1. Introduction
Potato (
Solanum tuberosum L.) is the largest vegetable crop grown in a wide range of countries worldwide, it ranks fourth in the world in terms of production volume after rice, wheat, and corn [
1]. It provides the world with the cheapest source of protein, carbohydrates, minerals, and vitamins [
2]. To ensure food security, a stable increase in potato production is required. At present, however, the main reliance is on the application of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, but the massive application of chemical fertilizers has led to the destruction of the soil and pollution of the environment, and triggered a series of problems such as pesticide residues in agricultural products [
3,
4]. From various considerations, the development of environmentally friendly, safe, green, and sustainable microbial fertilizers that can be applied to agricultural production has become a necessary path for modern agriculture.
Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are microorganisms living in the soil around plant roots or attached to the roots [
5], which can directly or indirectly promote plant growth by activating soil nutrients, improving plant inter-root nutrients [
6], producing plant growth regulators [
5,
7,
8] or antimicrobial actives [
9]. There is a rich variety of inter-root biotrophic bacteria, among which the most studied ones are
Bacillus,
Pseudomonas, Agrobacterium and so on [
10,
11]. Bacillus can produce spores, very strong resistance to a variety of stresses, in some extreme environments are able to survive [
12], which makes the Bacillus products have a long shelf life, field adaptability [
13]. For example,
B. amyloliquefaciens B9601-Y2 has the effect of promoting plant growth [
14];
B. velezensis Y6 has the effect of promoting plant growth and increasing yield [
15].
B. velezensis YYC could induce the expression of tomato genes related to auxin, gibberellin, jasmonic acid, and salicylic acid, which promote tomato growth [
16]. Bacillus is also one of the most diverse genera of PGPR, and its growth-promoting ability and some of its mechanisms have been widely studied, with a broad potential for application [
16,
17].
IAA is an important plant hormone belonging to the auxin family of indole derivatives. It is the most abundant and fundamental naturally occurring plant hormone that controls almost every aspect of plant growth and development, such as cell division, elongation, fruit development, and senescence [
18,
19]. It can also increase plant protection against external stress [
19,
20]. IAA can be synthesized not only in plants but also in many microorganisms that interact with plants, including bacteria and fungi [
21,
22]. Microbial biosynthesis of IAA can be classified into tryptophan-dependent and tryptophan-independent pathways based on whether tryptophan (Trp) is used as a precursor. These pathways produce IAA with some similarities to that of plants [
23,
24]. In the tryptophan-dependent pathways of microorganisms, there are different intermediate metabolites, and current research has roughly divided them into five pathways: the indole-3-acetamide pathway (IAM), the indole-3-pyruvic acid pathway (IPA/IpyA), the indole-3-acetonitrile pathway (IAN), the tryptamine pathway (TAM), and the tryptophan side-chain oxidase pathway (TSO) [
25,
26]. Current reports on the bacterial IAA synthesis pathway are mostly found in Gram-negative bacteria, with relatively few studies related to Gram-positive bacteria.
In addition to regulating their physiological functions and adapting to external stress and microbial–microbial communication, IAA produced by microorganisms can often participate as a signaling molecule in the interaction between microorganisms and plants, regulating plant growth and development, and causing physiological and pathological changes in plants [
27,
28]. However, there are fewer studies on the mechanism of interaction between IAA-producing strains and potato, and the mechanism of their growth-promoting effects is not clear. In this study, a strain of
Fitibacillus barbaricus WL35 with high IAA-producing capacity was isolated from the plant inter-root soil, and its growth-promoting effect on potato plants was verified by potting and field trials, and the metabolites during the growth process of WL35 were investigated to clarify the pathway of IAA synthesis. At the same time, transcriptomic analysis of potted potato root system was studied to investigate the interaction mechanism. The results will help to better explain the growth-promoting effect of
F. barbaricus WL35 on potato plants and provide a theoretical basis for the application of
F. barbaricus WL35.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of IAA-Producing Strains
Isolation soil samples were collected from the rhizosphere soil of crops in South China Farm, Guangzhou, China (23° 08′N 113° 16′E). Weigh 10.0 g of isolation soil samples and place in a 250 mL triangular flask with 90 mL sterile water (containing 5-7 glass beads), shaken for 30 min at 180 r·min
−1 to disperse the soil samples. 5 mL of supernatant was taken in a tube and heated at 90°C for 10 min, then make a gradient dilution to 10
-5 times, take the diluted solution and spread it on the Luria-Bertani (LB) agar medium, observe the morphology of the single colony cultured after inverted incubation at 37°C for 24 h, and take the single colonies with different morphology characteristics to be numbered and then preserved by the line of LB plate [
71].
The isolated strains were subjected to IAA qualitative test, the strains were inoculated into fresh 4 mL LB liquid medium test tubes (tryptophan content was 100 mg·L
-1), and put into the shaker at 30°C, 180r·min
-1 to incubate for 24 h. 100 μL of the culture solution was mixed with an equal amount of Salkowski’s colorimetric solution on the white ceramic plate, and then left to stand for 30 min away from the light to carry out. If the color of the color reaction mixture became red, it indicated that the strain had the ability to produce IAA, the strains that could produce IAA were recorded and photographed. IAA standard solution (50 mg·L
-1) and liquid LB medium (containing 100 mg·L
-1 L-tryptophan) were used as the positive control (CK+) and the negative control (CK-), respectively [
11].
For the quantitative test on the strains retained in the qualitative test, the strain were inoculated into tryptophan-containing LB liquid medium tubes with the same culture conditions as the qualitative test for 24 h, and the OD
600 value of the bacterial solution was determined by spectrophotometer (MV754N, Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co.), and then the bacterial solution was centrifuged at 8000r·min
-1 for 5min to take the supernatant, add an equal volume of Salkowski’s colorimetric solution, mix it well, let the liquid stand away from the light for 30min. The color reaction was carried out, and then the OD
530 was measured, at the same time, the IAA standard curve was made by preparing IAA standard solution, and the IAA content was calculated based on the constructed IAA standard curve when the OD
600=1.0. The strains with IAA-producing capacity above 15 mg·L
-1 were selected for purification and preserved in 50% glycerol and kept at -80°C for further study [
72].
2.2. Identification of IAA-Producing Strains
The identification of IAA-producing strains was performed by evaluating the 16S
rDNA gene sequences. Strains on LB were incubated at 37°C for 18 h, a single colony from the plate was picked and placed in a centrifuge tube containing 100 μL of sterile water, and then heated in a water bath at 95°C for 15 min to rupture the cells and release DNA. Amplification was carried out by PCR using two universal primers, namely 27F (5’-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’) and 1492R (5’-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3’). The PCR products were purified and sequenced by Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The comparison of the sequence similarity was performed using Blastn, and some related species of the 16S
rDNA sequence were downloaded and aligned using Mega7.0. The unrooted tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining method with a bootstrap value of 1,000 replicates [
73].
2.3. Potato Pot Experiment Design
The soil used was taken from South China Farm (23° 08′N 113° 16′E). The growth-promoting effects of WL35 was determined through pot experiments using potato cultivar Favorita. WL35 was mixed with 25 g of diatomaceous soil to make a microbial inoculum containing 10
8 cfu·g
−1 of cells, and CK with diatomaceous soil without bacteria was set aside. The potatoes were germinated in an Artificial Climate Chamber (temperature being 20°C for 16 h and 18°C for 8 h) until the shoots were as long as about 1 cm, cut into uniformly sized pieces with one shoot and mixed with CK and WL35 immediately. One piece of potato was planted in each pot (with height of 21.5 cm, diameter 34 cm, and contains10.0 kg soil from South China Farm) at a depth of about 5-6 cm, with 4 replicates of each treatment [
74].
On the 45th day after seedling emergence, the plant height, stem thickness, number of leaves, and chlorophyll content of potato plants were measured. Potato tubers were harvested 90 days after the emergence of potato seedlings and potato yield was measured for each treatment.
2.4. Potato Field Experiment Design
On January 7, 2023, at Zhucun, Zengcheng District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province (113°71′E, 23°98′N, 3.6 m a.s.l.), where the annual rainfall was 2039.5 mm and the mean annual temperature was 22.1°C. After turning the ground and starting the ridge, the organic and compound fertilizer was applied in the middle of the furrow. Commercial organic fertilizer: 400 kg/mu; potato compound fertilizer (15-8-22): 100 kg/mu (Ba tian China). Three replications were set up in a completely randomized block design (RCBD) with a plot area of 15.84 m
2, divided into three monopolies with a width of 1.2 m and a length of 4.4 m (Supplementary Figure S1). Two rows of 20 potato plants were planted at the spacing of 20 cm and a planting depth of 5-6 cm. The experiment consisted of five treatments, control: diatomaceous earth for CK1, conventional bacteriophage acquired in the market for CK2, and diatomaceous earth containing 10
8 cfu·g
-1 of IAA-producing strains cells for WL35, WL41, and WL56 (isolated from maize inter-root soils). Cfu count was determined based on the enzymatic method [
75]:
Number of cells·g-1 (cfu·g-1) = (number of colonies) × (dilution factor).
Moreover, 60 days after potato planting, we randomly collected 40 potato plants from the middle block of each plot, and we measured the number of seedlings, plant height, stem thickness, and chlorophyll content to assess the agronomic traits of each plot, and used three plots of the same treatments to determine the mean ± standard error of the mean and compare it with other treatments by Tukey’s test. After 90 days, the yield (commercial tubers were ≥ 75 g) and quality (vitamin C, protein, reducing sugars, starch content, and the accumulation of N, P, and K) of potatoes were measured. Protein content was determined by the Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 colorimetric method with bovine serum albumin as the standard; vitamin C content was measured by the 2,6-dichloroindophenol titrimetric method [
76]; reducing sugar content was evaluated by Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent method [
77]; and starch content was determined based on the enzymatic method described by Khabou [
42].
The yield was determined by weighing the tubers from the harvested rows and calculating the weight per hectare, and the percentage of dry weight was determined after drying the fresh sample at 105°C for 48 h [
60]. Plant material aliquot was digested in a mixture of sulfuric acid (H
2SO
4) and hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2). The total phosphorus concentration was measured by a colorimetric assay of the P in the digest according to the Mo-Sb colorimetric method [
78,
79]. Total nitrogen concentration was determined by the Kjeldahl method, whereas potassium using ICP-OES [
80]. The N, P, and K accumulation was calculated using data on yield and N, P, and K content.
2.5. Exploration of the IAA Synthesis Pathway in WL35
2.5.1. Determination of Metabolites of IAA Synthesis Pathway by UPLC-MS/MS
Take the bacterial solution cultured in LB medium overnight and add it to 1 mmol·L-1 of 100 mL LB-Trp medium at an inoculation ratio of 1%, inoculate with an equal amount of LB medium as CK, incubate for 48h at 30℃, 180 rpm, centrifuge at 4℃, 8000 rpm for 7 min, and the supernatant was acidified with 6 M HCl to pH=2.5, and extracted twice with two times the volume of ethyl acetate, extract the ethyl acetate layer, rotary evaporation at 37℃, and re-dissolve with 10 mL of methanol (HPLC grade), filtered with 0.22 μm organic membrane into brown feeder, and then stored in a refrigerator at -20 ℃ for later use. The test was repeated three times.
Chromatographic grade TAM, IAM, IAA, IAN, Indole-3-lactic acid(ILA), Tryptophol(TOL) were used as the test standards, and the HPLC-grade methanol was dissolved to form a master batch of 200 mg·L-1, and the same volume of the master batch was mixed to form a mixture of standards, and a single standard was used as a control, and was stored at 4℃. Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS): An ExionLC AC liquid chromatography system coupled with an AB SCIEX triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer (Woodlands Central Indus. Estate., Singapore) was used for the analysis of the analytes, and the analytes were operated with an electrospray ionization source (ESI) in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode (Supplementary Table S1), with an electrospray voltage of 4 kV, a capillary temperature of 330℃. The mass spectrometry was performed in the mass range of 10-300, and the data acquisition time was 21 min. The parameters of the MRM mass spectrometry are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The chromatographic column was a Bonshell C18 (2.1×50 mm, 2.7 μm) with a flow rate of 0.3 mL·min-1 and an injection volume of 1μL, and the temperature of the column was 30℃. The mobile phase consisted of 0.2% formic acid aqueous solution (A) and acetonitrile (B), and the gradient elution was carried out according to the gradient elution of 10%B for 0~8 min, 10%~90%B for 8~16 min, 90%~95%B for 16~21 min, and 10%B for 21~23 min.
2.5.2. Determination of Intermediate Content of Bacteria Solution at Different Incubation Times by HPLC
The culture time of the strains was set at 16 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 60 h and 72 h. Each treatment was repeated three times, and the concentration treatment was carried out after culture. The inoculation method, culture conditions, concentration treatment and storage conditions were the same as those in the UPLC-MS/MS experiment. Optimization of liquid chromatographic conditions: Agilent high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used, the column was CNWAthena C18 (4.6×250 mm, 5μm), the flow rate was 1 mL·min-1, the column temperature was 30 ℃, the detection wavelength was 280nm, and the detection time was 60 min. The mobile phases were 0.2% acetic acid aqueous solution (A) and acetonitrile (B), and the isocratic elution was performed in the ratio of 80% A, 20% B. The concentration of TAM, ILA, IAM, IAA, TOL and IAN mixed standards of 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5 and 15 mL·L-1 were prepared by using chromatographic methanol as the solvent. The standard curve was plotted by the peak area versus the concentration, and a single standard was used to determine the retention time of each standard, and the content of the metabolites in the bacterial solution was calculated by comparing with the corresponding peak area of the bacterial solution samples.
