1. Introduction
Salt and drought stress are among the major abiotic stresses that pose significant challenges to agricultural production, particularly when they occur simultaneously. Drought exacerbates the effects of salt stress, creating a compounded negative impact on crop growth and yield [
1]. Globally, over 800 million hectares of land are affected by salinity, especially in arid and semi-arid regions where limited water resources lead to the coexistence of salt and drought stresses, adversely impacting crop growth and productivity [
2,
3].
Rice (
Oryza sativa L.), one of the world's most important food crops, is moderately tolerant to salinity. Developing and cultivating salt-tolerant rice varieties is considered an effective approach to improve and utilize saline-alkali lands [
4]. However, rice grown in inland saline-alkali areas often faces the dual challenges of salt and drought stress, leading to stunted growth and reduced yields [
5]. Recent advancements in molecular biology and genetic engineering have significantly progressed our understanding of the physiological and molecular mechanisms underlying rice's responses to salt and drought stress.
This review summarizes the latest research progress on rice under salt and drought stress, focusing on key genes and molecular mechanisms and their applications in breeding practices. These research findings not only deepen our understanding of the stress resistance mechanisms in rice but also provide important theoretical foundations for breeding salt-tolerant and drought-resistant rice varieties.
2. Impact of Salt and Drought Stress on Rice
2.1. Effects on Morphology, Physiology, Biochemistry, and Yield
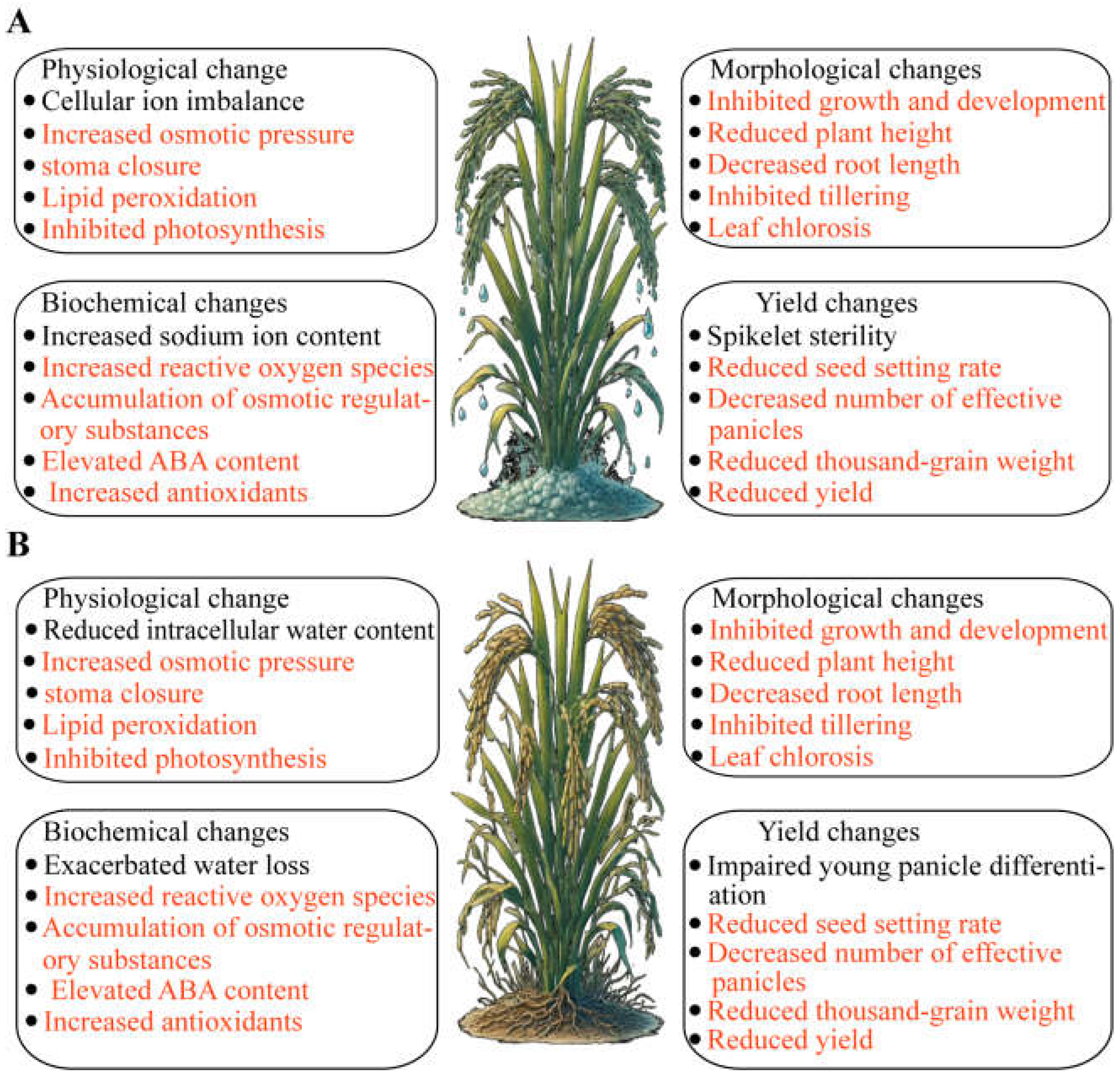
Salt and drought stress significantly affect the growth and development of rice (
Figure 1). Salt stress primarily influences plants through ionic toxicity and osmotic stress, leading to cellular ion imbalance and increased osmotic pressure, which in turn cause oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in membranes [
6]. Throughout the entire growth period of rice, salt stress hinders various stages of development. During the germination stage, salt stress inhibits seed germination. In the seedling stage, rice growth slows, leaves lose their green color, dry weight and fresh weight decrease, and survival rates drop. As rice enters the reproductive stage, salt stress more severely inhibits both the aerial and subterranean parts of the plant, resulting in reduced plant height, shorter root length, limited tillering, yellowing and wilting of leaves, and suppressed photosynthesis. Ultimately, these impacts lead to spikelet sterility, reduced fertility rates, fewer effective panicles, and lower thousand-grain weight, severely affecting yield [
7].
Physiologically and biochemically, salt stress triggers a series of complex responses, including ion imbalance, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, increased osmolyte levels, and hormonal changes. Salt stress raises the concentration of Na+ in cells, disrupting the normal function of K
+ and affecting cellular metabolism. It induces excessive ROS production, leading to oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, damaging cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. To cope with osmotic stress, rice accumulates significant amounts of proline, betaine, and soluble sugars, helping cells maintain osmotic balance. Simultaneously, salt stress significantly elevates abscisic acid (ABA) levels, regulating stomatal closure to reduce water transpiration and promoting root growth. Additionally, rice increases the levels of antioxidant enzymes (such as superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and catalase) and non-enzymatic antioxidants (such as ascorbic acid and glutathione) to remove excess ROS and mitigate oxidative damage [
7].
