Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
19 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. L. lecanii KMZW-1 Collection, and Culture
2.2. Insect Collection and Rearing
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification Materials
2.4. Complete Genome Sequencing, Assembly and Annotation
2.4.1. Genome Sequencing
2.4.2. Genome Assembly and Analysis
2.4.3. Genome Predictions
2.4.4. Genome Protein Annotations
2.5. Pathogenicity Test of L. lecanii KMZW-1 against B. dorsalis
2.5.1. Conidial Suspension Preparation
2.5.2. Bioassays
| Concentration | Female Insect | Male Insect |
|---|---|---|
| 1×104 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×105 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×106 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×107 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×108 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×109 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×1010 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| 1×1011 | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| Control | 3*30 | 3*30 |
| Total (Insect) | 720 | 720 |
2.5.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome Assembly
3.2. BUSCO Evaluation
3.3. General Database Annotations
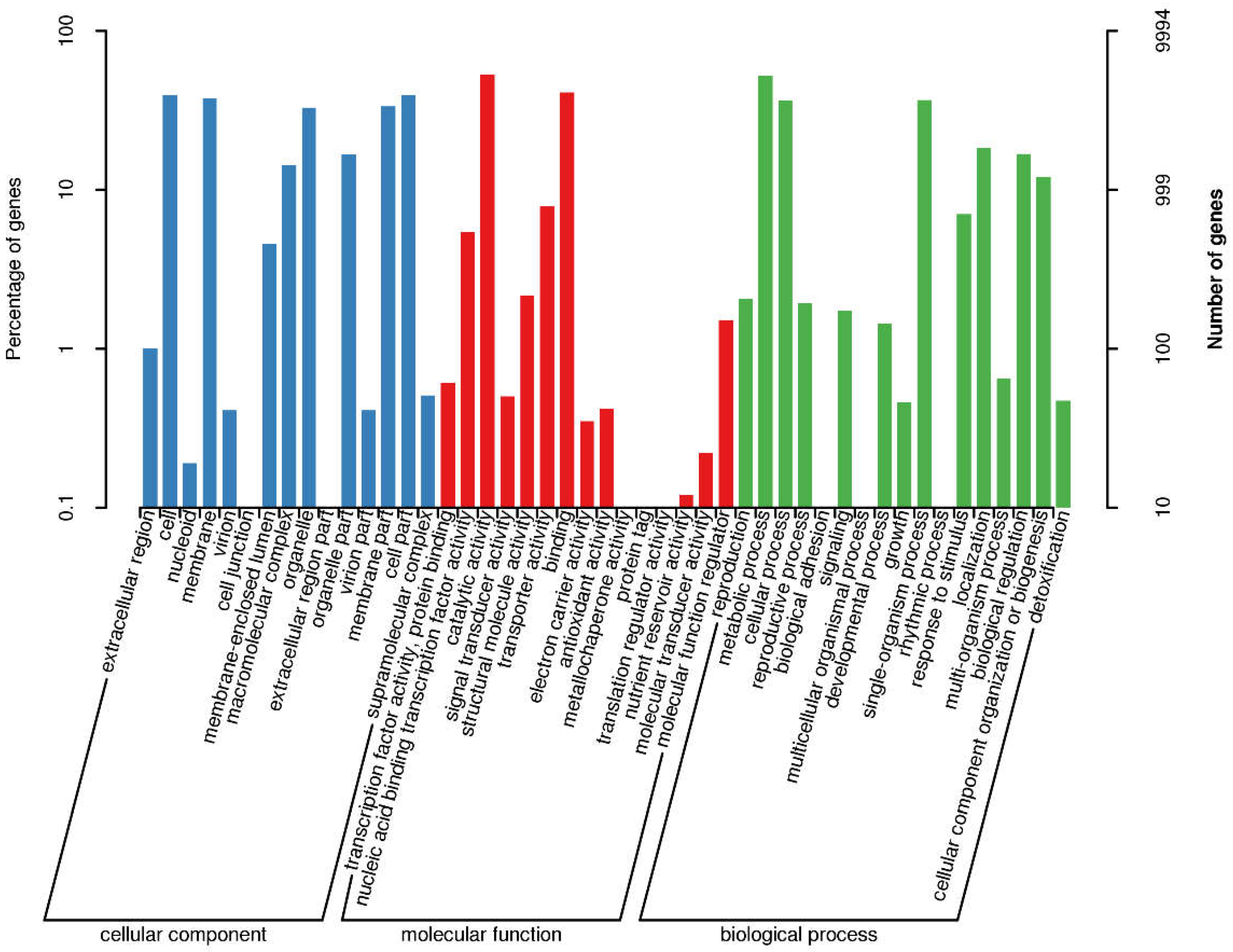
3.4. GO Annotations
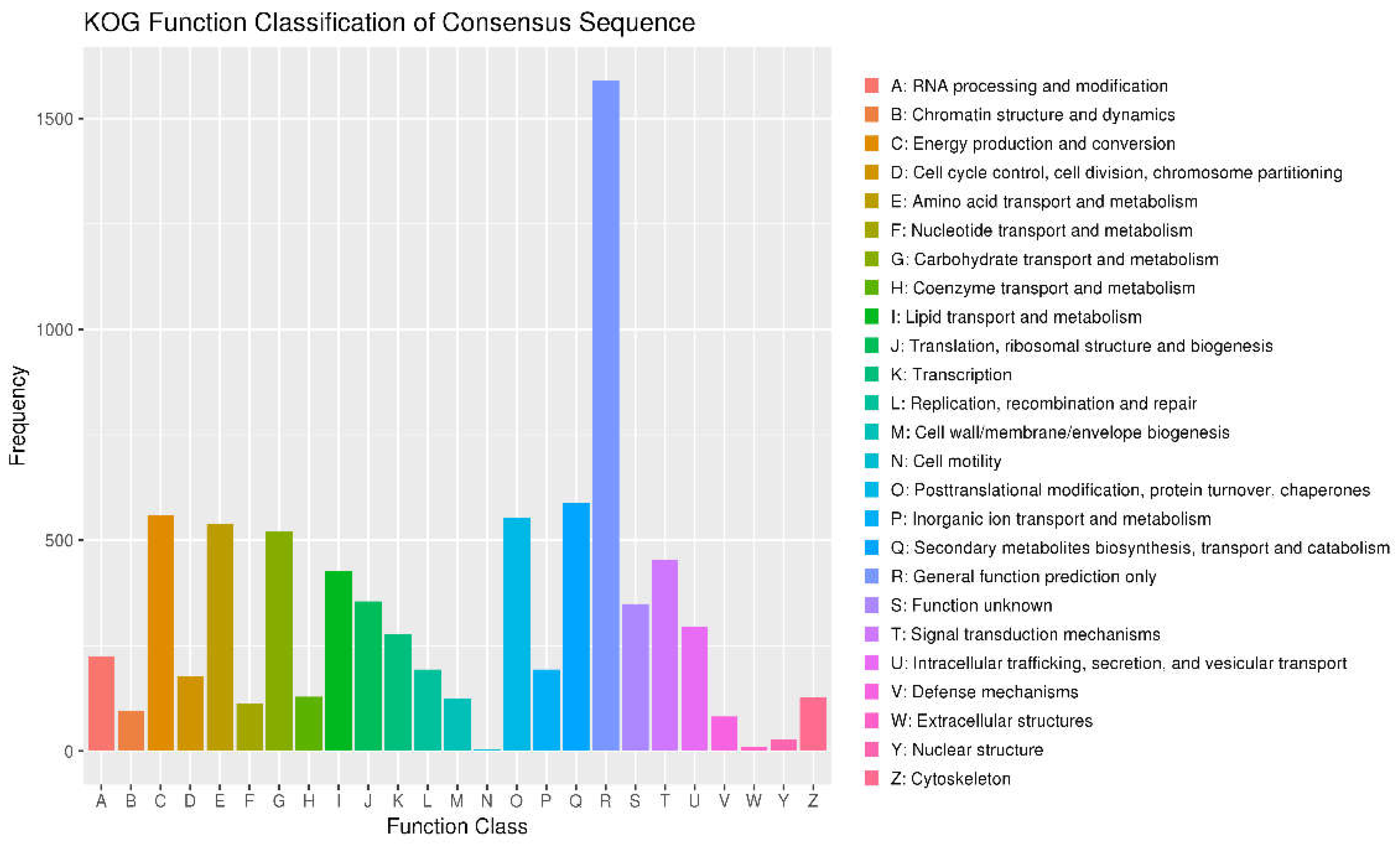
3.5. KOG Annotations
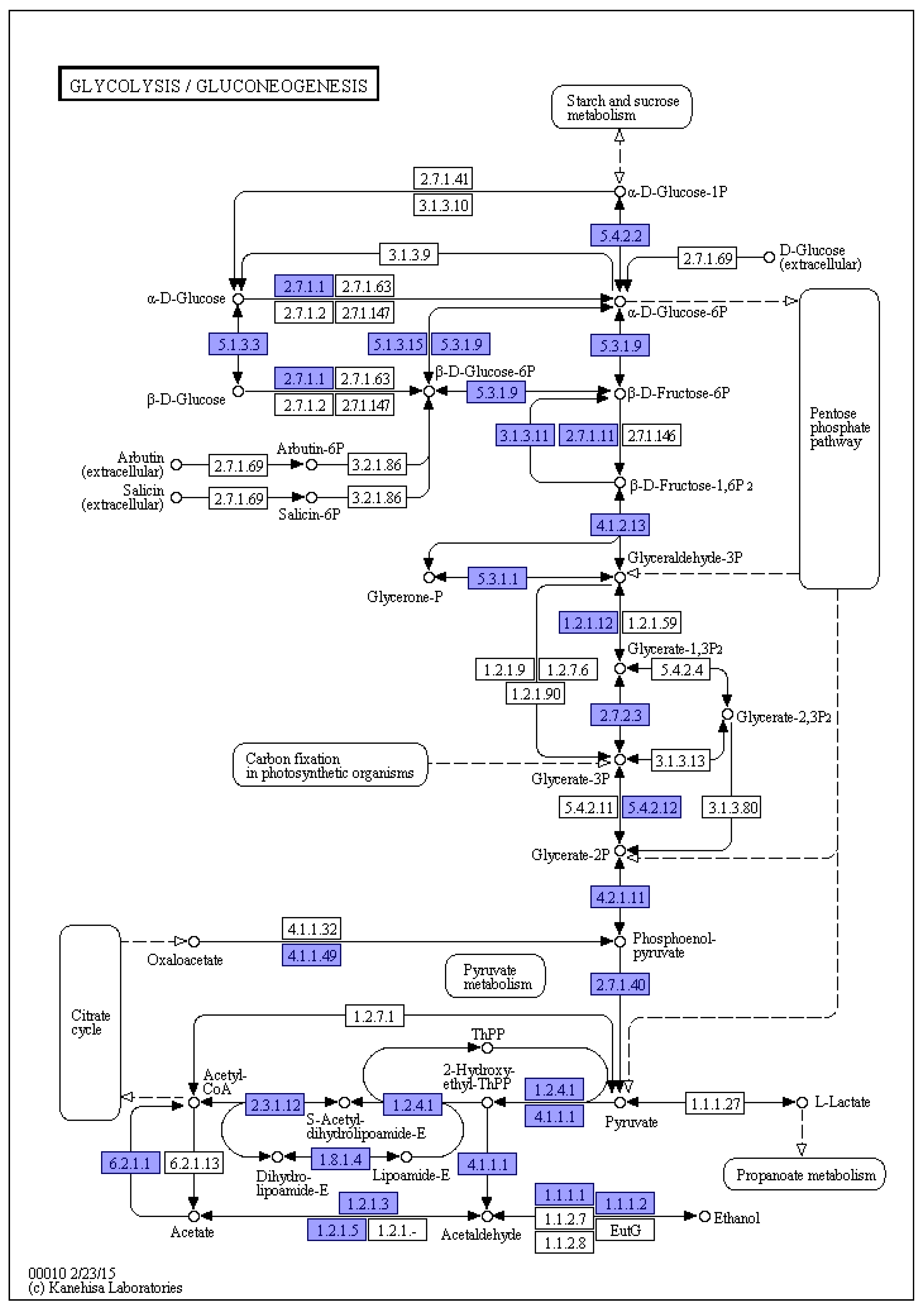
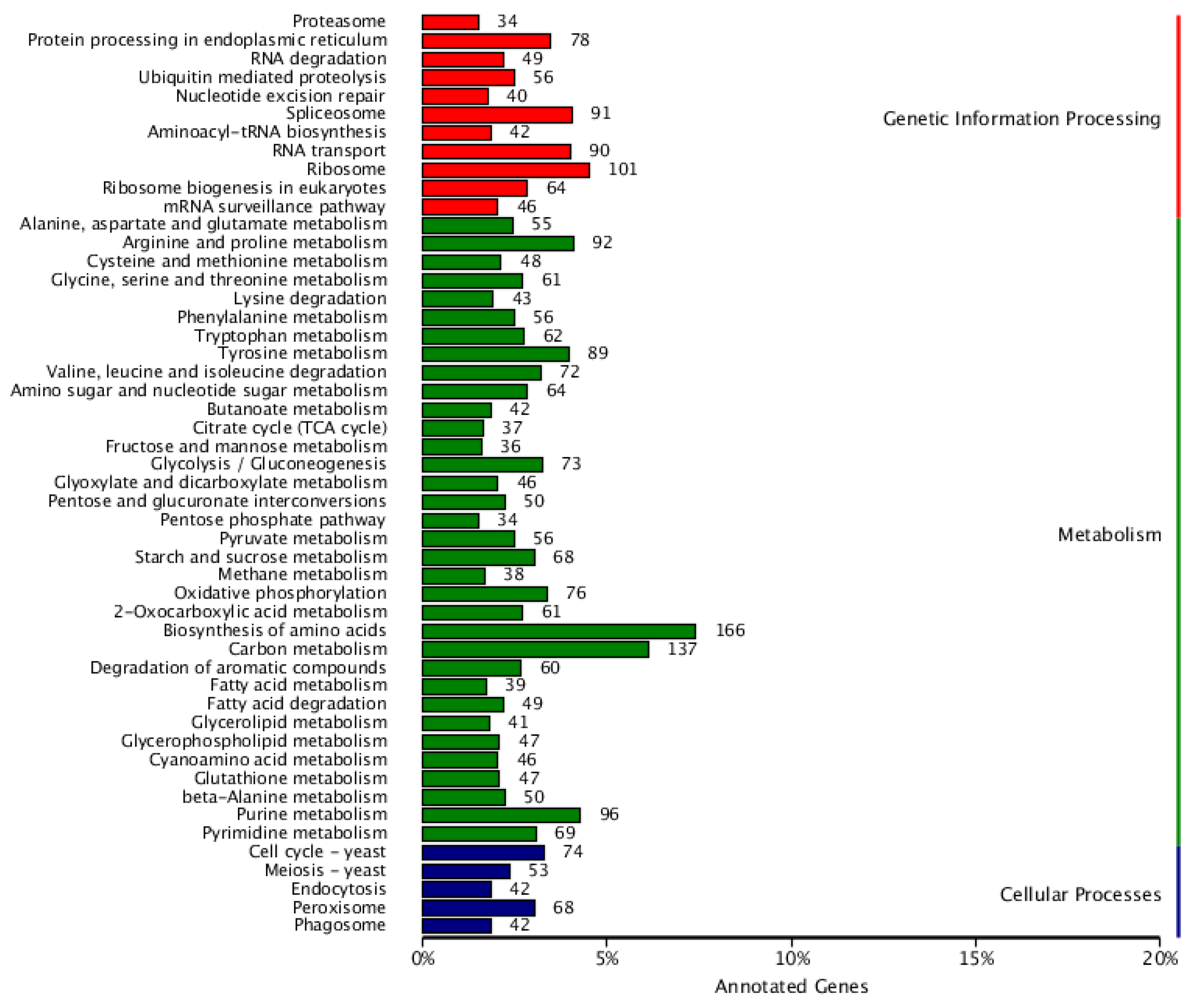
3.6. KEGG Annotations
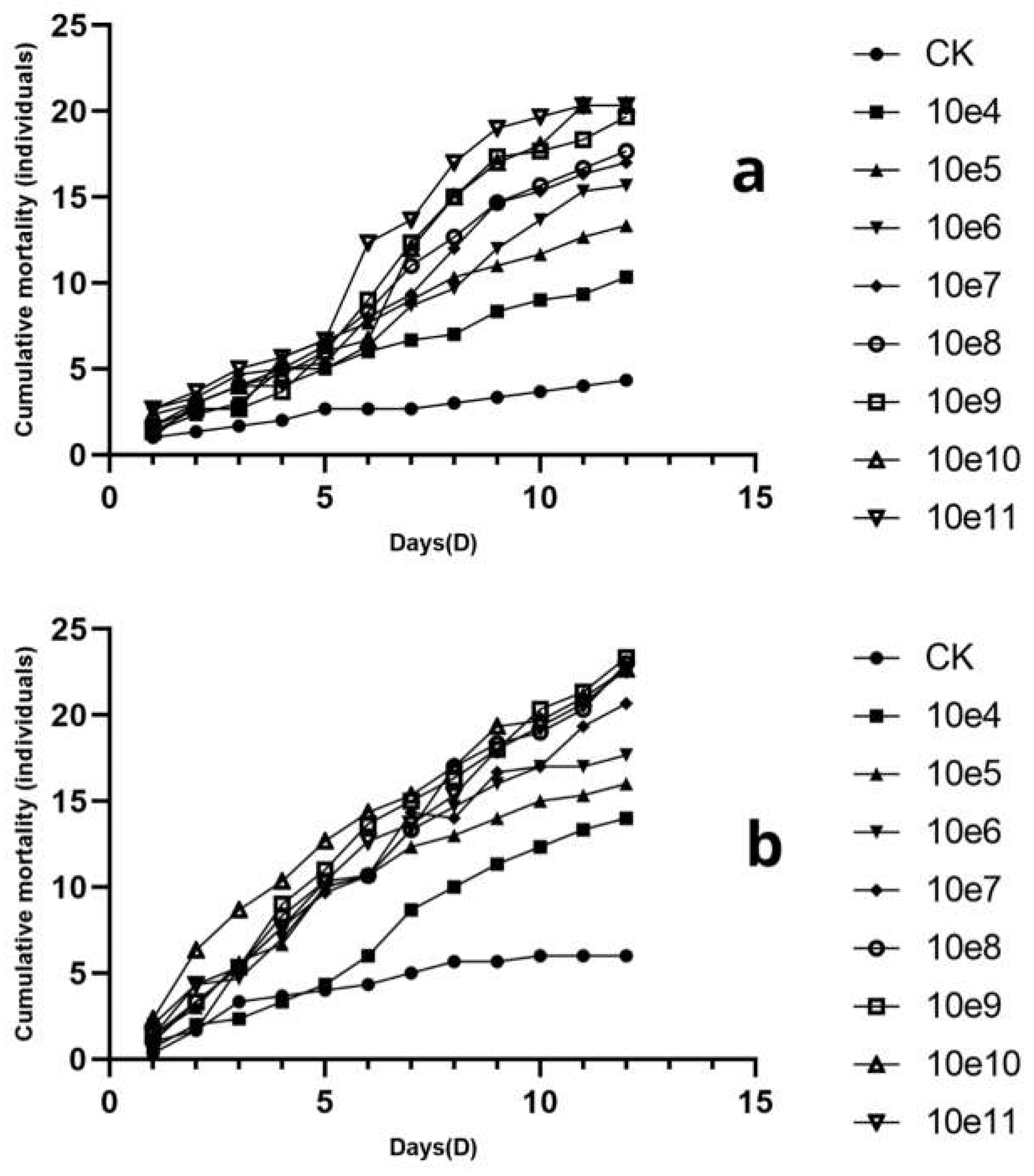
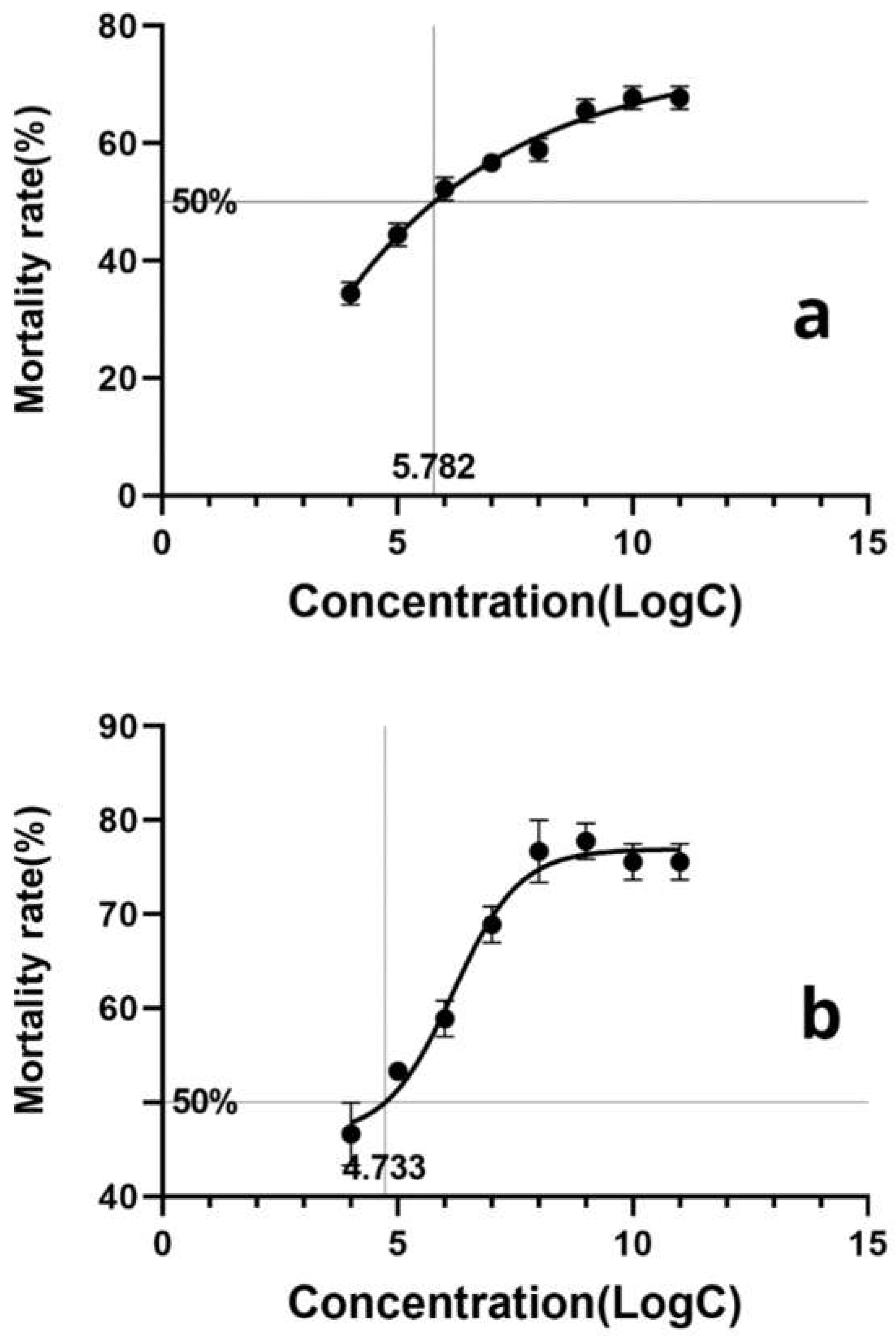
