Submitted:
16 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Energy issue: Energy is a limitation of the underwater sensor network, as batteries do not have solar energy to charge and are not easily replaced; Therefore, routing protocols should consider energy saving as a key element because the node is dead after the energy runs out and may cause the project to fail.
- Load Balancing: An optimal routing protocol uses network resources fairly and equitably. This approach can prevent the occurrence of Bottlenecks or Hotspots. Also, in case of such incidents, action should be taken to resolve the issue as soon as possible [3].
- Underwater Location: One of the important features that all routing protocols in the underwater network suffer from is the lack of GPS location information for nodes and their neighbours [4,8]. Knowing the location of nodes and neighbours reduces routing tables, reduces neighbour-finding efforts, and prevents loops and wandering packages in the network. Unfortunately, GPS was associated with errors in shallow water (less than 4 meters) and is unusable in deep water [9,10]. In the underwater network, the nodes use only one Z-axis, known as the depth gauge, and are equipped with it. A routing protocol with only the depth of the node from the water level and the neighbour’s list should act to transfer the node information to the base station at the water level, which is an unresolved challenge.
- Node mobility and instability of the fluid environment: The instability of the nodes underwater due to environmental factors such as hot and cold water currents, collisions of underwater organisms, and fluid waves is apparent [11]. Since the sensor nodes are connected to the seabed by chains and are suspended between the seabed and the sea surface, they are constantly moving. The node’s mobility causes the list of neighbours, the path is chosen, and the path to be explored and repaired to undergo fundamental changes.
- Lack of a fault detection system: If a failure or underwater network configuration problem occurs, it is not detected before retrieving and aggregating network data. This process may easily lead to the complete failure of the monitoring mission [10].
- Lack of real-time monitoring: Recorded data are unavailable at the base station until collection and processing. This process may occur several hours after each sampling [5].
- Impossibility of instantaneous system configuration: Interaction between coastal control systems and monitoring commands is impossible in real-time. This prevents the adaptive set of commands, and it is impossible to configure the system after a specific event [8].
2. Related Works
2.1. Underwater Sensor Routing without Location
| Variable | Definition | Variable | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| u, v | Node in graph | DPP | DODAG Preferred Parent |
| T | Temperature in degrees Celsius | DRL | DODAG Root List |
| S | Set of nodes | d | Depth in meters |
| B | Border routers | f | Frequency |
| N | Noise | Constant K is degree of graph | |
| p | Parent node | p’ | Alternative parent node |
| DODAG | Destination Oriented Directed Acyclic Graph | Root | Root node of graph (Sink) |
| Shipping factor (0–1) | DIO | DAG Information Object | |
| w | Wind speed | DAO | Destination Advertisement Object |
| P | Power of signal | DIS | DODAG Information Solicitation |
| CC | Capacity of channel | DAO-Ack | Acknowledgement for DAO |
| DT | Delay time | IC | Inconsistency |
| C | Consistency | Imin | Minimum interval |
| DTproc | Processing delay time | Imax | Maximum interval |
| DTqueue | Queuing delay time | ND | Neighbour Discovery |
| DTtrans | Transition delay time | NS | Neighbour Solicitation |
| Constant factor | NA | Neighbour Advertisement | |
| Absorption | RS | Router Solicitation | |
| Trx | Transition time | RA | Router Advertisement |
| r | Radios | Lt | Linkage Timer |
| R | Number hops of Root node | Mt | Mobility timer |
| J | Root node in graph | Rt | Response Timer |
| OF | Objective Function | M | Alive nodes |
| G | Graph | Predetermined lifetime | |
| V | Set of vertices | E | Set of edges |
| Year/Ref | Aim/Strategy | Strengths | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 [13] | Clustered geographic-opportunistic routing protocol (C-GCo-DRAR) for UWSNs. Aims to address challenges like high propagation delay and energy constraints through clustering and depth-based topology adjustments. | Demonstrated superior performance in packet delivery, energy efficiency (EE), and reduced delays via Aquasim simulator. Utilizes energy levels for cluster head election and depth adjustment for void recovery. | Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR), EC, E2E Dealy. |
| 2020 [14] | Energy-efficient routing in IoT-enabled UWSNs for smart cities using "Underwater (ACH)²" (U-(ACH)²). Incorporates depth considerations to optimize energy use across varied deployment scenarios. | Outperforms DBR and EEDBR in packet delivery rates, energy usage, and network lifetime (NL), promising for smart city applications. | EC, PDR, NL. |
| 2020 [15] | Game-Theoretic Routing Protocol (GTRP) for 3-D Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks (UASNs). Utilizes a strategic game with Nash equilibrium for packet forwarding, minimizing broadcasts for node degree estimation. | Shows enhanced packet delivery, reduced delay, and EE in Aqua-Sim simulations. Addresses latency, mobility, and bandwidth challenges effectively. | PDR, E2E delay, EC. |
| 2020 [16] | Distributed Multiagent Reinforcement Learning (DMARL) protocol for Underwater Optical Wireless Sensor Networks (UOWSNs). Focuses on dynamic topologies and energy optimization through distributed decision-making. | Improved energy usage, PDR, and load distribution validated through simulations. Demonstrates adaptability and efficiency in UOWSNs. | EC, PDR, load distribution. |
| 2020 [17] | Fuzzy Logic Cluster-Based Energy Efficient Routing Protocol (FLCEER) for UASNs. Implements multi-layer clustering and fuzzy logic for efficient routing and UCH election. | Enhances EE, packet delivery, throughput, and NL, outperforming MLCEE, DBR, and EEDBR in simulations. | EE, PDR, throughput, nNL. |
| 2020 [18] | Sleep-Scheduling Oil Detection Routing Protocol for UWSNs in smart oceans. Integrates IoT for energy-efficient oil spill detection using a 2D network architecture and sleep scheduling. | Extends NL and improves detection efficiency, focusing on environmental monitoring and protection. Demonstrates energy conservation in simulations. | Energy conservation, detection efficiency, NL. |
| 2020 [19] | FFRP introduces a self-learning dynamic firefly mating optimization for efficient and reliable data routing in IoUT. | Superior packet delivery ratio, lower latency and EC, enhancing network throughput. | Potential complexity in real-world deployment due to the bio-inspired, computation-intensive optimization process. |
| 2020 [20] | Stochastic modelling of opportunistic routing for IoUT, leveraging programmable physical layers and multi-modal communication. | Improved data delivery rates through innovative candidate-set selection, integrating acoustic modem and node selection. | Increased Energy Consumption trade-off, requiring efficient energy management strategies for practical application. |
| 2020 [21] | Hybrid optimization routing for AUVs in IoUT, focusing on EE and effective data collection via A-ANTD and TARD phases. | Reduces energy usage, improves data delivery efficiency, and enhances network performance for smart ocean applications. | The complexity of coordinating AUVs and sensor nodes might limit scalability and adaptability in diverse aquatic environments. |
| 2020 [22] | A novel Power-Controlled Routing (PCR) protocol for IoUT that dynamically adjusts transmission power based on environmental conditions. | Improves energy use and data delivery rates through dynamic power control and opportunistic routing. | Complex adjustment algorithms may increase computational overhead. |
| 2021 [23] | Utilizes Intelligent Data Analytics (IDA) for Optimized Energy Planning (OEP) in IoUT, enhancing data transmission efficiency and energy optimization. | Significant increase in packet delivery rate and latency and energy expenditure reductions. | The dual-stage programming framework could be complex to implement and manage in real time. |
| 2021 [24] | Discusses green energy harvesting and energy-efficient routing for IoUT, exploring sustainable and renewable energy sources. | Focuses on sustainability and tapping into unexplored energy resources, potentially reducing dependency on traditional power sources. | May require substantial initial investment and infrastructure for energy harvesting technologies. |
| 2021 [25] | Introduces an Adaptive-Location-Based Routing Protocol (UA-RPL) for UASNs, focusing on optimizing packet forwarding in three-dimensional spaces. | Enhanced network throughput and PDRs, reduced EC and communication delays. | The protocol’s efficiency could diminish in extremely dense or highly dynamic underwater environments. |
| 2021 [26] | Examines demur and routing protocols in UWSNs for IoUT applications, aiming to support smart city initiatives. | Highlights the potential of IoUT in environmental monitoring, underwater exploration, and disaster prevention. | Specific challenges and disadvantages related to the implementation in smart cities are not detailed. |
| Year/Ref | Aim/Strategy | Strengths | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 [27] | Energy-efficient routing in IoT-based UWSN using the Bald Eagle Search (BES) algorithm. Emulates bald eagle hunting behaviour for optimizing routing, comprising initialization, construction, and data transmission phases for effective energy use and path efficiency. | Demonstrates superior performance in EC, average residual energy, and NL over existing algorithms, addressing critical issues of E2E delay, EC, and reliable data delivery. | EC, average residual energy, NL, PDR, E2E (E2E) delay. |
| 2021 [28] | To enhance reliability, reduce delay, and improve EE in UASN using RLOR. / Merges opportunistic routing with reinforcement learning for dynamic node selection. | Demonstrated superior performance in reliability, low delay, and EE. Innovative recovery mechanism for void navigation. | Complexity of implementing reinforcement learning algorithms in real-time underwater environments. |
| 2021 [29] | Address energy consumption and void avoidance in UASNs with QL-EEVARP. / Uses Q-learning for dynamic, energy-efficient path selection and void avoidance. | Achieves better PDR and enhanced EE; adaptive void recovery enhances network performance. | Scalability issues in larger networks; the complexity of Q-learning algorithm implementation. |
| 2021 [30] | Improve IoUT data dissemination by mitigating void zones. / EVA framework focuses on preemptive void identification and intelligent routing. | Reduced energy consumption, extended NL, improved packet delivery, and reduced latency. | Advanced algorithms for void detection and navigation may increase system complexity. |
| 2021 [31] | Optimize underwater communication in IoUT with dynamic path adjustment. / ROBINA uses Path-Adjustment and path-loss models to maintain data flow in aquatic conditions. | Improved packet transmission, reduced transmission, and path loss; adaptively managed underwater routing. | Deployment complexity in variable environments due to intricate path adjustment mechanisms. |
| 2021 [32] | Facilitate reliable and energy-efficient UIoT communication. / ELW-CFR employs proactive routing with layering and watchman nodes for collision-free communication. | Low E2E delay and high PDR; address void hole challenge effectively. | The layering model and watchman node reliance may complicate implementation. |
| 2022 [33] | Enhance energy efficiency in UWSNs through optimized power control. / Introduces a power-controlled routing protocol that dynamically adjusts TPL based on various factors. | Significant improvements in data delivery rates and network longevity; optimizes energy usage. | Potential complexity in dynamic power adjustment and monitoring for effective implementation. |
| 2022 [34] | Enhance communication efficiency in underwater IoT with FBR./ Evaluate FBR performance across different angles to optimize resource use and packet delivery. | Narrower FBR angles led to better performance metrics, including energy conservation and reduced buffer strain. | Configuration of optimal FBR angles is critical and may not fit all operational scenarios in underwater IoT. |
| 2022 [35] | Optimize energy efficiency in UWSNs. /Metaheuristic-based clustering with Routing Protocol employing CEPOC for clustering and MHR-GOA for routing. | Notable improvements in energy efficiency and network lifespan; effective load balancing in data transmission. | Complex algorithm integration may challenge real-time applicability and scalability in diverse underwater conditions. |
| 2022 [36] | Enhance underwater IoUT communication. / Cooperative Routing Protocol based on Q-Learning for hybrid optical-acoustic networks, optimizing connectivity and energy use. | Improved network connectivity, lifetime, and efficiency; reduced packet loss and E2E delay. | Deployment complexity due to hybrid optical-acoustic communication needs and the learning-based routing decision process. |
| 2022 [37] | Improve UWSNs’ energy efficiency and network longevity. / Cooperative-Communication Based Underwater Layered Routing, integrating cooperative communication with hierarchical clustering. | Extended NL, improved throughput and packet delivery; effective energy consumption balance. | The intricate clustering and cooperative communication mechanisms may complicate protocol deployment. |
| 2022 [38] | Enhance energy efficiency and data transmission in UWSNs. / Energy Optimization using Swarm Intelligence (EORO) protocol, employing EFF-PSO for optimal forwarder node selection. | Superior throughput, EC, and latency metrics; improved PDR. | Complexity of swarm intelligence algorithms might increase computational overhead and affect real-time performance. |
