Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Human Gut Microbiota
3. The Influence of Human Metabolic Diseases on Gut Microbiota
3.1. Obesity
3.2. Type II Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
3.3. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
3.4. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
4. The Role of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Human Disease Treatment
4.1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
4.2. Bile Acids (BAs)
4.3. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO)
4.4. Tryptophan Metabolites
4.5. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
5. BPs and Their Therapeutic Potential
5.1. Definition and Classification of BPs
5.2. Chemical Structure of BPs
5.3. Biological Activities or Physiological Functions of BPs
5.3.1. Immunoregulatory
5.3.2. Regulate Blood Sugar
5.3.3. Regulate Blood Pressure
5.3.4. Hypolipidemic Effect
5.3.5. Antioxidation
5.3.6. Antitumor Activities
5.3.7. Hepatoprotective Effect
5.3.8. Antibacterial and Antivirus Effects
5.4. Mechanism of Actions of Gut Microbiota Mediated BPs in Metabolic Disease Treatment
5.4.1. Treating Obesity
| Bioactive Polysaccharides | Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Weight (Mw) | Dosage | Study Approaches | Major Findings | Mode of Action–Gut Microbiota | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auricularia auricula polysaccharide | Composed of mannose (50.84%), glucose (21.61%), xylose (9.24%), galactose (8.58%), glucuronic acid (5.78%) and fucose (3.96%); Mw: 1065.2 kDa | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Reduced body weight gain; Attenuated high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders | Decreased Mucispirillum and increased Peptococcus, Muribaculum, Anaerovorax, and Papillibacter | [207] |
| Auricularia auricula polysaccharide | Composed of mannose (77.0%), galacturonic acid (12.8%), fucose (5.2%), xylose (3.2%), galactose (1.4%), and rhamnose (0.3%); Mw: 1210 kDa | 50 and 100 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Ameliorated high-fat diet-induced IR, glucose, and lipid metabolism disorders; Protected intestinal barrier function | Reduced F/B ratio; Promoted Roseburia, Bacteroides, and Allobaculum; Increased levels of SCFAs, folate, and cobalamin | [197] |
| Astragalus polysaccharides | - | 1,000 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice | Reduced body weight, fat accumulation; Enhanced insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis | Enriched Bacteroides | [209] |
| Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan | Composed of carbohydrate (81.33%), uronic acid (12.53%), and sulfate (17.36%) | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice | Reduced fasting blood glucose and IR index along with improved glucose tolerance; Elevated hepatic antioxidant enzymes | Increased the abundance and diversity of gut microbiota | [210] |
| Ganoderma lucidum mycelium polysaccharides | Mw: >300 kDa | 4% and 8% | High-fat diet-induced obese mice | Reduced body weight, inflammation, and IR; Improve intestinal barrier integrity | Decreased F:B ratio; Enhanced Parabacteroides goldsteinii, Bacteroides spp., Anaerotruncus colihominis, Roseburia hominis, Clostridium methylpentosum; Reduces metabolic endotoxemia | [211] |
| Hirsutella sinensis polysaccharides | Mw: >300 kDa | 20 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice | Enhanced gut integrity, reduced intestinal and systemic inflammation, and improved insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism | Selectively promoted the growth of Parabacteroides goldsteinii | [212] |
| Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides | - | 150 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mouse model | Inhibited serum and hepatic lipid metabolic disorders; Alleviated hepatic steatosis and gut microbiota dysbiosis | Increased Alloprevotella, Parabacteroides, Parasutterella, Bacteroides, decreasing Blautia, Enterorhabdus, and Roseburia; Increased fecal butyric acid and BAs levels | [213] |
| Ganoderma amboinense polysaccharides | Composed of glucose (52.54%), mannose (15.78%), galactose (27.16%) and fucose (4.21%) | 100 and 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Prevented weight gain and fat accumulation; Improved glucose tolerance; Reduced serum and liver lipid concentrations and inflammation | Prevented obesity by regulating the abundance of Parabacteroides, Bacteroides, and Lachnospiracea_incertae_sedis; Altered microbial lipid metabolism, glycan biosynthesis | [175] |
| Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides | - | 150 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese golden hamster model | Improved blood lipid profiles; Elevated the relative abundances of beneficial bacteria | Enhanced Prevotella, Oscillibacter, and SCFA-producers | [195] |
| Edible brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida | Composed of mannuronic acid and guluronic acid at a ratio of 0.7; Mw: 800 kDa | 300 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Improved body composition, fat deposition in body tissues and organs, lipid abnormality, and inflammatory response | Increase in Bacteroidales and reduction in both Clostridiales and Lactobacillales | [214] |
| Lycium barbarum polysaccharides | Composed of D-mannose, L-rhamnose, D-glucose, D-galactosamine and D-xylose | 0.2% in drank water | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Decreasing serum total triglycerides and total cholesterol levels; Elevating serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased SCFA-producing bacteria Lacticigenium, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, and Butyricicoccus; Increased fecal SCFAs level | [174] |
| Lycium barbarum polysaccharide | Composed of fucose, rhamnose, amino-galactose, galactose, glucose, mannose, and fructose with the molar ratio of 0.02: 0.08: 0.03: 0.11: 46.67: 0.37: 4.72; Mw: 3.74 kDa | 150 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Increased weight loss, lowering FFA levels in serum and liver; Increased adiponectin and decreased fatty acid synthase gene expression in liver | Increased gut microbial β-diversity; Reduced F/B ratio; Enhanced Faecalibaculum, Pantoea, and uncultured_bacterium_f_Muribaculaceae | [202] |
| Saccharina japonica fucan | Composed of Fuc (5.2%), 1,3-linked Fuc (63.6%), 1,4-linked Fuc (3.2%), 1,2-linked Fuc (0.9%), 1,3,4-linked Fuc (5.9%) and 1,2,3-linked Fuc (21.2%); Mw: 5.1 kDa | 0.6 mg/mL solution in drinking water | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Suppressed high-fat diet-induced obesity, blood glucose metabolic dysfunction, dyslipidemia, and gut microbiota dysbiosis | Enhanced Bacteroides sartorii and Bacteroides acidifaciens; Increased fucoidan-degrading bacteria | [215] |
| Laminaria japonica fucoidan | Composed of fucose, galactose, mannose, xylose, glucose, and galacturonic acid in a molar ratio of 7.5: 1.0: 0.6: 0.2: 0.3: 0.3; Mw: 627.5 kDa | 300 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Ameliorated body weight gain, fat accumulation, IR, and adipocyte hypertrophy | Reduced F/B ratio; Greater relative abundance of the phylum Bacteroidetes and the families Muribaculaceae and Bacteroidaceae; Enhanced SCFAs production | [216] |
| Laminaria japonica polysaccharides | Composed of rhamnose, galacturonic acid, and glucose in a respective mass ratio of 11.6:10.1:78.2; Mw: 31.7 kDa~1700 kDa | 75 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Induced weight loss, reduced liver fat accumulation, reduced TC and LDL-C levels, reduced intestinal tissue inflammation | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Bacteroides acidifaciens, Lactobacillus intestinalis, and Lactobacillus murinus | [203] |
| Laminaria japonica polysaccharides | Composed of high content of uronic acid and fucose; Mw: 600 kDa | 0.25% in diet | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Reduced body weight gain; Reduced fat accumulation in the liver and adipose tissues | Increased gut microbial diversity and the abundance of Rikenellaceae and Bacteroidales S24_7 group; Increased gut microbial SCFAs production | [217] |
| Microalgae polysaccharides | Composed of rhamnose (38.6%), glucosamine (21.23%) and glucuronic acid (10.56%); Mw: 660 or 3640 kDa | 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Protection against overweight, glucose tolerance impairment, dyslipidemia, and fat deposition in the liver | Increased Clostridia, Bacterioidia, and Mollicutes and decreased Actinobacteria and Verrucomicrobia; Altered metabolism of SCFAs, secondary BAs, and trimethylamine | [218] |
| Seabuckthorn polysaccharide | Composed of rhamnose, arabinose, galactose, glucose, and galacturonic acid, the molar ratios of which were 2.1:44.6:19.7:28.2:5.3; Mw: 9940 Da | 0.1% in diet | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Reduced body weight gain, serum lipid level, and liver triglycerides level; Elevated p-AMPKα and PPARα proteins expression in liver | Increased Muribaculaceae_unclassified, Bifidobacterium, Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, Alistipes, and Bacteroides, and decreased Lactobacillus, Dubosiella Bilophila, and Streptococcus; Increased fecal SCFAs level | [173] |
| Bletilla striata polysaccharides | Composed by mannose and glucose in a molar ratio of 2.946:1; Mw: 373 kDa | 300 mg/kg/d | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Reduced the abnormal weight gain; Altered amino acid, purine, pyrimidine, ascorbate, and aldarate metabolisms in feces, urine, and liver | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Turicibacter, Romboutsia, and Anaerostipes, and decreased Bacillus, Helicobacter, and Colidextribacter | [219] |
| Aspergillus cristatus polysaccharide | Composed of ribose, glucose, galactose, and mannose in a molar ratio of 1:1.7:4.4:5.2; Mw: 21.16 kDa | 400 mg/kg/d | High-fat diet-induced obese rats model | Decrease body weight gain, adipose tissue weight, and the liver/body weight ratio; Improve IR | Increased Akkermansia, Akkermansia muciniphila, Bacteroides, Romboutsia, Blautia, and Desulfovibrio; Increased fecal SCFAs level; Elevated the content of unconjugated and conjugated BAs in the serum and liver | [220] |
| Raspberry polysaccharide | Composed of mannose, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, arabinose, and fucose in a molar ratio of 0.06: 0.33: 1.00: 0.08: 0.31: 0.15; Mw: 18 kDa | 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Decrease body weight gain, hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and fat accumulation; Enhance intestinal barrier integrity | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Ruminococcaceae_UCG − 014, Lactobacillus taiwanensis, Bifidobacterium pseudolongum, and Turicibacter; Increased fecal SCFAs level and decreased LPS level | [221] |
| Raspberry polysaccharide | Composed of arabinose (39.76 %) and galactose (39.43 %); Mw: 74.86 kDa | 100 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obese mice model | Decrease body weight gain, hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia, endotoxemia, hepatic inflammation, and oxidant stress; Enhance intestinal barrier integrity | Increased Dubosiella, Blautia, and Acetatifactor; Increased fecal butyrate production | [222] |
5.4.2. Anti-T2DM
| Bioactive Polysaccharides | Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Weight (Mw) | Dosage | Study Approaches | Major Findings | Mode of Action–Gut Microbiota | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic tea polysaccharides | Mw: 3.9285 × 104 Da | 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced rat models | Improve plasma and liver lipid metabolism | Increased Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Dorea, and Oscillospira, and reduction in Desulfovibrio and Lactobacillus; Improved secondary BA biosynthesis and primary BA biosynthesis | [230] |
| White hyacinth bean polysaccharides | Composed of glucose, rhamnose, galactonic acid, galactose, xylose, and arabinose in the molar ratio of 23.23: 6.2: 5.09: 2.76: 2.4: 0.48; Mw: 2.3 × 105 Da | 100 mg/kg | High fat and high sugar induced T2DM rat model | Reduction of blood glucose levels and improvement of intestinal impairment | Increased gut microbiota diversity and F/B ratio; Enriched Allobaculum, Eubacterium, Anarrobiospirillum, and Holdemania; Increased cecal SCFA level | [164] |
| Fu brick tea polysaccharides | Composed of arabinose (57.4%), rhamnose (25.2%), galactose (5.1%), mannose (3.3%), galacturonic acid (3.9%) and glucuronic acid (3.1%); Mw: > 8000 Da | 200 and 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced rat models | Relieved dyslipidemia (i.e. TC, TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C), IR, and pancreas oxidative stress | Increased Ruminococcus and Lactobacillus; Reduced Prevotella and Faecalibaculum; Elevated colonic SCFA levels | [176] |
| Fructus mori polysaccharides | Mw: 102.22 kDa, 8.71 kDa, and 5.62 kDa | 600 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Suppressed intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress; Enhanced the intestinal barrier function | Inhibiting endotoxin-producing Shigella and promoting Allobaculum and Bifidobacterium | [177] |
| Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides | β-glucan; Mw: 8000~12000 Da |
400 mg/kg/d | High-fat diet-induced T2DM mice model | Ameliorating IR; Fortifies intestinal barrier function | Favorable growth-promoting effects on Parabacteroides distasonis; Increased nicotinic acid level | [227] |
| Auricularia auricula polysaccharides | Composed of fucose, galactose, glucose, mannose, and glucuronic acid | 200 mg/kg/d | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Reduced fasting blood glucose level; Stabilized the weight | Decreased the abundance of Enterorhabdus, Desulfovibrio, and Helicobacter, and increased the abundance of beneficial genera such as Alloprevotella, Faecalibaculum, Dubosiella | [224] |
| Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan | High sulfate (14.55%) and rich in fucose (55.67%) and galactose (20.83%); Mw: 205.8 kDa | 40 mg/kg/d | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Decreased fasting blood glucose, improved glucose tolerance, decreased oxidative stress | Enriched Bacteroides, Faecalibacterium, and Blautia; Increased levels of (R)-carnitine and choline in the colon | [165] |
| Auricularia auricula-judae polysaccharides | Composed of mannose (62%), glucose (12.6%), galactose (4%), rhamnose (13.1%), xylose (4%) and fucose (3.8%) | 50 and 100 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Decreased inflammation, liver injury, and IR; improved glycolipid metabolism disorders by regulating the AKT and AMPK pathways | Elevated gut microbiota diversity; Increased Lactobacillus and Bacteroides; Decreased Clostridium and Allobaculum; Affected the amino acid metabolism and glycolipid metabolism pathways | [225] |
| Auricularia auricula-judae polysaccharides | Composed of arabinose, mannose, galactose, and xylose with a molar ratio of 15.59:1.52:4.76:1.0 | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia rat model | Reduce the levels of total cholesterol and LDL-C | Enriched several lower-abundance SCFA-producing bacteria such as Flavonifractor and Clostridium cluster IV | [231] |
| Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides | Composed of arabinose (5.32%), galactose (5.47%), glucose (57.63%), xylose (0.84%), mannose (25.41%), ribose (1.95%) and rhamnose (3.38%) |
500 and 1000 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Repaired islet cells and increased insulin secretion, promoted the liver synthesis and storage of glycogen; improved antioxidant enzymes and IR | Decreased the F/B ratio; Enriched Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, and Ruminococcaceae; Decreased the release of endotoxins | [228] |
| Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides | Composed of mannose, glucose, galactose, rhamnose, and arabinose in the molar ratio of 3.16: 16.17: 3.74: 1.65: 1; Mw: 13.7 kDa | 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM rat model | Decreases in the levels of fasting blood glucose and insulin | Reduced Aerococcus, Ruminococcus, Corynebacterium, and Proteus, and increased Blautia, Dehalobacterium, Parabacteroides, and Bacteroides; Restored the disturbed amino acids metabolism, carbohydrates metabolism | [232] |
| Lycium barbarum polysaccharides | Composed of carbohydrates (62.27%), uronic acid (25.03%), and protein (2.92%); Mw: 3.5 kDa | 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM rat model | Alleviated the symptoms of hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and IR; boosted the activities of CAT, SOD, and GSH-Px and reduced inflammation | Increasing Bacteroides, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-014, Intestinimonas, Mucispirillum, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-009 and decreasing Allobaculum, Dubosiella, Romboutsia; Increased SCFA production and decreased LPS | [233] |
| Lycium barbarum L. polysaccharides | Composed of rhamnose (8.37%), glucuronic acid (2.21%), glucose (7.95%), galactose (26.38%), xylose (7.91%) and arabinose (47.18%); Mw: 38.54 kDa | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced diabetes mice model | Improved fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin level and beta-cell function; guarded the intestinal barrier function | Induced Allobaculum | [234] |
| Dendrobium officinale leaf polysaccharides | Composed of glucose, mannose, glucuronic acid, and galactose at a molar ratio of 3.2:2.6:1.0:0.7; Mw: 9.91 kDa | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Ameliorated hyperglycemia, inhibited IR, reduced lipid concentration | Decreased the F/B ratio; Increased Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Akkermansia; Increased colonic SCFA levels | [235] |
| Morchella esculenta polysaccharides | Composed of mannose (5.77%), glucose (81.35%), galactose (3.543%) and arabinose (8.99%) | 200, 400, and 600 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Regulated hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia and improved insulin sensitivity; Improved intestinal permeability | Increased Lactobacillus, decreased Corynebacterium, and Facklamia; Increased indole biosynthesis and secondary BA biosynthesis gene expression | [236] |
| Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides | Mw: >3000 Da | 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Improved glycolipid metabolism disorders, inflammation and oxidative stress levels, and organ injury; Improved intestinal barrier | Inhibited Shigella and promoted Allobaculum and Lactobacillus | [237] |
| Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides | Composed of mannose and glucose at a molar ratio of 3.45:1 | 200 mg/kg | High fat and high sugar and streptozotocin-induced prediabetic mice model | Improved glucose, IR, and lipid metabolism | Decreased F/B ratio; Increased Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus and decreased Colidextribacter, Helicobacter, and Mucispirillum; Increased intestinal SCFAs level and decreased LPS level | [238] |
| Huanglian polysaccharides | Composed of glucuronic acid, glucose, galactose, and arabinose, with a molar ratio of 1.0:4.4:2.4:0.6; Mw: 12.1 kDa | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Improved hyperglycemia, IR, blood lipid levels, and β-cell function | Increased Akkermansia, and decreased Aerococcus, Providencia, Pseudochrobactrum; Increased fecal butyrate level | [239] |
| Laminaria japonica polysaccharide | Composed of fucose, galactose, glucose, and mannuronic acid, with a molar ratio of 0.848:0.097:0.039:0.016; Mw: 7.32 kDa | 100 or 200 mg/kg | High fat and high sugar and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice model | Reduced fasting blood glucose levels, insulin levels, and inflammatory factors | Increased Candidatus_Saccharimonas, Shinella, Akkermansia, and Ochrobactrum; Increased cecal SCFA level | [240] |
| Black quinoa polysaccharide | Composed of mannose (0.560%), ribose (0.418%), rhamnose (0.467%), glucuronide (1.889%), galacturonic acid (0.388%), glucose (91.169%), galactose (2.512%), xylose (0.305%), arabinose (2.031%), and fucose (0.262%); Mw: 8.087 kDa | 400 or 800 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Ameliorated blood glucose and lipid levels and improved oxidative stress levels and liver injury levels | Decreased F/B ratio; Increased Dubosiella, Akkermansia, Faecalibaculum, and Allobaculum; Increased cecal SCFA level | [241] |
| Phellinus linteus polysaccharide | - | 300 mg/kg | High fat and high sugar and streptozotocin-induced T2DM rat model | Promoted the secretion of GLP-1, stimulated insulin secretion, and reduced blood glucose | Increased Bacteroides, Parabacteroides, and Alistioes; Increased intestinal SCFAs production, and promoted conjugated BAs decomposition and the transformation of primary BAs to secondary BAs | [242] |
| Tegillarca granosa polysaccharide | Composed of mannose, glucosamine, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galactosamine, glucose, galactose, xylose, and fucose, with a molar ratio of 1:1.38:0.87:0.53:0.52:5.37:1.38:1.05:2.40; Mw: 5.1 kDa | 200 or 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Improved dyslipidemia and disorders in glucolipid metabolism, enhanced insulin sensitivity by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway | Increased Allobaculum, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, Akkermansia, and Bifidobacterium; Increased fecal butyrate level | [243] |
| Glycyrrhiza uralensis polysaccharide | Composed of galactose, xylose, mannose, and glucose, with a molar ratio of 1:0.22:1.2:0.22 | 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced T2DM mice model | Ameliorated hyperglycemia, IR, oxidative stress, enhanced gut barrier function, and reduced liver lipid levels | Increased Akkermansia, Lactobacillus, Romboutsia, and Faecalibaculum, decreased Bacteroides, Escherichia-Shigella, and Clostridium sensu stricto 1 | [244] |
5.4.3. Anti-NAFLD
| Bioactive Polysaccharides | Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Weight (Mw) | Dosage | Study Approaches | Major Findings | Mode of Action–Gut Microbiota | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auricularia auricula polysaccharide | Composed of mannose, glucose, and xylose at a molar ratio of 4.9:2.7:1.1; Mw: 1670 kDa | 200 mg/kg | High-fat and high-cholesterol diet-induced NAFLD mice model | Improved liver injury and abnormal lipid metabolism | Reduced Allobaculum, Olsenella, Ruminococcus, and Clostridium_XVIII and enriched Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Dorea, and Odoribacter; Increased deoxycholic acid (DCA) | [248] |
| Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide | Composed of rhamnose (1.6%), arabinose (23.39%), xylose (0.84%), glucose (70.55%), and galactose (3.61%) | 4% in HFD | High-fat diet-induced mice model | Suppressed hepatic fatty acid synthase (FASN) and CD36 protein expression | Enriched Desulfovibrio genus that produced acetic acid | [249] |
| Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide | Composed of glucose (84.86%), arabinose (4.49%), galactose (3.92%) and ribose (3.26%) | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD rat model | Decreased body weight; Prevented Liver injury; Improved IR Attenuated hepatic lipid accumulation |
Decreased the F/B ratio; Increased Proteobacteria and Epsilonbacteria; little effect on the profile of fecal SCFAs, decreased GPR 41 and 43 gene expression | [250] |
| Auricularia cornea var. Li. polysaccharides | Mw: > 7 kD | 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD rat model | Lowered HOMA-IR, body fat rate, liver index, and body weight gain; decrease in hepatic levels of TC, and TG; alleviated hepatic oxidative stress | Decreased the F/B ratio; Increased Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides, Odoribacter, Alloprevotella, Rikenellaceae RC9 gut group and Blautia; Decreased Parabacteroides and Lachnoclostridium | [178] |
| Lycium barbarum polysaccharide | Composed of mannose, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, and arabinose with a mole ratio of 1.00: 0.93: 12.55: 0.31: 0.53 | 50 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD rat model | Restore the intestinal tight junctions; inhibit hepatic inflammatory factors | Decreased the F/B ratio; Increased gut microbial diversity; Decreased intestinal LPS level | [251] |
| Laminaria japonica polysaccharide | Composed of fucose (40.6%), rhamnose (1.4%), arabinose (2.0%), galactose (27.3%), and mannose (26.7%); Mw: 200 kDa | 5% in diet | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD mice model | Attenuated obesity-related features; attenuated liver steatosis and hepatocellular ballooning | Reduced F/B ratio; Elevated propionate-producing bacteria Bacteroides and Akkermansia; Increased fecal propionate level | [252] |
| Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide | Mw: >5 kDa | 38 mg/kg | High-fat and high-fructose diet-induced NAFLD mice model | Inhibited the excessive exaltation of body weight, glucose tolerance, fasting blood glucose and lipid levels, hepatic TC, TG levels | Increased Aerococcus, Weissella, Corynebacterium_1, decreased Romboutsia, [Ruminococcus]_torques_group; Enriched microbial nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism and peptidoglycan biosynthesis | [253] |
| Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide | Composed of 12-hydroxyganoderic acid, ganoderic acid, ganoderic acid, poricoic acid, and ganoderic acid | 150 mg/kg | High-fat and high-fructose diet-induced NAFLD rat model | Alleviated dyslipidemia through decreasing the levels of serum TG, TC, and LDL-C, and inhibiting hepatic lipid accumulation and steatosis | Reduced F/B ratio; Promoted Alloprevotella, Prevotella, Alistipes; Decreased Anaerotruncus, Dorea, Barnesiella, Methanosphaera; Increased fecal BAs and SCFAs levels | [195] |
| Lentinan | β-glucan | 500 mg/kg in the diet | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD mice model | Improved gut microbiota dysbiosis; improved intestinal barrier integrity | Increased gut microbial diversity; Reduced F/B ratio; Enhanced Bifidobacterium Streptococcus, and Enterococcus; Reduced serum LPS level | [254] |
| Aureobasidium pullulans strain AFO-202 β-glucan | β-glucan | 1 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced NASH mice model | Decreased inflammation associated hepatic cell ballooning and steatosis | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Lactobacillus, Turicibacter, and Bilophila; Increased fecal succinic acid level | [255] |
| Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide | Composed of Fruf (2 → 1), and a side chain of Fruf (2 → 6) Fruf (2→) per average 2.8 of main chain residues; Mw: 3400 Da | 0.5% in diet | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD mice model | Ameliorated lipid accumulation, liver steatosis, and chronic inflammation | Increased Akkermansia muciniphila | [256] |
| Lonicerae flos polysaccharides | - | 100 and 200 mg/kg | High-fat and high-fructose diet-induced NAFLD mice model | Regulated glucose metabolism dysregulation, IR, lipid accumulation, inflammation, fibrosis, and autophagy by activating the AMPK signaling pathway | Increased Muribaculum and Desulfovibrio | [257] |
| Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma polysaccharide | Composed of galacturonic acid, arabinose, galactose, rhamnose, and glucose, with molar ratios of 17.9:1.3:1.7:1.2:1; Mw: 32.6 kDa | 10 and 20 mg/kg | High-fat-induced NAFLD mice model | Attenuated hepatocellular steatosis, hepatic fibrosis, and inflammation; Improved gut barrier function | Increased Bifidobacterium pseudolongum, Ruminococcus gnavus, Clostridium celatum, Clostridium cocleatum | [258] |
| Ostrea rivularis polysaccharide | Composed of galactose and glucose in a molar percent of 23.7% and 76.3%, respectively; Mw: 118 kDa | 100 and 400 mg/kg | High-fat-induced NAFLD ApoE−/− mice model | Reduced TC, TG, and LDL-C levels, and increased HDL level in serum; Enhanced intestinal barrier function | Reduced F/B ratio; Reduced Firmicutes and Proteobacteria | [259] |
| Smilax china L. polysaccharide | Composed of arabinose, galactose, glucose, xylose, galacturonic acid, with molar ratios of 2.47:7.17:34.62:10.82:1.38; Mw: 134 kDa | 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg | High-fat-induced NAFLD mice model | Improved dyslipidemia, decreased depositions of liver lipids and adipose tissues, regulated hepatic fat metabolism | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, Muribaculaceae, and Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, and decreased Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002, Faecalibaculum, and Allobaculum | [260] |
| Tegillarca granosa polysaccharide | Composed of mannose, glucosamine, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galactosamine, glucose, galactose, xylose, fucose, with molar ratios of 1:1.38:0.87:0.53:0.52:5.37:1.38:1.05:2.40; Mw: 5.1 kDa | 200 and 400 mg/kg | High-fat-induced NAFLD mice model | Reduced excessive hepatic lipid accumulation, dyslipidemia, abnormal liver function, and steatosis | Increased fecal SCFAs-producing bacteria (Lactobacillus, Dubosiella, and Akkermansia); Increased cecal SCFAs level | [261] |
| Panacis japonici rhizome polysaccharide | Composed of glucose (74 .99 5%), galactose (17.054%), and arabinose (7.949%); Mw: 167.178 kDa | 25 and 100 mg/kg | High-fat-induced NAFLD mice model | Reduced liver fat accumulation, blood lipids, and ALT | Reduced F/B ratio; Decreased Turicibacter, Dubosiella, and Staphylococcus, and increased Bacteroides, Blautia, and Lactobacillus; Decreased fecal acetate and propionate level | [262] |
| Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi polysaccharide | Composed of fucose (0.77%), arabinose (30.38%), galactose (24.43%), glucose (26.74%), xylose (3.23%), mannose (4.55%), galacturonic acid (9.37%), and glucuronic acid (0.52%) | 100 and 300 mg/kg | High-fat-induced NASH mice model | Improved liver lipid metabolism, reduced inflammation, and fibrosis, improved intestinal barrier function | Decreased Gammaproteobacteria, Clostridium, and Coprococcus, and increased Dehalobacteraceae and Dehalobacterium | [263] |
5.4.4. Anti-CVD
| Bioactive Polysaccharides | Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Weight (Mw) | Dosage | Study Approaches | Major Findings | Mode of Action–Gut Microbiota | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lycium barbarum polysaccharide | - | 100 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced myocardial injury mice model | Improved left ventricular function and serum trimethylamine N-oxide; Reduced intestinal permeability and inflammation and alleviated myocardial injury | Increased Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Romboutsia; decreased the Gordonibacter, Parabacteroides, and Anaerostipes; Increased tryptophan metabolites | [266] |
| Cipangopaludina chinensis polysaccharide | Composed of glucose (95.2%), rhamnose (4.2%) and fucose (0.6%) | 100 and 400 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis ApoE−/− mice model | Regulating plasma lipids balance, decreasing atherosclerotic index, and reducing atherosclerotic plaque area | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, Ruminiclostridium, Alloprevotella and Flavobacterium | [267] |
| Chenopodium quinoa Willd. polysaccharides | Composed of glucose and arabinose, with a mole ratio of 1.17:1; Mw: 82.7 kDa | 300 and 600 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia rat model | Decreased serum TG, LDL-C, MDA, ALT, and AST levels and reduced hepatic lipid accumulation | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Ruminiclostridium and decreased Desulfovibrio and Allobaculum | [268] |
| Ginger polysaccharides | - | 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia rat model | Decreased blood lipid, serum inflammatory markers, and enhanced antioxidant capacity | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased the growth of Akkermansia muciniphila | [269] |
| Auricularia auricula polysaccharide (AAP) and Tremella polysaccharide (TP) | AAP composed of glucose (59.19%), galactose (22.63%) mannose (7.76%), fucose (6.46%), xylose (3.97%) and glucuronic acid (3.46%); TP was mainly composed of glucose (19.62%), mannose (36.18%), fucose (22.25%), xylose (18.62%) and glucuronic acid (3.33%); Mw: > 8 kDa | 100 mg/kg AAP + 100 mg/kg TP | High-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia rat model | Inhibited the development of hyperlipidemia and reduced lipid levels and fat accumulation; improved intestinal barrier function | Reduced F/B ratio; Increased Lactobacillus, Rumincococcacea, and Muribaculaceae; Decreased Allobaculum, Corynebacterium, Blautia, and Turicibucter | [264] |
| Grifola frondose polysaccharide | Composed of mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, glucose, galactose, and fucose with molar ratio of 25.49: 5.18: 9.49 :7.30: 27.59: 15.02: 9.92; Mw: 15850 kDa, 280.7 kDa and 18.18 kDa | 200 and 900 mg/kg | High-fat diet-streptozotocin-induced diabetes mice model | Reduced serum levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C; enhanced hepatic BAs synthesis and excretion | Elevated Alistipes and reduced Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus and Aerococcus | [270] |
| Walnut green husk polysaccharide | Composed of glucuronic acid, arabinose, and galactose; Mw: 4813 Da | 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg | High-fat diet-induced obesity mice model | Improved hepatic steatosis and vascular endothelial dysfunction | Increased Akkermansia, Lachnoclostridium and norank_f__Muribaculaceae and decreased Prevotellaceae_UCG-001, Helicobacter, Alloprevotella and Allobaculum | [271] |
| Ganoderma lucidum spore polysaccharide | Composed of mannose (1.00%), glucose (42.17%), galactose (4.78%), and fucose (1.75%); Mw: >10 kDa (72.93%) and >20 kDa (52.74%) | 50 mg/kg | TMAO-induced cardiac dysfunction rat model | Reduced serum TMAO, TC, TG, and LDL-C levels; increased heart function | Increased Firmicutes and Proteobacteria and reduced Actinobacteria and Tenericutes | [265] |
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baky, M.H.; Salah, M.; Ezzelarab, N.; Shao, P.; Elshahed, M.S.; Farag, M.A. Insoluble dietary fibers: structure, metabolism, interactions with human microbiome, and role in gut homeostasis. Crit Rev Food Sci 2024, 64, 1954–1968. [CrossRef]
- Zong, A.; Cao, H.; Wang, F. Anticancer polysaccharides from natural resources: A review of recent research. Carbohyd Polym 2012, 90, 1395–1410. [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab 2017, 25, 43–56. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Lu, B.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zheng, H.H.; Zhong, D.M.; Liao, Z.Q.; Wang, M.X.; Ma, F.L.; Liao, Q.F.; et al. Metabolomics insights into the modulatory effects of long-term compound polysaccharide intake in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Nutr Metab 2018, 15. [CrossRef]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [CrossRef]
- Browne, H.P.; Forster, S.C.; Anonye, B.O.; Kumar, N.; Neville, B.A.; Stares, M.D.; Goulding, D.; Lawley, T.D. Culturing of ’unculturable’ human microbiota reveals novel taxa and extensive sporulation. Nature 2016, 533, 543–546. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Jia, H.J.; Cai, X.H.; Zhong, H.Z.; Feng, Q.; Sunagawa, S.; Arumugam, M.; Kultima, J.R.; Prifti, E.; Nielsen, T.; et al. An integrated catalog of reference genes in the human gut microbiome. Nat Biotechnol 2014, 32, 834–841. [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Li, R.Q.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59-U70. [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-Gut Microbiota Metabolic Interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.T.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.P.; Hu, X.S.; Chen, F. The gut microbiota: A treasure for human health. Biotechnol Adv 2016, 34, 1210–1224. [CrossRef]
- Perler, B.K.; Friedman, E.S.; Wu, G.D. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Relationship Between Diet and Human Health. Annu Rev Physiol 2023, 85, 449–468. [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Huang, L.X.; Shen, M.Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.H. Review of the relationships among polysaccharides, gut microbiota, and human health. Food Res Int 2021, 140. [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. Embo Rep 2006, 7, 688–693. [CrossRef]
- Ursell, L.K.; Clemente, J.C.; Rideout, J.R.; Gevers, D.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R. The interpersonal and intrapersonal diversity of human-associated microbiota in key body sites. J Allergy Clin Immun 2012, 129, 1204–1208. [CrossRef]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [CrossRef]
- Gosalbes, M.J.; Durbán, A.; Pignatelli, M.; Abellan, J.J.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A. Metatranscriptomic Approach to Analyze the Functional Human Gut Microbiota. PloS one 2011, 6. [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.L.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.D.; Weaver, C.T. Reciprocal interactions of the intestinal microbiota and immune system. Nature 2012, 489, 231–241. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.N. The triple interactions between gut microbiota, mycobiota and host immunity. Crit Rev Food Sci 2022, 66, 11604–11624. [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.; Maiti, T.K.; Mahajan, D.; Das, B. Human Gut Microbiota and Drug Metabolism. Microb Ecol 2023, 86, 97–111. [CrossRef]
- Kolodnitsky, A.S.; Ionov, N.S.; Rudik, A.V.; Filimonov, D.A.; Poroikov, V.V. HGMMX: Host Gut Microbiota Metabolism Xenobiotics Database. J Chem Inf Model 2023, 63, 6463–6468. [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology - Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.Y.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut Microbiota from Twins Discordant for Obesity Modulate Metabolism in Mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H.K. The critical role of gut microbiota in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 102506. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Q.H.; Jiang, C.K.; Lu, H.L.; Hu, W.J.; Yu, S.F.; Li, M.Q.; Tan, C.P.; Feng, Y.C.; Xiang, X.W.; et al. Sciadonic acid attenuates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice with alterations in the gut microbiota. Food Funct 2023, 14, 2870–2880. [CrossRef]
- Murga-Garrido, S.M.; Orbe-Orihuela, Y.C.; Díaz-Benítez, C.E.; Castañeda-Márquez, A.C.; Cornejo-Granados, F.; Ochoa-Leyva, A.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Cruz, M.; Burguete-García, A.I.; Lagunas-Martínez, A. Alterations of the Gut Microbiome Associated to Methane Metabolism in Mexican Children with Obesity. Children-Basel 2022, 9, 148. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 2021, 19, 55–71. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.V.; Frassetto, A.; Kowalik, E.J.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Lu, M.F.M.; Kosinski, J.R.; Hubert, J.A.; Szeto, D.; Yao, X.R.; Forrest, G.; et al. Butyrate and Propionate Protect against Diet-Induced Obesity and Regulate Gut Hormones via Free Fatty Acid Receptor 3-Independent Mechanisms. PloS one 2012, 7, e35240. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.S.; Bourwis, N.; Dolan, S.; Lang, S.; Spencer, J.; Craft, J.A. Characterisation of gut microbiota of obesity and type 2 diabetes in a rodent model. Biosci Microb Food H 2021, 40, 65–74. [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature that Differentiates Obese and Lean Humans and Contributes to Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab 2009, 9, 311–326. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.M.; Chung, Y.M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [CrossRef]
- Shelton, C.D.; Sing, E.; Mo, J.; Shealy, N.G.; Yoo, W.; Thomas, J.; Fitz, G.N.; Castro, P.R.; Hickman, T.T.; Torres, T.P.; et al. An early-life microbiota metabolite protects against obesity by regulating intestinal lipid metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1604–1619, e10. [CrossRef]
- Siptroth, J.; Moskalenko, O.; Krumbiegel, C.; Ackermann, J.; Koch, I.; Pospisil, H. Variation of butyrate production in the gut microbiome in type 2 diabetes patients. Int Microbiol 2023, 26, 601–610. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; van den Berg, F.W.J.; Nielsen, D.S.; Andreasen, A.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sorensen, S.J.; Hansen, L.H.; Jakobsen, M. Gut Microbiota in Human Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Differs from Non-Diabetic Adults. PloS one 2010, 5, e9085. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Xie, C.G.; Hu, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, S.H.; He, Y.C.; Kang, J.; Gao, H.; Yuan, H.P.; et al. Shenqi compound ameliorates type-2 diabetes mellitus by modulating the gut microbiota and metabolites. J Chromatogr B 2022, 1194, 123189. [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Li, Y.R.; Cai, Z.M.; Li, S.H.; Zhu, J.F.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.S.; Zhang, W.W.; Guan, Y.L.; Shen, D.Q.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergström, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Kanazawa, A.; Ikeda, F.; Yoshihara, T.; Goto, H.; Abe, H.; Komiya, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Shimizu, T.; Ogihara, T.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis and Detection of "Live Gut Bacteria" in Blood of Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes care 2014, 37, 2343–2350. [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab 2016, 24, 41–50. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, H.K.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Nielsen, H.B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Nielsen, T.; Jensen, B.A.; Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Prifti, E.; Falony, G. Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature 2016, 535, 376–381. [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat Med 2017, 23, 107–113. [CrossRef]
