Submitted:
19 September 2024
Posted:
20 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
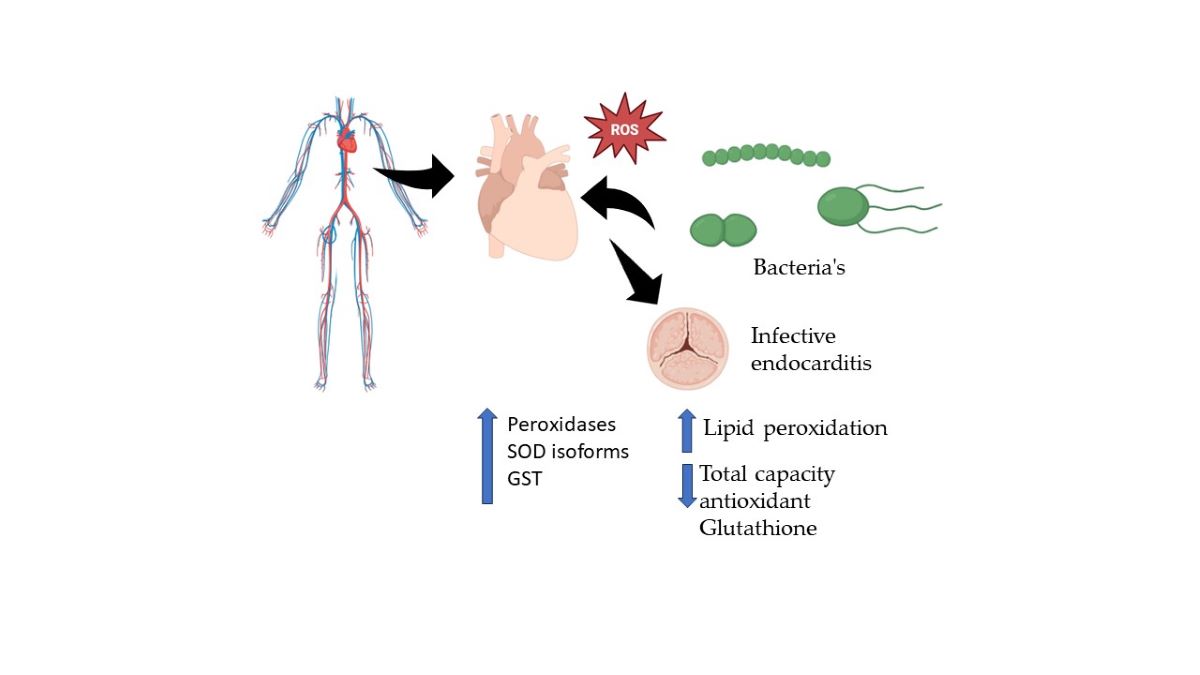
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruited Patients with IE and Control Subjects