| 2022 [39] | Mitigate signal transmission challenges in UWSNs. / Utilizes IoT and SNR analysis with OSDM modulation and improved channel estimation for efficient signal transmission. | Enhanced communication efficiency with improved SNR, reduced BER and minimized MSE. | The complexity of advanced modulation techniques and channel estimation may limit adaptability to all underwater conditions. |
| 2022 [40] | Extend network longevity and improve IoT WSN connectivity. / ESEERP optimizes CH selection using a Sail Fish Optimizer (SFO) for efficient route selection. | Achieves significant improvements in network longevity, energy utilization, and PDR. | The optimization technique’s complexity could impact the protocol’s scalability and adaptability to varying network sizes. |
| 2022 [41] | Optimize underwater IoUT communication. / Sector-based opportunistic routing (SectOR) integrates optical and acoustic communications to enhance packet delivery. | Significant improvements in underwater networks’ EE, delay reduction, and PDR. | Challenges in balancing communication range and beamwidth for optimal performance across underwater environments. |
| Year/Ref | Aim/Strategy | Strengths | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 [42] | Evaluate the efficacy of various IoUT routing protocols. / Simulation-based analysis of cluster-based and chain-based routing protocols to enhance efficient data transfer in UWSNs. | Comprehensive comparison revealed cluster-based protocols show varied efficiency, offering insights into effective routing strategies in IoUT. | Requires extensive simulations to capture real-world complexities and underwater conditions accurately. |
| 2022 [43] | Optimize data transfer performance in UWSNs. /Performance analysis of diverse routing protocols like AODV, DSR, and DYMO under varying conditions using QualNet simulator. | Identified protocols with lower power consumption and higher energy efficiency, crucial for improving UWSN performance. | Simulation-based approach may not fully replicate underwater environments’ unique physical and chemical challenges. |
| 2022 [44] | Enhance energy efficiency and information transmission in IoT-UWSNs. / Introduces adaptable power networking methods using Fastest Route Fist (FRF) and a business unit method for effective routing. | Proposed methods significantly reduce Electric Cost (EC) and Transmission Drop Rates (RTDR) with reasonable latency. | Complexity of implementing and tuning the proposed adaptable power networking methods in diverse underwater scenarios. |
| 2022 [45] | Enhance routing efficiency and energy conservation in UWSNs. / Introduces the Adaptive Clustering Routing Protocol (ACRP) with multi-agent reinforcement learning for adaptive cluster head selection, reducing communication overhead and EC. | Demonstrated improved routing efficiency, energy utilization, and network lifespan compared to existing methods. Efficiently mitigates hotspot issues through balanced EC. | Implementation complexity due to reinforcement learning integration; requires rigorous tuning to effectively adapt to diverse underwater environments. |
| 2022 [46] | Analyze UWSN performance using diverse routing protocols. /Evaluate protocols like AODV and DSR using simulations to explore their efficacy under various network conditions. | Provided comparative insights into protocol performance, identifying those with potential for UWSN enhancements. | Simulation-based evaluations may not fully capture the operational complexities of real-world underwater environments. |
| 2022 [47] | Enhance IoUT communication efficiency with DSPR. / Utilizes angle of arrival and depth information for directional data forwarding and selective power control to optimize energy use. | Demonstrated energy efficiency, achieving better performance in delivery ratios and network longevity. | May require sophisticated hardware to accurately determine the angle of arrival and implement selective power control effectively. |
| 2022 [48] | Review energy optimization techniques in UIoT. / Evaluates various energy optimization strategies, including wireless power transfer and artificial intelligence, to enhance network efficiency. | Highlighted potential efficiencies from mixed-medium communication and smarter battery management, identifying research gaps and future directions. | The breadth of the review may necessitate further empirical testing to validate the effectiveness of proposed optimizations in real-world applications. |
| 2022 [49] | Address energy optimization in UWSNs. / Proposes an energy-efficient routing protocol leveraging genetic algorithms for optimal routing and data fusion techniques for energy conservation. | Showed improvements in PDR and EC, offering a viable solution for extending NL. | The complexity of the genetic algorithm and data fusion process may impact the scalability and real-time applicability of the protocol. |
| 2022 [50] | Adaptive Transmission-based Geographic and Opportunistic Routing (ATGOR) protocol for UIoTs. Introduces a two-part strategy focusing on cube selection for transmission reduction and reliable node selection for optimal data forwarding. Incorporates Mobility Aware ATGOR (MA-ATGOR) to predict neighbour locations to avoid voids and ensure packet delivery. | Enhances packet delivery reliability, reduces void nodes, and optimizes energy consumption per packet in harsh underwater environments. | PDR, the number of void nodes, and EC per packet. |
| 2022 [51] | Stochastic Optimization-Aided Energy-Efficient Information Collection for IoUT. Utilizes heterogeneous AUVs for data collection, optimizing energy efficiency with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Lyapunov optimization considering AUV trajectory, resource allocation, and Age of Information (AoI). | Offers a holistic approach to optimizing energy usage and AoI in IoUT networks. Successfully balances energy consumption with system stability and information freshness through adaptive planning and optimization strategies. | EC, queue lengths, Age of Information (AoI). |
| 2022 [52] | Energy-Efficient Guiding-Network-Based Routing (EEGNBR) for UWSNs. Establishes a guiding network to direct packets via the shortest route with minimal hops, incorporating a concurrent working mechanism for reduced forwarding delay and energy conservation. | Reduces network delay significantly while ensuring reliable routing and EE. Innovative use of guiding network and concurrent data forwarding mechanism. | Network delay, EC, PDR, network service life. |
| 2022 [53] | Underwater Adaptive RPL (UA-RPL) for IoUT. Modifies RPL’s Objective Function (OF) and DODAG construction to improve NL and reliability in underwater conditions. Introduces dynamic trickle algorithm to reduce control message overhead. | Enhances communication reliability and EE in underwater IoUT networks. Successfully mitigates the impact of underwater noise and balances energy consumption across nodes. | PDR, throughput, control overhead, delay, EC. |
| Year/Ref | Aim/Strategy | Strengths | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 [54] | Opportunity Routing protocol based on Density Peaks Clustering (ORDP) for IoUT. Utilizes network clustering with Density Peaks Clustering (DPC), entropy weight-TOPSIS for cluster head election, and opportunistic data transmission. | Innovatively combines DPC with entropy weight-TOPSIS for efficient cluster head selection, significantly improving EE, transmission latency, and PDR. | EC, average transmission latency, PDR. |
| 2023 [55] | Delay and Reliability Aware Routing (DRAR) and Cooperative DRAR (Co-DRAR) protocols for UWSNs. Aims to enhance reliability with strategies for reducing delay and managing power consumption through regional network division and strategic sink node positioning. | Introduces cooperative transmission to improve data packet quality, effectively reducing E2E delay, balancing energy consumption, and ensuring reliable communication. | EC, E2E delay, PDR, dead nodes, packet drop ratio, alive nodes. |
| 2023 [56] | Neighboring-Based Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol (NBEER) for UWSNs. It focuses on Neighbor Head Node Selection (NHNS), cooperative load balancing, and performance enhancement mechanisms. | Excels in reducing energy consumption and latency while improving packet delivery ratio, NL, and total received packets through efficient neighbor-based routing and data forwarding. | EC, E2E delay, PDR, alive nodes, number of packets received. |
| 2023 [57] | Designing an Underwater-Internet of Things (U-IoT) network model for marine life monitoring. Utilizes autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and surface sinks for efficient data transfer using acoustic waves and RF techniques. | Addresses the overfishing problem by providing a system that supports effective marine life monitoring and data management, demonstrating efficient administration through the proposed network model. | Efficiency of data transfer, management of marine resources, impact on overfishing. |
| 2023 [58] | Shared Underwater Acoustic Communication Layer Scheme (SUACL) for enhancing UAC technology development and evaluation. Enables remote operation of communication units for data transmission and reception. | Offers a flexible and adaptable platform for underwater acoustic research, significantly improving communication efficiency with better SNR, lower BER, and minimized MSE. | Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR), Bit Error Rate (BER), Mean Square Error (MSE). |
| 2023 [59] | Opportunistic Hybrid Routing Protocol (RAOH) for Acoustic-Radio Cooperative Networks (ARCNet). Introduces a hybrid routing strategy that utilizes surface radio links for neighbor discovery and combines opportunistic and on-demand routing for efficient data forwarding. | Enhances packet delivery success, reduces route establishment times, and improves EE by leveraging the dual advantages of acoustic and radio communication. | Energy usage, average transmission latency, PDRs. |
| 2023 [60] | Opportunistic Routing-Based Reliable Transmission Protocol (OR-RTP) utilizing Artificial Rabbits Optimization (ARO) for energy-efficient routing in UIoT networks. Focuses on balancing energy consumption and PDR through meta-heuristic relay selection. | Offers an adaptive relay selection mechanism for dynamic underwater environments, improving network longevity and reliability while reducing overall energy consumption. | EC, PDR, throughput, NL. |
| 2023 [61] | Opportunistic Routing based on Directional Transmission (ORDT) for IoUT. Utilizes directional transmission for energy focus, improving packet delivery rates, minimizing latency, and conserving energy. | Combines directional transmission with opportunistic routing for targeted energy use and enhanced packet delivery, addressing underwater communication’s unique challenges. | Packet delivery success rate, transmission latency, energy usage. |
| 2023 [62] | Hybrid-Coding-Aware Routing Protocol (HCAR) for UASNs. Introduces interflow network coding within a reactive and opportunistic routing framework to enhance packet transmission efficiency and network performance. | Integrates network coding to correct errors and optimize transmission efficiency, significantly reducing transmission counts and adapting to UASN conditions. | EC, PDR, throughput, NL. |
| 2023 [63] | Member Nodes Supported Cluster-Based Routing Protocol (MNS-CBRP) for UWSNs. Utilizes clustering and leverages network member nodes for efficient information transfer, optimizing energy consumption. | Improves scalability and data integrity through clustering, significantly extending the network’s lifespan by optimizing energy use and enhancing data transmission reliability. | EC, PDR, throughput, NL, energy trade-off. |
| 2023 [64] | Efficient Geo-Routing-Aware MAC Protocol (GO-MAC) based on OFDM for UANs. Integrates geo-routing with OFDM, optimizing transmission delay and energy consumption through a cross-layer MAC protocol. | Reduces data collisions and enhances EE with optimized OFDM resource allocation and improved next-hop selection. | EC, PDR, throughput, NL. |
| 2023 [65] | Energy-Depth Aware Channel Routing Protocol (ED-CARP) for UWSNs in IoUT. Focuses on relay node selection based on Channel State Information (CSI), considering residual energy and depth. | Combines energy and depth awareness in relay selection, optimizing energy consumption and enhancing data delivery efficiency. | EC, PDR, throughput, NL, and balance between energy used in transmission and reception. |
| Year/Ref | Aim/Strategy | Strengths | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 [66] | Machine Learning-Based Optimal Cooperating Node Selection for IoUT. Employs ML algorithms for selecting cooperating nodes based on delay, energy, and collision rates. | Uses DDPG-SEC algorithm for improved EE, reduced latency, and enhanced packet delivery, showing significant advancements over traditional methods. | EC, PDR, throughput, NL, successful transmission probability, and E2E delay. |
| 2024 [67] | Enhancing Energy Efficiency of Underwater Sensor Network Routing to Achieve Reliability using a Fuzzy Logic-based Approach. Implements a clustering-based routing method utilizing fuzzy logic to optimize energy consumption and reliability by considering factors like residual energy, distance, depth, and number of neighbors for node selection. | Efficiently reduces energy consumption and improves network reliability. Balances traffic load and extends the network lifespan through dynamic clustering and fuzzy logic. | Residual energy, Distance to sink, Depth, Number of neighbors, Packet generation rate, Network topology, Communication range. |
| 2024 [68] | Energy-efficient routing protocol using a hybrid metaheuristic algorithm (GSLS) for UWSNs. Combines Global Search Algorithm (GSA) and Local Search Algorithm (LSA) for optimal routing paths. | Efficiently reduces energy consumption and routing discovery time by leveraging a parallel search mechanism, significantly improving UWSN performance. | EC, PDR, NL, algorithm speed. |
3. Network Settings
3.1. Speed of Sound in Water
3.2. Underwater Frequency Link Quality Criterion
3.3. Delay Time Model
3.4. Calculating Node Depth
3.5. Frequency Attenuation or Absorption Model
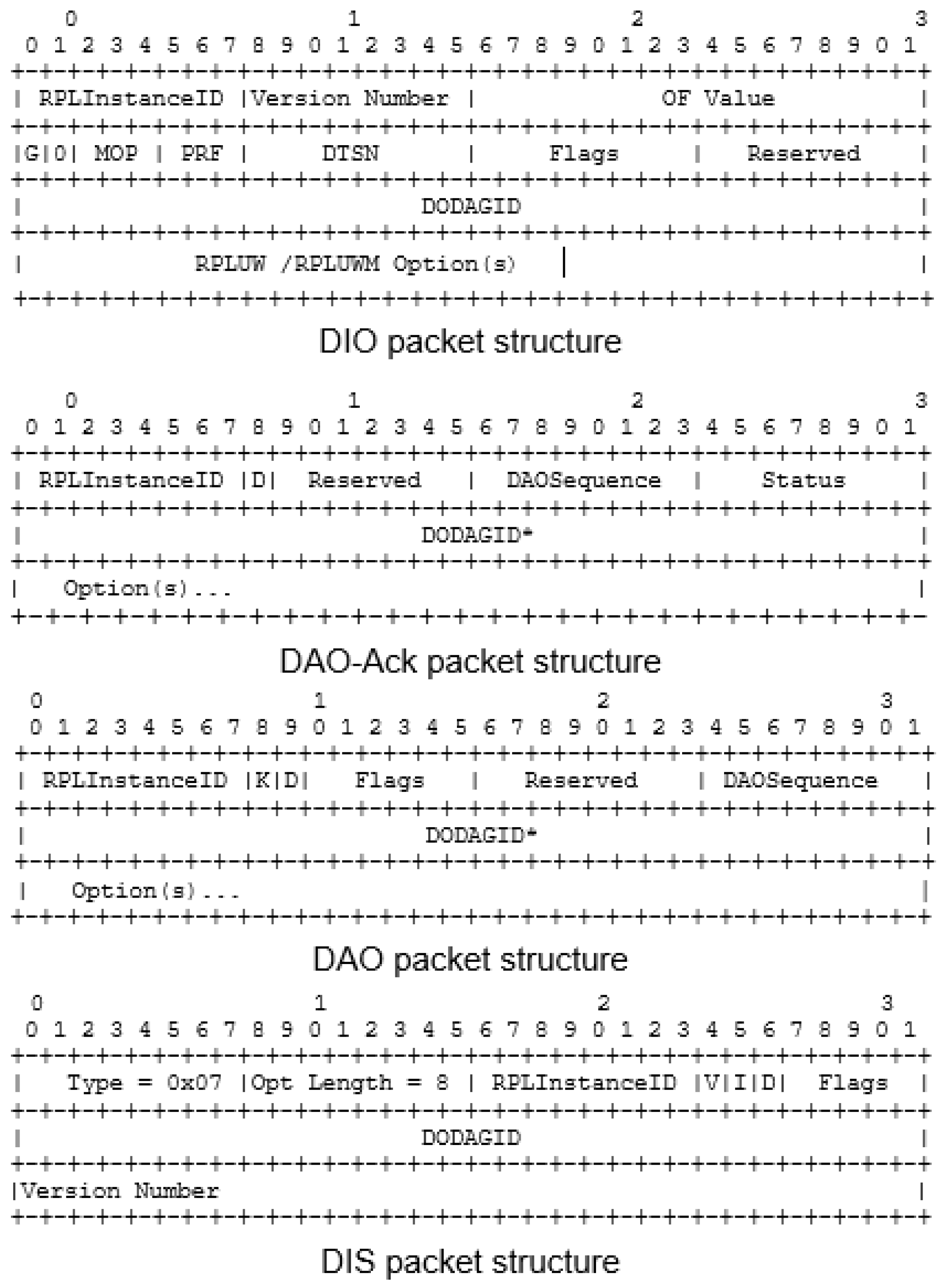
3.6. Structure of Control Packets
- The DIO packet is broadcasted by parents to the children to promote DODAG.
