Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Features and Inheritance
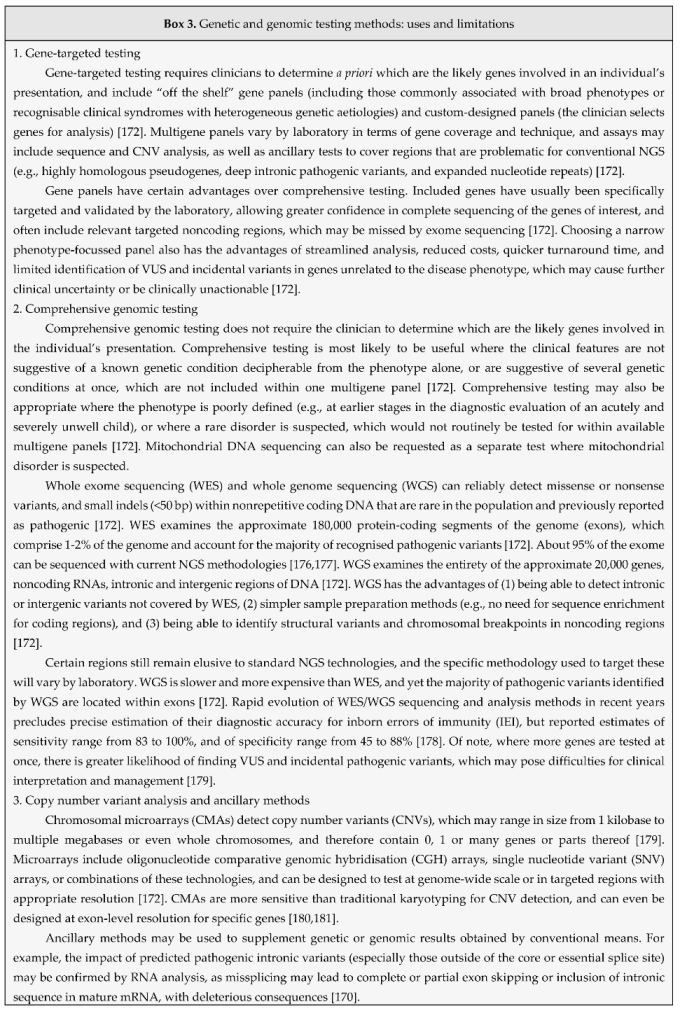
3. Molecular and Cellular Pathophysiology
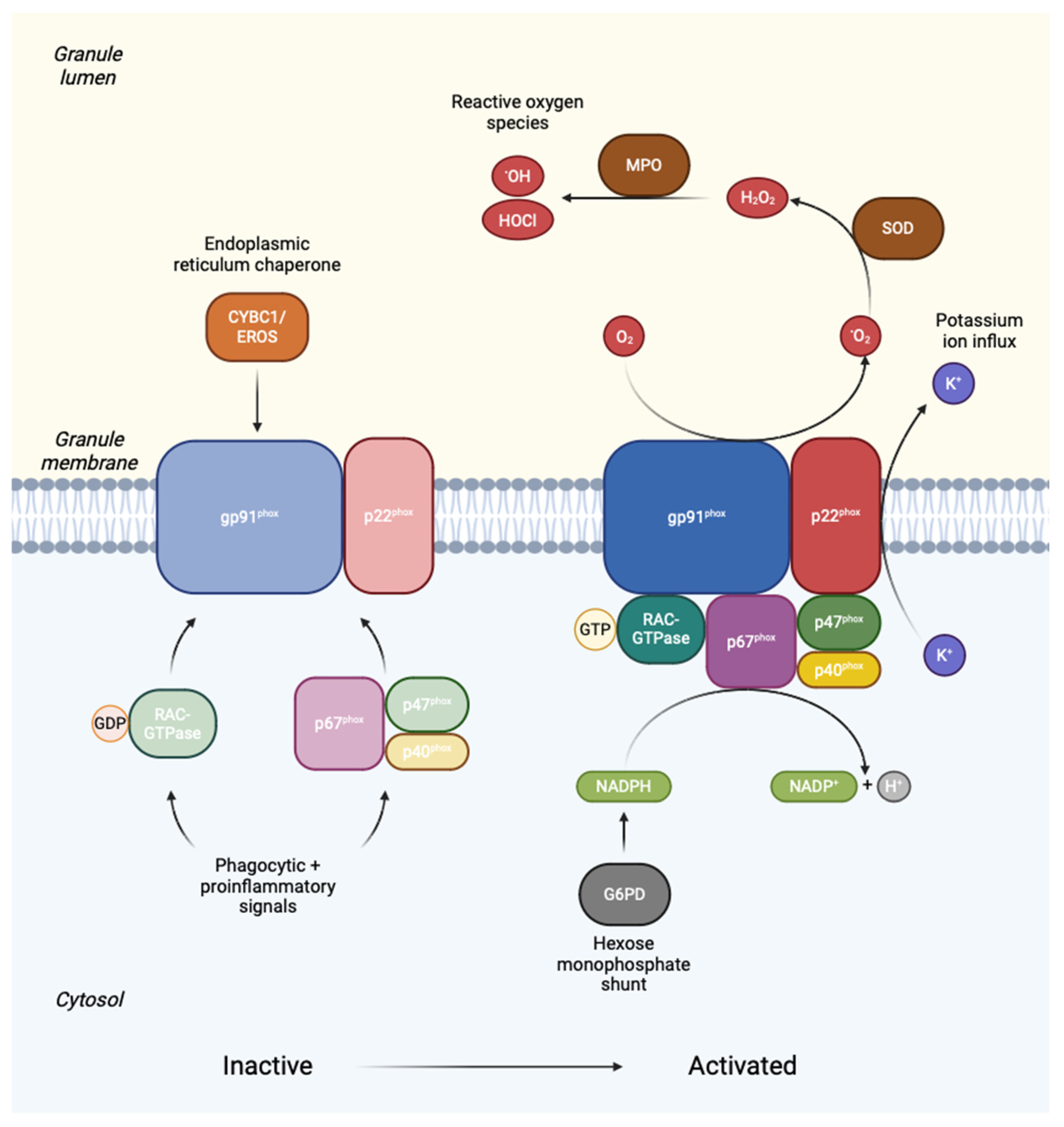
4. Benefits of Early Diagnosis of CGD
5. When to Suspect and Test for CGD

6. Testing of NADPH Oxidase Function
6.1. Measurement of Oxygen Consumption
6.2. Plate-Based Assays
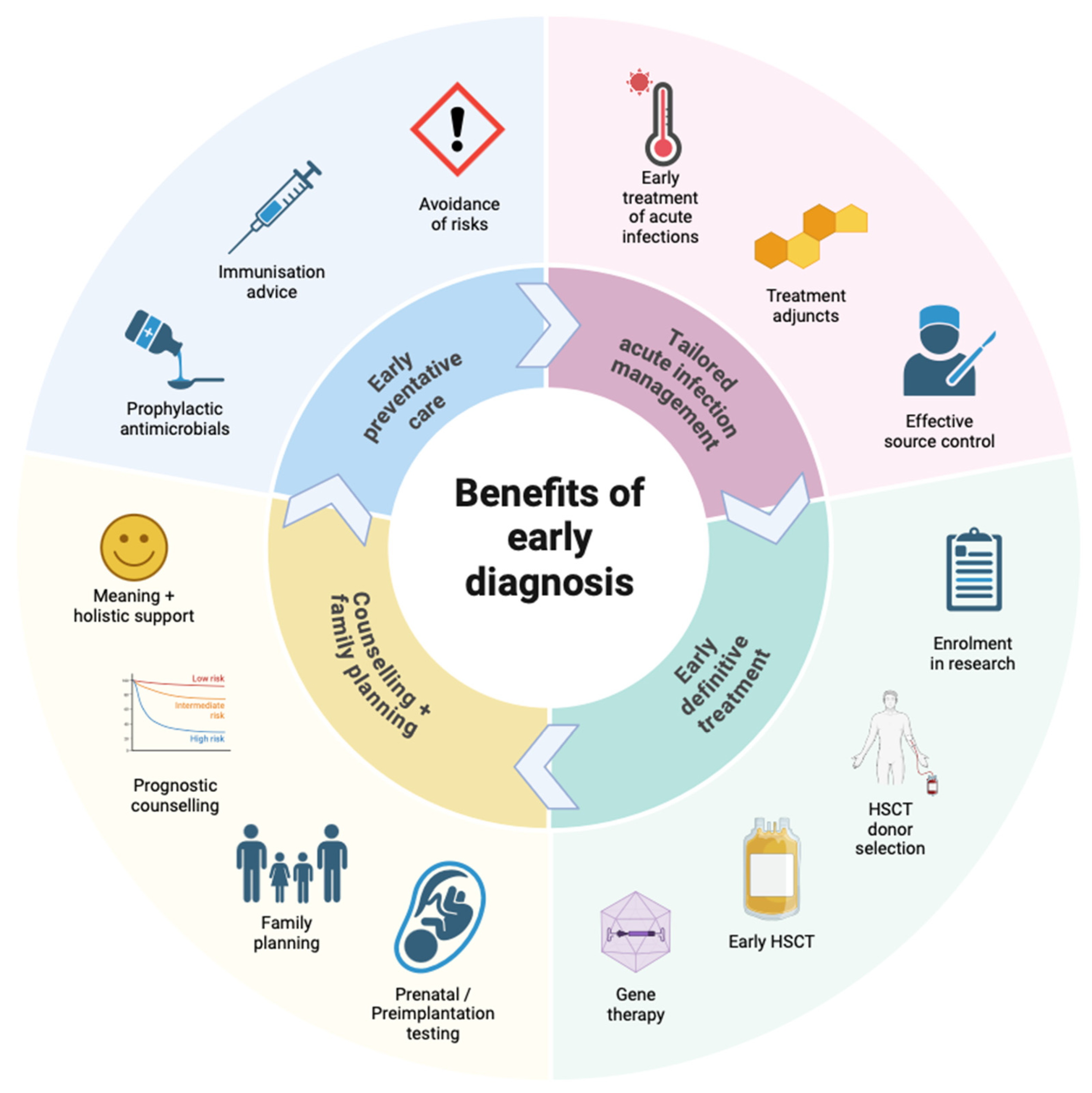
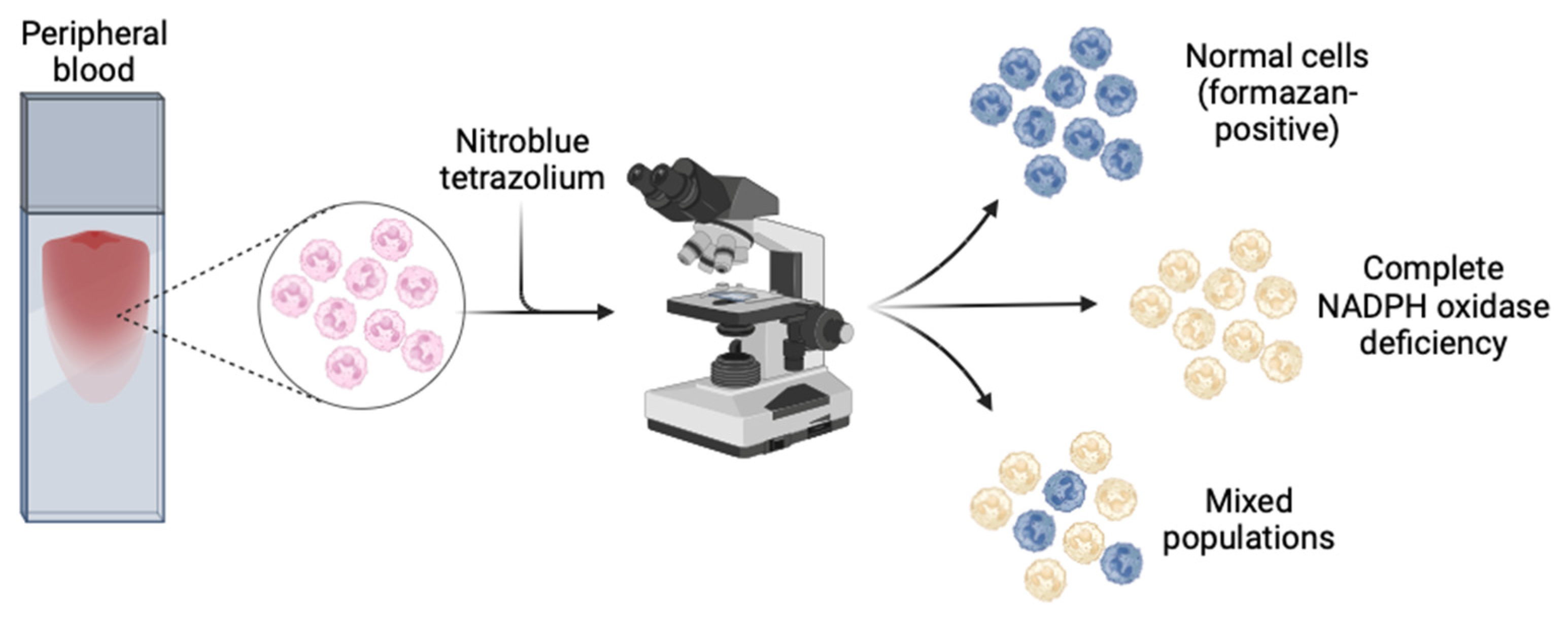
6.3. Nitroblue Tetrazolium (NBT)
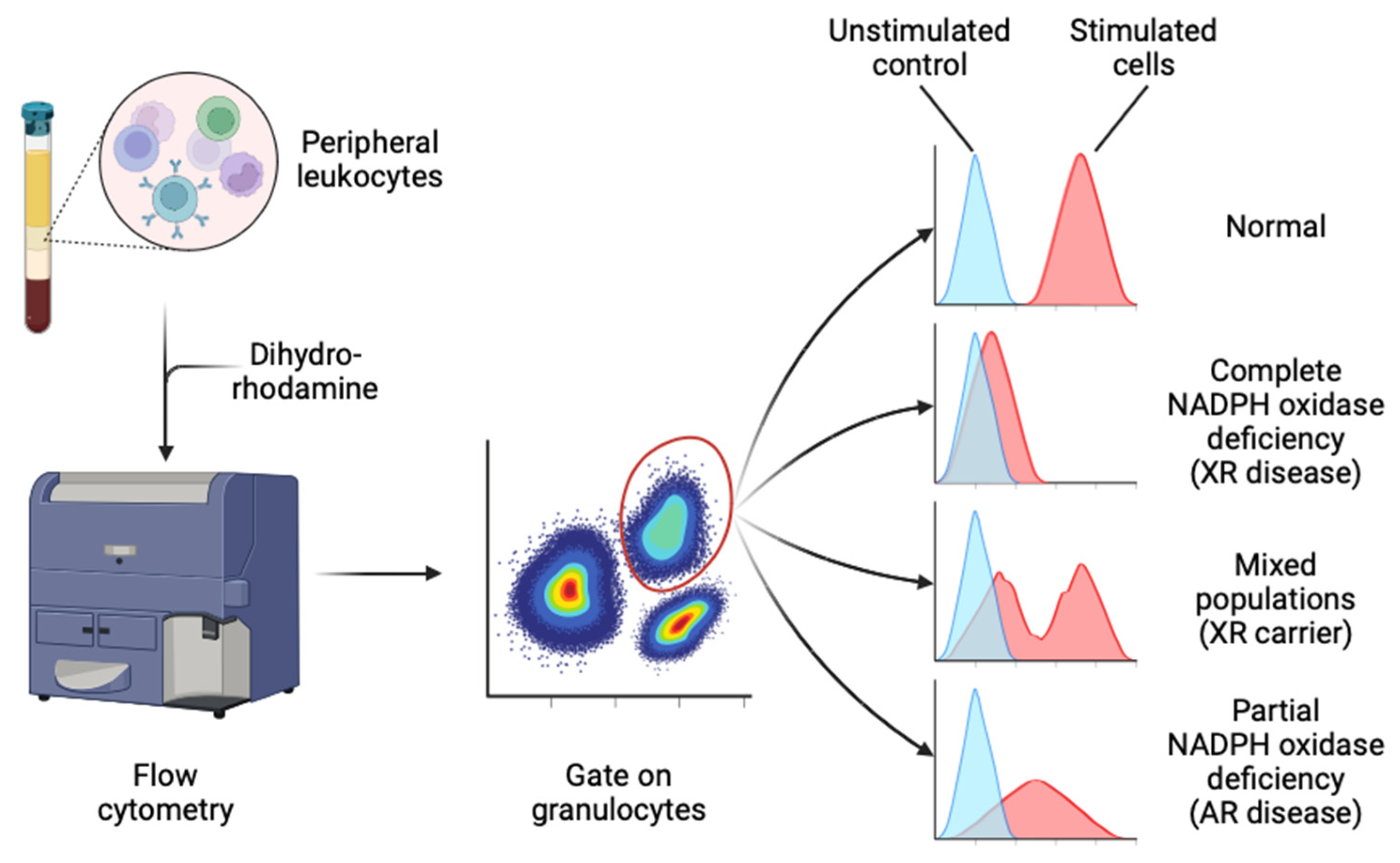
6.4. Dihydrorhodamine (DHR)
6.5. Dichlorofluorescein (DCF)
7. Molecular Diagnostics: Protein Assays
8. Molecular Diagnostics: Genetic Testing

9. Mutations in CGD
10. Limitations of Genetic Testing for CGD
11. Screening
12. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, D.E.; Heimall, J.R. A Review of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 2543–2557. [CrossRef]
- Nunoi, H.; Nakamura, H.; Nishimura, T.; Matsukura, M. Recent topics and advanced therapies in chronic granulomatous disease. Hum. Cell 2022, 36, 515–527. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chiang, B.-L. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: a Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 61, 101–113. [CrossRef]
- Roos D, Holland SM, Kuijpers TW. Chronic granulomatous disease. In: Ochs HD, Smith CIE, Puck JM, editors. Primary immunodeficiency diseases, a molecular and genetic approach. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2014. p. 689–722. [CrossRef]
- Justiz-Vaillant, A.A.; Williams-Persad, A.F.-A.; Arozarena-Fundora, R.; Gopaul, D.; Soodeen, S.; Asin-Milan, O.; Thompson, R.; Unakal, C.; Akpaka, P.E. Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD): Commonly Associated Pathogens, Diagnosis and Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2233. [CrossRef]
- Janeway CA, Craig J, Davidson M, Downey W, Gitlin D, Sullivan JC. Hypergammaglobulinemia associated with severe, recurrent and chronic non-specific infection. Am J Dis Child. 1954;88:388-92.
