Submitted:
19 July 2024
Posted:
19 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
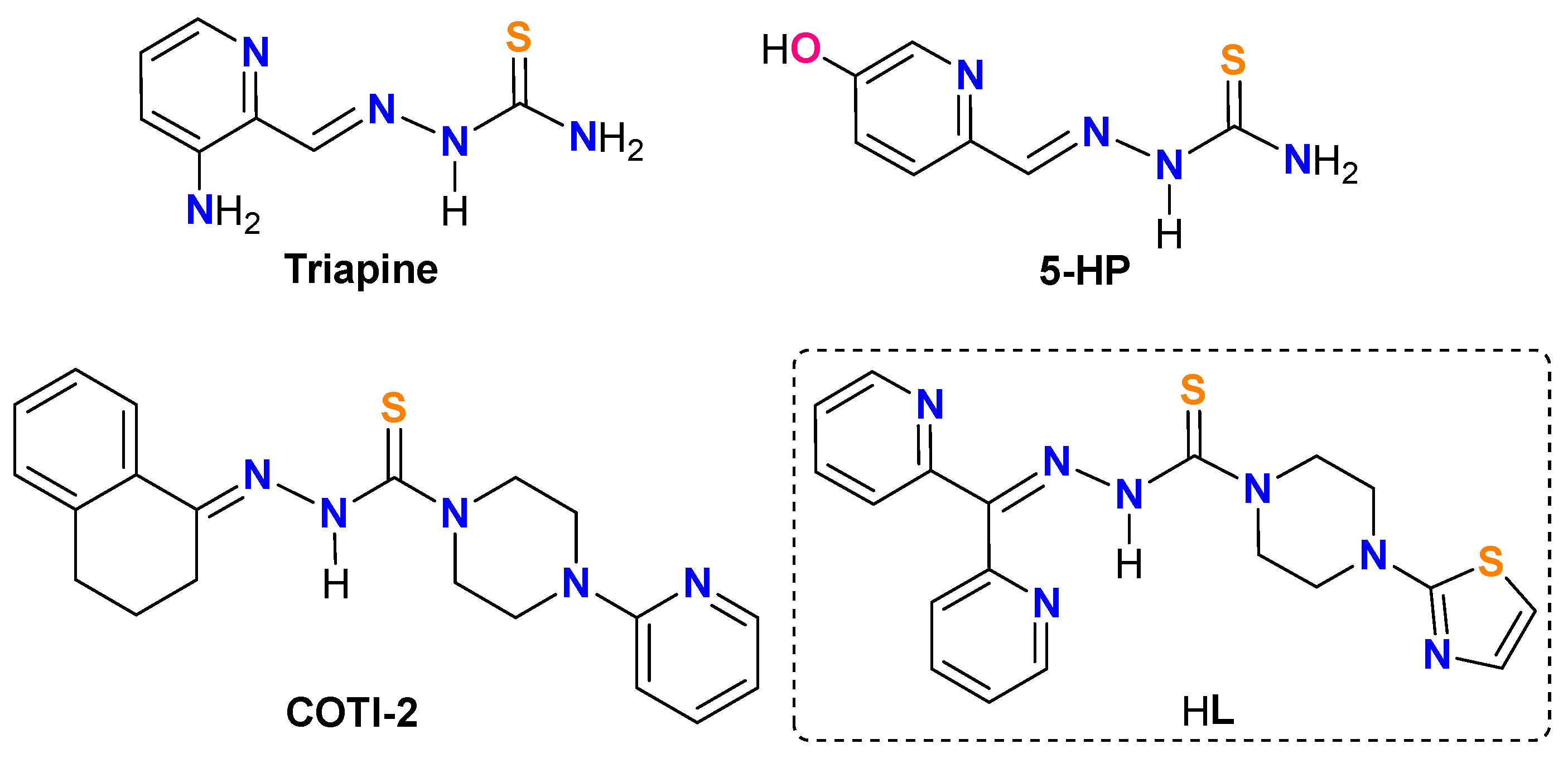
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
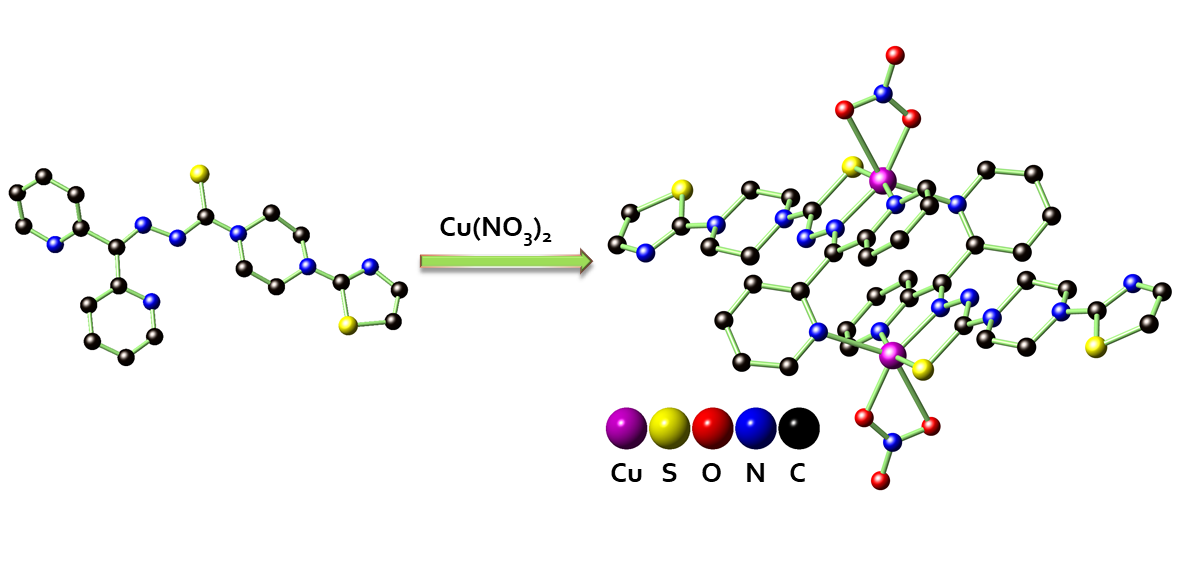
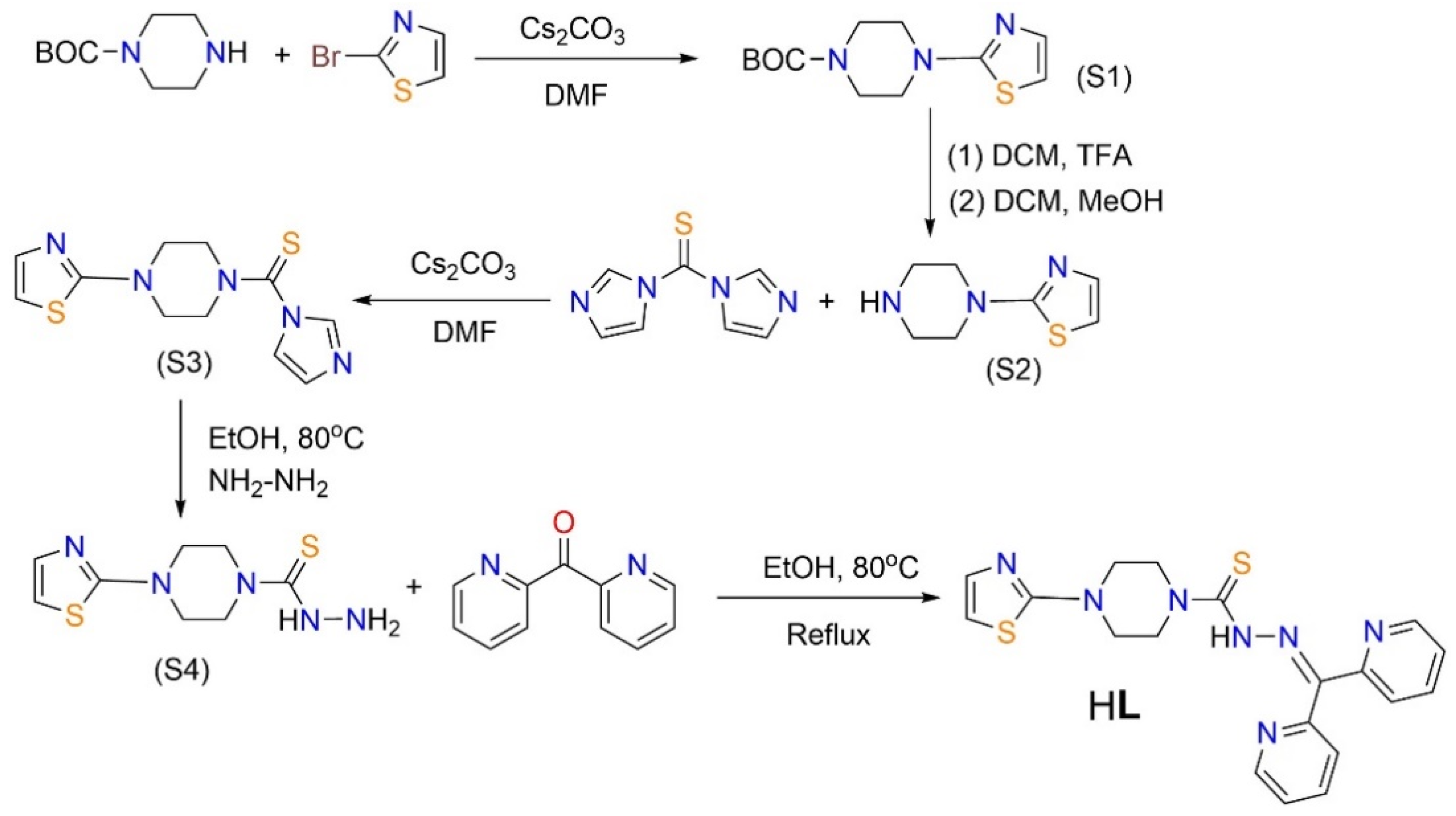
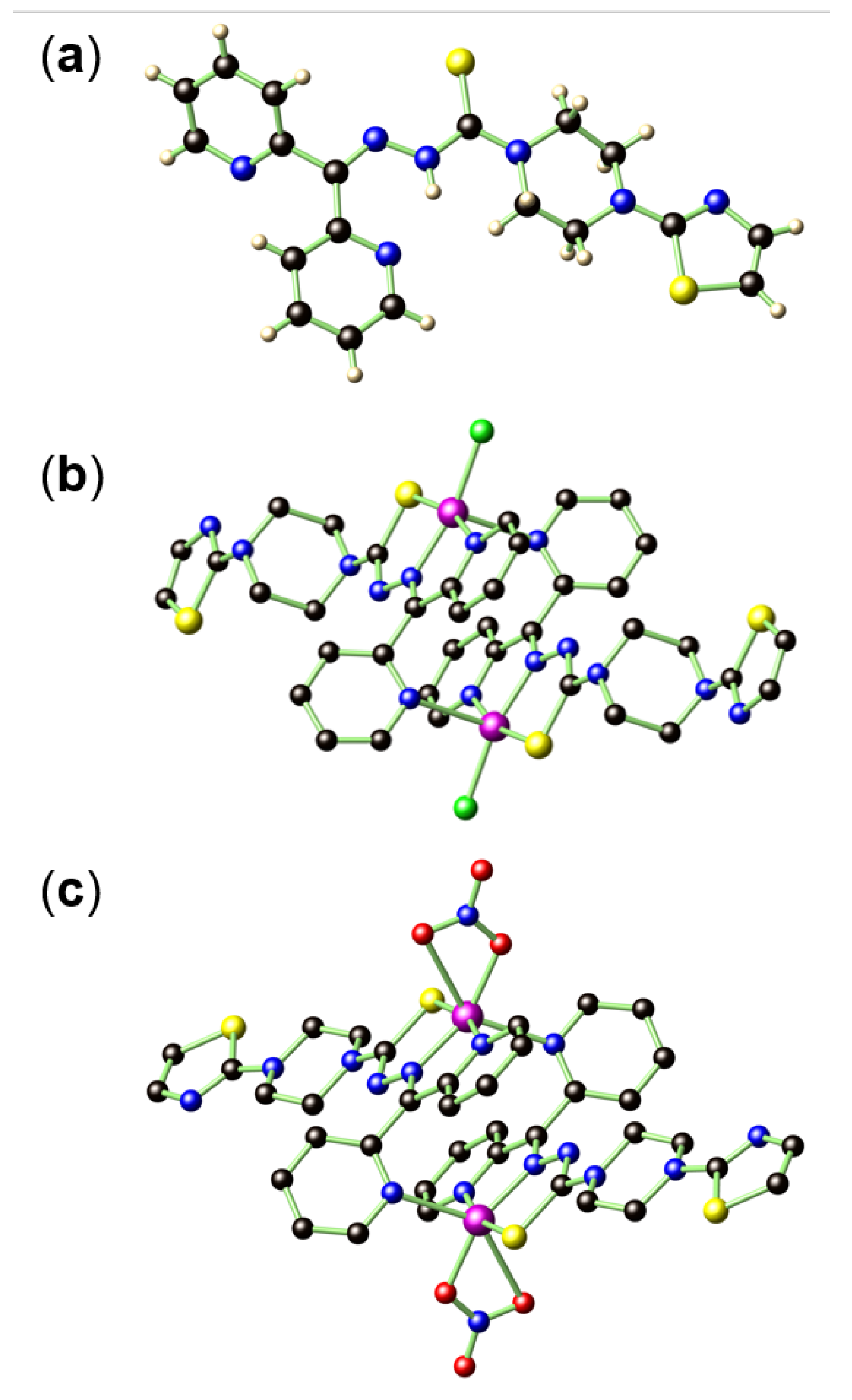
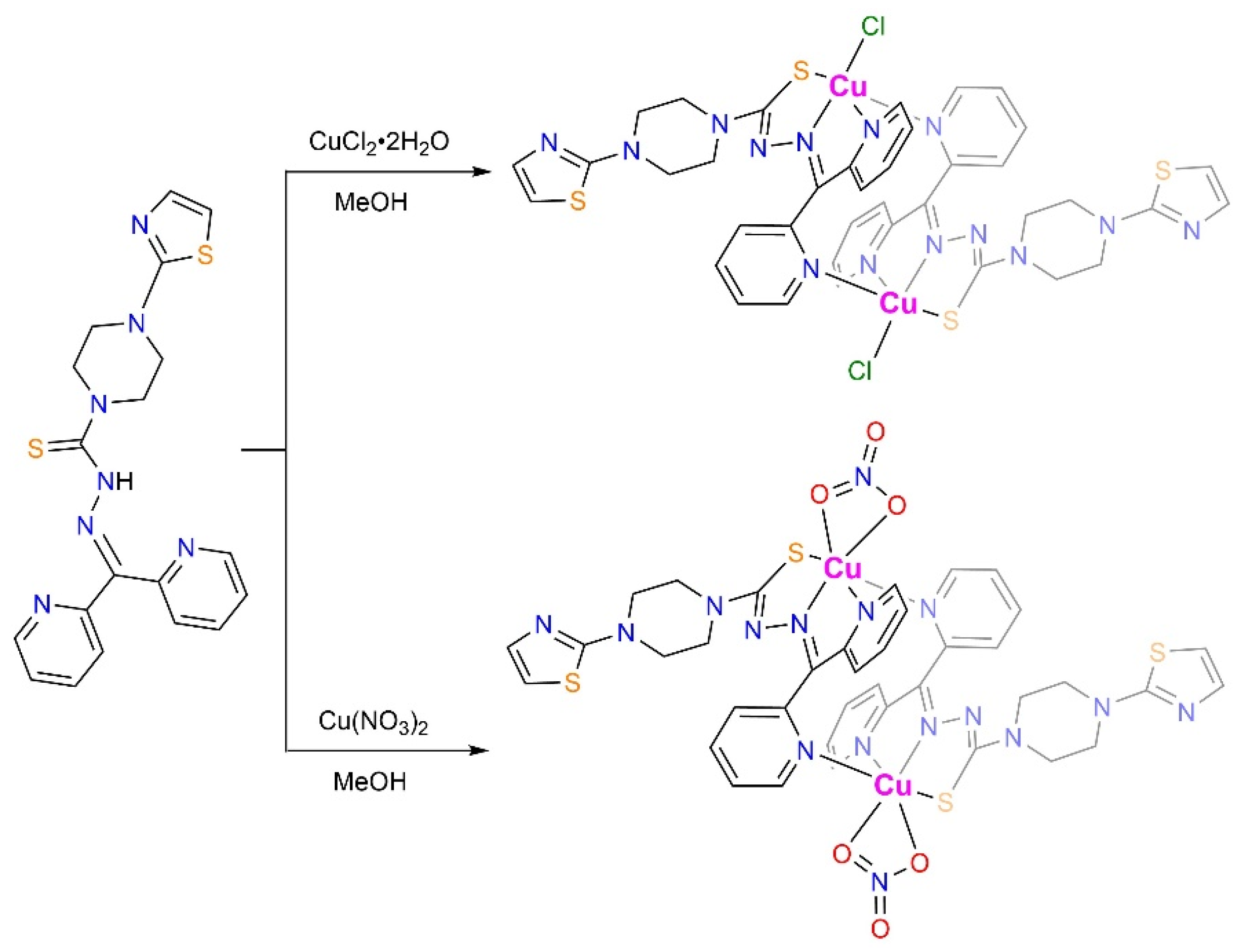
2.1. Synthesis and X-ray Structure Characterization of HL, [CuCl(L)]2 (1), and [Cu(NO3)(L)]2 (2)
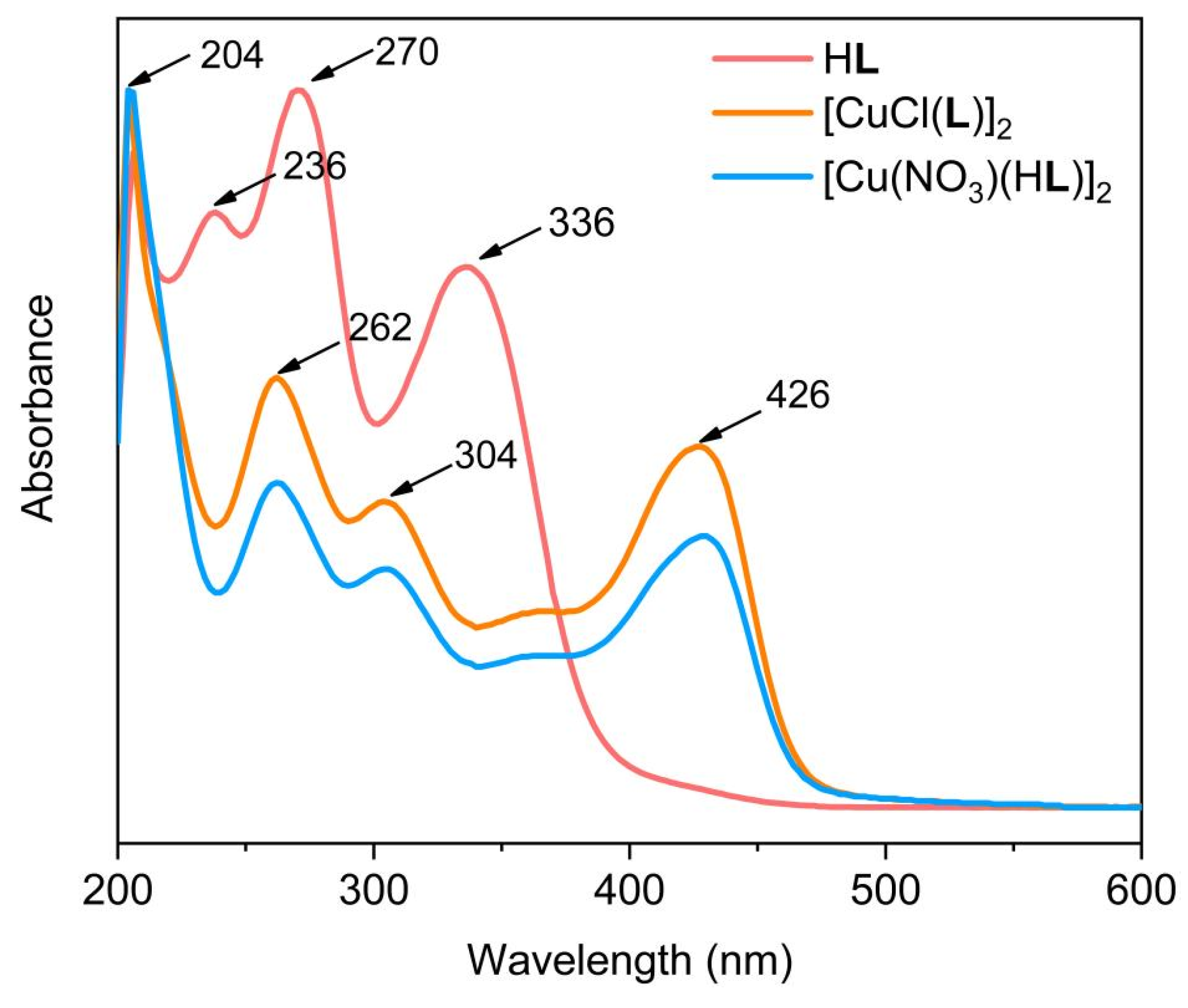
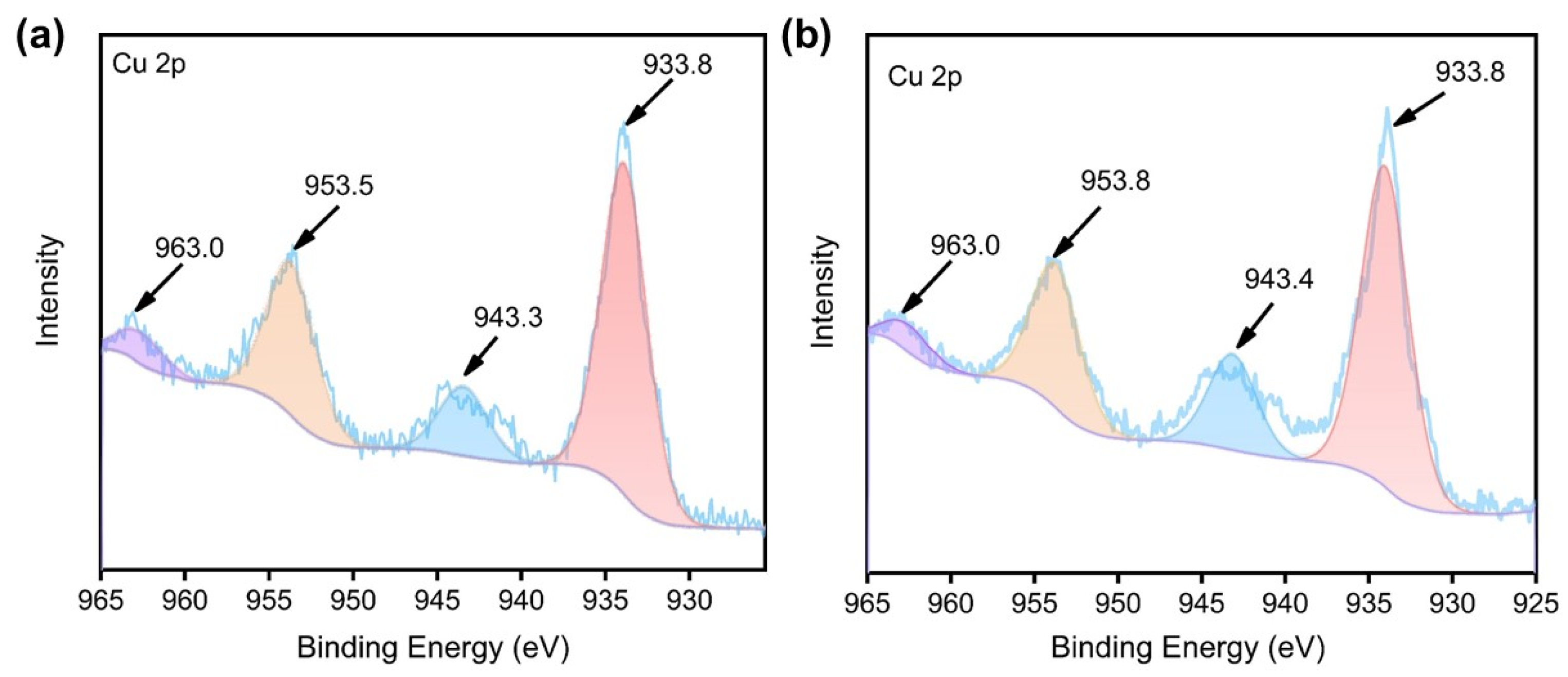
2.2. Spectroscopic Characterizations of HL, 1, and 2
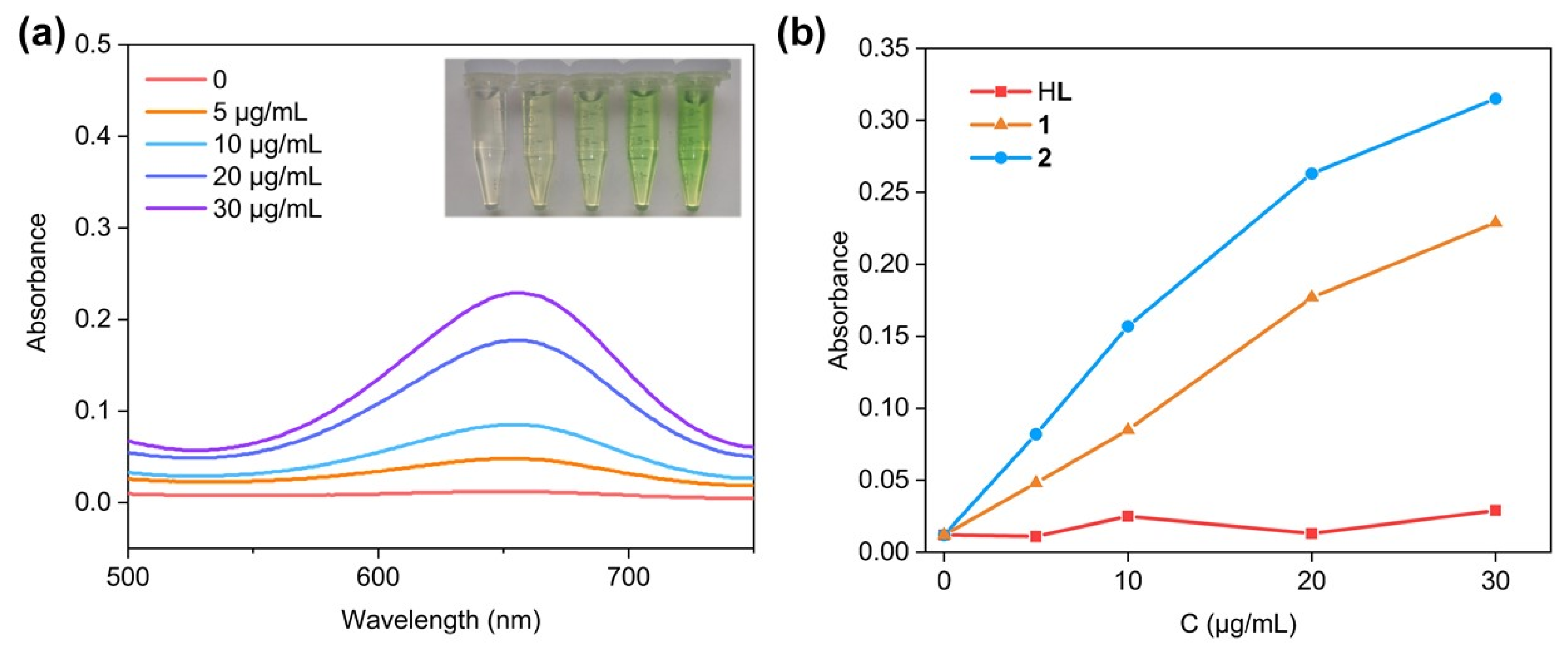
2.3. Hydroxyl Radical (•OH) Production
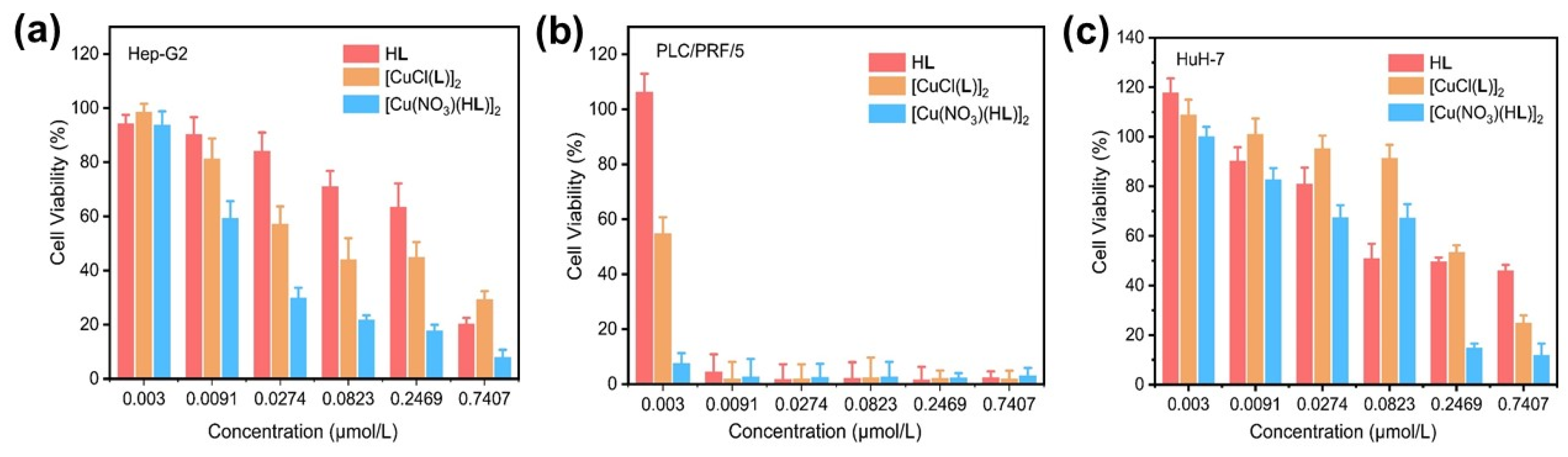
2.4. CCK-8 Assay for HL, 1, and 2
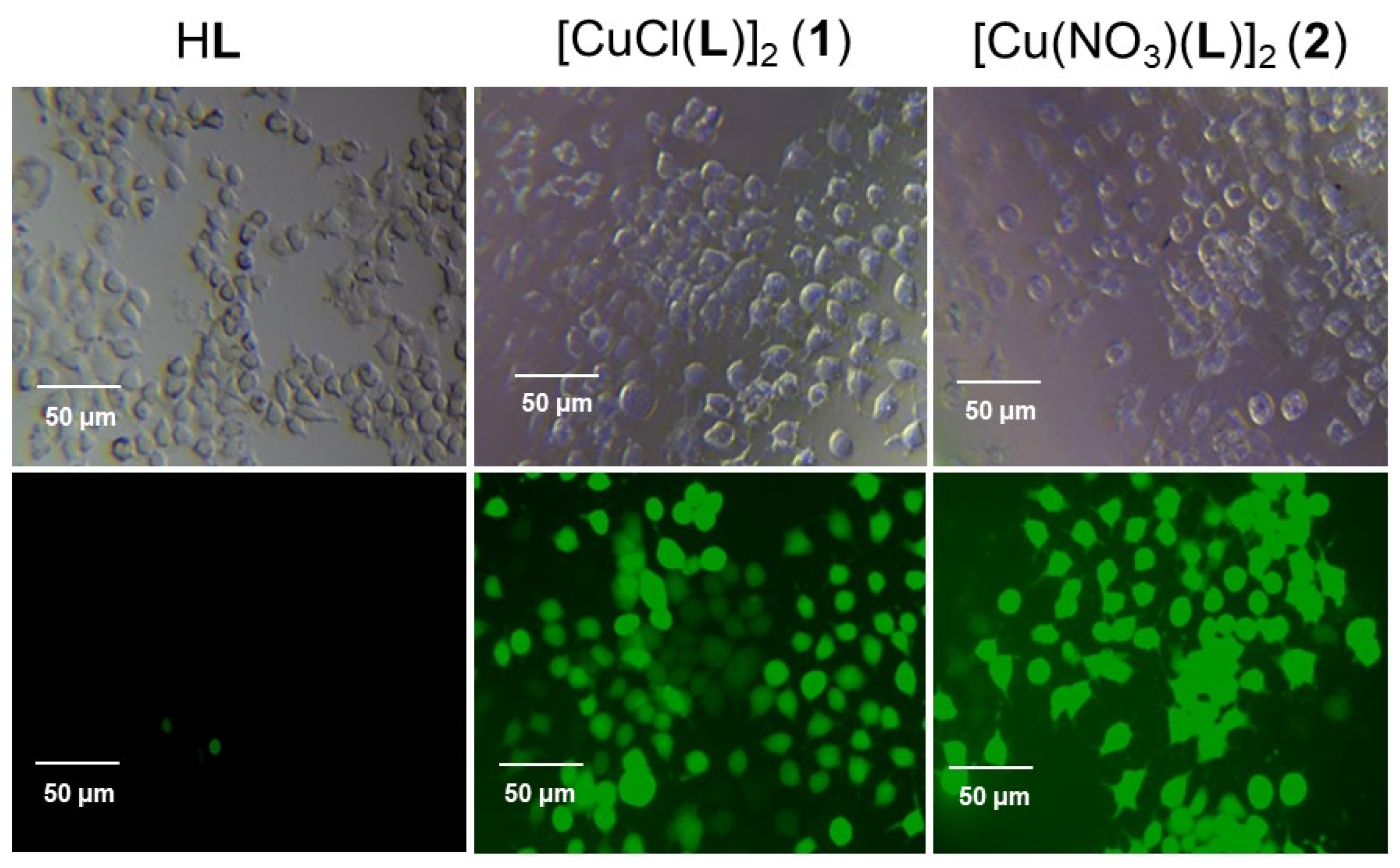
2.5. Intracellular ROS Generation by HL, 1, and 2
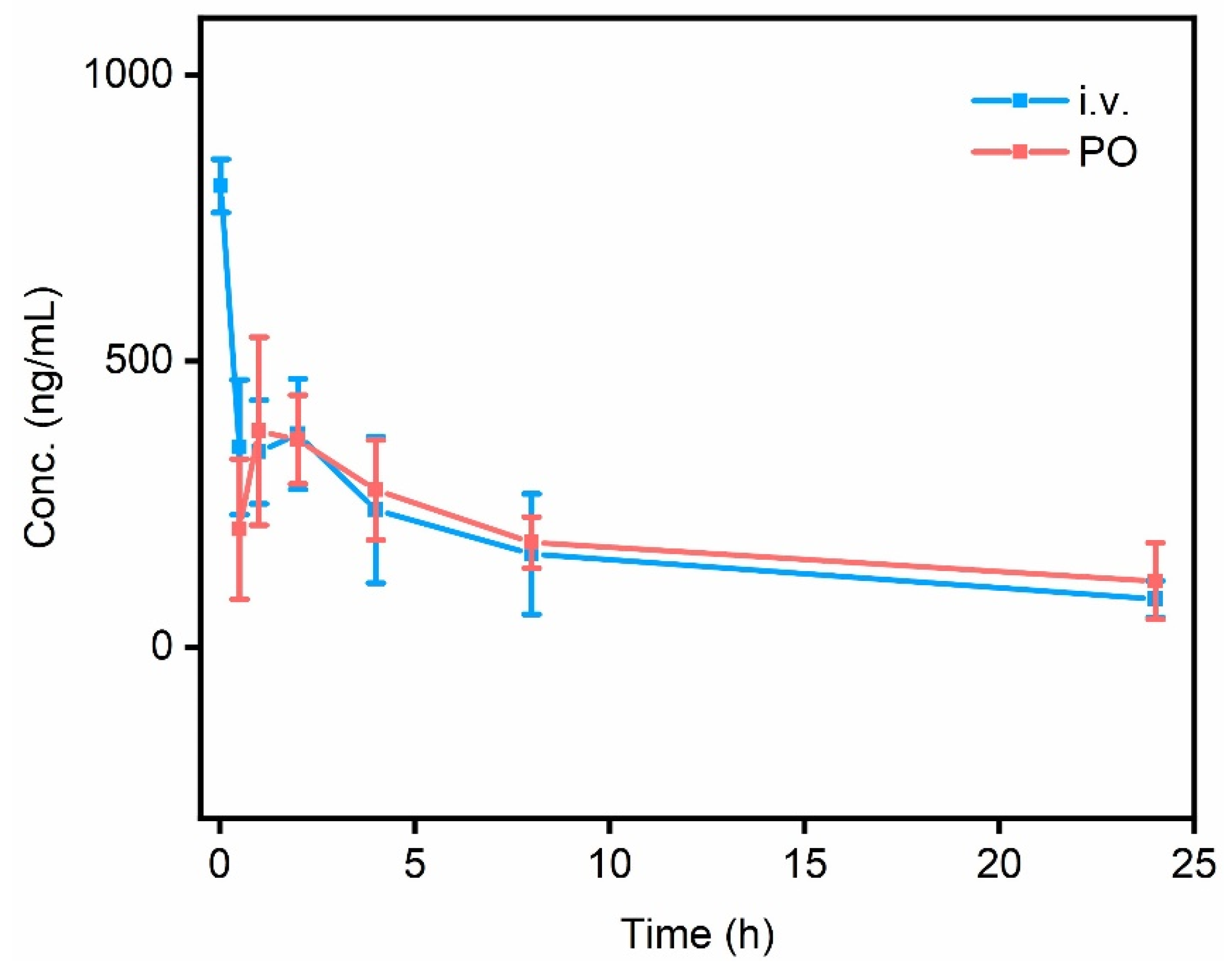
2.6. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study of HL.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthetic Steps for HL
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization of [CuCl(L)]2 (1)
3.4. Synthesis and Characterization of [Cu(NO3)(L)]2 (2)
3.5. Single Crystal X-ray Crystallography
3.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation by CCK-8 Assay
3.7. Detection of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
3.8. Pharmacokinetics of HL
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klayman, D.L.; Scovill, J.P.; Bartosevich, J.F.; Mason, C.J. 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones. 2. N4,N4-Disubstituted derivatives as potential antimalarial agents. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beraldo, H.; Gambinob, D. The wide pharmacological versatility of semicarbazones, thiosemicarbazones and their metal complexes. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalinowski, D.S.; Quach, P.; Richardson, D.R. Thiosemicarbazones: The new wave in cancer treatment. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, B.; Yadav, N.P. Thiosemicarbazones as potent anticancer agents and their modes of action. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 638–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serda, M.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Rasko, N.; Potůčková, E.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A.; Musiol, R.; Małecki, J.G.; Sajewicz, M.; Ratuszna, A.; Muchowicz, A. , et al. Exploring the anti-cancer activity of novel thiosemicarbazones generated through the combination of retro-fragments: Dissection of critical structure-activity relationships. Plos One 2014, 9, e110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilworth, J.R.; Hueting, R. Metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones for imaging and therapy. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 389, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Richardson, D.R. Novel di-2-pyridyl–derived iron chelators with marked and selective antitumor activity: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Blood 2004, 104, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.R. Iron chelators as therapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, P.; Shi, J. Nanomedicine remodels tumor microenvironment for solid tumor immunotherapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 10217–10233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-M.; Li, R.-T.; Yu, L.; Huang, T.; Peng, J.; Meng, W.; Sun, B.; Zhang, W.-H.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Chen, J. , et al. Reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment using a PCN-224@IrNCs/d-Arg nanoplatform for the synergistic PDT, NO, and radiosensitization therapy of breast cancer and improving anti-tumor immunity. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 10715–10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.-K.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Li, R.-T.; Peng, J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Yue, Y.-R.; Zhang, W.-H.; Sun, B.; Chen, J.-X.; Zhou, Q. Remodeling the tumor microenvironment with core–shell nanosensitizer featuring dual-modal imaging and multimodal therapy for breast cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Goh, B.C.; Tan, E.H.; Lam, K.C.; Soo, R.; Leong, S.S.; Wang, L.Z.; Mo, F.; Chan, A.T.C.; Zee, B. , et al. A multicenter phase II trial of 3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (3-AP, Triapine®) and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with pharmacokinetic evaluation using peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Invest. New Drugs 2008, 26, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeConti, R.C.; Toftness, B.R.; Agrawal, K.C.; Tomchick, R.; Mead, J.A.R.; Bertino, J.R.; Sartorelli, A.C.; Creasey, W.A. Clinical and pharmacological studies with 5-hydroxy-2-formylpyridine thiosemicarbazone. Cancer Res. 1972, 32, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westin, S.N.; Nieves-Neira, W.; Lynam, C.; Salim, K.Y.; Silva, A.D.; Ho, R.T.; Mills, G.B.; Coleman, R.L.; Janku, F.; Matei, D. Abstract CT033: Safety and early efficacy signals for COTI-2, an orally available small molecule targeting p53, in a phase I trial of recurrent gynecologic cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, CT033–CT033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormio Nunes, J.H.; Hager, S.; Mathuber, M.; Pósa, V.; Roller, A.; Enyedy, É.A.; Stefanelli, A.; Berger, W.; Keppler, B.K.; Heffeter, P. , et al. Cancer cell resistance against the clinically investigated thiosemicarbazone COTI-2 is based on formation of intracellular copper complex glutathione adducts and ABCC1-mediated efflux. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13719–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowol, C.R.; Trondl, R.; Heffeter, P.; Arion, V.B.; Jakupec, M.A.; Roller, A.; Galanski, M.S.; Berger, W.; Keppler, B.K. Impact of metal coordination on cytotoxicity of 3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (triapine) and novel insights into terminal dimethylation. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5032–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowol, C.R.; Berger, R.; Eichinger, R.; Roller, A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Schmidt, P.P.; Arion, V.B.; Keppler, B.K. Gallium(III) and iron(III) complexes of α-N-heterocyclic thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, and interaction with ribonucleotide reductase. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.R.; Sharpe, P.C.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Senaratne, D.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Islam, M.; Bernhardt, P.V. Dipyridyl thiosemicarbazone chelators with potent and selective antitumor activity form iron complexes with redox activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6510–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.