- The DAO packet is unicast from membership by the child to the parent.
- The DAO-Ack packet is also unicast from the parent to the child to confirm the membership of the child node in the parent list.
- If the node is orphaned or located in an area where the network instability has reached the threshold, the DIS packet will be broadcasted by the parentless node in the network.
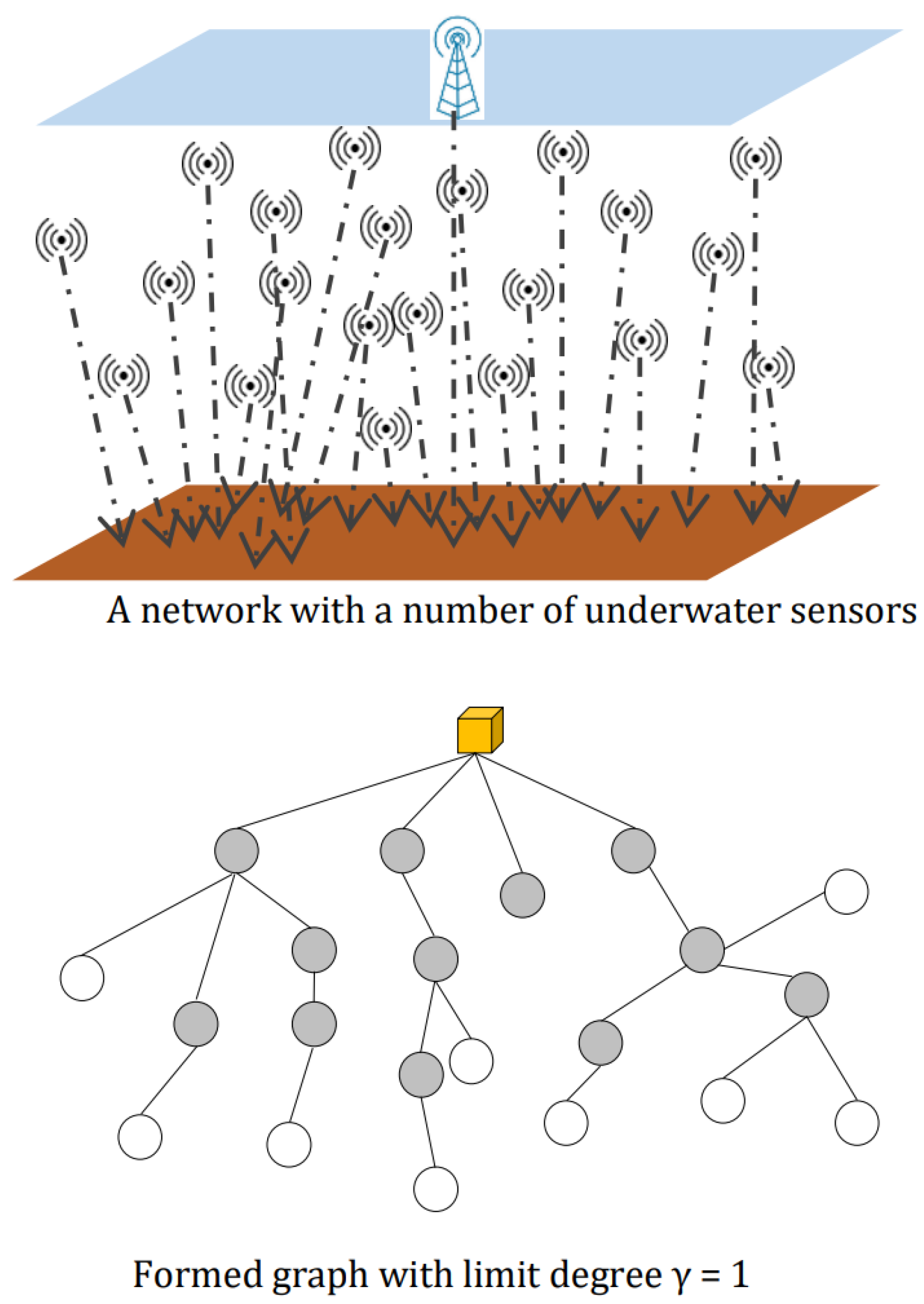
4. The Proposed Rpluw Method
4.1. The System Model
- The rank is a measure that defines the logical distance of node u as a subset of from the root of the network graph J, by the objective function (OF) of the RPL protocol. The R rate will often increase as it moves away from the graph’s root. In the underwater network, this criterion can be defined according to the application, such as the amount of node depth from the water surface or as a combination of step and node depth.
- The Preferred Parent DODAG (DPP): Suppose u is a node of G, its one-hop neighbors, and a finite subset of . For each node , we have , if it has the lowest rank up to the root specified DODAG . In the improved version of RPL, we will have several preferred parents for each node, and the best parent will be chosen by node u when the node sends the packet.
- DODAG (DRL) root list: Each node must broadcast DIO packets. The root location of DODAG should be included in these packets. Thus, is a list of DODAG root locations stored at each node u in the network.
4.2. Detection and Management of Displacement in Underwater RPL