- Landing, B.H.; Shirkey, H.S. A syndrome of recurrent infection and infiltration of viscera by pigmented lipid histiocytes. Pediatrics 1957, 20, 431–438. [CrossRef]
- A Bridges, R.; Berendes, H.; A Good, R. A fatal granulomatous disease of childhood; the clinical, pathological, and laboratory features of a new syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1959, 97, 387–408. [CrossRef]
- Holmes B, Quie PG, Windhorst DB, Good RA. Fatal granulomatous disease of childhood.: an inborn abnormality of phagocytic function. Lancet. 1966;287(7449):1225-8.
- Babior BM. The respiratory burst oxidase. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988;2(2):201-12.
- Gennery, A. Recent advances in understanding and treating chronic granulomatous disease. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1427. [CrossRef]
- Winkelstein, J.A.; Marino, M.C.; Johnston, R.B.; Boyle, J.; Curnutte, J.; Gallin, J.I.; Malech, H.L.; Holland, S.M.; Ochs, H.; Quie, P.; et al. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Report on a National Registry of 368 Patients. Medicine 2000, 79, 155–169. [CrossRef]
- Wolach, B.; Gavrieli, R.; de Boer, M.; Gottesman, G.; Ben-Ari, J.; Rottem, M.; Schlesinger, Y.; Grisaru-Soen, G.; Etzioni, A.; Roos, D. Chronic granulomatous disease in Israel: Clinical, functional and molecular studies of 38 patients. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 103–114. [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, F.; Badalzadeh, M.; Sedighipour, L.; Movahedi, M.; Fazlollahi, M.R.; Mansouri, S.D.; Khotaei, G.T.; Bemanian, M.H.; Behmanesh, F.; Hamidieh, A.A.; et al. Inheritance Pattern and Clinical Aspects of 93 Iranian Patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 792–801. [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.B.K.R.; McGrogan, P.; Flood, T.J.; Gennery, A.R.; Morton, L.; Thrasher, A.; Goldblatt, D.; Parker, L.; Cant, A.J. Special Article: Chronic granulomatous disease in the United Kingdom and Ireland: a comprehensive national patient-based registry. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 211–218. [CrossRef]
- Rider, N.L.; Jameson, M.B.; Creech, C.B. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Genetic Basis of Disease. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2018, 7, S2–S5. [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.v.D.; van Koppen, E.; Åhlin, A.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Bernatowska, E.; Corbeel, L.; Español, T.; Fischer, A.; Kurenko-Deptuch, M.; Mouy, R.; et al. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: The European Experience. PLOS ONE 2009, 4, e5234. [CrossRef]
- Martire, B.; Rondelli, R.; Soresina, A.; Pignata, C.; Broccoletti, T.; Finocchi, A.; Rossi, P.; Gattorno, M.; Rabusin, M.; Azzari, C.; et al. Clinical features, long-term follow-up and outcome of a large cohort of patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease: An Italian multicenter study. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 155–164. [CrossRef]
- Leiding JW, Holland SM. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. 2022 2012 Aug 9 [updated 2022 Apr 21]. In: GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle.
- Baxter, J.; Smith, D.; Webb, C. Adult-diagnosed Chronic Granulomatous Disease: The Need to Increase Awareness. Mil. Med. 2021, 188, e410–e411. [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, G.; Finocchi, A. Late diagnosis and advances in genetics of chronic granulomatous disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 203, 244–246. [CrossRef]
- Barkai, T.; Somech, R.; Broides, A.; Gavrieli, R.; Wolach, B.; Marcus, N.; Hagin, D.; Stauber, T. Late diagnosis of chronic granulomatous disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 201, 297–305. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Bosi, I.; Peacock, K.; Lau, C.; Ford, L.S.; Wong, M.; Hsu, P. Novel infantile presentations of chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 35, e14190. [CrossRef]
- Magnani, A.; Mahlaoui, N. Managing Inflammatory Manifestations in Patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Pediatr. Drugs 2016, 18, 335–345. [CrossRef]
- Mouy, R.; Fischer, A.; Vilmer, E.; Seger, R.; Griscelli, C. Incidence, severity, and prevention of infections in chronic granulomatous disease. J. Pediatr. 1989, 114, 555–560. [CrossRef]
- Falcone EL, Holland SM. Gastrointestinal Complications in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. In: Knaus UG, Leto TL, editors. NADPH Oxidases: Methods and Protocols. 1982: Humana Press; 2019. p. 573-86. [CrossRef]
- Grammatikos, A.; Gennery, A.R. Inflammatory Complications in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1092. [CrossRef]
- Rieber, N.; Hector, A.; Kuijpers, T.; Roos, D.; Hartl, D. Current Concepts of Hyperinflammation in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2011, 2012, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Staudacher O, von Bernuth H. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic granulomatous disease. Front Pediatr. 2024;12:1384550. [CrossRef]
- Marciano, B.E.; Spalding, C.; Fitzgerald, A.; Mann, D.; Brown, T.; Osgood, S.; Yockey, L.; Darnell, D.N.; Barnhart, L.; Daub, J.; et al. Common Severe Infections in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 60, 1176–1183. [CrossRef]
- Prince, B.T.; Thielen, B.K.; Williams, K.W.; Kellner, E.S.; E Arnold, D.; Cosme-Blanco, W.; Redmond, M.T.; Hartog, N.L.; Chong, H.J.; Holland, S.M. Geographic Variability and Pathogen-Specific Considerations in the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Pediatr. Heal. Med. Ther. 2020, ume 11, 257–268. [CrossRef]
- Buvelot, H.; Posfay-Barbe, K.M.; Linder, P.; Schrenzel, J.; Krause, K.-H. Staphylococcus aureus, phagocyte NADPH oxidase and chronic granulomatous disease. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 41, 139–157. [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Segal, B.H.; Holland, S.M.; Miller, G.F.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. Virulence of catalase-deficient aspergillus nidulans in p47(phox)-/- mice. Implications for fungal pathogenicity and host defense in chronic granulomatous disease.. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1843–1850. [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.G.; Reeves, E.P.; Roes, J.; Segal, A.W. Catalase negative Staphylococcus aureus retain virulence in mouse model of chronic granulomatous disease. FEBS Lett. 2002, 518, 107–110. [CrossRef]
- Kottilil, S.; Malech, H.; Gill, V.; Holland, S. Infections with Haemophilus species in chronic granulomatous disease: insights into the interaction of bacterial catalase and H2O2 production. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 106, 226–230. [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach J, Lopatin U, Mahlaoui N, Beovic B, Siler U, Zbinden R, et al. Actinomyces in chronic granulomatous disease: an emerging and unanticipated pathogen. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49(11):1703-10. [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Singh, S.; Suri, D.; Gupta, A.; Saikia, B.; Minz, R.W.; Sehgal, S.; Vaiphei, K.; Kamae, C.; Honma, K.; et al. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Two Decades of Experience From a Tertiary Care Centre in North West India. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 34, 58–67. [CrossRef]
- van Montfrans, J.M.; Rudd, E.; van de Corput, L.; Henter, J.; Nikkels, P.; Wulffraat, N.; Boelens, J.J. Fatal hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease associated with a perforin gene variant. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 52, 527–529. [CrossRef]
- Parekh, C.; Hofstra, T.; Church, J.A.; Coates, T.D. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children with chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 56, 460–462. [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto P, Lyman K, Camacho A, Fricchione M, Khanolkar A, Katz BZ. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: A Large, Single-center US Experience. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015;34(10):1110-4. [CrossRef]
- Falcone EL, Holland SM. Invasive fungal infection in chronic granulomatous disease: insights into pathogenesis and management. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012;25(6):658-69. [CrossRef]
- Beaute J, Obenga G, Le Mignot L, Mahlaoui N, Bougnoux ME, Mouy R, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of invasive fungal diseases in patients with chronic granulomatous disease: a multicenter study in France. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30(1):57-62. [CrossRef]