3.7. Pathogenicity Test of L. lecanii KMZW-1 at Different Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandramohan B, Sathiyabama M, Senthil-Nathan S 2016. Efficacy Of Metarhizium Anisopliae And Beauveria Bassiana Against Bactrocera Dorsalis And Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae). Journal Of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 19: 929-934.
- Huang Z H, Song C L, Cui Z X 2014. The Insecticidal Activity Of Lecanicillium Lecanii And Beauveria Bassiana Against Bactrocera Dorsalis Adults. Journal Of Fruit Science, 31: 1046-1051.
- Zhang L, Chen X, Hou Q, Et Al. 2018. Genome Sequencing And Comparative Genomics Reveal The Potential Pathogenic Mechanism Of Cercospora Sojina Hara On Soybean. Scientific Reports, 8: 1796.
- Li X, Liu Y, Fan Z, Et Al. 2022b. Comparative Genomics And Evolutionary Analysis Of Trichoderma Harzianum And Its Biocontrol Potential Against Plant Pathogens. *Frontiers In Microbiology. Frontiers In Microbiolog, 13.
- Cao Y, Wang Y, Feng M G 2020. Whole-Genome Sequence Of Lecanicillium Attenuatum Strain Lec8, An Entomopathogenic Fungus With High Potential As A Biocontrol Agent. *Microbiology Resource Announcements, 9: E01480-01499.
- Huang L, Fan G, Fang W, Et Al. 2021. Genome Sequencing And Analysis Of Lecanicillium Lecanii 1502, A Potential Entomopathogenic Fungus For Controlling Aphids. *Archives Of Microbiology : 4329-4334.
- Weems, H.V. , Heppner J.B. Caribbean Fruit Fly (Anastrepha Suspense Loew (Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae)) Featured Creatures EENY-196: July Reviews. UF/IFAS; Gainesville, FL, USA: 2014.