2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis
The expression levels of genes in the RNA sequencing results were determined by performing Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction(qRT-PCR) analysis of selected DEGs. The primers used were designed with Primer 5.0 (Supplementary Table S2). F. barbaricus WL35 was incubated in LB medium with or without tryptophan, and samples were taken at 16 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 60 h, and 72 h. A total of 800 ng of RNA was used to synthesize cDNA. 1μL gDNA Remover and 1μL 10 × gDNA Remover Buffer, and then added into the RNA-free tube with ice bath. The volume of RNase-free double-distilled H2O was fixed to 10μL. The reaction mixture was gently mixed, centrifuged for 3-5s, centrifuged at 60°C for 5 min, immersed in ice bath for 2 min, and centrifuged again for 3-5s. The following reagents were added to the test tube with ice bath: 4μL of 5× RT Reaction Mix, 1.0μL of SynScriptTM III RT Enzyme Mix (SynScriptTM III cDNA Synthesis Mix, China), and fixed to 20μL use RNase-free double-distilled H2O. The mixture was gently mixed and centrifuged for 3-5 s. The reverse transcription reaction was carried out on the PCR instrument at 25°C for 10 min, 50°C for 15 min, and 85°C for 5 min. The mixed solution was stored at -20°C. The cDNA sample was diluted 10 times as the template for on-board detection. Three technical replicates for each sample were obtained for qRT-PCR, which was run at 95°C for 1 min and then at 40 cycles each of 95°C for 10s and 60°C for 30s. The pyrG2 gene was used as the control, and the 2-ΔΔCt method was adopted to calculate the relative expression of the gene to be tested. A real-time PCR system (QuantStudio 6 Flex, Biosystems) was used for qRT-PCR.
2.7. Sample Collection, RNA Extraction, Library Construction and Sequencing
To evaluate the effect of WL35 on the transcriptome of potato, the following experiments were performed. Firstly, samples were collected from the tender portion of the potato root system in each of the CK and WL35 treatments in the field at 45 days after potato seedlings emerged. The potato roots were washed with sterile water three times, blotted dry with sterile filter paper, wrapped in tinfoil, labeled and frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately, and then stored at -80°C for subsequent RNA extraction. Three independent biological replicates of each sample were taken. The samples were sorted and sent to Nanjing Paisano Gene Technology for RNA extraction and transcriptome sequencing.
Total RNA was extracted with Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies), and the concentration, quality and integrity of the RNA were determined by using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). The mRNA was purified from total RNA by using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads. Fragmentation was carried out with divalent cations under elevated temperature in an Illumina proprietary fragmentation buffer. After adenylation of the 3′ends of the DNA fragments, Illumina PE adapter oligonucleotides were ligated to prepare for hybridization. To select cDNA fragments of the preferred 400-500 bp in length, the library fragments were purified by using the AMPure XP system (Beckman Coulter, Beverly, CA, United States). DNA fragments with ligated adaptor molecules on both ends were selectively enriched with Illumina PCR Primer Cocktail in a 15 cycle PCR reaction. Products were purified (AMPure XP system) and quantified by use of the Agilent high sensitivity DNA assay on a Bioanalyzer 2100 system (Agilent). The sequencing library was then sequenced on NovaSeq 6000 platform (Illumina) in Shanghai Personal Biotechnology Cp. Ltd.
2.8. Transcriptome Analysis
2.8.1. Quality Control and Differential Expression Analysis
Samples were sequenced on the platform to get image files, which were transformed by the sequencing platform software, and the original data in FASTQ format (Raw Data) was generated. Cutadapt (v1.15) software was used to filter the sequencing data to get high-quality sequence (Clean Data) for further analysis. The reference genome and gene annotation files were downloaded from genome website. The filtered reads were mapped to the reference genome by using HISA T2 (v2.0.5).
The differences in the gene expressions were analyzed by DESeq (1.39.0) with screened conditions as follows: expression difference multiple |log2FoldChange| > 1, significant p < 0.05. At the same time, R language Pheatmap (1.0.8) software package was used to perform bi-directional clustering analysis of different genes of samples. The heat map was got according to the expression levels of the same gene in different samples and the expression patterns of different genes in the same sample with Euclidean method to calculate the distance and Complete Linkage method to cluster.
2.8.2. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
All the genes were mapped to Terms in the Gene Ontology (GO)database and the number of differentially enriched genes was calculated in each Term. TopGO (2.40.0) was used to perform GO enrichment analysis on the differential genes, and p was calculated by the hypergeometric distribution method (the standard of significant enrichment is p < 0.05), and the GO term with significantly enriched differential genes was found to determine the main biological functions performed by differential genes. ClusterProfiler (3.16.1) software was used to carry out the enrichment analysis of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway of differential genes, focusing on the significant enrichment pathway with p < 0.05.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with Microsoft Excel 2013 and IBM SPSS Statistics 26. Duncan’s test and independent-samples t-test(p < 0.05) were used for significance testing. Origin was used to create graphs.
3. Results
3.1. The Screening and Identification of IAA-Producing Strains
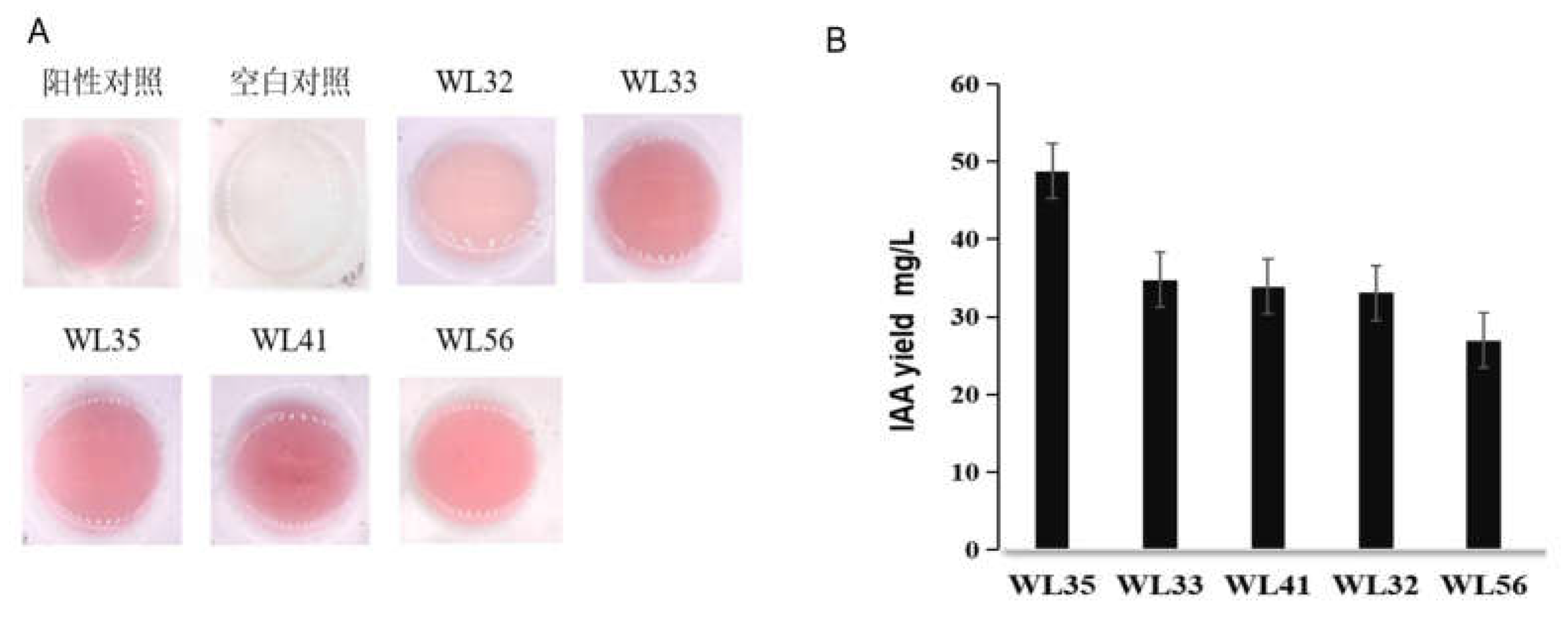
Several IAA-producing strains were isolated from the rhizosphere soil of maize (23°08′N 113°16′E) at the farm of South China Agricultural University (SCAU), and the IAA-producing ability of the strains was determined qualitatively and quantitatively by the Salkowski colorimetric assay, among which, the strains that produced higher amounts of IAA were WL35, WL41, and WL56, with the IAA yields of 48.79 mg·L
-1, 33.91 mg·L
-1, and 26.97 mg·L
-1 (
Figure 1), and these strains were observed morphologically on LB medium after 24h of growth. The strains were observed under the microscope as Gram-positive, spore-producing bacteria with rod-shaped cells (Supplementary Figure S2). The strains with better IAA-producing ability were preserved and subjected to a further study.
By 16S rDNA sequencing, WL35, WL41 and WL56 were identified as Bacillus sp. Among them, WL35 was identified as a Fitibacillus barbaricus with 99% homology (Supplementary Figure S3), and WL35 16S rDNA sequencing was uploaded to the GenBank database to obtain the GenBank accession number of PP068887.
3.2. Growth Promotion and Yield-Increasing Efficacy of WL35 in Pot Experiment
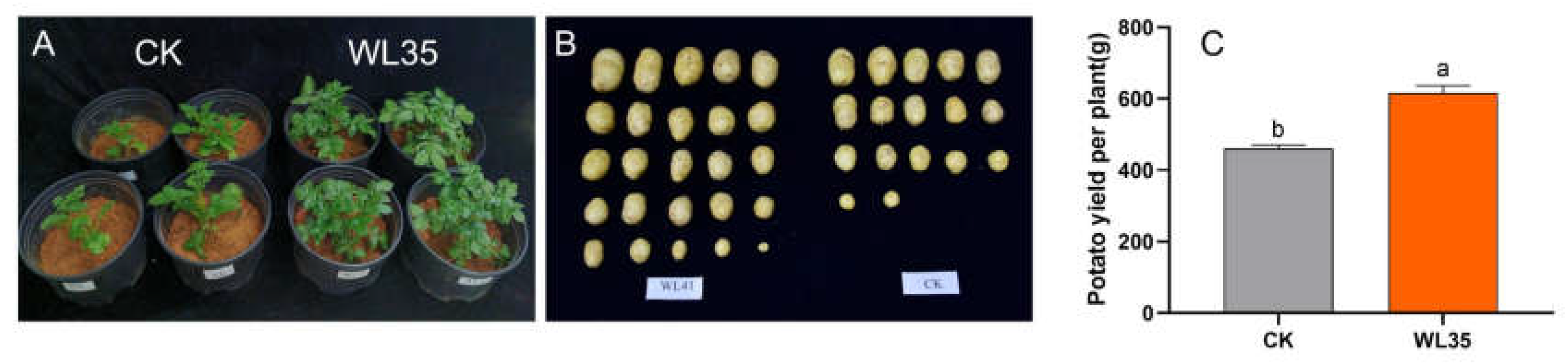
Pot experiments were conducted to determine whether WL35 promotes potato growth and increases yield. 45 days after the emergence of potato seedlings (
Figure 2A-B), the potato plants treated with the strain WL35 seed dressing had a significant growth promotion effect relative to CK, and the strain WL35 enhanced the plant height, stem thickness, chlorophyll content and number of leaves of potato plants by 31.68%, 30.03%, 32.93% and 36.59%, respectively (
Table 1). Potato tubers were harvested 90 days after the emergence of potato seedlings and their yields were determined, the results showed that strain-treated pots showed significant increase in potato yield compared to the control, with 31.86% increase in WL35 potato weight. In addition, WL35-treated potatoes had a more compact root structure, significantly longer root length, and more fibrous roots (
Figure 2C).
3.3. Growth Promotion, Yield-Increasing and Quality Enhancement Efficacy of WL35 in Field Conditions
In order to evaluate the effect of the strain on growth, yield and quality of potato under natural environment, a field experiment was conducted in this study. The results showed that treatment with microbial seed dressing made from IAA-producing strains significantly increased seedling emergence, plant height and chlorophyll content of potato by 14.26-28.99%, 20.58-23.93% and 11.10-31.79%, compared with control (Supplementary Table S3).
