3.1. Preparation and Characterization of SeNPs
SeNPs has attracted the attention of many researchers because its surface activity is higher than other selenium compounds, so it can be better absorbed by intestinal tract. In our study, we wanted to establish a convenient method to prepare SeNPs with high biological activity and low toxicity. In this paper, SeNPs was prepared by chemical method which is that sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was used as dispersant, ascorbic acid was used as reducing agent and SeNPs was used as target. The morphology was observed by transmission electron microscopy, and then the particle size, potential and other indicators were determined to characterize it, and the stability was analyzed by dual-wavelength colorimetry.
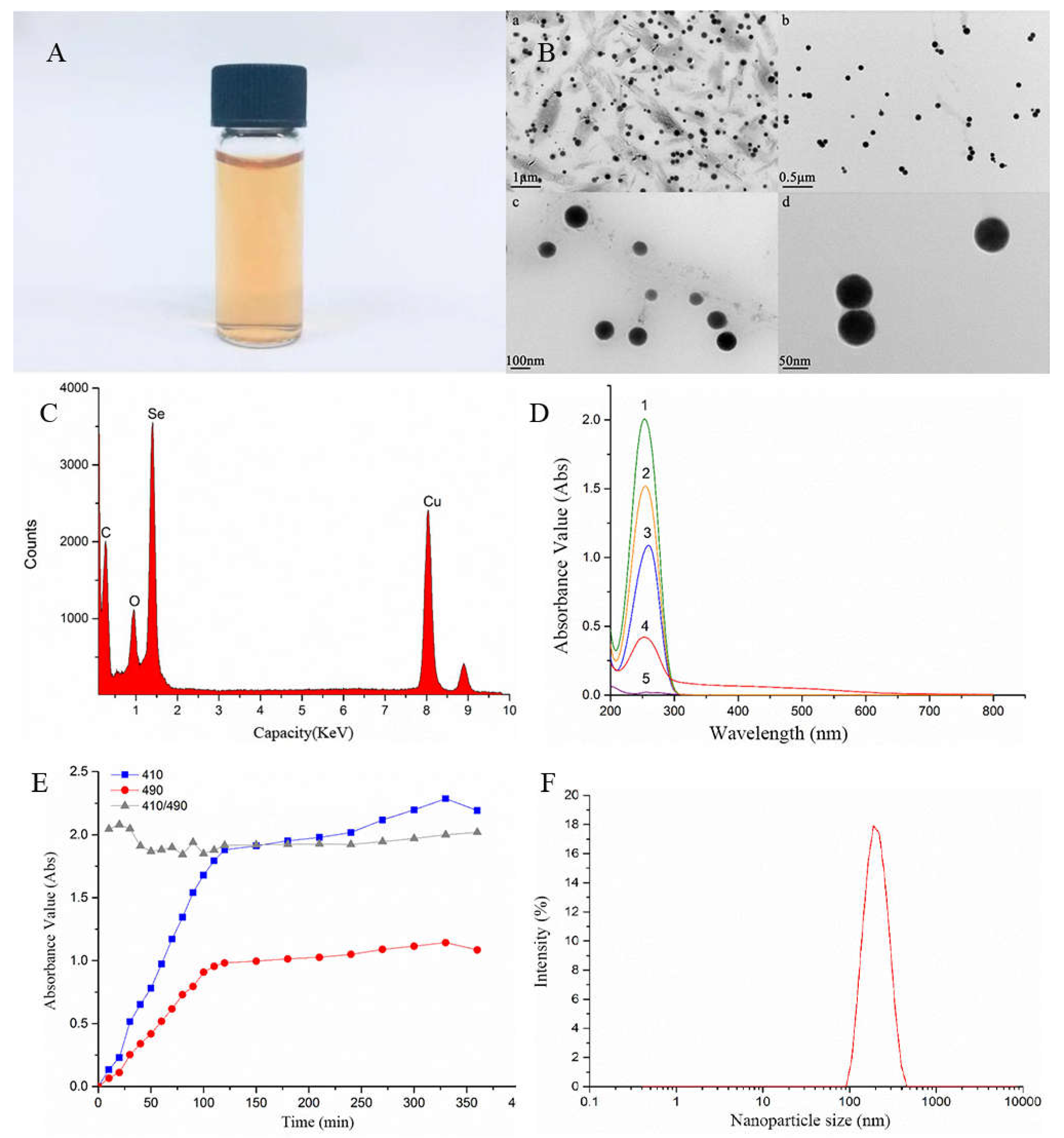
SeNPs prepared with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as dispersant and ascorbic acid as reducing agent is a bright orange red solution with no precipitation and can be stably preserved (
Figure 2A). Under TEM ( transmission electron microscope), the SeNPs was well dispersed in sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and there was no obvious agglomeration phenomenon, which was uniform spherical with a particle size of about 70nm (
Figure 2B). The size of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii single cell is about 10 μm,so SeNPs can be totally absorbed by
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EDS analysis showed that the elements with peaks were C, O, Se and Cu, in which C and O were the C and O elements in sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and Cu were the copper elements in the copper mesh carried by transmission electron microscope, indicating that SeNPs was Se elemental(
Figure 2C). According to the colloidal solution of double wavelength colorimetry [
41], when the wavelength λ1 and λ2 were fixed, if the A2/A1 absorbance ratio remains unchanged, colloid particle size remains the same in a stable state[
42]. The mixed solution with Vc had an obvious absorption peak at 260 nm (
Figure 2D), while the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution had no characteristic absorption within the measured wavelength range. Therefore, in order to avoid the absorption of Vc and facilitate the determination, 410 nm and 490 nm[
32] were selected as the determination wavelengths of SeNPs solution. The larger the ratio of A410/A490 is, the smaller the particle size of colloidal particles will be. When the ratio is unchanged, the particle size of colloidal particles will not change[
31]. UV-vis absorption spectra showed that the absorbance of the solution at 410 nm and 490 nm gradually increased from the mixing of the reaction system, and the ratio of A410/A490 at the two wavelengths continued to fluctuate, and gradually stabilized after 2 h with a ratio of about 2 (
Figure 2E). This indicates that the size of the SeNPs particles formed at this time does not change and is in a uniform and stable state. The particle size analysis of SeNPs using Malvern nanoscale analyzer shows that the spectral line of particle size distribution presents a single peak, and the peak shape is narrow, reaching the highest point at 186nm (
Figure 2F). Therefore, 186nm is the most frequent particle size of nano-system system, indicating that the particle size of SeNPs is uniform and stable. Zeta Potential is one of the indicators to detect the stability of particle dispersion in the system, and it is a measure of mutual repulsion or attraction strength between particles. It not only determines the surface structure of ancient particles, but also depends on dispersant, so it can be used to predict the stability of dispersion solution. The smaller the molecule or dispersed particle is, the lower the absolute value (positive or negative) of the Zeta potential will reach, and the more likely it is to condense or condense.