2.2. Echocardiographic Study
2.3. Cardiac Valve Homogenization
2.4. Determination of the Malondialdehyde
2.5. Evaluation of Total Antioxidant Capacity
2.6. Carbonylation
2.7. GSH and thiols.
2.8. NO3−/NO2− Ratio Determination.
2.9. Determinations of Antioxidant Enzymes That Employ GSH
2.1. Determinations of Super Oxide Dismutase Isoforms and Peroxidases Activities
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics the Cases and Controls
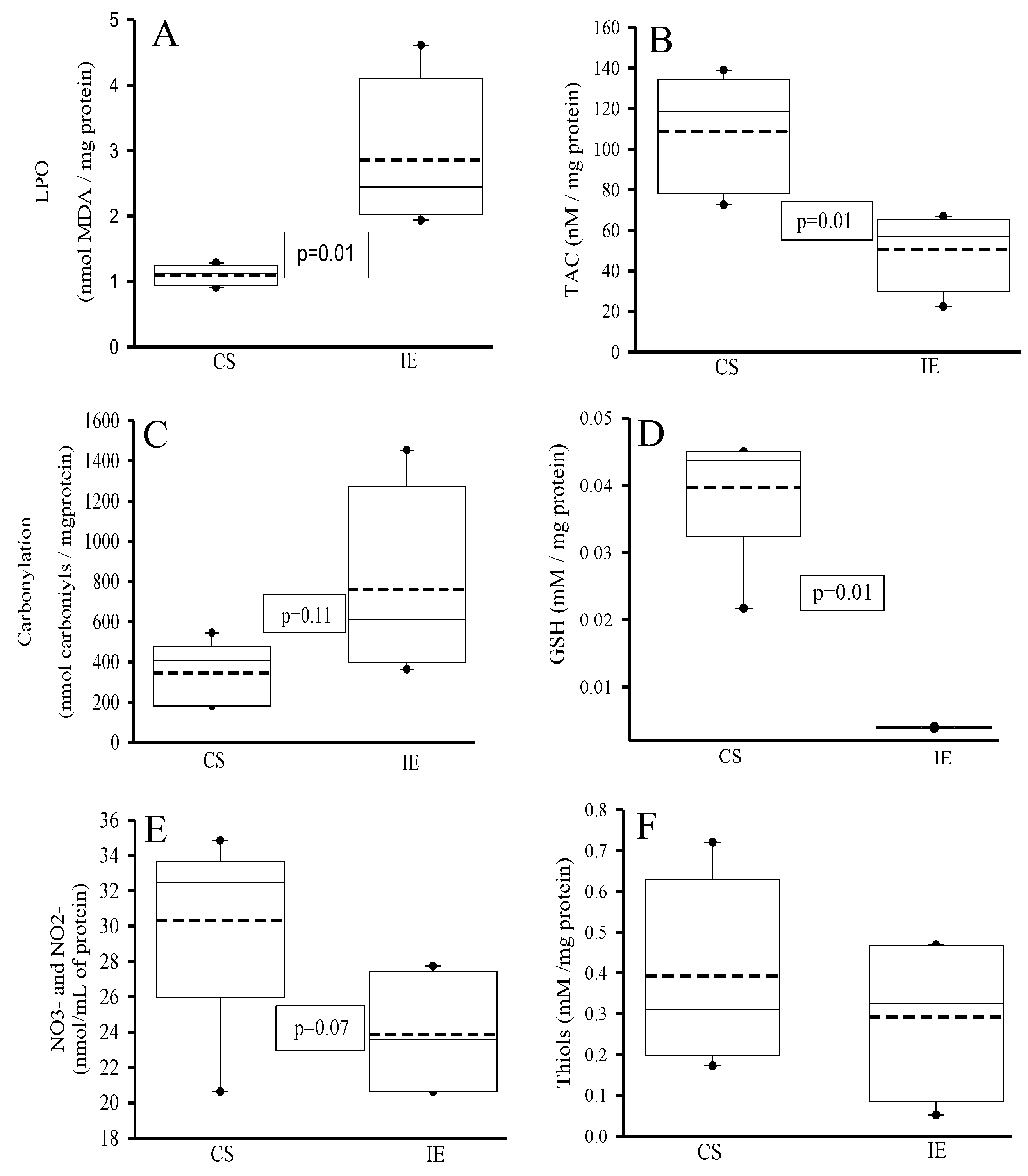
3.2. Oxidative Markers
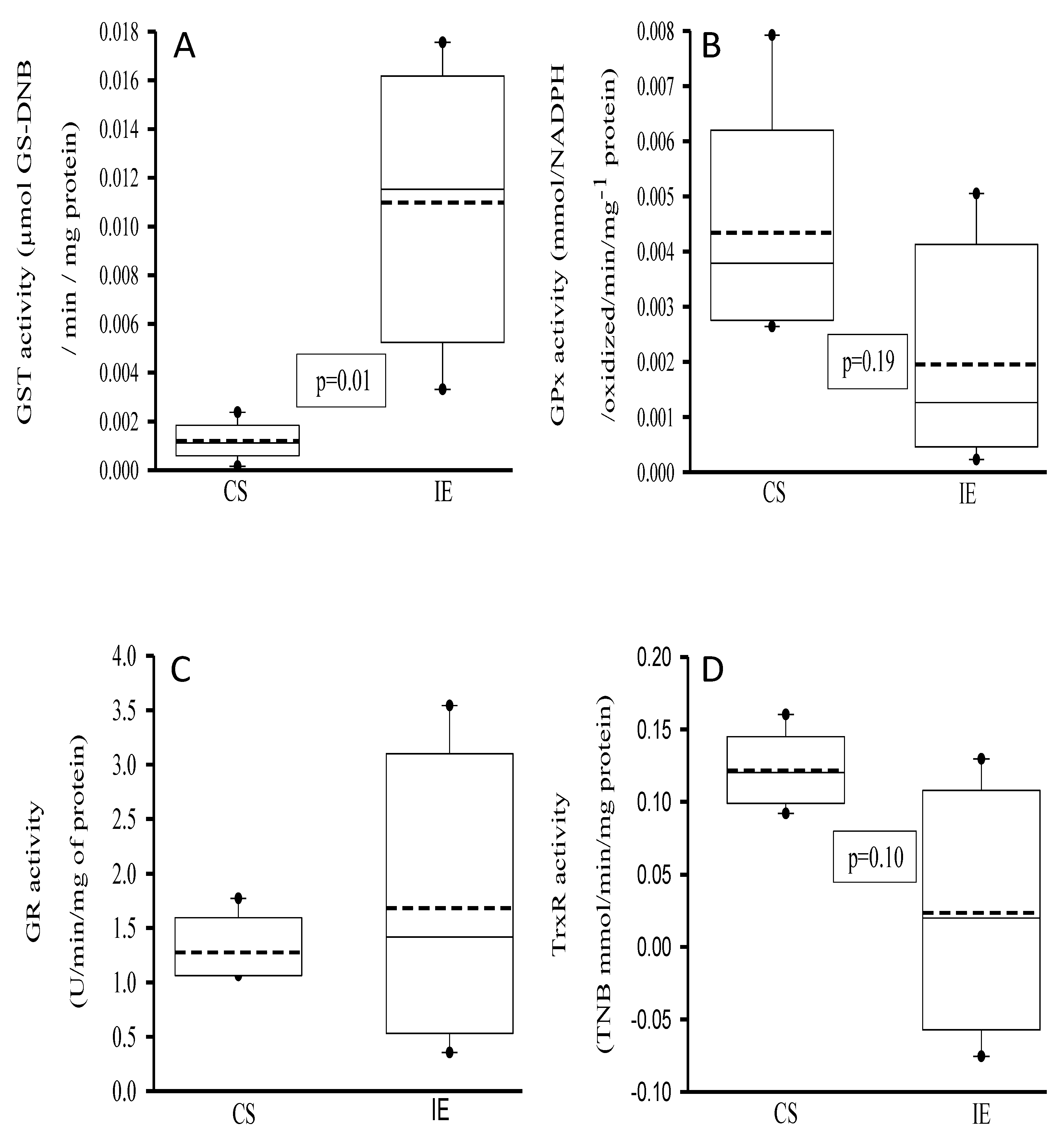
3.3. Activities of the Antioxidant Enzymes That Employ the Glutathione
3.4. Peroxidases and SOD Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alifragki, A.; Kontogianni, A.; Protopapa, I.; Baliou, S.; Ioannou, P. Infective Endocarditis by Pasteurella Species: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 50372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Østergaard, L.; Lauridsen, T.K.; Iversen, K.; Bundgaard, H.; Søndergaard, L.; Ihlemann, N.; Moser, C.; Fosbøl, E. Infective endocarditis in patients who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veve, M.P.; McCurry, E.D.; Cooksey, G.E.; Shorman, M.A. Epidemiología y resultados de la endocarditis infecciosa no relacionada con HACEK en el sureste de los Estados Unidos. PLoS. ONE. 2020, 15, e0230199. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, L.L.; Otto, C.M. Infective Endocarditis: Update on Epidemiology, Outcomes, and Management. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, H.; Kinugawa, S.; Matsushima, S. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in myocardial remodelling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 81, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, S.; Kasielski, M.; Kordiak, J.; Zwolinska, A.; Wlodarczyk, A.; Nowak, D. Myocardial oxidative stress in patients with active infective endocarditis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Kinugawa, S.; Suematsu, N.; Hayashidani, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Utsumi, H.; Machida, Y.; Egashira, K. Takeshita, A. Direct evidence for increased hydroxyl radicals originating from superoxide in the failing myocardium. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, T.; Chen, L.; Zhan, J.