1. Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the most pressing global public health threats, jeopardizing the effectiveness of otherwise life-saving antibiotics and posing a significant challenge to healthcare systems worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), AMR is one of the top 10 threats to global public health with alarmingly high levels of bacterial resistance observed in pathogens responsible for bloodstream infections (BSIs).[
1] This concern is particularly acute in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where multiple studies have documented significantly elevated rates of AMR.[
2]
BSIs are a major source of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with regional variations in both the spectrum of causative pathogens and their anti-microbial susceptibility. For example, in China,
Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus were the most prevalent Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria responsible for BSIs, respectively[
2,
3]. Similarly, European surveillance networks, such as the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net), have identified
E. coli and
Staphylococcus aureus as the dominant BSI pathogens[
4]. Other regions exhibit distinct trends, with South Korea mainly reporting
Streptococcus spp. and
Klebsiella spp. alongside
E. coli and
Staphylococcus aureus [
5], while in Japan
Streptococcus spp. and
Klebsiella spp. as prominent BSI pathogens [
5]. In Malawi, a 19-year study revealed non-typhoidal
Salmonella,
Salmonella typhi, and
Streptococcus pneumoniae as the leading causes of BSIs [
6]. A recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study has estimated 1.05 million deaths were associated with AMR in Africa in 2019, 5.3% of them associated with BSIs[
7]. Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) bears the brunt of AMR mortality, with a rate of 23.5 deaths per 100,000 populations in 2019 – the highest globally.[
8] Eastern Africa ranked second following SSA, with a rate of 21.4 deaths per 100,000. Several factors contribute to this disproportionate burden in SSA, including poverty, self-medication, inadequate regulation or stewardship of antimicrobial use, and limited access to effective alternatives when resistance is identified [
8].
Rwanda has witnessed a concerning rise in the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among bacterial infections. A recent study conducted in Rwandan referral hospitals revealed high resistance rates to commonly prescribed antibiotics for BSIs. Resistance[
9]. Rates of resistance in in Gram-negative isolates to penicillin, trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, and ampicillin and ceftriaxone were about 92%, 83%, 82%, and 76% respectively with resistance associated with factors such as prior attendance to multiple healthcare facilities, recent surgery or antibiotic exposure, and hospital-acquired infection.[
9]
However, data on BSIs in Rwanda and the wider region remain largely limited, often restricted to local settings. In response to this gap in evidence, we implemented this study.
2. Results
A total of 1532 blood cultures were available for analysis. KFH had the highest number of positive cultures 822 (54%), followed by CHUK with 539 (35%), and CHUB with 171 (11%) (
Table 1). Annual distribution of the BSIs was almost stable throughout the three years of the study around the average of 510 +/- 50 cases with slight increase in 2021. Overall, the proportions of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria were 48.2% and 51.8%, respectively.
Klebsiella spp.,
E. coli and
Acinetobacter spp were the most prevalent Gram-negative bacteria with 300 (40.7%), 131 (17.8%) and 111 (15.0 %) respectively while
Staphylococcus aureus (50%) and
Coagulase Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) (35.6%) were the most common gram-positive bacteria (
Table 1).
To identify patients or population group at high risk of BSIs, we further analyzed the distribution of different BSI pathogens by the medical department requesting the blood culture test. Most of gram-negative bacteria were from Paediatric (23%), ICU (20%), and Internal Medicine (16%) departments (
Table 2). For Gram-positive bacteria, the majority were from Emergency (23%), Paediatric (18%), Internal Medicine (17%), and ICU (17%) departments (
Table 2).