Table 1 shows the relationship between Zeta potential and stability. The measured zeta potential of SeNPs solution is -44.20±3.10, indicating that the SeNPs distribution system had a good stability according to
Table 1.
Table 1.
The relationship between Zeta potential and stability.
Table 1.
The relationship between Zeta potential and stability.
| Zeta potential(mV) |
Colloid stability |
| 0~±5 |
Rapid coagulation or condensation |
| ±10~±30 |
Start to get unstable |
| ±30~±40 |
Poor stability |
| ±40~±60 |
Good stability |
| >±61 |
Excellent stability |
Table 2.
Particle size and Zeta potential of CMC-SeNPs.
Table 2.
Particle size and Zeta potential of CMC-SeNPs.
| Particle size under TEM(nm) |
70 |
| Particle size in hydrology(nm) |
186.13±1.40 |
| Zeta potential(mV) |
-44.20±3.10 |
3.2. Effects of SeNPs on the Growth of Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii under Cadmium Stress
Selenium can reduce the toxicity of heavy metals. SeNPs has attracted wide attention due to its higher biological activity and lower toxicity. One study showed that SeNPs can ameliorate the nonspecific immune function and antioxidant capacity decline of tilapia caused by cadmium stress to a certain extent[
43]. However, there are few reports on the effect of SeNPs on heavy metals in algae. In this paper, different concentrations of SeNPs were applied to the wild-type Chlamydomonas rheinhardtii CC125 under cadmium stress and the cell wall deficient type Chlamydomonas rheinhardtii CC400, to explore the changes in biomass and chlorophyll content of Chlamydomonas rheinhardtii caused by cadmium toxicity in the presence of SeNPs, so as to observe that in the presence of SeNPs, direct effects of cadmium toxicity on the growth of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Table 3 shows the growth curve of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in 96 h under different Cd
2+ concentrations. The area surrounded by each concentration and the coordinate axis are calculated according to the formula. The fitting equation takes the area as the abscissa and the Cd
2+ concentration as the ordinate. According to the equation, the semi-maximum effect concentration EC50 of Cd
2+ on the two species of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was calculated (i.e. the Cd
2+ concentration corresponding to the biomass was suppressed by half). The results showed that the EC50 concentration of Cd
2+ was about 53.95±0.36 μmol/L against the wild type CC125 and 56.39±0.39 μmol/L against the cell wall defective type CC400. This experiment determined the Cd
2+ concentration used in subsequent experiments, which were all the EC50 concentration of Cd
2+.
Table 4 shows the semi-maximum effect concentration EC50 of SeNPs on two species of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The results showed that the EC50 concentration of SeNPs was about 1.88±0.08 μmol/L for wild type CC125 and 0.53±0.03 μmol/L for cell wall defective type CC400. The concentration of SeNPs used in subsequent experiments was determined according to this experiment. It can also be seen from the comparison of the above two algae data that Cd
2+ has a slightly lower EC50 concentration than CC400 for wild-type
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (no significant difference), while SeNPs has a higher EC50 concentration than CC400 for wild-type
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CC125. In the experiment, it was found that the range from the active concentration of Cd
2+ and SeNPs to the lethal concentration was narrower in CC400 than in CC125. This may be related to the small size and defective cell wall of CC400.
In
Figure 3A, (a) and (b) show the growth curves of CC125 and CC400 within 96 h, respectively. The solid lines are CK group (algae only) and SeNPs group (algae+SeNPs). The dashed lines are Cd
2+ group (alga +Cd
2+) and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group (algae+SeNPs+Cd
2+). In CC125 cells, the biomass of SeNPs group was not inhibited at the concentrations of 0.005, 0.01 and 0.2 μmol/L, which was not significantly different from that of CK group. The biomass of Cd
2+ group was inhibited, which was about 50% of that of CK group. The biomass of SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups with 0.005 μmol/L concentration increased slightly, while that of SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups with 0.01, 0.2, 1 and 2 concentrations did not increase significantly, and the growth was very slow. After 48 hours of culture, cells entered the logarithmic growth phase, in which the biomass increased logarithmically on the basis of transitional growth and accumulation, and the distinction between groups became more and more obvious. The biomass of low concentration SeNPs group was slightly higher than that of CK group, and the biomass of 2μmol/L, which is close to the EC50 concentration of SeNPs, only was half suppressed, which was close to that of Cd
2+ group. The growth curve of SeNPs+Cd
2+ group was lower than that of Cd
2+ group, and the growth inhibition was very significant. These results showed that low concentration of SeNPs had no significant inhibitory effect on the growth of wild type CC125, but high concentration of SeNPs had inhibitory effect on the growth of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Cd
2+ itself can inhibit the growth of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and the addition of SeNPs can aggravate this inhibitory effect. The growth of CC400 cells was not significantly inhibited within 48 h of the transition period in every group, showing a concentration-dependent relationship, and the biomass growth was slightly different but not significant. After entering the logarithmic growth phase, the differentiation between groups became more and more obvious. The biomass of SeNPs group showed an extremely significant logarithmic growth, and the biomass was obviously concentration-dependent, while the biomass of Cd
2+ group was inhibited, about 50% of that of CK group. SeNPs+Cd
2+ group and Cd
2+ group had no significant difference. The results showed that the growth inhibition of SeNPs+Cd
2+ in CC400 cells with cell wall defect was not significantly different from that in Cd
2+ group. From the overall trend, at SeNPs concentration without growth inhibition effect on
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, in the presence of Cd
2+, the growth of CC125 was inhibited and the biomass of CC125 was significantly lower than that of Cd
2+ group. The simultaneous presence of SeNPs and Cd
2+ showed no significant difference in the growth inhibition of CC400 compared with that of Cd
2+ alone. The possible reason for this phenomenon is that in CC125, the addition of SeNPs enhanced the toxicity of Cd
2+, while in CC400, SeNPs did not have this effect.