Yield of potatoes treated with IAA-producing strains was significantly higher, where the yield of commercial and non-commercial potatoes increased by 10.04-16.45% and 11.15-22.90%, respectively. The most effective
Fitibacillus barbaricus WL35 treated potato commercial and non-commercial potatoes increased by 16.45 and 14.93%, respectively (
Table 2). Meanwhile, the use of IAA-producing strains increased vitamin C content by 14.13-17.42%, protein content by 49.62-77.41% and starch content by 0.78-6.81% (
Table 3), the accumulation of N, P and K by 5.26-9.98%, 4.30-12.70% and 13.97-26.76%, respectively. Among them, WL35 increased vitamin C content by 16.35%, protein content by 75%, starch content by 6.60%, nitrogen accumulation by 9.98%, phosphorus accumulation by 12.70% and potassium accumulation by 26.76% (
Table 4).
3.4. Metabolomic Analysis of the IAA Synthesis Pathway
3.4.1. Metabolites of IAA Synthesis Pathway in WL35
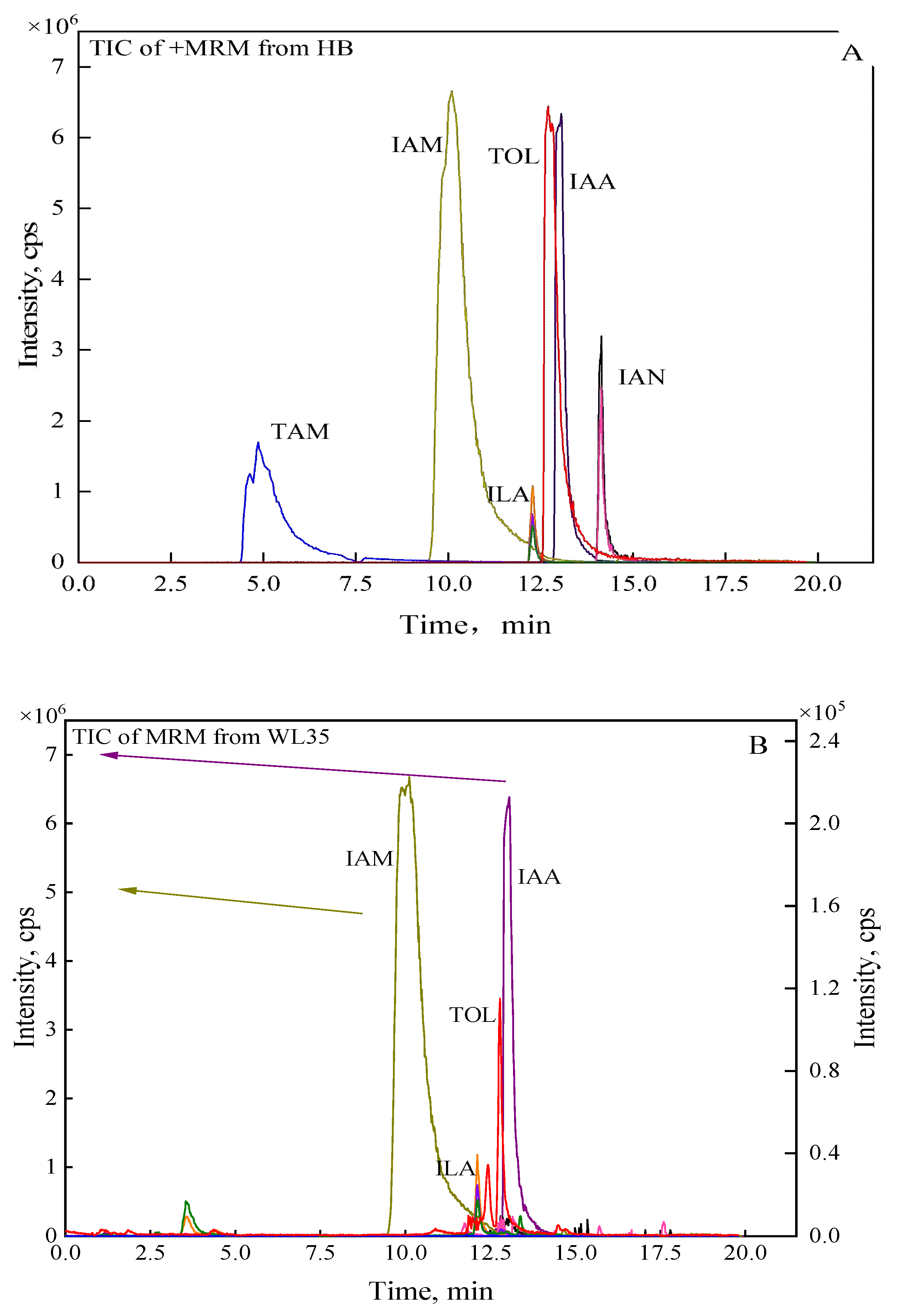
Based on the results of tryptophan supplementation experiments (Supplementary Figure S4), it was initially determined that the IAA synthetic pathway of WL35 was mainly tryptophan-dependent, and six metabolites in the tryptophan-dependent synthetic pathway of IAA in the bacterial solution were further detected by UPLC-MS/MS. The results showed that, comparing with the standard samples, corresponding fragmentation ion peaks of IAM, ILA, TOL and IAA were detected in the supernatant of strain WL35, while TAM and IAN were not detected, and the retention time of each fragment ion was consistent with the corresponding standards (
Figure 3A-B).
3.4.2. Effect of Incubation Time on IAA Synthesis Pathway in WL35
According to the results of the kinetic determination of IAA production by the strain, after 16 h of incubation, the IAA production of WL35 reached more than 30 mg·L
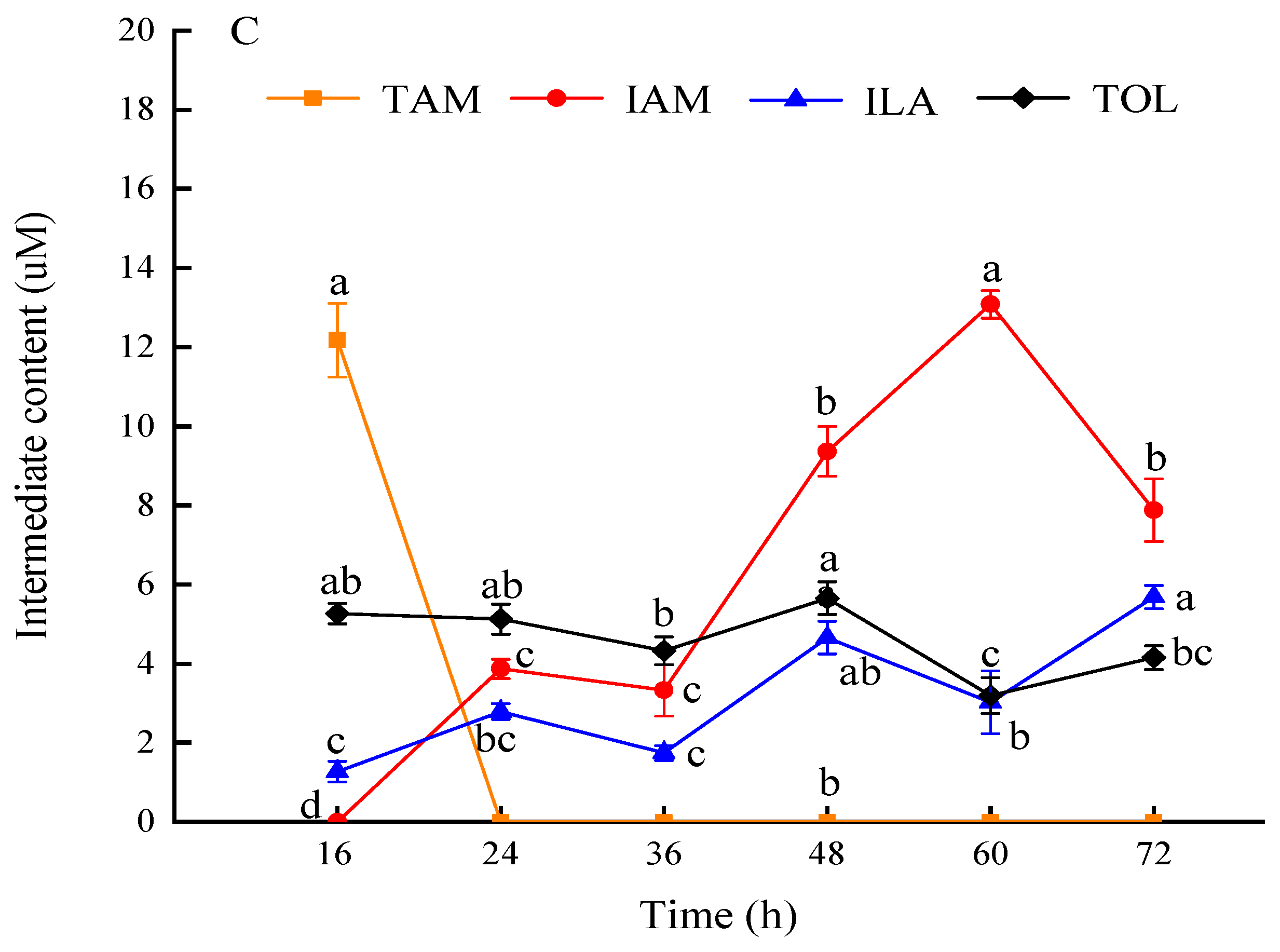
-1, so the sampling was started at 16 h of incubation under the same conditions, and 72 h was the termination point of the sampling, and the metabolism products produced by the strain at different times were determined by HPLC after the characterization of the detection by UPLC-MS/MS. The retention times of the standards TAM, ILA, IAM, IAA, TOL and IAN were 4.812, 12.294, 10.053, 13.066, 12.956 and 14.145 min, respectively, and the RSDs of the retention times of the standards were 0.50%-1.56%, which were less than 2%, with the high degree of separation and the peaks were good and did not tail, indicating that the chromatographic conditions were feasible. The results (
Figure 3C) showed that ILA and TOL were consistently detected in the WL35 bacterial solution, and their contents ranged from 1.24-5.69μM and 3.18-5.75μM, respectively. TAM was only detected at 16 h with higher content than other metabolites, and the signal disappeared after 24 h of incubation, IAM began to accumulate with an almost significant upward trend in concentration, and ILA and TOL content fluctuated within a certain range, ILA is the enzymatic reduction product of IPA, an intermediate of IPA pathway, and TOL is the reduction product of Indole-3-acetaldehyde (IAAld), a common intermediate of IPA, TSO and TAM pathways. Therefore, it is hypothesized that the TAM pathway, IAM pathway and IPA pathway work together to promote IAA synthesis.
3.5. qRT-PCR Analysis
In order to verify the IAA synthesis pathway related genes in the pathway were analyzed based on the above results. A total of 8 genes related to IAA synthesis in WL35 were identified, and quantitative primers were designed based on the sequences of these eight genes (Supplementary Table S2). qRT-PCR analysis revealed that the gene expression levels were up-regulated in WL35 grown under tryptophan treatment compared with non-tryptophan treatment, which is consistent with the results of the above mentioned UPLC-MS/MS (Supplementary Figure S5).
3.6. Analysis of Gene Transcript Levels in Potato Roots Inoculation with WL35
3.6.1. Transcriptomic Analysis Using Illumina-Based RNA Sequencing
Three samples each from the two treatments (CK and WL35) were subjected to RNA sequencing (
Table 5). The sequencing results showed that the total number of bases was about 6G (not less than 95% of 6G) and the Q30 (%) was 93.55-93.85%. In addition, some low-quality Reads with connectors were filtered out from the data, and the percentage of high-quality sequence bases in the sequenced bases ranged from 92.25-93.2%, all of which were highly stable, indicating that the sequencing results were stable and reliable. Additionally the total and uniquely alignment rates of sequencing results was higher than 80% and 90%, respectively, with high and stable match rates, while the multiple match rate was lower and stable, both below 4%, indicating that the samples have a high match with the selected reference genome and can be used for subsequent reference transcriptome analysis.
