Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
19 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Lactate Metabolism in the Brain
3. Lactate as a Signaling Molecule in the Brain
4. Protein Lactylation in the Brain
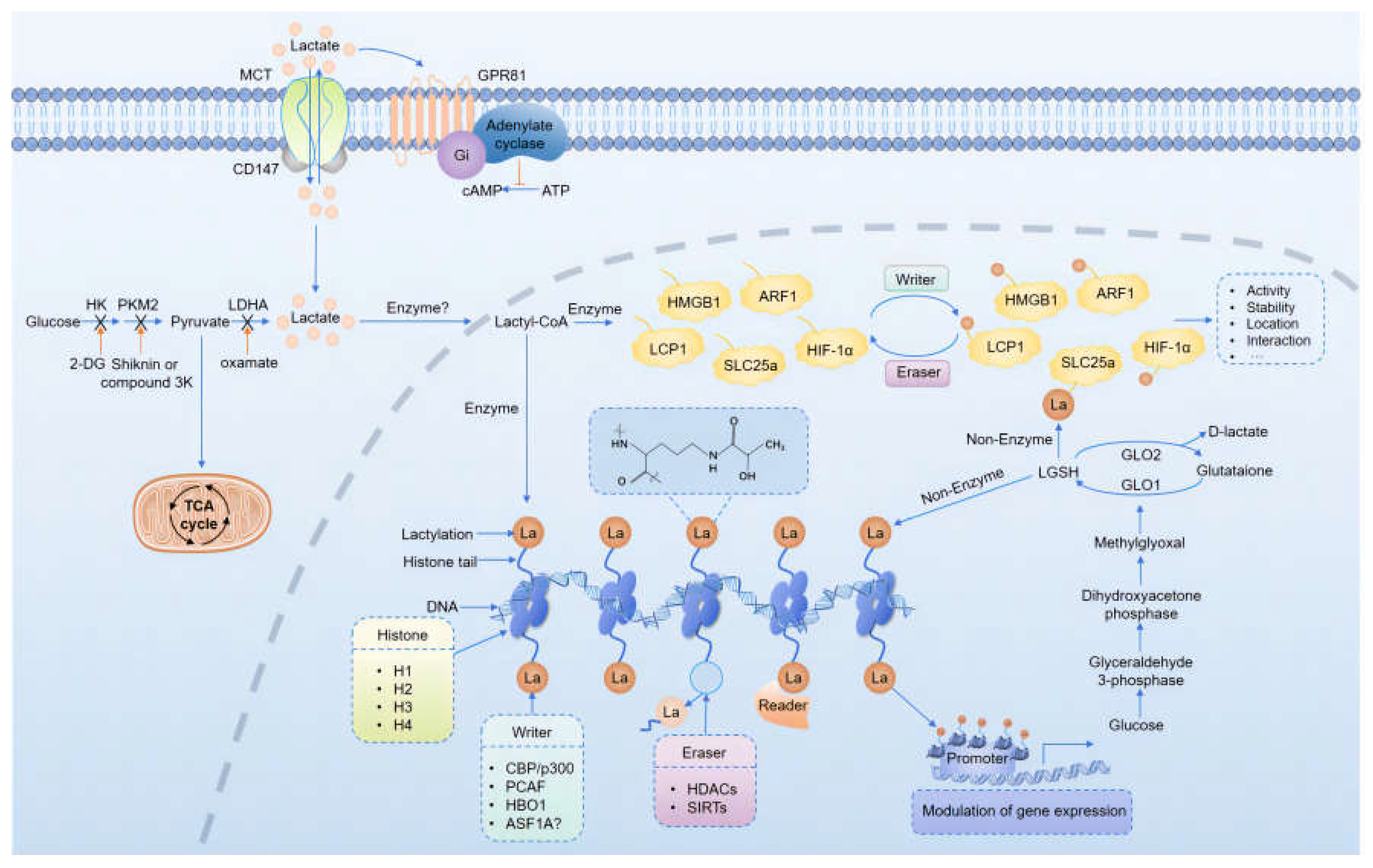
4.1. Mechanisms of Protein Lactylation
4.2. Regulation of Protein Lactylation
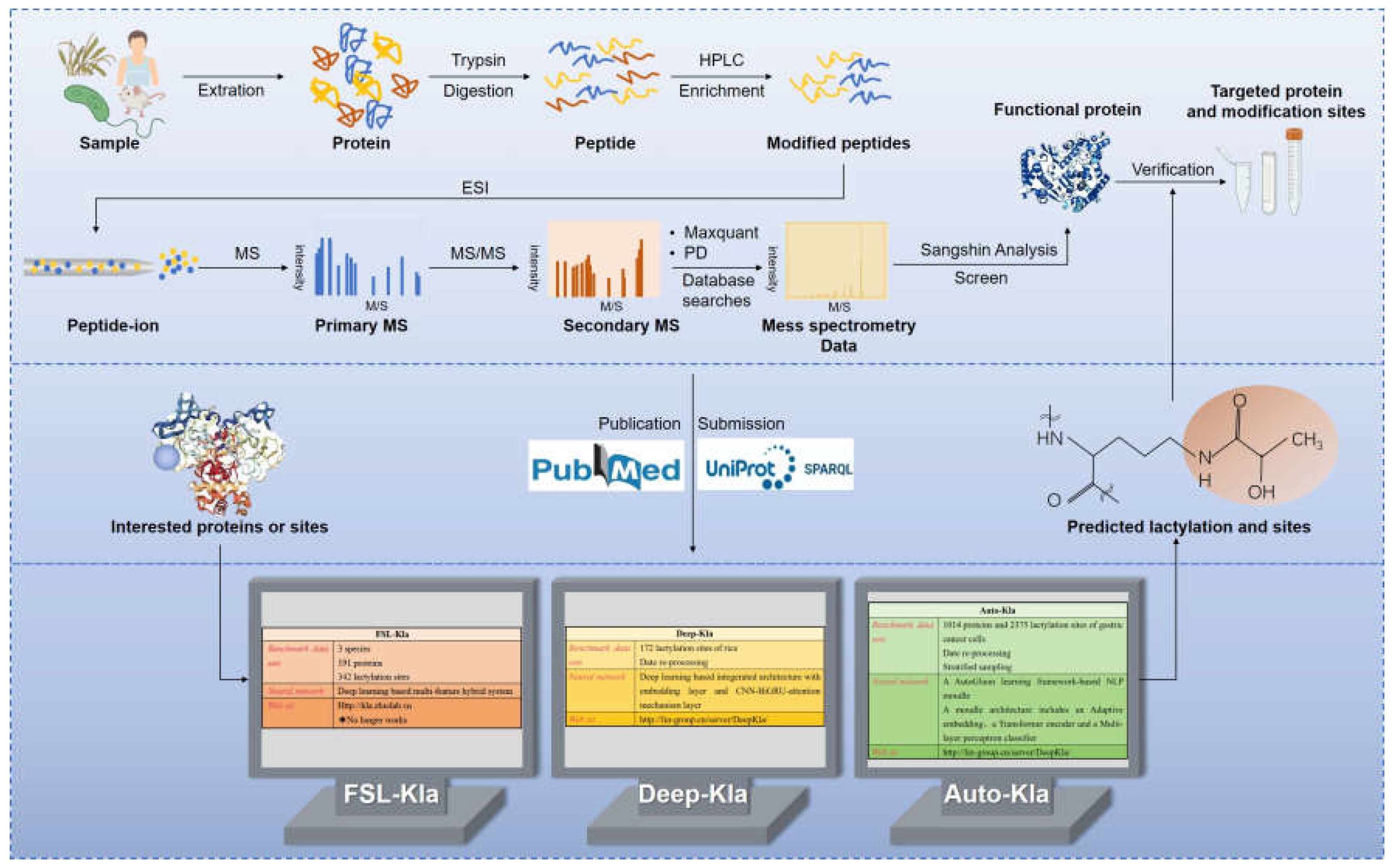
4.3. Detection of Protein Lactylation
4.4. Lactylation and Neural Development
4.5. Lactylation and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
4.6. Lactylation and Glioblastoma
4.7. Lactylation and Hypoxia-Related Brain Damages
| Lactylation proteins | Protein targets |
Regulation | Keyfindings | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Neuropsychiatric disorders |
Depression and Anxiety | H1 | C-Fos | 4-CIN, Oxamate |
Stress-associated neural excitation stimulates H1 lactylation, which correlates with decreased social behavior. | [86] |
| AD | H4K12 | PKM2 | Glycolysis/H4K12la/PKM2 positive feedback loop | Glycolysis/H4K12la/PKM2 positive feedback loop exacerbates microglial dysfunction. | [97] | |
| H3K18 | Rela NF-κB |
Lactate | H3K18la/NF-κB/SASP positive feedback loop exacerbates AD pathology. | [68] | ||
| H3 | Arg1 VEGF |
Exercise-induced Lactate | Exercise-induced lactate directs microglia to a repair/anti-inflammatory state via H3Lactylation | [101] | ||
| PD | H3K9 | Slc7a11 | 2-DG | H3K9la enhances transcription of Slc7a11, promoting pro-inflammatory microglial activation | [102] | |
| SCZ | H3K9 H3K18 |
Mybe HMGB1 | 2-DG | In SCZ model, both glycolysis and lactylation were elevated, these increases could be inhibited by 2-DG | [103] | |
| PTSD | HIF-1α | HIF-1α lactylation and dysfunction play a critical role in the pathological development of PTSD | [104] | |||
| Cerebral neoplasms |
GBM | Histon | IL-10 | The PERK-ATF4-driven glucose metabolism | Histone lactylation drivess immunosuppressive programs, increasess IL-10 expression, and suppresses T cell activity | [69] |
| H3K18 | LINC01127 | NF-κB promotes lactate production | H3K18la plays an important role in regulating GSCs self-renewal. | [110] | ||
| H3K18 | CD39, CD73 | Oxamate | H3K18la enhances immune suppression | [107] | ||
| H3K9 | LUC7L2 | Stiripentol enhances the sensitivity of GBM cells to TMZ by inhibiting H3 lactylation | [70] | |||
| VE-cadherin VEGFR2 |
P4-135aa mediates KLF15 phosphorylation, promoting LDHA transcription and facilitating VE-cadherin and VEGFR2 lactylation. | The lactylation of VE-cadherin and VEGFR2 induces VM formation in GBM | [111] | |||
| Hypoxia-related brain damages | Stroke (CIRI) |
496 proteins 1003 sites | Elevated lactylation in CIRI rats contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal apoptosis through Ca2+ overload | [13] | ||
| LCP1 | 2-DG reduces LCP1 lactylation and stability | LCP1 lactylation facilitates CI progression by enhancing its stability | [114] | |||
| ARF1K73 | LRP1 reduces ARF1- K73la | LRP1 reduces ARF1K73la, promoting mitochondrial transfer and neuroprotection in CIRI | [115] | |||
4.7.1. Energy Metabolism Regulation
4.7.2. Oxidative Stress Management
4.7.3. Inflammatory Response Modulation
5. Targeted Therapy
6. Conclusion and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaupel, P.A.-O.; Multhoff, G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding. J Physiol 2021, 6, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Thorne, R.F.; Shi, R.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, M.; Liu, L. DDIT3 Directs a Dual Mechanism to Balance Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation during Glutamine Deprivation. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 2021, 8, e2003732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Certo, M.; Llibre, A.; Lee, W.; Mauro, C. Understanding lactate sensing and signalling. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism: TEM 2022, 33, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbert, L.E.; El Alam, M.B.; Wang, R.; Karpinets, T.; Lo, D.; Lynn, E.J.; Harris, T.A.; Elnaggar, J.H.; Yoshida-Court, K.; Tomasic, K.; et al. Tumor-resident Lactobacillus iners confer chemoradiation resistance through lactate-induced metabolic rewiring. Cancer cell 2023, 41, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Fu, Q.; Long, Q.; Liu, S.; Zou, Y.; Fu, D.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. PDK4-dependent hypercatabolism and lactate production of senescent cells promotes cancer malignancy. Nature metabolism 2023, 5, 1887–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Fu, X.; An, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T. Lactate metabolism in human health and disease. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2022, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Lee, D.; Xiong, W.C. Lactate Metabolism, Signaling, and Function in Brain Development, Synaptic Plasticity, Angiogenesis, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Cui, C.; Weng, Y.; Liu, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Perez-Neut, M.; et al. Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature 2019, 574, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Guo, Y. Ubiquitous protein lactylation in health and diseases. Cellular & molecular biology letters 2024, 29, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, P.; Xin, T. Integrated single-cell and bulk RNA-sequencing data reveal molecular subtypes based on lactylation-related genes and prognosis and therapeutic response in glioma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkuri, F.; Rothstein, M.; Simoes-Costa, M. Histone lactylation couples cellular metabolism with developmental gene regulatory networks. Nature communications 2024, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Mo, N.; Tong, L.; Dong, J.; Fan, Z.; Jia, M.; Yue, J.; Wang, Y. Microglia lactylation in relation to central nervous system diseases. Neural regeneration research 2025, 20, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Bade, R.; Li, G.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, H.; Fan, L.; Zhu, R.; Yuan, J. Global-Scale Profiling of Differential Expressed Lysine-Lactylated Proteins in the Cerebral Endothelium of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Rats. Cellular and molecular neurobiology 2023, 43, 1989–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, J.D.; Enerbäck, S. Lactate: the ugly duckling of energy metabolism. Nature metabolism 2020, 2, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.A. Lactate as a fulcrum of metabolism. Redox biology 2020, 35, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. We need to talk about the Warburg effect. Nature metabolism 2020, 2, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, C.M.; Mongeon, R.; Lahmann, C.; Koveal, D.; Zucker, H.; Yellen, G. Neuronal Stimulation Triggers Neuronal Glycolysis and Not Lactate Uptake. Cell metabolism 2017, 26, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kann, O. Lactate as a supplemental fuel for synaptic transmission and neuronal network oscillations: Potentials and limitations. Journal of neurochemistry 2024, 168, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Jimenez-Blasco, D.; Bolaños, J.P. Cross-talk between energy and redox metabolism in astrocyte-neuron functional cooperation. Essays in biochemistry 2023, 67, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, M.; Allaman, I.; Magistretti, P.J. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell metabolism 2011, 14, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell metabolism 2018, 27, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Ni, Y.; Shen, P.; Han, X. Lactate shuttle: from substance exchange to regulatory mechanism. Human cell 2022, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Xu, M.D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.T.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.F.; Chen, W.B.; Liu, J.; Huang, G.B.; Sun, W.J.; et al. Astrocytic lactate dehydrogenase A regulates neuronal excitability and depressive-like behaviors through lactate homeostasis in mice. Nature communications 2023, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, A.; Gallopin, T.; Lacroix, A.; Plaisier, F.; Piquet, J.; Geoffroy, H.; Hepp, R.; Naudé, J.; Le Gac, B.; Egger, R.; et al. Lactate is an energy substrate for rodent cortical neurons and enhances their firing activity. eLife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Mendez, A.; Almeida, A.; Fernández, E.; Maestre, C.; Moncada, S.; Bolaños, J.P. The bioenergetic and antioxidant status of neurons is controlled by continuous degradation of a key glycolytic enzyme by APC/C-Cdh1. Nature cell biology 2009, 11, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandebura, A.N.; Paumier, A.; Onur, T.S.; Allen, N.J. Astrocyte contribution to dysfunction, risk and progression in neurodegenerative disorders. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 2023, 24, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumes, H.; Pellerin, L.; Bouzier-Sore, A.K. Astrocytes as metabolic suppliers to support neuronal activity and brain functions. Essays in biochemistry 2023, 67, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Duan, F.; Wu, K.; Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Jiang, X.; Sun, X. Lactate and Lactylation in the Brain: Current Progress and Perspectives. Cellular and molecular neurobiology 2023, 43, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.I.; Malkov, A.E.; Waseem, T.; Mukhtarov, M.; Buldakova, S.; Gubkina, O.; Zilberter, M.; Zilberter, Y. Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in neurons and astrocytes during network activity in hippocampal slices. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2014, 34, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, G.A. Brain Glucose Metabolism: Integration of Energetics with Function. Physiological reviews 2019, 99, 949–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaffer, A.; Mineta, K.; Magistretti, P.; Gojobori, T. Lactate-mediated neural plasticity genes emerged during the evolution of memory systems. Scientific reports 2022, 12, 19238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzoli, E.; Calì, C.; De Roo, M.; Ponzoni, L.; Sogne, E.; Gagnon, N.; Francolini, M.; Braida, D.; Sala, M.; Muller, D.; et al. Ultrastructural Evidence for a Role of Astrocytes and Glycogen-Derived Lactate in Learning-Dependent Synaptic Stabilization. Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 2020, 30, 2114–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, K.; Pellerin, L. Monocarboxylate transporters in the central nervous system: distribution, regulation and function. Journal of neurochemistry 2005, 94, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medel, V.; Crossley, N.; Gajardo, I.; Muller, E.; Barros, L.F.; Shine, J.M.; Sierralta, J. Whole-brain neuronal MCT2 lactate transporter expression links metabolism to human brain structure and function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2022, 119, e2204619119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dana, P.; Saisomboon, S.; Kariya, R.; Okada, S.; Obchoei, S.; Sawanyawisuth, K.; Wongkham, C.; Pairojkul, C.; Wongkham, S.; Vaeteewoottacharn, K. CD147 augmented monocarboxylate transporter-1/4 expression through modulation of the Akt-FoxO3-NF-κB pathway promotes cholangiocarcinoma migration and invasion. Cellular oncology (Dordrecht) 2020, 43, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasadonte, J.; Scemes, E.; Wang, Z.; Boison, D.; Haydon, P.G. Connexin 43-Mediated Astroglial Metabolic Networks Contribute to the Regulation of the Sleep-Wake Cycle. Neuron 2017, 95, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaume, C.; McCarthy, K.D. Control of gap-junctional communication in astrocytic networks. Trends in neurosciences 1996, 19, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morland, C.; Lauritzen, K.H.; Puchades, M.; Holm-Hansen, S.; Andersson, K.; Gjedde, A.; Attramadal, H.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Bergersen, L.H. The lactate receptor, G-protein-coupled receptor 81/hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1: Expression and action in brain. Journal of neuroscience research 2015, 93, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, M.; Osorio-Forero, A.; Lüthi, A.; Chatton, J.Y. The lactate receptor HCAR1: A key modulator of epileptic seizure activity. iScience 2024, 27, 109679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarzynska, D.; Sun, H.; Williamson, J.; Kasprzak, I.; Kapur, J. Glycolysis regulates neuronal excitability via lactate receptor, HCA1R. Brain : a journal of neurology 2023, 146, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Abrantes, H.; Briquet, M.; Schmuziger, C.; Restivo, L.; Puyal, J.; Rosenberg, N.; Rocher, A.B.; Offermanns, S.; Chatton, J.Y. The Lactate Receptor HCAR1 Modulates Neuronal Network Activity through the Activation of G(α) and G(βγ) Subunits. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2019, 39, 4422–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-López, G.; Griego, E.; Galván, E.J. Lactate induces synapse-specific potentiation on CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus. PloS one 2020, 15, e0242309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Allaman, I. Lactate in the brain: from metabolic end-product to signalling molecule. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 2018, 19, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Stern, S.A.; Bozdagi, O.; Huntley, G.W.; Walker, R.H.; Magistretti, P.J.; Alberini, C.M. Astrocyte-neuron lactate transport is required for long-term memory formation. Cell 2011, 144, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Tan, Y.; Du, A.; Wen, G.; Ren, X.; Yao, H.; Ren, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; et al. Redistribution of Monocarboxylate 1 and 4 in Hippocampus and Spatial Memory Impairment Induced by Long-term Ketamine Administration. Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 2020, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadi, M.; Allaman, I.; Lengacher, S.; Grenningloh, G.; Magistretti, P.J. Learning-Induced Gene Expression in the Hippocampus Reveals a Role of Neuron -Astrocyte Metabolic Coupling in Long Term Memory. PloS one 2015, 10, e0141568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzahualcoyotzi, C.; Pellerin, L. Neuronal and astroglial monocarboxylate transporters play key but distinct roles in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory formation. Progress in neurobiology 2020, 194, 101888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, E.; Liu, M.; Mu, S.; Hang, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Astrocyte-derived lactate/NADH alters methamphetamine-induced memory consolidation and retrieval by regulating neuronal synaptic plasticity in the dorsal hippocampus. Brain structure & function 2022, 227, 2681–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Moon, C.; Zheng, F.; Luo, Y.; Soellner, D.; Nuñez, J.L.; Wang, H. N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated ERK1/2 signaling and the transcriptional up-regulation of plasticity-related genes are developmentally regulated following in vitro neuronal maturation. Journal of neuroscience research 2009, 87, 2632–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ruchti, E.; Petit, J.M.; Jourdain, P.; Grenningloh, G.; Allaman, I.; Magistretti, P.J. Lactate promotes plasticity gene expression by potentiating NMDA signaling in neurons. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2014, 111, 12228–12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.E.; Kayser, C.; Maiellaro, I.; Nemec, K.; Möller, J.; Koschinski, A.; Zaccolo, M.; Annibale, P.; Falcke, M.; Lohse, M.J.; et al. Receptor-associated independent cAMP nanodomains mediate spatiotemporal specificity of GPCR signaling. Cell 2022, 185, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, T.; Nguyen, P.V.; Barad, M.; Deuel, T.A.; Kandel, E.R.; Bourtchouladze, R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 1997, 88, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.O.; Zhang, Y.; Cho, C.E.; Engelke, D.S.; Smolen, P.; Byrne, J.H.; Do-Monte, F.H. Enhancing Associative Learning in Rats With a Computationally Designed Training Protocol. Biological psychiatry global open science 2024, 4, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Egervari, G.; Wang, Y.; Berger, S.L.; Lu, Z. Regulation of chromatin and gene expression by metabolic enzymes and metabolites. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 2018, 19, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Pan, H.; Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Histone lactylation: from tumor lactate metabolism to epigenetic regulation. International journal of biological sciences 2024, 20, 1833–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Han, Z.; Halabelian, L.; Yang, X.; Ding, J.; Zhang, N.; Ngo, L.; Song, J.; Zeng, H.; He, M.; et al. Identification of lysine isobutyrylation as a new histone modification mark. Nucleic acids research 2021, 49, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Yruela, C.; Bæk, M.; Monda, F.; Olsen, C.A. Chiral Posttranslational Modification to Lysine ε-Amino Groups. Accounts of chemical research 2022, 55, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, D.O.; Jennings, E.Q.; Anderson, C.C.; Marentette, J.O.; Shi, T.; Schou Oxvig, A.M.; Streeter, M.D.; Johannsen, M.; Spiegel, D.A.; Chapman, E.; et al. Non-enzymatic Lysine Lactoylation of Glycolytic Enzymes. Cell chemical biology 2020, 27, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yin, J.; Shan, L.; Yi, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Y. Identification of lysine-lactylated substrates in gastric cancer cells. iScience 2022, 25, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, X.; Tan, F. Systematic identification of the lysine lactylation in the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Parasites & vectors 2022, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Stielow, J.B.; de Hoog, S.; Li, R. Post-translational changes in Phialophora verrucosa via lysine lactylation during prolonged presence in a patient with a CARD9-related immune disorder. Frontiers in immunology 2022, 13, 966457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, N.; Liang, W. Systematic Analysis of Lysine Lactylation in the Plant Fungal Pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Frontiers in microbiology 2020, 11, 594743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Q.C.; Kong, J.; Yang, J.T.; Liu, J.F. Global profiling of lysine lactylation in human lungs. Proteomics 2023, 23, e2200437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Liu, J.; Hua, F. Protein acylation: mechanisms, biological functions and therapeutic targets. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2022, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Z.; Huang, W. Effects of the Acetyltransferase p300 on Tumour Regulation from the Novel Perspective of Posttranslational Protein Modification. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, B.; Lu, S.; Lu, X.; You, S.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; et al. α-myosin heavy chain lactylation maintains sarcomeric structure and function and alleviates the development of heart failure. Cell research 2023, 33, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Gill, P.S.; Ha, T.; Liu, L.; Lewis, N.H.; Williams, D.L.; Li, C. Lactate promotes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Snail1 lactylation after myocardial infarction. Science advances 2023, 9, eadc9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Yu, A. H3K18 lactylation of senescent microglia potentiates brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease through the NFκB signaling pathway. Journal of neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, A.; Ugolini, A.; Yu, X.; Scirocchi, F.; Scocozza, D.; Peixoto, B.; Pace, A.; D’Angelo, L.; Liu, J.K.C.; Etame, A.B.; et al. Glucose-driven histone lactylation promotes the immunosuppressive activity of monocyte-derived macrophages in glioblastoma. Immunity 2024, 57, 1105–1123.e1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zuo, B.; Zeng, T.; et al. Histone H3K9 Lactylation Confers Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma via LUC7L2-Mediated MLH1 Intron Retention. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 2024, 11, e2309290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.K.; Liu, P.P.; Li, X.; Jiao, L.F.; Teng, Z.Q.; Liu, C.M. Dynamic profiling and functional interpretation of histone lysine crotonylation and lactylation during neural development. Development (Cambridge, England) 2022, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, M.; Muñoz-Viana, R.; Del Blanco, B.; Marquez-Galera, A.; Medrano-Relinque, J.; Caramés, J.M.; Szczepankiewicz, A.A.; Fernandez-Albert, J.; Navarrón, C.M.; Olivares, R.; et al. KAT3-dependent acetylation of cell type-specific genes maintains neuronal identity in the adult mouse brain. Nature communications 2020, 11, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, E.Q.; Ray, J.D.; Zerio, C.J.; Trujillo, M.N.; McDonald, D.M.; Chapman, E.; Spiegel, D.A.; Galligan, J.J. Sirtuin 2 Regulates Protein LactoylLys Modifications. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2021, 22, 2102–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, H.; Li, C.; Dai, C.; Pan, Y.; Ding, C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Zang, J.; Mo, X. SIRT2 functions as a histone delactylase and inhibits the proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma cells. Cell discovery 2022, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Yruela, C.; Zhang, D.; Wei, W.; Bæk, M.; Liu, W.; Gao, J.; Danková, D.; Nielsen, A.L.; Bolding, J.E.; Yang, L.; et al. Class I histone deacetylases (HDAC1-3) are histone lysine delactylases. Science advances 2022, 8, eabi6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, R.; Hagelkruys, A.; Matthias, P.; Zhang, H.; et al. HDAC1 and HDAC2 Regulate Intermediate Progenitor Positioning to Safeguard Neocortical Development. Neuron 2019, 101, 1117–1133.e1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhong, H.; Cheng, L.; Li, L.P.; Zhang, D.K. Post-translational protein lactylation modification in health and diseases: a double-edged sword. Journal of translational medicine 2024, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Baine, J.M.; Yan, T.; Wang, S. Comprehensive Analysis of Lysine Lactylation in Rice (Oryza sativa) Grains. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2021, 69, 8287–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ning, W.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Mo, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, K.; Guo, Y. FSL-Lactylation: A few-shot learning-based multi-feature hybrid system for lactylation site prediction. Computational and structural biotechnology journal 2021, 19, 4497–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Dao, F.Y.; Lin, H. DeepLactylation: An attention mechanism-based deep neural network for protein lysine lactylation site prediction. iMeta 2022, 1, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.L.; Gao, F. Auto-Lactylation: a novel web server to discriminate lysine lactylation sites using automated machine learning. Briefings in bioinformatics 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Gotoh, Y. HMGA regulates the global chromatin state and neurogenic potential in neocortical precursor cells. Nature neuroscience 2012, 15, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, K.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Xing, G.; Chen, M.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ma, B.; et al. Glis1 facilitates induction of pluripotency via an epigenome-metabolome-epigenome signalling cascade. Nature metabolism 2020, 2, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Azambuja, A.P.; Simoes-Costa, M. Metabolic Reprogramming Promotes Neural Crest Migration via Yap/Tead Signaling. Developmental cell 2020, 53, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Su, L.; Ji, F.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiao, J. BACH1 changes microglial metabolism and affects astrogenesis during mouse brain development. Developmental cell 2024, 59, 108–124.e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, H.; Shoji, H.; Otabi, H.; Toyoda, A.; Katoh, K.; Namihira, M.; Miyakawa, T. Protein lactylation induced by neural excitation. Cell reports 2021, 37, 109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Liang, J.; Zhou, B. Glucose Metabolic Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases-New Mechanistic Insights and the Potential of Hypoxia as a Prospective Therapy Targeting Metabolic Reprogramming. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, B.S.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. Evidence for altered energy metabolism, increased lactate, and decreased pH in schizophrenia brain: A focused review and meta-analysis of human postmortem and magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Schizophrenia research 2020, 223, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, H.; Han, T.; Wang, H. Lactate: a prospective target for therapeutic intervention in psychiatric disease. Neural regeneration research 2024, 19, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.B.; Huang, A.Y.; Kim, J.; Zhou, Z.; Kirkham, S.L.; Maury, E.A.; Ziegenfuss, J.S.; Reed, H.C.; Neil, J.E.; Rento, L.; et al. Somatic genomic changes in single Alzheimer’s disease neurons. Nature 2022, 604, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here? Nature reviews. Neurology 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodburn, S.C.; Bollinger, J.L.; Wohleb, E.S. The semantics of microglia activation: neuroinflammation, homeostasis, and stress. Journal of neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Microglial lactate metabolism as a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular neurodegeneration 2022, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Mai, W.; Chen, L.; Cao, K.