- Maestri, M.; Santopaolo, F.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Gut microbiota modulation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Effects of current treatments and future strategies. Front Nutr 2023, 10, 1110536. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.W.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.M.; Chi, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Qiu, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.L. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8096. [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Seguritan, V.; Li, W.Z.; Long, T.; Klitgord, N.; Bhatt, A.; Dulai, P.S.; Caussy, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Highlander, S.K.; et al. Gut Microbiome-Based Metagenomic Signature for Non-invasive Detection of Advanced Fibrosis in Human Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (vol 25, pg 1054, 2017). Cell Metab 2019, 30, 607–607. [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Maurizi, V.; Rinninella, E.; Tack, J.; Di Berardino, A.; Santori, P.; Rasetti, C.; Procopio, A.C.; Boccuto, L.; Scarpellini, E. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in NAFLD Treatment. Medicina-Lithuania 2022, 58, 1559. [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, E.; Muthiah, M.D.; Narayan, N.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Puri, P.; Luketic, V.A.; Contos, M.J.; Idowu, M.; Chuang, J.C.; Billin, A.N.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming of the intestinal microbiome with functional bile acid changes underlie the development of NAFLD. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1811–1824. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wei, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.N.; Wang, L.M.; Wang, M.X.; Rong, Y.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wang, H.J.; et al. Biotransformed bear bile powder ameliorates diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice through modulating arginine biosynthesis via FXR/ PXR-PI3K-AKT-NOS3 axis. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 168, 115640. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Ruan, Y.F.; Chen, Y.P.; Liu, Q. Disease-Associated Gut Microbiota Reduces the Profile of Secondary Bile Acids in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front Cell Infect Mi 2021, 11, 698852. [CrossRef]
- Pant, K.; Venugopal, S.K.; Pisarello, M.J.L.; Gradilone, S.A. The Role of Gut Microbiome-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acid Butyrate in Hepatobiliary Diseases. Am J Pathol 2023, 193, 1455–1467. [CrossRef]
- An, L.X.; Wirth, U.; Koch, D.; Schirren, M.; Drefs, M.; Koliogiannis, D.; Niess, H.; Andrassy, J.; Guba, M.; Bazhin, A.V.; et al. The Role of Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and the Intestinal Barrier in Fatty Liver Diseases. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 671–683. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.H.; Sichler, A.; Ecker, J.; Laschinger, M.; Liebisch, G.; Höring, M.; Basic, M.; Bleich, A.; Zhang, X.J.; Kübelsbeck, L.; et al. Gut microbiota promote liver regeneration through hepatic membrane phospholipid biosynthesis. J Hepatol 2023, 78, 820–835. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.X.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.S.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of Gut Microbiomes in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Patients: A Connection Between Endogenous Alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.J.; Relja, B. The Impact of Acute or Chronic Alcohol Intake on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Al Samarraie, A.; Pichette, M.; Rousseau, G. Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Development of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 5420. [CrossRef]
- Jie, Z.Y.; Xia, H.H.; Zhong, S.L.; Feng, Q.; Li, S.H.; Liang, S.S.; Zhong, H.Z.; Liu, Z.P.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 845. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Chen, J.R.; Tao, J.E.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.L.; Liu, W.B.; Cui, Q.H.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.N.; Yan, A.; Lin, P.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.P. Trimethylamine N-oxide-a marker for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 787–797. [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.Z.; Nelson, E.; Chu, P.Y.; Horlock, D.; Fiedler, A.; Ziemann, M.; Tan, J.K.; Kuruppu, S.; Rajapakse, N.W.; El-Osta, A.; et al. High-Fiber Diet and Acetate Supplementation Change the Gut Microbiota and Prevent the Development of Hypertension and Heart Failure in Hypertensive Mice. Circulation 2017, 135, 964–977. [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Hazen, S.L. Microbial modulation of cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 2018, 16, 171–181. [CrossRef]
- Yntema, T.; Koonen, D.P.Y.; Kuipers, F. Emerging Roles of Gut Microbial Modulation of Bile Acid Composition in the Etiology of Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1850. [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.P.; Wang, Y. The health benefits of dietary short-chain fatty acids in metabolic diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci 2023, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, K.X.; Wei, J.G.; Ding, Y.Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, H.Q.; Wu, J.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wang, B.M.; Cao, H.L. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulate gastrointestinal tumor immunity: a novel therapeutic strategy? Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158200. [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Frost, G. Control of appetite and energy intake by SCFA: what are the potential underlying mechanisms? P Nutr Soc 2015, 74, 328–336. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.Y.; Fei, W.D.; Ye, Y.Q.; Zhao, M.D.; Zheng, C.H. The role of short-chain fatty acids in immunity, inflammation and metabolism. Crit Rev Food Sci 2022, 62, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Lednovich, K.; Xu, K.; Nnyamah, C.; Layden, B.T.; Xu, P.W. Y Central and peripheral regulations mediated by short-chain fatty acids on energy homeostasis. Transl Res 2022, 248, 128–150. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Kotlo, K.U.; Dudeja, P.K.; Layden, B.T. Role of Short Chain Fatty Acid Receptors in Intestinal Physiology and Pathophysiology. Compr Physiol 2018, 8, 1091–1115. [CrossRef]
- Luu, M.; Pautz, S.; Kohl, V.; Singh, R.; Romero, R.; Lucas, S.; Hofmann, J.; Raifer, H.; Vachharajani, N.; Carrascosa, L.C.; et al. The short-chain fatty acid pentanoate suppresses autoimmunity by modulating the metabolic-epigenetic crosstalk in lymphocytes. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 760. [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. P Nutr Soc 2021, 80, 37–49. [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.A.G.; Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Blaak, E.E. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate in Body Weight Control and Insulin Sensitivity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1943. [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2015, 11, 577–591. [CrossRef]
- May, K.S.; den Hartigh, L.J. Modulation of Adipocyte Metabolism by Microbial Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3666. [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Xie, G.X.; Jia, W.P. Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Gastro Hepat 2018, 15, 111–128. [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.R.; Want, E.J.; Geier, F.M.; Spagou, K.; Wilson, I.D.; Sidaway, J.E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E. Systemic gut microbial modulation of bile acid metabolism in host tissue compartments. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2011, 108, 4523–4530. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.K.; Hang, X.M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.L.; Li, D.T.; Yang, H. Diversity of bile salt hydrolase activities in different lactobacilli toward human bile salts. Ann Microbiol 2010, 60, 81–88. [CrossRef]
- Li, R.M.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Kuipers, F.; Fu, J.Y. Gut microbiome and bile acids in obesity-related diseases. Best Pract Res Cl En 2021, 35, 101493. [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Talavera, O.; Tailleux, A.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Bile Acid Control of Metabolism and Inflammation in Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1679–1694. [CrossRef]
- Lun, W.; Yan, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhou, M.; Bai, Y.; He, J.; Cao, H.; Che, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Mechanism of action of the bile acid receptor TGR5 in obesity. Acta Pharm Sin B 2023. [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.M.; Qin, L.; Wu, D.; Xie, J.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.R.; He, Y.Q. Research Progress of Takeda G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5 in Metabolic Syndrome. Molecules 2023, 28, 5870. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.L.; Wang, J.R.; Li, X.J.; Li, Y.; Ye, C. Deoxycholic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus-induced endometritis through regulating TGR5/PKA/NF-xB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 118, 110004. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Chen, T.L.; Jiang, R.Q.; Zhao, A.H.; Wu, Q.; Kuang, J.L.; Sun, D.N.; Ren, Z.X.; Li, M.C.; Zhao, M.L.; et al. Hyocholic acid species improve glucose homeostasis through a distinct TGR5 and FXR signaling mechanism. Cell Metab 2021, 33, 791–803. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Chen, T.L.; Zhao, A.H.; Ning, Z.C.; Kuang, J.L.; Wang, S.L.; You, Y.J.; Bao, Y.Q.; Ma, X.J.; Yu, H.Y.; et al. Hyocholic acid species as novel biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1487. [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Li, M.C.; Zhao, M.L.; Ge, K.; Zheng, D.; Cheung, K.C.P.; Liao, B.Y.; Wang, S.L.; et al. Hyodeoxycholic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through modulating the gut-liver axis. Cell Metab 2023, 35, 1752–1766. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.T.; Xie, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.M.; Nichols, R.G.; Krausz, K.W.; Cai, J.W.; Qi, Y.P.; Fang, Z.Z.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Intestinal farnesoid X receptor signaling promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 2015, 125, 386–402. [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, A.; Wahlström, A.; Marschall, H.U. Role of Bile Acids in Metabolic Control. Trends Endocrin Met 2018, 29, 31–41. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. The Role of Bile Acids in Cardiovascular Diseases: from Mechanisms to Clinical Implications. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 261–282. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Dong, L.-W.; Liu, S.; Meng, F.-H.; Xie, C.; Lu, X.-Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Luo, J.; Song, B.-L. Bile acids-mediated intracellular cholesterol transport promotes intestinal cholesterol absorption and NPC1L1 recycling. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 6469. [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zou, Y.; Han, X.; Bae, J.-W.; Jeon, C.O. Gut microbiome-mediated mechanisms for reducing cholesterol levels: Implications for ameliorating cardiovascular disease. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 76–91. [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.C.; Bisanz, J.E.; Okafor, C.D.; Patterson, A.D. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 21, 236–247. [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, D.; Zhao, J.; Tobin, I.; Zhao, J. Alginate alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by promoting Bifidobacterium animalis and intestinal hyodeoxycholic acid synthesis in mice. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10, e02979-02922. [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, D.; Han, D.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Ye, H.; Lian, S. Gut microbiota-derived ursodeoxycholic acid alleviates low birth weight-induced colonic inflammation by enhancing M2 macrophage polarization. Microbiome 2023, 11, 19. [CrossRef]
- Seth, M.; Mondal, P.; Ghosh, D.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K. The foul play of two dietary metabolites trimethylamine (TMA) and trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) on human health and the role of microbes in mitigating their effects. Nutrire 2023, 48, 52. [CrossRef]