Drought stress primarily affects the water status and balance within plants, significantly impacting both the aerial and subterranean parts of rice. Under drought conditions, intracellular water content decreases, turgor pressure drops, causing wilting and slow growth. Under mild drought stress, rice adjusts the water potential inside and outside cells through osmotic regulation and increases cell wall elasticity to maintain normal root growth. However, under moderate to severe drought stress, lateral root growth is significantly inhibited, total root length decreases, and root development is severely affected, further exacerbating the negative impact of water deficiency on overall growth. Drought stress also noticeably affects the aerial parts of rice, significantly reducing plant height, leaf area, tiller number, and biomass. Leaves curl and yellow, photosynthetic capacity weakens, young panicle differentiation is hindered, fertility rates, effective panicle numbers, and thousand-grain weight decrease, ultimately leading to a significant decline in yield. Stomatal closure reduces stomatal conductance, thereby reducing transpiration to conserve water, but also limiting CO2 absorption, further inhibiting photosynthesis [
8].
On the physiological and biochemical level, drought stress induces a series of complex reactions. Firstly, stomatal conductance decreases, reducing water transpiration and CO2 absorption. Secondly, drought conditions lead to ROS accumulation, causing oxidative stress and damaging cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. To cope with drought stress, the levels of osmolytes such as proline, betaine, and soluble sugars in rice cells increase to maintain osmotic balance. Additionally, drought stress significantly elevates ABA levels, regulating stomatal closure and promoting root growth. The levels of antioxidant enzymes (such as superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and catalase) and non-enzymatic antioxidants (such as ascorbic acid and glutathione) also increase to remove excess ROS and mitigate oxidative damage [
9].
Both salt and drought stress significantly affect rice growth and development, primarily through impacts on water status, ion balance, and physiological and biochemical processes. Morphologically, both stresses lead to significant reductions in plant height, leaf area, tiller number, and biomass, with leaves wilting and yellowing. Physiologically and biochemically, both stresses reduce stomatal conductance, limiting water transpiration and CO2 absorption, affecting photosynthesis. Additionally, both stresses lead to ROS accumulation, inducing oxidative stress and damaging cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. To mitigate these stresses, rice accumulates osmolytes (such as proline, betaine, and soluble sugars) and increases the levels of antioxidant enzymes and non-enzymatic antioxidants, alleviating damage. Ultimately, these stresses result in reduced yield and quality of rice.
2.2. Impact on Rice Quality
When discussing the morphological, physiological, biochemical, and yield changes in rice under salt and drought stress, it is equally important to consider the changes in rice quality. Rice quality is influenced by multiple factors, including variety, climate change, irrigation conditions, and cultivation practices. These factors become more difficult to control under stress conditions, resulting in limited research on rice quality under stress conditions.
We particularly focus on the changes in nutritional composition of rice under salt stress. Saline-alkali soils are rich not only in Na
+ and Cl
- but also in Ca
2+, Mg
2+, and various trace elements such as Fe
2+, Mn
2+, Zn
2+, and Cu
2+. Does rice grown in saline-alkali soils accumulate more trace elements in the grains? Does such rice have higher nutritional value? These questions are worthy of in-depth research and discussion. Numerous studies have shown that rice under salt stress exhibits quality changes characterized by low starch, high protein, and multiple nutrient elements [
10,
11]. These changes provide new ideas for the development and utilization of saline-alkali land, such as breeding functional rice with high protein and multi-mineral nutrition as selling points, which is beneficial for market promotion and further advances related research.
Research on drought stress is mainly conducted under normal conditions, focusing on indicators such as chalkiness and brown rice rate. There is limited research on changes in the nutritional composition of rice under drought stress and even fewer studies on rice under combined salt and drought stress. Therefore, research in this area has significant scientific and practical value.
3. Mechanisms of Rice Responses to Salt and Drought Stress
Rice exhibits a series of typical response mechanisms under salt stress. Firstly, it eliminates or isolates toxic ions through ion balance systems such as the sodium-potassium pump, salt glands, and sodium transport proteins [
12]. Secondly, it maintains cellular osmotic pressure by accumulating osmolytes such as proline and betaine [
13]. Additionally, rice increases the levels of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT), as well as non-enzymatic antioxidants like ascorbic acid and glutathione, to remove reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protect cells from oxidative damage [
14]. Rice also enhances stress tolerance by activating transcription factors to regulate stress-responsive genes and through hormone regulation of growth and development. Under drought stress, rice exhibits similar osmotic regulation, antioxidant regulation, transcriptional regulation, and hormone regulation mechanisms as seen under salt stress, along with unique stomatal regulation (
Figure 2) [
15].
3.1. Synthesis and Accumulation of Osmolytes
To cope with osmotic stress, rice synthesizes and accumulates osmolytes such as proline, betaine, and soluble sugars under both salt and drought stress. These substances help maintain cellular osmotic balance and protect cell structures [
13]. For instance, the expression of
OsP5CS is induced by high salt and drought treatments. Under high salt conditions, salt-tolerant varieties express higher levels of
OsP5CS compared to salt-sensitive varieties, leading to more proline accumulation and enhanced stress tolerance [
16].
OsTPS1 is induced by drought, high salt, low temperature, and ABA treatments, increasing the contents of trehalose and proline and regulating stress-related gene expression to enhance rice's tolerance to abiotic stresses [
17].
3.2. Regulation of Ion Balance
Although drought stress does not directly involve salt ions, plants regulate ion balance to adapt to both stresses. Under salt stress, plants need to exclude excess Na+ while maintaining K
+/Na
+ balance. High-affinity potassium transporters (HKT) have been shown to be crucial for maintaining K
+/Na
+ homeostasis in rice under salt stress [
18]. The HKT gene family in rice includes
OsHKT1;5,
OsHKT2;1, and
OsHKT1;1, which are located in the vascular bundles, parenchyma cells around the xylem vessels, cortical and endodermal cells of the roots, and phloem of the leaves, respectively [
18,
19,
20]. These genes play essential roles in loading Na
+ into the xylem, loading Na
+ and K
+ into the phloem, and the long-distance transport of Na
+ and K
+. The transcription complex composed of
OsBAG4,
OsMYB106, and
OsSUVH7 regulates the expression of the key salt tolerance gene
OsHKT1;5 [
18]. The
OsPRR73 protein binds to the promoter of
OsHKT2;1, recruiting histone deacetylase HDAC10 to inhibit
OsHKT2;1 expression, thereby reducing Na+ uptake and avoiding excessive accumulation [
21].
OsMYBc positively regulates salt tolerance in rice by binding to the AAANATNC(C/T) sequence in the OsHKT1;1 promoter and upregulating its expression [
22].
Studies on HKT genes in other crops have shown that HKT also positively affects drought tolerance. For example, in Arabidopsis
hkt1-1 mutants, overexpression of sorghum
SbHKT1;4,
SbHKT1;5, and
SbHKT2;1 genes significantly enhances drought tolerance in transgenic plants [
23]. Maize
ZmHKT1 preferentially expresses in the root stele, altering the stele diameter to form thicker roots to cope with drought stress [
24].
3.3. Regulation of the Antioxidant System
ROS are highly reactive by-products of normal cellular metabolism that readily react with lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Both salt and drought stress elevate ROS levels, leading to oxidative damage and severely affecting plant growth and development [
25]. To prevent ROS accumulation, rice enhances the activity of the antioxidant system under these stresses, increasing the expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes (such as SOD, CAT, and APX) to remove ROS and protect cells from oxidative damage. The antioxidant system includes non-enzymatic components such as tocopherol, ascorbic acid, and glutathione, as well as enzymatic components including SOD, CAT, and enzymes of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle like APX, MDHAR, DHAR, and GSH [
26].