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lou, H.; Duan, S.; Gao, Z. mTOR-mediated metabolic reprogramming shapes distinct microglia functions in response to lipopolysaccharide and ATP. Glia 2020, 68, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, A.; Mela, V.; Harty, C.; Minogue, A.M.; Costello, D.A.; Kerskens, C.; Lynch, M.A. Iron accumulation in microglia triggers a cascade of events that leads to altered metabolism and compromised function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain pathology (Zurich, Switzerland) 2019, 29, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, A.K.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Lactate induces tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1beta release in microglial- and astroglial-enriched primary cultures. Journal of neurochemistry 2005, 93, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.Y.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liao, Y.; Gao, J.; Liao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; et al. Positive feedback regulation of microglial glucose metabolism by histone H4 lysine 12 lactylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell metabolism 2022, 34, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, C.; You, M.J.; Nahm, M.; Kwon, M.S. Emerging role of senescent microglia in brain aging-related neurodegenerative diseases. Translational neurodegeneration 2024, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overholtzer, M. Senescent cells feed on their neighbours. Nature 2019, 574, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohesara, S.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Thiagalingam, S. Potential for New Therapeutic Approaches by Targeting Lactate and pH Mediated Epigenetic Dysregulation in Major Mental Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhao, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; et al. Exercise improves cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation in mice through Histone H3 lactylation in microglia. Immunity & ageing : I & A 2023, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, D.; Qu, Y.; Li, J.; An, K.; Mao, Z.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y.; Min, Z.; Xue, Z. Enhanced glycolysis-derived lactate promotes microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease via histone lactylation. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Hong, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, R. Inhibition of glycolysis prevents behavioural changes in mice with MK801-induced SCZ model by alleviating lactate accumulation and lactylation. Brain research 2023, 1812, 148409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlakidis, Z.; Shi, P.; Abarbanel, G.; Klein, C.; Sfera, A. Recent Developments in Protein Lactylation in PTSD and CVD: Novel Strategies and Targets. Biotech (Basel (Switzerland)) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatibi, V.A.; Salimi, M.; Rahdar, M.; Rezaei, M.; Nazari, M.; Dehghan, S.; Davoudi, S.; Raoufy, M.R.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J.; Javan, M.; et al. Glycolysis inhibition partially resets epilepsy-induced alterations in the dorsal hippocampus-basolateral amygdala circuit involved in anxiety-like behavior. Scientific reports 2023, 13, 6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Liu, C.; Hu, A.; Zhang, D.; Yang, H.; Mao, Y. Understanding the immunosuppressive microenvironment of glioma: mechanistic insights and clinical perspectives. Journal of hematology & oncology 2024, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, S.; Tan, H.; Cai, L.; Zhang, S.; Qi, X.; et al. Oxamate enhances the efficacy of CAR-T therapy against glioblastoma via suppressing ectonucleotidases and CCR8 lactylation. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR 2023, 42, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T. Glioblastoma-initiating cell heterogeneity generated by the cell-of-origin, genetic/epigenetic mutation and microenvironment. Seminars in cancer biology 2022, 82, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalej, K.M.; Merhi, M.; Inchakalody, V.P.; Mestiri, S.; Alam, M.; Maccalli, C.; Cherif, H.; Uddin, S.; Steinhoff, M.; Marincola, F.M.; et al. CAR-cell therapy in the era of solid tumor treatment: current challenges and emerging therapeutic advances. Molecular cancer 2023, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Qin, J.; Sun, N.; Tian, K.; et al. Histone lactylation-derived LINC01127 promotes the self-renewal of glioblastoma stem cells via the cis-regulating the MAP4K4 to activate JNK pathway. Cancer letters 2023, 579, 216467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ruan, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, W.; Yang, C.; Xue, Y. Pseudogene MAPK6P4-encoded functional peptide promotes glioblastoma vasculogenic mimicry development. Communications biology 2023, 6, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. International review of cell and molecular biology 2012, 298, 229–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y. Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: From mechanisms to treatment (Review). International journal of molecular medicine 2022, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J. Inhibition of the Glycolysis Prevents the Cerebral Infarction Progression Through Decreasing the Lactylation Levels of LCP1. Molecular biotechnology 2023, 65, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Huang, A.; Du, F.; Liao, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Astrocytic LRP1 enables mitochondria transfer to neurons and mitigates brain ischemic stroke by suppressing ARF1 lactylation. Cell metabolism 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Chandel, N.S.; Simon, M.C. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia through hypoxia inducible factors and beyond. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 2020, 21, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.W.; Bae, M.K.; Ahn, M.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Sohn, T.K.; Bae, M.H.; Yoo, M.A.; Song, E.J.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, K.W. Regulation and destabilization of HIF-1alpha by ARD1-mediated acetylation. Cell 2002, 111, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.Y.; Jung, J.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Woo, S.R.; Jeong, J.M.; Park, E.R.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, J.J.; Kim, J.; Yun, M.; et al. NADH elevation during chronic hypoxia leads to VHL-mediated HIF-1α degradation via SIRT1 inhibition. Cell & bioscience 2023, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, P. HIF1α lactylation enhances KIAA1199 transcription to promote angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry in prostate cancer. International journal of biological macromolecules 2022, 222, 2225–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Qu, K.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Lactylation: a Passing Fad or the Future of Posttranslational Modification. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lin, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Hypoxia induces mitochondrial protein lactylation to limit oxidative phosphorylation. Cell research 2024, 34, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, P.; Deng, K.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Xia, J. H3K18 lactylation-mediated VCAM1 expression promotes gastric cancer progression and metastasis via AKT-mTOR-CXCL1 axis. Biochemical pharmacology 2024, 222, 116120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Shi, R.; An, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Histone lactylation promotes malignant progression by facilitating USP39 expression to target PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α signal pathway in endometrial carcinoma. Cell death discovery 2024, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yang, S.; Chu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Pang, X.W.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.Q.; Chen, M.; Tian, D.S.; Wang, W. Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2022, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, R.M.; Dingman, A.L.; Herson, P.S. Cerebral ischemia in the developing brain. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2022, 42, 1777–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Mang, G.; Chen, J.; Yan, X.; Tong, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; et al. Histone Lactylation Boosts Reparative Gene Activation Post-Myocardial Infarction. Circulation research 2022, 131, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgeorges, T.; Galle, E.; Zhang, J.; von Meyenn, F.; De Bock, K. Histone lactylation in macrophages is predictive for gene expression changes during ischemia induced-muscle regeneration. Molecular metabolism 2024, 83, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Fu, D.; Lu, X.; Lu, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.; Wu, K.; Xu, Y.; et al. The glycolytic enzyme PFKFB3 drives kidney fibrosis through promoting histone lactylation-mediated NF-κB family activation. Kidney international 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Fan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tu, F.; Gill, P.S.; Ha, T.; Liu, L.; Williams, D.L.; et al. Lactate promotes macrophage HMGB1 lactylation, acetylation, and exosomal release in polymicrobial sepsis. Cell death and differentiation 2022, 29, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Peng, P.; Kong, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ding, Z.; Liu, L. Hepatocyte HSPA12A inhibits macrophage chemotaxis and activation to attenuate liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppressing glycolysis-mediated HMGB1 lactylation and secretion of hepatocytes. Theranostics 2023, 13, 3856–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Lv, X.; Thompson, E.W.; Ostrikov, K.K. Histone lactylation: epigenetic mark of glycolytic switch. Trends in genetics : TIG 2022, 38, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, O.; Mayer, M.; Leischner, C.; Burkard, M.; Berger, A.; Lauer, U.M.; Venturelli, S.; Bischoff, S.C. Systematic Review of Gossypol/AT-101 in Cancer Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sada, N.; Lee, S.; Katsu, T.; Otsuki, T.; Inoue, T. Epilepsy treatment. Targeting LDH enzymes with a stiripentol analog to treat epilepsy. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2015, 347, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raez, L.E.; Papadopoulos, K.; Ricart, A.D.; Chiorean, E.G.; Dipaola, R.S.; Stein, M.N.; Rocha Lima, C.M.