- Feld, J.J.; Hussain, N.; Wright, E.C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Ahlawat, S.; Anderson, V.; Hilligoss, D.; Gallin, J.I.; Liang, T.J.; et al. Hepatic Involvement and Portal Hypertension Predict Mortality in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1917–1926. [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, D.B.; Alvord, W.G.; Heller, T.; Feld, J.J.; Pike, K.M.; Marciano, B.E.; Uzel, G.; DeRavin, S.S.; Priel, D.A.L.; Soule, B.P.; et al. Residual NADPH Oxidase and Survival in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2600–2610. [CrossRef]
- Marciano, B.E.; Zerbe, C.S.; Falcone, E.L.; Ding, L.; DeRavin, S.S.; Daub, J.; Kreuzburg, S.; Yockey, L.; Hunsberger, S.; Foruraghi, L.; et al. X-linked carriers of chronic granulomatous disease: Illness, lyonization, and stability. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 365–371. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Junior, E.B.; Zurro, N.B.; Prando, C.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Pereira, P.V.S.; Schimke, L.-F.; Klaver, S.; Buzolin, M.; Blancas-Galicia, L.; Santos-Argumedo, L.; et al. Clinical and Genotypic Spectrum of Chronic Granulomatous Disease in 71 Latin American Patients: First Report from the LASID Registry. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 2101–2107. [CrossRef]
- Köker, M.Y.; Camcıoğlu, Y.; van Leeuwen, K.; Kılıç, S..; Barlan, I.; Yılmaz, M.; Metin, A.; de Boer, M.; Avcılar, H.; Patıroğlu, T.; et al. Clinical, functional, and genetic characterization of chronic granulomatous disease in 89 Turkish patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1156–1163.e5. [CrossRef]
- El Kares, R.; Barbouche, M.R.; Elloumi-Zghal, H.; Bejaoui, M.; Chemli, J.; Mellouli, F.; Tebib, N.; Abdelmoula, M.S.; Boukthir, S.; Fitouri, Z.; et al. Genetic and mutational heterogeneity of autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease in Tunisia. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 51, 887–895. [CrossRef]
- Wolach, B.; Gavrieli, R.; Wolach, O.; Salamon, P.; De Boer, M.; van Leeuwen, K.; Abuzaitoun, O.; Broides, A.; Gottesman, G.; Grisaru-Soen, G.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Insights From a Large National Cohort. Blood J. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Battersby, A.C.; Cale, C.M.; Goldblatt, D.; Gennery, A.R. Clinical Manifestations of Disease in X-Linked Carriers of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 1276–1284. [CrossRef]
- Hauck, F.; Koletzko, S.; Walz, C.; von Bernuth, H.; Klenk, A.; Schmid, I.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Klein, C.; Bufler, P.; Albert, M.H. Diagnostic and Treatment Options for Severe IBD in Female X-CGD Carriers with Non-random X-inactivation. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2015, 10, 112–115. [CrossRef]
- Roesler, J. Carriers of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease at risk. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 233. [CrossRef]
- Stasia, M.J.; Li, X.J. Genetics and immunopathology of chronic granulomatous disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2008, 30, 209–235. [CrossRef]
- Zerbe, C.S.; Holland, S.M. Functional neutrophil disorders: Chronic granulomatous disease and beyond. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 322, 71–80. [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; van Leeuwen, K.; Hsu, A.P.; Priel, D.L.; Begtrup, A.; Brandon, R.; Rawat, A.; Vignesh, P.; Madkaikar, M.; Stasia, M.J.; et al. Hematologically important mutations: The autosomal forms of chronic granulomatous disease (third update). Blood Cells, Mol. Dis. 2021, 92, 102596. [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; van Leeuwen, K.; Hsu, A.P.; Priel, D.L.; Begtrup, A.; Brandon, R.; Stasia, M.J.; Bakri, F.G.; Köker, N.; Köker, M.Y.; et al. Hematologically important mutations: X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (fourth update). Blood Cells, Mol. Dis. 2021, 90, 102587. [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Patriarca, P.; Solero, G.P.; Baralle, F.E.; Romano, M. Genetic characterization of myeloperoxidase deficiency in Italy. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 496–505. [CrossRef]
- Njålsson, R. Glutathione synthetase deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1938–1945. [CrossRef]
- Battersby, A.C.; Braggins, H.; Pearce, M.S.; Cale, C.M.; Burns, S.O.; Hackett, S.; Hughes, S.; Barge, D.; Goldblatt, D.; Gennery, A.R. Inflammatory and autoimmune manifestations in X-linked carriers of chronic granulomatous disease in the United Kingdom. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 628–630.e6. [CrossRef]
- Cale, C.M.; Morton, L.; Goldblatt, D. Cutaneous and other lupus-like symptoms in carriers of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease: incidence and autoimmune serology. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148, 79–84. [CrossRef]
- Dinauer, M.C.; A Pierce, E.; A Bruns, G.; Curnutte, J.T.; Orkin, S.H. Human neutrophil cytochrome b light chain (p22-phox). Gene structure, chromosomal location, and mutations in cytochrome-negative autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1729–1737. [CrossRef]
- Arnadottir, G.A.; Norddahl, G.L.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Agustsdottir, A.B.; Sigurdsson, S.; Jensson, B.O.; Bjarnadottir, K.; Theodors, F.; Benonisdottir, S.; Ivarsdottir, E.V.; et al. A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Charbonnier, L.-M.; Schejtman, A.; Aldhekri, H.; Coomber, E.L.; Dufficy, E.R.; E Beenken, A.; Lee, J.; Clare, S.; O Speak, A.; et al. EROS/CYBC1 mutations: Decreased NADPH oxidase function and chronic granulomatous disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(2):782-5 e1. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Clare, S.; Sowerby, J.; Pardo, M.; Juss, J.; Goulding, D.; Van Der Weyden, L.; Storisteanu, D.; Prakash, A.; Espéli, M.; et al. Eros is a novel transmembrane protein that controls the phagocyte respiratory burst and is essential for innate immunity. J Exp Med. 2017;214(4):1111-28. [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, P.M.; Nichols, E.; Thomas, J.; Shanbhag, R.; Singh, N.; Coomber, E.L.; Malik, T.H.; Pickering, M.C.; Randzavola, L.; Rae, W.; et al. A novel mutation in EROS (CYBC1) causes chronic granulomatous disease. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 255, 109761. [CrossRef]
- Chiriaco, M.; De Matteis, A.; Cifaldi, C.; Di Matteo, G.; Rivalta, B.; Passarelli, C.; Perrone, C.; Novelli, A.; De Benedetti, F.; Insalaco, A.; et al. Characterization of AR-CGD female patient with a novel homozygous deletion in CYBC1 gene presenting with unusual clinical phenotype. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 251, 109316. [CrossRef]
- Nunoi, H.; Rotrosen, D.; Gallin, J.I.; Malech, H.L. Two Forms of Autosomal Chronic Granulomatous Disease Lack Distinct Neutrophil Cytosol Factors. Science 1988, 242, 1298–1301. [CrossRef]
- Curnutte, J.; Kuver, R.; Scott, P. Activation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase in a cell-free system. Partial purification of components and characterization of the activation process.. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5563–5569. [CrossRef]
- Umei, T.; Takeshige, K.; Minakami, S. NADPH-binding component of the superoxide-generating oxidase in unstimulated neutrophils and the neutrophils from the patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Biochem. J. 1987, 243, 467–472. [CrossRef]
- Matute JD, Arias AA, Wright NA, Wrobel I, Waterhouse CC, Li XJ, et al. A new genetic subgroup of chronic granulomatous disease with autosomal recessive mutations in p40 phox and selective defects in neutrophil NADPH oxidase activity. Blood. 2009;114(15):3309-15. [CrossRef]
- van de Geer, A.; Nieto-Patlán, A.; Kuhns, D.B.; Tool, A.T.; Arias, A.A.; Bouaziz, M.; de Boer, M.; Franco, J.L.; Gazendam, R.P.; van Hamme, J.L.; et al. Inherited p40phox deficiency differs from classic chronic granulomatous disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3957–3975. [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Demaurex, N.; Dinauer, M.C. Regulation of the NADPH Oxidase and Associated Ion Fluxes During Phagocytosis. Traffic 2013, 14, 1118–1131. [CrossRef]
- Belambri, S.A.; Rolas, L.; Raad, H.; Hurtado-Nedelec, M.; Dang, P.M.; El-Benna, J. NADPH oxidase activation in neutrophils: Role of the phosphorylation of its subunits. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12951. [CrossRef]
- Bréchard, S.; Plançon, S.; Tschirhart, E.J. New Insights into the Regulation of Neutrophil NADPH Oxidase Activity in the Phagosome: A Focus on the Role of Lipid and Ca2+Signaling. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 661–676. [CrossRef]
- A Williams, D.; Tao, W.; Yang, F.; Kim, C.; Gu, Y.; Mansfield, P.; E Levine, J.; Petryniak, B.; Derrow, C.W.; Harris, C.; et al. Dominant negative mutation of the hematopoietic-specific Rho GTPase, Rac2, is associated with a human phagocyte immunodeficiency. Blood. 2000;96(5):1646-54.