- Trickle timer algorithm: A dynamic schedule based on network stability/instability rate prevents repetitive sending of control packets and keeps the network graph’s repair mechanism dynamic. The trickle timer of the t-period is limited by the interval , where is the minimum interval defined in milliseconds by the base value of 2 (e.g., ms) and is used to limit the number of times can be doubled. Assuming , the maximum interval is calculated as The trickle timer algorithm can update the topology in a short time. When the incompatibilities of 13 nodes are reached, i.e., , it sets the value of t equal to and updates the tree. If the network is stable, i.e., , the value I double until the constant value is reached. If the network nodes are moved, the number of DIS packets in the network increases, and this causes the to converge to the value of k, and the scheduler returns to . As the timing of DIO packet periods in the network decreases, the overhead network will increase, and the network will be involved in resolving incompatibilities.
-
IPv6 Neighbour discovery method: RPL can use neighbor discovery to detect environmental changes with an optimal version of ND. ND makes it possible to detect neighbor inaccessibility and discover new neighbors, which is supported by four ICMPv6 control packets:
- -
- Neighbour Solicitation (NS): Checks the node’s availability by checking the neighbor’s MAC address.
- -
- Neighbour Advertisement (NA): Responds to NS packets, is also sent intermittently to announce link changes.
- -
- Router Solicitation (RS): The host node (mobile node in the proposed model) solicits information from the router.
- -