Numerous genes have been reported to be involved in the antioxidant system to cope with stress. For example,
OsDjC46 enhances rice's antioxidant defense capacity under drought and salt stress by regulating the expression and activity of SOD and CAT. Overexpression of
OsDjC46 increases tolerance to salinity and drought by enhancing SOD and CAT enzyme activities, while knockout lines are more sensitive to salt and drought stress with reduced SOD and CAT activities [
27].
OsCYBDOMG1 positively regulates rice's salt tolerance, plant growth, and grain yield by affecting ascorbic acid biosynthesis and redox state [
28]. OsRLCK5 interacts with rice glutaredoxin
GRX20, participating in the ascorbate-glutathione cycle to maintain protein stability and membrane integrity, enhancing rice's resistance to high levels of ROS [
29]. Through these complex physiological and molecular mechanisms, rice can maintain growth and productivity under salt and drought stress, demonstrating remarkable adaptability and stress tolerance.
4. Transcriptional Regulatory Networks
Recent genomic and transcriptomic studies have identified numerous key genes and regulatory networks associated with rice's salt and drought tolerance [
30,
31]. Under salt and drought stress, some identical or similar transcription factors (TFs), such as members of the DREB, NAC, and bZIP families, are activated. These TFs enhance the plant's stress adaptation by regulating the expression of downstream stress-responsive genes [
32].
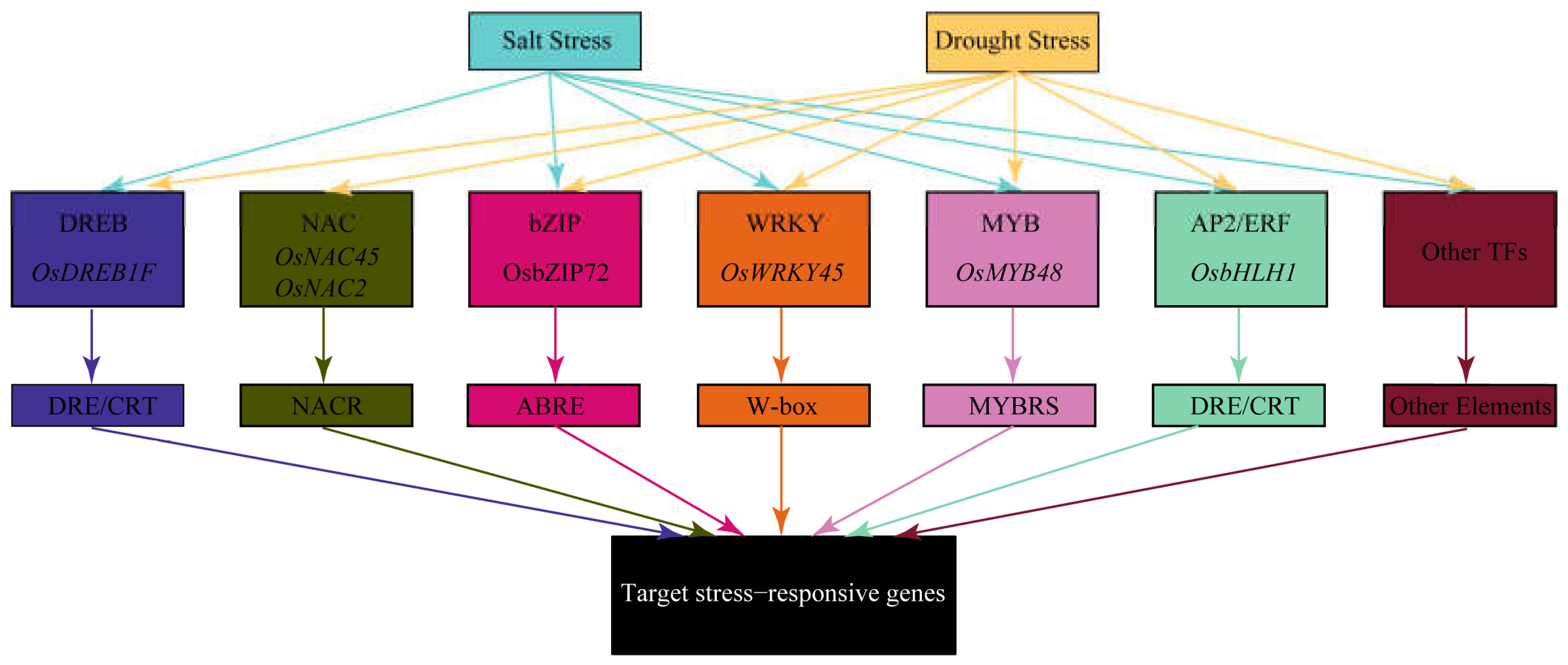
Figure 3.
Transcription Factor Network in Rice Responding to Salt and Drought Stress. This diagram illustrates the transcription factor regulatory network in rice under salt and drought stress conditions. It includes several key transcription factors such as DREB, NAC, bZIP, WRKY, MYB, AP2/ERF, and other transcription factors, along with their specific binding elements like DRE/CRT, NACR, ABRE, W-box, MYBRS, and others. These transcription factors regulate the expression of target stress-responsive genes through these binding elements, aiding the plant in coping with environmental stress. The arrows represent the regulatory relationships between different transcription factors and their impact on target genes, highlighting the complex gene regulatory networks involved in plant stress resistance.
Figure 3.
Transcription Factor Network in Rice Responding to Salt and Drought Stress. This diagram illustrates the transcription factor regulatory network in rice under salt and drought stress conditions. It includes several key transcription factors such as DREB, NAC, bZIP, WRKY, MYB, AP2/ERF, and other transcription factors, along with their specific binding elements like DRE/CRT, NACR, ABRE, W-box, MYBRS, and others. These transcription factors regulate the expression of target stress-responsive genes through these binding elements, aiding the plant in coping with environmental stress. The arrows represent the regulatory relationships between different transcription factors and their impact on target genes, highlighting the complex gene regulatory networks involved in plant stress resistance.
4.1. DREB Transcription Factors
DREB transcription factors contain a conserved AP2/ERF DNA-binding domain of approximately 60-70 amino acids, which specifically binds to the DRE/CRT (Dehydration-Responsive Element/C-repeat) element with the core sequence (A/GCCGAC). DREB TFs help plants adapt to environmental stresses by regulating the expression of stress-responsive genes [
33,
34]. DREB TFs are divided into DREB1 and DREB2 subgroups, primarily involved in low-temperature response and drought, high salt stress, respectively. Under salt and drought stress, DREB genes are induced. Transgenic plants overexpressing DREB genes exhibit enhanced stress tolerance by improving plant phenotypes, increasing the synthesis and accumulation of organic osmolytes, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activities, participating in oxidative stress responses, and regulating downstream stress genes [
35]. For example, the AP2/EREBP TF gene
OsDREB1F is induced by high salt, drought, cold stress, and ABA treatment, and transgenic rice and Arabidopsis show enhanced tolerance to high salt, drought, and low temperatures [
36].
OsDREB6 has transcriptional activation activity, specifically binds to the DRE cis-element, mediates the expression of specific genes, improves rice germination rates, affects the accumulation of osmolytes and ROS, and positively regulates rice tolerance to osmotic stress, salt stress, and cold stress [
37].
