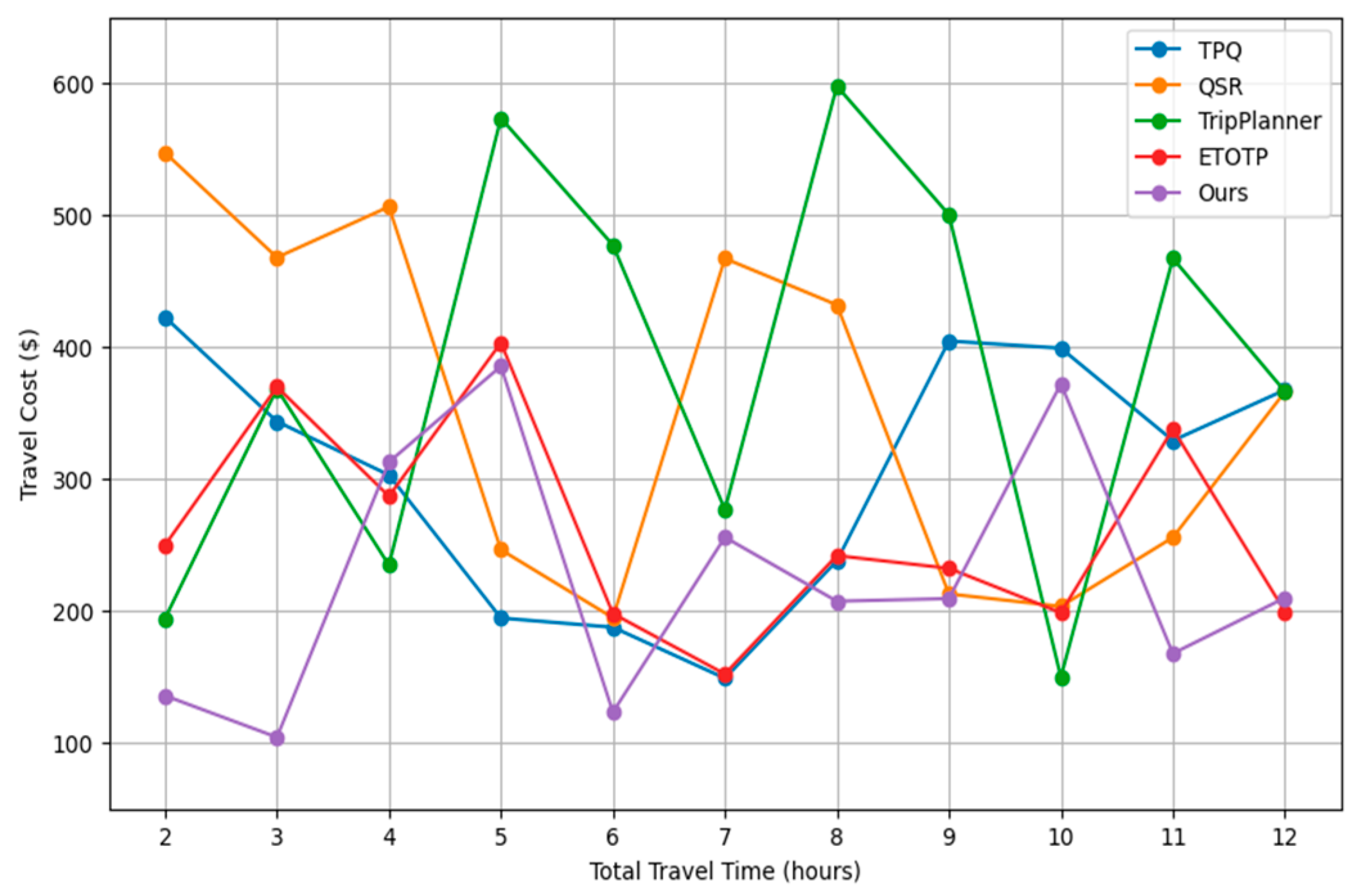
Travel cost is one of the important indicators to evaluate the effectiveness of travel planning algorithms, covering all the expenses related to the trip, such as transportation costs, accommodation fees, and admission fees to points of interest. An efficient travel planning algorithm should not only provide a travel itinerary that meets the user experience, but also seek to minimize the total cost on top of that.
