1. Introduction
Cocoa bean shells (CBSs, also reported as “testa” and “husks” in the past), which constitute the 10%-17% of the beans total weight, are derived from the removal of the external layer of cocoa beans during the industrial process called winnowing. The winnowing is a procedure aimed to blow the shells during the pre-roasting phase [
1]. This product is currently considered as a waste material, even if its many positive nutritional features have been investigated in the recent past. CBSs are significantly rich in dietary fibers and proteins, with interesting amounts of several antioxidant bioactive compounds [
2,
3].
Even if CBSs represent a part of the cocoa plant that is not suitable for direct consumption (principally depending on the microbiological profile and the potential presence of xenobiotics and mycotoxins) and, in addition, considered a waste material from chocolate production, the chemical composition indicates a very good set of macro, micro, fibers and antioxidant qualities that deserve to be considered. In a future prospective, the implementation of the use of this matrix could be crucial for the development of new CBSs-based products which could claim healthy and functional characteristics.
An adequate amount of dietary fibers in human diet has been indicated as a key point to maintain a good health of our gastrointestinal system, gut microbiota colonization, absorption of nutrients and lower odds to develop diseases [
4,
5].
In Europe, the definition of dietary fibers is defined by EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) which takes under control the food labeling, trade and security. EFSA, following the regulation 1169/2011, define fibers as ‘carbohydrate polymers with three or more monomeric units, which are neither digested or absorbed in the human small intestine”.
The US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) gives a slightly different definition of what fibers are. FDA defines fibers as ‘non-digestible soluble and insoluble carbohydrates (with 3 or more monomeric units), and lignin that are intrinsic and intact in plants beneficial to human health’ [
6]. Many definitions were proposed by different world’s authorities, in this sense the CODEX Alimentarius Commission tried to sum up these definitions focusing the attention on the healthy significance that dietary fibers have un human health, this created guidelines that can be followed by all the world food authorities and citizens [
7].
The main fibers present in CBSs are pectin, cellulose, and hemicellulose. As previously enlightened, fibers have been linked with many health benefits for humans: improvement of the gastrointestinal mobility [
4], a positive action on the microbiota regulation in the human gut [
5,
8]. Dietary fibers, soluble especially, are the most recognized regulator of the gut microbiota. The bacteria that compose our gastrointestinal microbiota can use the oligosaccharides we cannot digest to produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Short chain fatty acids can actively influence the human central nervous system by the gut-brain axis, the action of these molecules is important for the modulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic syndromes [
9].
Few attempts in the literature are reported to firstly evaluate the prebiotic potential of CBSs and secondly to enhance the fermentability by the gut microbiota. The work of Disca et al., (2024) highlighted that the CBSs enzymatically hydrolyzed improved SCFAs production (mainly acetate and butyrate) in simulated colon environment despite no change in solubility of the dietary fibers [
10]. Instead the work of Younes & Karboune, (2023) highlighted the possibility, through enzymatic treatment, to enhance oligosaccharides in CBSs [
11].
The primary objective of the study was to investigate the effects of enzymatic treatments using three different enzymes (cellulase, xylanase and pectinase), both individually and in various combinations, on raw and defatted cocoa bean shells. The focus was to assess whether these treatments could increase the solubility of the dietary fiber fraction without compromising the antioxidant properties of the cocoa bean shells. The enzymatic treatment was aimed at enhancing the health and functional properties inherent in the substrate. This approach is in line with the principles of the circular economy [
12] and aims to transform cocoa shells from a mere by-product of the chocolate industry into a novel ingredient with improved nutritional and functional properties. In essence, the research aimed to demonstrate that enzymatic treatments can effectively modify cocoa bean shells to make them more suitable for food-related industrial applications, thereby contributing to waste reduction and sustainability in the chocolate industry.
2. Materials and Methods
Materials
Reagents and solvents utilized in the experiment were procured from Sigma–Aldrich (Milano, Italy). Dichloromethane was acquired from Carlo Erba (Rodano, Milano, Italy). Methanol, water (LC-MS grade), and formic acid (50%, LC–MS grade) were sourced from Sigma–Aldrich (Milano, Italy). Water, utilized in the procedures, was obtained through the Milli-Q instrument (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA, USA). The reagents and standard chemicals for assessing total phenol content and antiradical activity were also obtained from Sigma–Aldrich (Milano, Italy).
Samples
The samples that have been used for the research were kindly provided by a leader Italian chocolate producer. The cocoa bean shells (CBSs) are Nacional variety originating from Ecuador.
Lipid Removal
Firstly, the cocoa bean shells were finely minced with a ball millet. The lipidic fraction removal was carried out with a semi-automatic extraction system BÜCHI B-811 LSV (BÜCHI, Switzerland) using dichloromethane as solvent with a cycle of 6h.
Enzymatic Treatment
The enzymatic treatment was performed utilizing 3 food grade enzymes (cellulase, EC 3.2.1.4; xylanase, EC 3.2.1.8.; pectinase, EC 3.2.1.15) in different combinations. The enzymes were produced and kindly donated by a leader supplier. The enzymatic reaction was performed by stabilizing the enzymes in a buffer solution to reach the optimal conditions for enzymes activity (citrate buffer pH 5; 1 mol/L). Four different combinations of the enzymes were tested: cellulase, xylanase, cellulase + xylanase, cellulase + xylanase + pectinase. For both the single enzyme and the combination, the enzymes concentration was calculated in order to reach a final enzymatic activity of 16.67 µkat/L of buffer. The treatment has been performed in duplicate, for both raw and defatted cocoa bean shells, in Erlenmeyer flask. A magnetic anchor on a magnetic plate has been used to avoid the formation of grumes. Enzymatic solution was transferred into the flasks in a ratio of enzymatic buffer/sample of 1:10 p/v. The flasks were then placed in a shaking incubator at 150 rpm for 2 hours with a constant temperature of 60 °C. After the end of the incubation time the enzymatic reaction was interrupted by thermal shock (80 °C for 5 min), subsequently the flasks were cooled on ice for 15-20 min. All the samples were stabilized by freeze drying and stored at -80 °C for the analysis.
Total, Insoluble and Soluble Dietary Fibers
Quantification of Soluble Dietary Fiber (SDF) and Insoluble Dietary Fiber (IDF) was conducted using the AOAC 991.43 method with a MES-Tris buffer as described elsewhere [
10]. In this procedure, samples underwent partial digestion with alpha-amylase, followed by subsequent digestion with protease and amyloglucosidase enzymes. Filtration was employed to remove the mass of undigested IDF, which was then dried and weighed. To precipitate soluble dietary fiber, ethanol 95% was used. The mass of undigested SDF was isolated, dried, and weighed. The determination of dietary fiber involved calculating the residue’s weight minus the protein and ash weights, expressed as a percentage of the original sample weight.
Total Phenolic Content
The determination of total phenolic content (TPC) followed the classical Folin-Ciocalteu assay, as outlined elsewhere [
13]. The results were expressed as mg catechin equivalents (CE) using a calibration curve (R
2=0.9905).