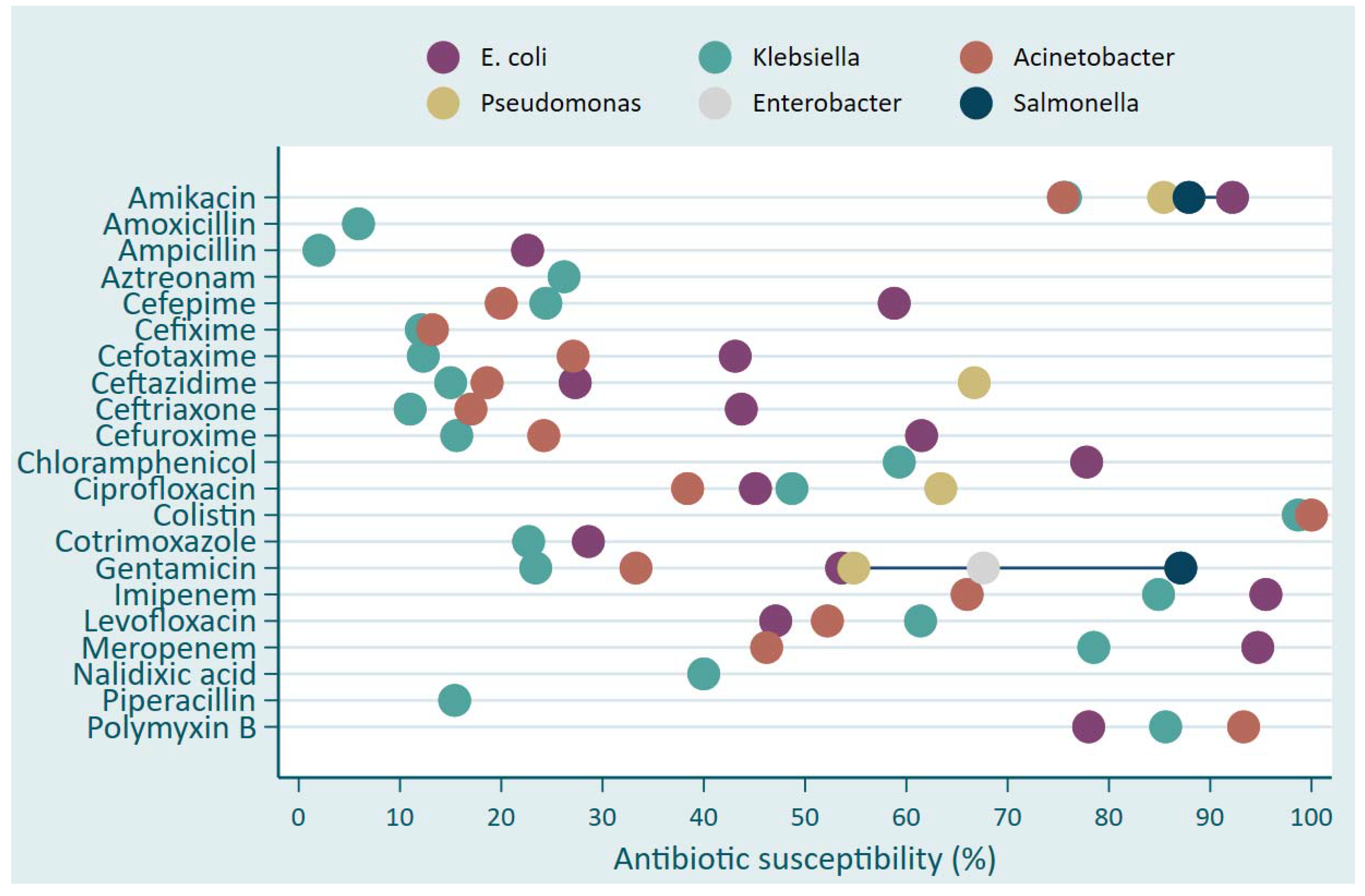
Klebsiella and
Acinetobacter ssp. showed predominantly higher resistance (less than 30% of isolates susceptible) to various antibiotics including Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Aztreonam, Cefepime, Cefixime, Cefotaxime, Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime, Cotrimoxazole, Gentamicin and Piperacillin (
Figure 1). The antibiotics with the highest susceptibility level were Colistin, Amikacin, Polymyxin B. Meropenem and Imipinem to
E. coli (above 90%) and
Klebsiella (around 80%) and less susceptible to Acinetobacter where the susceptibility level was 67% for Imipinem and 45% for Meropenem (
Figure 1).