- Router Advertisement (RA): The router periodically sends its presence packet and graph and link parameter information to respond to the RS packet.
4.3. The RPLUWM Method Timers
- Linkage timer (): To increase the response of network nodes, they must periodically monitor the activity of the communication channel. An timer is installed for this process, the sequence value of which is determined by a trickle timer (). During this process, the moving node listens to the channel and monitors the input packets from the parent. After the timer expires, the discovery phase begins if the parent exchanges reach zero. Also, the link timer is reset upon receipt of any packet from the parent (such as trickle DIO, unicast DIO, or data packet).
- Mobility timer (): After receiving the unicast DIO packet, the quality of the Average received signal strength indicator (ARSSI) is evaluated to evaluate the reliability of the link. As the ARSSI rate decreases, the moving node begins to explore to find a new parent. The node data generation rate sets this timer during network setup.
- Response timer (): If the parent detects disconnection and receives a DIS packet from the neighbors, it must send a DIO packet at certain times. Selecting the wrong response moment may cause data packets to collide, activating the exploration phase. The parent node monitors the other children’s packets, estimates the packets’ sequence and response time, and sends a DIO packet outside.
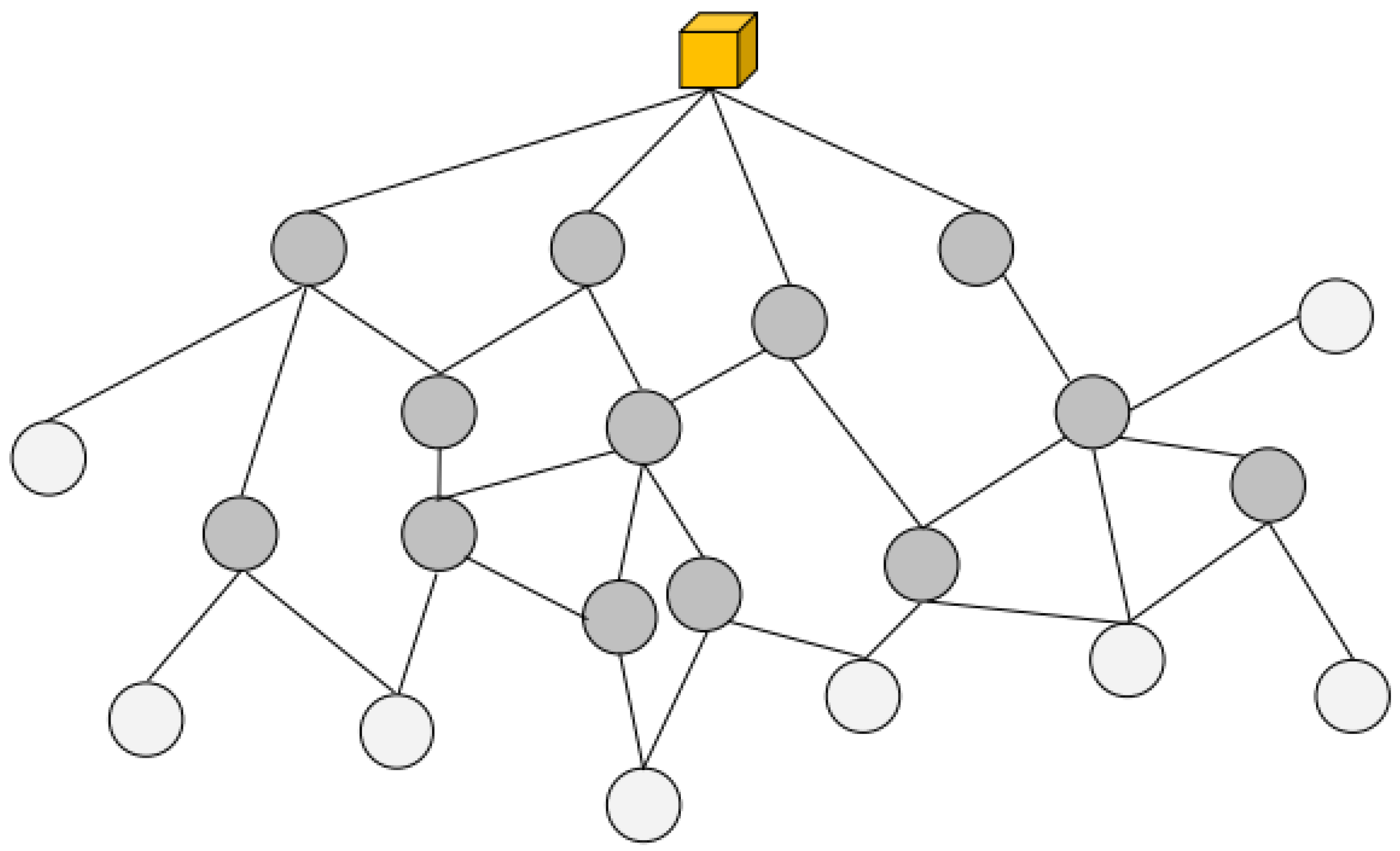
4.4. RPLUWM Network Graph Construction Method
4.5. Routing in the RPLUWM Network
| Algorithm 1 RPLUWM Protocol Network Graph Formation |