Total Flavonoid Content
To have the assessment of the total flavonoid content the colorimetric method with aluminum chloride (AlCl2) has been used. The aluminum chloride can react with flavones and flavonoids’ ketonic (C-4) and hydroxyl groups (C-3 or C-5) forming stable acids and changing its color giving a rose tonality. The results are expressed through interpolation of a calibration curve of (±)-catechin hydrate (R2=0.9996).
Total Procyanidins Content
For the determination of proanthocyanidin (PAC) content, the protocol described by Prior et al., (2010) was used, with some modifications [
14]. Phenolic extracts were opportunely diluted with a mixture of acetone, water and acetic acid (75:24.5:0.5,
v/v). Then, 280 μL of diluted extract (or 280 μL of solvent for the control) were added to 840 μL of DMAC (4-(dimethylamino) cinnamaldehyde) ethanolic solution (0.01%
w/v). The solution was left to react until the maximum absorbance value was reached (20 min), at 20 °C and away from the light, then the absorbance was read at 640 nm. Results were expressed as mg of catechin equivalents (CE) through a calibration curve.
Antiradical Activity
The assessment of radical scavenging activity employed the DPPH• assay, following the methodology reported elsewhere [
13]. CBSs extracts were subjected to triplicate assays, and the outcomes were articulated as mg of Trolox equivalent (TE).
HPLC-PDA Analysis
RP-HPLC-PDA analysis was carried out following the work of Bordiga et al., [
15] with minor modification. A Thermo Scientific chromatographic system equipped with a diode array detector (Accela PDA Detector) was used, the separation was performed on a reversed-phase Supelco Ascentis Amide (15 cm x 2.1 mm, 3µm, 100 Å) at 35 °C. Eluent A of the mobile phase consisted of water/ formic acid (99.9 : 0.1, v/v), while eluent B consisted of acetonitrile/ formic acid (99.9 : 0.1, v/v). The applied program gradient was the following: isocratic 2.5% B (10 min), from 2.5 to 12% B (10 min), isocratic 12% B (15 min), from 12% to 100% B (24 min), from 100 to 2.5% B (2 min), isocratic 2.5% B (9 min), with a total run time of 80 minutes. The flow rate and the injection volume were 400 μL/min and 5 μL, respectively. PDA detection was performed at 280 and 330 and quantification were performed based on calibration curves obtained with the corresponding standard compounds.
Statistics
The statistical analysis was conducted using the R software (version 4.3.0). The analysis test of one-factor variance (ANOVA) was used to determine the difference significant between samples followed by the Tukey multiple comparisons. In addition, multivariate hierarchical clustering on the principal components (HCPC) was performed.
4. Discussion
Authors should discuss the results and how they can be interpreted from the perspective of previous studies and of the working hypotheses. The findings and their implications should be discussed in the broadest context possible. Future research directions may also be highlighted.
The pre-treated CBSs characteristics in terms of moisture (%), ashes, fats, proteins, and dietary fibers, the fibers have been divided in total dietary fibers (TDF), insoluble dietary fibers (IDF) and soluble dietary fibers (SDF) are reported in
Table 1. Moisture excepted; the other values are referred to g/100 grams of CBSs.
According to the study performed by Agus et al., (2018) the average moisture value in roasted cocoa bean shells is around 4.32%, a value that is very close to the moisture that has been found in the provided CBSs samples of this study. A moisture below 7% has been reported to be effective in limiting the microbial growth in foods, increasing the storability and shelf life [