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Z. The global, regional, and national burden and trends of infective endocarditis from 1990 to 2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 774224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, M.A.; Delgado, V. The 'Ten Commandments' for the 2023 European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart. J. 2024, 45, 1697–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, A.J.K.; Herbst, P.G.; Pienaar, C.; Taljaard, J.; Prozesky, H.; Janson, J.; Doubell, A.F. Modified Duke/European Society of Cardiology 2015 clinical criteria for infective endocarditis: time for an update? Open. Heart. 2022, 9, e001856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.E.; Pérez-Torres, I.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Soria-Castro, E.; Morales-Marín, A.; Ramírez-Marroquín, E.S.; Martínez-Hernández, H.; Herrera-Alarcón, V.; Guarner-Lans, V. Reduced levels of selenium and thioredoxin reductase in the thoracic aorta could contribute to aneurysm formation in patients with Marfan syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarría, A.P.; Vázquez, R.R.V.; Cherit, J.G.D.; Bello, H.H.; Suastegui, H.C.; Moreno-Castañeda, L.; Estrada, A.G.; Hernández, F.; González-Marcos, O.; Saucedo-Orozco, H.; et al. Antioxidants and pentoxifylline as coadjuvant measures to standard therapy to improve prognosis of patients with pneumonia by COVID-19. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erel, O.; Neşelioğlu, S.; Tunçay, M.E.; Oğuz, E.F.; Eren, F.; Akkuş, M.S.; Güner, H.R.; Ateş, İ. A sensitive indicator for the severity of COVID-19: Thiol. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.E.; Manzano-Pech, L.G.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Díaz-Galindo, J.A.; Vásquez, X.; Castrejón-Tellez, V.; Gamboa, R.; Huesca, C.; Fuentevilla-Alvárez, G.; Pérez-Torres, I. Oxidant/Antioxidant Profile in the Thoracic Aneurysm of Patients with the Loeys-Dietz Syndrome. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 5392454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Venegas, G.; Fernández-Rojas, B.; Rosas-Martínez, M.; Manuel Alejandro Sánchez-Carballido, M.A. Rutin prevents LTA induced oxidative changes in H9c2 cells. Prev. Nutr. Food. Sci. 2020, 25, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cheng, G. Recombinant myeloperoxidase as a new class of antimicrobial agents. