Submitted:
20 July 2024
Posted:
22 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
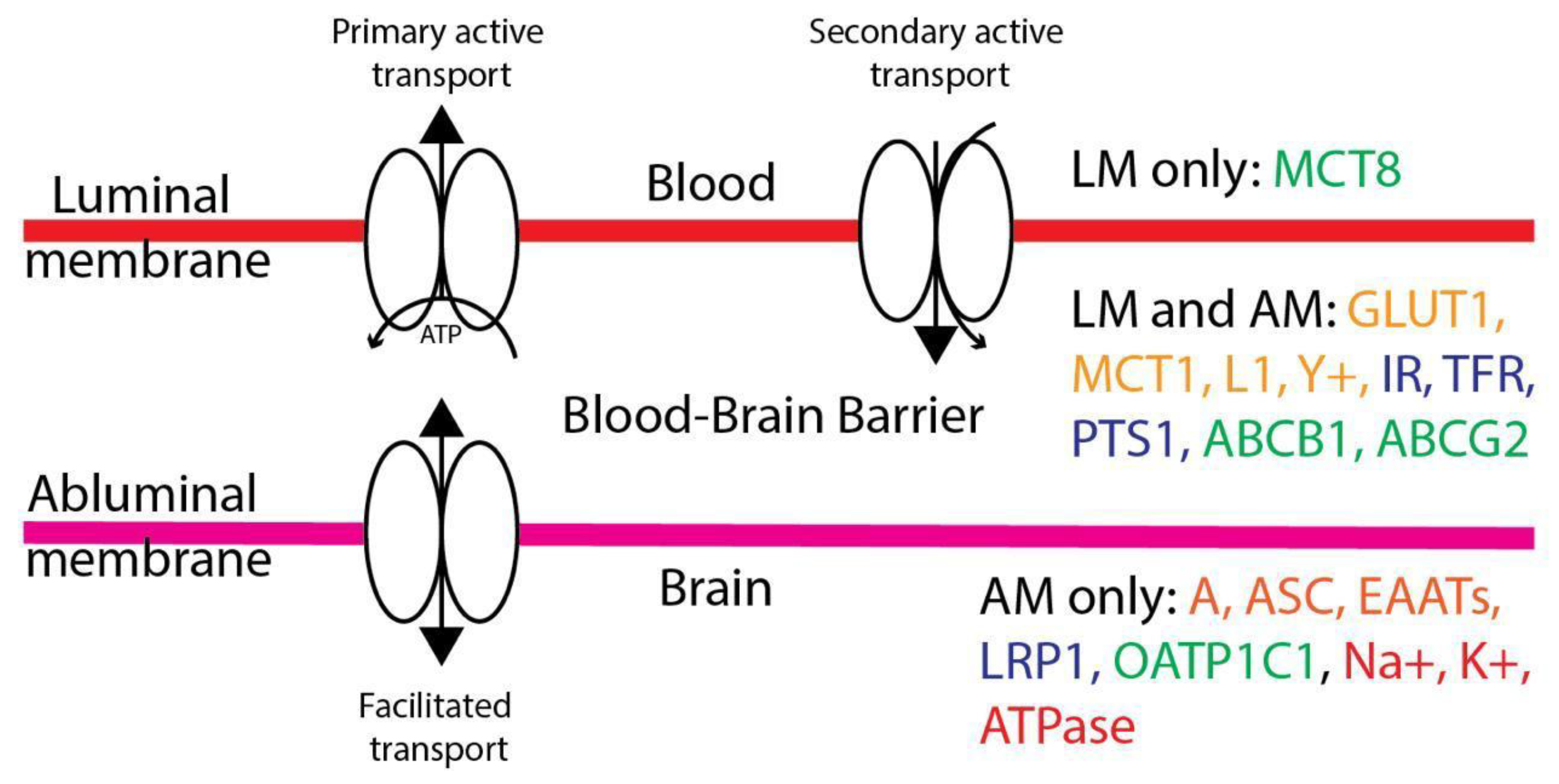
Active Transporters
Personalised and Precision Medicine
2. Materials and Methods
Implicated Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
3. Results
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Linked to P-Glycoprotein Function
SNPs Linked to Drug Transport
SNPs Linked to Drug Response and Pharmacokinetics
SNPs with Limited Available Information
4. Discussion
Implications and Next Steps
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D. Wu, Q. Chen, X. Chen, F. Han, Z. Chen and Y. Wang, Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8, 217–217.
- A. Kalliokoski and M. Niemi, Br J Pharmacol, 2009, 158, 693–705.
- Y. Zhou, J. Yuan, Z. Li, Z. Wang, D. Cheng, Y. Du, W. Li, Q. Kan and W. Zhang, Pharmacology, 2015, 95, 201–208.
- J. Wang, J. J. Wang, J. Yin, W. Li, C. Xiao, J. Han and F. Zhou, Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 2020, 34.
- A. R. Erdman, L. M. Mangravite, T. J. Urban, L. L. Lagpacan, R. A. Castro, M. de la Cruz, W. Chan, C. C. Huang, S. J. Johns, M. Kawamoto, D. Stryke, T. R. Taylor, E. J. Carlson, T. E. Ferrin, C. M. Brett, E. G. Burchard and K. M. Giacomini, American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology, 2006, 290, F905–F912.
- W. -Y. Liu, Z.-B. Wang, L.-C. Zhang, X. Wei and L. Li, CNS Neurosci Ther, 2012, 18, 609–615.