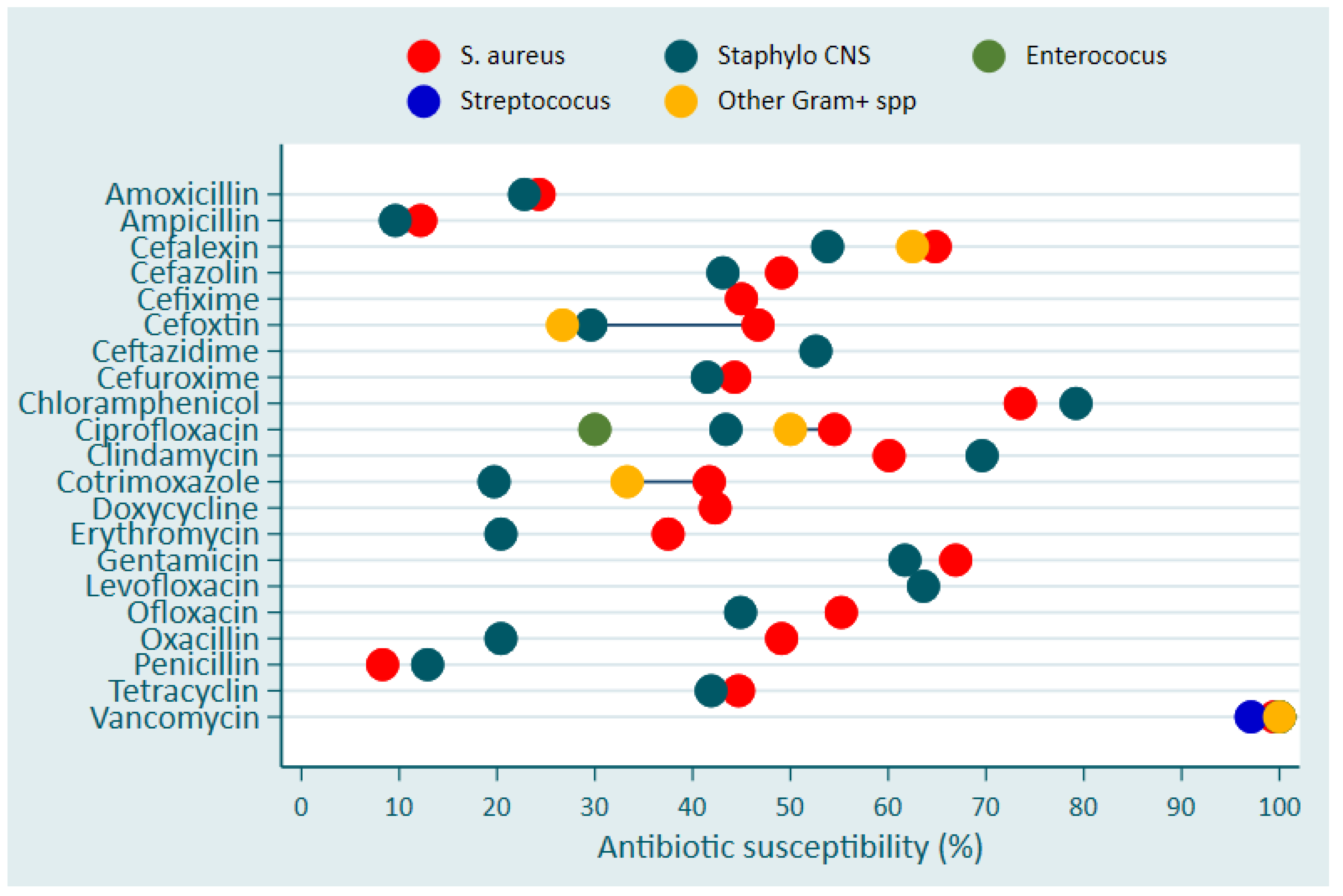
Vancomycin was the only antibiotics that exhibited a nearly full susceptibility followed by Chloramphenicol, which showed a susceptibility level between 70% - 80% for
S. aureus (
Figure 2). The effectiveness of other antibiotics (Gentamicin, Cephalexin and Clindamycin) on
S. aureus ranged between 60-70% (
Figure 2).
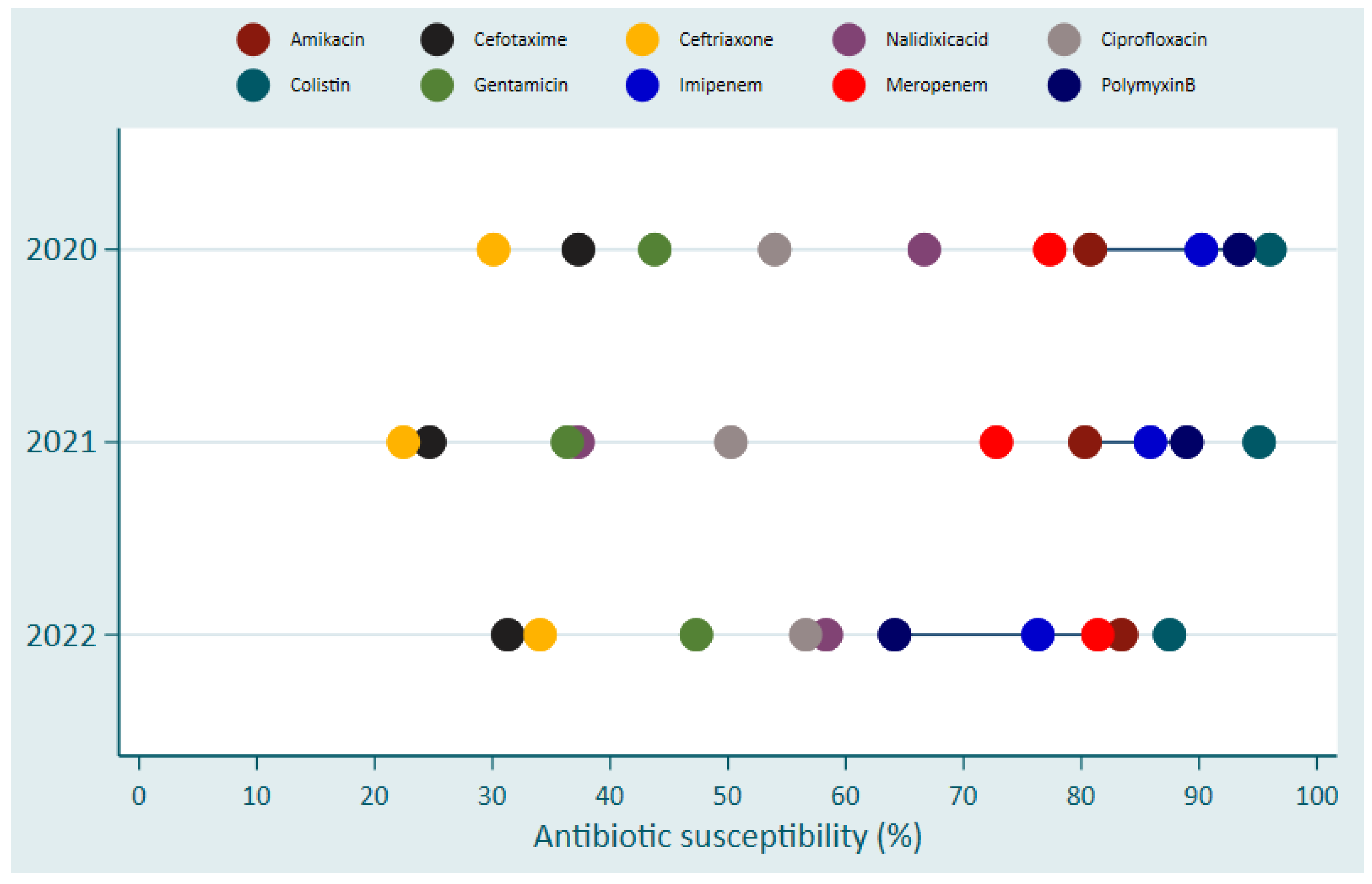
Despite increased susceptibility of Colistin, Polymyxin B, Imipinem, Amikacin and Meropenem in Gram-negative bacteria causing BSIs, a trend in development of resistance against Colistin was observed. This was indicated by that the susceptibility was 96% (48/50) in 2020, 95% (97/102) in 2021 and 87.5% (35/40) in 2022 (
Figure 3). Similar trends were observed for Polymyxin B where susceptibility was 93.4% in 2020, 88.9 in 2021 and 64.1 in 2022 (
Figure 3).
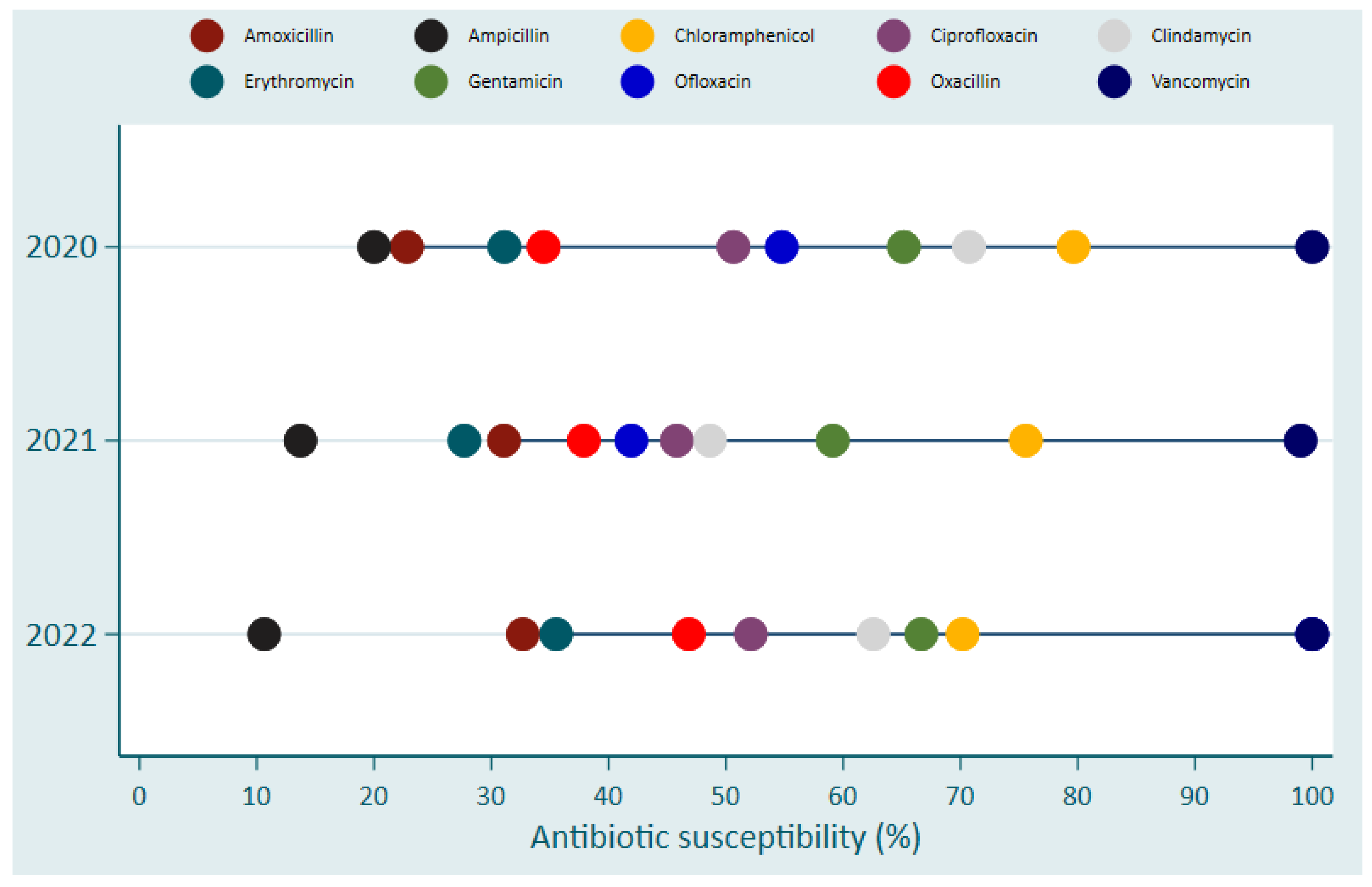
Vancomycin and Chloramphenicol were the two most effective antibiotics over the 3-years period against Gram-positive bacteria with sensitivity of over 90% and 70-80%, respectively (
Figure 4).
3. Discussion
Antimicrobials, particularly antibiotics, are crucial for treating many potentially fatal infections, but their effectiveness is threatened by the emergence and spread of resistance. This issue is particularly pressing in LMICs including Rwanda, where bacterial AMR is among the top health concerns[