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0052221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauseef, W.M. Biological roles for the NOX family NADPH oxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16961–16965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville, M.J.; Kovalyova, Y.; Mejías-Luque, R.; Gerhard, M.; Hatzios, S.K. Isotope tracing reveals bacterial catabolism of host-derived glutathione during Helicobacter pylori infection. PLoS. Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Galiniak, S.; Bartosz, G.; Rachel, M. Oxidative modification of proteins in pediatric cystic fibrosis with bacterial infections. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 389629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, C.; Ernst, D.; Falke, M.; Speicher, P.; Ziaka, M. Systemic embolization due to non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis: An autopsy case report and mini review of the literature. SAGE. Open. Med. Case. Rep. 2024, 12, 2050313X241229576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, I.; Sinha, R.; Kumar, P. ; Schaf B, Berkowitz L: A 'Decrescendo' in a woman with ascending paralysis: A diagnostic challenge. Cureus. 2024, 16, e59479. [Google Scholar]
- Adedoyin, F.T.; Sridhar, B.B.M.; Rosenzweig, J.A. Impact of metal exposure on environmentally isolated Serratia marcescens' growth, oxidative-stress resistance, biofilm formation, and proliferation in eukaryotic co-culture models. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ried, I.D.; Omran, H.; Potratz, M.; Rudolph, T.K.; Scholtz, S.; Bleiziffer, S.; Piper, C. Infective endocarditis after isolated aortic valve replacement: comparison between catheter-interventional and surgical valve replacement. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2024, 113, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrucci, F.; Bacchi, B.; Codecasa, R.; Stefàno, P. Case report: Infective endocarditis after transcatheter aortic valve implantation surgically treated with sutureless prosthesis and ascending aorta replacement. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1194304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.F.; Levy, J.M.; Hong, R.; Viseskul, C.; Henshaw, C. Takayasu's arteriopathy with involvement of aortic valve and bacterial endocarditis. J. Pediatr. 