-G.; Zheng, Y.; Qi, J. Advances in thiosemicarbazone metal complexes as anti-lung cancer agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1018951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, A.G.; M. Pérez, J.; López-Solera, I.; Montero, E.I.; Masaguer, J.R.; Alonso, C.; Navarro-Ranninger, C. Binuclear chloro-bridged palladated and platinated complexes derived from p-isopropylbenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone with cytotoxicity against cisplatin resistant tumor cell lines. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1998, 69, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.A.C.; Costa, W.R.P.; de F. Faria, E.; Bessa, M.A.d.S.; Menezes, R.d.; Martins, C.H.G.; Maia, P.I.S.; Deflon, V.M.; Oliveira, C.G. Copper(II) complexes based on thiosemicarbazone ligand: Preparation, crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface, energy framework, antiMycobacterium activity, in silico and molecular docking studies. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 223, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcelli, M.; Tegoni, M.; Bartoli, J.; Marzano, C.; Pelosi, G.; Salvalaio, M.; Rogolino, D.; Gandin, V. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of tridentate thiosemicarbazone copper complexes: Unravelling an unexplored pharmacological target. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 194, 112266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliá, F. Ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) photochemistry at 3d-metal complexes: An emerging tool for sustainable organic synthesis. ChemCatChem 2022, 14, e202200916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ding, Y.; Molina, S.E.V.; Li, Y. A mixed-valence CuII/CuI coordination polymer based on bridged thiocyanate and in situ formed di(N-heterocyclic) sulfide: Synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, L.; Ranghino, G.; Moretti, G.; Cerofolini, G.F. XPS detection of some redox phenomena in Cu-zeolites. Surf. Interface Anal. 2002, 33, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.-M.; Luo, S.-Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, F.-L.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhang, W.-H.; Dai, C.-L.; Young, D.J. A porphyrin-based 3D metal-organic framework featuring [Cu8Cl6]10+ cluster secondary building units: Synthesis, structure elucidation, anion exchange, and peroxidase-like activity. Chem. Asian J. 2024, 19, e202400237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-J.; Yu, X.-Z.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Chen, X.-L.; Long, Z.-J.; Hu, H.-Z.; Xie, D.-H.; Zhang, W.-H.; Chen, J.-X. , et al. Hydrogel with ROS scavenging effect encapsulates BR@Zn-BTB nanoparticles for accelerating diabetic mice wound healing via multimodal therapy. iScience 2023, 26, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, B.-W.; Zou, Y.-M.; Niu, R.-J.; Chen, J.-X.; Zhang, W.-H.; Young, D.J. Nanoscale two-dimensional FeII- and CoII-based metal−organic frameworks of porphyrin ligand for the photodynamic therapy of breast cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephy, P.D.; Eling, T.; Mason, R.P. The horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of 3,5,3′,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Free radical and charge-transfer complex intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 3669–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chou, H.