- Ambruso, D.R.; Knall, C.; Abell, A.N.; Panepinto, J.; Kurkchubasche, A.; Thurman, G.; Gonzalez-Aller, C.; Hiester, A.; Deboer, M.; Harbeck, R.J.; et al. Human neutrophil immunodeficiency syndrome is associated with an inhibitory Rac2 mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4654–4659. [CrossRef]
- Alkhairy, O.K.; Rezaei, N.; Graham, R.R.; Abolhassani, H.; Borte, S.; Hultenby, K.; Wu, C.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Williams, D.A.; Behrens, T.W.; et al. RAC2 loss-of-function mutation in 2 siblings with characteristics of common variable immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 135, 1380–1384.e5. [CrossRef]
- van Bruggen R, Bautista JM, Petropoulou T, de Boer M, van Zwieten R, Gómez-Gallego F, et al. Deletion of leucine 61 in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase leads to chronic nonspherocytic anemia, granulocyte dysfunction, and increased susceptibility to infections. Blood. 2002;100(3):1026-30. [CrossRef]
- Ristoff, E.; Larsson, A. Inborn errors in the metabolism of glutathione. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 16–16. [CrossRef]
- Reeves, E.P.; Lu, H.; Jacobs, H.L.; Messina, C.G.M.; Bolsover, S.; Gabella, G.; Potma, E.O.; Warley, A.; Roes, J.; Segal, A.W. Killing activity of neutrophils is mediated through activation of proteases by K+ flux. Nature 2002, 416, 291–297. [CrossRef]
- Trevelin, S.C.; Shah, A.M.; Lombardi, G. Beyond bacterial killing: NADPH oxidase 2 is an immunomodulator. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 221, 39–48. [CrossRef]
- Klebanoff, S.J.; Kettle, A.J.; Rosen, H.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Nauseef, W.M. Myeloperoxidase: a front-line defender against phagocytosed microorganisms. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 185–198. [CrossRef]
- Kenny EF, Herzig A, Kruger R, Muth A, Mondal S, Thompson PR, et al. Diverse stimuli engage different neutrophil extracellular trap pathways. Elife. 2017;6. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi M, Hakkim A, Brinkmann V, Siler U, Seger RA, Zychlinsky A, et al. Restoration of NET formation by gene therapy in CGD controls aspergillosis. Blood. 2009;114(13):2619-22. [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 134–147. [CrossRef]
- Roxo-Junior P, Simao HM. Chronic granulomatous disease: why an inflammatory disease? Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(11):924-8. [CrossRef]
- Hartl, D.; Lehmann, N.; Hoffmann, F.; Jansson, A.; Hector, A.; Notheis, G.; Roos, D.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Wintergerst, U. Dysregulation of innate immune receptors on neutrophils in chronic granulomatous disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 375–382.e9. [CrossRef]
- Garay, J.A.; Silva, J.E.; Di Genaro, M.S.; Davicino, R.C. The Multiple Faces of Nitric Oxide in Chronic Granulomatous Disease: A Comprehensive Update. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2570. [CrossRef]
- Segal, B.H.; Leto, T.L.; Gallin, J.I.; Malech, H.L.; Holland, S.M. Genetic, Biochemical, and Clinical Features of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Medicine 2000, 79, 170–200. [CrossRef]
- Sacco, K.A.; Gazzin, A.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Delmonte, O.M. Granulomatous inflammation in inborn errors of immunity. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1110115. [CrossRef]
- A Connelly, J.; Marsh, R.; Parikh, S.; Talano, J.-A. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Controversies and State of the Art. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2018, 7, S31–S39. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Huang, X.; Zang, W.; Kiselev, S.; Bolkov, M.A.; Tuzankina, I.A.; Chereshnev, V.A. Health-related quality of life in patients with inborn errors of immunity: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1371124. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, B.; Goodman, R.; Day, J.; Worth, A.; Carpenter, B.; Sandford, K.; Morris, E.C.; Burns, S.O.; Ridout, D.; Titman, P.; et al. Quality of Life and Social and Psychological Outcomes in Adulthood Following Allogeneic HSCT in Childhood for Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1451–1460. [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Herten, M.H.; Landgraf, J.M.; Korfage, I.J.; Raat, H. Childhood chronic conditions and health-related quality of life: Findings from a large population-based study. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0178539. [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.; McKendrick, F.; Titman, P.; Cant, A.J.; Pearce, M.S.; Cale, C.M.; Goldblatt, D.; Gennery, A.R. Health Related Quality of Life and Emotional Health in Children with Chronic Granulomatous Disease: A Comparison of Those Managed Conservatively with Those That Have Undergone Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 33, 8–13. [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.S.; Jones, L.K.R.; McGrogan, P.; Pearce, M.S.; Flood, T.J.; Cant, A.J.; Goldblatt, D.; Thrasher, A.J.; Gennery, A.R.; McKendrick, F.; et al. Emotional and behavioural difficulties in chronic granulomatous disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 97, 87–87. [CrossRef]
- Battersby, A.C.; Braggins, H.; Pearce, M.S.; McKendrick, F.; Campbell, M.; Burns, S.; Cale, C.M.; Goldblatt, D.; Gennery, A.R. Health-Related Quality of Life and Emotional Health in X-Linked Carriers of Chronic Granulomatous Disease in the United Kingdom. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 195–199. [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, F.; Sangerardi, M.; Plebani, A.; Soresina, A.; Finocchi, A.; Pignata, C.; Cirillo, E.; Trizzino, A.; Aiuti, A.; Migliavacca, M.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and Emotional Difficulties in Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Data on Adult and Pediatric Patients from Italian Network for Primary Immunodeficiency (IPINet). J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 40, 289–298. [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, H.Y.; Porteus, M.H. Gene regulation in inborn errors of immunity: Implications for gene therapy design and efficacy. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 322, 157–177. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A. Gene therapy for inborn errors of immunity: past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 23, 397–408. [CrossRef]
- Gennery, A.R. Progress in treating chronic granulomatous disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 192, 251–264. [CrossRef]
- Overwater, E.; Smulders, Y.; van der Burg, M.; Lombardi, M.P.; Meijers-Heijboer, H.E.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Houweling, A.C. The value of DNA storage and pedigree analysis in rare diseases: a 17-year-old boy with X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP) caused by a de novo SH2D1A mutation. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2014, 173, 1695–1698. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Peng, C.; Chen, H.; Zhou, F.; Keqie, Y.B.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, S.; Ren, J. Preimplantation genetic testing for X-linked chronic granulomatous disease induced by a CYBB gene variant: A case report. Medicine 2024, 103, e37198. [CrossRef]
- Modarresi, S.Z.; Sabetkish, N.; Badalzadeh, M.; Tajik, S.; Esmaeili, B.; Fazlollahi, M.R.; Houshmand, M.; Gharehdaghi, J.; Niroomanesh, S.; Sherbaf, F.R.; et al. The Critical Role of Prenatal Genetic Study in Prevention of Primary Immunodeficiency in High-risk Families: The Largest Report of 107 Cases. Iran. J. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2020, 19, 478–483. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.; Gupta, M.; Madkaikar, M. Phenotypic Prenatal Diagnosis of Chronic Granulomatous Disease: A Useful Tool in The Absence Of Molecular Diagnosis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 86, 486–490. [CrossRef]
- Yu JE, Azar AE, Chong HJ, Jongco AM, 3rd, Prince BT. Considerations in the Diagnosis of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2018;7(suppl_1):S6-S11.
- Roos, D.; Boer, M. Molecular diagnosis of chronic granulomatous disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 175, 139–149. [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.G.; Kindle, G.; Gathmann, B.; Quinti, I.; Buckland, M.; van Montfrans, J.; Scheible, R.; Rusch, S.; Gasteiger, L.M.; Grimbacher, B.; et al. The European Society for Immunodeficiencies (ESID) Registry Working Definitions for the Clinical Diagnosis of Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2019, 7, 1763–1770. [CrossRef]
- Rosen, Y. Pathology of Granulomatous Pulmonary Diseases. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 146, 233–251. [CrossRef]
- Moskaluk CA, Pogrebniak HW, Pass HI, Gallin JI, Travis WD. Surgical pathology of the lung in chronic granulomatous disease American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1994;102(5):684–91.