3.6.2. Biological Links between Differential Gene Expressions
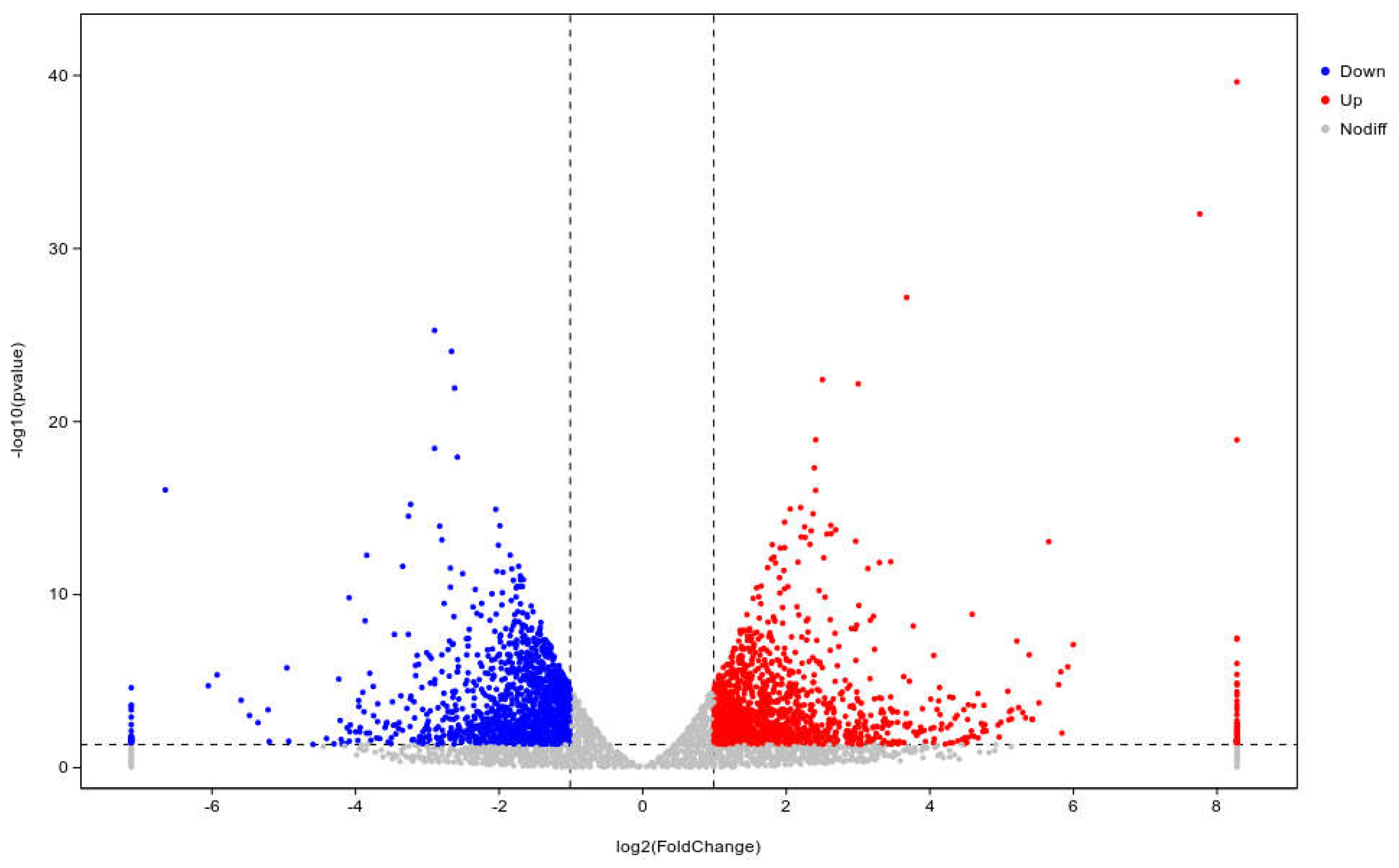
DESeq was used to analyze gene expression differentially, 2,875 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were expressed in the WL35 treated potato roots, including 1,458 up-regulated genes and 1,417 down-regulated genes, compared with CK. The R ggplots2 software was used to draw the volcano plot of DEGs (
Figure 4) to show the gene distribution, the fold difference in gene expression, and the significance results, which should be roughly symmetrical for the left and right differential gene distribution. Cluster analysis was used to determine the expression patterns of DEGs under different experimental conditions; genes with high expression correlation among samples were grouped together, and usually these genes were actually linked in some biological processes, or a metabolic or signaling pathway. Therefore, through expression clustering analysis (
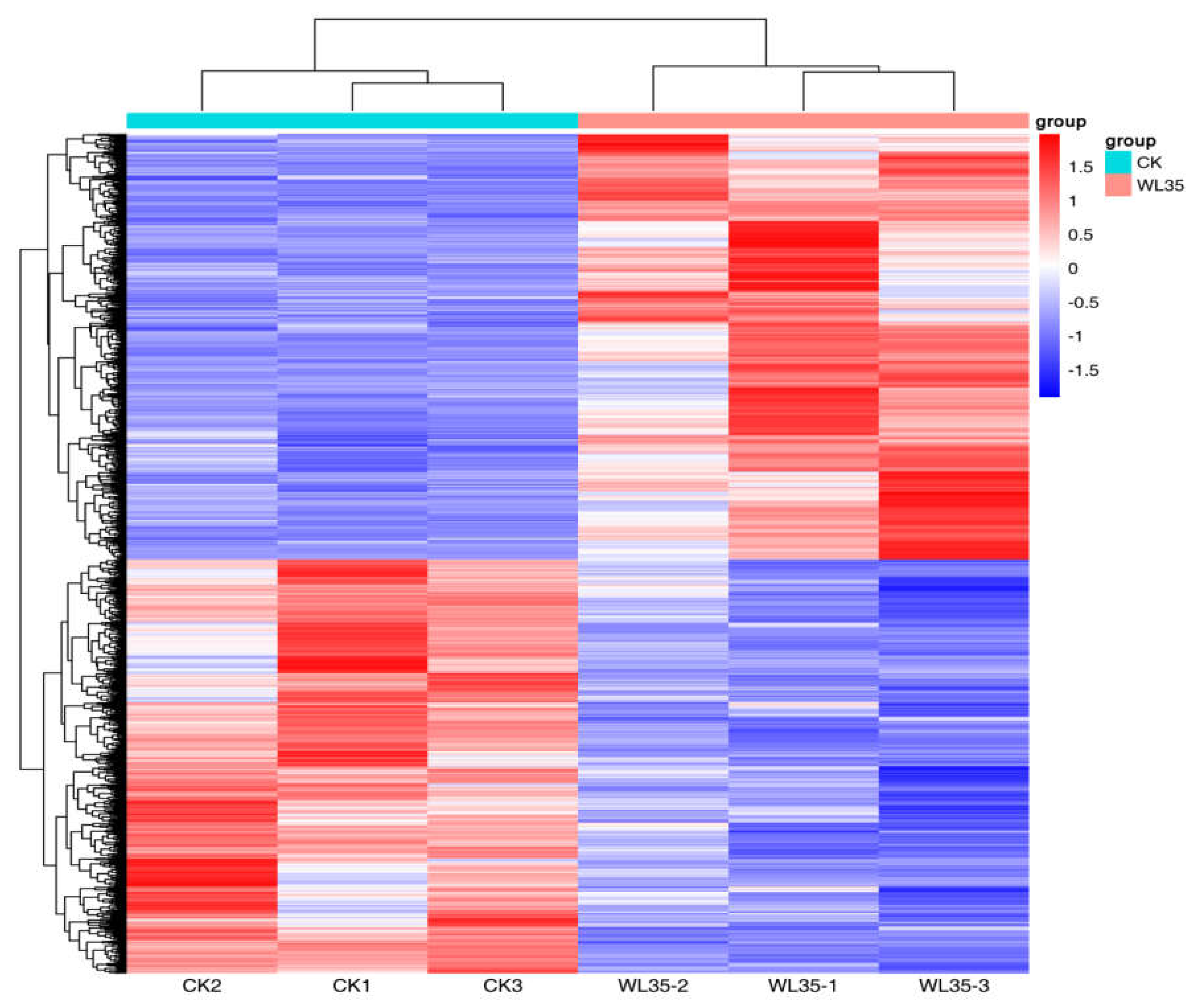
Figure 5), we can find genes with unknown biological connections were linked to each other.
3.6.3. Analysis of Differential Enrichment of Gene Expression in Potato Roots
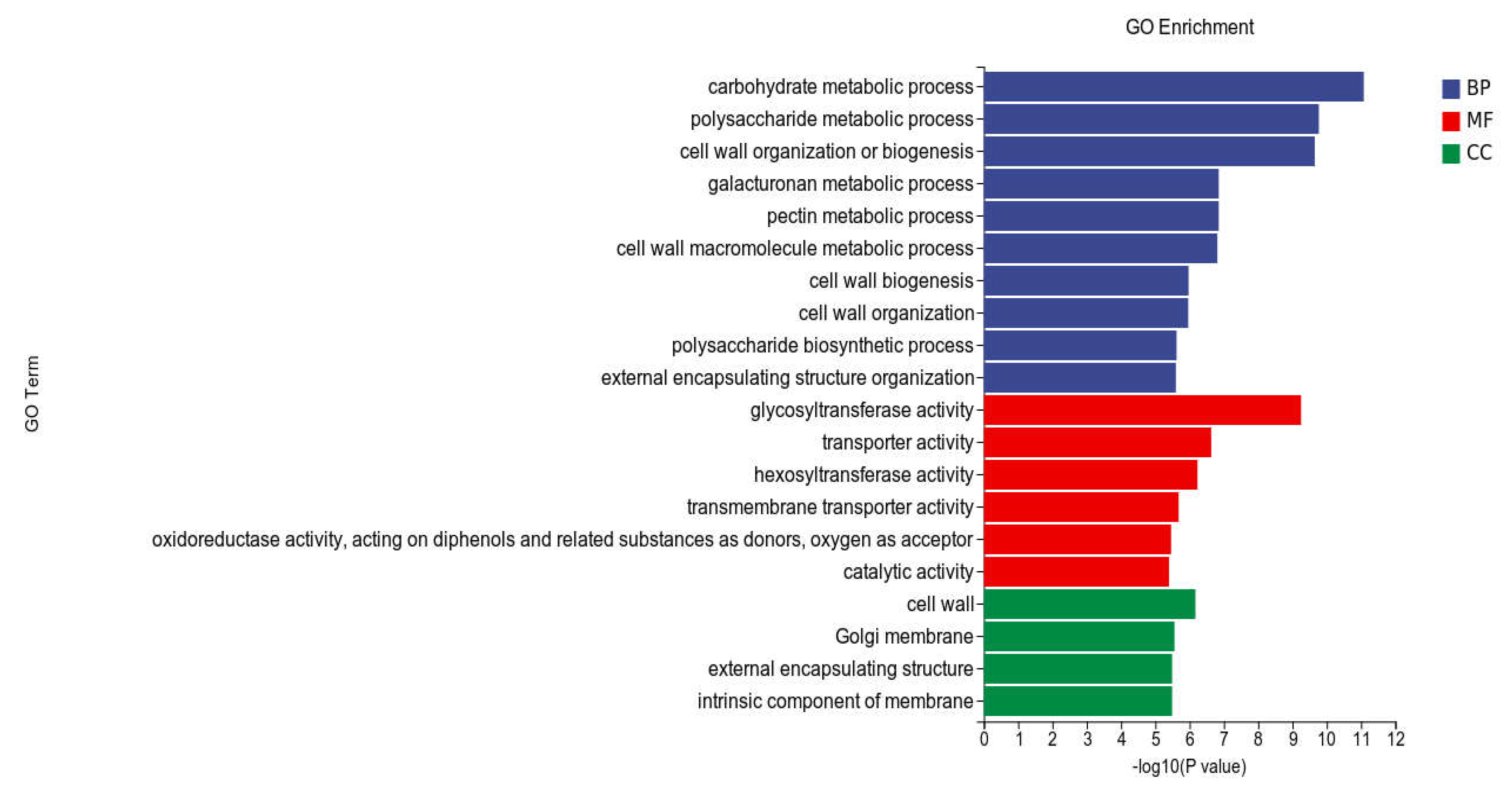
GO analysis: In this experiment, compared with CK, 53,932 DEGs were enriched in the GO classification of potato roots treated with WL35, with a total of 2,824 functional entries, of which 16,957 DEGs were enriched in 720 functional entries in Molecular Function(MF) and 9594 DEGs into 246 functional entries in Cellular Component(CC), and 27381 DEGs were enriched into 1858 functional entries in Biological Process(BP). Among these functional entries, we performed GO enrichment analysis using topGO (
p < 0.05) (
Figure 6).