4.2. NAC Transcription Factors
The NAC TF family is characterized by a conserved NAC domain usually located at the N-terminus of the protein, including the NAM domain (NAC TFs, ATAF1/2, CUC2) and a variable C-terminal transcriptional activation region. The NAC domain regulates target gene transcription through DNA binding [
38].
OsNAC45 plays a significant role under various abiotic stresses by regulating the expression of genes related to root POD activity and development. Overexpressing
OsNAC45 in transgenic rice enhances tolerance to salt and drought stress, potentially by reducing ABA's inhibitory effect on root growth, mitigating stress inhibition of root growth, increasing lignin synthesis in roots, and reducing ROS accumulation [
39].
OsNAC2 regulates abiotic stress and ABA-mediated responses, acting as a connection point between ABA and abiotic stress pathways. Overexpression of
OsNAC2 decreases resistance under high salt and drought conditions, leading to yield reduction at the flowering stage [
40].
4.3. bZIP Transcription Factors
Rice bZIP TFs are characterized by a conserved bZIP domain, consisting of a basic region and a leucine zipper region. The basic region contains the DNA binding site, while the leucine zipper region is used for TF dimerization [
41].
OsbZIP72 can directly bind to the promoters of
OsSWEET13 and
OsSWEET15 and activate their expression, regulating sucrose transport and distribution to respond to abiotic stress, helping maintain sugar homeostasis under drought and salt stress.
OsbZIP72 also binds to the ABA response element in the promoter region of the high-affinity potassium transporter gene
OsHKT1;1 and activates its expression, participating in ABA signaling pathways mediating salt and drought tolerance [
42].
4.4. WRKY Transcription Factors
The WRKY TF family is a significant and diverse TF family in plants, playing key roles in regulating plant growth, development, disease defense, and environmental stress responses. WRKY TFs are named for their unique WRKY domain, which specifically binds to W-box elements (TTGAC[C/T]) [
43].
OsWRKY45 encodes a rice WRKY TF, with
OsWRKY45-1 and
OsWRKY45-2 being two alleles at this locus. These alleles have opposite functions in rice-Xoo interactions, mediating different defense response signaling pathways. Similarly, transgenic plants of these two alleles show differential expression in ABA and abiotic stress response genes but exhibit similar responses under cold and drought stress.
OsWRKY45-1 negatively regulates ABA signaling, while
OsWRKY45-2 positively regulates ABA signaling. Additionally,
OsWRKY45-2 positively regulates salt stress responses, while
OsWRKY45-1 negatively regulates them [
44].
4.5. MYB Transcription Factors
MYB TFs have a DNA-binding domain composed of one to three repeat sequences (R1, R2, R3), each containing approximately 52 amino acids forming a helix-turn-helix structure. These repeats specifically bind to specific elements in DNA, such as MBS (MYB binding site). The C-terminus of MYB TFs typically contains transcriptional activation or repression domains for regulating downstream gene expression [
45]. The MYB TF
OsMYB48 plays a critical role in rice's drought and salt tolerance by regulating stress-induced ABA synthesis [
46].
4.6. AP2/ERF Transcription Factors
The AP2/ERF family is named after APETALA2 (AP2) and Ethylene-Responsive Factor (ERF). Members of this family have one or more AP2/ERF DNA-binding domains. Based on the structure and number of these domains, they can be divided into four main subfamilies: AP2, ERF, RAV, and Soloist. Studies have found that ERF and RAV are mainly involved in stress responses [
47]. Salt and PEG treatments can rapidly induce the expression of ERF and RAV TFs, regulating the expression of related stress-responsive genes and enhancing rice's adaptability to stress. Through the regulation of these TFs, rice effectively responds to salt and drought stress, improving its survival and productivity [
48].
5. Regulation by Plant Hormones
In addition to transcription factors, plant hormones are key factors influencing rice's stress tolerance, playing a crucial role in adapting to various stresses. Plant hormones are endogenous compounds that act as growth regulators in plants, functioning either at their site of synthesis or after translocation within the plant under different environmental and stress conditions [
49].
5.1. Abscisic Acid (ABA)
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a vital plant hormone distributed widely in various plant tissues and organs, playing a crucial role in regulating plant growth and development. It is a key factor in plant responses to salt and drought stress, encompassing functions such as stomatal regulation, ion balance, stress-responsive gene expression, and metabolic changes [
50]. Many genes have been verified to mediate ABA synthesis and degradation in response to stress.
OsMLP423 is a positive regulator of drought and salt tolerance in rice, modulating abiotic stress tolerance through an ABA-dependent pathway. Transgenic rice overexpressing
OsMLP423 shows increased sensitivity to ABA and enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stress. Physiological analyses indicate that overexpressing
OsMLP423 may reduce membrane damage and ROS accumulation by regulating water loss rate and ABA-responsive gene expression under drought and salt stress [
51]. Conversely,
OsCBE1 negatively regulates abiotic stress responses and the ABA signaling pathway, with mutants exhibiting significantly higher survival rates under salt, drought, and cold stress compared to wild-type and overexpression lines [
52].
5.2. Gibberellins (GA)
Gibberellins (GA) are hormones critical for plant growth and also regulate growth under abiotic stress [
53].
OsDSK2a interacts with the GA deactivation enzyme EUI. Under salt stress,
OsDSK2a levels decrease, leading to increased EUI accumulation, promoting GA metabolism, and reducing plant growth. Thus,
OsDSK2a and
EUI have opposing roles in regulating rice growth under salt stress through GA metabolism and homeostasis [
54]. The GA catabolism pathway genes
OsGA2ox5 and
OsCYP71D8L enhance plant salt tolerance by reducing GA accumulation through delayed growth, indicating a negative regulatory role of GA in rice salt tolerance [
55].
5.3. Other Hormones
Other hormones, such as ethylene (ETH), cytokinins (CK), and jasmonic acid (JA), also play roles in environmental stress responses, participating in abiotic stress responses. Many genes have been verified to regulate these hormones and contribute to rice stress tolerance.
MHZ6 acts downstream of the ethylene signal positive regulator
OsEIN2 and positively regulates ethylene response in rice roots. Overexpression of
MHZ6 makes rice more sensitive to salt, indicating that
MHZ6 negatively regulates salt tolerance in rice [
56].
AGO2 regulates cytokinin distribution in plants by activating
BG3, which enhances grain length and salt tolerance in rice.
BG3 encodes a purine permease involved in cytokinin transport. Overexpression of
AGO2 or
BG3 alters the spatial distribution of cytokinins, positively regulating grain length and ABA response, thus improving rice salt tolerance. Overexpression lines of
AGO2 show increased sensitivity to ABA [
57].
OsJAZ9 interacts with
OsCOI1a, indicating its role in JA signaling regulation. As a transcriptional regulator,
OsJAZ9 interacts with
OsNINJA and
OsbHLH to form a transcriptional regulatory complex, modulating the expression of JA-responsive genes under salt stress. JA levels increase under salt stress. Upon JA perception,
SCFCOI1 recruits
OsJAZ9 for ubiquitination and degradation via the 26S proteasome, releasing
OsbHLH062 and
OsNINJA to activate target gene expression.