- Marks, D.J.B.; Miyagi, K.; Rahman, F.Z.; Novelli, M.; Bloom, S.L.; Segal, A.W. Inflammatory Bowel Disease in CGD Reproduces the Clinicopathological Features of Crohn’s Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 104, 117–124. [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.; Kumarasinghe, M.P. Granulomas in the gastrointestinal tract: deciphering the Pandora’s box. Virchows Arch. 2017, 472, 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Khangura, S.K.; Kamal, N.; Ho, N.; Quezado, M.; Zhao, X.; Marciano, B.; Simpson, J.; Zerbe, C.; Uzel, G.; Yao, M.D.; et al. Gastrointestinal Features of Chronic Granulomatous Disease Found During Endoscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 395–402.e5. [CrossRef]
- Marciano, B.E.; Rosenzweig, S.D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Anderson, V.L.; Darnell, D.N.; Anaya-O’Brien, S.; Hilligoss, D.M.; Malech, H.L.; Gallin, J.I.; Holland, S.M. Gastrointestinal Involvement in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 462–468. [CrossRef]
- Alimchandani M, Lai JP, Aung PP, Khangura S, Kamal N, Gallin JI, et al. Gastrointestinal Histopathology in Chronic Granulomatous Disease: A Study of 87 Patients. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2013;37(9):1365-72.
- Levine S, Smith VV, Malone M, Sebire NJ. Histopathological features of chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) in childhood. Histopathology. 2005;47(5):508-16.
- Grenier, P.A.; Brun, A.L.; Longchampt, E.; Lipski, M.; Mellot, F.; Catherinot, E. Primary immunodeficiency diseases of adults: a review of pulmonary complication imaging findings. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 4142–4154. [CrossRef]
- Salvator, H.; Mahlaoui, N.; Catherinot, E.; Rivaud, E.; Pilmis, B.; Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Tcherakian, C.; Suarez, F.; Dunogue, B.; et al. Pulmonary manifestations in adult patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1613–1623. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Koethe, Y.; Ling, A.; Kamal, N.; Khangura, S.; Alimchandani, M.; Quezado, M.M.; Zerbe, C.S.; Malech, H.L.; Gallin, J.I.; et al. Gastrointestinal Computed Tomography Findings in Chronic Granulomatous Disease with Subgroup Clinicopathologic Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 67, 1831–1842. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Ko, S.Y.; Jeong, S.Y. Spectrum of imaging findings of chronic granulomatous disease: a single center experience. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 23, 472–477. [CrossRef]
- Towbin AJ, Chaves I. Chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40(5):657-68; quiz 792-3.
- Jefferson, L.; Ramanan, A.V.; Jolles, S.; Bernatoniene, J.; Mathieu, A.-L.; Belot, A.; Roderick, M.R. Phenotypic Variability in PRKCD: a Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 1692–1705. [CrossRef]
- Neehus AL, Tuano K, Le Voyer T, Nandiwada SL, Murthy K, Puel A, et al. Chronic Granulomatous Disease-Like Presentation of a Child with Autosomal Recessive PKCdelta Deficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2022;42(6):1244-53.
- Hafsi W, Yarrarapu SNS. Job Syndrome Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [.
- Kuhns DB. Diagnostic Testing for Chronic Granulomatous Disease. In: Knaus UG, Leto TL, editors. Methods Mol Biol. 1982. New York: Humana Press; 2019. p. 543-71.
- Roos D. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. In: Knaus UG, Leto TL, editors. NADPH Oxidases: Methods and Protocols. 1982: Humana Press; 2019. p. 531-42.
- Marrocco, I.; Altieri, F.; Peluso, I. Measurement and Clinical Significance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Roesler, J. Remarks on the article Genetics and immunopathology of chronic granulomatous disease by Marie José Stasia and Xing Jun Li. Semin. Immunopathol. 2008, 30, 365–365. [CrossRef]
- Quach, A.; Glowik, S.; Putty, T.; Ferrante, A. Delayed Blood Processing Leads to Rapid Deterioration in the Measurement of the Neutrophil Respiratory Burst by the Dihydrorhodamine-123 Reduction Assay. Cytom. Part B: Clin. Cytom. 2019, 96, 389–396. [CrossRef]
- Weening, R.S.; Roos, D.; A Loos, J. Oxygen consumption of phagocytizing cells in human leukocyte and granulocyte preparations: a comparative study. J Lab Clin Med. 1974, 83, 570–7.
- Elloumi HZ, Holland SM. Diagnostic assays for chronic granulomatous disease and other neutrophil disorders. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;412:505-23.
- Ríos N, Prolo C, Álvarez MN, Piacenza L, Radi R. Peroxynitrite Formation and Detection in Living Cells. Nitric Oxide2017. p. 271-88.
- Dahlgren C, Karlsson A, Bylund J. Measurement of respiratory burst products generated by professional phagocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;412:349-63.
- Zhou, M.; Diwu, Z.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N.; Haugland, R.P. A Stable Nonfluorescent Derivative of Resorufin for the Fluorometric Determination of Trace Hydrogen Peroxide: Applications in Detecting the Activity of Phagocyte NADPH Oxidase and Other Oxidases. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 162–168. [CrossRef]
- Baehner, R.L.; Nathan, D.G. Quantitative Nitroblue Tetrazolium Test in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. New Engl. J. Med. 1968, 278, 971–976. [CrossRef]
- Ochs, H.D.; Igo, R.P. The NBT slide test: A simple screening method for detecting chronic granulomatous disease and female carriers. J. Pediatr. 1973, 83, 77–82. [CrossRef]
- Roesler J, Emmendorffer A. Diagnosis of chronic granulomatous disease [letter; comment]. Blood. 1991;78(5):1387-9.
- Israeli, S.; Golden, A.; Atalig, M.; Mekki, N.; Rais, A.; Storey, H.; Barbouche, M.-R.; Peck, R. A Novel Point-of-Care Rapid Diagnostic Test for Screening Individuals for Antibody Deficiencies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 42, 394–403. [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, T.; Deribessa, S.J. A First Case Report of DiGeorge Syndrome from Ethiopia Highlights Challenges in Identifying and Treating Children with Primary T-Cell Deficiencies in Low Resource Settings. Case Rep. Immunol. 2020, 2020, 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Kosack, C.S. Experience of Médecins Sans Frontières in laboratory medicine in resource-limited settings. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2012, 50, 1221–1227. [CrossRef]
- Emmendörffer, A.; Hecht, M.; Lohmann-Matthes, M.-L.; Roesler, J. A fast and easy method to determine the production of reactive oxygen intermediates by human and murine phagocytes using dihydrorhodamine 123. J. Immunol. Methods 1990, 131, 269–275. [CrossRef]
- Holland SM. Chronic granulomatous disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013;27(1):89-99, viii.
- Jirapongsananuruk, O.; Malech, H.L.; Kuhns, D.B.; Niemela, J.E.; Brown, M.R.; Anderson-Cohen, M.; Fleisher, T.A. Diagnostic paradigm for evaluation of male patients with chronic granulomatous disease, based on the dihydrorhodamine 123 assay. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 374–379. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Ki, C.-S.; Kim, D.W.; Yoo, K.H.; Kang, E.-S. Rapid Determination of Chimerism Status Using Dihydrorhodamine Assay in a Patient with X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease Following Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Ann. Lab. Med. 2013, 33, 288–292. [CrossRef]
- Rösen-Wolff, A.; Soldan, W.; Heyne, K.; Bickhardt, J.; Gahr, M.; Roesler, J. Increased susceptibility of a carrier of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) to Aspergillus fumigatus infection associated with age-related skewing of lyonization. Ann. Hematol. 2001, 80, 113–115. [CrossRef]
- Mauch, L.; Lun, A.; O’gorman, M.R.; Harris, J.S.; Schulze, I.; Zychlinsky, A.; Fuchs, T.; Oelschlägel, U.; Brenner, S.; Kutter, D.; et al. Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD) and Complete Myeloperoxidase Deficiency Both Yield Strongly Reduced Dihydrorhodamine 123 Test Signals but Can Be Easily Discerned in Routine Testing for CGD. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 890–896. [CrossRef]
- Milligan KL, Mann D, Rump A, Anderson VL, Hsu AP, Kuhns DB, et al. Complete Myeloperoxidase Deficiency: Beware the “False-Positive” Dihydrorhodamine Oxidation. J Pediatr. 2016;176:204-6. [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, P.J.; Lokuta, M.A.; El-Shanti, H.I.; Muhle, L.; Bing, X.; Huttenlocher, A. Neutrophil dysfunction in a family with a SAPHO syndrome–like phenotype. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 3264–3269. [CrossRef]
- Mott, J.; Rikihisa, Y. Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis Agent Inhibits Superoxide Anion Generation by Human Neutrophils. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6697–6703. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee R, Anguita J, Roos D, Fikrig E. Cutting edge: infection by the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis prevents the respiratory burst by down-regulating gp91phox. J Immunol. 2000;164(8):3946-9.