10]. This research highlights the diversity of BSI pathogens, their distribution in different departments, and their antimicrobial susceptibility profiles.
Findings from this study showed that majority of positive cultures were from Paediatric, ICU, and Internal Medicine departments. Our findings concur with previous studies conducted in Rwanda[
17], Ethiopia, and Ghana [
11]. This could be justified by the fact that children and in particular neonates are more prone to BSIs mainly due to their weak immunity[
12]. Also, in LMICs, children are more affected by infections because of poor sanitation and other environmental factors associated with low social economic living conditions. Also, BSIs are the third most common infection in ICU (up to 15% among inpatients in their first month of hospitalization)[
13], resulting in a disproportionate burden of extended hospital stay or death. Internal medicine wards can host people with advanced age who have comorbidities or indwelling caters which increase the risk of developing BSIs[
11,
14].
High diversity of bloodstream bacterial infections among patients hospitalized in three hospitals of Rwanda were observed, with over 20 species of gram-negative bacteria and around 10 species of gram-positive bacteria isolated.
S. aureus,
Klebsiella spp., Staphylococcus (CNS) were the most prevalent pathogens (65%), contributing (26%), (20%), and (19%), respectively. These findings align with regional studies, highlighting
S. aureus and
Klebsiella spp. as leading causes of BSIs in the WHO African region[
8]. However,
Staphylococcus (CNS) and aka
coagulase negative Staphylococcus it is commonly understudied because it is considered part of the commensal flora or microbiome of the skin[
15]. Nevertheless, it is reported among the top prevalent causes of BSIs in high income countries[
16]. It has recently been reported to constitute about 34% of the BSIs in Morocco[
15].
Our analysis also showed that both gram-negative (
Klebsiella species,
E. coli Acinetobacter species) and gram-positive bacteria (
S. aureus) are prevalent pathogens associated with BSIs. These finding are consistent with previous reports including EARS-Net, Kor-GLASS and HBARSS[
4,
5,
13], and reports from other African countries[
6,
17,
18].
Notably, our findings revealed a concerning trend of rapidly growing and spreading resistance to commonly used antibiotics, particularly among Klebsiella spp. and Acinetobacter ssp., which was associated with higher mortality rates. Drug-resistant
S. aureus,
Klebsiella spp., E. coli have been associated with high mortality rates owing to the complexity involved in their clinical management and treatment[
17].