1973, 83, 463–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcelik, A.; Karacay, S.; Hakyemez, I.N.; Akin, B.; Ozturk, S.; Savli, H. Takayasu arteritis initially mimicking infective endocarditis. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3, e2011040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Ren, L.; Nappi, F.; Ma, X.; Jiang, Y.; Han, S. Postoperative follow-up of 221 patients with infective endocarditis from Gaoligong mountain area of Yunnan in China: a retrospective, single-center, observational cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 3325–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G. Infective endocarditis after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: the worst that can happen. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2018, 7, e010287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone-Marsan, N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, K.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Casell, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Ederhy, S.; Erb, P.A.; Foldager, D.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart. J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar]
- Yumoto, T.; Ichiba, S.; Umei, N.; Morisada, S.; Tsukahara, K.; Sato, K.; Ujike, Y. Septic shock due to Aeromonas hydrophila bacteremia in a patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis: a case report. J. Med. Case. Rep. 2014, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouqui P, Raoult D: Endocarditis due to rare and fastidious bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 177–207. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benic, C.; Nicol, P.P.; Hannachi, S.; Gilard, M.; Didier, R.; Nasr, B. Vascular complications following transcatheter aortic valve implantation, using MANTA (Collagen Plug-Based) versus PROSTAR (Suture-Based), from a French single-center retrospective registry. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.; Dunn, L. The declaration of Helsinki on medical research involving human subjects: A review of seventh revision. J. Nepal. Health. Res. Counc. 2020, 7, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M. Buenas prácticas clínicas (BPC ICH) de la conferencia internacional de armonización. https://codigof.mx/buenas-practicas-clinicas-bpc-ich-de-la-conferencia-internacional-de armonizacion, 2017, 1–61.