- Canyelles, M.; Borrás, C.; Rotllan, N.; Tondo, M.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Gut Microbiota-Derived TMAO: A Causal Factor Promoting Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease? Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 1940. [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; Lorente-Ros, Á.; Briones-Figueroa, A.; Morán-Alvarez, P.; García-Fernández, A.; Garrote-Corral, S.; Amil-Casas, I.; Carrasco-Sayalero, Á.; Tejada-Velarde, A.; Camino-López, A.; et al. Serological short-chain fatty acid and trimethylamine N-oxide microbial metabolite imbalances in young adults with acute myocardial infarction. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20854. [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhuang, R.L.; Yu, P.; Xu, Z.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Xi, X.L.; Zhou, X.H.; Fan, H.M. The Gut Microbial Metabolite Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Hypertension Risk: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis. Adv Nutr 2020, 11, 66–76. [CrossRef]
- Crisci, G.; Israr, M.Z.; Cittadini, A.; Bossone, E.; Suzuki, T.; Salzano, A. Heart failure and trimethylamine N-oxide: time to transform a ’gut feeling’ in a fact? Esc Heart Fail 2023, 10, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Witkowski, M.; Friebel, J.; Buffa, J.A.; Li, X.M.S.; Wang, Z.N.; Sangwan, N.; Li, L.; DiDonato, J.A.; Tizian, C.; et al. Vascular endothelial tissue factor contributes to trimethylamine N-oxide-enhanced arterial thrombosis. Cardiovasc Res 2022, 118, 2367–2384. [CrossRef]
- Querio, G.; Antoniotti, S.; Geddo, F.; Levi, R.; Gallo, M.P. Modulation of Endothelial Function by TMAO, a Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolite. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 5806. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Wang, Z.N.; Li, X.M.S.; Fan, Y.Y.; Li, D.S.; Wu, Y.P.; Hazen, S.L. Increased Trimethylamine N-Oxide Portends High Mortality Risk Independent of Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 297–306. [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, P.; Farhangi, M.A.; Nikniaz, L.; Nikniaz, Z.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Gut microbiota-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) potentially increases the risk of obesity in adults: An exploratory systematic review and dose-response meta- analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12993. [CrossRef]
- Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Sheehy, B.T.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med 2013, 19, 576–585. [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.C.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Zhu, W.; Wagner, M.A.; Bennett, B.J.; Li, L.; DiDonato, J.A. Transmission of atherosclerosis susceptibility with gut microbial transplantation. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 5647–5660. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.W.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Koeth, R.A.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, S.L. Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. New Engl J Med 2013, 368, 1575–1584. [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Melita, H.; Manolis, A.S. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease: Symbiosis Versus Dysbiosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 4050–4077. [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.B. Kynurenine pathway and human systems. Exp Gerontol 2020, 129, 110770. [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous Bacteria from the Gut Microbiota Regulate Host Serotonin Biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [CrossRef]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Pan, T.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H.C.; Zhu, J.L.; Tian, F.W.; Lu, W.W.; Chen, W. The therapeutic potential of dietary intervention: based on the mechanism of a tryptophan derivative-indole propionic acid on metabolic disorders. Crit Rev Food Sci 2023, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.; Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Lamas, B.; Jarry, A.C.; Martin, R.; Michel, M.L.; Chong-Nguyen, C.; Roussel, R.; Straube, M.; et al. Impaired Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand Production by the Gut Microbiota Is a Key Factor in Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab 2018, 28, 737–749. [CrossRef]
- Agus, A.; Clément, K.; Sokol, H. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut 2021, 70, 1174–1182. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Sun, S.Y.; Liang, L.; Lou, C.X.; He, Q.J.; Ran, M.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yan, C.; Yuan, H.J.; et al. Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Sulforaphane Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. Front Nutr 2021, 8, 756565. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, W.Z. Indole-3-Acetic Acid Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice via Attenuation of Hepatic Lipogenesis, and Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2062. [CrossRef]
- de Mello, V.D.; Paananen, J.; Lindström, J.; Lankinen, M.A.; Shi, L.; Kuusisto, J.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Auriola, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Rolandsson, O.; et al. Indolepropionic acid and novel lipid metabolites are associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46337. [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, R.; de Mello, V.D.; Männistö, V.; Lindström, J.; Tuomilehto, J.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Uusitupa, M. Indolepropionic Acid, a Gut Bacteria-Produced Tryptophan Metabolite and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4695. [CrossRef]
- Tuomainen, M.; Lindström, J.; Lehtonen, M.; Auriola, S.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Peltonen, M.; Tuomilehto, J.; Uusitupa, M.; de Mello, V.D.; Hanhineva, K. Associations of serum indolepropionic acid, a gut microbiota metabolite, with type 2 diabetes and low-grade inflammation in high-risk individuals. Nutr Diabetes 2018, 8, 35. [CrossRef]
- Cussotto, S.; Delgado, I.; Anesi, A.; Dexpert, S.; Aubert, A.; Beau, C.; Forestier, D.; Ledaguenel, P.; Magne, E.; Mattivi, F.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolic Pathways Are Altered in Obesity and Are Associated With Systemic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 557. [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.H.; Qiao, Q.Q.; Yin, R.P.; Zhang, L.Z.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhou, J.Q.; Li, Z.Y. Identification of a Novel Strain Lactobacillus Reuteri and Anti- Obesity Effect through Metabolite Indole-3-Carboxaldehyde in Diet- Induced Obese Mice. J Agr Food Chem 2023, 71, 3239–3249. [CrossRef]
- Kappel, B.A.; De Angelis, L.; Heiser, M.; Ballanti, M.; Stoehr, R.; Goettsch, C.; Mavilio, M.; Artati, A.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Adamski, J.; et al. Cross-omics analysis revealed gut microbiome-related metabolic pathways underlying atherosclerosis development after antibiotics treatment. Mol Metab 2020, 36, 100976. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, E.R.; Tuseth, N.; Eussen, S.J.P.M.; Ueland, P.M.; Strand, E.; Svingen, G.F.T.; Midttun, O.; Meyer, K.; Mellgren, G.; Ulvik, A.; et al. Associations of Plasma Kynurenines With Risk of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Stable Angina Pectoris. Arterioscl Throm Vas 2015, 35, 455–462. [CrossRef]
- Konopelski, P.; Chabowski, D.; Aleksandrowicz, M.; Kozniewska, E.; Podsadni, P.; Szczepanska, A.; Ufnal, M. Indole-3-propionic acid, a tryptophan-derived bacterial metabolite, increases blood pressure via cardiac and vascular mechanisms in rats. Am J Physiol-Reg I 2021, 321, R969-R981. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Koay, Y.C.; Pan, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wilson Tang, W.H.; Wilcox, J.; Li, X.S.; Zagouras, A.; Marques, F.; Allayee, H.; et al. Indole-3-Propionic Acid Protects Against Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ Res 2024, 134, 371–389. [CrossRef]
- Paeslack, N.; Mimmler, M.; Becker, S.; Gao, Z.L.; Khuu, M.P.; Mann, A.; Malinarich, F.; Regen, T.; Reinhardt, C. Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites in vascular inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 1339–1356. [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.C.; Heinrichs, D.E. Branching out: Alterations in bacterial physiology and virulence due to branched-chain amino acid deprivation. mBio 2018, 9, e01188-01118. [CrossRef]
- Tajiri, K.; Shimizu, Y. Branched-chain amino acids in liver diseases. Transl Gastroent Hep 2018, 3. [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; He, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X. Branched chain amino acids: beyond nutrition metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 954. [CrossRef]
- Ooi, D.S.; Ling, J.Q.; Sadananthan, S.A.; Velan, S.S.; Ong, F.Y.; Khoo, C.M.; Tai, E.S.; Henry, C.J.; Leow, M.K.; Khoo, E.Y. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation does not preserve lean mass or affect metabolic profile in adults with overweight or obesity in a randomized controlled weight loss intervention. J Nutr 2021, 151, 911–920. [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.; Mora, S.; Madu, G.; Adegoke, O.A. Branched-chain amino acids: catabolism in skeletal muscle and implications for muscle and whole-body metabolism. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 702826. [CrossRef]
- Cummings, N.E.; Williams, E.M.; Kasza, I.; Konon, E.N.; Schaid, M.D.; Schmidt, B.A.; Poudel, C.; Sherman, D.S.; Yu, D.; Arriola Apelo, S.I. Restoration of metabolic health by decreased consumption of branched-chain amino acids. J Physiol 2018, 596, 623–645. [CrossRef]
- Lueders, B.; Kanney, B.C.; Krone, M.J.; Gannon, N.P.; Vaughan, R.A. Effect of branched-chain amino acids on food intake and indicators of hunger and satiety-a narrative summary. Hum Nutr Metab 2022, 200168. [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, A.C. Branched-chain amino acid catabolism by brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa060. [CrossRef]
- Yoneshiro, T.; Wang, Q.; Tajima, K.; Matsushita, M.; Maki, H.; Igarashi, K.; Dai, Z.; White, P.J.; McGarrah, R.W.; Ilkayeva, O.R. BCAA catabolism in brown fat controls energy homeostasis through SLC25A44. Nature 2019, 572, 614–619. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, S.; Zou, D.; Dong, D.; He, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, W.; Huang, L. Metabolic shifts and structural changes in the gut microbiota upon branched-chain amino acid supplementation in middle-aged mice. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2731–2745. [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Newgard, C.B. Branched-chain amino acids in disease. Science 2019, 363, 582–583. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Shao, J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Shu, L.; Dong, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wynn, R.M.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Targeting BCAA catabolism to treat obesity-associated insulin resistance. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1730–1746. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.J.; Adams, S.H. Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2014, 10, 723–736. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.-S. The emerging role of branched-chain amino acids in insulin resistance and metabolism. Nutrients 2016, 8, 405. [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acids and ammonia metabolism in liver disease: therapeutic implications. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1186–1191. [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, P.; Capparelli, R.; Iannelli, A.; Iannelli, D. Role of branched-chain amino acid metabolism in type 2 diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 4325. [CrossRef]
- Surugihalli, C.; Muralidaran, V.; Ryan, C.E.; Patel, K.; Zhao, D.; Sunny, N.E. Branched-chain amino acids alter cellular redox to induce lipid oxidation and reduce de novo lipogenesis in the liver. Am J Physiol-Endoc M 2023, 324, E299-E313. [CrossRef]
- Alqaraleh, M.; Kasabri, V.; Al-Majali, I.; Aljaafreh, A.; Al-Othman, N.; Khleifat, K.; Al-Tawarah, N.M.; Qaralleh, H.; Khwaldeh, A.S.; Alalawi, S. Branched chain amino acids as in vitro and in vivo anti-oxidation compounds. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 2021, 14, 3899–3904. [CrossRef]
- McGarrah, R.W.; White, P.J. Branched-chain amino acids in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2023, 20, 77–89. [CrossRef]
- Karwi, Q.G.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in the Failing Heart. Cardiovasc Drug Ther 2023, 37, 413–420. [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Dan, B.; Lü, L. Bioactive effects advances of natural polysaccharides. J Future Foods 2023, 3, 234–239. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.L.; Guo, S.C.; Wen, L.; Yu, M.L.; Feng, L.; Jia, X.B. Structural Elucidation, Modification, and Structure-Activity Relationship of Polysaccharides in Chinese Herbs: A Review. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 908175. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.J.; Wang, C.L.; Chen, B.T.; Kang, M.J.; Wang, M.C.; Liu, K.; Wang, M. Recent advances in polysaccharides from lentinus (Berk.): Isolation, structures and bioactivities. Food Chem 2021, 358, 129883. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Feng, J.; Chen, H. Polysaccharide of Ganoderma and Its Bioactivities. In Ganoderma and Health: Biology, Chemistry and Industry, Lin, Z., Yang, B., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2019; pp. 107–134.