- Almutairi, A.; Zaman, F.; Day-Lewis, M.; Tsitsikov, E.; Reiter, A.; Xue, K.; Geha, R.S.; Chou, J.; Yee, C.S. Acetaminophen Inhibits the Neutrophil Oxidative Burst: Implications for Diagnostic Testing. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 3543–3548. [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, M.; Suzuki, M.; Miura, S.; Nagata, H.; Oshio, C.; Asakura, H.; Watanabe, M.; Tsuchiya, M. Sulfasalazine and its metabolites attenuate respiratory burst of leukocytes--a possible mechanism of anti-inflammatory effects. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1987;23(1):31-3.
- Costa, D.; Marques, A.P.; Reis, R.L.; Lima, J.L.; Fernandes, E. Inhibition of human neutrophil oxidative burst by pyrazolone derivatives. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 40, 632–640. [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.R.; Curnutte, J.T. The Cytosolic Activating Factors p47phox and p67phox Have Distinct Roles in the Regulation of Electron Flow in NADPH Oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1995, 270, 6543–6548. [CrossRef]
- Accetta, D.; Syverson, G.; Bonacci, B.; Reddy, S.; Bengtson, C.; Surfus, J.; Harbeck, R.; Huttenlocher, A.; Grossman, W.; Routes, J. Human phagocyte defect caused by a Rac2 mutation detected by means of neonatal screening for T-cell lymphopenia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 535–538.e2. [CrossRef]
- Vowells, S.; Sekhsaria, S.; Malech, H.; Shalit, M.; Fleisher, T. Flow cytometric analysis of the granulocyte respiratory burst: a comparison study of fluorescent probes. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 178, 89–97. [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi A, Yu L, Potgens AJ, Kuribayashi F, Nunoi H, Kanegasaki S, et al. Location of the epitope for 7D5, a monoclonal antibody raised against human flavocytochrome b558, to the extracellular peptide portion of primate gp91phox. Microbiol Immunol. 2001;45(3):249-57. [CrossRef]
- Köker, M.Y.; Sanal, .; Van Leeuwen, K.; De Boer, M.; Metin, A.; Patıroğlu, T.; Özgür, T.T.; Tezcan, I.; Roos, D. Four different NCF2 mutations in six families from Turkey and an overview of NCF2 gene mutations. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 942–951. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura M, Murakami M, Koga T, Tanaka Y, Minakami S. Monoclonal antibody 7D5 raised to cytochrome b558 of human neutrophils: immunocytochemical detection of the antigen in peripheral phagocytes of normal subjects, patients with chronic granulomatous disease, and their carrier mothers. Blood. 1987;69(5):1404-8. [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Muraoka, M.; Toma, T.; Imai, T.; Shigemura, T.; Agematsu, K.; Haraguchi, K.; Moriuchi, H.; Oh-Ishi, T.; Kitoh, T.; et al. Rapid Detection of Intracellular p47phox and p67phox by Flow Cytometry; Useful Screening Tests for Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 857–864. [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Gupta, K.; Rawat, A.; Jindal, A.; Pandiarajan, V.; Suri, D.; Gupta, A.; Kaur, G.; Kumar, I.; Gummadi, A.; et al. Utility of Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence in Determining the Pathogenic Variants of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 42, 85–93. [CrossRef]
- Blom, M.; Bredius, R.G.M.; van der Burg, M. Future Perspectives of Newborn Screening for Inborn Errors of Immunity. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 74. [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.J.; Yi, F.; Dayuha, R.; Whiteaker, J.R.; Ochs, H.D.; Freeman, A.; Su, H.C.; Paulovich, A.G.; Segundo, G.R.S.; Torgerson, T.; et al. Multiplexed Proteomic Analysis for Diagnosis and Screening of Five Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders From Dried Blood Spots. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 464. [CrossRef]
- Rawat A, Bhattad S, Singh S. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Indian J Pediatr. 2016;83(4):345-53.
- Tsunawaki, S.; Mizunari, H.; Nagata, M.; Tatsuzawa, O.; Kuratsuji, T. A Novel Cytosolic Component, p40phox, of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Associates with p67phox and Is Absent in Patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease Who Lack p67phox. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 199, 1378–1387. [CrossRef]
- Anjani, G.; Vignesh, P.; Joshi, V.; Shandilya, J.K.; Bhattarai, D.; Sharma, J.; Rawat, A. Recent advances in chronic granulomatous disease. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 84–92. [CrossRef]
- Molshanski-Mor S, Mizrahi A, Ugolev Y, Dahan I, Berdichevsky Y, Pick E. Cell-free assays: the reductionist approach to the study of NADPH oxidase assembly, or “all you wanted to know about cell-free assays but did not dare to ask”. In: Quinn MT, DeLeo FR, Bokoch GM, editors. Neutrophil Methods and Protocols. 412. New Jersey: Humana Press; 2007. p. 385-428.
- Chanock, S.J.; Faust, L.R.; Barrett, D.; Bizal, C.; Maly, F.E.; Newburger, P.E.; Ruedi, J.M.; Smith, R.M.; Babior, B.M. O2- production by B lymphocytes lacking the respiratory burst oxidase subunit p47phox after transfection with an expression vector containing a p47phox cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10174–10177. [CrossRef]
- Batlle-Masó, L.; Rivière, J.G.; Franco-Jarava, C.; Martín-Nalda, A.; Garcia-Prat, M.; Parra-Martínez, A.; Aguiló-Cucurull, A.; Castells, N.; Martinez-Gallo, M.; Soler-Palacín, P.; et al. Molecular Challenges in the Diagnosis of X-Linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease: CNVs, Intronic Variants, Skewed X-Chromosome Inactivation, and Gonosomal Mosaicism. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 1953–1963. [CrossRef]
- Dremsek, P.; Schwarz, T.; Weil, B.; Malashka, A.; Laccone, F.; Neesen, J. Optical Genome Mapping in Routine Human Genetic Diagnostics—Its Advantages and Limitations. Genes 2021, 12, 1958. [CrossRef]
- Wallace SE, Bean LJH. Educational Materials — Genetic Testing: Current Approaches. 2020. In: GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle.
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [CrossRef]
- Kelly P, Mahon S, Friend P. When Germline Genetic Testing Results Are Unclear: Highlighting Variants of Uncertain Significance. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2023;14(7):631-8. [CrossRef]
- East K, Chung W, Foreman K, Gilmore M, Gornick M, Hindorff L, et al. Guide to interpreting genomic reports: A genomics toolkit. In: Research CSE, editor. 2017. p. 2020-04.
- Gahl, W.A.; Markello, T.C.; Toro, C.; Fajardo, K.F.; Sincan, M.; Gill, F.; Carlson-Donohoe, H.; Gropman, A.; Pierson, T.M.; Golas, G.; et al. The National Institutes of Health Undiagnosed Diseases Program: Insights into rare diseases. Genet Med. 2012;14(1):51-9. [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis KN, Schahl KA, Cousin MA, Babovic-Vuksanovic D, Riegert-Johnson DL, Gavrilova RH, et al. Outcome of Whole Exome Sequencing for Diagnostic Odyssey Cases of an Individualized Medicine Clinic: The Mayo Clinic Experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91(3):297-307. [CrossRef]
- Yska, H.A.F.; Elsink, K.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Frederix, G.W.J.; van Gijn, M.E.; van Montfrans, J.M. Diagnostic Yield of Next Generation Sequencing in Genetically Undiagnosed Patients with Primary Immunodeficiencies: a Systematic Review. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 577–591. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Martin, H.C.; Lise, S.; Broxholme, J.; Cazier, J.-B.; Rimmer, A.; Kanapin, A.; Lunter, G.; Fiddy, S.; Allan, C.; et al. Factors influencing success of clinical genome sequencing across a broad spectrum of disorders. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 717–726. [CrossRef]
- Manning M, Hudgins L, Professional P, Guidelines C. Array-based technology and recommendations for utilization in medical genetics practice for detection of chromosomal abnormalities. Genet Med. 2010;12(11):742-5. [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.T.; Adam, M.P.; Aradhya, S.; Biesecker, L.G.; Brothman, A.R.; Carter, N.P.; Church, D.M.; Crolla, J.A.; Eichler, E.E.; Epstein, C.J.; et al. Consensus Statement: Chromosomal Microarray Is a First-Tier Clinical Diagnostic Test for Individuals with Developmental Disabilities or Congenital Anomalies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 749–764. [CrossRef]
- de Boer M, van Leeuwen K, Geissler J, Weemaes CM, van den Berg TK, Kuijpers TW, et al. Primary immunodeficiency caused by an exonized retroposed gene copy inserted in the CYBB gene. Hum Mutat. 2014;35(4):486-96. [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, J.; A Arias, A.; Vogt, G.; Picard, C.; Galicia, L.B.; Prando, C.; Grant, A.V.; Marchal, C.C.; Hubeau, M.; Chapgier, A.; et al. Germline CYBB mutations that selectively affect macrophages in kindreds with X-linked predisposition to tuberculous mycobacterial disease. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 213–221. [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, J. Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease: recent discoveries. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 993–1000. [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.C.; Zoghbi, H.Y.; Moseley, A.B.; Rosenblatt, H.M.; Belmont, J.W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1992, 51, 1229–39.