OsbHLH062 activates downstream gene transcription, potentially further regulating adaptation to salt stress [
58]. Through these complex regulatory mechanisms involving hormones, rice effectively responds to salt and drought stress, enhancing its adaptability and survival.
6. Breeding for Salt and Drought Tolerance in Rice
Breeding new rice varieties with enhanced tolerance to salt and drought stresses is a significant focus in current rice breeding research. Both salt and drought tolerance breeding primarily rely on conventional breeding techniques, which involve traditional artificial hybridization to introduce tolerance genes into elite rice varieties. Over multiple generations of stress screening and identification, breeders select lines with excellent comprehensive traits and stable inheritance (
Table 1).
The first global efforts in screening and breeding salt-tolerant rice varieties began in 1939 when Sri Lanka developed the world's first strongly salt-tolerant rice variety, Pokkali [
67]. Subsequently, countries and institutions such as India and the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) have conducted salt-tolerant germplasm screening, leading to the development and promotion of several salt-tolerant varieties . Chinese breeders have also employed conventional breeding methods and identified salt-tolerant germplasm resources. They have conducted salt-tolerant germplasm screening and variety selection under salt stress, resulting in the development and widespread agricultural application of rice varieties tolerant to varying salt concentrations [
68].
Drought tolerance breeding follows a similar approach, involving the screening and identification of drought-tolerant germplasm as a basis for developing drought-tolerant varieties. Cultivated rice has two ecological types: upland rice and lowland rice. Upland rice, typically grown in high-altitude or drought-prone environments, has unique advantages in drought tolerance. Screening and systematic breeding of upland rice have led to the development of a series of drought-tolerant varieties [
69].
In addition to conventional breeding, marker-assisted selection (MAS) is commonly used in developing stress-tolerant varieties. With the advancement of molecular marker technology and high-throughput sequencing, many stress-related quantitative trait loci (QTLs) have been identified, providing a foundation for fine-mapping, gene markers, and MAS in rice stress tolerance. Introducing major QTLs related to yield under stress conditions is a common strategy for improving stress tolerance in rice.
For example, researchers have used the salt-tolerant variety FL478 as a donor of the
Saltol QTL for salt tolerance and the high-yielding variety PB1 as the recipient parent. Through two backcrosses and three generations of selfing, combined with foreground and background selection, they obtained 24 near-isogenic lines (NILs) with enhanced seedling-stage salt tolerance and similar traits to the parents [
59]. Another study introduced the
Saltol QTL from FL478 into the high-yielding but salt-sensitive variety ADT45, resulting in NILs that maintain high yields in both normal and saline fields [
67]. Similarly, drought tolerance breeding involves the introduction of major drought QTLs. One study introduced the QTLs
qDTY2.1 and
qDTY3.1 into the recipient parent Pusa 44, resulting in 14 NILs with high background recovery rates and significantly better yield and grain quality under drought conditions compared to the parent [
60]. Another study introduced the QTLs
qDTY2.2,
qDTY3.1, and
qDTY12.1 into MR219, resulting in NILs with higher yield and improved drought tolerance, with different QTL combinations showing varying performances [
61].
Numerous studies have generated genetic populations through hybridization between tolerant and sensitive varieties, identifying many stress-related QTLs [
70,
71,
72]. However, due to the complexity and polygenic regulation of stress tolerance in rice, many QTLs have not yet been applied in breeding, with most efforts focusing on improving existing high-yielding varieties. Further in-depth research on QTLs is needed in the future.
7. Future Research Directions and Application Prospects
Future rice research should integrate multi-omics technologies and genome editing techniques, combined with epigenetic regulation, microbial symbiosis, smart agriculture, and research on combined stresses, to develop multifunctional rice varieties that are tolerant to salt, drought, and heat. Additionally, breeding water-saving and drought-resistant rice (WDR) will enhance the efficiency of agricultural production in saline and drought-prone areas, providing new directions for sustainable agriculture (
Figure 4).
7.1. Epigenetic Regulation
Research on DNA methylation, histone modifications, and small RNAs in stress responses can facilitate the development of epigenetic marker-assisted breeding techniques. Many studies have demonstrated that epigenetics play a crucial role in regulating important agronomic traits in crops. For example, the
OsSPL14 gene, which controls the ideal plant architecture in rice, is negatively regulated by
miR156. A single nucleotide variation in the
miR156 target site weakens its regulatory effect, leading to moderate
OsSPL14 expression, ideal plant architecture, and high disease resistance [
73]. Similarly, overexpression of
miR397 enhances its negative regulation of the laccase gene LAC, which is involved in lignin biosynthesis, significantly increasing spikelet number and seed size. Epigenetics also play a vital role in regulating stress tolerance;
miR168a-5p targets
OsOFP3,
OsNPF2.4, and
OsAGO1a, regulating seed length, nitrogen allocation, and salt tolerance, thereby providing a series of important agronomic traits for rice breeding [
74].
7.2. Microbial Symbiosis
Microbes have shown great potential in enhancing rice salt tolerance. Many studies have indicated that certain rhizosphere microbes can alleviate Na
+ ion toxicity, reduce ROS, and induce hormone regulation under salt stress, thus improving rice salt tolerance. Utilizing beneficial rhizosphere and endophytic microbes to enhance rice's salt and drought tolerance is a promising method to increase yield in saline-alkali environments through microbiome research [
75].
7.3. Smart Agriculture Technologies
With the development of intelligent technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, cloud computing, and 5G, smart agriculture technologies are continuously evolving and integrating. Agricultural production is gradually becoming greener, standardized, digital, networked, and intelligent. The use of sensors, drones, and big data technologies to achieve precision irrigation and fertilization, optimizing field management, is a future direction to improve rice production efficiency in saline and drought-prone areas [
76].
7.4. Research on Combined Stresses and Multi-Stage Stress Tolerance
Currently, most studies separately address salt and drought stresses, with few reports on the combined effects of salt and drought stress on rice growth and development and their physiological mechanisms. Additionally, most research focuses on short-term effects of stress, lacking systematic studies on the impacts at different growth stages (such as tillering, heading, and grain filling) throughout the entire growth period [
77]. Investigating the comprehensive tolerance mechanisms of rice under multiple environmental stresses and developing multifunctional rice varieties with tolerance to salt, drought, and heat throughout the entire growth period is a crucial direction for future breeding [
78].
7.5. Improvement of Water-Saving and Drought-Resistant Rice for Salt-Alkaline Tolerance
Water-saving and drought-resistant rice (WDR) is a new type of cultivated rice that combines the high-yield and quality traits of lowland rice with the water-saving and drought-resistant characteristics of upland rice [
69]. Under irrigation, WDR yields and grain quality are comparable to lowland rice, but it can save more than 50% of water. In rainfed low-yield fields, WDR shows good drought resistance, allowing both water-saving cultivation in paddies and direct seeding in dry fields. Extensive promotion and application have demonstrated WDR's high utilization value in dry fields. Using superior WDR germplasm as a foundation, breeding new germplasm with combined salt and drought tolerance through hybridization offers a new direction for agricultural production in saline and drought-prone areas [
79].