Our analysis indicated varying degrees of susceptibility to different antibiotics, with
E. coli showing high sensitivity to Amikacin and Imipenem in 2020. While
S. aureus remained predominantly sensitive to Vancomycin throughout the study periods. However, resistance to meropenem and imipenem among Gram-negative bacteria was noticed for some pathogens. Similar resistance varying from 1.2%-3.1% has been reported in North America and Asia[
19]. Both antibiotics belong to carbapenem class which are considered as last resort antibiotics which should be restricted to special cases like infections caused by multidrug-resistant pathogens Resistance [
20,
21]. to carbapenem antibiotics is of great concern as they are limited alternative antibiotics to be used against carbapenem- producing enterobacteriaceae[
22]. Furthermore, resistance to Colistin and Polymyxin B was recorded. Both belong to Polymyxin class which target the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) membrane of Gram-negative bacteria resulting in death due to the destruction of LPS and leaking of cellular content[
23].
The temporal analyses of AMR show a rapid change in trends of pathogens-specific drug resistance. Interestingly, this change in the antibiotics-resistance profiles of different species of bacteria is not uni-directional. This suggests that through implementing proper antimicrobial stewardship strategies and interventions, the effectiveness of these drugs could be preserved or restored over time, at least partially for some pathogens[
24]. Moreover, these findings emphasize the critical need for the implementation of Rwanda National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (NAPAMR) to regulate antibiotics usage, prevent the spread of bacterial AMR, and improve both case management and infection control in the country. Achieving these objectives will necessitate a multi-sectoral collaboration led health authorities from various domains, including human, animal, and environmental health sectors.
The growing burden of AMR is not conclusive to Rwanda but affecting all African countries[
25]. However, due to several risk factors including the globalization, climate change, and cross-borders dynamics of human and animal populations, the emergence of resistant bacterial infections including TB strains as well as the emergence of zoonotic infectious diseases are increasing growing[
26]. Considering that AMR is not only affecting the cost-effectiveness of bacterial infections but also fungal infections[
27]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to strengthen the surveillance of AMR among bacterial and fungal pathogens among human and animal populations, using a transdisciplinary multisectoral integrated One Health strategy[
28,
29]. Advanced technology such as the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) might improve the cost-effectiveness of prevention and control measures through the early prediction, monitoring population dynamic, and enhancing the diagnostic capacity by integrating AI-powered diagnostic algorithm. Furthermore, additional investment is needed to strengthen the implementation of the guidelines of the World Health Organization (WHO) for infection prevention and control in healthcare facilities to reduce the burden of healthcare facility-acquired infection[
31]-[
33].
In response to this growing threat, Rwanda through Rwanda Biomedical Centre (RBC) have invested in multidimensional strategic interventions to counteract AMR and the associated reduction in antibiotic effectiveness. This includes the expansion of the integrated surveillance and response system to be implemented throughout the country and includes veterinary surveillance under a multi-sectoral “Rwanda National Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Operational Plan 2024-2028”. Furthermore, RBC is currently piloting the implementation of Wastewater-Based Epidemiology supported by Genomic surveillance to monitor and track the dynamic of infectious diseases and AMR at the community level. Moreover, these strategic interventions will be supported by the establishment of Biotechnology Centre in the country to lead innovation, development, and repurposing of novel and existed drugs and vaccines. These strategies and interventions are mainly tailored to low resources settings like Rwanda and other African countries.
4. Materials and Methods
Study design and study sites
This was a retrospective, observational (non-interventional) study of blood cultures processed in laboratories of three tertiary referral hospitals in Rwanda from January 2020 to August 2022. These included the University Teaching Hospital of Kigali (CHUK), the University Teaching Hospital of Butare (CHUB), and the King Faisal Hospital (KFH), and are serving as the central network for national AMR surveillance. CHUK is located in Nyarugenge district of Kigali City and it is the biggest referral hospital in Rwanda with a capacity of 519 beds, CHUB and is situated in Huye District of the Southern Province with a capacity of 500 beds, and KFH is located in Kigali City and it is the largest private and university teaching hospital in Rwanda with 160 beds.
Data collection and laboratory methods
Blood culture isolates and corresponding antimicrobial susceptibility profiles were collected from laboratory registers used in routine clinical care. These microbiological data where linked to clinical data by patient name. Blood samples were obtained where clinically indicated, using aseptic methods by trained healthcare staff and inoculated to BD BACTEC (Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, USA) bottles. Blood samples were sent to the bacteriology laboratory and incubated in BACTEC FX automated system for 5 days as per standard blood culture protocol. Gram staining was performed on blood culture signalling positive growth. A subculture onto blood agar (BA) and MacConkey agar (MCA) was performed for Gram-positive and Gram-negative isolates, respectively and in accordance with standardised operating procedures, followed by biochemical testing using Analytical Profile Indexing (API-20). At CHUK and KFH, Phoenix M50 (Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, USA) was used for bacterial identification in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction. CHUB used the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method for antibiotic susceptibility testing. Here, the turbidity of the normal saline bacterial suspension was adjusted to match the 0.5 McFarland standards. Mueller-Hinton agar was used and incubated aerobically at 37°C for 16-18 hours. Inhibition zones were measured and interpreted as sensitive or resistant based on Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) breakpoints. For Quality control, the following reference strains (ATCC25923, 25922, 27852, 49619, or 49247) were used.