By comprehensively considering various cost elements and finding the most cost-effective solution, this evaluation index helps to determine the performance of the algorithm in terms of economy, so that users can enjoy a high-quality travel experience while also obtaining reasonable cost optimization. Further, Following
Figure 2 shows the cost comparison results under identical 70% user satisfaction score.
The above
Figure 2 illustrates a comparison of travel costs across different travel planning methods—TPQ, QSR, TripPlanner, ETOTP, and our method (Ours)—as total travel time increases from 2 to 12 hours. Each line represents how the cost associated with each method trends over varying durations. This visualization helps in identifying which methods are more cost-effective over time and how each approach manages costs as travel durations extend.
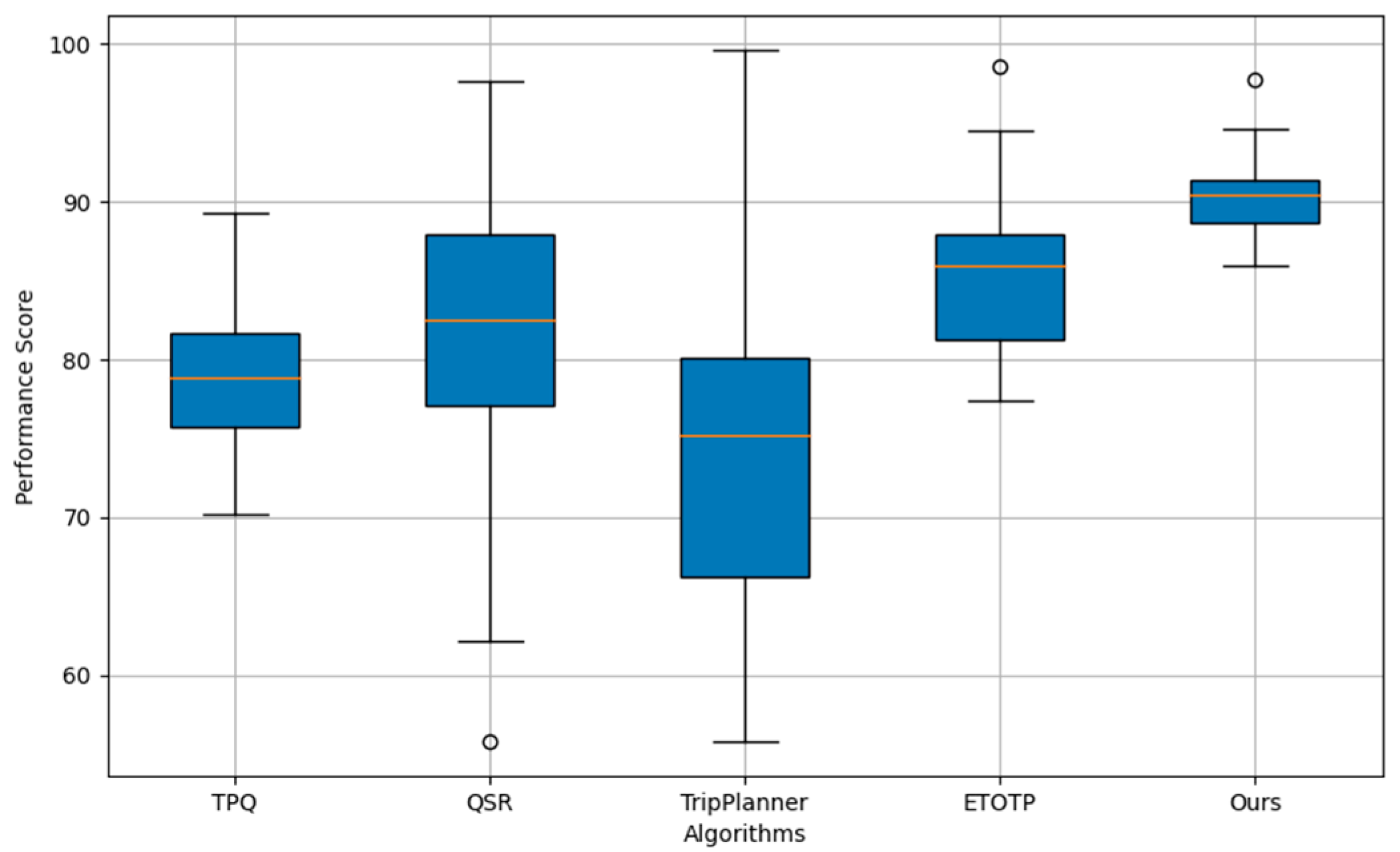
The stability of the algorithm is an evaluation index that is used to measure the consistency and reliability of the performance of the travel planning algorithm under different operating conditions. This includes whether the algorithm is able to consistently deliver high-quality and accurate output in the face of various variations, such as changes in the density of points of interest, diversity of user input. The highly stable algorithm shows that it is robust and able to adapt to different environments and needs without large performance fluctuations due to slight changes in input or environment. Following
Figure 3 compares the algorithm stability comparison results for different models.