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Yan, M.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, J. Structural characterization and immuno-enhancing activity of a highly branched water-soluble β-glucan from the spores of Ganoderma lucidum. Carbohyd Polym 2017, 167, 337–344. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nie, S.; Cui, S.W.; Xu, M.; Ding, H.; Xie, M. Characterization of a bioactive polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum: Re-elucidation of the fine structure. Carbohyd Polym 2017, 158, 58–67. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Fang, L.; Zhang, K.-C. Structure and bioactivities of a galactose rich extracellular polysaccharide from submergedly cultured Ganoderma lucidum. Carbohyd Polym 2007, 68, 323–328. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.-J.; Nie, S.-P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Xie, M.-Y. Structural characterisation of a novel bioactive polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum. Carbohyd Polym 2012, 88, 1047–1054. [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.J.; Liang, T.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Ding, G.T.; Zhang, F.M.; Ma, Z.R. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Biological Functions of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 389. [CrossRef]
- Kiddane, A.T.; Kim, G.D. Anticancer and Immunomodulatory Effects of Polysaccharides. Nutr Cancer 2021, 73, 2219–2231. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Li, C.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; Dong, H. Current advances in the anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of natural polysaccharides. Crit Rev Food Sci 2023, 63, 5890–5910. [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.R.; de Carvalho, R.J.r. Polysaccharides obtained from natural edible sources and their role in modulating the immune system: Biologically active potential that can be exploited against COVID-19. Trends Food Sci Tech 2021, 108, 223–235. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Zheng, J.J.; Qu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Li, F.F.; Jin, Q.X.; Li, H.H.; Meng, F.P.; Jin, G.H.; Jin, D. Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide ameliorates dextran sulphate sodium induced colitis involving modulation of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance. Artif Cell Nanomed B 2019, 47, 757–766. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, B.C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, M.J.; Zhao, W. Natural Polysaccharides with Immunomodulatory Activities. Mini-Rev Med Chem 2020, 20, 96–106. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Bai, J.W.; Bu, X.Y.; Yin, Y.T.; Wang, L.B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.Q. Characterization of selenized polysaccharides from Ribes nigrum L. and its inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase. Carbohyd Polym 2021, 259, 117729. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Zeng, F.S.; Fu, W.W.; You, H.T.; Mu, X.Y.; Chen, G.F.; Lv, H.; Li, W.J.; Xie, M.Y. White hyacinth bean polysaccharide ameliorates diabetes via microbiota-gut-brain axis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 253, 127307. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.F.; Wu, S.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.S.; Mao, G.X.; Li, S.J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.J.; Tong, H.B. Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan modifies gut microbiota and intestinal metabolites during alleviation of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice. Food Funct 2021, 12, 3572–3585. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Li, H.L.; Hou, Y.T.; Zhang, P.J.; Tan, M.Q. Plant polysaccharides: sources, structures, and antidiabetic effects. Curr Opin Food Sci 2023, 51, 101013. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Lu, J.; Li, H.; Song, H.Z. Advances in dietary polysaccharides as hypoglycemic agents: mechanisms, structural characteristics, and innovative applications. Crit Rev Food Sci 2023, 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.T.; Tao, W.L.; Wu, F.J.; Wu, K.L.; Huang, X.J.; Ling, G.S.; Zhao, C.A.Y.; Lv, Q.; Wang, Q.J.; Zhou, X.H.; et al. Anti-hypertensive and cardioprotective activities of traditional Chinese medicine-derived polysaccharides: A review. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 185, 917–934. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Qidwai, T. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition Properties and Antioxidant Effects of Plants and their Bioactive Compounds as Cardioprotective Agent. Lett Drug Des Discov 2023, 20, 457–468. [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammad, K.; Sewell, R.D.E.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Mechanisms of Medicinal Plant Activity on Nitric Oxide (NO) Bioavailability as Prospective Treatments for Atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Design 2020, 26, 2591–2601. [CrossRef]
- Naumann, S.; Haller, D.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Mechanisms of Interactions between Bile Acids and Plant Compounds-A Review. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 6495. [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.Y.; Shi, S.; Liu, B.; Shan, M.X.; Tang, D.L.; Zhang, W.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, H.M.; Lu, C.; et al. Bioactive compounds from herbal medicines to manage dyslipidemia. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 118, 109338. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.Y.; Chang, L.L.; Peng, J.; Zhang, M.Q.; Ding, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.K.; Liu, X.B.; Lan, Y. A natural anti-obesity reagent derived from sea buckthorn polysaccharides: Structure characterization and anti-obesity evaluation in vivo. Food Chem 2022, 375, 131884. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Tan, B.; Chen, J. Supplementation With Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Reduce Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 719967. [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Meng, C.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, W.X. Ganoderma amboinense polysaccharide prevents obesity by regulating gut microbiota in high-fat-diet mice. Food Biosci 2021, 42, 101107. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.N.; Li, Q.N.; Han, N.; Song, C.F.; Lin, Y.N.; Zhang, L.S.; Ren, D.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.B.; Li, T. Effects of Fu brick tea polysaccharides on gut microbiota and fecal metabolites of HFD/STZ-induced type 2 diabetes rats. Food Funct 2023, 14, 10910–10923. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Wu, J.L.; Fu, X.; Wang, P.P.; Chen, C. Fructus mori polysaccharide alleviates diabetic symptoms by regulating intestinal microbiota and intestinal barrier against TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 249, 126038. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Mao, X.; Jiang, W.; Pan, Y.; Chen, X.J.; Hu, J.H.; Kong, X.H.; Xia, H.H. Assessment of Auricularia cornea var. Li. polysaccharides potential to improve hepatic, antioxidation and intestinal microecology in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Nutr 2023, 10, 1161537. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fu, M.X.; Wu, D.T.; Zhao, Y.X.; Li, H.; Li, H.B.; Gan, R.Y. Structural Characteristics of Crude Polysaccharides from 12 Selected Chinese Teas, and Their Antioxidant and Anti-Diabetic Activities. Antioxidants-Basel 2021, 10, 1562. [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Liu, P.; Zhang, N.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, M.S. Comparison on Bioactivities and Characteristics of Polysaccharides From Four Varieties of Gastrodia elata Blume. Front Chem 2022, 10, 956724. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ran, L.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Wan, P.; Zhou, H.L. Basic characterization, antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides from sea buckthorn leaves. Fitoterapia 2023, 169, 105592. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, P.; Liu, H.P.; Zhang, X.W. Extraction, Rheological, and Physicochemical Properties of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides with Antioxidant Capacity from Penthorum chinense Pursh. Foods 2023, 12, 2335. [CrossRef]
- Siu, K.C.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.Y. Constituents actually responsible for the antioxidant activities of crude polysaccharides isolated from mushrooms. J Funct Foods 2014, 11, 548–556. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, T.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Du, B.; Liu, C.Y. Comparison of structural, antioxidant and immuno-stimulating activities of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides from in two different regions of China. Int J Food Sci Tech 2018, 53, 1942–1953. [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.B.; Cui, Y.L. Antioxidant Activities of Natural Polysaccharides and Their Derivatives for Biomedical and Medicinal Applications. Antioxidants-Basel 2022, 11, 2491. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, D.H. Codonopsis lanceolata polysaccharide CLPS alleviates high fat/high sucrose diet-induced insulin resistance via anti-oxidative stress. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 145, 944–949. [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.L.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 4777. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.H.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.C.; Lin, X.F.; Chen, A.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Gong, E.S.; Liu, D.; Zou, Q.; Wang, X.Y. Advances in health-promoting effects of natural polysaccharides: Regulation on Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Front Nutr 2023, 10, 1102146. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhi, J.; Xing, R.N.; He, L.Q. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect mice from hyperuricaemia through promoting kidney excretion of uric acid and inhibiting liver xanthine oxidase. Pharm Biol 2020, 58, 944–949. [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Bae, M.S.; Park, D.H.; Cho, S.S. Strong inhibition of xanthine oxidase and elastase of Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC stem extract and analysis of biologically active constituents. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1160330. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Pang, G.B.; Chen, C.; Qin, J.Z.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, X.H.; Song, Z.T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, F.J.; et al. Effective cancer immunotherapy by Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide-gold nanocomposites through dendritic cell activation and memory T cell response. Carbohyd Polym 2019, 205, 192–202. [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.C.; Duan, G.Z.; Fan, G.H.; Peng, N. Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on cell signal transduction pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 147, 112620. [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.C.; Gong, P.X.; Li, H.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.J. Recent trends in anti-cancer activities of terrestrial plants-based polysaccharides: A review. Carbohydr Polym Tech 2023, 6, 100341. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, C.L.; Sang, T.T.; Peng, H.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.J.; Lin, X.J.; et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide inhibits HSC activation and liver fibrosis via targeting inflammation, apoptosis, cell cycle, and ECM-receptor interaction mediated by TGF-β/Smad signaling. Phytomedicine 2023, 110, 154626. [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.J.; Hu, R.K.; Wu, L.X.; Lv, X.C.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.N.; Liu, B. polysaccharide and chitosan synergistically ameliorate lipid metabolic disorders and modulate gut microbiota composition in high fat diet-fed golden hamsters. J Food Biochem 2020, 44, e13109. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.N.; Zhang, M.W.; Ma, J.M.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yang, J.J. Metabolomics analysis of the serum metabolic signature of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease combined with prediabetes model rats after the intervention of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides combined with aerobic activity. Biomed Chromatogr 2023, 37, e5562. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Jia, Y.Z.; Xu, N.; Tang, L.H.; Chang, Y.N. Auricularia auricula polysaccharides improve obesity in mice by regulating gut microbiota and TLR4/JNK signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 250, 126172. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Luan, Z.X.; Fan, Z.B.; Wu, X.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhou, T.Z.; Wang, H.J. Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides Obtained from Fresh Sarcotesta of Ginkgo biloba: Bioactive Polysaccharide that Can Be Exploited as a Novel Biocontrol Agent. Evid-Based Compl Alt 2021, 2021, 5518403. [CrossRef]