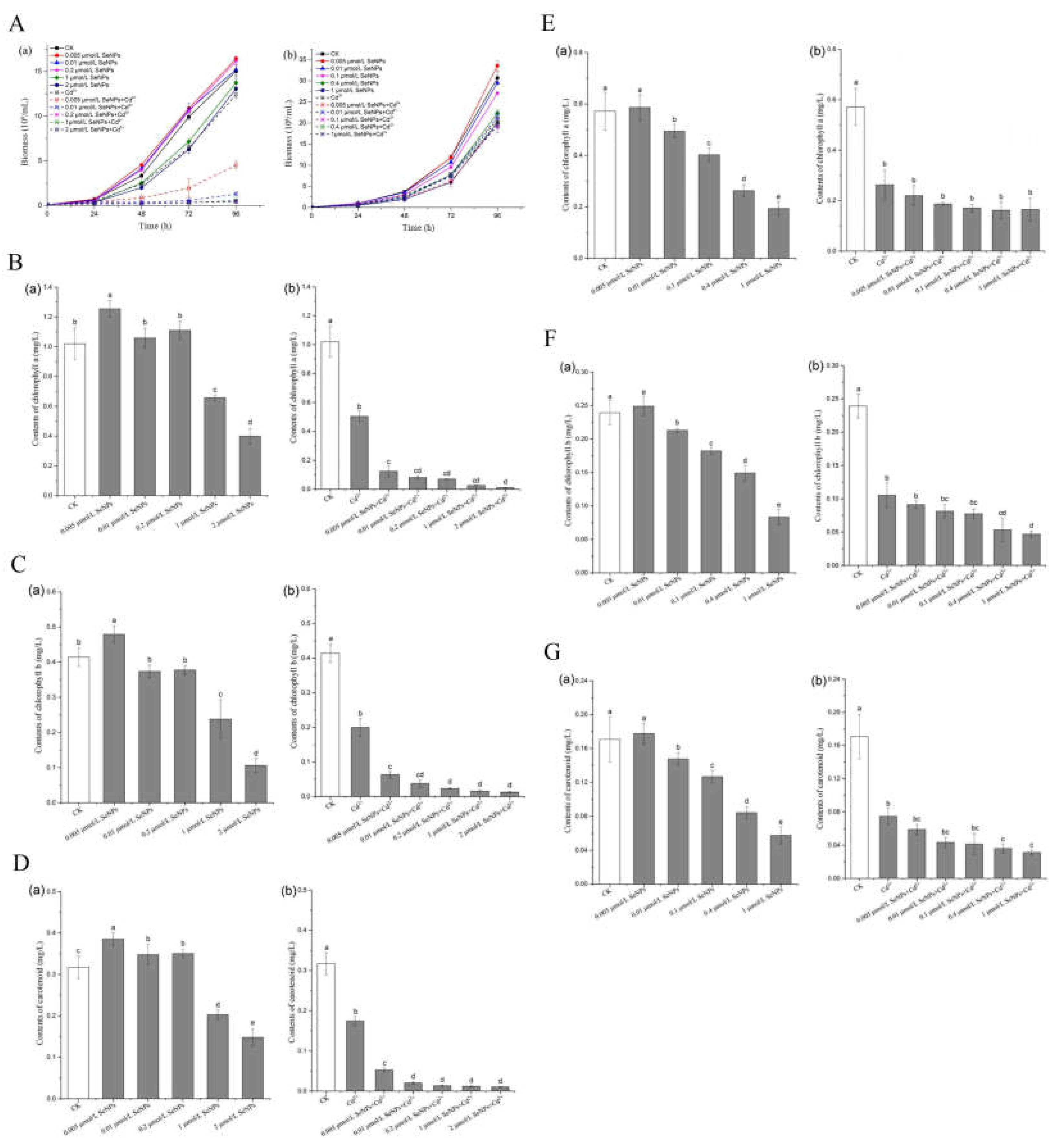
Chlorophyll is the main pigment in plant photosynthesis. It is a kind of lipid pigment and plays a core role in light absorption in photosynthesis so chlorophyll content in algae cells can reflect the growth and physiological conditions of algae.
Figure 3B to
Figure 3G show the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoid of CC125 and CC400 after 72 h growth in different treatment groups (CK group, SeNPs group, Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group).
In
Figure 3B(a), the change of chlorophyll a content showed concentration-dependent relationship at different concentrations of SeNPs, among which 0.005, 0.01 and 0.2μmol/L groups were slightly higher than CK group, possibly due to the low toxicity excitatory effect. Low concentration of SeNPs promoted the synthesis of chlorophyll in algal cells, resulting in increased content. It may be because that algal cells open their own protective mechanism, which greatly increases energy consumption and respiration, prompting algal cells to synthesize more chlorophyll, thus ensuring the supply of substrate for respiration[
44]. In
Figure 3B (b), the chlorophyll a content in group Cd
2+ is about 50% of that in group CK, while that in group SeNPs+Cd
2+ is relatively low. The chlorophyll a of the lowest SeNPs concentration of 0.005μmol/L was significantly decreased compared with that of the Cd
2+ group, and the growth of algal cells was severely inhibited at higher SeNPs concentration with extremely low chlorophyll contents. The contents of chlorophyll b and carotenoid in Fig. 3C and Fig. 3D were also concentration-dependent in CK group and SeNPs group, and the single action of SeNPs showed low toxicity excitation below 0.2μmol/L. The contents of chlorophyll b and carotenoid in SeNPs+Cd
2+ group were significantly lower than those in Cd
2+ group, which showed the same trend as that in biomass between SeNPs+Cd
2+ group and Cd
2+ group.