From above
Figure 3 visualizes the stability comparison of different travel planning algorithms: TPQ, QSR, TripPlanner, ETOTP, and our method ("Ours"). Each box represents the distribution of performance scores under varying conditions, reflecting the algorithm's stability. The median is indicated by the line inside the box, while the whiskers extend to show the range of the data. A smaller interquartile range (the height of the box) and less spread in the whiskers suggest greater stability. This visualization helps in assessing which algorithms demonstrate consistent performance across different scenarios, with "Ours" showing the least variability, suggesting high stability.
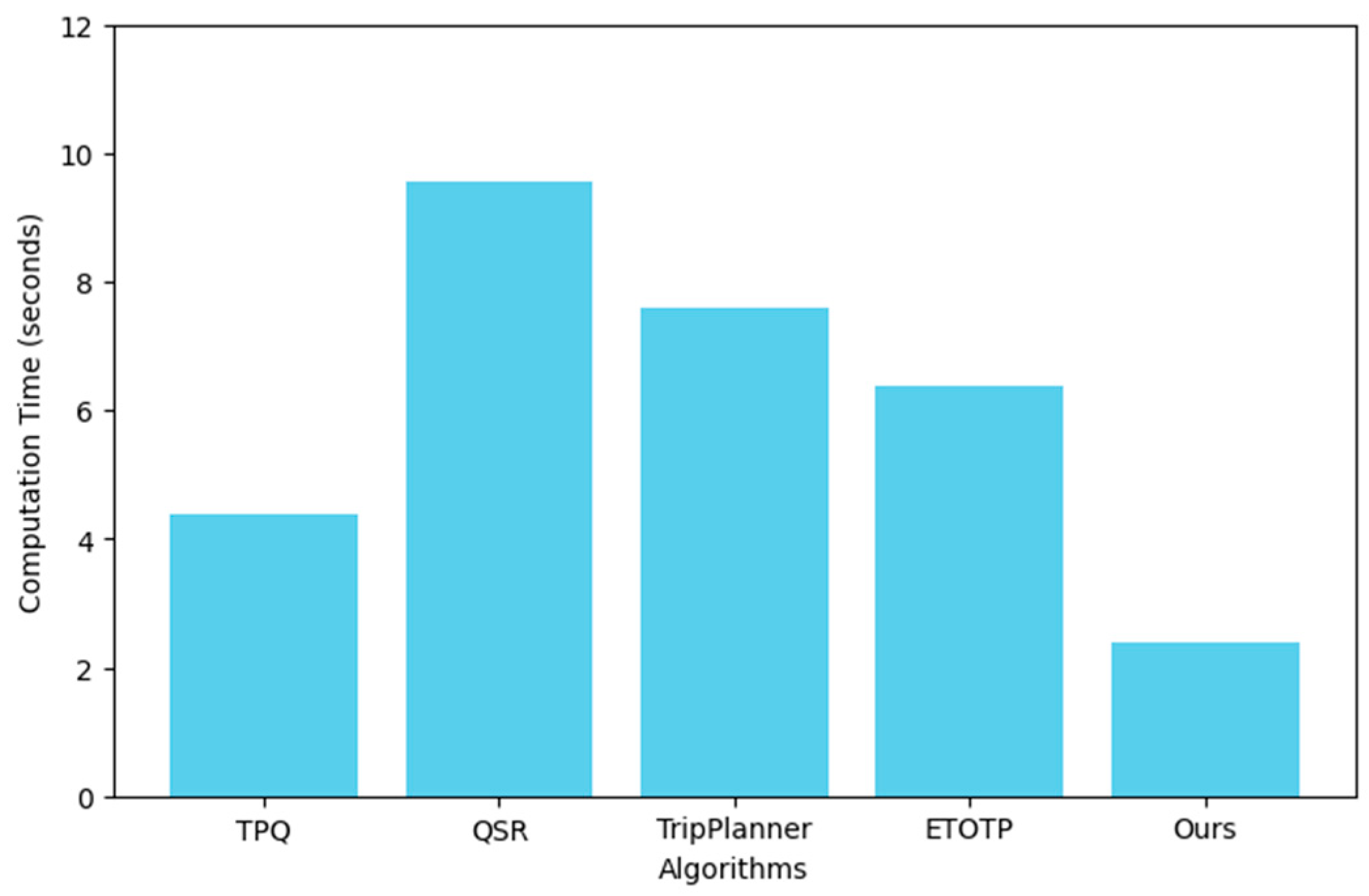
Computation time is a key metric for evaluating the efficiency of a travel planning algorithm, which refers to the total time required from the initiation of the algorithm to the completion of optimal route planning. In modern travel planning applications, especially for real-time responses, reducing computation time is critical. An efficient optimization algorithm should be able to quickly process large amounts of data and generate travel itineraries to ensure a smooth and responsive user experience.