In the three broad categories of CC, MF, and BP, the top 20 GO entries with the most significantly enriched, were selected to be displayed by bar charts, as shown in
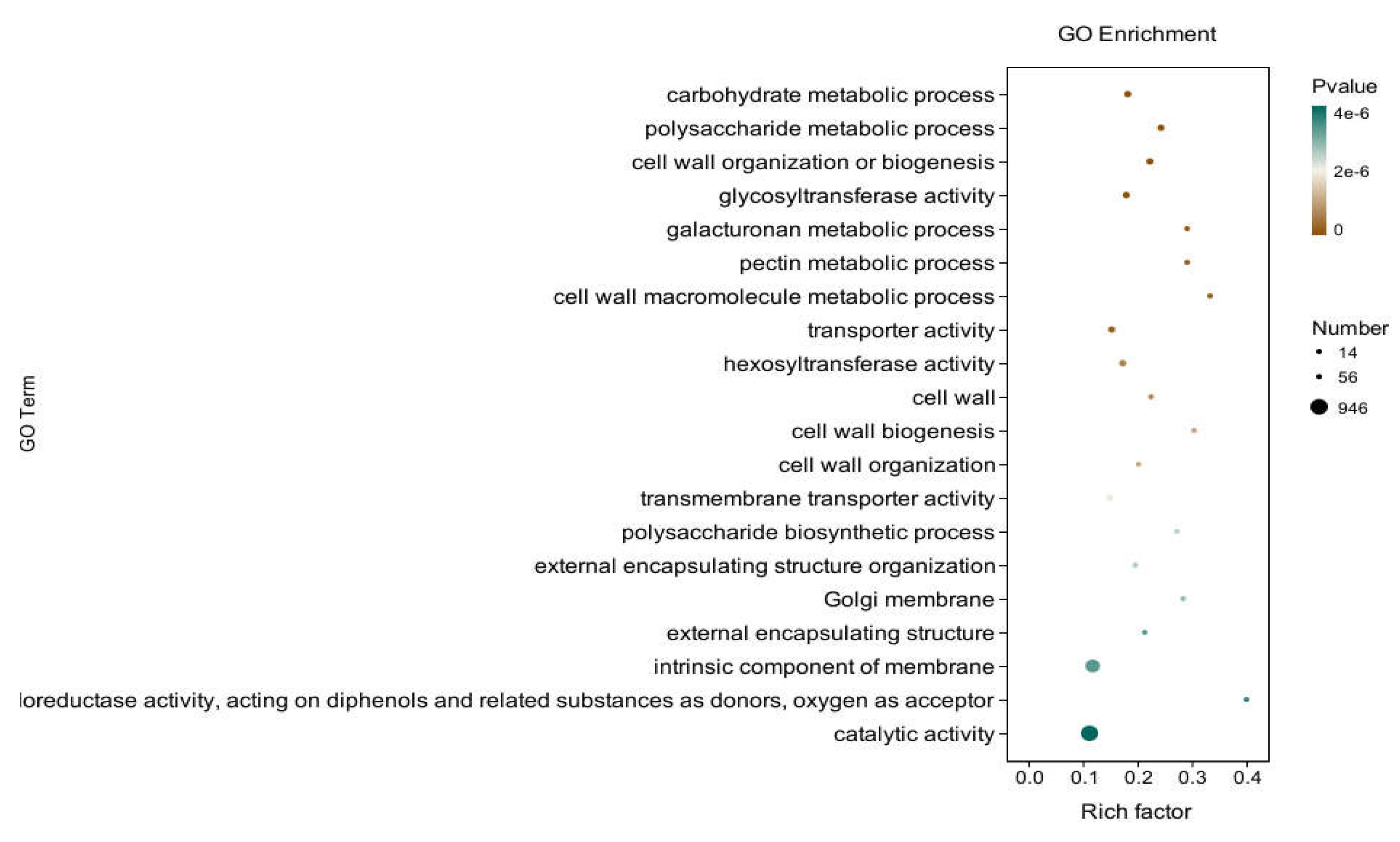
Figure 7. Significantly differentially expressed genes in potato roots using WL35 were mainly enriched in the CC in terms of the cell wall (GO:0005618), Golgi membrane (GO:0000139), external encapsulating structure (GO: 0030312) and intrinsic component of membrane (GO:0031224). In MF, it was mainly enriched in glycosyltransferase activity (GO:0016757), transporter activity (GO:0005215), hexosyltransferase activity (GO:0016758), transmembrane transporter activity (GO:0022857), oxidoreductase activity, acting on diphenols and related substances as donors, oxygen as acceptor (GO:0016682), and catalytic activity (GO:0003824). The DEGs in BP were mainly enriched in carbohydrate metabolic process (GO:0005975), polysaccharide metabolic process (GO:0005976), cell wall organization or biogenesis (GO:0071554), and galacturonan metabolic process (GO:0010393), pectin metabolic process (GO:0045488), cell wall macromolecule metabolic process (GO:0044036), cell wall biosynthesis (GO:0042546), cell wall organization (GO:0071555), polysaccharide biosynthetic process (GO:0000271), external encapsulating structure organization (GO:0045229). And in the GO factor diagram (
Figure 8), DEGs were mainly distributed in the carbohydrate metabolism process (GO:0005975), polysaccharide metabolic process (GO:0005976), glycosyltransferase activity (GO:0016757), transporter activity (GO:0005215), intrinsic component of membrane (GO:0031224) and catalytic activity (GO:0003824).
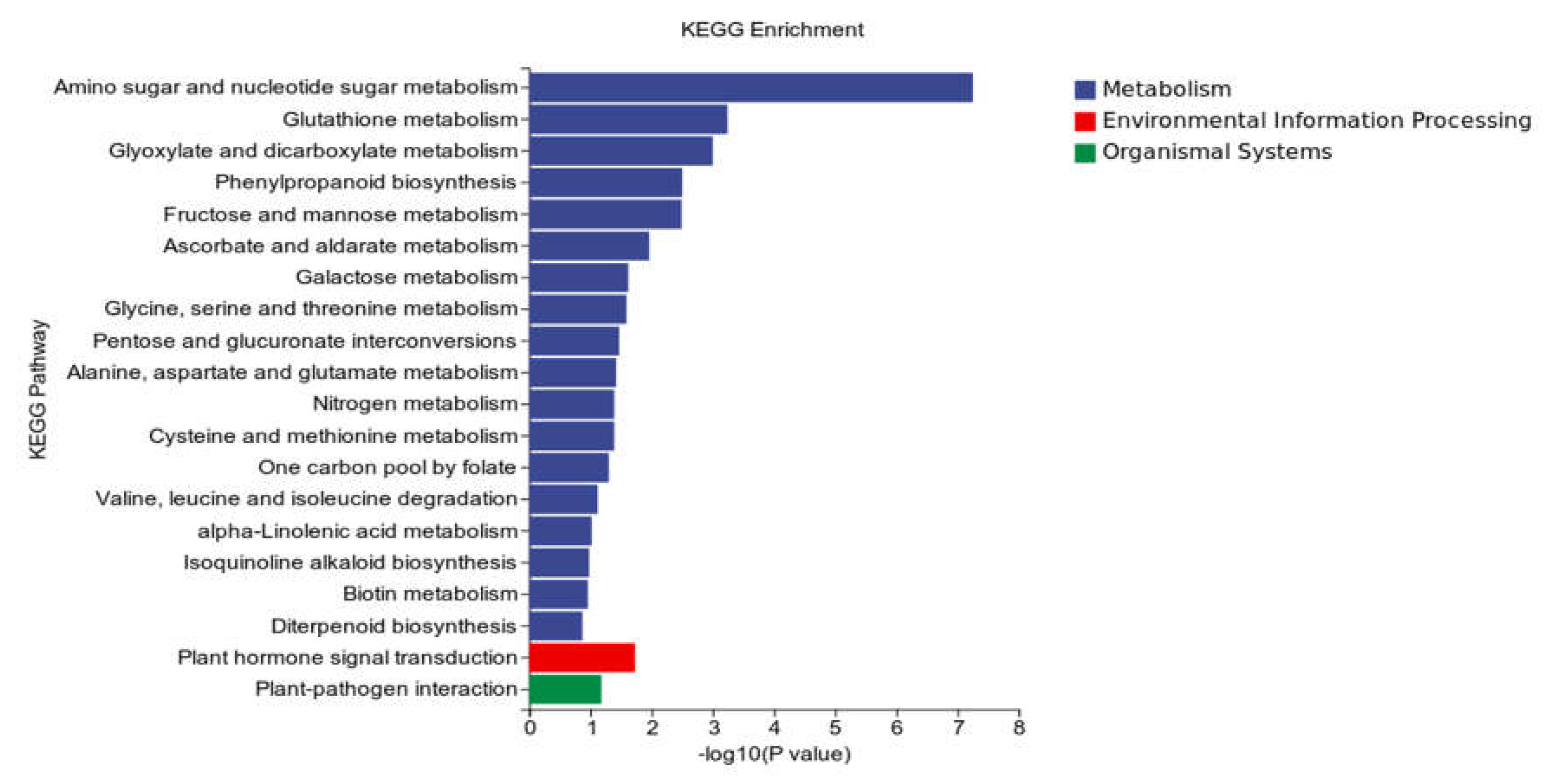
KEGG analysis: KEGG analysis plots showed that 747 DEGs were annotated to 109 categorical metabolic pathways in the KEGG database for the DEGs in potato roots were treated with WL35 (
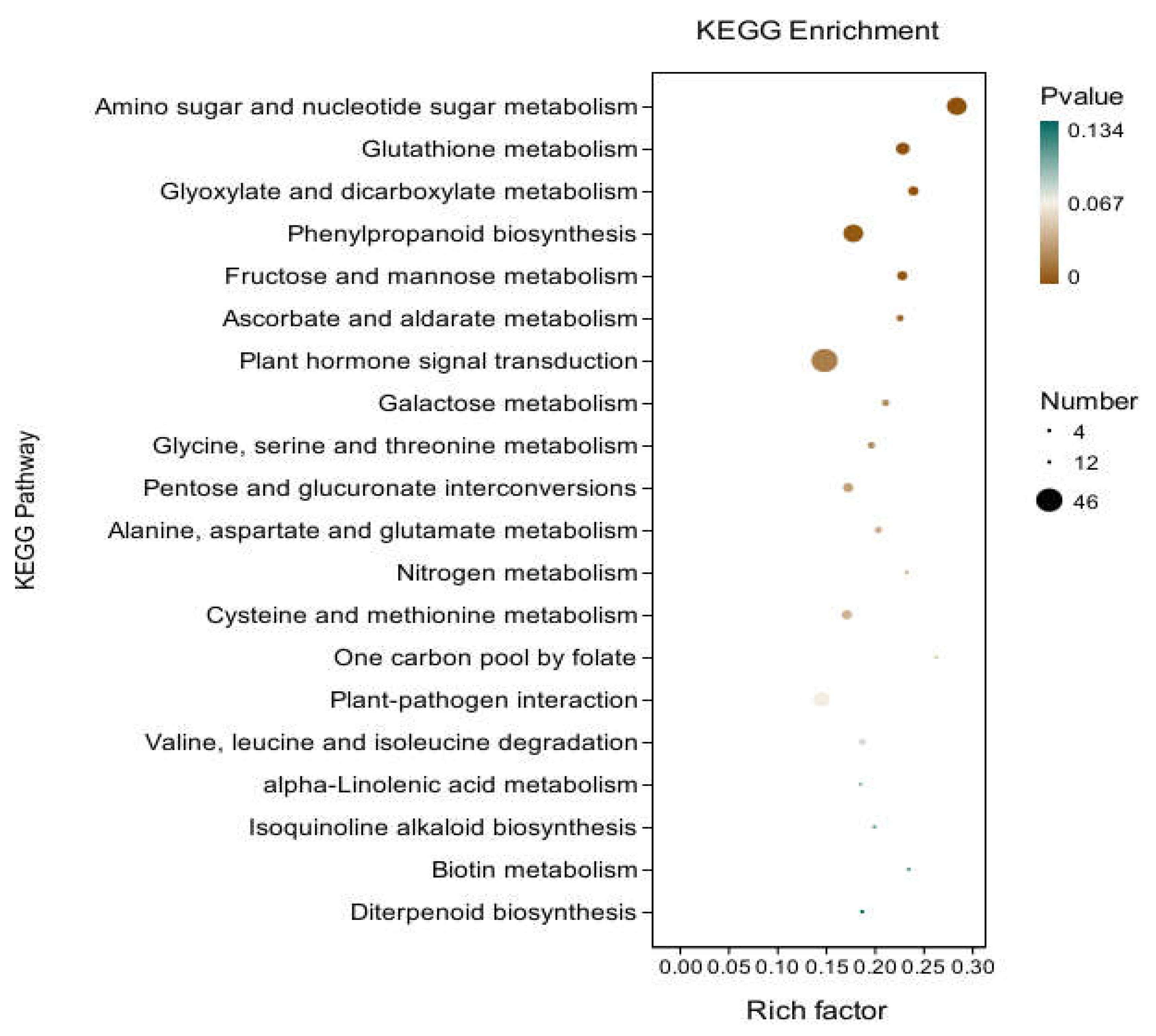
Figure 8). The 20 most significant pathways were mainly related to amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism (sot00520), glutathione metabolism (sot00480), Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism (sot00630), phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (sot00940), fructose and mannose metabolism (sot00051), ascorbate and aldarate metabolism (sot00053), galactose metabolism (sot00052), glycine, serine and threonine metabolism (sot00260), pentose and glucuronate interconversions (sot00040), alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism (sot00250), nitrogen metabolism (sot00910), cysteine and methionine metabolism (sot00270), one carbon pool by folate (sot00670), valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation (sot00280), alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism (sot00592), Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis (sot00950), biotin metabolism (sot00780), diterpenoid biosynthesis (sot00904); plant hormone signal transduction (sot04075) by environmental Information processing pathways; and plant-pathogen interaction (sot04626) by organismal systems. In addition, a large number of enriched genes were distributed in plant hormone signal transduction (sot04075), amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism (sot00520), glutathione metabolism (sot00480), phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (sot00940), plant-pathogen interaction (sot04626), etc (
Figure 9).
4. Discussion
4.1. The Screening and Identification of IAA-Producing Strains
Indole-3-acetic acid, a phytohormone that plays an important regulatory role in plants, is synthesized not only by plants themselves, but also by microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi [
27,
31,
32]. It was shown that
Bacillus aryabhattai CH07 screened from the inter-root of maize had IAA yields of 30.93 mg·L
-1 [
33]. Lin screened 22 strains of plant rhizosphere-promoting bacteria from the inter-root of Camphorus balsamifera, of which the
Pseudomonas (
Pseudomonas sp.) strain XZ11 and
Bacillus pumilus XZ13 had the strongest ability to produce IAA, with yields of 46.82 and 46.19 mg·L
-1 [
34], respectively.