8. Conclusions
Rice exhibits many similar physiological responses under salt and drought stress, including osmotic regulation, ion balance, antioxidant responses, signal transduction, and gene expression regulation. These similarities reflect the shared adaptive mechanisms and stress-resistance strategies plants employ when facing different environmental stresses. Many reported genes have been found to mediate physiological responses under both salt and drought stress, enhancing rice's tolerance to these conditions and providing valuable references for breeding rice suitable for arid and saline soils.
In summary, research on rice salt and drought tolerance is of paramount importance for ensuring food security and sustainable agricultural development. In recent years, many key genes and regulatory networks associated with salt and drought tolerance have been identified, and the molecular mechanisms are gradually becoming clearer. However, further exploration of the functions of these genes and their complex regulatory networks is needed. Utilizing advanced genomic and molecular technologies, combined with ecological agricultural management practices, will aid in developing more efficient multi-stress tolerant varieties and practical application strategies. This will provide a solid foundation for improving rice productivity and addressing global environmental changes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: J.X., X.Y.and G.L., Writing—original draft preparation: Q.L. and P.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Science and Technology (Grant No. 21N11900200), the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System-Rice (CARS-01), and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (INV-033236-3).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous researchers, breeders, technicians, and students who are not listed as the authors for their contributions or help to this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
References
- Shaar-Moshe, L., Blumwald, E., & Peleg, Z. (2017). Unique Physiological and Transcriptional Shifts under Combinations of Salinity, Drought, and Heat. Plant physiology, 174(1), 421–434. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R., & Tester, M. (2008). Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annual review of plant biology, 59, 651–681. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J. K. (2002). Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annual review of plant biology, 53, 247–273. [CrossRef]
- Alfatih, A., Zhang, J., Song, Y., Jan, S. U., Zhang, Z. S., Xia, J. Q., Zhang, Z. Y., Nazish, T., Wu, J., Zhao, P. X., & Xiang, C. B. (2023). Nitrate-responsive OsMADS27 promotes salt tolerance in rice. Plant communications, 4(2), 100458. [CrossRef]
- Nongpiur, R. C., Singla-Pareek, S. L., & Pareek, A. (2016). Genomics Approaches For Improving Salinity Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants. Current genomics, 17(4), 343–357. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J. K. (2001). Plant salt tolerance. Trends in plant science, 6(2), 66–71. [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A., Ali, A., Safdar, L. B., Zafar, M. M., Rui, Y., Shakeel, A., Shaukat, A., Ashraf, M., Gong, W., & Yuan, Y. (2020). Salt stress induces physiochemical alterations in rice grain composition and quality. Journal of food science, 85(1), 14–20. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. I. R., Palakolanu, S. R., Chopra, P., Rajurkar, A. B., Gupta, R., Iqbal, N., & Maheshwari, C. (2021). Improving drought tolerance in rice: Ensuring food security through multi-dimensional approaches. Physiologia plantarum, 172(2), 645–668. [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M., Wahid, A., Kobayashi, N., Fujita, D., & Basra, S. M. A. (2009). Plant drought stress: Effects, mechanisms and management. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 29(1), 185-212. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C., Niu, S., Yan, Y., Zhou, G., Peng, Y., He, Y., Zhou, J., Li, Y., & Xie, X. (2024). Moderate Salinity Stress Affects Rice Quality by Influencing Expression of Amylose- and Protein-Content-Associated Genes. International journal of molecular sciences, 25(7), 4042. [CrossRef]
- Thitisaksakul, M., Tananuwong, K., Shoemaker, C. F., Chun, A., Tanadul, O. U., Labavitch, J. M., & Beckles, D. M. (2015). Effects of timing and severity of salinity stress on rice (Oryza sativa L.) yield, grain composition, and starch functionality. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 63(8), 2296–2304. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S., & Cuin, T.A. (2008). Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance. Physiologia plantarum, 133 4, 651-69. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C., Lei, L., Guo, H., Zhou, S., Xu, C., Liu, Z., Wu, Z., Deng, Y., Miao, Y., Han, Y., Zhang, M., Li, H., Huang, S., Yang, C., Zhang, F., Li, Y., Liu, L., Liu, X., Abbas, H. M. K., Fernie, A. R., … Luo, J. (2023). Disease resistance conferred by components of essential chrysanthemum oil and the epigenetic regulation of OsTPS1. Science China. Life sciences, 66(5), 1108–1118. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q., Ni, L., Cui, Z., Jiang, J., Chen, C., & Jiang, M. (2022). The NADPH oxidase OsRbohA increases salt tolerance by modulating K+ homeostasis in rice. The Crop Journal. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V., & Shukla, A.K. (2015). Acclimation and Tolerance Strategies of Rice under Drought Stress. Rice Science, 22, 147-161. [CrossRef]
- Sripinyowanich, S., Klomsakul, P., Boonburapong, B., Bangyeekhun, T., Asami, T., Gu, H., Buaboocha, T., & Chadchawan, S. (2013). Exogenous ABA induces salt tolerance in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.): The role of OsP5CS1 and OsP5CR gene expression during salt stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 86, 94-105. [CrossRef]
- Zang, B., Li, H., Li, W., Deng, X. W., & Wang, X. (2011). Analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family suggests the formation of TPS complexes in rice. Plant molecular biology, 76(6), 507–522. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Nan, N., Li, N., Liu, Y., Wang, T. J., Hwang, I., Liu, B., & Xu, Z. Y. (2020). A DNA Methylation Reader-Chaperone Regulator-Transcription Factor Complex Activates OsHKT1;5 Expression during Salinity Stress. The Plant cell, 32(11), 3535–3558. [CrossRef]
- Wei, H., Wang, X., He, Y., Xu, H., & Wang, L. (2021). Clock component OsPRR73 positively regulates rice salt tolerance by modulating OsHKT2;1-mediated sodium homeostasis. The EMBO journal, 40(3), e105086. [CrossRef]
- Prodjinoto, H., Irakoze, W., Gandonou, C., Quinet, M., & Lutts, S. (2023). Comparison between the impact of osmotic and NaCl treatments on the expression of genes coding for ion transporters in Oryza glaberrima Steud. PloS one, 18(11), e0290752. [CrossRef]
- Wei, H., Wang, X., He, Y., Xu, H., & Wang, L. (2021). Clock component OsPRR73 positively regulates rice salt tolerance by modulating OsHKT2;1-mediated sodium homeostasis. The EMBO journal, 40(3), e105086. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L., Shi, Y., Wang, R., Feng, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Shi, X., Jing, G., Deng, P., Song, T., Jing, W., & Zhang, W. (2022). The transcription factor OsMYBc and an E3 ligase regulate expression of a K+ transporter during salt stress. Plant physiology, 190(1), 843–859. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P., Katschnig, D., & de Boer, A. H. (2013). HKT transporters--state of the art. International journal of molecular sciences, 14(10), 20359–20385. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Cao, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, Z. Q., Shi, J., Liang, X., Song, W., Chen, Q., Lai, J., & Jiang, C. (2018). A retrotransposon in an HKT1 family sodium transporter causes variation of leaf Na+ exclusion and salt tolerance in maize. The New phytologist, 217(3), 1161–1176. [CrossRef]