Therefore, the pursuit of lower computation time can not only improve the usefulness of the algorithm, but also enhance the user's satisfaction and trust in the travel planning tool. In practice, developers strive to reduce computing time by optimizing algorithms, improving data processing processes, or using more efficient computing resources to provide more efficient services. Following
Figure 4 shows the computation cost comparison results with existing planning methods under identical setups.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the application of large language models in travel route planning optimization has shown remarkable potential. Our proposed model enables more intelligent and personalized route suggestions, taking into account various factors such as user preferences, local conditions, and real-time information. Through the power of language understanding and generation, these models can provide detailed and tailored travel routes, enhancing the travel experience. However, further research and development are needed to address potential limitations and continuously improve the accuracy and effectiveness of the optimization process. Specifically, researchers can provide more accurate traffic predictions or incorporating dynamic events can make the travel route planning even more seamless and efficient in the future.
References
- Cao, Sha. "An Optimal Round-Trip Route Planning Method for Tourism Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm." Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2022.1 (2022): 7665874. [CrossRef]
- Li, Sidi, et al. "Tourism route optimization based on improved knowledge ant colony algorithm." Complex & Intelligent Systems 8.5 (2022): 3973-3988.
- Geng, Yuanzhe, et al. "Deep reinforcement learning based dynamic route planning for minimizing travel time." 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops). IEEE, 2021.
- Zhu, Siying. "Multi-objective route planning problem for cycle-tourists." Transportation Letters 14.3 (2022): 298-306.
- Ntakolia, Charis, and Dimitris K. Iakovidis. "A swarm intelligence graph-based pathfinding algorithm (SIGPA) for multi-objective route planning." Computers & Operations Research 133 (2021): 105358.
- Albalawneh, Da’ad Ahmad, and M. A. Mohamed. "A new federated genetic algorithm-based optimization technique for multi-criteria vehicle route planning using ArcGIS network analyst." International Journal of Pervasive Computing and Communications 20.2 (2024): 206-227. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Boliang, et al. "Integrating traffic routing optimization and train formation plan using simulated annealing algorithm." Applied Mathematical Modelling 93 (2021): 811-830.
- Li, Feifei, et al. "On trip planning queries in spatial databases." International symposium on spatial and temporal databases. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2005.
- Sharifzadeh, Mehdi, Mohammad Kolahdouzan, and Cyrus Shahabi. "The optimal sequenced route query." The VLDB journal 17 (2008): 765-787.
- Chen, Chao, et al. "TripPlanner: Personalized trip planning leveraging heterogeneous crowdsourced digital footprints." IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 16.3 (2014): 1259-1273.
- Dai, Junqiang, et al. "An efficient trust-oriented trip planning method in road networks." 2014 IEEE 11th Intl Conf on Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing and 2014 IEEE 11th Intl Conf on Autonomic and Trusted Computing and 2014 IEEE 14th Intl Conf on Scalable Computing and Communications and Its Associated Workshops. IEEE, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ntakolia, Charis, and Dimitris K. Iakovidis. "A route planning framework for smart wearable assistive navigation systems." SN Applied Sciences 3.1 (2021): 104.
- Li, Peisong, et al. "A dynamic and scalable user-centric route planning algorithm based on polychromatic sets theory." IEEE transactions on intelligent transportation systems 23.3 (2021): 2762-2772. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).