|
| Algorithm 2 Multi-Criteria Decision Making AHP Matrix |
 |
5. System Model and Simulation
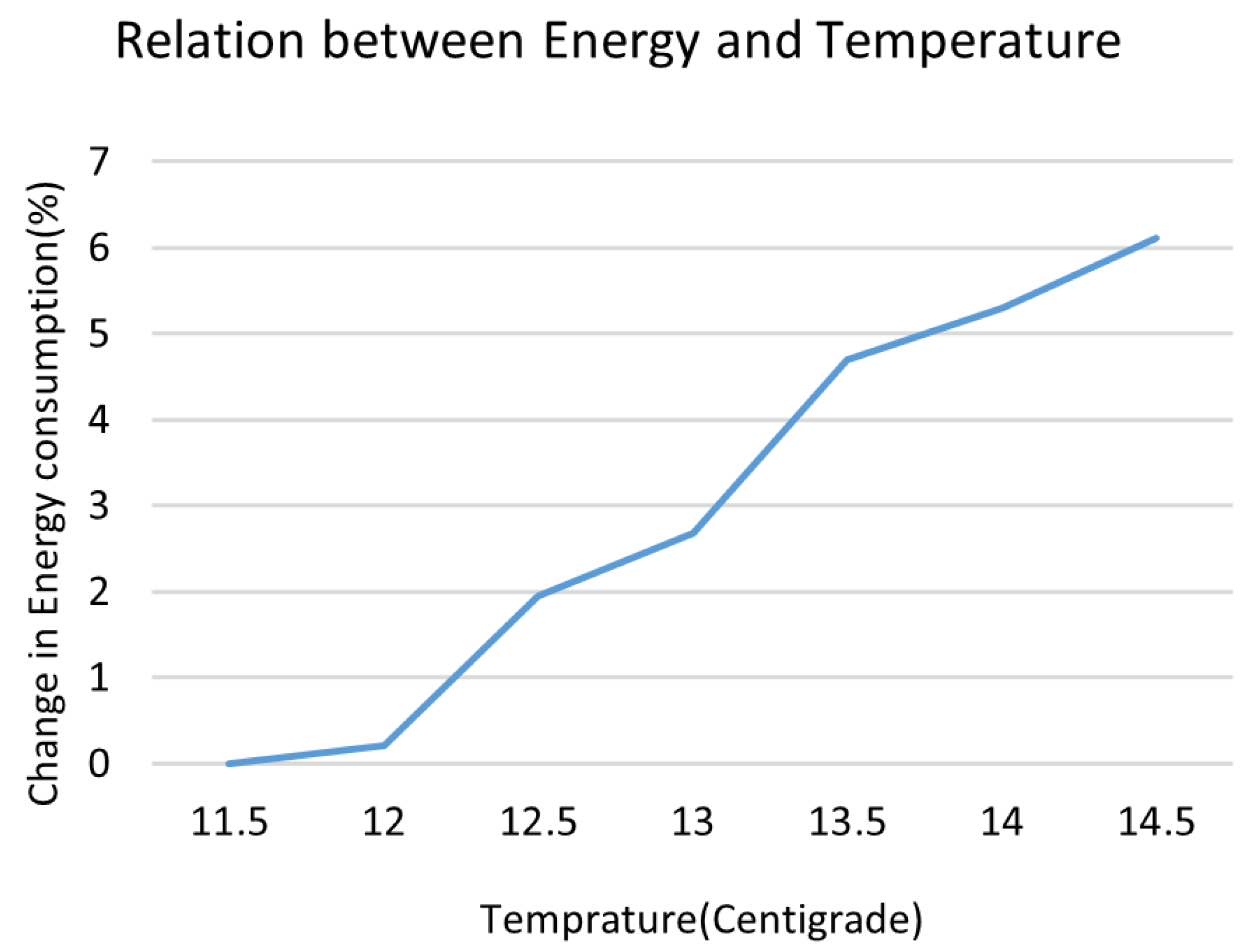
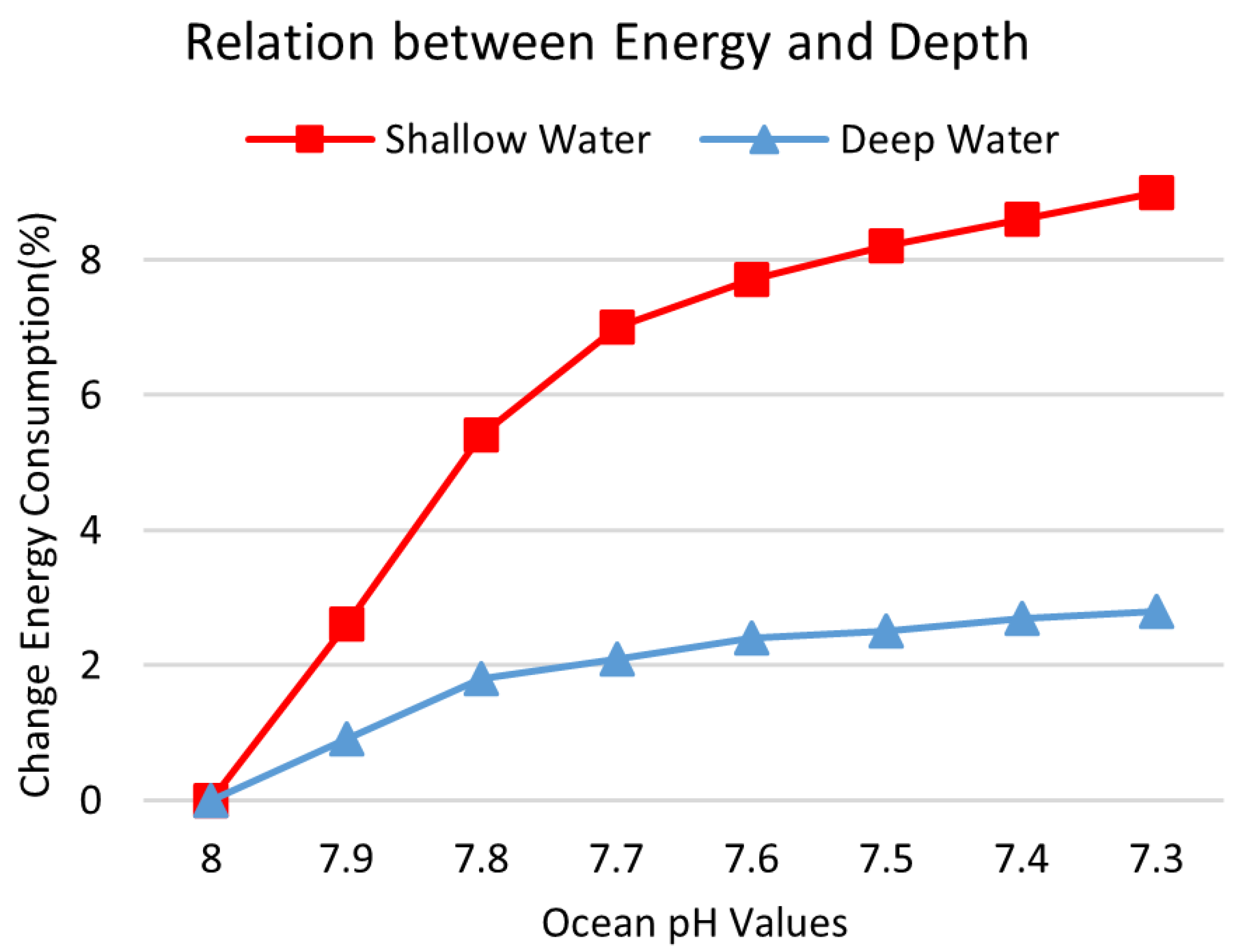
5.1. Testing the Effect of Environment on Network Energy Consumption Rate
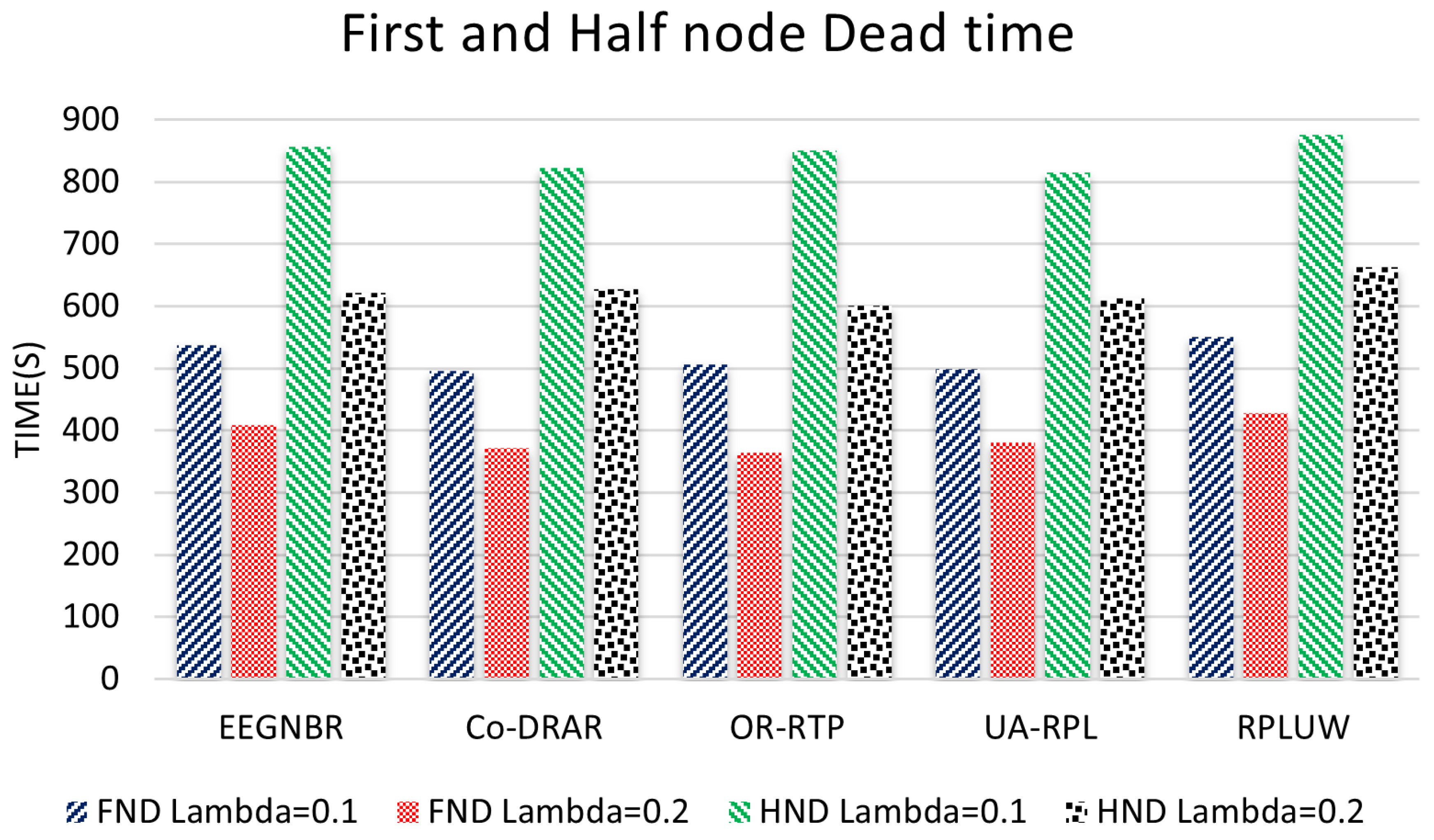
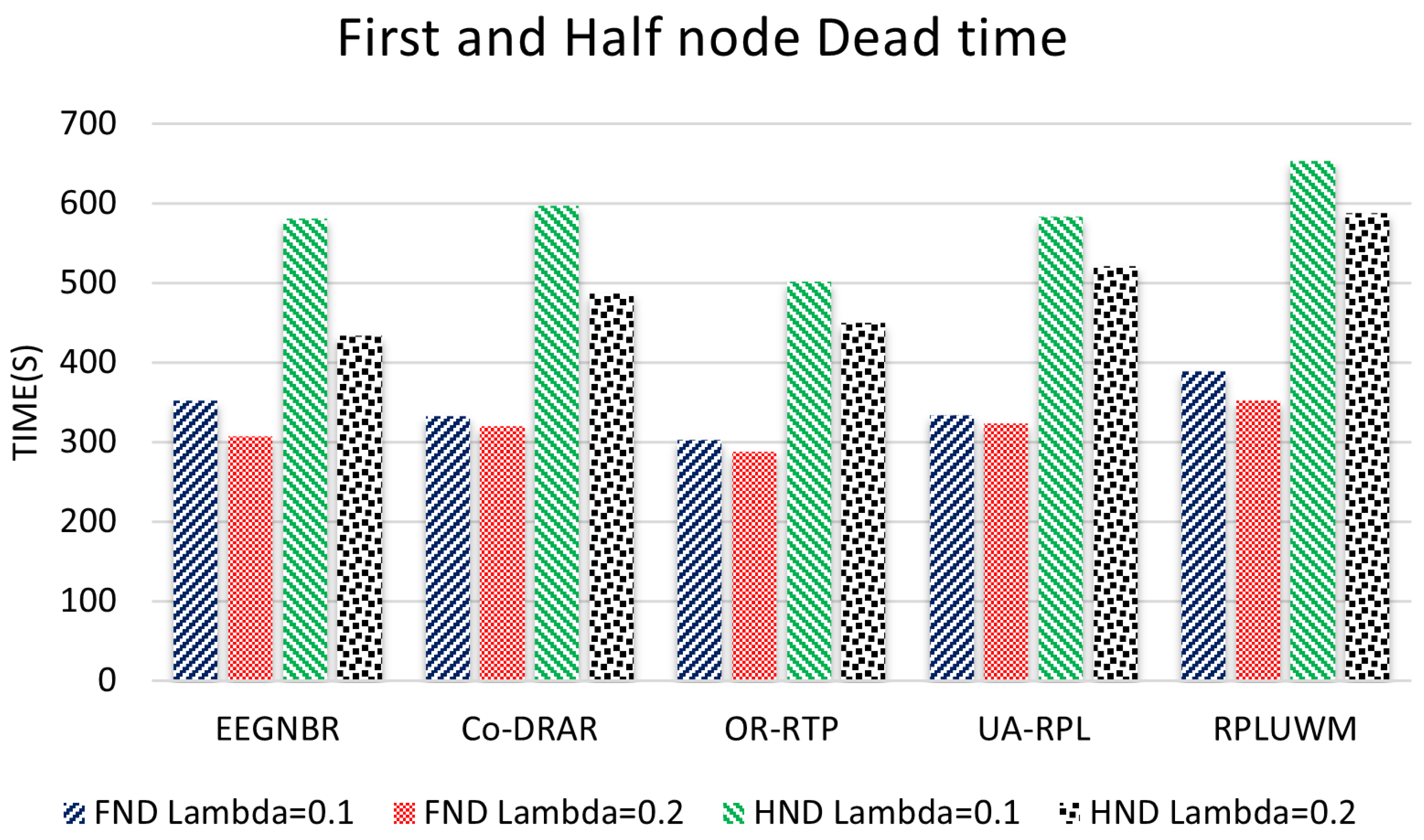
5.2. Network Lifetime Test
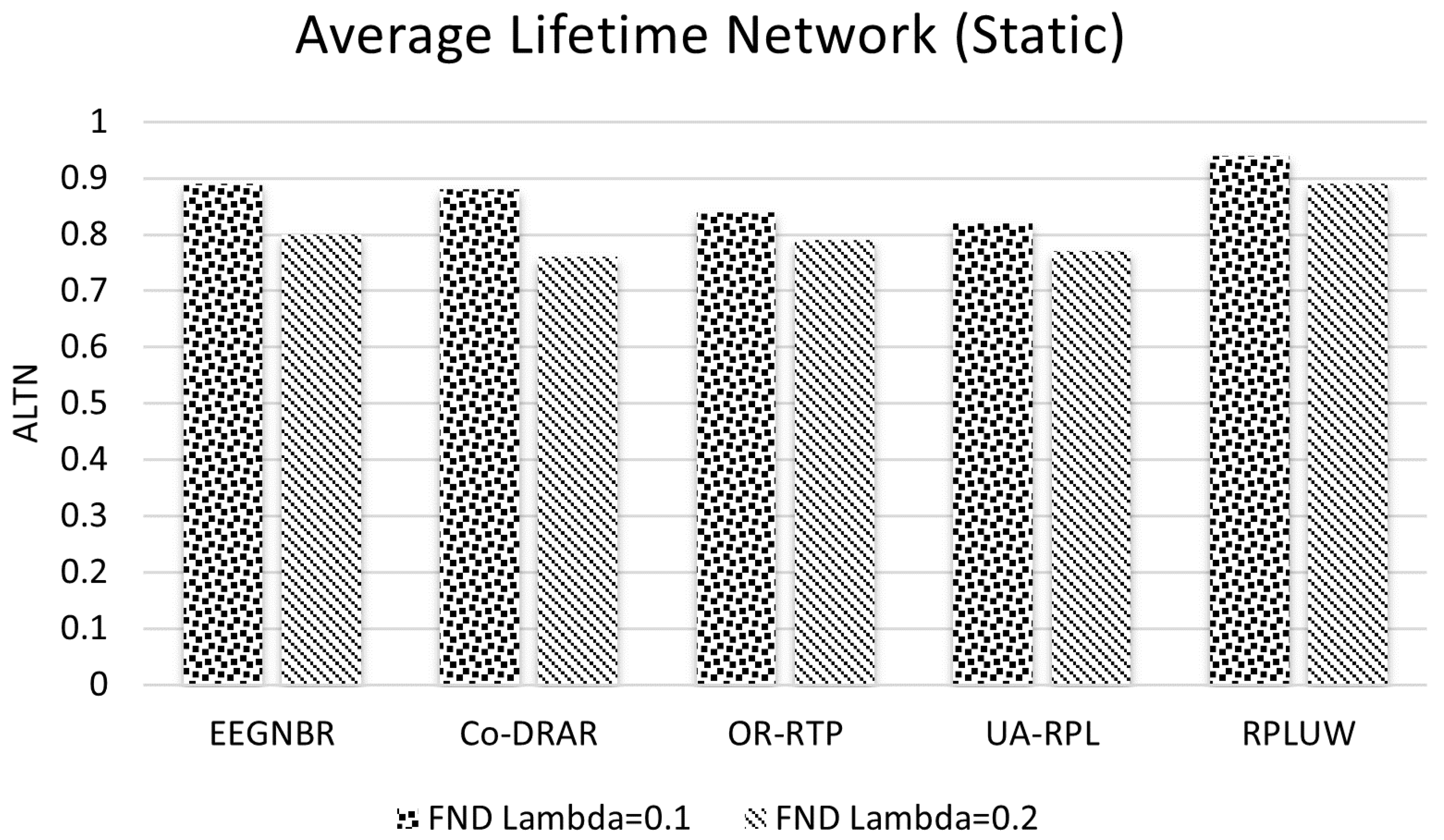
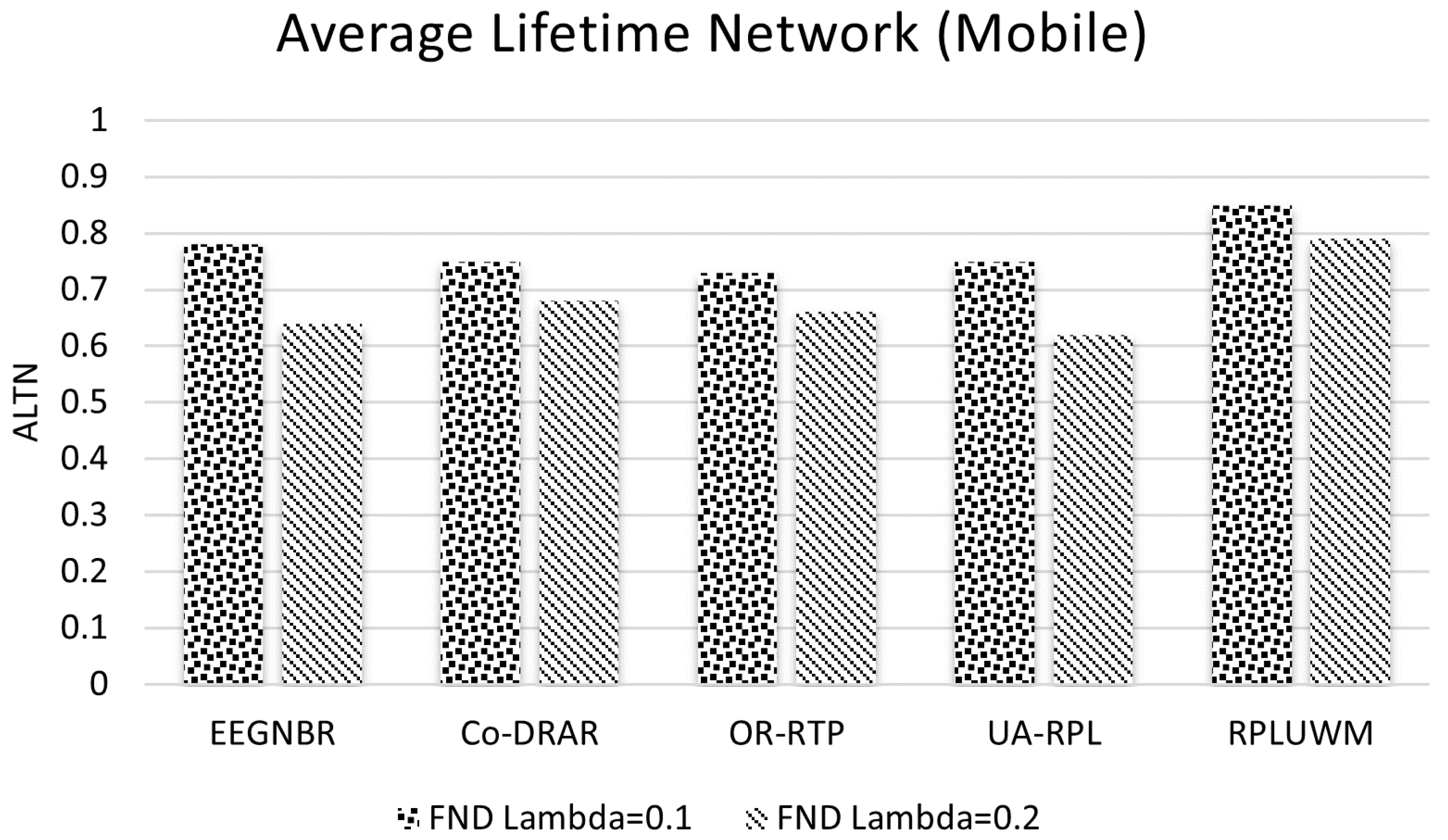
5.3. Average Lifetime Networl
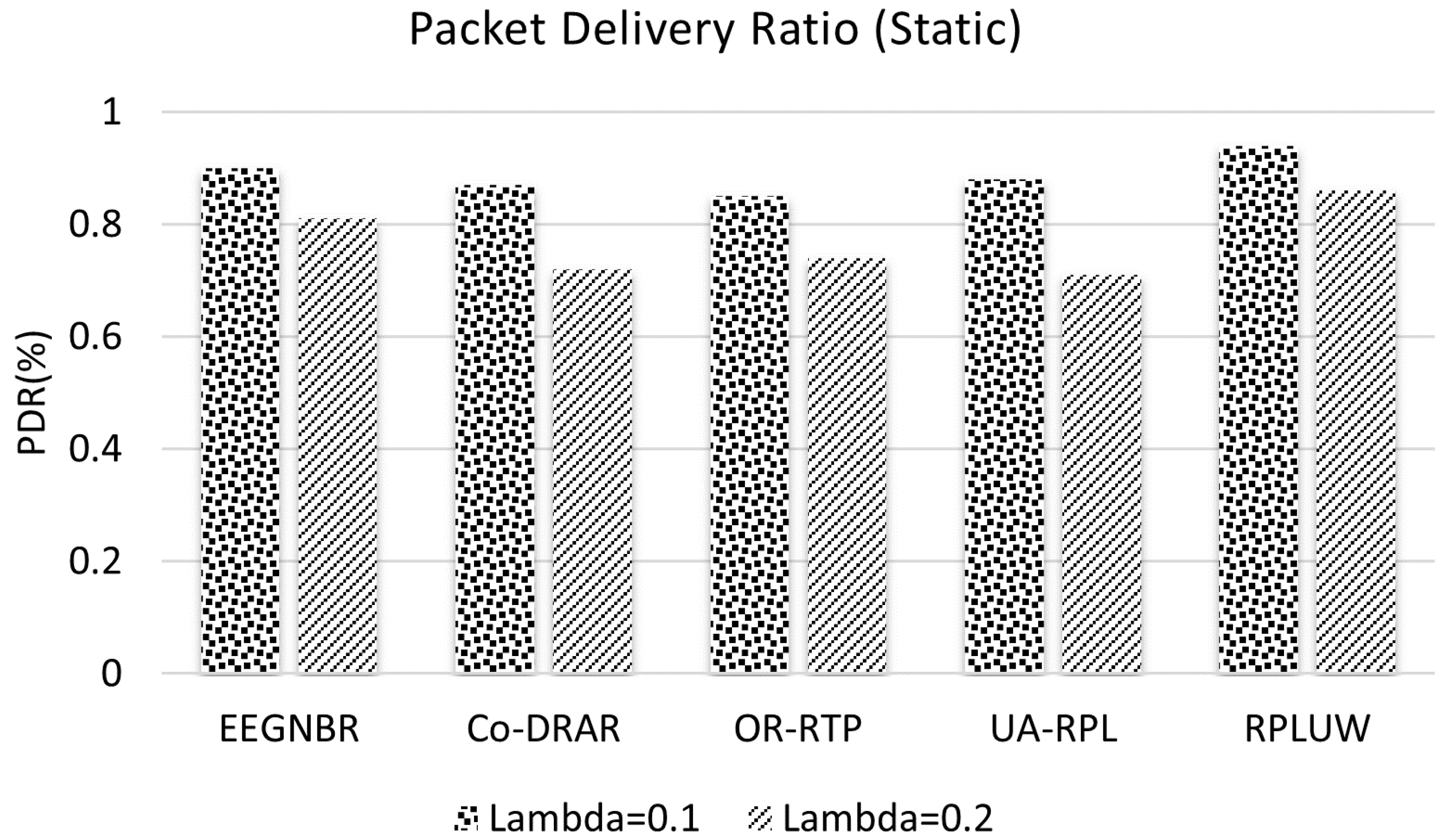
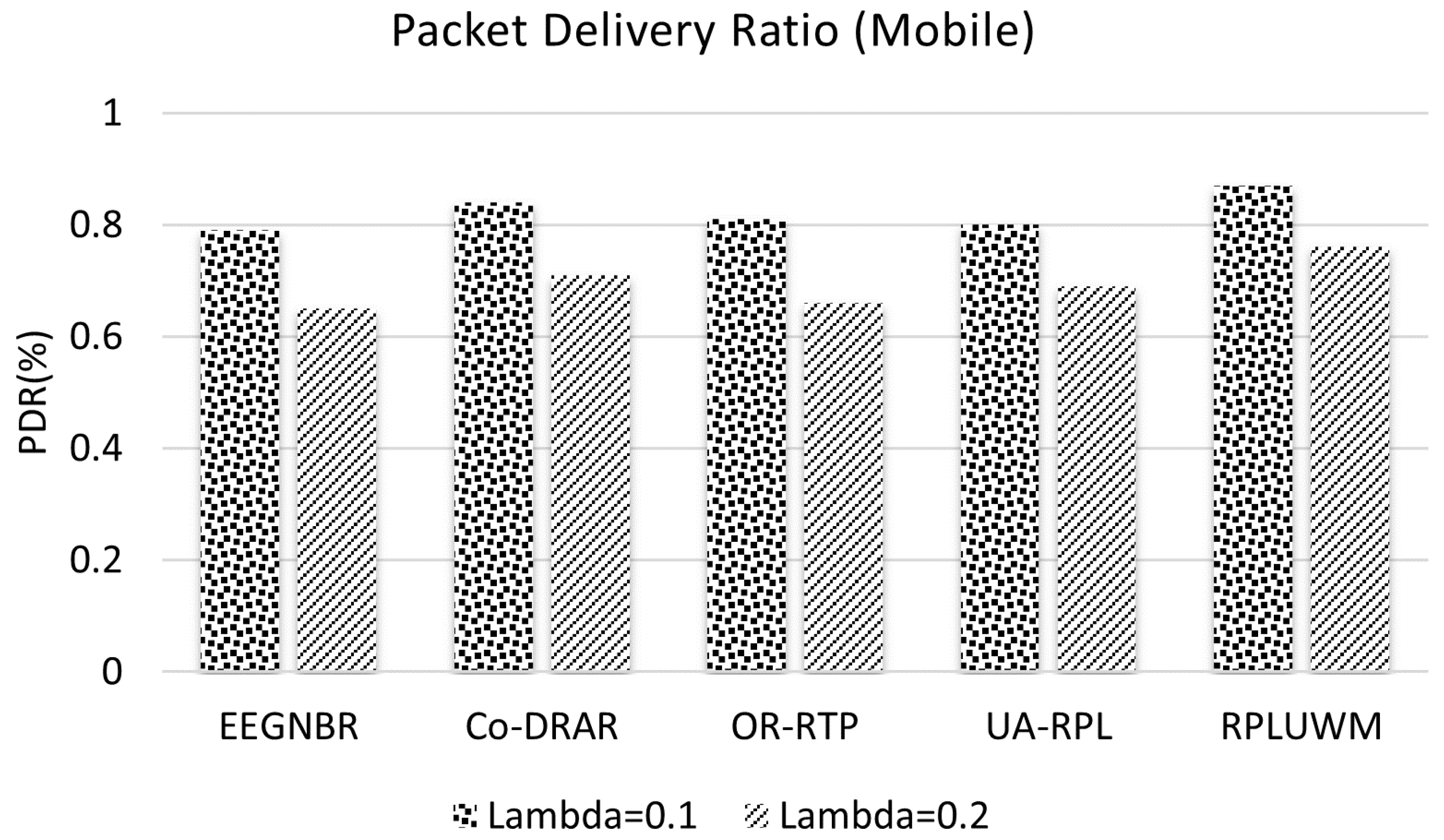
5.4. Packet Delivery Ratio
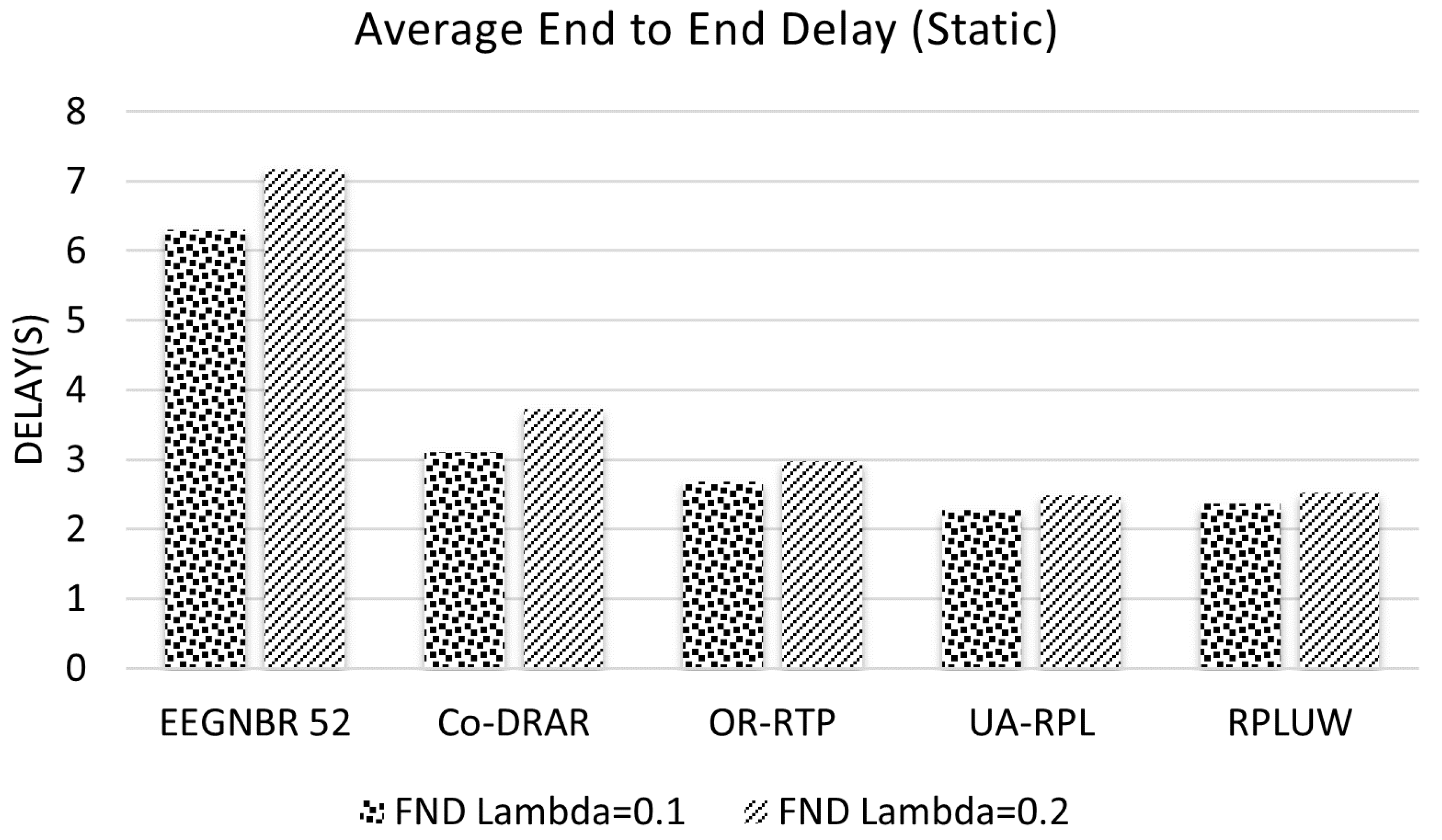
5.5. Average End-to-End Delay
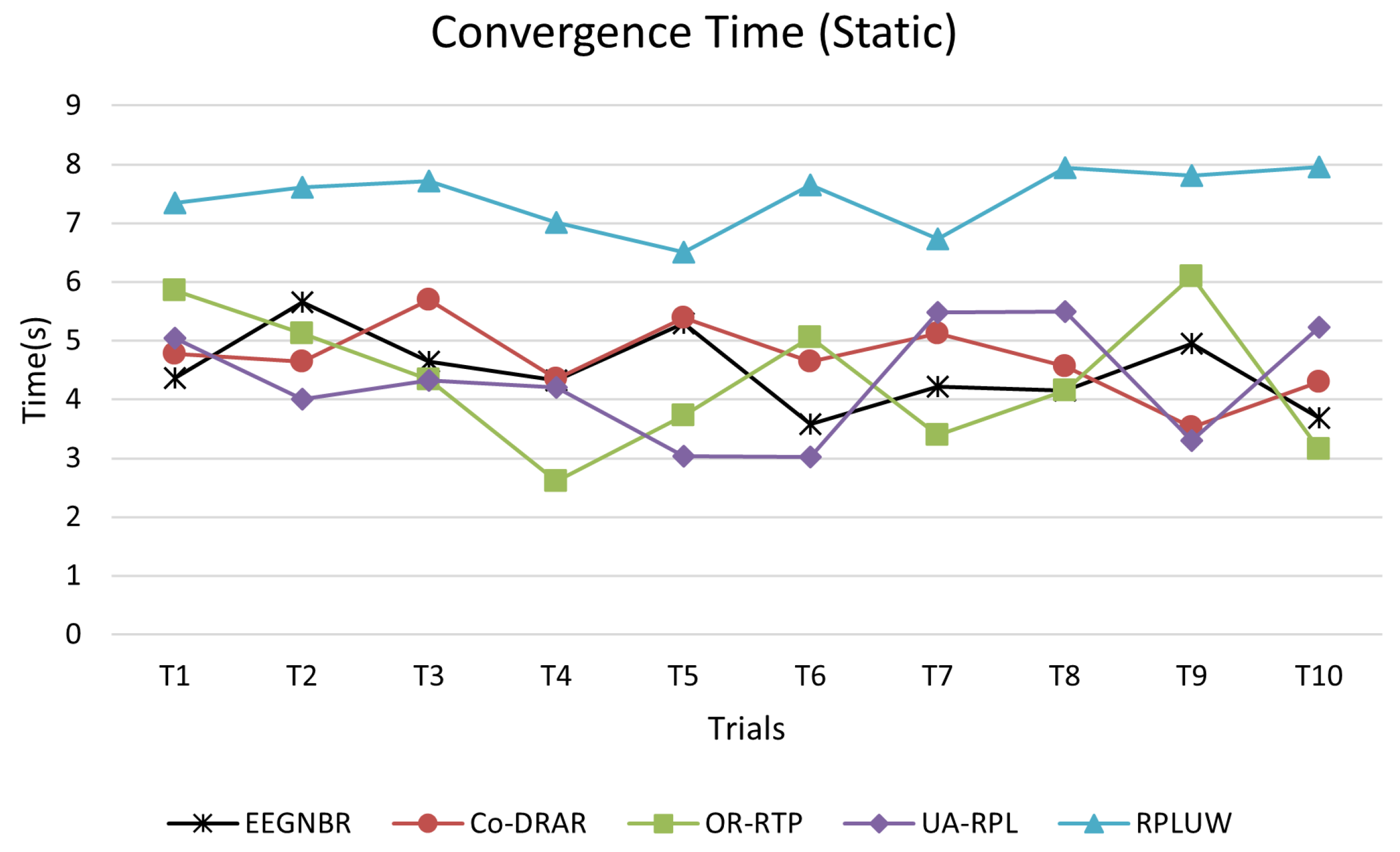
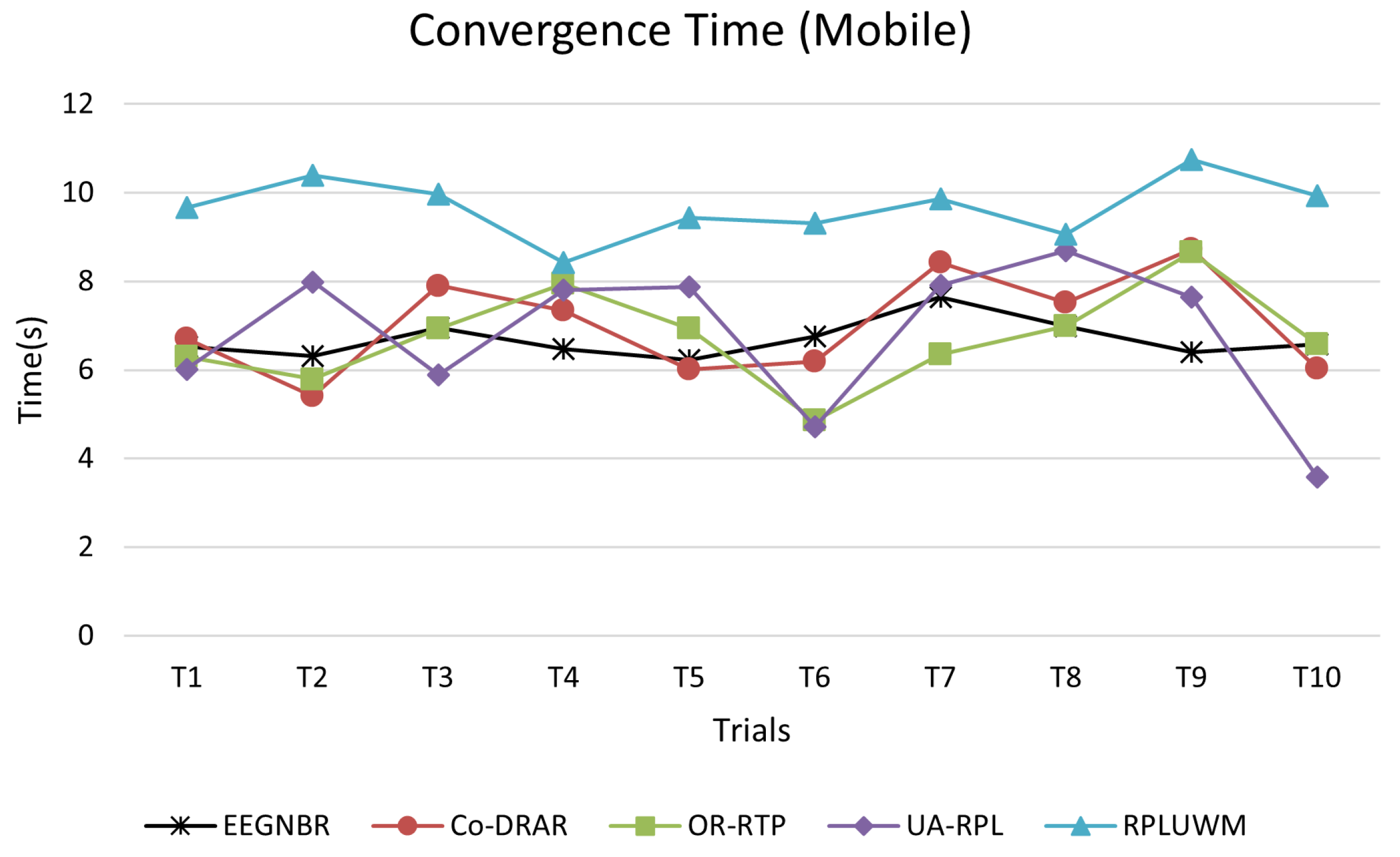
5.6. Network Convergence Time Test
6. Conclusion
Appendix A
-
Shallow Water Energy Consumption Model: This model assesses the energy consumption in shallow waters. It is based on a linear distribution of sensor nodes featuring nodes where the distance between consecutive nodes is denoted as d. The calculations in this model address the transmission of packets containing B bits to the sink node, using either a single-hop or a multi-hop process involving relay nodes. The model adopts a linear chain configuration of nodes, which is considered a worst-case scenario for analysis. As illustrated in Figure 3, the propagation of sound signals in shallow waters is modeled cylindrically, necessitating the application of cylindrical spatial geometry for accurate calculations.Figure A1. Cylindrical environment around each underwater sensor node.