- Gill, S. S., & Tuteja, N. (2010). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant physiology and biochemistry: PPB, 48(12), 909–930. [CrossRef]
- Ray, P. D., Huang, B. W., & Tsuji, Y. (2012). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cellular signalling, 24(5), 981–990. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., Huang, L., Zhao, X., Jia, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, M., & Jiang, M. (2022). A J-Protein OsDjC46 Interacts with ZFP36 to Participate in ABA-Mediated Antioxidant Defense in Rice. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 11(2), 207. [CrossRef]
- Deng, P., Cao, C., Shi, X., Jiang, Q., Ge, J., Shen, L., Guo, C., Jiang, L., Jing, W., & Zhang, W. (2023). OsCYBDOMG1, a cytochrome b561 domain-containing protein, regulates salt tolerance and grain yield in rice. TAG. Theoretical and applied genetics. Theoretische und angewandte Genetik, 136(4), 76. [CrossRef]
- Wang, A., Shu, X., Jing, X., Jiao, C., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Ma, L., Jiang, Y., Yamamoto, N., Li, S., Deng, Q., Wang, S., Zhu, J., Liang, Y., Zou, T., Liu, H., Wang, L., Huang, Y., Li, P., & Zheng, A. (2021). Identification of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genes involved in sheath blight resistance via a genome-wide association study. Plant biotechnology journal, 19(8), 1553–1566. [CrossRef]
- Smita, S., Katiyar, A., Chinnusamy, V., Pandey, D. M., & Bansal, K. C. (2015). Transcriptional Regulatory Network Analysis of MYB Transcription Factor Family Genes in Rice. Frontiers in plant science, 6, 1157. [CrossRef]
- Jwa, N. S., Agrawal, G. K., Tamogami, S., Yonekura, M., Han, O., Iwahashi, H., & Rakwal, R. (2006). Role of defense/stress-related marker genes, proteins and secondary metabolites in defining rice self-defense mechanisms. Plant physiology and biochemistry: PPB, 44(5-6), 261–273. [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M., Sharoni, A. M., & Kikuchi, S. (2013). Roles of NAC transcription factors in the regulation of biotic and abiotic stress responses in plants. Frontiers in microbiology, 4, 248. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q., Kasuga, M., Sakuma, Y., Abe, H., Miura, S., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., & Shinozaki, K. (1998). Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. The Plant cell, 10(8), 1391–1406. [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y., Maruyama, K., Qin, F., Osakabe, Y., Shinozaki, K., & Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2006). Dual function of an Arabidopsis transcription factor DREB2A in water-stress-responsive and heat-stress-responsive gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(49), 18822–18827. [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, J., Shinozaki, K., & Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2012). AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1819(2), 86–96. [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y., Yang, Z., Yu, S., Li, T., Wu, J., Gao, H., Fu, Y., & Luo, L. (2014). Characterization of OsDREB6 responsive to osmotic and cold stresses in rice. Journal of Plant Biology, 57, 150 - 161. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Lu, S., Guan, X., Jiang, Y., Wang, B., Hua, J., & Zou, B. (2022). Dehydration-Responsive Element Binding Protein 1C, 1E, and 1G Promote Stress Tolerance to Chilling, Heat, Drought, and Salt in Rice. Frontiers in plant science, 13, 851731. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A. N., Ernst, H. A., Leggio, L. L., & Skriver, K. (2005). NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends in plant science, 10(2), 79–87. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S., Huang, A., Li, J., Gao, L., Feng, Y., Pemberton, E., & Chen, C. (2018). OsNAC45 plays complex roles by mediating POD activity and the expression of development-related genes under various abiotic stresses in rice root. Plant Growth Regulation, 84, 519-531. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D., Zhou, L., Chen, W., Ye, N., Xia, J., & Zhuang, C. (2019). Overexpression of a microRNA-targeted NAC transcription factor improves drought and salt tolerance in Rice via ABA-mediated pathways. Rice (New York, N.Y.), 12(1), 76. [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, A., Jain, M., Tyagi, A. K., & Khurana, J. P. (2008). Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant physiology, 146(2), 333–350. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X., Liu, C., Li, Y., Liao, S., Cheng, H., Tu, Y., Zhu, X., Chen, K., He, Y., & Wang, G. (2021). The coordination of OsbZIP72 and OsMYBS2 with reverse roles regulates the transcription of OsPsbS1 in rice. The New phytologist, 229(1), 370–387. [CrossRef]
- Eulgem, T., Rushton, P. J., Robatzek, S., & Somssich, I. E. (2000). The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends in plant science, 5(5), 199–206. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z., Kou, Y., Liu, H., Li, X., Xiao, J., & Wang, S. (2011). OsWRKY45 alleles play different roles in abscisic acid signalling and salt stress tolerance but similar roles in drought and cold tolerance in rice. Journal of experimental botany, 62(14), 4863–4874. [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A., Smita, S., Lenka, S. K., Rajwanshi, R., Chinnusamy, V., & Bansal, K. C. (2012). Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC genomics, 13, 544. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W., Wang, X., Zhang, Q., Zheng, Q., Yao, H., Gu, X., Liu, D., Tian, X., Wang, X., Li, Y., & Zhu, Z. (2022). H3K36 demethylase JMJ710 negatively regulates drought tolerance by suppressing MYB48-1 expression in rice. Plant physiology, 189(2), 1050–1064. [CrossRef]
- Licausi, F., Ohme-Takagi, M., & Perata, P. (2013). APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. The New phytologist, 199(3), 639–649. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zhao, X., Yang, S., Huang, L., Du, F., Li, Z., Zhao, X., Fu, B., & Wang, W. (2020). Overexpression of the Transcription Factor Gene OsSTAP1 Increases Salt Tolerance in Rice. Rice (New York, N.Y.), 13(1), 50. [CrossRef]
- Verma, V., Ravindran, P., & Kumar, P. P. (2016). Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC plant biology, 16, 86. [CrossRef]
- Cutler, S. R., Rodriguez, P. L., Finkelstein, R. R., & Abrams, S. R. (2010). Abscisic acid: emergence of a core signaling network. Annual review of plant biology, 61, 651–679. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., Fan, J., Zhang, J., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zan, X., Li, X., Wan, J., Gao, X., Chen, R., Huang, Z., Xu, Z., & Li, L. (2022). OsMLP423 Is a Positive Regulator of Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stresses in Rice. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 11(13), 1653. [CrossRef]
- Choi, J., Lee, W., An, G., & Kim, S. R. (2021). OsCBE1, a Substrate Receptor of Cullin4-Based E3 Ubiquitin Ligase, Functions as a Regulator of Abiotic Stress Response and Productivity in Rice. International journal of molecular sciences, 22(5), 2487. [CrossRef]