16]. The average value of ashes has been reported to be 7,76 g /100 g, this value is very similar to what obtained by Mellinas et al., (2020) (6.0 ± 0.1) but distant from the results of Agus et al., (2018) with almost 11% for roasted cocoa shells; Arlorio et al., (2005) have reported an ashes percentage, in Italian roasted cocoa shells around 2%, and so very low [
16,
17,
18].
The fat content in the provided CBSs is reported to be around 8 g/100 g, this value is again in line with what claimed for other studies, the value is attested to be around 7% (g /100 g dry weight) [
19], depending on the processing and the plants. In terms of protein content, the amount of protein in CBSs is reported to be 10%, which is in line with other findings, but is reported to be quite low compared to various studies that have reported CBSs containing protein between 12-25% [
18,
19]. Also in this case, the origin of cocao as well as the ecotype can stronlgy impact on this parameter. The amount of protein of a given cocoa quality may be relevant to the use of CBSs as a source of protein to be extracted and used as an ingredient in other foods [
20], as unconventional source of proteins. The high value of the cocoa’s proteins could be related to the absence of common allergens, considering the very low frequence of appearance of adverse reaction to these proteins [
21].
The most relevant value characterizing CBSs is represented by the fiber content. In this case, the CBS samples have a total fiber content of more than 60 g/100 g dry weight, this value can be broken down into insoluble fiber (44 g/100 g) and soluble fiber (17 g/100 g). The average dietary fiber reported in literature for CBSs corresponds to the value reported for the samples of this experiment, 20-66 g/100 g dry weight of TDF, depending on the type of cocoa. The values of insoluble and soluble fibers correspond to those reported in the literature, with 2/3 of the fibers being insoluble and 1/3 soluble [
20,
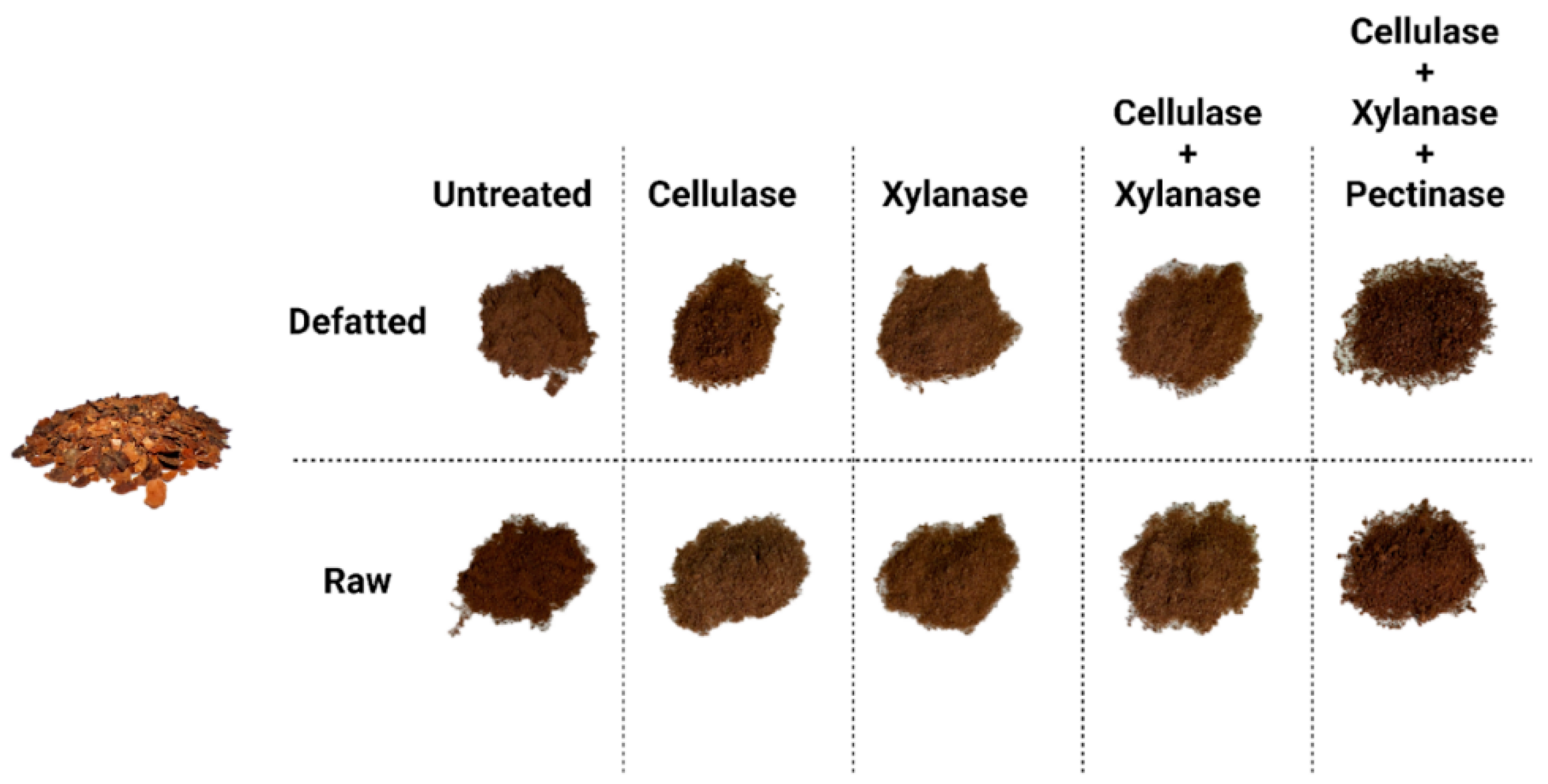
22]. After the enzymatic treatment performed on CBSs and defatted CBSs some appearance differences over the samples have been registered as shown in
Figure 1. After the freeze-drying the samples obtained were again milled in a fine powder, as shown in
Figure 1.
Dietary Fibers Analysis
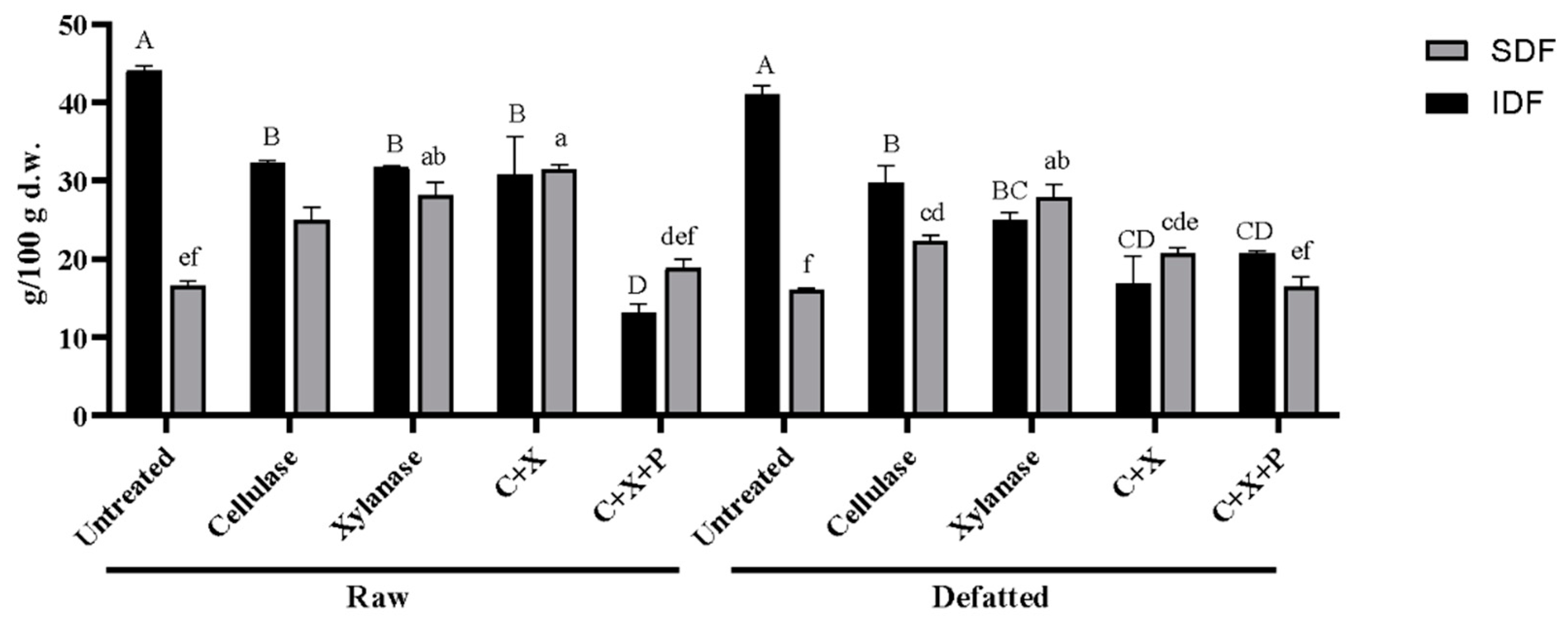
Figure 2 shows the measured amount of insoluble and soluble fiber in raw and defatted CBSs and the same treated with the enzymes. The aim of the enzymatic treatment was to use the enzymes to break down polysaccharides, releasing oligosaccharides and enriching the samples in simple carbohydrates. These sugars can be functionally used by microbial bacterial species for energy production. Most enzymes on the market catalyze the breakdown of plant cell walls to give fermentable monosaccharides; moreover, most high performing enzymes are isolated from bacteria [
23].
Results related to the IDF and the SDF are reported in
Figure 2, expressed as g over 100 g dw. For the raw samples, the untreated SDF content was 16.61/100 g. Treatment with cellulase increased the SDF to 24.93 ± 1.72 g/100 g dw and xylanase further increased it to 28.18 ± 1.58 g/100 g dw. The combination of cellulase and xylanase (C+X) resulted in the highest SDF of 31.57 ± 0.47 g/100 g dw, while the addition of pectinase (C+X+P) reduced it to 18.94 ± 1.05 g/100 g.
In defatted samples, untreated SDF was 16.04 ± 0.28 g/100 g. Cellulase treatment increased the SDF to 22.37 ± 0.69 g/100 g dw, and xylanase to 27.90 ± 1.51 g/100 g de. The combination of cellulase and xylanase (C+X) yielded an SDF of 20.79 ± 0.62 g/100 g dw, and the addition of pectinase (C+X+P) resulted in 16.53 ± 12.37 g/100 g dw. Enzymatic treatments significantly increased the SDF content, particularly with xylanase and the combination of cellulase and xylanase.