Bacillus aryabhattai HL379 strain screened showed an IAA yield of 47.8 mg·L
-1 [
35] (Li et al., 2020). In this study, a strain of
Fitibacillus barbaricus WL35 with high-yielding IAA was screened from the inter-root soil of maize, and the yields were 48.79 mg·L
-1 after 24 h of incubation in LB medium containing 100mg·L
-1 tryptophan, which were higher than that of the optimal
Bacillus sp. P3-3 with 36 h of incubation of 36.6 mg·L
-1, and that of Y18-3 with a yield of 34.74 mg·L
-1 [
25,
36].
In addition, many studies have shown that
Bacillus sp. could synergistically promote plant growth through one or more actions [
37]. However, most of the IAA-producing strains have been reported to be monofunctional and unstable. Therefore, the screening of novel multifunctional strains with IAA production ability is of great significance for the research and application of microbial fertilizers.
4.2. The Effects of IAA-Producing Strains on Potato Plant Growth and Yields
IAA-producing strains have a broad-spectrum growth-promoting effect, which significantly promotes seed germination and plant growth in cabbage, potato, maize, sugarcane, tobacco, and tomato [
38,
39,
40]. Xing isolated one strain of
Bacillus sp. for the treatment of pakchoi, and the fresh weight of the plant increased by 1.16% and 2.97% compared with the non-inoculated control [
41]. Liu treated maize with different concentrations of
Bacillus subtilis B9 solution and found that the growth promoting effect on maize increased and then decreased as the multiplicity of the bacterial solution increased, and the treatment of maize and sugarcane single shoots with the same concentration found that the strains acted well in the seedling and sprouting stages of both crops [
6]. In the pot experiment of the present study, the plant height, stem thickness, chlorophyll content and number of leaves of potato plants in the pregrowth stage, and the yield at maturity were significantly higher than that of CK, and the application of seed dressing treatments incorporating strains significantly enhanced the number of emergence of potato seedlings, plant height, stem thickness and chlorophyll content in the seedling stage of the potato plant in the field experiments, the yields of the plots were significantly increased, which was consistent with the results of the pot planting test, indicating that the use of IAA-producing
Bacillus sp. as a seed dressing could promote the growth of potato plants and enhance the yield of potatoes. More importantly, the application of IAA-producing strains can improve the yield and quality of commercial potatoes, such as vitamin C, protein, starch content and elemental content, thus increase the income of farmers.
4.3. Exploration of the Synthesis Pathway of IAA in Growth-Promoting Strains
When different concentrations of tryptophan were added, the IAA production of WL35 was all significantly higher than that of the no-tryptophan condition, which indicates that tryptophan has an important effect on the strain’s IAA synthesis, and that its synthetic pathway is dominated by the tryptophan-dependent type. The tryptophan-dependent pathway is divided into five branches, IAM, TAM, IPA, TSO, and IAN [
42]. The IAM pathway is a two-step reaction IAA synthesis pathway, in which the tryptophan monooxygenase encoded by iaaM catalyzes the conversion of L-tryptophan to IAM, which is then converted to IAA by the indoleacetamide hydrolase encoded by the iaaH gene [
43]. The TAM pathway involves the conversion of L-tryptophan to TAM by tryptophan decarboxylase, followed by conversion of TAM to indole acetaldehyde IAAld by amine oxidase, and finally to IAA by aldehyde dehydrogenase [
44]. The IPA pathway has been characterized in a variety of bacteria, where L-tryptophan is converted by aminotransferase to IPA followed by decarboxylase-catalyzed production of indole In this branch, L-tryptophan is converted to IPA by aminotransferase, followed by the production of IAAld catalyzed by decarboxylase, and finally the conversion of IAAld to IAA by aldehyde dehydrogenase [
45]. It is worth noting that indole pyruvic acid and indole acetaldehyde are unstable and can be easily reduced to ILA and TOL. IAN can be converted directly to IAA by nitrile hydrolase or in a two-step reaction, first to IAM by nitrile hydratase or amidase, and then to IAA by indoleacetamide hydrolase [
46]. TSO pathway, in which L-tryptophan is oxidized directly by tryptophan side-chain oxidase to IAAld and then converted to IAA, has only been detected on Pseudomonas fluorescens with tryptophan side-chain oxidase activity has only been detected in Pseudomonas fluorescens [
47,
48]. The tryptophan-independent pathway was first proposed because of the increased levels of IAA synthesis in Arabidopsis tryptophan synthesis-deficient mutants [
49].
In this study, UPLC-MS/MS and HPLC were used to determine the metabolites in WL35 cultured at different times. ILA and TOL were consistently detected in WL35 at different times, TAM was detected at 16 h, TAM signals disappeared and IAM began to accumulate at 24 h, so it was hypothesized that IAM, TAM and IPA pathways existed in WL35. By characterizing the enzyme activity, Phi determined that
B. polymyxa E681 possesses the IPA pathway, and the construction of mutants of the key enzyme putative gene revealed the presence of the IAN pathway in
B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42 [
50,
51]. Shao identified, by a combination of chemical and genetic analyses, the presence of
B. velezensis SQR9 candidate genes for IPA pathway-associated enzymes and validated the potential intact IPA pathway of SQR9 [
52]. Meanwhile, the results of qRT-PCR showed that the addition of tryptophan significantly up-regulated the genes iaaM and
iaaH related to the IAM synthesis pathway, as well as the genes
patB, encoding a conserved hypothetical protein predicted to be an aminotransferase;
dhaS, encoding indole 3-acetaldehyde dehydrogenase;
yclC, encoding a UbiD family decarboxylase; in the IPA synthesis pathway. The TAM pathway-related genes
ysnE: encoding α-acetyltransferase,
yobN: encoding monoamine oxidase, and
TDC1: encoding tryptophan decarboxylase were also upregulated.
4.4. Differential Enrichment Analysis of Gene Expression in Potato Roots
Transcriptome analysis of potato roots showed that a considerable number of genes were differentially expressed in response to inoculation with strain WL35. Strain WL35 enhances growth hormone signaling in potato. The expression of the SAUR family of protein genes, the GH3 gene family of growth hormone response genes and the Class III PERs genes that regulate IAA catabolism were up-regulated, whereas the expression of the differential genes that regulate the synthesis of endogenous growth hormones was down-regulated, suggesting that there may be a transport conduction of exogenous plant IAA in the root system of the potato and participate in the growth and metabolic process of the plant. The SAUR gene family, the largest of the early response gene families, influences growth hormone synthesis and transport involved in plant growth through the up-regulation of growth-promoting factors and the down-regulation of growth-inhibiting factors [
53,
54]. The amide synthase encoded by the Gretchen Hagen 3 (GH3) gene catalyzes the binding of phytohormones such as IAA, jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) to amino acids to regulate the concentration of phytohormones, and feedback regulates the growth, development and stress response process of the plant [
55]. The Aux/IAA gene is a transcriptional repressor of the ARF gene, which regulates the downstream growth hormone-regulated genes through the regulation of the ARF gene [
56]. In addition, Aux/IAA genes function in a number of different phytohormone signaling pathways, such as the JA, SA [
57], ethylene [
58] and oleaginous steroid [
59]. High expression levels of these growth hormone early response gene families promote potato growth. Moreover, brassinosteroid (BR) hormone is essential for root growth [
29], and inoculation with strain WL35 resulted in up-regulation of the expression of BR-related genes in potato roots and an increase in the concentration of BR, which promoted the growth of the potato root system.
Genes encoding UGE, Chitinase, Pectinases, Class III PERs, Hexokinase, and PRDX were differentially up-regulated in the transcriptome of potato interacting with WL35. These genes are all involved in the cell wall’s organization or biogenesis. UDP-glucose is the substrate for the synthesis of cellulose, the basis of synthesizing cell wall polysaccharides, and plays an important role in the interconversion of nucleotide sugars in the metabolism of cell wall polysaccharides, while UGE is a key enzyme in the conversion of UDP-glucose to the synthesis of hemicelluloses and pectins [
60,
61]. Plant chitinases play a key role in combating biotic and abiotic stresses. Class III PERs are a class of plant-specific oxidoreductases involved in many physiological processes in the plant body, possessing IAA oxidase activity, controlling the catabolism of growth hormone affecting cell growth and cell wall modification, and also involved in lignin synthesis and plant stress response [
62,
63]. Plant chitinases were strongly expressed when plant cells were under pathogen stress or, various abiotic stresses such as plant trauma, osmotic pressure, cold, heavy metal stress, and salt [
64]. Pectinases affect the regulation of cell wall mechanical stability during fruit ripening, stem lengthening, tuber yield and root formation [
65]. It has also been demonstrated that pectinesterase contributes to the plant’s defense against pathogen attack. Hexokinase regulates the utilization of stored and free sugars in plants, catalyzes the phosphorylation of hexose into the glycolytic pathway [
66], provides energy and intermediate metabolites for plant physiological activities, has a key role in glucose signaling, and interacts with ethylene signaling [
67]. PRDX is one of the phytoprotective enzymes that increase plant resistance [
68]. The up-regulation of these genes indicates that strain WL35, as a potato seed dressing, can promote the growth of potato cell wall, lignin synthesis, cellulose and pectin synthesis, maintain the carbon flow and respiration of starch synthesized by potato, which can help to improve the environmental resilience of potato, and improve the yield and quality of potato.
Furthermore, analysis of other growth hormone differentially expressed genes revealed that both gibberellin and ethylene-related signaling pathways were activated in the potato root system. According to related studies, high levels of expression of gibberellin GA2oxs genes could reduce active GA content, which reduces the plant fruit set rate, seed number, fruit quality, inhibits lateral branching development and reduces fiber yield [
69]. Down-regulation of gibberellin GA2oxs and GA3oxs gene expression in WL35-treated potato roots, and down-regulation of GA2oxs gene expression in response to the ethylene precursor substance ACC [
29], resulting in increased GA levels, while the up-regulation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase gene expression in the ethylene synthesis pathway promotes the synthesis of ethylene in the potato root system [
70], which collectively promotes the growth and development of potato and improves potato yield. It suggests that in potato the same gene regulatory response mechanism may exist, and IAA may act as a signaling molecule in this process to regulate the growth and development of potato plants, thereby reducing the input of exogenous IAA.
5. Conclusion
In this study, a highly efficient IAA-producing strain, Fitibacillus barbaricus WL35, was screened by the Salkowski colorimetric assay, and its IAA production was 48.79 mg·L-1. Application of WL35 in pots and field trials significantly increased plant biomass, increased yield and improved quality. The analysis of the intermediates identified the tryptophan-dependent pathway as the main synthesis pathway in strain WL35, and the optimal concentration was 2.0 mM. It was initially inferred that IAA synthesis in strain WL35 was the result of the combined action of the IAM, TAM and IPA pathways, and that the pathways that acted at different times were different. In addition, the results of transcriptional analyses showed that potato root expression differential genes were enriched in processes such as carbohydrate metabolism process and cellular polysaccharide metabolism, and strain WL35 regulated the growth and development of potato plants by inducing the gene expression of phytohormone signaling, metabolism of amino acid sugars and nucleotide sugars, glutathione metabolism, and phenylpropane biosynthesis process. This study will help to reveal the IAA synthesis pathway of Fitibacillus barbaricus WL35 and its molecular mechanism to promote potato growth, and provide a theoretical basis for the application and production of WL35 to improve potato yield.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Xiaoyu Li; Data curation, Xiaoyu Li, Huan Tao, Ling Ma, Shisong Wang and Di Zhang; Formal analysis, Huan Tao and Ling Ma; Funding acquisition, Xianyu Chen, Xingyao Xiong and Yanfei Cai; Methodology, Xiaoyu Li, Huan Tao, Ling Ma, Shisong Wang, Di Zhang and Yanfei Cai; Project administration, Xianyu Chen, Xingyao Xiong and Yanfei Cai; Software, Xiaoyu Li; Writing – original draft, Xiaoyu Li; Writing – review & editing, Xiaoyu Li, Huan Tao, Ling Ma, Shisong Wang, Di Zhang, Xianyu Chen, Xingyao Xiong and Yanfei Cai.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Special Funds of Hunan Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) repository, accession number PRJNA1119397.
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants for their participationand support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
References
- Zhang, H., Xu, F., Wu, Y., Hu, H., Dai, F. (2017). Progress of potato staple food research and industry development in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 16, 2924-2932. [CrossRef]
- Batool, T., Ali, S., Seleiman, M. F., Naveed, N. H., Ali, A., Ahmed, K., et al. (2020). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria alleviates drought stress in potato in response to suppressive oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes activities. Sci. Rep. 10:16975. [CrossRef]
- Onodera, S., Okuda, N., Ban, S., Saito, M., Paytan, A., Iwata, T. (2020). Phosphorus cycling in watersheds: from limnology to environmental science[J]. Limnology, 21(3):327-328.