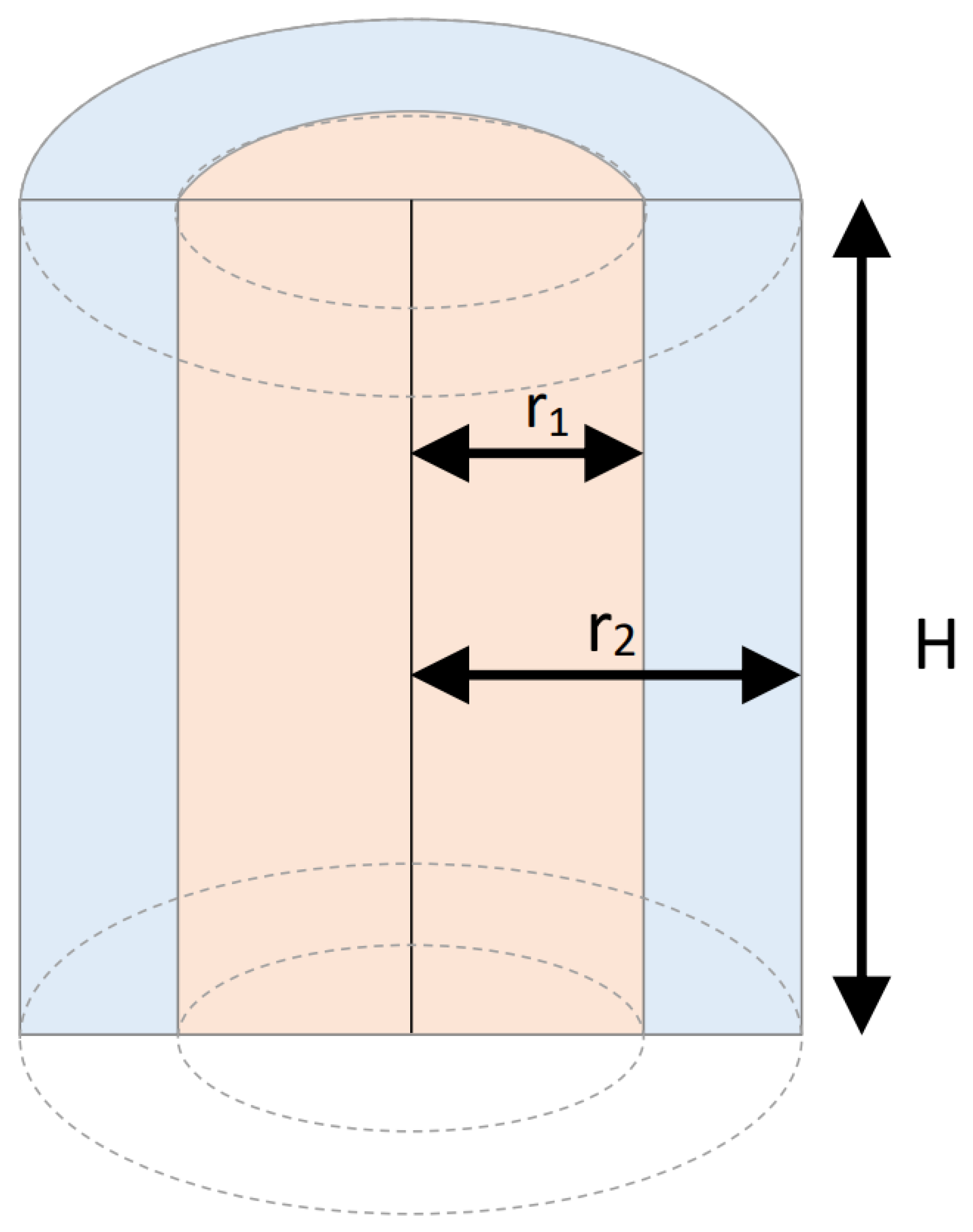 As illustrated in Figure A1, we utilize the subsequent equations to calculate the transmission power at two distinct points, and :The variable H is defined as the height of the cylinder, equivalent to the depth of the node. The rate at which transmission diminishes between and is determined by Equation A3:Equations A1 and A2 describe the transmission power related to the radial distances and from the central axis of the cylindrical underwater environment surrounding a sensor node, as depicted in Figure A1.Now consider that a node located at a distance of from the sink node needs to send K packets. The required power level and energy consumption during its transfer are calculated through Equations A4 and A5:The parameter d is the distance between two nodes, N indicates the number of steps to the Sink, is the transmission time of a packet. When each node is in the process of transferring m packets and this transfer is a multi-hop relay mechanism, the energy consumption is equal to Equation A12:However, if the sensor node wants to interact with a single-hop connection and directly with the sink, then the power consumption of the node will be obtained from Equation A13:In this relation is the distance between each node and the sink. Total energy consumption in this scenario uses Equation A8:
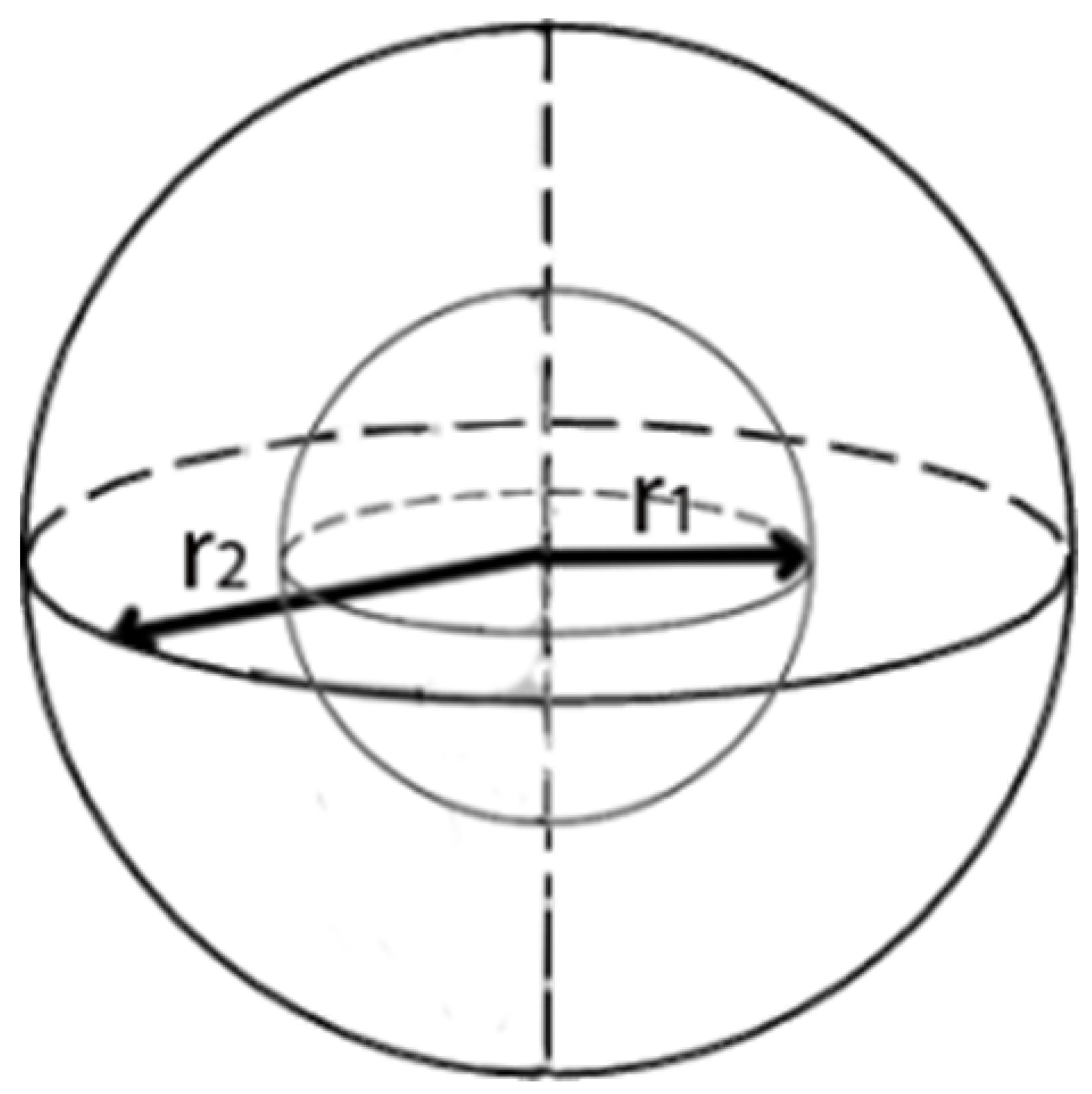
As illustrated in Figure A1, we utilize the subsequent equations to calculate the transmission power at two distinct points, and :The variable H is defined as the height of the cylinder, equivalent to the depth of the node. The rate at which transmission diminishes between and is determined by Equation A3:Equations A1 and A2 describe the transmission power related to the radial distances and from the central axis of the cylindrical underwater environment surrounding a sensor node, as depicted in Figure A1.Now consider that a node located at a distance of from the sink node needs to send K packets. The required power level and energy consumption during its transfer are calculated through Equations A4 and A5:The parameter d is the distance between two nodes, N indicates the number of steps to the Sink, is the transmission time of a packet. When each node is in the process of transferring m packets and this transfer is a multi-hop relay mechanism, the energy consumption is equal to Equation A12:However, if the sensor node wants to interact with a single-hop connection and directly with the sink, then the power consumption of the node will be obtained from Equation A13:In this relation is the distance between each node and the sink. Total energy consumption in this scenario uses Equation A8: - Deep Water Energy Consumption Model: Unlike shallow waters, the propagation of sound signals in deep water is spherical. In a network scenario, as in the case of shallow water, the power P is generated at the source and propagated in all directions as a sphere, as shown in Figure A2.Figure A2. Signal propagation model in deep water.