Instead, for the IDF fraction, the raw untreated CBSs shown a quantity of 44.08 ± 0.61 g/100 g dw. Cellulase treatment reduced the IDF to 32.29 ± 0.22 g/100 g dw, and xylanase further reduced it to 31.75 ± 0.09 g/100 g dw. The combination of cellulase and xylanase (C+X) resulted in an IDF of 30.87 ± 4.82 g/100 g dw, and the addition of pectinase (C+X+P) significantly reduced it to 13.17 ± 1.08 g/100 g dw.
In defatted samples, untreated IDF was 41.01 ± 1.15 g/100 g dw. Cellulase treatment reduced the IDF to 29.78 ± 2.17 g/100 g dw, and xylanase reduced it further to 25.02 ± 0.94 g/100 g dw. The combination of cellulase and xylanase (C+X) resulted in an IDF of 16.94 ± 3.43 g/100 g dw, while the addition of pectinase (C+X+P) led to an IDF of 20.77 ± 2.6 g/100 g dw.
The
Table 2 shows the SDF/IDF ratio. This value offers insight into the proportion of soluble to insoluble fibers. Enzymatic treatments generally increased the ratio, indicating a shift towards higher soluble fiber content. For raw samples, the untreated ratio was 0.38, which increased to 1.30 with cellulase treatment, 1.13 with xylanase, and 0.98 with the combination of cellulase and xylanase (C+X). The addition of pectinase (C+X+P) reduced the ratio to 0.69.
Considering the defatted samples, the ratio in untreated samples was 0.39, which increased to 1.33 after cellulase treatment, 0.89 with xylanase, and 0.81 with the combination of cellulase and xylanase (C+X). The addition of pectinase resulted in a ratio of 1.26. These changes in the SDF/IDF ratio are consistent with the literature, suggesting that enzymatic treatments enhance the solubility of dietary fibers, thus improving their functional properties and health benefits.
The combined action of the enzymes theoretically allowed the breakdown of bonds of the main polysaccharides of cocoa peels, generating smaller chains and soluble and oligosaccharides potentially prebiotic. Few works have investigated the effect of enzymatic treatments on cocoa bean shells. A study performed by Ramos et al., (2008) has investigated the effect of a wide range enzyme sets. Applying the enzymatic treatment the researchers obtained a matrix rich in fibers which can be potentially used by humans’ gut microorganisms to produce short chain fatty acids. Other works have investigated the action of similar enzymes on different substrates like in Napolitano et al., (2009) with the investigation of the enzymatic treatment’s effects on
Triticum durum [
24,
25]. The registered increment in this matrix was almost 300% in soluble fiber fraction. A boost of prebiotic effect in post-enzymatic treated food samples have been confirmed in other works. Some examples are the experiments performed on okara (pasta obtained after soymilk squeezing, during soy milk production) where an increased prebiotic effect has been registered [
26] and the production of a functional strawberries-based beverage, with an increased amount of dietary fibers. mainly represented by fructo-oligosaccharides [
30].
A recent work of Disca et al., (2024) highlighted that the enzymatic treatment on CBSs permitted to boost SCFAs production in simulated proximal colon environment. The production of acetate and butyrate was higher after 24 hours of fermentation. Despite these findings, the enzymatic treatment did not augment the soluble fiber portion and the SDF/IDF ratio [
10]. Moreover, a recent study of Younes & Karboune, (2023) investigates the enzymatic generation of CBSs oligosaccharides using bi-enzymatic and multi-enzymatic systems, focusing on structural characterization and prebiotic activity assessment, enzymatically generated non-digestible oligosaccharides from CBSs have shown significant prebiotic activity, promoting the growth of probiotic strains like
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and
Bifidobacterium longum [
11]. In addition, a very recent study, enlighten the possibility to pilot produce oligosaccharides from CBSs by isolating the pectic fraction through alkaline treatment and hydrolyze the fiber utilizing Depol
TM 670L, showing prebiotic and antioxidant properties [
27].
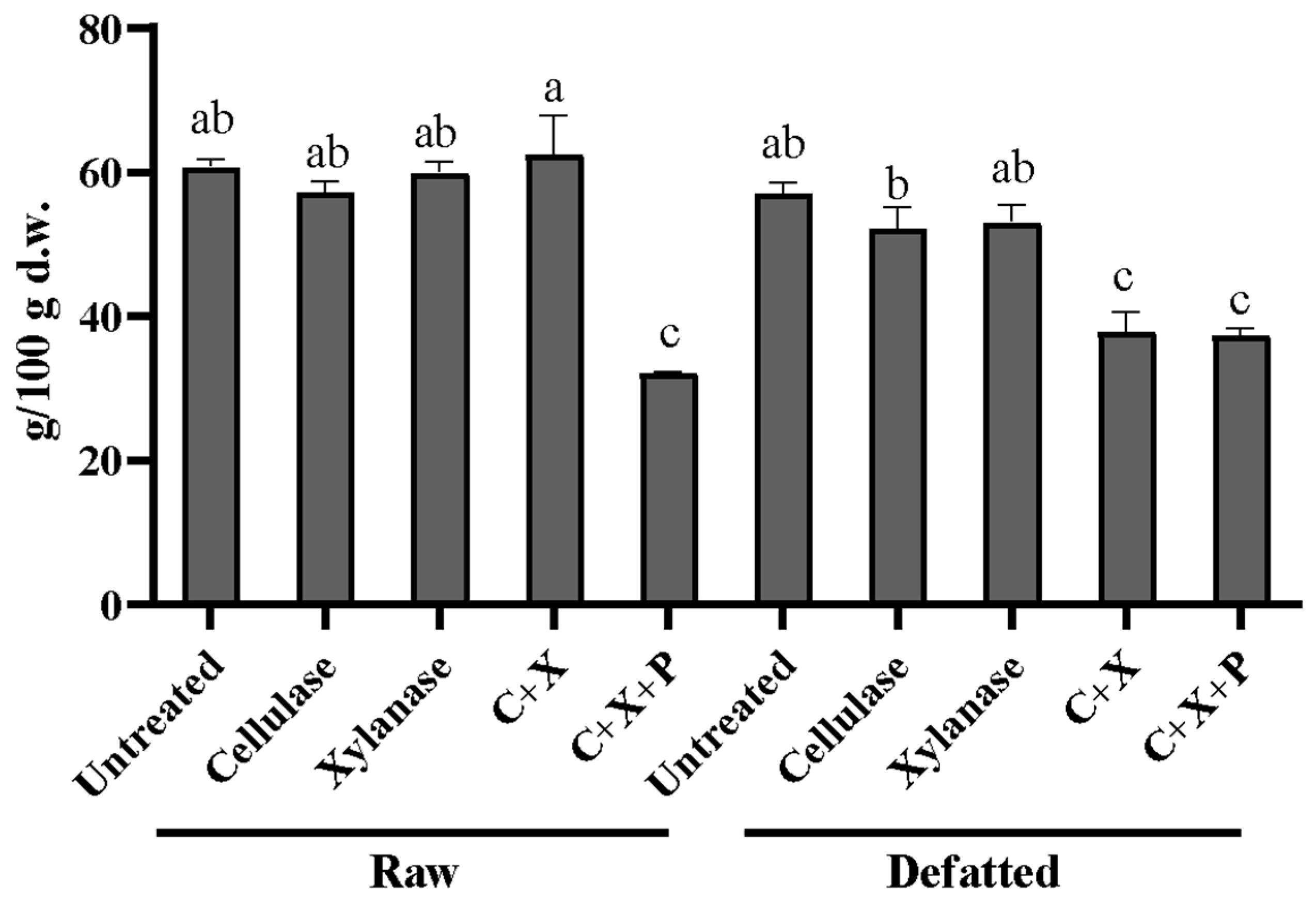
Peculiar is the reduction in TDF for samples treated with the combination of the three enzymes (C+X+P) for both defatted and raw CBSs and the treatment with xylanase on defatted CBSs as reported in
Figure 3. This could be explained by a very strong hydrolysis that generated soluble oligosaccharides that escaped precipitation in ethanol. Similar results were obtained by Jagelaviciute et al. (2023) who treated apple pomace with a commercially available carbohydrase and obtained a decrease in IDF and SDF by obtaining oligomers and monomers that do not precipitate in ethanol [
28]. In fact, recent observations published by McCleary and McLoughlin reported that more advanced methods allow the quantification of SDF that escapes the precipitation step [
29].