- Vargas, R.I.; Piñero, J.C.; Leblanc, L. An Overview of Pest Species of Bactrocera Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) and the Integration of Biopesticides with Other Biological Approaches for Their Management with a Focus on the Pacific Region. Insects 2015, 6, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Gulzar, S.; Wakil, W.; Piñero, J.C.; Leskey, T.C.; Nixon, L.J.; Oliveira-Hofman, C.; Wu, S.; Shapiro-Ilan, D. Potential of entomopathogenic nematodes against the pupal stage of the apple maggot Rhagoletis pomonella (Walsh) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Nematol. 2020, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulzar, S.; Wakil, W.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I. Combined Effect of Entomopathogens against Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae): Laboratory, Greenhouse and Field Trials. Insects 2021, 12, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakil, W.; Tahir, M.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Shapiro-Ilan, D. Interactions Between Two Invertebrate Pathogens: An Endophytic Fungus and an Externally Applied Bacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M.; Wakil, W.; Ali, A.; Sahi, S.T. Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae isolates against larvae of the polyphagous pest Helicoverpa armigera. Èntomol. Gen. 2019, 38, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Gao X, Wang S, Et Al. 2010. Biological Characteristics And Pathogenicity Of Lecanicillium Lecanii On Diseased Bactrocera Dorsalis. Anhui Agricultural Science : 7909-7912.
- Walker B J, Abeel T, Shea T, Et Al. 2014. Pilon: An Integrated Tool For Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection And Genome Assembly Improvement. Plos One, 9: E112963.
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows—Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, H. LTR_FINDER: an efficient tool for the prediction of full-length LTR retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W265–W268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wessler, S.R. MITE-Hunter: a program for discovering miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements from genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e199–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.L.; Jones, N.C.; Pevzner, P.A. De novo identification of repeat families in large genomes. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, i351–i358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Myers, E.W. PILER: identification and classification of genomic repeats. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, i152–i158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicker, T.; Sabot, F.; Hua-Van, A.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Capy, P.; Chalhoub, B.; Flavell, A.; Leroy, P.; Morgante, M.; Panaud, O.; et al. Reply: A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements should reflect their phylogeny. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 276–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurka, J.; Kapitonov, V.V.; Pavlicek, A.; Klonowski, P.; Kohany, O.; Walichiewicz, J. Repbase Update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 110, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Chen, N. Using RepeatMasker to Identify Repetitive Elements in Genomic Sequences. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2009, 25, 4.10.1–4.10.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge C, Karlin S 1997. Prediction Of Complete Gene Structures In Human Genomic DNA. J. Mol. Biol., 268: 78-94.
- Stanke, M.; Waack, S. Gene prediction with a hidden Markov model and a new intron submodel. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, ii215–ii225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majoros, W.H.; Pertea, M.; Salzberg, S.L. TigrScan and GlimmerHMM: two open source ab initio eukaryotic gene-finders. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2878–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alioto, T.; Blanco, E.; Parra, G.; Guigó, R. Using geneid to Identify Genes. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2018, 64, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilwagen J, Wenk M, Erickson J L, Et Al. 2016. H: Using Intron Position Conservation For Homology-Based Gene Prediction. Nucleic Acids Research, 44: E89-E89.
- Haas B J, Salzberg S L, Zhu W, Et Al. 2008. Automated Eukaryotic Gene Structure Annotation Using Evidencemodeler And The Program To Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biol., 9: R7.
- Lowe T M, Eddy S R 1997. Trnascan-SE: A Program For Improved Detection Of Transfer RNA Genes In Genomic Sequence. Nucleic Acids Res., 25: 955-964.
- Nawrocki E P, Eddy S R 2013. Infernal 1.1: 100-Fold Faster RNA Homology Searches. Bioinformatics, 29: 2933-2935.
- She R, Chu J S C, Wang K, Et Al. 2009. Genblasta: Enabling BLAST To Identify Homologous Gene Sequences. Genome Res., 19: 143-149.
- Birney, E.; Clamp, M.; Durbin, R. GeneWise and Genomewise. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng Y Y, Li J Q, Wu S F 2006. Integrated Nr Database In Protein Annotation System And Its Localization. J]. Comput Eng, 32: 71-74.
- Boeckmann B, Bairoch A, Apweiler R, Et Al. 2003. The SWISS-PROT Protein Knowledgebase And Its Supplement Trembl In 2003. Nucleic Acids Res., 31: 365-370.
- Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Et Al. 2004. The KEGG Resource For Deciphering The Genome. Nucleic Acids Res., 32: D277-280.
- Tatusov, R.L.; Galperin, M.Y.; Natale, D.A.; Koonin, E.V. The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez J, Et Al. 2004. Blast2GO: A Universal Annotation And Visualization Tool For Functional Genomics Research.