- Xiong, C., Guo, Z., Chen, S., Gao, Q., Kishe, M., Shen, Q. (2020). Understanding the pathway of phosphorus metabolism in urban household consumption system: a case study of dar es salaam, tanzania[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 274:122874.
- Pang, Z., Yu, D. (2020). Plant root system-microbial interaction system under drought stress and its application[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 56 (2): 109-126.
- Liu, H., Wang, J., Sun, H., Han, X., Peng, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2020). Transcriptome profiles reveal the growth-promoting mechanisms of Paenibacillus polymyxa YC0136 on tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Front. Microbiol. 11:584174. [CrossRef]
- Lata, H., Li, X. C., Silva, B., Moraes, R. M., Halda-Alija, L. (2006). Identification of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria from micro propagated Echinacea plants using 16S rRNA sequencing. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 85, 353–359. [CrossRef]
- Bottini, R., Cassan, F., Piccoli, P. (2004). Gibberellin production by bacteria and its involvement in plant growth promotion and yield increase. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 65, 497–503. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y., Pi, H., Chandrangsu, P., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, H., et al. (2018). Antagonism of two plant-growth promoting Bacillus velezensis isolates against Ralstonia solanacearum and Fusarium oxysporum. Sci. Rep. 8:4360. [CrossRef]
- Chai, J., Yao, T., Wang, Z., Han, J., Zhang, W., Liu, X., et al. (2022). Screening and characterization of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria from rhizosphere of forage species in an alpine region. Pratacultural Science, 39(9): 1752-1762.
- Zhang, H., Wang, H., Niu, B., Guo, K., Liu,L., Jiang, Y., et al. (2022). Screening, identification and broad-spectrum application of efficient IAA-producing bacteria dissolving phosphorus and potassium. Biotechnology Bulletin, 38(5):100-111.
- Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Pratush, A. (2014). Molecular diversity and functional variability of environmental isolates of Bacillus species[J]. SpringerPlus, 3(1): 1-11..
- Adesemoye, A., Yuen, G., Watts, D., Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Sharma, S., et al. (2017) Microbial inoculants for optimized plant nutrient use in integrated pest and in-put management systems. Probiotics and plant health, 21-40.
- Cui, X., He, P., Yang, L., He, P., He, P., Wu,Y., et al. (2019). Phosphorus-and potassium-dissolving and nitrogen-fixing capabilities and growth-promotion effect of B9601-Y2 on maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sci-ences, 27(3): 155-160.
- Tao, H., Wang, S., Li, X., Li, X., Cai, J., Zhao, L., et al. (2023). Biological control of potato common scab and growth promotion of potato by Bacillus velezensis Y6. Front. Microbiol. 14:1295107. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y., Xu, W., Hu, Y., Tian, R., and Wang, Z. (2022). Bacillus velezensis YYC promotes tomato growth and induces resistance against bacterial wilt. Biol. Control 172:104977. [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, J., Solano, B., Lucas, J. A., Lobo, A. P., García-Villaraco, A., Gutiérrez Mañero, F. J. (2008). Ecology, genetic diversity and screening strategies of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). plant-bacteria interactions. Strategies and techniques to promote plant growth, 1-17.
- Grossmann, K. (2010). Auxin herbicides: Current status of mechanism and mode of action. Pest Manag. Sci. 66, 113–120.
- McSteen, P.(2010). Auxin and monocot development. Csh. Perspect. Biol., 2, 17.
- Bianco, C., Defez, R.(2009). Medicago truncatula improves salt tolerance when nodulated by an indole-3-acetic acid-overproducing Sinorhizobium meliloti strain. J. Exp. Bot. 60, 3097–3107.
- Limtong, S., Koowadjanakul, N. (2012). Yeasts from phylloplane and their capability to produce indole-3-acetic acid. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 3323–3335.
- Ruanpanun, P.; Tangchitsomkid, N.; Hyde, K.D.; Lumyong, S.(2010). Actinomycetes and fungi isolated from plant-parasitic nema tode infested soils: Screening of the effective biocontrol potential, indole-3-acetic acid and siderophore production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26, 1569–1578.
- Spaepen, S., Vanderleyden, J., Remans, R.(2007). Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 31 (4): 425-448.
- Zhao, Y. (2010). Auxin biosynthesis and its role in plant development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. , 61, 49–64.
- Spaepen, S., Vanderleyden, J. (2011). Auxin and plant-microbe interactions. Csh. Perspect. Biol.3, a001438.
- Teale, W.D., Paponov, I.A., Palme, K. (2006). Auxin in action: Signalling, transport and the control of plant growth and development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.7, 847–859.
- Barriuso, J., Hogan, D.A., Keshavarz, T., Martinez, M.J.(2018). Role of quorum sensing and chemical communication in fungal biotechnology and pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev.42, 627–638.
- Lata, H., Li, X. C., Silva, B., Moraes, R. M., Halda-Alija, L. (2006). Identification of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria from micro propagated Echinacea plants using 16S rRNA sequencing. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 85, 353–359. [CrossRef]
- Vukasinovic, N., Wang, Y., Vanhoutte, I., Fendrych, M., Guo, B., Kvasnica, M., et al. (2021). Local brassinosteroid biosynthesis enables optimal root growth. Nat. Plants 7,619–632. [CrossRef]
- Liu, K., Kang, B. C., Jiang, H., Moore, S. L., Li, H., Watkins, C. B., et al. (2005). A GH3-like gene, CcGH3, isolated from Capsicum chinense L. fruit is regulated by auxin and ethylene. Plant Mol. Biol. 58, 447–464. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S., Wei, J., Chen, H., Liu, Y., Lu, H., Chou, J. (2015). Indole-3-acetic acid:a widespread physiological code in interactions of fungi with other organisms[J]. Plant Signaling&Behavior, 10(8): e1048052. JUNCAO.
- Sun, L., Yang, L., Fang, W., Zhao, X., Guo, L., Dai, J. (2018). The plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Variovorax boronicumulans CGMCC 4969 regulates the level of indole-3-acetic acid synthesized from indole-3-acetonitrile. Applied and environmental microbiology, 84(16), e00298-18.
- Wan, X., Wang, J., Li, F., Jiang, Y., Xu,W., Liu, Z. (2020). Screening and identifica-tion of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from maize rhizosphere soil and its growth promoting effect[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 36(5): 98-103.
- Lin, Y., Si, C., Huang, L., Huang, Y., Liao, Y. (2019). Isolation and promoting characteristics of the rhizospheric bacteria of Cinnamomum camphora[J]. Northern Horticulture, (4): 59-64.
- Li, P., Yao, Y., Song, J., Wang, T., Zhou, B., Wang, B., et al..(2020). Isolation and identification of IAA-producing Bacillus sp. on potato rhizosphere and its growth-promoting effect[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 36(9): 109-116.
- He, S., Xie D., Song, M., Pan, T., Dong, W. (2021). Screening and characterization of an ionic rare-earth mineralized plant inter-root growth-promoting Bacillus sp.[J]. Journal of Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 42(01):52-58.
- Yasmin, F., Othman, R., Saad, M., Sijam, K. (2006). Screening forbeneficial properties of rhizobacteria isolated from sweet potato rhizosphere[J]. Biotechnology (Faisalabad), 6(1):49-52.
- Chen, Y., Li, H., Zhu, S., Yan, H., Lang, B., Ji, W. (2020). Isolation and characterization of indole acetic acid (IAA)-producing bacterium and its effect on seed germination and seedling growth and development of tobacco[J]. Crop Journal, (02):176-181.
- Gao, Y., Zhu, S., Wu, Q., Lei, X., An, Q., Wang, Q., et al. (2017). Screening of IAA endophytic bacteria in Dendrobium chrysogenum and its effect on corn seed germination under drought stress[J]. Seed, 36(04):36-41.
- Yuan, Y., Xu, C. (2017). Effectiveness of Bacillus subtilis SQR9 in promoting cucumber growth[J]. Chinese Melon and Vegetable, 30(03):25-28.
- Xing, F., Gao, M., Hu, Z., Li, X. (2016). Screening and characterization of a high-yielding IAA strain and its growth-promoting effect on cabbage[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 44(10):1002-1302.
- Duca, D., Lorv, J., Patten, C. L., Rose, D., Glick, B. R. (2014). Indole-3-acetic acid in plant–microbe interactions[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 106(1):85-125.
- Li, M., Guo, R., Yu, F., Chen, X., Zhao, H., Li, H., et al. (2018). Indole-3-Acetic Acid Biosynthesis Pathway in the Plant-Beneficial Bacterium Arthrobacter pascens ZZ21[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2):443.
- Perley, J. E., Stowe, B. B. (1966). On the ability of Taphrina deformans to produce indoleacetic acid from tryptophan by way of tryptamine[J]. Plant Physiology, 41(2):234-237.
- Zhang, P., Jin, T., Kumar Sahu, S., Xu, J., Shi, Q., Liu, H. (2019). The distribution of tryptophan-dependent indole-3-acetic acid synthesis pathways in bacteria unraveled by large-scale genomic analysis. Molecules, 24(7), 1411.
- Xie, S. X., Kato, Y., Komeda, H., Yoshida, S., Asano, Y. (2003). A gene cluster responsible for alkylaldoxime metabolism coexisting with nitrile hydratase and amidase in Rhodococcus globerulus A-4. Biochemistry, 42(41), 12056-12066.
- Beyeler, M., Keel, C., Michaux, P., Haas, D.(1999). Enhanced production of indole-3-acetic acid by a genetically modified strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 affects root growth of cucumber, but does not improve protection of the plant against Pythium root rot[J]. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 28:225-233.
- Hammer, B. K., Tateda, E. S., Swanson, M. S. (2002). A two-component regulator induces the transmission phenotype of stationary-phase Legionella pneumophila[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 44(1):107-118.
- Normanly, J., Cohen, J. D., Fink, G. R. (1993). Arabidopsis thaliana auxotrophs reveal a tryptophan-independent biosynthetic pathway for indole-3-acetic acid[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 90(21):10355 10359.
- Idris, E. E., Iglesias, D. J., Talon, M., Borriss, R. (2007). Tryptophan-dependent production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) affects level of plant growth promotion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 20(6):619-626.
- Phi, T. Q., Park, Y. M., Ryu, C. M., Park, S. H. (2008). Functional Identification and Expression of Indole-3-Pyruvate Decarboxylase from Paenibacillus polymyxa E681[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 47 ,18(07):1235-1244.
- Shao, J., Xu, Z., Zhang, N., Shen, Q., Zhang, R. (2015). Contribution of indole-3-acetic acid in the plant growth promotion by the rhizospheric strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 51(3):321-330.
- Du, M. M., Spalding, E. P., Gray, W. M. (2020). Rapid auxin-mediated cell expansion. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 71, 379–402. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X., Xiao, Z., Liu, Y., Fu, L., He, Y., Jiang, A. (2017). The small auxin-up RNA OsSAUR45 affects auxin synthesis and transport in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 94,97–107. [CrossRef]
- Park, J., Park, J., Kim, Y., Staswick, P., Jeon, J., Yun, J., et al. (2007). GH3-media-ted auxin homeostasis links growth regulation with stress adaptation response in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 282,10036–10046.
- Szemenyei, H., Hannon, M., Long, J.A. (2008). TOPLESS mediates auxin-dependent transcriptional repression during Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Science 319, 1384–1386.
- Wang, D., Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K., Culler, A.H., Dong, X.(2007). Salicylic acid inhibits pathogen growth in plants through repression of the auxin signaling pathway, Curr. Biol., 17(20): 1784-1790.
- Strader, C., Chen, L., Bartel, B. (2010). Ethylene directs auxin to control root cell expansion. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology, 64(5): 874-884.
- Song, Y., You, J., Xiong, L. (2009). Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis, Plant Mol. Biol., 70(3): 297–309.
- Samet, M., Ghazala, I., Karray, F., Abid, C., Chiab, N., Nouri-Ellouz, O., et al. (2022).Isolation of bacterial strains from compost teas and screening of their pgpr properties on potato plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 75365–75379. [CrossRef]
- Seifert, G. J. (2004). Nucleotide sugar interconversions and cell wall biosynthesis: how to bring the inside to the outside[J]. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 7(3): 277-284.
- Kidwai, M., Ahmad, I. Z., Chakrabarty, D. (2020). Class III peroxidase: an indispensable enzyme for biotic/abiotic stress tolerance and a potent candidate for crop improvement[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 39(11): 1381-1393.
- Yan, J., Su, P., Li, W., Xiao, G., Zhao,Y., Ma, X., et al. (2019). Genome-wide and evolutionary analysis of the class III peroxidase gene family in wheat and Aegilops tauschii reveals that some members are involved in stress responses[J]. BMC Genomics, 20(1): 666. [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, B., Vashi, R., Rajput, K., Joshi, R. (2022). Plant chitinases and their role in plant defense: a comprehensive review. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 159:110055. [CrossRef]
- Fries, M., Ihrig, J., Brocklehurst, K., Shevchik, V. E., Pickersgill, R. W. (2007). Molecular basis of the activity of the phytopathogen pectin methylesterase. EMBO J. 26,3879–3887. [CrossRef]
- Moore, B., Zhou, L., Rolland, F., Hall, Q., Cheng, W., Liu, Y., et al. (2003). Role of the Arabidopsis glucose sensor HXK1 in nutrient, light, and hormonal signaling[J]. Science, 300(5617): 332-336.