Total Phenolic Content
The quantification of the total phenolic content of post-enzymatic treatment CBSs and defatted CBSs has been performed through the
Folin-Ciocalteu assay. The results are expressed as mg of catechin equivalent (mg/g of dry weight) in
Table 3.
The results in this case were not statistically significant in terms of difference between the untreated CBSs and the treated samples. This is a quite positive result because the amounts of bioactive phenolics in the samples are preserved despite the treatments. This indicates that the enzymatic treatment, which has been positively linked with the amounts of dietary fibers in many of these samples, did not negatively affect the total phenolic content of the samples, which remains very similar in all the cases.
The results give a suggestion that the stabilization through freeze-drying could be a solution if compared to conventional oven drying. In fact the thermal stability and the phenolic content has already been investigated by a study which has shown that a thermal procedure of only 60 °C has the power to decrease the total phenolic content of 15-20% [
30]. Thermal treatments. below or above 100 °C impact the TPC with a possible reduction of 30-50% on average [
31]. Another study performed by Huynh et al., (2023) investigated the phenolic content of cocoa bean shells after sonication procedure and enzymatic treatment with Viscozyme® L (mixture of beta-glucanases, pectinases, hemicellulases and xylanases) [
32]. In that case, the more the enzymes’ concentration was high and more the TPC increased, while the incubation time wasn’t correlated with a TPC incrementation. In the same study the stabilization procedure has not been investigated.
These results are very encouraging because the polyphenols are very powerful antioxidants important in the human diet. The antioxidant power of polyphenols can decrease inflammation and prevent the development of cardiovascular and gastrointestinal diseases, like previously discussed in this work. These results can encourage future works to further investigate enzymatic treatment retaining the anti-inflammatory potential of the substrate.
Total Flavonoid Content
The total flavonoid content has been investigated using aluminum chloride assay. The final concentration of flavonoids has been found by interpolation between the calibration curve and the results expressed as mg/equivalent catechin [
33].
As the
Table 3 shows, untreated CBSs and enzymatically treated CBSs registered almost no change in the final flavonoids content. For defatted CBSs the results are mildly different. Defatted untreated CBSs shows more flavonoids content than raw CBSs (9.5 and 7.6 mg/g dw, respectively) but, after enzymatic hydrolysis, the defatted samples showed a similar content when compared to the raw untreated and treated CBSs, ranging from 6.5 to 7 mg/g dw. After the quantification of the total flavonoid content, it was possible to investigate how the content of flavonoids, another class of antioxidants and pigments present in cocoa and cocoa bean shells, changed after the enzymatic treatments of the samples.
The results contrast with the work of Huynh et al., (2023) which has registered very low TFC in CBSs samples after the treatment with Viscozyme® L, with a TFC around 3.5 mg/g dw that was not correlated with the enzymes used [
32]. The incubation time affected more the final TFC, besides this result, increasing the incubation time did not increase the final TFC content. In another work the TFC has been evaluated using sonication and modern extractive systems. the results obtained from the CBS was 7.47 mg of rutin equivalent per gram of dry weight [
34].
Antiradical Activity
The antiradical activity (AA) quantification has been obtained thanks to the DPPH (2.2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical quenching assay. The results have been expressed as mg of Trolox equivalent (mg T.E./g dw).
As
Table 3 shows, the results remained very stable. The only reduction in AA registered has been given by the sample treated with C+X.