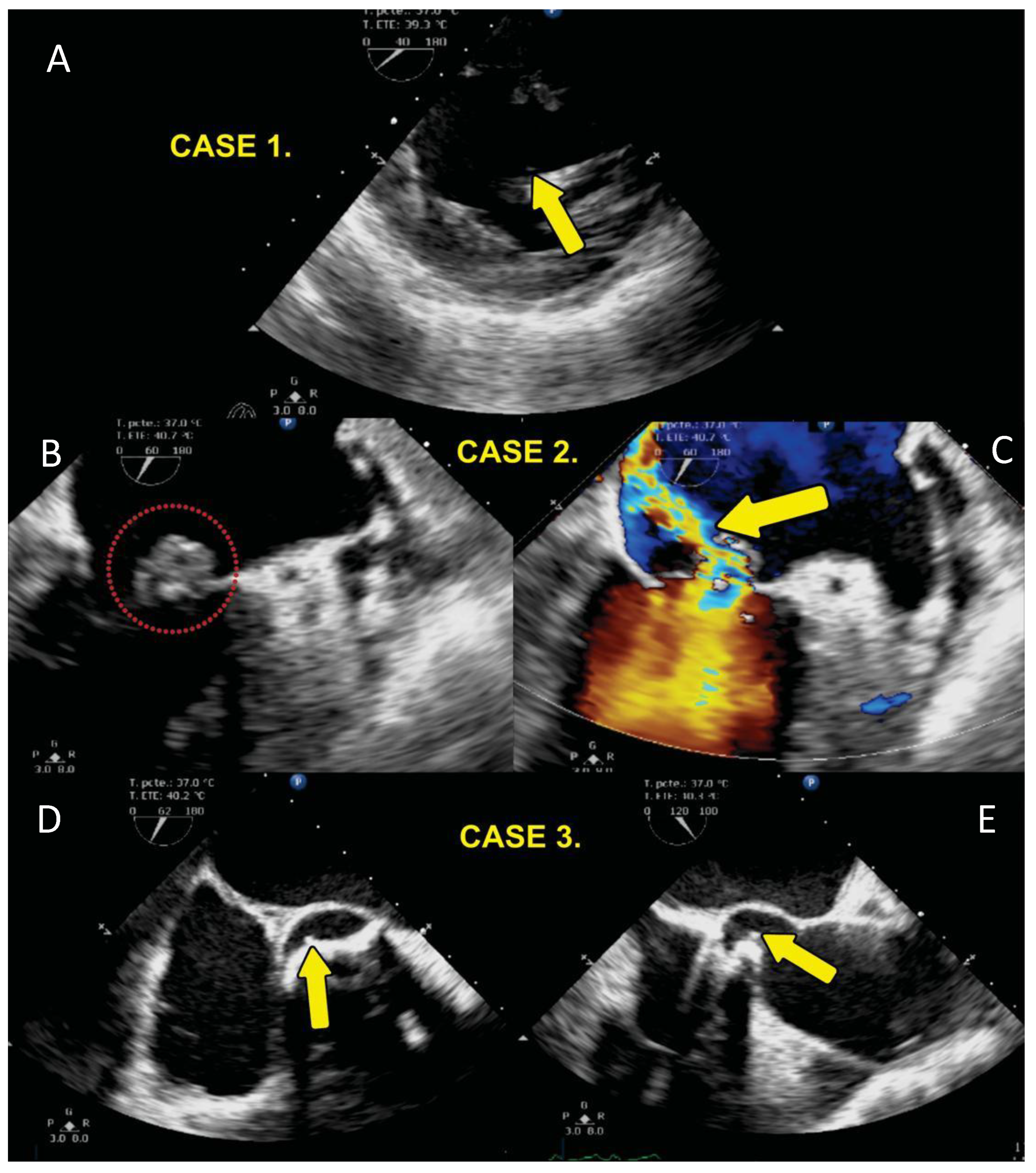

| Endocarditis | Control Subjects | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 70 (64-83) | 65 (43-67) |
| Body Mass Index | 22 (20-25) | 29 (28-33) |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1 (33) | 1 (33) |
| Systemic Arterial Hypertension | 2 (66) | 2 (66) |
| Dyslipidemia | 1 (33) | 1 (33) |
| Smoking | 2 (66) | 2 (66) |
| Laboratories | ||
| Glucose | 119 (85-131) | 115(109-164) |
| Creatinine | 0.81 (0.7-1.5) | 1.4 (0.98-1.7) |
| Blood urea nitrogen | 30 (22-41) | 18 (15-23) |
| Uric acid | 6.7 (3.8-7) | 9.8 (5.3-10.1) |
| Natriuretic peptide NT-Pro-BNP | 7339 (1971-22494) | 200 (170-278) |
| Hemoglobin | 11.8 (11.1-14.7) | 14.4 (13.5-15.9) |
| Platelets | 172 (152-200) | 160 (91-230) |
| Leukocytes | 8.4 (5.6-16.1) | 8 (6.5-10) |
| Lymphocytes | 1.1 (1-8.7) | 2.5 (1.2-2.7) |
| Neutrophils | 6.6 (4.5-13.9) | 6.1 (3.1-7) |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate mm/ | 30 (27-43) | 18 (16-32) |
| C-reactive protein mg/L | 47.5 (40-200) | 2.5 (0.7-6.9) |
| Total cholesterol | 173 (138-325) | 112 (108-186) |
| High Density Lipoprotein | 53.4 (45.5-53.8) | 44 (28.5-44.5) |
| Low Density Lipoprotein | 98 (92-196) | 122 (101-125) |
| Triglycerides | 131 (130-211) | 2123 (70-221) |
| Aorta diameters | ||
| Aortic valve plane | 29 (20-38) | 26 (22-27) |
| Sinus of Valsalva | 37 (20-40) | 28 (21-58) |
| Sino tubular junction | 38 (18-40) | 27 (21-58) |
| Ascending aorta | 37 (16-39) | 30 (20-37) |
| Ejection fraction of the left ventricle | 20 (20-45) | 44 (30-65) |
| Case | Age | G | BMI | Diagnosis | Evolution | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 55 | F | 20 | 2009 diagnosis of Arteritis de Takayasu plus bicuspid aortic valve SAH 1999 AVR by severe AoI (Medtronic Hall). | Endocarditis in 2016. univalve prosthetic valve with pannus and abscess with tissue destruction at level of interventricular septum with bacterial growth with Staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis. Surgery AVR and implantation of, dual-chamber pacemaker, by complete BAV, she had ischemic stroke and left hemiparesis with evolution with reduced heart failure LVEF 25% died in 2017 one year after surgery. | yes |