Data management and Statistical analysis
Data from laboratory records were entered into the Demography and Health Surveys (DHS) platform and extracted into Microsoft Excel. Descriptive statistics (frequency and percentage) were computed using R software version 4.1.3.
5. Conclusions
This study provides valuable insights into the prevailing pathogens associated with BSIs and their antimicrobial susceptibility profiles at three tertiary referral hospitals in Rwanda. K. pneumoniae, E. coli, A. baumannii, and S. aureus were among the predominant pathogens associated with BSIs. Antibiotic susceptibility testing results show that clinically relevant drug-resistant BSI bacterial are prevalent in the studied population with resistance to carbapenem antibiotics and Polymixin class antibiotics also noted, raising concerns about the limited alternatives for treating multidrug-resistant pathogens. This underscores the urgent need for strengthening antimicrobial stewardship programs and adopting a surveillance system to combat the emergence of AMR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G., A.A., and C.C.M.; methodology, M.G., A.A., and C.C.M.; formal analysis, V.N.; investigation, M.G., M.G. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G. V.N., A.A., and C.C.M; writing—review and editing, M.G., V.N., A.A., and C.C.M.; visualization, M.G. V.N., A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because it analyzes secondary data that was collected by the routine surveillance anonymously without personal identifiers.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data produced this study is included in the published paper.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to our colleagues at Rwandan Tertiary Hospitals, Ministry of Health, RBC, WHO, and the East, Central and Southern Africa Health Community (ECSA-HC) for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Donkor ES, Muhsen K, Johnson SAM, et al. Multicenter Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Bloodstream Infections in Ghana. Antibiotics (Basel). Jan 27 2023;12(2). [CrossRef]
- Sharma A, Singh A, Dar MA, et al. Menace of antimicrobial resistance in LMICs: Current surveillance practices and control measures to tackle hostility. Journal of Infection and Public Health. 2022/02/01/ 2022;15(2):172-181. [CrossRef]
- Gagliotti C, Balode A, Baquero F, et al. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: bad news and good news from the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net, formerly EARSS), 2002 to 2009. Euro Surveill. Mar 17 2011;16(11). [CrossRef]
- Lee H, Yoon EJ, Kim D, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of major clinical pathogens in South Korea, May 2016 to April 2017: first one-year report from Kor-GLASS. Euro Surveill. Oct 2018;23(42). [CrossRef]
- Hattori H, Maeda M, Nagatomo Y, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for mortality in bloodstream infections: A single-center retrospective study in Japan. Am J Infect Control. Dec 2018;46(12):e75-e79. [CrossRef]
- Musicha P, Cornick JE, Bar-Zeev N, et al. Trends in antimicrobial resistance in bloodstream infection isolates at a large urban hospital in Malawi (1998-2016): a surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis. Oct 2017;17(10):1042-1052. [CrossRef]
- Tomislav Mestrovic GRA, Lucien R Swetschinski, et al. The burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO European region in 2019: a cross-country systematic analysis. Lancet Public Health. Nov 2022;7(11):e897-e913. [CrossRef]
- Kariuki S, Kering K, Wairimu C, Onsare R, Mbae C. Antimicrobial Resistance Rates and Surveillance in Sub-Saharan Africa: Where Are We Now? Infect Drug Resist. 2022;15:3589-3609. [CrossRef]
- Sutherland T, Mpirimbanyi C, Nziyomaze E, et al. Widespread antimicrobial resistance among bacterial infections in a Rwandan referral hospital. PLOS ONE. 2019;14(8):e0221121. [CrossRef]
- Zhou N, Cheng Z, Zhang X, et al. Global antimicrobial resistance: a system-wide comprehensive investigation using the Global One Health Index. Infectious Diseases of Poverty. 2022/08/23 2022;11(1):92. [CrossRef]
- Deku JG, Dakorah MP, Lokpo SY, et al. The Epidemiology of Bloodstream Infections and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns: A Nine-Year Retrospective Study at St. Dominic Hospital, Akwatia, Ghana. J Trop Med. 2019;2019:6750864. [CrossRef]
- Habyarimana T, Murenzi D, Musoni E, Yadufashije C, F NN. Bacteriological Profile and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Bloodstream Infection at Kigali University Teaching Hospital. Infect Drug Resist. 2021;14:699-707. [CrossRef]
- Kallel H, Houcke S, Resiere D, et al. Epidemiology and Prognosis of Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Bloodstream Infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. Jul 2020;103(1):508-514. [CrossRef]