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Tolba, K.; Langmuir, V.K.; et al. A phase I dose-escalation trial of 2-deoxy-D-glucose alone or combined with docetaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology 2013, 71, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Lin, H.; Jeyamohan, C.; Dvorzhinski, D.; Gounder, M.; Bray, K.; Eddy, S.; Goodin, S.; White, E.; Dipaola, R.S. Targeting tumor metabolism with 2-deoxyglucose in patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer and advanced malignancies. The Prostate 2010, 70, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, E.M.; Coats, B.S.; Shroads, A.L.; Langaee, T.; Lew, A.; Forder, J.R.; Shuster, J.J.; Wagner, D.A.; Stacpoole, P.W. Phase 1 trial of dichloroacetate (DCA) in adults with recurrent malignant brain tumors. Investigational new drugs 2014, 32, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.F.; Mazurczak, M.; Dib, E.G.; Bleeker, J.S.; Geeraerts, L.H.; Tinguely, M.; Lohr, M.M.; McGraw, S.C.; Jensen, A.W.; Ellison, C.A.; et al. Phase II study of dichloroacetate, an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase, in combination with chemoradiotherapy for unresected, locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Investigational new drugs 2022, 40, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halford, S.; Veal, G.J.; Wedge, S.R.; Payne, G.S.; Bacon, C.M.; Sloan, P.; Dragoni, I.; Heinzmann, K.; Potter, S.; Salisbury, B.M.; et al. A Phase I Dose-escalation Study of AZD3965, an Oral Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2023, 29, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Zheng, Z.H.; Wei, D.; Wen, A.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, J.Q.; Kang, W.Z.; Hao, C.Q.; Wang, J.; Xie, R.H.; et al. Safety and efficacy of meplazumab in healthy volunteers and COVID-19 patients: a randomized phase 1 and an exploratory phase 2 trial. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2021, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, W.; Li, N.; Ma, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, G.; He, S.; Li, W.; Tan, J.; Lu, Q.; et al. YY1 lactylation in microglia promotes angiogenesis through transcription activation-mediated upregulation of FGF2. Genome biology 2023, 24, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, H.; Terry, A.R.; Chronis, C.; Hay, N. Hexokinase 2-mediated gene expression via histone lactylation is required for hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. Cell metabolism 2023, 35, 1406–1423.e1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Harihar, D.; Chatterji, B.P. Recent histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer 2023, 129, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, D.; Ding, W.; Cao, Z.; Yan, P.; Li, Y.; Xi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. SIRT3-dependent delactylation of cyclin E2 prevents hepatocellular carcinoma growth. EMBO reports 2023, 24, e56052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, A.; Mo, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Yuan, Y.; et al. HBO1 catalyzes lysine lactylation and mediates histone H3K9la to regulate gene transcription. Nature communications 2024, 15, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Tan, Y.; Min, J.; He, X.; Liu, F.; Gu, J.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, L.; et al. ASF1A-dependent P300-mediated histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation promotes atherosclerosis by regulating EndMT. Acta pharmaceutica Sinica. B 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.; Xie, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhou, F. Alanyl-tRNA synthetase, AARS1, is a lactate sensor and lactyltransferase that lactylates p53 and contributes to tumorigenesis. Cell 2024, 187, 2375–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Lu, C.; Chen, C.; Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Zhai, G.; et al. YiaC and CobB regulate lysine lactylation in Escherichia coli. Nature communications 2022, 13, 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Physiological process |
Lactylation proteins | Protein targets | Regulation | Keyfindings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Neural development |
H3K18 | Genes involved in neuronal differentiation and maturation | HDAC1-3 inhibition Induces genome-wide enhancement of H3K18la | Unraveling the dynamics of histones Kcr and Kla and their functions in neural development | [71] |
| H3K18 | Pluripotency genes and “second wave” genes | Glis1 upregulates the expression of glycolysis-related genes |
The central role of histone Kac and Kla in epigenetic regulation driven by glycolytic metabolism | [83] | |
| H3K18 | Genes that contribute to NCC-specific features | Genomic regions containing SOX and TEAD motifs tend to be lactylated in NCC | The role of lactylation as a mechanism linking NCC metabolic states with GRN and developmental gene expression | [11] | |
| Histone | LRRC15 | Bach1 suppresses HK2 and GAPDH expression, thereby downregulating glycolysis | Maintenance of microglia metabolic homeostasis is important to astrocytogenesis during early brain development | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