- Cho, J. I., Ryoo, N., Ko, S., Lee, S. K., Lee, J., Jung, K. H., et al. (2006). Structure, expression, and functional analysis of the hexokinase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta, 224, 598-611.
- Sirokmány, G., Geiszt, M. (2019). The Relationship of NADPH Oxidases and Heme Peroxidases: Fallin’ in and Out[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,10, pp384. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S., Wang, X., Zhang, L., Lin, S., Liu, D., Wang, Q., et al. (2016). Identification and characterization of tomato gibberellin 2-oxidases (GA2oxs) and effects of fruit-specific SlGA2ox1 overexpression on fruit and seed growth and development. Horticulture research, 3.
- Vriezen, W., Achard, P., Harberd, N., Van Der Straeten. (2004). Ethylene-mediated enhancement of apical hook formation in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings is gibberellin dependent[J]. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology.37(4): 505-516.
- Li, J., Li, X., Hou, W., Zheng, S., Zhu, X. (2019). Screening, identification and characterization of a broad spectrum antagonistic strain in banyan rhizosphere soil. The Journal of Applied Ecology.30(11): 3894-3902.
- Shao, D. , Lv, Z., Li, W., Zhou, P., Lai, C.,Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Isolation, identification and growth-promoting characteristics of an endophytic bacteria from a strain of grass[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 52(01):33-40. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H., Li, Y., Cai, Y., Cao, Y., Wang, Y. (2015). Isolation of bacillus amyloliquefaciens JK6 and identification of its lipopeptides surfactin for suppressing tomato bacterial wilt. RSC Adv. 5, 82042–82049. [CrossRef]
- Lin, L., Li, C., Ren, Z., Qin, Y., Wang, R., Wang, J., et al.(2023). Transcriptome profiling of genes regulated by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria Bacillus megaterium P68 in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Front. Microbiol. 14:1140752. [CrossRef]
- Djuuna, I. A. F., Prabawardani, S., and Massora, M. (2022). Population distribution of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in agricultural soil. Microbes Environ. 37:n/a. [CrossRef]
- Sha, S., Zhao, X., Li, Y., Li, C., Zhu, L., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Nutrient expert system optimizes fertilizer management to improve potato productivity and tuber quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102, 1233–1244. [CrossRef]
- Khatri, D., Chhetri, S. (2020). Reducing sugar, total phenolic content, and antioxidant potential of nepalese plants. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020:7296859. [CrossRef]
- Miquel, E., Alegria, A., Barbera, R., and Farre, R. (2004). Microdetermination of phosphorus from infant formulas, casein and casein phosphopeptides. Eur. Food Res.Technol. 219, 639–642. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q., Echigo, K., Raboy, V., and Saneoka, H. (2020). Seedling growth, physiological characteristics, nitrogen fixation, and root and nodule phytase and phosphatase activity of a low-phytate soybean line. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 149, 225–232. [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W., Lewicki, A., Pochwatka, P., Czekała, A., Wojcieszak, D., Jóźwiakowski, K., et al. (2020). Digestate management in polish farms as an element of the nutrient cycle.Clean. Prod. 242:118454. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Qualitative and quantitative testing of strains.
Figure 1.
Qualitative and quantitative testing of strains.
Figure 2.
Promoting effect of WL35 on potato plants in pot experiment. (A) Compared with CK, WL35 significantly promoted plant growth on the 45 days after planting. (B) Compared with CK, WL35 significantly promoted plant yield on the 90 days after planting. (C) Potato yield per plant of different treatments.
Figure 2.
Promoting effect of WL35 on potato plants in pot experiment. (A) Compared with CK, WL35 significantly promoted plant growth on the 45 days after planting. (B) Compared with CK, WL35 significantly promoted plant yield on the 90 days after planting. (C) Potato yield per plant of different treatments.
Figure 3.
Total ion spectra of standard and WL35 in MRM mode.
Figure 3.
Total ion spectra of standard and WL35 in MRM mode.
Figure 4.
Volcano map of differentially expressed genes of CK and WL35. The X-axis is the log2 of the Fold Change, and the Y-axis is the value of the −log 10 at the significance level. The two dotted lines in the figure represent the threshold values of the difference multiples. The dotted line is the threshold of significance level. Red dots indicating upregulated genes in this group; blue dots indicating downregulated genes, and gray dots indicating non-significantly differentially expressed genes.
Figure 4.
Volcano map of differentially expressed genes of CK and WL35. The X-axis is the log2 of the Fold Change, and the Y-axis is the value of the −log 10 at the significance level. The two dotted lines in the figure represent the threshold values of the difference multiples. The dotted line is the threshold of significance level. Red dots indicating upregulated genes in this group; blue dots indicating downregulated genes, and gray dots indicating non-significantly differentially expressed genes.
Figure 5.
Cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes of CK and WL35. Each row represents a gene, and each column represents a sample (WL35-1, WL35-2, and WL35-3 represent three replicates of P68 sample. CK1, CK2, and CK 3 represent three replicates of CK sample). Different colors in the clustering heat map represent the different expression levels of genes. Red indicates high-expression genes and blue indicates low-expression genes,respectively.
Figure 5.
Cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes of CK and WL35. Each row represents a gene, and each column represents a sample (WL35-1, WL35-2, and WL35-3 represent three replicates of P68 sample. CK1, CK2, and CK 3 represent three replicates of CK sample). Different colors in the clustering heat map represent the different expression levels of genes. Red indicates high-expression genes and blue indicates low-expression genes,respectively.
Figure 6.
DEGs in potato tuberous of CK and WL35. Top 20 pathways with the most significant enrichment in GO term between CK and WL35. The X-axis is GO term, indicates the number and percentage of DEGs under each functional classification, whereas the Y-axis is GO term enriched -log10 (p-value), represents the enriched GO functional classification, which is divided into three categories: cellular component, molecular function and biological process.
Figure 6.
DEGs in potato tuberous of CK and WL35. Top 20 pathways with the most significant enrichment in GO term between CK and WL35. The X-axis is GO term, indicates the number and percentage of DEGs under each functional classification, whereas the Y-axis is GO term enriched -log10 (p-value), represents the enriched GO functional classification, which is divided into three categories: cellular component, molecular function and biological process.
Figure 7.
GO-enriched pathways of CK and WL35. The X-axis is rich factor (the number of differential genes annotated to GO Term/the total number of genes annotated to GO Term), and the Y-axis is GO Term. The size of points in the figure represents the number of differential genes annotated to corresponding term (upregulated or downregulated, related to the gene set selected during analysis). The depth of the color indicates the level of significance.
Figure 7.
GO-enriched pathways of CK and WL35. The X-axis is rich factor (the number of differential genes annotated to GO Term/the total number of genes annotated to GO Term), and the Y-axis is GO Term. The size of points in the figure represents the number of differential genes annotated to corresponding term (upregulated or downregulated, related to the gene set selected during analysis). The depth of the color indicates the level of significance.
Figure 8.
Results of KEGG enrichment analysis of CK and WL35. Top 20 pathways with the most significant enrichment in KEGG pathway between CK and WL35. The X-axis is pathway, indicates the number and percentage of DEGs under each functional classification, whereas the Y-axis is pathway enriched-log10 (value of p), represents the enriched KEGG pathway classification.
Figure 8.
Results of KEGG enrichment analysis of CK and WL35. Top 20 pathways with the most significant enrichment in KEGG pathway between CK and WL35. The X-axis is pathway, indicates the number and percentage of DEGs under each functional classification, whereas the Y-axis is pathway enriched-log10 (value of p), represents the enriched KEGG pathway classification.
Figure 9.
Pathways enriched in KEGG analysis of CK and WL35. The X-axis is rich factor (the number of differentially annotated genes in Pathway/the total number of genes annotated in this Pathway), and the Y-axis is Pathway. The size of dots in the figure represents the number of differentially annotated genes in corresponding pathway (upregulated or downregulated, related to the gene set selected for analysis). The depth of the color indicates the level of significance.
Figure 9.
Pathways enriched in KEGG analysis of CK and WL35. The X-axis is rich factor (the number of differentially annotated genes in Pathway/the total number of genes annotated in this Pathway), and the Y-axis is Pathway. The size of dots in the figure represents the number of differentially annotated genes in corresponding pathway (upregulated or downregulated, related to the gene set selected for analysis). The depth of the color indicates the level of significance.
Table 1.
Growth condition of potato in IAA-producing strains treatments.
Table 1.
Growth condition of potato in IAA-producing strains treatments.
| Treatment |
Plant height (cm) |
stem thickness (mm) |
chlorophyll content (SPAD) |
Number of leaves |
Root length (cm) |
| CK |
18.75±1.30b |
7.70±0.50b |
25.75±1.05b |
41.00±1.83b |
22.04±2.17b |
| WL35 |
24.70±1.44a |
10.02±0.21a |
34.23±2.08a |
56.00±2.94a |
25.10±2.51a |
| WL41 |
22.58±0.93ab |
10.03±0.37a |
32.10±1.66a |
52.75±2.32a |
24.65±2.05ab |
| WL56 |
24.48±2.12a |
9.96±0.20a |
33.90±1.53a |
57.25±1.25a |
24.20±1.62ab |
Table 2.
Effect of IAA-producing strains on potato field yield.
Table 2.
Effect of IAA-producing strains on potato field yield.
| Treatment |
Commercial potato yield (t·ha-1) |
First grade potato yield (t·ha-1) |
Secondary potato yield (t·ha-1) |
Non-commercial potato yield (t·ha-1) |
Potato yield
(t·ha-1) |
Yield increase
Rate (%) |
| CK |
35.38±1.39b |
19.14±0.49b |
16.24±0.31b |
3.23±0.33a |
38.61±1.09b |
/ |
| WL35 |
41.16±1.31a |
21.31±0.74a |
19.85±0.51a |
3.71±0.28a |
44.87±1.31a |
16.19 |
| WL41 |
39.05±1.66a |
19.67±1.60b |
19.38±1.16a |
3.97±0.27a |
43.02±2.66a |
11.42 |
| WL56 |
38.93±1.16a |
20.11±1.57ab |
18.82±0.86a |
3.59±0.13a |
42.52±1.16a |
10.11 |
Table 3.
Effect of IAA-producing strains on potato quality.
Table 3.
Effect of IAA-producing strains on potato quality.
| Treatment |
Vitamin C (mg·kg-1) |
Protein (g·kg-1) |
Reducing sugar (%) |
Starch (%) |
| CK |
191.83±7.73a |
7.88±1.48b |
0.13±0.01a |
17.87±1.06a |
| WL35 |
223.19±12.11a |
13.79±0.99a |
0.12±0.00a |
19.05±0.46a |
| WL41 |
225.12±8.87a |
13.98±1.67a |
0.14±0.01a |
19.08±0.89a |
| WL56 |
218.93±11.89a |
11.79±2.01a |
0.12±0.00a |
18.01±0.34a |
Table 4.
Effect of IAA-producing strains on the accumulation of N, P, and K in potato tubers.
Table 4.
Effect of IAA-producing strains on the accumulation of N, P, and K in potato tubers.
| Treatment |
N accumulation (kg·ha-1) |
P accumulation (kg·ha-1) |
K accumulation (kg·ha-1) |
| CK |
72.24±0.45a |
9.07±0.45b |
142.43±3.24c |
| WL35 |
79.45±0.63a |
10.21±0.42a |
180.55±3.13a |
| WL41 |
76.52±0.61a |
9.56±0.43ab |
162.33±6.90b |
| WL56 |
77.30±0.59a |
9.46±0.61b |
170.40±4.11a |
Table 5.
Summary of sequencing results and comparison results.
Table 5.
Summary of sequencing results and comparison results.
| Sample |
CK-1 |
CK-2 |
CK-3 |
WL35-1 |
WL35-2 |
WL35-3 |
| Bases (G) |
6.56 |
6.51 |
5.64 |
5.62 |
6.46 |
5.59 |
| Q30(%) |
93.68 |
93.85 |
93.55 |
93.69 |
93.76 |
93.73 |
| Clean Data (G) |
6.05 |
6.03 |
5.24 |
5.20 |
6.02 |
5.18 |
| Clean Data (%) |
92.25 |
92.53 |
92.88 |
92.5 |
93.2 |
92.67 |
| Total Mapped |
35,526,861 (88.69%) |
33,477,679 (83.88%) |
30,124,258 (86.88%) |
30,039,906 (87.23%) |
34,444,858 (86.42%) |
28,631,000 (83.42%) |
| Multiple Mapped |
1,246,958 (3.51%) |
1,212,078 (3.62%) |
1,122,133 (3.73%) |
1,015,168 (3.38%) |
1,228,651 (3.57%) |
924,566 (3.23%) |
| Uniquely Mapped |
34,279,903 (96.49%) |
32,265,601 (96.38%) |
29,002,125 (96.27%) |
29,024,738 (96.62%) |
33,216,207 (96.43%) |
27,706,434 (96.77%) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).