| 2 | 67 | M | 30 | 2019 DAoI and AoI severe bicuspid aortic valve LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction LVEF 20%, smoking. | 2020 native valve endocarditis with mobile vegetation of left non-coronary valve plus ascending aortic aneurysm, Surgery AVR Medtronic Hall with bacterial growth with Streptococcus viridansj. 2024 normal functioning prosthesis, LVEF 57%. | no |
| 3 | 78 | F | 24 | DAoI and stenosis Ao, tri-valve Aortic valve. 2019 March she received intervention with Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) Portico 25 mm plus Boston Scientific DDD Pacemaker Tachycardia Bradycardia Syndrome Comorbidities: Smoking, systemic arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia. | 2019 April she had TAVI endocarditis with vegetation in the aortic valve. Mitroaortic junction abscess plus aortitis aortic wall abscess. Valve crop Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella Oxytocic She was treated with aortic valve explanation surgery, ascending aorta resection. Bentall and Bo, MVR Edwards Peri mount. Mitroaortic command surgery. 2024 she is live LVEF 40%. | no |
| 4 | 60 | F | 30 | Ischemic heart disease, Tri valvular disease 2014 angioplasty in right coronary artery, 2017 aortic stenosis, AVR with mechanical prosthesis St Jude Masters HP 21, LVEF 52%. Comorbidities: Mellitus diabetes. | 2024 asymptomatic LVEF 58%. | no |
| 5 | 37 | M | 28 | 2018 Ascending aortic aneurysm aortic insufficiency, 4-cavity dilatation eccentric hypertrophy LV severe mild mitral insufficiency PAP 74 mmHg, Surgery AVR, DM, Systolic. arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperuricemia, positive smoking. LVEF 44%. | 2019 Gout, asymptomatic cardiovascular LVEF 50%, systolic dysfunction GLS 14.5. | no |
| 6 | 62 | M | 34 | Ventricular dysfunction, severe aortic and mitral insufficiency, generalized hypokinesia LVEF 30%. 2014 Surgery due to Aortic Dissection Stanford A, DeBakey 1 plus Severe tricuspid regurgitation and mechanical AVR St. Jude. SAH, Smoking. | 2017 Asymptomatic, controlled high blood pressure stopped coming since that date. | no |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