In
Figure 3E(a), SeNPs with different concentrations showed concentration-dependent changes in chlorophyll a content. In
Figure 3E(b), compared with the CK group, the chlorophyll a content in Cd
2+ group was about 50% of that in CK group, while the chlorophyll a content in SeNPs+Cd
2+ group was slightly reduced but had no significant difference from that in Cd
2+ group. The contents of chlorophyll b and carotenoid in Fig 3F and Fig 3G were also concentration-dependent in CK group and SeNPs group. The contents of chlorophyll b and carotenoid in SeNPs+Cd
2+ group were decreased compared with those in Cd
2+ group, but with the increase of concentration, there was no obvious differentiation among several concentrations. The results showed the same trend as those of biomass. In summary, the 96 h growth curve of CC125 showed that 0.005 and 0.01 μmol/L SeNPs had no inhibitory effect on the growth of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, but the inhibitory effect was obvious in the presence of Cd
2+. The chlorophyll content of CC125 was determined and the same phenomenon was found. However, there was no such phenomenon in CC400 with cell wall defects, and there was no significant difference between the growth inhibition of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in the presence of SeNPs and Cd
2+ and the growth inhibition of CC400 by Cd
2+ itself. The results of chlorophyll content showed the same trend.
3.3. Effects of SeNPs on Physiology of Chlamydomonas Rheinensis under Cadmium Stress
Reactive oxygen refers to some oxygen metabolites and their derivatives which contain oxygen atoms but have stronger oxidation capacity than oxygen. In normal growth cells, a very low level of Reactive Oxygen Species will not cause harm, and the production and removal of Reactive Oxygen Species in algal cells are generally in a dynamic equilibrium state. Trace Reactive Oxygen Species play an important role in the regulation of some physiological phenomena, but when the dynamic balance of Reactive Oxygen Species is broken, it may cause harm to the body [
45]. The objective of this study was to investigate the enzyme activities of total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) and catalase (CAT), the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) and the relative content of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the cells of two kinds
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under different treatments. The change of enzyme activities of total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) and catalase (CAT), the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) and the relative content of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) were compared in two kinds of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with and without cadmium.
According to the results of the experiment in the previous chapter, the concentration range of SeNPs in the experiment was further narrowed, and only two lower concentrations with no toxic effect on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were selected: 0.005 and 0.01 μmol/L.
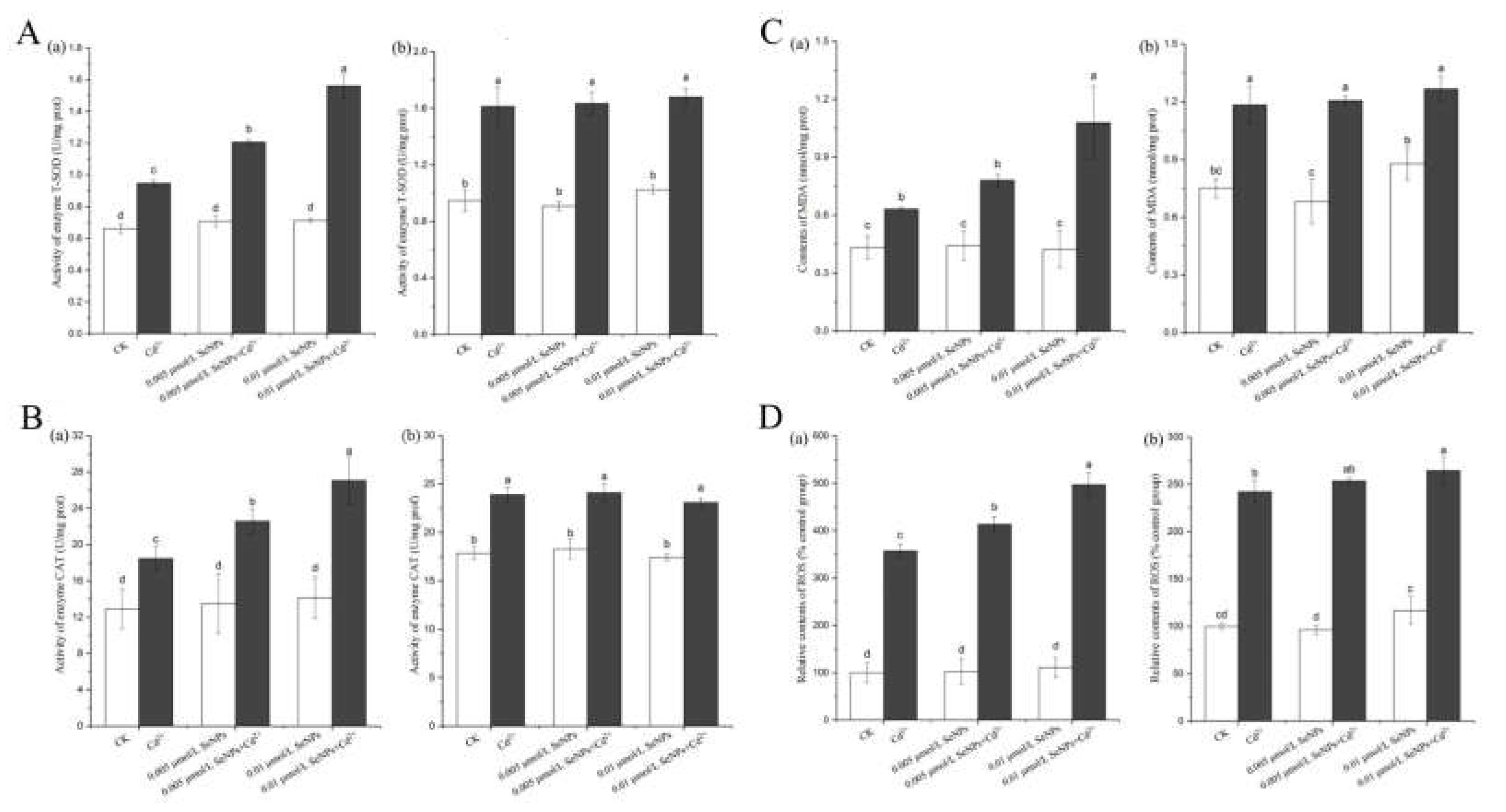
Figure 4A (a) shows the T-SOD activity of CC125. There is no significant difference between the CK and SeNPs groups, and the two concentrations in SeNPs+Cd
2+ group are significantly increased compared with CK and Cd
2+ groups. Compared with CK group, SeNPs+Cd
2+ in 0.01 μmol/L group was nearly doubled. The reason may be that SeNPs+Cd
2+ increased the content of superoxide anion radical in the cells, and promoted the production of a large amount of superoxide dismutase in the enzyme system in order to maintain the intracellular balance, indicating that the addition of SeNPs and Cd
2+ at the same time had a greater toxic effect on CC125 algae cells.