- Eddy S R 1998. Profile Hidden Markov Models. Bioinformatics : 755-763.
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saier M H, JR. , Tran C V, Barabote R D 2006. TCDB: The Transporter Classification Database For Membrane Transport Protein Analyses And Information. Nucleic Acids Res., 34: D181-186.
- Winnenburg, R. PHI-base: a new database for pathogen host interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D459–D464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Knoll, M.; Sirim, D.; Wagner, F.; Funke, S.; Pleiss, J. The Cytochrome P450 Engineering Database: a navigation and prediction tool for the cytochrome P450 protein family. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2015–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Yao, B.; Zhang, C. DFVF: database of fungal virulence factors. Database 2012, 2012, bas032–bas032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh A, Larsson B, Von Heijne G, Et Al. 2001. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology With A Hidden Markov Model: Application To Complete Genomes. J. Mol. Biol., 305: 567-580.
- Sperschneider, J.; Gardiner, D.M.; Dodds, P.N.; Tini, F.; Covarelli, L.; Singh, K.B.; Manners, J.M.; Taylor, J.M. EffectorP: predicting fungal effector proteins from secretomes using machine learning. New Phytol. 2015, 210, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao S F, Liu A Q, Sang L W, Et Al. 2018. Whole-Genome Sequencing And Comparative Genomics Analysis Of Bacillus Subtilis VD18R19, A Biocontrol Agent Against Phytophthora Foot Rot Disease In Pepper. Journal Of Tropical Crop Science, 39: 2021-2027.
- Zhao M X, Bai Z Y, Zhang X H, Et Al. 2022. Biocontrol Effects Of Strain CSR-2 Against Maize Stalk Rot And Its Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis. Chinese Journal Of Biological Control, 38: 242-249.
- Wang Q, Bao H F, Ding R R, Et Al. 2022. Whole-Genome Sequencing And Analysis Of Biofilm-Related Genes In Bacillus Subtilis Strain DNKAS As A Biocontrol Agent. Herbivorous Livestock : 56-64.
- Li S R, Li X, Feng J L, Et Al. 2023. Whole-Genome Sequencing And Bioinformatic Analysis Of The Biocontrol Agent Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens SQ-2. Bulletin Of Microbiology, 50: 1073-1097.
- Li H M, He M C, Gao X, Et Al. 2022a. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis Of The Biocontrol Agent Bacillus Velezensis MC2-1. Southern Agricultural Journal, 53: 3420-3432.
- Cherry A J, Moore D 2006. Infection Of The Non-Target Invertebrate Pests Bactrocera Dorsalis And Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae) With Metarhizium Anisopliae And Beauveria Bassiana. Biocontrol Science And Technology, 16: 701-713.
- Reddy N P, Prashanthi S K 2015. Evaluation Of Indigenous Beauveria Bassiana And Metarhizium Anisopliae Isolates Against Bactrocera Dorsalis (Hendel) And Their Prospects In The Fruit Fly Control Programme. Journal Of Biopesticides, 8: 104-108.
- Jackson M A, Dunlap C A 2012. Laboratory Evaluation Of Isaria Fumosorosea CCM 8367 For Controlling Bactrocera Dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Florida Entomologist, 95: 62-69.
| Contig Length (bp) | Contig Number | Contig N50 (bp) | Contig N90 (bp) | GC content (%) | Gaps Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47,239,278 | 27 | 2,751,789 | 1,018,923 | 51.16 | 0 |
| Complete BUSCOs(C) | Complete and single-copy BUSCOs(S) | Complete and duplicated BUSCOs(D) | Fragmented BUSCOs(F) | Missing BUSCOs(M) | Total Lineage BUSCOs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 284 (97.93%) | 281 (96.90%) | 3 (1.03%) | 4 (1.38%) | 2 (0.69%) | 290 |
| Database | Number | 100<=length<300 | length>=300 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO_Annotation | 9,994 | 2,279 | 7,603 |
| KEGG_Annotation | 3,775 | 913 | 2,788 |
| KOG_Annotation | 7,059 | 1,422 | 5,575 |
| Pfam_Annotation | 10,510 | 2,346 | 8,076 |
| Swissprot_Annotation | 8,390 | 1,692 | 6,608 |
| TrEMBL_Annotation | 13,862 | 3,729 | 9,992 |
| nr_Annotation | 13,864 | 3,730 | 9,993 |
| All_Annotated | 13,867 | 3,733 | 9,993 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