Multivariate Analysis (HCPC)
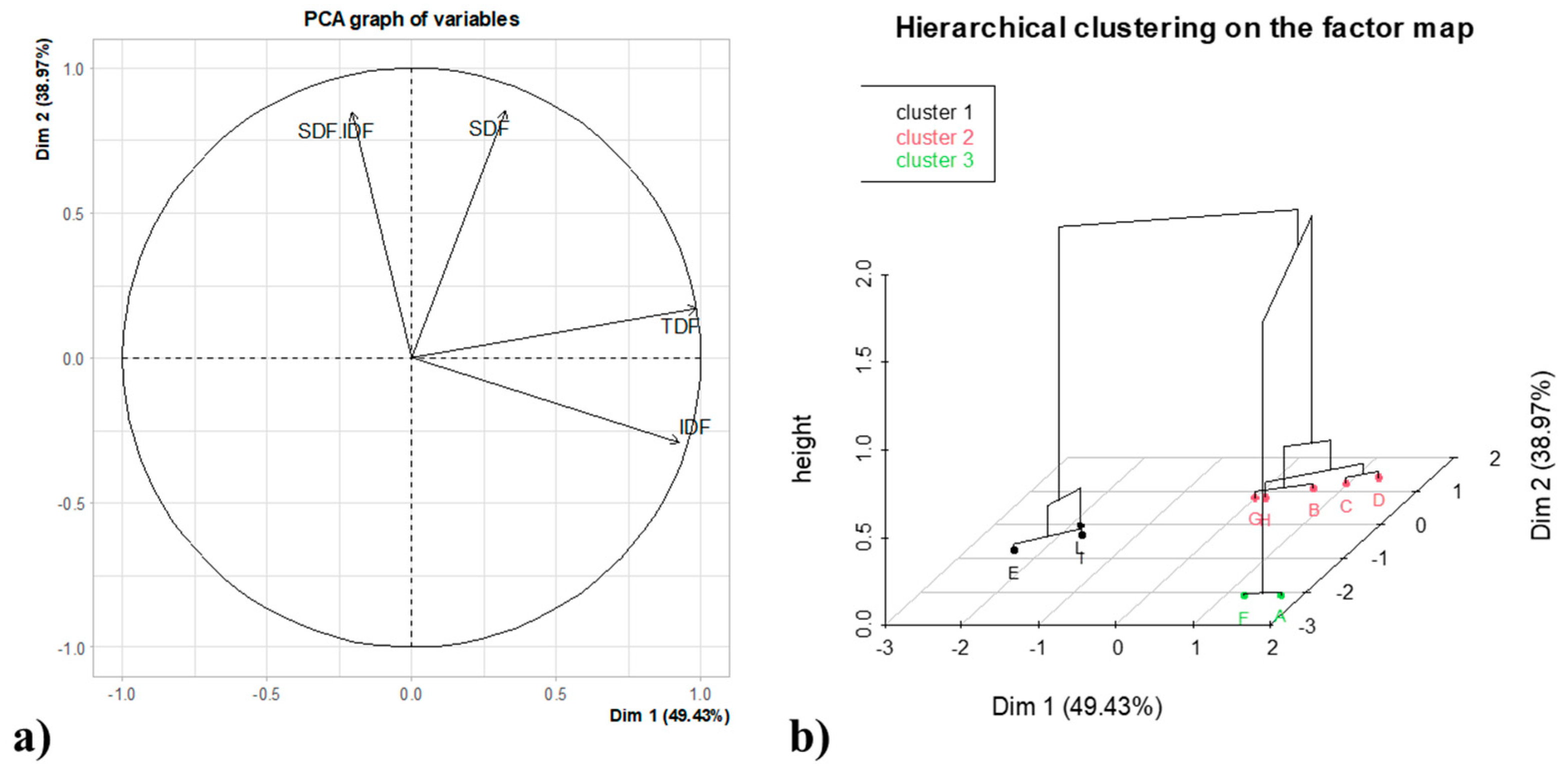
The multivariate analysis was carried out by applying the hierarchical clustering based on principal component analysis. The statistical analysis performed was applied in order to evaluate the differences among the treated and untreated samples, as reported in
Figure 4. The samples have been grouped in three different clusters, depending on IDF, SDF, TDF and SDF/IDF ratio of all samples tested; the coding of the samples is reported in the caption of the
Table 4.
Based on the clustering obtained (
Figure 4), it is possible to appreciate that the enzymatically treated samples clustered on their own (cluster 1 and 2); contrary, the untreated samples are clustered together (cluster 3). It is interesting to observe a cluster represented by samples that were hydrolyzed with pectinase that showed a lower total dietary fiber content. The clustering highlights the strong impact of the various treatments compared to the untreated sample more specifically, as previously discussed for the SDF portion.
RP-HPLC-PDA Analysis
Analysis through the HPLC-PDA system permitted the evaluation of selected molecules in all the samples. The molecules investigated were: gallic acid, caffeic acid. epicatechin, theobromine and caffeine; the results have been expressed as µg/g dw.
The quantification was performed on the main molecules present in the cocoa matrix. No peculiar trends have been observed over the various treatments. The amount of methylxanthines in enzymatically hydrolyzed CBSs both raw and defatted seems to be conserved compared with untreated CBSs. The theobromine and caffeine levels of these samples resulted in the range with the amounts indicated in the work of Rojo-Poveda et al., (2021) on cocoa bean shells [
35]. The same work highlights epicatechin (flavanols) content in CBSs, that is in range with the results obtained. The phenolic acid concentrations seem to be in range with the usual concentration found in CBSs as well [
35].
Table 5.
Gallic acid. caffeic acid. epicatechin. theobromine and caffeine quantification (expressed as µg/g dw) through HPLC-PDA. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different (p<0.05).
Table 5.
Gallic acid. caffeic acid. epicatechin. theobromine and caffeine quantification (expressed as µg/g dw) through HPLC-PDA. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different (p<0.05).
| |
Gallic acid |
Caffeic acid |
Epicatechin |
Theobromine |
Caffeine |
| Raw CBSs |
| Untreated |
2.33±0.22 |
1.04±0.06 |
25.84±0.3a
|
161.4±6.31ab
|
29.1±1.37 |
| Cellulase |
2.12±0.14 |
1.01±0.09 |
23.6±0.41b
|
160.1±3.22ab
|
25.91±1 |
| Xylanase |
2.12±0.18 |
1.02±0.05 |
23.33±0.49b
|
159.8±4.46bc
|
26.13±1.38 |
| C+X |
2.06±0.22 |
0.94±0.07 |
21.51±1.36b
|
156.4±4.24bc
|
25.23±1.63 |
| C+P+X |
2.29±0.23 |
0.99±0.08 |
17.9±1.14c
|
177.2±5.7a
|
26.08±1.97 |
| Defatted CBSs |
| Untreated |
1.86±0.43 |
0.94±0.14 |
23.59±2.45b
|
147.9±13.9c
|
22.97±2.55 |
| Cellulase |
1.92±0.07 |
0.95±0.11 |
21.96±1.23b
|
153±4.77bc
|
23.56±0.5 |
| Xylanase |
1.96±0.11 |
0.98±0.04 |
23.88±1b
|
155.3±3.18bc
|
25.41±0.32 |
| C+X |
1.93±0.02 |
0.98±0.11 |
22.91±1.07b
|
156.3±1.79bc
|
25.07±0.62 |
| C+P+X |
2.19±0.09 |
1.02±0.1 |
21.01±0.57b
|
156.3±1.79bc
|
24.83±0.67 |
5. Conclusions
The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of different enzymatic treatments on cocoa bean shells in order to evaluate the potential reuse of this food up-cycled ingredient as a high added value by-product. Cocoa bean shells are an example of an extremely interesting product, possessing several potential intrinsic nutritional properties, that are closely linked to benefits for human health, those studied in this work being dietary fiber and antioxidant potential. Enzymatic treatment can be a key step to make CBSs available as new industrial products to add nutritional value as functional ingredients. The enzymatic treatments carried out in this work have indeed been shown to be suitable for CBSs. The analysis carried out has registered an increase in soluble dietary fibers and a preservation of antioxidant power after the treatments, both of which are correlated with positive health properties.
The samples treated with cellulase, xylanase and the combination of both enzymes are those that, both for raw and defatted CBSs, showed the highest SDF yield, TDF, total phenolic content, antiradical activity and total flavonoid content. The increased quantity of soluble fiber leaves room for further investigations, such as the full characterization of the oligosaccharide profile (prebiotics?) and the simple sugar content, largely impacting in the taste as well as in the fermentability properties. Furthermore, the enzymatic treatment did not negatively affect the concentrations of the main antioxidant compounds in CBSs. Further studies will be necessary to investigate the feasibility of this solution at an industrial level, but the results obtained are encouraging. The enzymatic treatments carried out could be the first step of new industrial approaches to reuse, up-cycle and valorize cocoa shells, which can be exploited as new food ingredients both in food and food supplements, adding value to the nutritional profile.