Figure 4A (b) shows the T-SOD activity of CC400. There is no significant difference in T-SOD activity between CK and SeNPs groups at 0.005 μmol/L concentration, but it is slightly higher in 0.01 μmmol/L SeNPs group. The activity of T-SOD in Cd
2+ and SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups was significantly increased compared with that in CK group, while there was no significant difference between the two concentrations in SeNPs+Cd
2+ and Cd
2+ groups. These results indicated that although Cd
2+ was toxic, but the simultaneous addition of SeNPs and Cd
2+ did not produce more toxic effects on CC400 algal cells.
Figure 4B (a) shows the CAT enzyme activity of CC125. There is no significant difference between the CK and SeNPs groups, and the two concentrations of SeNPs+Cd
2+ group are significantly increased compared with CK and Cd
2+ groups. The activity of CAT enzyme in 0.01 μmol/L SeNPs+Cd
2+ group was about twice that in CK group. When SeNPs and Cd
2+ were added at the same time, the external stress increased the hydrogen peroxide in CC125 cells and promoted the activity of CAT enzyme, thus reducing the formation of oxygen free radicals and reducing the toxic effect. These results indicated that the simultaneous addition of SeNPs and Cd
2+ destroyed the homeostasis of the body cells, resulting in a certain degree of cell damage.
Figure 4B (b) shows the CAT enzyme activity of CC400. There is no significant difference in CAT enzyme activity between CK group and 0.005μmol /L SeNPs group, while catalase is slightly increased in 0.01 μmol/L SeNPs+Cd
2+ group, but there is no significant difference among the three groups. Therefore, it cannot be inferred that SeNPs increase Cd
2+ toxicity in CC400.
Figure 4C (a) shows the MDA content of CC125. There is no significant difference in MDA content between CK group and SeNPs group. 0.005μmol/L and 0.01 μmol/L SeNPs alone do not produce toxicity. MDA content in SeNPs+Cd
2+ group was significantly increased compared with CK and Cd
2+ groups. The results indicated that the simultaneous addition of SeNPs and Cd
2+ had a significant toxic effect on CC125 algal cells. The addition of SeNPs and Cd
2+ at the same time produced significant toxic effects on CC125 algal cells resulting in the increase of oxygen free radicals. Lipid peroxidation occurs between oxidizing free radicals and polyunsaturated fatty acids in biofilms, resulting in the increase of lipid peroxides.
Figure 4C (b) shows the MDA content of CC400, and there is no significant difference between the CK group and the three SeNPs groups. Compared with CK group, MDA contents in Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group were significantly increased, but there was no significant difference between the two concentrations in SeNPs+Cd
2+ group and Cd
2+ group.
Figure. 4D (a) shows the relative ROS content of CC125. There is no significant difference between the ROS relative content of CK group and that of SeNPs group, and the two concentrations of SeNPs+Cd
2+ group have extremely significant increases compared with CK group and Cd
2+ group. It may be due to the toxic effects of SeNPs+Cd
2+ that lead to the destruction of the defense enzyme system in
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. Excessive oxygen free radicals cannot be removed in time in the cell, which breaks the ROS balance. Electron transfer in the photosynthetic system or respiratory system is blocked, and electrons are transferred to molecular oxygen O2 to form O2-, thus leading to ROS increase.
Figure 4D (b) shows the ROS relative content of CC400. The ROS relative content of Cd
2+ and SeNPs+Cd
2+groups is significantly increased compared with that of CK group, while the ROS relative content of 0.005μmol /L between CK and SeNPs groups has no significant difference.