- Del Bono V, Giacobbe DR. Bloodstream infections in internal medicine. Virulence. 2016/04/02 2016;7(3):353-365. [CrossRef]
- Houssaini ZE, Harrar N, Zerouali K, Belabbes H, Elmdaghri N. [Prevalence of coagulase-negative staphylococci in blood cultures at the Ibn-Rochd University Hospital in Casablanca]. Pan Afr Med J. 2019;33:193. Prévalence des staphylocoques à coagulase négative dans les hémocultures au Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Ibn Rochd de Casablanca. [CrossRef]
- Kern WV, Rieg S. Burden of bacterial bloodstream infection-a brief update on epidemiology and significance of multidrug-resistant pathogens. Clin Microbiol Infect. Feb 2020;26(2):151-157. [CrossRef]
- The burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO European region in 2019: a cross-country systematic analysis. Lancet Public Health. Nov 2022;7(11):e897-e913. [CrossRef]
- Eibach D, Belmar Campos C, Krumkamp R, et al. Extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae causing bloodstream infections in rural Ghana, 2007-2012. Int J Med Microbiol. Jun 2016;306(4):249-54. [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak KM, Karlowsky JA, de Jonge BLM, Stone GG, Sahm DF. Epidemiology of Carbapenem Resistance Determinants Identified in Meropenem-Nonsusceptible Enterobacterales Collected as Part of a Global Surveillance Program, 2012 to 2017. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. Jun 17 2021;65(7):e0200020. [CrossRef]
- Ssekatawa K, Byarugaba DK, Wampande E, Ejobi F. A systematic review: the current status of carbapenem resistance in East Africa. BMC Research Notes. 2018/08/31 2018;11(1):629. [CrossRef]
- Jousset AB, Bernabeu S, Bonnin RA, et al. Development and validation of a multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of the five families of plasmid-encoded colistin resistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents. Mar 2019;53(3):302-309. [CrossRef]
- Leshaba TMS, Mbelle NM, Osei Sekyere J. Current and emerging polymyxin resistance diagnostics: A systematic review of established and novel detection methods. J Appl Microbiol. Jan 2022;132(1):8-30. [CrossRef]
- Abebe W, Tegene B, Feleke T, Sharew B. Bacterial Bloodstream Infections and their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns in Children and Adults in Ethiopia: a 6-Year Retrospective Study. Clin Lab. Nov 1 2021;67(11). [CrossRef]
- Baker S, Thomson N, Weill FX, Holt KE. Genomic insights into the emergence and spread of antimicrobial-resistant bacterial pathogens. Science. May 18 2018;360(6390):733-738. [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, B., Gray, A.P., Weaver, N.D., Aguilar, G.R., Swetschinski, L.R., Ikuta, K.S., Mestrovic, T., Chung, E., Wool, E.E., Han, C. and Hayoon, A.G., 2024. The burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO African region in 2019: a cross-country systematic analysis. The Lancet Global Health, 12(2), pp.e201-e216.
- Remera, E., Rwagasore, E., Muvunyi, C.M. and Ahmed, A., Emergence of the first molecularly-confirmed outbreak of Rift Valley fever among humans in Rwanda, calls for institutionalizing One Health Strategy. IJID One Health.
- Muvunyi, C.M., Ngabonziza, J.C.S., Florence, M., Mukagatare, I., Twagirumukiza, M., Ahmed, A. and Siddig, E.E., 2024. Uncovering the Diversity and Distribution of Fungal Infections in Rwanda: Assessing Risks and Documenting Knowledge and Policy Gaps.
- Fasina, F.O., Fasanmi, O.G., Makonnen, Y.J., Bebay, C., Bett, B. and Roesel, K., 2021. The one health landscape in Sub-Saharan African countries. One Health, 13, p.100325.
- Langfeldt, A., Gold, J.A. and Chiller, T., 2022. Emerging fungal infections: from the fields to the clinic, resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and dermatophyte species: a one health perspective on an urgent public health problem. Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, 9(4), pp.46-51.
- Siddig, E.E., Eltigani, H.F. and Ahmed, A., 2023. The rise of AI: how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing infectious disease control. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 51(12), pp.2636-2637.
- Allegranzi, B., Kilpatrick, C., Storr, J., Kelley, E., Park, B.J. and Donaldson, L., 2017. Global infection prevention and control priorities 2018–22: a call for action. The Lancet Global Health, 5(12), pp.e1178-e1180.
- World Health Organization, 2020. Guidelines on core components of infection prevention and control programmes at the national and acute health care facility level. World Health Organization. Country Office for Thailand.
- World Health Organization, 2019. Minimum requirements for infection prevention and control programmes.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).