- Sauteraud, R.; Stahl, J.M.; James, J.; Englebright, M.; Chen, F.; Zhan, X.; Carrel, L.; Liu, D.J. Inferring genes that escape X-Chromosome inactivation reveals important contribution of variable escape genes to sex-biased diseases. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 1629–1637. [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Redman, C.M.; Wu, X.; Song, X.; Walker, R.H.; Westhoff, C.M.; Lee, S. Insights into extensive deletions around the XK locus associated with McLeod phenotype and characterization of two novel cases. Gene 2007, 392, 142–150. [CrossRef]
- E Watkins, C.; Litchfield, J.; Song, E.; Jaishankar, G.B.; Misra, N.; Holla, N.; Duffourc, M.; Krishnaswamy, G. Chronic granulomatous disease, the McLeod phenotype and the contiguous gene deletion syndrome-a review. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2011, 9, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Görlach, A.; Lee, P.L.; Roesler, J.; Hopkins, P.J.; Christensen, B.; Green, E.D.; Chanock, S.J.; Curnutte, J.T. A p47-phox pseudogene carries the most common mutation causing p47-phox- deficient chronic granulomatous disease.. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1907–1918. [CrossRef]
- Tarazona-Santos, E.; Machado, M.; Magalhães, W.C.; Chen, R.; Lyon, F.; Burdett, L.; Crenshaw, A.; Fabbri, C.; Pereira, L.; Pinto, L.; et al. Evolutionary Dynamics of the Human NADPH Oxidase Genes CYBB, CYBA, NCF2, and NCF4: Functional Implications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2157–2167. [CrossRef]
- Hayrapetyan, A.; Dencher, P.C.; van Leeuwen, K.; de Boer, M.; Roos, D. Different unequal cross-over events between NCF1 and its pseudogenes in autosomal p47phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 1662–1672. [CrossRef]
- Dekker, J.; de Boer, M.; Roos, D. Gene-scan method for the recognition of carriers and patients with p47phox-deficient autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease. Exp. Hematol. 2001, 29, 1319–1325. [CrossRef]
- Roos D, de Boer M, Koker MY, Dekker J, Singh-Gupta V, Ahlin A, et al. Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mutations other than the common GT deletion in NCF1, the gene encoding the p47phox component of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase. Hum Mutat. 2006;27(12):1218-29. [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, D.B.; Hsu, A.P.; Sun, D.; Lau, K.; Fink, D.; Griffith, P.; Huang, D.W.; Priel, D.A.L.; Mendez, L.; Kreuzburg, S.; et al. NCF1 (p47phox)–deficient chronic granulomatous disease: comprehensive genetic and flow cytometric analysis. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 136–147. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, J.; Deng, Y.; A Kelly, J.; Kim, K.; Bang, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Li, Q.-Z.; Wakeland, E.K.; Qiu, R.; et al. A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 433–437. [CrossRef]
- Leusen, J.H.; Bolscher, B.G.; Hilarius, P.M.; Weening, R.S.; Kaulfersch, W.; A Seger, R.; Roos, D.; Verhoeven, A.J. 156Pro-->Gln substitution in the light chain of cytochrome b558 of the human NADPH oxidase (p22-phox) leads to defective translocation of the cytosolic proteins p47-phox and p67-phox.. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 2329–2334. [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; van Buul, J.D.; Tool, A.T.; Matute, J.D.; Marchal, C.M.; Hayee, B.; Köker, M.Y.; de Boer, M.; van Leeuwen, K.; Segal, A.W.; et al. Two CGD Families with a Hypomorphic Mutation in the Activation Domain of p67phox. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2014;5(3):1000231.
- Lavelle TA, Feng X, Keisler M, Cohen JT, Neumann PJ, Prichard D, et al. Cost-effectiveness of exome and genome sequencing for children with rare and undiagnosed conditions. Genet Med. 2022;24(6):1349-61. [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, M.O.; Suwanwela, N.C.; Yaria, J. Barriers to implementation of evidence into clinical practice in low-resource settings. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 451–452. [CrossRef]
- Barbouche, M.; Galal, N.; Ben-Mustapha, I.; Jeddane, L.; Mellouli, F.; Ailal, F.; Bejaoui, M.; Boutros, J.; Marsafy, A.; Bousfiha, A.A. Primary immunodeficiencies in highly consanguineous North African populations. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2011, 1238, 42–52. [CrossRef]
- North Thames Genomic Medicine Service. Genetic test turnaround times. 2023 [Available from: https://norththamesgenomics.nhs.uk/genetic-test-ordering/turn-around-times/] Last accessed 2024-06-25.
- Horton, R.; Lucassen, A. Ethical issues raised by new genomic technologies: the case study of newborn genome screening. Camb. Prism. Precis. Med. 2022, 1, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Genomics England. Newborn Genomes Programme: Vision Document. 2021 [Available at https://files.genomicsengland.co.uk/documents/Newborns-Vision-Final_SEP_2021-11-02-122418_jjne.pdf] Last accessed 2024-06-25.
- Genomics England. Newborn Genomes Programme Generation Study: List of conditions and genes. 2024 [Available from: https://www.genomicsengland.co.uk/initiatives/newborns/choosing-conditions/conditions-list-generation-study] Last accessed 2024-06-25.
| Gene symbol | CYBB | CYBA | NCF1 | NCF2 | NCF4 |
| NCBI gene ID | 1536 | 1535 | 653361 | 4688 | 4689 |
| Gene name | Cytochrome b558 beta | Cytochrome b558 alpha | Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 | Neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 | Neutrophil cytosolic factor 4 |
| Gene location | Xp21.1-p11.4 | 16q24.2 | 7q11.23 | 1q25.3 | 22q12.3 |
| Exon count | 14 | 6 | 11 | 20 | 12 |
| Protein | gp91phox / NOX2 | p22phox | p47phox | p67phox | p40phox |
| Protein location | Specific granule membrane, plasma membrane | Specific granule membrane, plasma membrane | Cytosol, cytoskeleton | Cytosol, cytoskeleton | Cytosol, cytoskeleton |
| Frequency | 65-70% | 5% | 20% | 5% | Rare |
| Inheritance | XR | AR | AR | AR | AR |
| Clinical severity | Severe$Early onset | Severe$Early onset | Mild$Late onset | Severe$Early onset | Mild$Atypical |
| Mutations | Missense$Nonsense$Missplicing$Large or small deletions$Insertions$Duplications$Transposable elements | Insertions$Deletions$Missense$Nonsense$Missplicing | Unequal meiotic crossover events with neighbouring pseudogenes$Missense$Nonsense$Insertions$Deletions$Missplicing | Insertions$Deletions$Missense$Nonsense$Missplicing | Insertions$Deletions$Missense$Nonsense$Missplicing |
| Pickup on sequence analysis | 85% | 85% | 75% | 85% | 90% |
| Pickup on deletion/duplication analysis | 15% | 15% | 25% | 15% | 10% |
| Gene symbol | CYBC1 | RAC2 | G6PD | MPO | GSS |
| NCBI gene ID | 79415 | 5880 | 2539 | 4353 | 2937 |
| Gene name | Cytochrome b558 chaperone 1 | Rac family small GTPase 2 | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase | Myeloperoxidase | Glutathione synthetase |
| Gene location | 17q25.3 | 22q13.1 | Xq28 | 17q22 | 20q11.22 |
| Exon count | 8 | 8 | 14 | 12 | 15 |
| Protein | CYBC1/Eros | Rac2-GTPase | G6PD | MPO | GSS |
| Protein location | Endoplasmic reticulum | Cytosol | Cytosol | Granule lumen | Cytosol, nucleus, mitochondria |
| Frequency | Rare | Rare | Severe deficiency is rare | Common but unlikely to cause CGD-like features | Rare |
| Inheritance | AR | AD | XR | AR | AR |
| Clinical severity | Few cases described | Few cases described | Spectrum from mild to severe | Asymptomatic or susceptible to Candida | Spectrum from mild to severe |
| Mutations | Nonsense$Missense$Missplicing | Nonsense$Missense | Deletion$Missense | Nonsense$Missense$Missplicing$Deletions | Indels$Nonsense$Missense$Missplicing |
| Notes | Also regulates expression of proteins other than gp91phox-p22phox, e.g., P2X7 | Also associated with abnormalities of neutrophil chemotaxis and lymphocyte function | Mild cases: relatively common but lack CGD-like features$Severe cases: generally mild CGD features | Rarely solely responsible for immunodeficiency | Mild cases: haemolytic anaemia only$Moderate: metabolic acidosis$Severe: progressive neurological dysfunction and infection susceptibility |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