3.4. Effects of SeNPs on Photosynthetic System and Intracellular Cadmium Content of Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii under Cadmium Stress
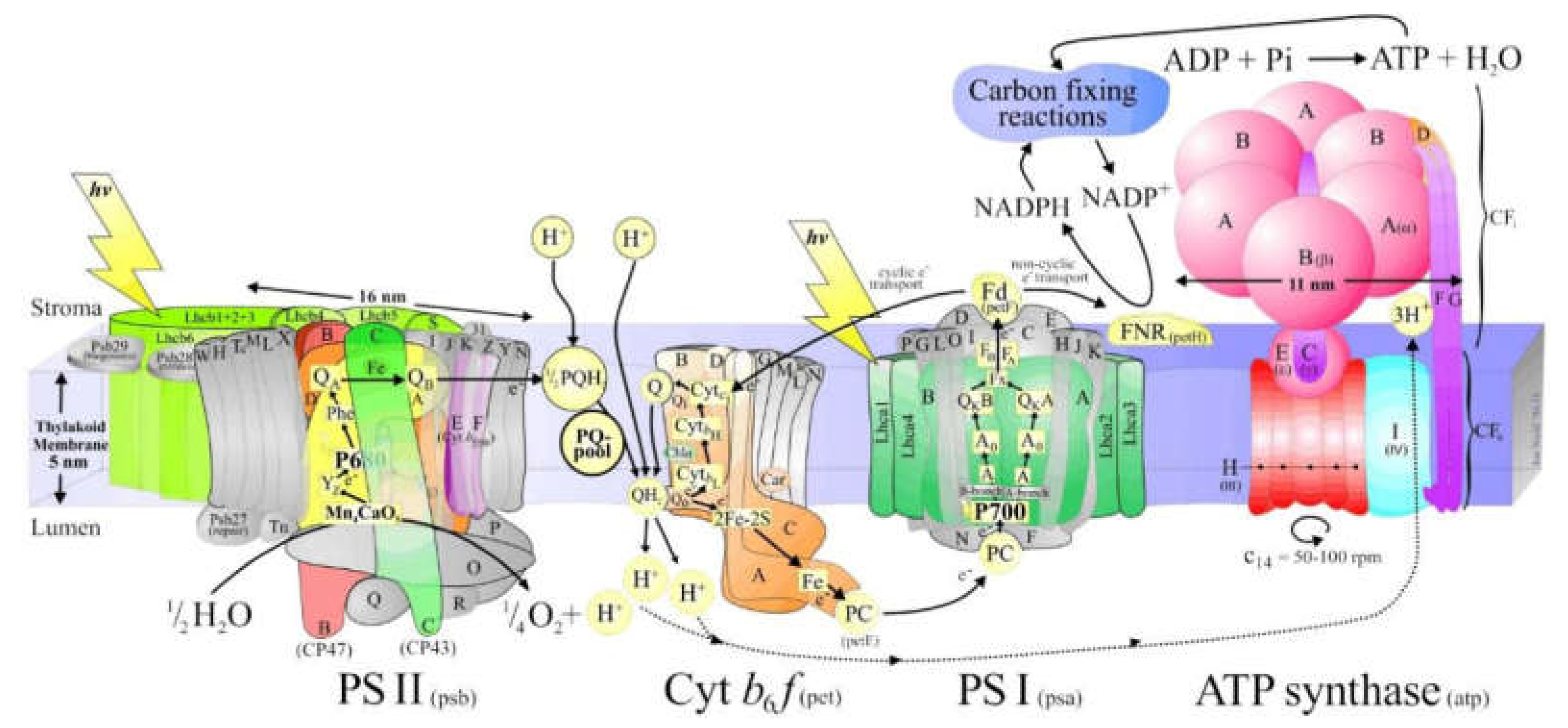
Photosynthesis is a unique physiological function of plants. It is the process of converting solar energy into chemical energy on the largest scale on Earth, synthesizing inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide and water into organic matter while releasing oxygen. Chloroplasts are the organelles that carry out the core reactions of photosynthesis. The basic processes of energy conversion and carbon assimilation in photosynthesis are carried out in chlorophylls. The thylakoid membrane is a lipid bilayer membrane required for energy conversion in photosynthesis. It contains the pigment protein and enzyme system necessary for capturing light and converting light energy into chemical energy in photosynthesis. Many different complexes are involved in the photosynthesis process, most of which are embedded in the thylakoid membrane, and four membrane-bound supramolecular complexes are directly involved in photosynthesis: photosystem I (PSI), photosystem II (PS II), ATP synthase complex, and cytochromatin b6f complex (Cyt b6f) [
46]. The structure of PSI and PSII are as
Figure 5 shows.
The PSI complex consists of photoreaction center pigment (P700), light trapping complex (LHC I), and electron acceptor, and its function is to transfer electrons from Plastocyanin (PC) to Ferredoxin (Fd). When the pigment molecules in the reaction center of PSI absorb light energy and are excited, they transfer electrons to various electron acceptors, and by Fd, NADP+ is reduced to NADPH with the participation of NADP reductase. NADPH participates in the dark reaction stage of photosynthesis and carries out solid carbonization reaction. Specific transmission route: LHCI transfers the absorbed light energy to P700→ primary electron acceptor A0 (Chla)→ primary electron acceptor A1 (possibly folloquinone VK1)→ iron-sulfur center (Fx→FA→FB)→ ferredodoredoin Fd.
PSII contains the PSII reaction center (PSII), light-harvesting complex II (LHCII), and oxygen-evolving complex (OEC). Its function is to use the energy absorbed from light to split water and transfer its released electrons to plastiquinone, while establishing an H+ proton gradient on both sides of the thylakoid membrane through oxidation of water and reduction of PQB2-. PSII transfers the light energy absorbed by LCHII to the PSII reaction center complex, causing it to produce a high-energy electron, which is passed to the primary electron acceptor. This process creates a positively charged donor (P680+) and a negatively charged primary electron acceptor (Pheo-). P680+ can be used as an oxidizing agent to trigger the photolysis of water, resulting in the transfer of electrons released by water oxidation to PSII. Pheo- can be used as a reducing agent to lose an electron, causing electron transfer to QA and QB[
47].
The light reaction takes place on the chloroplast thylakoid membrane. The electrons produced by cracking water molecules in the oxygen-releasing complex pass through PSII, Cyt b6f, and PSI, and are finally transferred to nicotinamide adenine dinucleoside phosphate (NADP) to form NADPH. The transmembrane proton gradient generated during this process drives ATP synthase to form ATP. Such electron transport flow is called linear electron flow, and the ATP formation process coupled with it is called non-cyclic photophosphorylation (NCPSP). If the electron is not transferred to NADP after PPI, but is returned to PSI via Cyt b6f or plastoquinone (PQ), only a transmembrane proton gradient is formed during the transfer process, and ATP is synthesized. Such electron transport around PSI is called cyclic electron flow (CEF), and the ATP synthesis process coupled with CEF is called cyclic photophosphorylation (CPSP)[
48].