-L.; Peng, Y.-K. Disclosing the origin of transition metal oxides as peroxidase (and catalase) mimetics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 22728–22736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Qian, H. Recent advances on modulation of H2O2 in tumor microenvironment for enhanced cancer therapeutic efficacy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 481, 215049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Li, X.; Niu, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y. Tumor microenvironment-responsive Fenton nanocatalysts for intensified anticancer treatment. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.-H.; Zeng, C.-M.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Cao, F.-L.; Zhang, W.-H.; Chen, J.-X.; Young, D.J. [FeIIICl(TMPPH2)][FeIIICl4]2: A stand-alone molecular nanomedicine that induces high cytotoxicity by ferroptosis. Molecules 2024, 29, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Tang, X.-Y.; Meng, W.; Lai, Y.-H.; Zhou, X.; Yu, X.-Z.; Zhang, W.-H.; Chen, J.-X. Immunogenic radiation therapy for enhanced antitumor immunity via a core–shell nanosensitizer-mediated immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment modulation. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 19853–19864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, R.; Ye, Q.; Zou, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y. Mn3O4 nanoshell coated metal–organic frameworks with microenvironment-driven O2 production and GSH exhaustion ability for enhanced chemodynamic and photodynamic cancer therapies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS (Version 2.03): Program for empirical absorption correction of area detector data; University of Göttingen: Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HL | [CuCl(L)]2 (1) | [Cu(NO3)(L)]2 (2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC number | 2341904 | 2341905 | 2341906 |
| Formula | C19H19N7S2 | C38H40Cl2Cu2N14S4 | C38H36Cu2N16O6S4 |
| Formula weight | 409.53 | 1019.06 | 1068.15 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Triclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P-1 | P-1 | P21/n |
| a/Å | 10.4251(14) | 9.342(2) | 10.7226(16) |
| b/Å | 10.7193(14) | 10.714(2) | 9.6646(15) |
| c/Å | 11.0200(15) | 11.378(3) | 21.695(3) |
| α/° | 105.347(5) | 93.542(10) | 90 |
| β/° | 103.115(5) | 109.660(10) | 104.187(2) |
| γ/° | 117.474(5) | 108.609(9) | 90 |
| V/Å3 | 962.0(2) | 998.0(4) | 2179.7(6) |
| Z | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Dc/(g cm–3) | 1.414 | 1.696 | 1.627 |
| F(000) | 428 | 522 | 1092 |
| μ /mm–1 | 0.298 | 8.151 | 1.235 |
| Total reflns. | 25863 | 16310 | 33191 |
| Uniq. reflns. | 3928 | 4037 | 4404 |
| Observed reflns. | 1855 | 3572 | 3194 |
| Parameters | 253 | 274 | 298 |
| Rint | 0.1570 | 0.0818 | 0.0905 |
| Ra | 0.0882 | 0.0592 | 0.0677 |
| wRb | 0.1738 | 0.1658 | 0.1470 |
| GOFc | 1.029 | 1.079 | 1.048 |
| aR = Σ||Fo|–|Fc||/Σ|Fo|. b wR= {Σw(Fo2–Fc2)2/Σw(Fo2)2}1/2. c GOF = {Σw((Fo2–Fc2)2)]/(n–p)}1/2, where n = number of reflections and p = total number of parameters refined. | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