Author Contributions
conceptualization, V.D, Y.J.; investigation, V.D., Y.J., F.F., M.M.; resources and conceptualization M.A.; data curation, V.D.; writing—original draft preparation, V.D.; writing—review and editing, V.D., Y.J., F.F., M.B., F.T.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to kindly thank Dr. Lorenzo Vecchio who contributed to the analysis. This publication is part of the project NODES which has received funding from the MUR – M4C2 1.5 of PNRR funded by the European Union - NextGenerationEU (Grant agreement no. ECS00000036).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Younes, A.; Li, M.; Karboune, S. Cocoa Bean Shells: A Review into the Chemical Profile, the Bioactivity and the Biotransformation to Enhance Their Potential Applications in Foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2022, 0, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinar, Z.Ö.; Atanassova, M.; Tumer, T.B.; Caruso, G.; Antika, G.; Sharma, S.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Pezzani, R. Cocoa and Cocoa Bean Shells Role in Human Health: An Updated Review. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2021, 103, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, G.; Boffa, L.; Binello, A.; Mantegna, S.; Cravotto, G.; Chemat, F.; Dizhbite, T.; Lauberte, L.; Telysheva, G. Cocoa Bean Shell Waste Valorisation; Extraction from Lab to Pilot-Scale Cavitational Reactors. Food Research International 2019, 115, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.M.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Weickert, M.O. The Health Benefits of Dietary Fibre. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, P.; Joyce, S.A.; O’Toole, P.W.; O’Connor, E.M. Dietary Fibre Modulates the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www-fda-gov.translate.goog/?_x_tr_sl=en&_x_tr_tl=it&_x_tr_hl=it&_x_tr_pto=sc (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Jones, J.M. CODEX-Aligned Dietary Fiber Definitions Help to Bridge the “Fiber Gap”. Nutr J 2014, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, H.C.; Morrison, D.J.; Edwards, C.A. Impact of the Source of Fermentable Carbohydrate on SCFA Production by Human Gut Microbiota in Vitro - a Systematic Scoping Review and Secondary Analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2021, 61, 3892–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.-W.; Yu, E.-Z.; Feng, Q. Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disca, V.; Capuano, E.; Arlorio, M. Colonic Fermentation of Enzymatically Treated Cocoa Bean Shells (CBSs) and Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Production. LWT 2024, 202, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Karboune, S. Enzymatic Generation of Cocoa Bean Shells Oligosaccharides and Feruloylated Oligo/Polysaccharides. Food Bioscience 2023, 56, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouhari, Y.; Travaglia, F.; Giovannelli, L.; Picco, A.; Oz, E.; Oz, F.; Bordiga, M. From Industrial Food Waste to Bioactive Ingredients: A Review on the Sustainable Management and Transformation of Plant-Derived Food Waste. Foods 2023, 12, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papillo, V.A.; Locatelli, M.; Travaglia, F.; Bordiga, M.; Garino, C.; Coïsson, J.D.; Arlorio, M. Cocoa Hulls Polyphenols Stabilized by Microencapsulation as Functional Ingredient for Bakery Applications. Food Research International 2019, 115, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, R.L.; Fan, E.; Ji, H.; Howell, A.; Nio, C.; Payne, M.J.; Reed, J. Multi-Laboratory Validation of a Standard Method for Quantifying Proanthocyanidins in Cranberry Powders. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2010, 90, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiga, M.; Locatelli, M.; Travaglia, F.; Coïsson, J.D.; Mazza, G.; Arlorio, M. Evaluation of the Effect of Processing on Cocoa Polyphenols: Antiradical Activity, Anthocyanins and Procyanidins Profiling from Raw Beans to Chocolate. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 2015, 50, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, B.A.P.; Mohamad, N.N.; Hussain, N. Composition of Unfermented, Unroasted, Roasted Cocoa Beans and Cocoa Shells from Peninsular Malaysia. Food Measure 2018, 12, 2581–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlorio, M.; Coïsson, J.D.; Travaglia, F.; Varsaldi, F.; Miglio, G.; Lombardi, G.; Martelli, A. Antioxidant and Biological Activity of Phenolic Pigments from Theobroma Cacao Hulls Extracted with Supercritical CO2. Food Research International 2005, 38, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinas, A.C.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Cocoa Bean Shell Waste and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant, Physicochemical and Functional Properties. LWT 2020, 127, 109361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, Z.S.; de Carvalho Neto, D.P.; Pereira, G.V.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; de Oliveira, P.Z.; Tiburcio, P.B.; Rogez, H.L.G.; Góes Neto, A.; Soccol, C.R. Biotechnological Approaches for Cocoa Waste Management: A Review. Waste Management 2019, 90, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Poveda, O.; Zeppa, G.; Ferrocino, I.; Stévigny, C.; Barbosa-Pereira, L. Chemometric Classification of Cocoa Bean Shells Based on Their Polyphenolic Profile Determined by RP-HPLC-PDA Analysis and Spectrophotometric Assays. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.P.; Kattan, J.; Doppelt, A.; Nowak-Węgrzyn, A.; Bunyavanich, S. Not so Sweet: True Chocolate and Cocoa Allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2019, 7, 2868–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, T.F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Cocoa By-Products: Characterization of Bioactive Compounds and Beneficial Health Effects. Molecules 2022, 27, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominiak, M.; Søndergaard, K.M.; Wichmann, J.; Vidal-Melgosa, S.; Willats, W.G.T.; Meyer, A.S.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Application of Enzymes for Efficient Extraction, Modification, and Development of Functional Properties of Lime Pectin. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 40, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Moulay, L.; Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Vilanova, O.; Muguerza, B.; Goya, L.; Bravo, L. Hypolipidemic Effect in Cholesterol-Fed Rats of a Soluble Fiber-Rich Product Obtained from Cocoa Husks. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6985–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Costabile, A.; Martin-Pelaez, S.; Vitaglione, P.; Klinder, A.; Gibson, G.R.; Fogliano, V. Potential Prebiotic Activity of Oligosaccharides Obtained by Enzymatic Conversion of Durum Wheat Insoluble Dietary Fibre into Soluble Dietary Fibre. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2009, 19, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Suárez, M.-J.; Pérez-Cózar, M.-L.; Mateos-Aparicio, I.; Redondo-Cuenca, A. Potential Fat-Lowering and Prebiotic Effects of Enzymatically Treated Okara in High-Cholesterol-Fed Wistar Rats. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 2016, 67, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Razmjooyhassankhani, N.; Waglay, A.; Mdimagh, A.; Karboune, S. Pilot Plant Extraction of Oligo/Polysaccharides from Cocoa Bean Shells and Their Incorporation into Chocolate Based Formulations. Food Chemistry 2024, 437, 137893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagelaviciute, J.; Staniulyte, G.; Cizeikiene, D.; Basinskiene, L. Influence of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Composition and Technological Properties of Apple Pomace and Its Application for Wheat Bread Making. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 2023, 78, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleary, B.V.; McLoughlin, C. Determination of Insoluble, Soluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Using a Rapid Integrated Procedure of Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography: First Action 2022.01. Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL 2023, 106, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, I.; Ignat, I.; Neamtu, M.; Popa, V.I. Thermal Stability, Antioxidant Activity, and Photo-Oxidation of Natural Polyphenols. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlorio, M.; Locatelli, M.; Travaglia, F.; Coïsson, J.-D.; Grosso, E.D.; Minassi, A.; Appendino, G.; Martelli, A. Roasting Impact on the Contents of Clovamide (N-Caffeoyl-L-DOPA) and the Antioxidant Activity of Cocoa Beans (Theobroma Cacao L.). Food Chemistry 2008, 106, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, G.H.; Van Pham, H.; Hong Nguyen, H.V. Effects of Enzymatic and Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Cocoa Bean Shells. Food Measure 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękal, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Evaluation of Aluminium Complexation Reaction for Flavonoid Content Assay. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yusof, A.H.; Abd Gani, S.S.; Zaidan, U.H.; Halmi, M.I.E.; Zainudin, B.H. Optimization of an Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Condition for Flavonoid Compounds from Cocoa Shells (Theobroma Cacao) Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2019, 24, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Belviso, S.; Ferrocino, I.; Rojo-Poveda, O.; Zeppa, G. Characterization and Classification of Cocoa Bean Shells from Different Regions of Venezuela Using HPLC-PDA-MS/MS and Spectrophotometric Techniques Coupled to Chemometric Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Powdered samples after the enzymatic treatments.