So, as all above, photosynthesis involves multiple electron transfers and energy conversion, so it is crucial for cell growth in autotrophs, especially algae cells.
According to the change of chlorophyll fluorescence intensity caused by the effect of SeNPs on the toxicity of cadmium-induced
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, rapid fluorescence kinetic analysis was carried out to obtain the OJIP kinetic curve and QA-reoxidation kinetic curve. OJIP-test was analyzed and relevant photosynthetic parameters were deduced, so as to determine the changes in the donor side, recipient side and reaction center of PSII under the conditions of SeNPs and cadmium treatment[
49], and thus the influence on the photosynthetic system of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was known. The toxicity mechanism of heavy metals to algae is mainly the destruction of cell membrane and the damage of antioxidant enzyme system of algae, and algae have a certain biological accumulation of heavy metals[
50]. The possible mechanism of SeNPs enhancing Cd
2+ toxicity could be further determined by the determination of cadmium and selenium contents in algal cells.
When plants or parts of tissues with photosynthetic organs transfer from dark conditions to visible light, the green tissues of plants emit a dark red fluorescence with ever-changing intensity, which increases with the change of time, rises to a maximum value, then declines, and finally reaches a stable value. This phenomenon is known as chlorophyll fluorescence induction phenomenon, also known as Kautsky effect[
51]. The curve of fluorescence over time is called chlorophyll fluorescence induced kinetic curve. Generally, the lowest fluorescence measured just after exposure to light is O point, and the maximum fluorescence is defined as P point. The fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetics curve refers to the fluorescence change process of plant leaves or cells from O point to P point under different measured light irradiation[
52]. It mainly reflects the changes of the primary photochemical reaction of PSII, the structure and state of photosynthetic apparatus, etc. The descending stage mainly reflects the changes of photosynthetic carbon metabolism, and the fluorescence intensity gradually decreases with the increase of photosynthetic carbon metabolism rate[
53]. Typical fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetics curves generally include phases such as O-J-I-P, which records the whole process from initial fluorescence (F0) to maximum fluorescence (Fp or Fm)[
54].
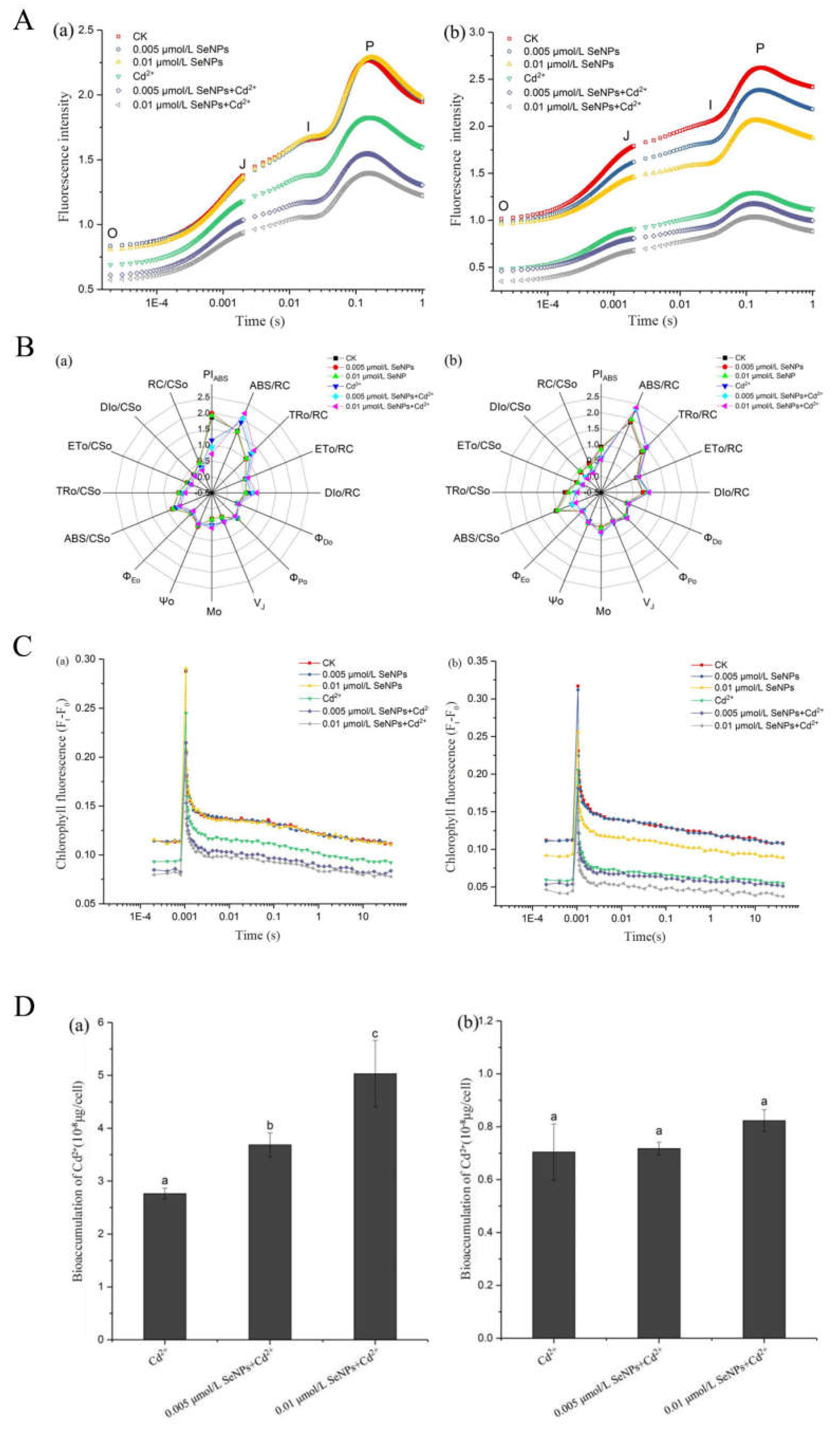
After being treated with SeNPs and Cd
2+ at different concentrations for 72 h, the OJIP test was carried out (Fig.6A). As can be seen from the curve in
Figure 6A (a), the curve of CK group and SeNPs group in CC125 increased significantly, and FJ, FI and FM were higher than those in Cd
2+ and SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups, indicating that Cd
2+ and SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups had an inhibitory effect on PSII activity of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Among them, there was no significant difference between the two concentrations of SeNPs group and CK group, while the addition of Cd
2+ reduced the fluorescence intensity successively, and there was no significant difference between CK group and SeNPs groups, indicating that under the SeNPs concentration that had no effect on
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, after the addition of Cd
2+, the inhibitory effect of cadmium on PSII activity of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was enhanced in different degrees, and the trend was concentration dependent. As can be seen from the curve in
Figure 6A (b), the curve of CK group and SeNPs group increased significantly in CC400, among which the CK group was the highest and the two groups 0.005 and 0.01 μmol/L decreased successively, indicating that the PSII activity of SeNPs groups were slightly inhibited compared with CK group. Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups were significantly lower than CK group and SeNPs groups, but the difference between groups was not significant. The results indicated that Cd
2+ and SeNPs+Cd
2+ groups inhibited the PSII activity of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, but the addition of SeNPs could not enhance the inhibitory effect of Cd
2+.