- Rubini, D.; Varthan, P.V.; Jayasankari, S.; Vedahari, B.N.; Nithyanand, P. Suppressing the phenotypic virulence factors of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli using marine polysaccharide. Microb Pathogenesis 2020, 141, 103973. [CrossRef]
- Chaisuwan, W.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Chaiyaso, T.; Techapun, C.; Leksawasdi, N.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Rachtanapun, P.; Wangtueai, S.; Sommano, S.R.; You, S.; et al. The Antiviral Activity of Bacterial, Fungal, and Algal Polysaccharides as Bioactive Ingredients: Potential Uses for Enhancing Immune Systems and Preventing Viruses. Front Nutr 2021, 8, 772033. [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Mártinez-González, M.A.; Hu, F.B.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nature reviews. Disease primers 2017, 3, 17034. [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhou, B.J.; Sui, J.; Ma, W.Q.; Wang, S.K.; Yang, L.G.; Sun, G.J. Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide Regulates the Lipid Metabolism and Alters Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Induced Obese Mice. Int J Env Res Pub He 2022, 19, 12093. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.A.; Guo, M.K.; Zheng, P.; Liu, R.Y.; Wang, D.D.; Zhao, D.Q.; Wang, M.X. Effects of sulfated polysaccharides from Laminaria japonica on regularating the gut microbiotan and alleviating intestinal inflammation in obese mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2022, 168, 113401. [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Sun, W.Z.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Wang, B.W.; Sun, B.G. Protective Effects of Natural Polysaccharides on Intestinal Barrier Injury: A Review. J Agr Food Chem 2022, 70, 711–735. [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, M. The role of dietary fibers in regulating appetite, an overview of mechanisms and weight consequences. Crit Rev Food Sci 2022, 70, 711–735. [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, C.E.; Spalding, K.L. White adipocyte dysfunction and obesity-associated pathologies in humans. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 2024, 25, 270–289. [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Deehan, E.C.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. Auricularia auricula polysaccharides attenuate obesity in mice through gut commensal Papillibacter cinnamivorans. J Adv Res 2023, 52, 203–218. [CrossRef]
- Recharla, N.; Geesala, R.; Shi, X.-Z. Gut Microbial Metabolite Butyrate and Its Therapeutic Role in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2275. [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.J.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Feng, W.W.; Gao, H.; Tang, Y.P.; Yan, D. Anti-obesity and Gut Microbiota Modulation Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides Combined with Berberine on High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese Mice. Chin J Integr Med 2023, 29, 617–625. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, J.H.; Yan, L.P.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.J.; Wu, S.Y.; Chen, L.; Thring, R.W.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.T.; et al. Fucoidan Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance Associated with the Improvement of Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota Profile. J Agr Food Chem 2020, 68, 10626–10638. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-S.; Lu, C.-C.; Martel, J.; Ko, Y.-F.; Ojcius, D.M.; Tseng, S.-F.; Wu, T.-R.; Chen, Y.-Y.M.; Young, J.D.; et al. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 7489. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.R.; Lin, C.S.; Chang, C.J.; Lin, T.L.; Martel, J.; Ko, Y.F.; Ojcius, D.M.; Lu, C.C.; Young, J.D.; Lai, H.C. Gut commensal Parabacteroides goldsteinii plays a predominant role in the anti-obesity effects of polysaccharides isolated from Hirsutella sinensis. Gut 2019, 68, 248–262. [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.C.; Guo, W.L.; Li, L.; Yu, X.D.; Liu, B. Polysaccharide peptides from Ganoderma lucidum ameliorate lipid metabolic disorders and gut microbiota dysbiosis in high-fat diet-fed rats. J Funct Foods 2019, 57, 48–58. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Jia, J.H.; Jiang, P.R.; Zheng, W.Y.; Li, X.F.; Song, S.; Ai, C.Q. Polysaccharides from edible brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida are effective against high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice through the modulation of intestinal microecology. Food Funct 2022, 13, 2581–2593. [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, B.; Du, A.Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Lu, D.Z.; Zhu, Z.H.; Ke, S.Z.; Wang, S.J.; Yu, Y.L.; Chen, J.W.; et al. Saccharina japonica fucan suppresses high fat diet-induced obesity and enriches fucoidan-degrading gut bacteria. Carbohyd Polym 2022, 290, 119411. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; You, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Ai, C.Q.; Huang, L.L.; Wang, S.T.; Wang, Z.F.; Song, S.; Zhu, B.W. Anti-obesity effects of Laminaria japonica fucoidan in high-fat diet-fed mice vary with the gut microbiota structure. Food Funct 2022, 13, 6259–6270. [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.M.; Sun, X.N.; Ma, N.; Liu, Y.L.; Luo, T.R.; Song, S.; Ai, C.Q. Polysaccharides from Laminaria japonica alleviated metabolic syndrome in BALB/c mice by normalizing the gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 121, 996–1004. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhu, S.Q.; Li, S.Y.; Feng, Y.N.; Wu, H.H.; Zeng, M.Y. Microalgae polysaccharides ameliorates obesity in association with modulation of lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in high-fat-diet fed C57BL/6 mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 182, 1371–1383. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zeng, R.; Tang, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, C. The “crosstalk” between microbiota and metabolomic profile in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice supplemented with Bletilla striata polysaccharides and composite polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 130018. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shang, B.; Zhou, F.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, F.; Cao, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, K.; Zeng, X.; Li, M. Polysaccharides of Aspergillus cristatus attenuate obesity by regulating gut microbiota and gut microbiota-related metabolites. Food Sci Hum Well 2024, 13, 1513–1530. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Xia, Q.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Shao, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, S.; Huang, P. Amelioration of obesity and inflammation by polysaccharide from unripe fruits of raspberry via gut microbiota regulation. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 261, 129825. [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, H.; Luo, H.; Yin, X.; Zheng, H. Raspberry polysaccharides attenuate hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress in diet-induced obese mice by enhancing butyrate-mediated intestinal barrier function. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 262, 130007. [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Kubota, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Tsugawa, H.; Suda, W.; Kwon, A.T.J.; Yazaki, J.; Ikeda, K.; Nemoto, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; et al. Gut microbial carbohydrate metabolism contributes to insulin resistance. Nature 2023, 621, 389–395. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Chen, M.Y.; Song, J.N.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Gong, P.; Chen, X.F. Effects of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharides on Gut Microbiota Composition in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 6061. [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lu, X.Y.; Chang, Y.N. Auricularia auricula-judae (Bull.) polysaccharides improve type 2 diabetes in HFD/STZ-induced mice by regulating the AKT/AMPK signaling pathways and the gut microbiota. J Food Sci 2021, 86, 5479–5494. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Chen, X.F.; Song, J.N.; Chen, M.Y.; Gong, P.; Jia, W.; Li, G.L. Hypoglycemic effects of Auricularia auricula polysaccharides on high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice using metabolomics analysis. Food Funct 2021, 12, 9994–10007. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, S.; He, H.; Zuo, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; et al. Parabacteroides distasonis ameliorates insulin resistance via activation of intestinal GPR109a. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 7740. [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.M.; Xiao, C.; Yong, T.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hu, H.P.; Xie, T.; Liu, R.J.; Huang, L.H.; Li, X.M.; Xie, Y.Z.; et al. A polysaccharide isolated from Ganoderma lucidum ameliorates hyperglycemia through modulating gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 197, 23–38. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, D.; Liu, W.; Song, Y.; Zou, B.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Cai, Y.; Liu, D.; Liao, Q.; et al. Intake of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides reverses the disturbed gut microbiota and metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 155, 890–902. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zeng, W.Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.F. Characterization of Acidic Tea Polysaccharides from Yellow Leaves of Wuyi Rock Tea and Their Hypoglycemic Activity via Intestinal Flora Regulation in Rats. Foods 2022, 11, 617. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Zhao, W.Y.; Xie, B.Z.; Liu, H. Effects of Auricularia auricula and its polysaccharide on diet-induced hyperlipidemia rats by modulating gut microbiota. J Funct Foods 2020, 72, 104038. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Xiao, D.; Liu, W.; Song, Y.F.; Zou, B.R.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Cai, Y.; Liu, D.L.; Liao, Q.F.; et al. Intake of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides reverses the disturbed gut microbiota and metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 155, 890–902. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Y.; Zhai, R.H.; Xie, X.Q.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, H.C.; Nie, C.X.; Yuan, X.J.; Tu, A.B.; Tian, B.M.; et al. Hypoglycemic Effects of Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice Modulating Gut Microbiota. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 916271. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.T.; Yang, T.T.; Xu, W.Q.; Huang, Y.J.; Ran, L.W.; Yan, Y.M.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.X.; et al. The polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. confer anti-diabetic effect by regulating gut microbiota and intestinal barrier. Carbohyd Polym 2022, 291, 119626. [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Lin, Y.; Xie, H.L.; Farag, M.A.; Feng, S.M.; Li, J.J.; Shao, P. Dendrobium officinale leaf polysaccharides ameliorated hyperglycemia and promoted gut bacterial associated SCFAs to alleviate type 2 diabetes in adult mice. Food Chem X 2022, 13, 100207. [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Farooqui, N.A.; Alam, G.; Gul, A.; Ahmad, B.; Asim, M.; Khan, A.I.; Xin, Y.; Zexu, W.; et al. Morchella esculenta mushroom polysaccharide attenuates diabetes and modulates intestinal permeability and gut microbiota in a type 2 diabetic mice model. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 984695. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Chen, C.; Fu, X. Hypoglycemic effect of the polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus on type 2 diabetic mice based on the "gut microbiota-mucosal barrier". Food Funct 2022, 13, 10121–10133. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.D.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Ren, X.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Dai, J.Y.; Xiu, Z.L.; Yu, S.Q.; Dong, Y.S. Dendrobium officinale Polysaccharide Prevents Diabetes via the Regulation of Gut Microbiota in Prediabetic Mice. Foods 2023, 12, 2310. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; An, G.Q.; Peng, X.Z.; Zhong, F.R.; Zhao, K.; Qi, L.M.; Ma, Y.T. Effects of three Huanglian-derived polysaccharides on the gut microbiome and fecal metabolome of high-fat diet/streptozocin-induced type 2 diabetes mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 273, 133060. [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Ge, X.; Zhao, R.; Liu, B.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, C. Laminaria japonica polysaccharide alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating the microbiota-gut-liver axis: A multi-omics mechanistic analysis. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 258, 128853. [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C. Effects of Black Quinoa Polysaccharides on Obesity and Intestinal Flora Dysbiosis in T2DM Mice. J Food Biochem 2024, 2024, 5473584. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.; Fu, Z.; Jin, T.; Song, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, C. Polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus attenuate type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 262, 130062. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Deng, S.; Shen, G.; Liu, S.; Xiang, X. Hypoglycemic mechanism of Tegillarca granosa polysaccharides on type 2 diabetic mice by altering gut microbiota and regulating the PI3K-akt signaling pathway. Food Sci Hum Well 2024, 13, 842–855. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ma, J.; Rozi, P.; Kong, L.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, H. The polysaccharides from seeds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis ameliorate metabolic disorders and restructure gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 264, 130622. [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Sheng, L.L.; Zhong, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, W.Z.; Ma, J.L.; Yan, J.; Zhao, A.H.; Zheng, X.J.; Wu, G.S.; et al. Desulfovibrio vulgaris, a potent acetic acid-producing bacterium, attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut microbes 2021, 13, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.Y.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, H.S.; Rong, A.; Xu, G.Q.; Cai, F.J.; Yang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.G. Astragalus mongholicus polysaccharides ameliorate hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation as well as modulate gut microbiota in NAFLD rats. Food Funct 2022, 13, 7287–7301. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gu, X.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Increased Plasma LPS and TMAO Levels in Patients With Preeclampsia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 409. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Dong, W.; Fan, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, G.J.; Zeng, X.X.; Ye, H. The polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease modulating gut microbiota and bile acids metabolism. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 246, 125662. [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Sheng, L.; Zhong, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, W.; Ma, J.; Yan, J.; Zhao, A.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G.; et al. Desulfovibrio vulgaris, a potent acetic acid-producing bacterium, attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.Y.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, H.S.; Rong A.; Xu, G.Q.; Cai, F.J.; Yang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.G. Astragalus mongholicus polysaccharides ameliorate hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation as well as modulate gut microbiota in NAFLD rats. Food Funct 2022, 13, 7287–7301. [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.L.; Ma, J.M.; Fan, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ge, R.; Tao, X.J.; Zhang, M.W.; Gao, Q.H.; Yang, J.J. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide combined with aerobic exercise ameliorated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through restoring gut microbiota, intestinal barrier and inhibiting hepatic inflammation. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 183, 1379–1392. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Yang, L.H.; Zhao, N.N.; Hong, Z.; Cai, B.; Le, Q.Q.; Yang, T.; Shi, L.J.; He, J.L. Soluble Polysaccharide Derived from Laminaria japonica Attenuates Obesity-Related Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Gut Microbiota Regulation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 699. [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.C.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Y.J.; Li, L.; Guo, W.L.; Lin, X.B.; Huang, Z.R.; Rao, P.F.; Ai, L.Z.; Ni, L. Organic chromium derived from the chelation of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide and chromium (III) alleviates metabolic syndromes and intestinal microbiota dysbiosis induced by high-fat and high-fructose diet. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 219, 964–979. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Zheng, M.X.; Zhou, M.L.; Zhou, L.M.; Ge, X.; Pang, N.; Li, H.C.; Li, X.Y.; Li, M.D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Lentinan Supplementation Protects the Gut-Liver Axis and Prevents Steatohepatitis: The Role of Gut Microbiota Involved. Front Nutr 2022, 8, 803691. [CrossRef]
- Preethy, S.; Ikewaki, N.; Levy, G.A.; Raghavan, K.; Dedeepiya, V.D.; Yamamoto, N.; Srinivasan, S.; Ranganathan, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Senthilkumar, R.; et al. Two unique biological response-modifier glucans beneficially regulating gut microbiota and faecal metabolome in a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis animal model, with potential applications in human health and disease. Bmj Open Gastroenter 2022, 9, e000985. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. MDG, an Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide, inhibits non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating the abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 196, 23–34. [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Li, Z.S.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, X.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Geng, Z.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Pan, X.Z.; et al. Lonicerae flos polysaccharides improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating the adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase pathway and reshaping gut microbiota. J Sci Food Agr 2023, 103, 7721–7738. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Lan, X.T.; Peng, X.; Shi, S.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, W.T.; Luo, Q.H.; Jia, L.L.; Feng, B.; Chen, Z.L.; et al. Polysaccharide from Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma Attenuates the Progress of Obesity-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Modulating Intestinal Microbiota-Related Gut-Liver Axis. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 10620. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Xiao, M.M.; Luo, J.G.; Li, S.J.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, J.C.; Song, Z.Y. Polysaccharides from Ostrea rivularis rebuild the balance of gut microbiota to ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in ApoE-/- mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 235, 123853. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, G. Smilax china L. polysaccharide prevents HFD induced-NAFLD by regulating hepatic fat metabolism and gut microbiota. Phytomedicine 2024, 127, 155478. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yao, S.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Shen, G.; Xiang, X.; Chen, L. Exploring the Regulatory Effect of Tegillarca granosa Polysaccharide on High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice Based on Intestinal Flora. Mol Nutr Food Res 2024, 2300453. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yin, W.; Hao, P.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H. Polysaccharide from Panax japonicus CA Mey prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development based on regulating liver metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 260, 129430. [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Wu, J.; Tang, B.; He, X.; Ding, X.; Ren, X.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, S. Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi polysaccharides ameliorates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and intestinal flora disorders in mice. J Funct Foods 2024, 117, 106247. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Yue, Z.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, Y.D.; Li, C.; Liu, X.T.; Shi, R.H.; Huo, N.N.; Li, D.D.; Gao, S.; et al. Synergistic effect of polysaccharides and flavonoids on lipid and gut microbiota in hyperlipidemic rats. Food Funct 2023, 14, 921–933. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Lai, G.X.; Guo, Y.R.; Tang, X.C.; Shuai, O.U.; Xie, Y.Z.; Wu, Q.P.; Chen, D.L.; Yuan, X.J. Protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum spore extract in trimethylamine-oxide-induced cardiac dysfunction in rats. J Food Sci 2021, 86, 546–562. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, B.; Tao, H.T.; Li, J.P.; Wu, Z.Z.; Liu, G.M.; Yuan, C.; Guo, L.; Cui, B. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide attenuates myocardial injury in high-fat diet-fed mice through manipulating the gut microbiome and fecal metabolome. Food Res Int 2020, 138, 109778. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.P.; Zhu, L.J.; Zhang, F.M.; Li, H.L.; Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Yuan, J.; Shi, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.H.; Hu, Y.D. Protective activities of polysaccharides from Cipangopaludina chinensis against high-fat-diet-induced atherosclerosis regulating gut microbiota in ApoE-deficient mice. Food Funct 2019, 10, 6644–6654. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.N.; Zou, L.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Zhao, G.; Hu, Y.C. Dietary quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) polysaccharides ameliorate high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia and modulate gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 163, 55–65. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.H.; Luo, L.M.; Luo, Q.; Xu, L.; Ma, Q.T.; Hong, T.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.Y. Dietary ginger polysaccharides (Gps) improve symptoms in hyperlipidemia rats via alterations in gut microbiota. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17534. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.L.; Deng, J.C.; Pan, Y.Y.; Xu, J.X.; Hong, J.L.; Shi, F.F.; Liu, G.L.; Qian, M.; Bai, W.D.; Zhang, W.; et al. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides and their relationships with the modulation of intestinal microflora in diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 153, 1231–1240. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, R.G.; Pan, J.L.; Qi, D.F.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.Y. The protective effects of walnut green husk polysaccharide on liver injury, vascular endothelial dysfunction and disorder of gut microbiota in high fructose-induced mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 162, 92–106. [CrossRef]
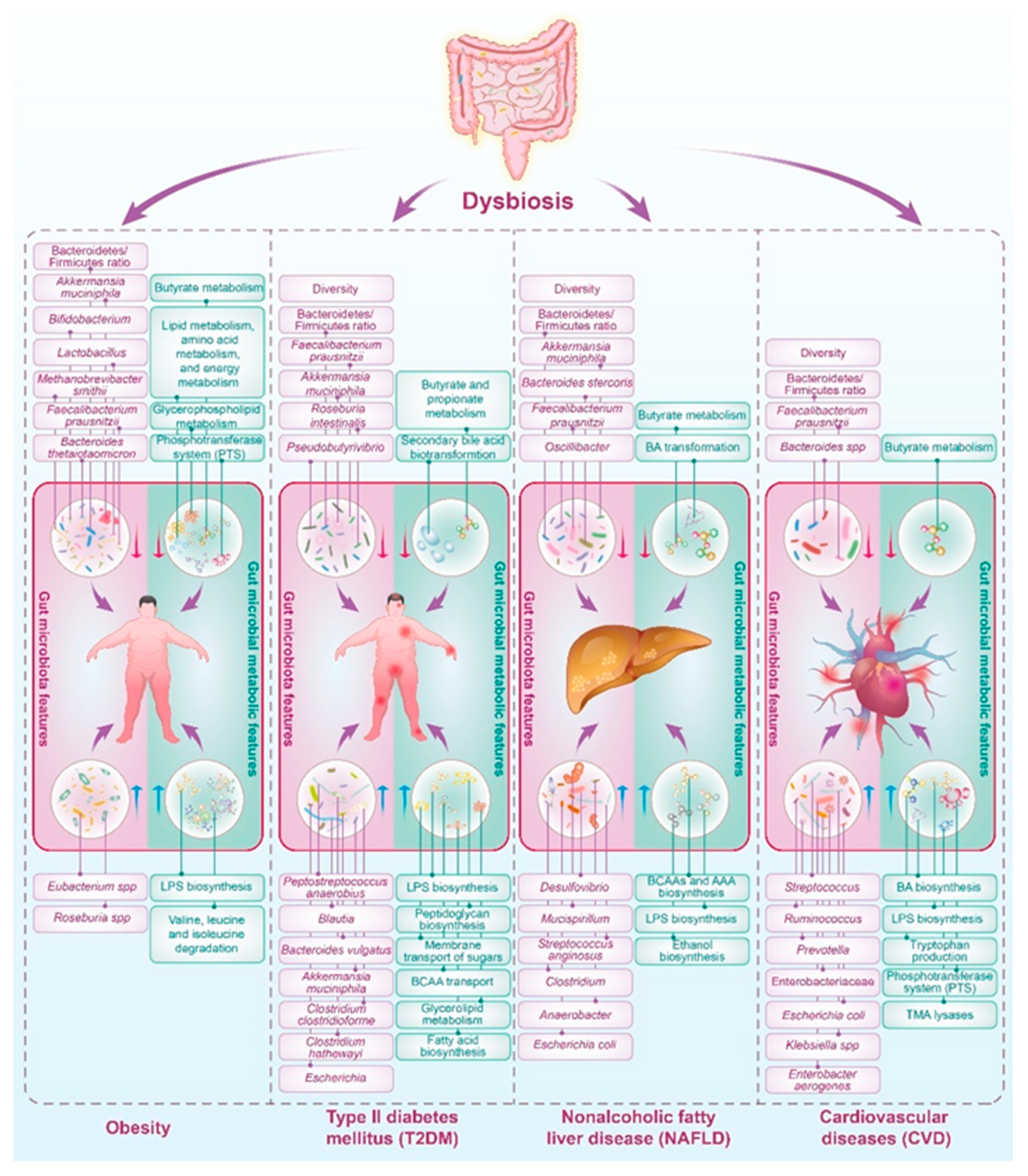
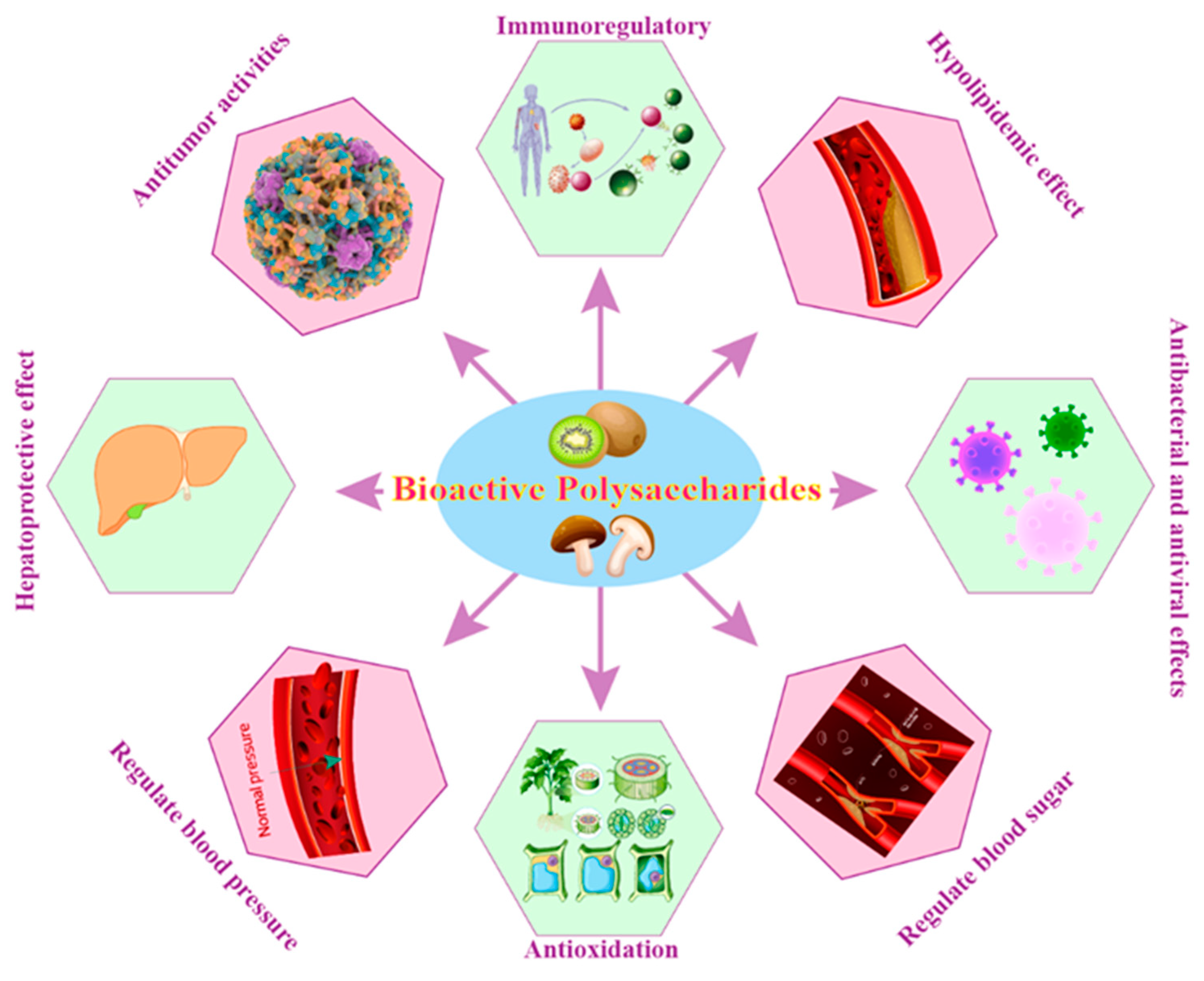
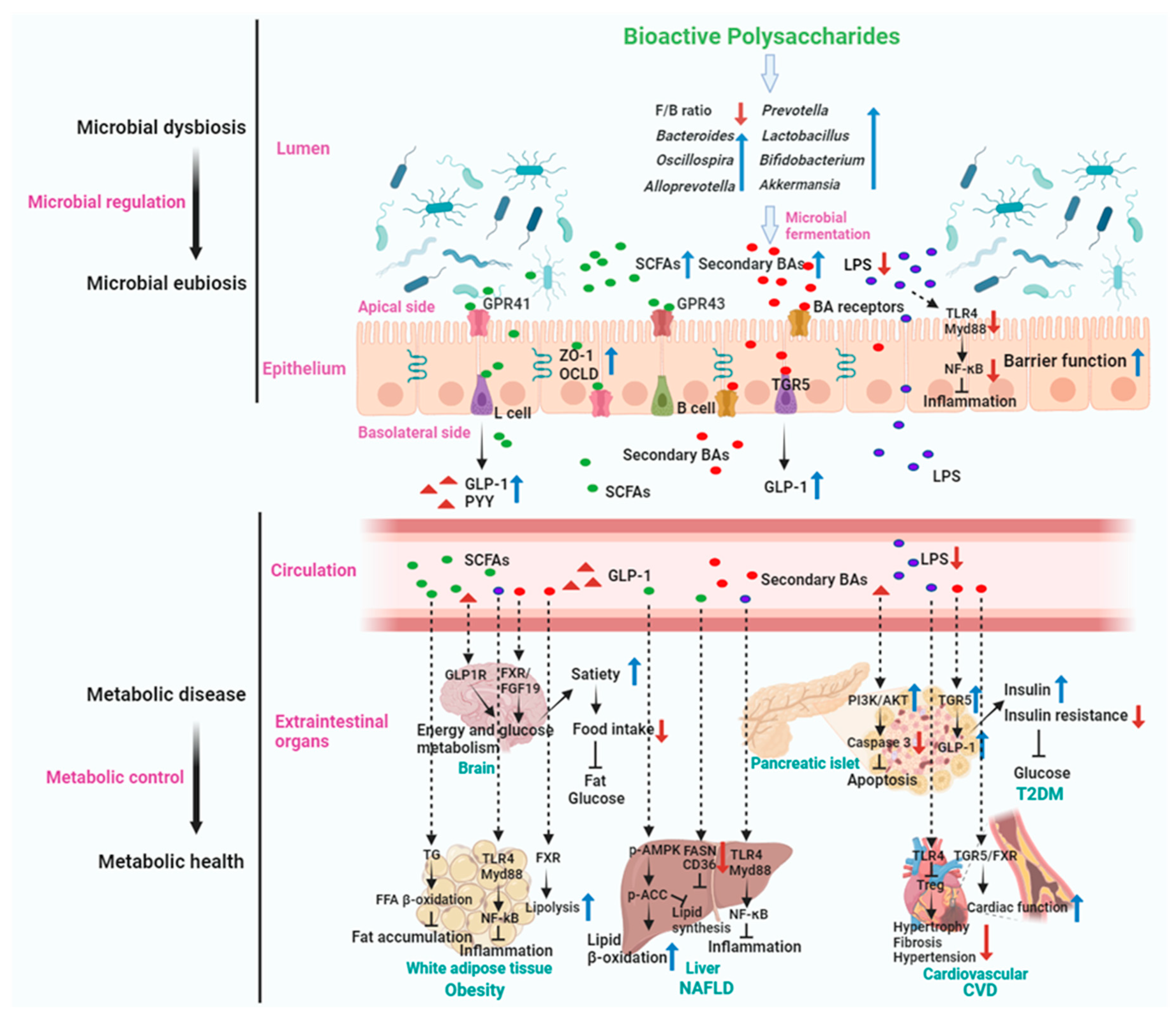
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