- Colebrook, E. H., Thomas, S. G., Phillips, A. L., & Hedden, P. (2014). The role of gibberellin signalling in plant responses to abiotic stress. The Journal of experimental biology, 217(Pt 1), 67–75. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Qin, H., Zhou, S., Wei, P., Zhang, H., Zhou, Y., Miao, Y., & Huang, R. (2020). The Ubiquitin-Binding Protein OsDSK2a Mediates Seedling Growth and Salt Responses by Regulating Gibberellin Metabolism in Rice. The Plant cell, 32(2), 414–428. [CrossRef]
- Shan, C., Mei, Z., Duan, J., Chen, H., Feng, H., & Cai, W. (2014). OsGA2ox5, a gibberellin metabolism enzyme, is involved in plant growth, the root gravity response and salt stress. PloS one, 9(1), e87110. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C., Ma, B., He, S. J., Xiong, Q., Duan, K. X., Yin, C. C., Chen, H., Lu, X., Chen, S. Y., & Zhang, J. S. (2015). MAOHUZI6/ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE1 and ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE2 Regulate Ethylene Response of Roots and Coleoptiles and Negatively Affect Salt Tolerance in Rice. Plant physiology, 169(1), 148–165. [CrossRef]
- Yin, W., Xiao, Y., Niu, M., Meng, W., Li, L., Zhang, X., Liu, D., Zhang, G., Qian, Y., Sun, Z., Huang, R., Wang, S., Liu, C. M., Chu, C., & Tong, H. (2020). ARGONAUTE2 Enhances Grain Length and Salt Tolerance by Activating BIG GRAIN3 to Modulate Cytokinin Distribution in Rice. The Plant cell, 32(7), 2292–2306. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. P., Mani, B., & Giri, J. (2021). OsJAZ9 is involved in water-deficit stress tolerance by regulating leaf width and stomatal density in rice. Plant physiology and biochemistry: PPB, 162, 161–170. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. K., Singh, B. D., Kumar, A., Maurya, S., Krishnan, S. G., Vinod, K. K., Singh, M. P., Ellur, R. K., Bhowmick, P. K., & Singh, A. K. (2018). Marker-Assisted Introgression of Saltol QTL Enhances Seedling Stage Salt Tolerance in the Rice Variety "Pusa Basmati 1". International journal of genomics, 2018, 8319879. [CrossRef]
- Saminadane, T., Geddam, S., Krishnaswamy, P., Jothiganapathy, K., Tamilselvan, A., Ramadoss, B. R., Sri Hari Reddy, P., Singh, U. S., Singh, R. K., Platten, J. D., Gregorio, G. B., Singh, N. K., Bisht, D. S., Kota, S., Ponnuvel, S., & Guntupalli, P. (2024). Development of early maturing salt-tolerant rice variety KKL(R) 3 using a combination of conventional and molecular breeding approaches. Frontiers in genetics, 14, 1332691. [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P., Ramawat, N., Raju, D., Dhawan, G., Gopala Krishnan, S., Chinnusamy, V., Bhowmick, P. K., Vinod, K. K., Pal, M., Nagarajan, M., Ellur, R. K., Bollinedi, H., & Singh, A. K. (2022). Drought Tolerant Near Isogenic Lines of Pusa 44 Pyramided With qDTY2.1 and qDTY3.1, Show Accelerated Recovery Response in a High Throughput Phenomics Based Phenotyping. Frontiers in plant science, 12, 752730. [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, N. A., Swamy, B. P., Ratnam, W., Sta Cruz, M. T., Raman, A., & Kumar, A. (2016). Marker assisted pyramiding of drought yield QTLs into a popular Malaysian rice cultivar, MR219. BMC genetics, 17, 30. [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S., Singh, A., Sandhu, N., Bhandari, A., Vikram, P., & Kumar, A. (2017). Combining drought and submergence tolerance in rice: marker-assisted breeding and QTL combination effects. Molecular breeding: new strategies in plant improvement, 37(12), 143. [CrossRef]
- Rekha, G., Abhilash Kumar, V., Gokulan, C. G., Koushik, M. B. V. N., Laxmi Prasanna, B., Kulkarni, S., Aleena, D., Harika, G., Hajira, S. K., Pranathi, K., Punniakoti, E., Kale, R. R., Dilip Kumar, T., Ayyappa, D., Anila, M., Sinha, P., Manohara, K. K., Padmavathi, G., Subba Rao, L. V., Laha, G. S., … Sundaram, R. M. (2022). DRR Dhan 58, a Seedling Stage Salinity Tolerant NIL of Improved Samba Mahsuri Shows Superior Performance in Multi-location Trials. Rice (New York, N.Y.), 15(1), 45. [CrossRef]
- Bizimana, J. B., Luzi-Kihupi, A., W Murori, R., & Singh, R. K. (2017). Identification of quantitative trait loci for salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using IR29/Hasawi mapping population. Journal of genetics, 96(4), 571–582. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S., Septiningsih, E. M., Singh, R. K., & Thomson, M. J. (2022). Mapping QTLs for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice Using a Cross between Hasawi and BRRI dhan28. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(19), 11376. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S., Jain, M., Singla-Pareek, S. L., Bhalla, P. L., Singh, M. B., & Pareek, A. (2023). Pokkali: A Naturally Evolved Salt-Tolerant Rice Shows a Distinguished Set of lncRNAs Possibly Contributing to the Tolerant Phenotype. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(14), 11677. [CrossRef]
- Qin, H., Li, Y., & Huang, R. (2020). Advances and Challenges in the Breeding of Salt-Tolerant Rice. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(21), 8385. [CrossRef]
- Luo L. J. (2010). Breeding for water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR) in China. Journal of experimental botany, 61(13), 3509–3517. [CrossRef]
- Bizimana, J. B., Luzi-Kihupi, A., W Murori, R., & Singh, R. K. (2017). Identification of quantitative trait loci for salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using IR29/Hasawi mapping population. Journal of genetics, 96(4), 571–582. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S., Septiningsih, E. M., Singh, R. K., & Thomson, M. J. (2022). Mapping QTLs for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice Using a Cross between Hasawi and BRRI dhan28. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(19), 11376. [CrossRef]
- de Ocampo, M. P., Ho, V. T., Thomson, M. J., Mitsuya, S., Yamauchi, A., & Ismail, A. M. (2022). QTL mapping under salt stress in rice using a Kalarata-Azucena population. Euphytica: Netherlands journal of plant breeding, 218(6), 74. [CrossRef]
- Miao, C., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., Yao, J., Hua, K., Liu, X., Shi, H., & Zhu, J. K. (2019). The grain yield modulator miR156 regulates seed dormancy through the gibberellin pathway in rice. Nature communications, 10(1), 3822. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, L., Wu, D., Cheng, H., Du, X., Mao, D., Zhang, C., & Jiang, X. (2020). miR164c and miR168a regulate seed vigor in rice. Journal of integrative plant biology, 62(4), 470–486. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y., Zou, H., Wang, B., & Yuan, F. (2022). Progress and Applications of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria in Salt Tolerance of Crops. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(13), 7036. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E., Costa, N., & Pereira, A. (2020). A Systematic Review of IoT Solutions for Smart Farming. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 20(15), 4231. [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S. I., & Mittler, R. (2022). Plant responses to multifactorial stress combination. The New phytologist, 234(4), 1161–1167. [CrossRef]
- Rivero, R. M., Mittler, R., Blumwald, E., & Zandalinas, S. I. (2022). Developing climate-resilient crops: improving plant tolerance to stress combination. The Plant journal: for cell and molecular biology, 109(2), 373–389. [CrossRef]
- Xia, H., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Bi, J., Ma, X., Zhang, A., Liu, H., Chen, L., Zhou, S., Gao, H., Xu, K., Wei, H., Liu, G., Wang, F., Zhao, H., Luo, X., Hou, D., Lou, Q., Feng, F., Zhou, L., … Luo, L. (2022). Blue revolution for food security under carbon neutrality: A case from the water-saving and drought-resistance rice. Molecular plant, 15(9), 1401–1404. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).