A large amount of original data can be obtained from the chlorophyll fluorescence induction curve, including a large amount of information about the primary photochemical reaction of the PSII reaction center. By analyzing the data according to parameters related to the chlorophyll fluorescence induction curve, it can be known that the structure and function of the plant photosynthetic system are affected under external stress conditions[
55,
56]. PIABS is a performance index of light energy absorption, which can comprehensively reflect the electron transport efficiency of the acceptor side, the number of active reaction centers and the maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII, and can more accurately reflect the influence of stress on the state and functional activity of PSII [
57,
58]. As shown in Fig.6B (a), PIABS values in Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group of CC125 were significantly lower than those in CK and SeNPs groups, indicating that the presence of Cd
2+ had a strong toxic effect on PSII, and the addition of SeNPs at the same time would promote this effect. In Fig.6B (b), the CK group and SeNPs group of CC400 were different from the Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group, and there was no significant difference within the groups, indicating that the concurrent addition of SeNPs would not promote the toxic effect of Cd
2+ on PSII. Mo reflects the maximum rate at which QA is reduced and reflects the changes on the receptor side of PSII reaction center [
59,
60]. When the downward electron transfer rate of QA- decreases, the reduction rate of QA is accelerated, so Mo correspondingly increases, that is, the increase of Mo indicates that the downward electron transfer of QA- is inhibited [
61]. In Fig. 6B (a), Mo values of CC125 in Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+group were slightly higher than those in CK and SeNPs groups, indicating that electron transport in Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group was inhibited to a certain extent, but the difference was not significant. In Fig 6B (b), CC400 is similar to CC125. VJ reflects the openness of the reaction center, that is, the amount of QA- accumulation. The increase of VJ indicates that the amount of QA- accumulation in the photosynthetic electron transport chain increases, while the relative electron transport capacity of PSII decreases. In
Figure 6B (a), the VJ values of CC125 in Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group were slightly higher than that in CK and SeNPs groups, indicating that the relative electron transport capacity of PSII in Cd
2+ group and SeNPs+Cd
2+ group were lower, and the difference was not significant. In
Figure 6B (b), there is no significant difference between the groups of CC400, indicating that the QA-to-QB electron transfer of CC400 is not affected by Cd
2+ and SeNPs. ABS/RC, TRo/RC, ETo/RC and DIo/RC respectively reflect the light energy absorbed by unit reaction center, the energy captured by unit reaction center for reducing QA, the energy captured by unit reaction center for electron transfer and the energy dissipated by unit reaction center. The difference in these values was not significant between the two algal cells.
QA-reoxidation kinetics was used to further investigate the effect of SeNPs and Cd2+ treatments at different concentrations on the PSII accepter side electron transport efficiency of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In Fig 6C (a), there was no significant difference between CK group and SeNPs group in CC125, while the Cd2+ group and SeNPs+Cd2+ group decreased successively. These results indicated that Cd2+ group and SeNPs+Cd2+ group improved the sensitivity of electron acceptor side of PSII and inhibited the reoxidation process of QA-. In Fig. 6C (b), there was no significant difference between CK group and SeNPs group in CC400 at 0.005 μmol/L, but the 0.01 μmol/L in SeNPs group was slightly decreased, indicating that the reoxidation process of QA- was also inhibited at 0.01 μmol/L. There was no significant difference between the Cd2+ group and SeNPs+Cd2+ group at 0.005 μmol/L, but the SeNPs+Cd2+ group at 0.01 μmol/L was lower.
Figure 6D shows the effect of SeNPs on the intracellular Cd content of
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Fig.6D(a) shows the intracellular cadmium content of CC125 under conditions of Cd
2+, 0.005 μmol/LSeNPs+Cd
2+, and 0.01 μmol/LSeNPs+Cd
2+. It can be seen that, compared with the Cd
2+ group, the addition of SeNPs increased the intracellular Cd
2+ content, and the difference was significant, and showed a concentration dependent trend with the increase of SeNPs concentration.
Figure 6D(b) shows the determination result of cadmium content in CC400 algae cells. Different from the results of CC125, the intracellular Cd
2+ content of CC400 algae was not significantly increased due to the presence of SeNPs, and there was no significant difference in Cd
2+ content among the three groups.
The SeNPs concentrations in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii culture are about 0.395µg/L and 0.79µg/L. Because the concentration is too low and is too close to the detection limit of the instrument, the error of the measurement results is large, and the trend is covered up. Therefore, the results of the determination of the intracellular selenium content by ICP-MS cannot be trusted.