Figure 1.
Powdered samples after the enzymatic treatments.
Figure 2.
Insoluble and soluble dietary fibers expressed as g over 100 g of dry weight in enzymatically treated raw defatted CBSs. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; IDF, insoluble dietary fibers; SDF, soluble dietary fibers; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate sample statistically different (p<0.05).
Figure 2.
Insoluble and soluble dietary fibers expressed as g over 100 g of dry weight in enzymatically treated raw defatted CBSs. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; IDF, insoluble dietary fibers; SDF, soluble dietary fibers; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate sample statistically different (p<0.05).
Figure 3.
Total dietary fibers expressed as g over 100 of dry weight in enzymatically treated raw defatted CBSs. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; TDF, total dietary fibers; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different (p<0.05).
Figure 3.
Total dietary fibers expressed as g over 100 of dry weight in enzymatically treated raw defatted CBSs. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; TDF, total dietary fibers; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different (p<0.05).
Figure 4.
a) Scores and b) loadings of the principal components-based hierarchical cluster (HCPC). IDF, Insoluble dietary fibers; SDF, soluble dietary fibers; TDF, total dietary fibers.
Figure 4.
a) Scores and b) loadings of the principal components-based hierarchical cluster (HCPC). IDF, Insoluble dietary fibers; SDF, soluble dietary fibers; TDF, total dietary fibers.
Table 1.
Raw CBSs proximate composition.
Table 1.
Raw CBSs proximate composition.
| Parameter |
Amount |
| Moisture (%) |
4.42±0.2 |
| Ashes (g/100) |
7.76±0.02 |
| Fats (g/100) |
8.04±0.01 |
| Protein (g/100) |
10.5±0.42 |
| Carbohydrates (g/100) |
11.13±0.86 |
| TDF (g/100) |
58.14±1.11 |
| IDF (g/100) |
42.22±0.59 |
| SDF (g/100) |
15.91±0.51 |
Table 2.
SDF/IDF ratio. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; IDF, insoluble dietary fibers; SDF, soluble dietary fibers; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different (p<0.05).
Table 2.
SDF/IDF ratio. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; IDF, insoluble dietary fibers; SDF, soluble dietary fibers; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different (p<0.05).
| |
SDF/IDF |
| Raw CBSs |
|
| Untreated |
0.38 |
| C |
1.30 |
| X |
1.13 |
| C+X |
0.98 |
| C+X+P |
0.69 |
| Defatted CBSs |
|
| Untreated |
0.39 |
| C |
1.33 |
| X |
0.89 |
| C+X |
0.81 |
| C+X+P |
1.26 |
Table 3.
Total flavonoid content, expressed as mg CE/ g dw (TFC). Antiradical activity, expressed as mg TE/ g dw (AA). Total phenolic content, expressed as mg CE/ g dw (TPC) and Total Procyanidins Content, expressed as mg CE/ g dw (TPC) in raw CBSs and defatted CBSs. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different p<0.05.
Table 3.
Total flavonoid content, expressed as mg CE/ g dw (TFC). Antiradical activity, expressed as mg TE/ g dw (AA). Total phenolic content, expressed as mg CE/ g dw (TPC) and Total Procyanidins Content, expressed as mg CE/ g dw (TPC) in raw CBSs and defatted CBSs. CBSs, cocoa bean shells; C, cellulase; X, xylanase; P, pectinase. Different letters indicate samples statistically different p<0.05.
| |
TFC |
AA |
TPC |
PAC |
| Raw CBSs |
| Untreated |
7.69±0.05b
|
41.34±0.11ab
|
22.32±2.49 |
2.33±0.2a
|
| Cellulase |
6.93±0.09b
|
42.48±3.27ab
|
20.37±0.54 |
2.38±0.16a
|
| Xylanase |
6.85±0.09b
|
45.61±3.28a
|
19.28±0.17 |
2.37±0.16a
|
| C+X |
6.58±0.24b
|
36.1±1.4b
|
19.52±1.36 |
2.14±0.1abc
|
| C+X+P |
6.75±0.52b
|
42.6±1.9ab
|
20.03±0.81 |
1.9±0.14bcd
|
| Defatted CBSs |
| Untreated |
9.5±0.35a
|
46.68±0.55a
|
24.35±1.61 |
1.65±0.17cd
|
| Cellulase |
6.75±0.11b
|
46.51±3.96a
|
21.3±0.59 |
1.82±0.19d
|
| Xylanase |
7.12±0.15b
|
42.94±3.27ab
|
20.07±2.21 |
2.03±0.12ab
|
| C+X |
6.8±0.25b
|
39.41±4.64ab
|
19.56±0.47 |
2.01±0.09abcd
|
| C+X+P |
7.15±0.53b
|
46.67±1.06a
|
23.3±2.54 |
1.89±0.09bcd
|
Table 4.
Sample coding of the HCPC analysis.
Table 4.
Sample coding of the HCPC analysis.
| Samples |
HCPC coding |
| Pre-treatment |
Enzymatic treatment |
| Raw |
Untreated |
A |
| Raw |
Cellulase |
B |
| Raw |
Xylanase |
C |
| Raw |
C+X |
D |
| Raw |
C+X+P |
E |
| Defatted |
Untreated |
F |
| Defatted |
Cellulase |
G |
| Defatted |
Xylanase |
H |
| Defatted |
C+X |
I |
| Defatted |
C+X+P |
L |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).