References
- Mary, D.R.K.; Ko, E.; Kim, S.G.; Yum, S.H.; Shin, S.Y.; Park, S.H. A Systematic Review on Recent Trends, Challenges, Privacy and Security Issues of Underwater Internet of Things. Sensors 2021, 21, 8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.; Yang, Y. A Survey of Routing Protocols for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2021, 23, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.; Zeadally, S. Internet of underwater things communication: Architecture, technologies, research challenges and future opportunities. Ad Hoc Networks 2022, 135, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.S.; Wang, X.; Hawbani, A.; Alsamhi, S.; Abdel Aziz, S. Routing protocols classification for underwater wireless sensor networks based on localization and mobility. Wireless Networks 2022, 28, 797–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.; Goyal, N.; Benslimane, A.; Awasthi, L.K.; Alwadain, A.; Singh, A. Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks: Enabling Technologies for Node Deployment and Data Collection Challenges. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 3500–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Li, Y.; Sadiq, M.; Liang, J.; Khan, M.A. Recent Advances, Future Trends, Applications and Challenges of Internet of Underwater Things (IoUT): A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2023, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Han, G.; Lin, C. A survey on opportunistic routing protocols in the Internet of Underwater Things. Computer Networks 2023, 225, 109658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkenyereye, L.; Nkenyereye, L.; Ndibanje, B. Internet of Underwater Things: A Survey on Simulation Tools and 5G-Based Underwater Networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Gang, Q.; Muhammad, A.; Muzzammil, M.; Khan, S.U.; Affendi, M.E.; Ali, G.; Ullah, I.; Khan, J. A Comprehensive Survey of Energy-Efficient MAC and Routing Protocols for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.S.; Saeed, R.A.; Eltahir, I.K.; Khalifa, O.O. A systematic review on energy efficiency in the internet of underwater things (IoUT): Recent approaches and research gaps. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2023, 213, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovon, I.I.; Shin, S. Survey on Multi-Path Routing Protocols of Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks: Advancement and Applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.; Thubert, P. Routing for RPL (Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks) Leaves; Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranidharan, V.; Sivaradje, G.; Varadharajan, K.; Vignesh, S. Clustered geographic-opportunistic routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks. Journal of Applied Research and Technology 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, N.; Alfandi, O.; Usman, S.; Khattak, A.M.; Awais, M.; Hayat, B.; Sajid, A. An Energy Efficient Routing Approach for IoT Enabled Underwater WSNs in Smart Cities. Sensors 2020, 20, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Qi, Q.; Zhou, P.; Wu, D.O. A Game-Theoretic Routing Protocol for 3-D Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 9846–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L. Routing Protocol Design for Underwater Optical Wireless Sensor Networks: A Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 9805–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, S.; Krishnan, R. FLCEER: Fuzzy Logic Cluster-Based Energy Efficient Routing Protocol for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Network. International Journal of Information Technology and Web Engineering 2020, 15, 76–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; El-Howayek, G. A Sleep-Scheduling Oil Detection Routing Protocol for Smart Oceans Using Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT); IEEE, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Butt, R.A.; Raza, B.; Alquhayz, H.; Ashraf, M.W.; Raza, S.; Ngadi, M.A.B. FFRP: Dynamic Firefly Mating Optimization Inspired Energy Efficient Routing Protocol for Internet of Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39587–39604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, R.W.L.; Boukerche, A. Stochastic Modeling of Opportunistic Routing in Multi-Modal Internet of Underwater Things. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2020 - 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference; IEEE, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, Y.H.; Vimal, S.; Julie, E.G.; Khari, M.; Expósito-Izquierdo, C.; Martínez, J. Hybrid optimization routing management for autonomous underwater vehicle in the internet of underwater things. Earth Science Informatics 2020, 14, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, R.W.; Boukerche, A.; Loureiro, A.A. A novel opportunistic power controlled routing protocol for internet of underwater things. Computer Communications 2020, 150, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, R.; Alroobaea, R.; Mechti, S.; Rubaiee, S.; Andejany, M.; Tariq, U.; Iftikhar, S. Intelligent data analytics in energy optimization for the internet of underwater things. Soft Computing 2021, 25, 12507–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.I.; Mahfooz, O.; Ahmed, W. Green Energy Harvesting and Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol in Internet of Underwater Things. In Advances in Environmental Engineering and Green Technologies; IGI Global, 2021; pp. 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Qi, Q.; Zhou, P.; Wu, D.O. An Adaptive-Location-Based Routing Protocol for 3-D Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 6853–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, S. Demur and Routing Protocols With application in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks for Smart City. In Advances in Environmental Engineering and Green Technologies; IGI Global, 2021; pp. 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapileswar, N.; Phani Kumar, P. Energy efficient routing in IOT based UWSN using bald eagle search algorithm. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Reinforcement Learning-Based Opportunistic Routing Protocol for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 2756–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Karim, O.A.; Abbas, S.; Javaid, N.; Zikria, Y.B.; Tariq, U. Q-learning based energy-efficient and void avoidance routing protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks. Computer Networks 2021, 197, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, A.M.; Altalhi, M.; Kumar, A.; Aggarwal, G.; Kaiwartya, O.; Khalifeh, A.; Al-Khasawneh, M.A.; Alarood, A.A. An Efficient Void Aware Framework for Enabling Internet of Underwater Things. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2021, 9, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U.; Yasin, S.; Ali, T.; Ali, A.; Faheem, Z.B.; Zhang, N.; Jamal, M.H.; Suh, D.Y. ROBINA: Rotational Orbit-Based Inter-Node Adjustment for Acoustic Routing Path in the Internet of Underwater Things (IoUTs). Sensors 2021, 21, 5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draz, U.; Ali, A.; Bilal, M.; Ali, T.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Jolfaei, A.; Suh, D.Y. Energy Efficient Proactive Routing Scheme for Enabling Reliable Communication in Underwater Internet of Things. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering 2021, 8, 2934–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narla, V.L.; Kachhoria, R.; Arun, M.; Haldorai, A.; Vijendra Babu, D.; Jos, B.M. IoT based energy efficient multipath power control for underwater sensor network. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulla, E. Performance evaluation of Focused Beam Routing for IoT applications in underwater environment. Internet of Things 2022, 17, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, N.; Mohan, P.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alghamdi, S.; Khalaf, O.I. An Efficient Metaheuristic-Based Clustering with Routing Protocol for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yin, H.; Jing, L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J. A Cooperative Routing Protocol Based on Q-Learning for Underwater Optical-Acoustic Hybrid Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sensors Journal 2022, 22, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y. The Cooperative-Communication Based Underwater Layered Routing Protocol for Underwater Wireless Sensor Network. Wireless Personal Communications 2022, 125, 3019–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavali, A.B.; Kadam, M.V.; Patil, S. Energy optimization using swarm intelligence for IoT-Authorized underwater wireless sensor networks. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2022, 93, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellore, K.; Polasi, P.K. An improved underwater wireless sensor network communication using Internet of Things and signal to noise ratio analysis. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies 2022, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, R.; Rani, S.; Kavita; Shafi, J.; Kim, S.; Ijaz, M.F. ESEERP: Enhanced Smart Energy Efficient Routing Protocol for Internet of Things in Wireless Sensor Nodes. Sensors 2022, 22, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, A.; Saeed, N.; Shihada, B.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Alouini, M.S. Opportunistic Routing for Opto-Acoustic Internet of Underwater Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Shaikh, F.K.; Chowdhry, B.S. Simulation-based quantitative analysis of efficient data transfer routing protocols for Internet of Underwater Things. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 2022, 121, 102645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, K.; Ravikumar, C.V.; Srinivasulu, A.; Rajesh, A.; Oyerinde, O.O. Performance and Improvement Analysis of the Underwater WSN Using a Diverse Routing Protocol Approach. Journal of Computer Networks and Communications 2022, 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker Reddy, P.C.; Sucharitha, Y. IoT-Enabled Energy-efficient Multipath Power Control for Underwater Sensor Networks. International Journal of Sensors, Wireless Communications and Control 2022, 12, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, M.; Han, X.; Li, S.; Yin, J. Adaptive clustering routing protocol for underwater sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks 2022, 136, 102953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, K.; Ravikumar, C.V.; Rajesh, A.; Pau, G. Underwater Wireless Sensor Network Performance Analysis Using Diverse Routing Protocols. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 2022, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bzoor, M.; Musa, A.; Alzoubi, K.; Gharaibeh, T. A Directional Selective Power Routing Protocol for the Internet of Underwater Things. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2022, 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari Mary, D.R.; Ko, E.; Yoon, D.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Park, S.H. Energy Optimization Techniques in Underwater Internet of Things: Issues, State-of-the-Art, and Future Directions. Water 2022, 14, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilhore, U.K.; Khalaf, O.I.; Simaiya, S.; Tavera Romero, C.A.; Abdulsahib, G.M.; M, P.; Kumar, D. A depth-controlled and energy-efficient routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2022, 18, 155013292211171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, T.A.; Khan, Z.A.; Javaid, N. A novel geo-opportunistic routing algorithm for adaptive transmission in underwater internet of things. International Journal of Web and Grid Services 2022, 18, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, J.; Du, J.; Hou, X.; Ren, Y.; Han, Z. Stochastic Optimization-Aided Energy-Efficient Information Collection in Internet of Underwater Things Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, K.; Guan, X. Energy-Efficient Guiding-Network-Based Routing for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 21702–21711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, R.; Sakthivel, T.; Karpagam, P.; Gunasekaran, K. Towards an Adaptive Routing Protocol for Low Power and Lossy Networks (RPL) for Reliable and Energy Efficient Communication in the Internet of Underwater Things (IoUT). International Journal of Computer Networks and Applications 2022, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yan, Q.; Han, G. An Opportunity Routing Protocol Based on Density Peaks Clustering in the Internet of Underwater Things. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Communication and Networking (ICN); IEEE, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Saleem, A.; Hassan, N.; Muhammad, G.; Shin, J.; Minhas, Q.A.; Khan, M.K. Reliable and Delay Aware Routing Protocol for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 116932–116943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.; Sun, Z.; Zaman, K.; Hussain, A.; Ullah, I.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Khan, M.A.; Nasimov, R. Advancements in Neighboring-Based Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol (NBEER) for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazzad, A.; Nawer, N.; Mahbub Rimi, M.; Habibul Kabir, K.; Foysal Haque, K. Designing of an Underwater-Internet of Things (U-IoT) for Marine Life Monitoring. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer Nature Singapore, 2023; pp. 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Tong, F. Internet of Underwater Things Infrastructure: A Shared Underwater Acoustic Communication Layer Scheme for Real-world Underwater Acoustic Experiments. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Guan, Q.; Chen, F.; Wei, N.; Ji, F.; Yu, H. Opportunistic Hybrid Routing Protocol for Acoustic-Radio Cooperative Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 19014–19026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Elaveini, M.A.; Kapileswar, N.; Kumar, P.P. ARO-RTP: Performance analysis of an energy efficient opportunistic routing for underwater IoT networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications 2023, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yan, Q.; Han, G.; Wang, H. An Opportunistic Routing Based on Directional Transmission in the Internet of Underwater Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 16392–16403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Fan, R. HCAR: A Hybrid-Coding-Aware Routing Protocol for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 10790–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, K.; Hamdi, M.; Chinthaginjala, R.; Pau, G.; Ksibi, A.; Anbazhagan, R.; Abbas, M.; Usman, M. Reliable Data Transmission in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks Using a Cluster-Based Routing Protocol Endorsed by Member Nodes. Electronics 2023, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, B.; Cui, J.H. An Efficient Geo-Routing-Aware MAC Protocol Based on OFDM for Underwater Acoustic Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 9809–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, S.; Khalil Afzal, M.; Tahir, M.; Raza Jafri, M.; Raza, N. Energy-efficient selection of relay for UWSNs in the Internet of underwater things. International Journal of Communication Systems 2023, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Narmeen, R.; Kaleem, Z.; Almadhor, A.; Alkhrijah, Y.; Ho, P.H.; Yuen, C. Machine Learning-Based Optimal Cooperating Node Selection for Internet of Underwater Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarif, M.; Effatparvar, M.; Moghadam, B.N. Enhancing Energy Efficiency of Underwater Sensor Network Routing Aiming to Achieve Reliability. In Proceedings of the 2024 Third International Conference on Distributed Computing and High Performance Computing (DCHPC); IEEE, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saemi, B.; Goodarzian, F. Energy-efficient routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks using a hybrid metaheuristic algorithm. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2024, 133, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, K.V. Nine-term equation for sound speed in the oceans. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 1981, 70, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, C.C.; Robinson, S.P.; Goldsmith, M.J. A new equation for the accurate calculation of sound speed in all oceans. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2008, 124, 2774–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahapur, S.S.; Khanai, D.R.; Torse, D.D.A. Comparative Analysis of OFDM MIMO and IDMA OFDM MIMO using Aqua Sim Simulator for Underwater Communication. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 1921, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryecroft, S.; Shaw, A.; Fergus, P.; Kot, P.; Hashim, K.; Moody, A.; Conway, L. A First Implementation of Underwater Communications in Raw Water Using the 433 MHz Frequency Combined with a Bowtie Antenna. Sensors 2019, 19, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Du, X.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Li, C. A MAC Protocol of Concurrent Scheduling Based on Spatial-Temporal Uncertainty for Underwater Sensor Networks. Journal of Sensors 2021, 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, S.; Homaei, M.H. An Enhanced Distributed Data Aggregation Method in the Internet of Things. Sensors 2019, 19, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainslie, M.A.; McColm, J.G. A simplified formula for viscous and chemical absorption in sea water. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 1998, 103, 1671–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Short Biography of Authors
 |
MOHAMMADHOSSEIN HOMAEI (M’19) was born in Hamedan, Iran. He obtained his B.Sc. in Information Technology (Networking) from the University of Applied Science and Technology, Hamedan, Iran, in 2014 and his M.Sc. from Islamic Azad University, Malayer, Iran, in 2017. He is pursuing his Ph.D. at Universidad de Extremadura, Spain, where his prolific research has amassed over 100 citations. Since December 2019, Mr. Homaei has been affiliated with Óbuda University, Hungary, initially as a Visiting Researcher delving into the Internet of Things and Big Data. His tenure at Óbuda University seamlessly extended into a research collaboration with J. Selye University, Slovakia, focusing on Cybersecurity from January 2020. His research voyage then led himto the National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Taiwan, where he served as a Scientific Researcher exploring IoT and Open-AI from January to September 2021. His latest role was at the Universidade da Beira Interior, Portugal, in the Assisted Living Computing and Telecommunications Laboratory (ALLab), from June 2023 to January 2024, where he engaged in cutting-edge projects on digital twins and machine learning. He is the author of ten scholarly articles and holds three patents, highlighting his diverse research interests in Digital Twins, Cybersecurity, Wireless Communications, and IoT. An active IEEE member, Mr. Homaei has carved a niche for himself with notable contributions to Digitalization, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Information SecurityManagement, and Environmental Monitoring. His substantial body of work profoundly influences the technological and cybersecurity landscape. |

| Parents / Parameters | ||||
| Hop-Count (n) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Remaining Energy (j) | 167.5 | 183.2 | 179 | 138.8 |
| ARSSI | ||||
| Delay Time (ms) | ||||
| ETX | ||||
| Link’s PDR (%) | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.88 |
| Depth (m) | 129.8 | 141.2 | 155.4 | 117.4 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Network topology | Random position |
| Deployment area | 1000 × 500 m3 |
| Initial node energy | 50 J |
| Initial sink energy | 50kJ |
| Number of nodes | 50, 100, 200 |
| Nodes mobility | 1 m/s–5 m/s |
| Mobility model | Random mobility |
| Percentage of Mobile Nodes | 40% |
| Cost of long transmission | 1.3 W |
| Cost of short transmission | 0.8 W |
| Cost of reception | 0.7 W |
| Idle power | 0.008 W |
| Data aggregation power | 0.22 W |
| Communication range of ASN | 150 m |
| Acoustic transmission range(sink) | 200 m |
| Spreading values | 1.3 |
| Frequency | 30.5 kHz |
| Channel | Underwater channel |
| Maximum Bandwidth | 30 kbps |
| DIO packet size | 50 bytes |
| DAO packet size | 4 bytes |
| DAO-ACK packet size | 4 bytes |
| DIS packet size | 4 byte |
| Packet generation rate | pkt/s |
| Memory size | 12 MB |
| Sink position | Surface (500 × 500 × 0) |
| Antenna | Omni-directional |
| Simulation time | 600 |
| Iterations | 10 |
| Number of Channels | 11 (30.511, 30.518, … 30.581) kHz |
| * Bellhop is used to calculate the path loss between each node in a given location. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