- C. Greene, N. Hanley and M. Campbell, Fluids Barriers CNS, 2019, 16, 3–3.
- N. C. f. B. Information, ClinVar, [VCV000828556.2], https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/variation/VCV000828556.2.
- L. M. Hodges, S. M. Markova, L. W. Chinn, J. M. Gow, D. L. Kroetz, T. E. Klein and R. B. Altman, Pharmacogenetics and genomics, 2011, 21, 152–161.
- T. M. Sissung, C. E. Baum, C. T. Kirkland, R. Gao, E. R. Gardner and W. D. Figg, Mol Biotechnol, 2010, 44, 152–167.
- E. A. Ashley, Nature Reviews Genetics, 2016, 17, 507–522.
- A. M. Vicente, W. Ballensiefen and J.-I. Jönsson, J Transl Med, 2020, 18, 180–180.
- D. Siskind, V. Siskind and S. Kisely, Can J Psychiatry, 2017, 62, 772–777.
- M. Wang, R. S. Herbst and C. Boshoff, Nature Medicine, 2021, 27, 1345–1356.
- J. Angst, Psychopharmacologia, 1961, 2, 381–407.
- P. Grof, A. Duffy, P. Cavazzoni, E. Grof, J. Garnham, M. MacDougall, C. O’Donovan and M. Alda, The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 2002, 63, 942–947.
- M. J. Arranz and J. de Leon, Molecular Psychiatry, 2007, 12, 707–747.
- M. J. Arranz, M. Rivera and J. C. Munro, CNS Drugs, 2011, 25, 933–969.
- V. David, B. Fylan, E. Bryant, H. Smith, G. S. Sagoo and M. Rattray, Front Genet, 2021, 12, 698148–698148.
- J. O’Shea, M. Ledwidge, J. Gallagher, C. Keenan and C. Ryan, The pharmacogenomics journal, 2022, 22, 89–99.
- A. M. Madejczyk, F. Canzian, J. Góra-Tybor, D. Campa, T. Sacha, D. Link-Lenczowska, I. Florek, W. Prejzner, M. Całbecka, M. Rymko, M. Dudziński, M. J. Orzechowska and K. Jamroziak, Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 952640–952640.
- K. Tsuchiya, T. Hayashida, A. Hamada, S. Oki, S. Oka and H. Gatanaga, Pharmacogenetics and Genomics, 2017, 27, 416–419.
- E. Ngaimisi, A. Habtewold, O. Minzi, E. Makonnen, S. Mugusi, W. Amogne, G. Yimer, K.-D. Riedel, M. Janabi, G. Aderaye, F. Mugusi, L. Bertilsson, E. Aklillu and J. Burhenne, PLoS One, 2013, 8, e67946–e67946.
- A. V. C. Coelho, S. P. S. Silva, L. C. A. de Alencar, G. Stocco, S. Crovella, L. A. C. Brandão and R. L. Guimarães, The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2013, 53, 1286–1293.
- K. Zaorska, P. Zawierucha, M. Świerczewska, D. Ostalska-Nowicka, J. Zachwieja and M. Nowicki, J Transl Med, 2021, 19, 130–130.
- S. Iwersen-Bergmann, S. Plattner, S. Hischke, A. Müller, H. Andresen-Streichert, H. Jungen, R. Erb and B. Beer-Sandner, Int J Legal Med, 2021, 135, 473–482.
- Z. Zahari, C. S. Lee, M. A. Ibrahim, N. Musa, M. A. Mohd Yasin, Y. Y. Lee, S. C. Tan, N. Mohamad and R. Ismail, Nursing Research, 2017, 66, 134–144.
- W. -W. Xie, L. Zhang, R.-R. Wu, Y. Yu, J.-P. Zhao and L.-H. Li, Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2015, 11, 1967–1971.
- T. Fujii, M. Ota, H. Hori, D. Sasayama, K. Hattori, T. Teraishi, N. Yamamoto, M. Hashikura, M. Tatsumi, T. Higuchi and H. Kunugi, Journal of Psychiatric Research, 2012, 46, 555–559.
- P. Menu, F. Gressier, C. Verstuyft, P. Hardy, L. Becquemont and E. Corruble, Neuropsychobiology, 2010, 62, 193–197.
- K. -M. Lin, Y.-F. Chiu, I. J. Tsai, C.-H. Chen, W. W. Shen, S. C. Liu, S.-C. Lu, C.-Y. Liu, M.-C. Hsiao, H.-S. Tang, S.-I. Liu, L.-H. Chang, C.-S. Wu, H.-H. Tsou, M.-H. Tsai, C.-Y. Chen, S.-M. Wang, H.-W. Kuo, Y.-T. Hsu and Y.-L. Liu, Pharmacogenetics and Genomics, 2011, 21, 163–170.
- A. B. Singh, C. A. Bousman, C. H. Ng, K. Byron and M. Berk, Transl Psychiatry, 2012, 2, e198–e198.
- M. Kato, T. Fukuda, A. Serretti, M. Wakeno, G. Okugawa, Y. Ikenaga, Y. Hosoi, Y. Takekita, L. Mandelli, J. Azuma and T. Kinoshita, Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 2008, 32, 398–404.
- Piatkov, D. Caetano, Y. Assur, S. L. Lau, T. Jones, S. C. Boyages and M. McLean, Pharmgenomics Pers Med, 2017, 10, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- A. P. Athanasoulia, C. Sievers, M. Ising, A. C. Brockhaus, A. Yassouridis, G. K. Stalla and M. Uhr, European Journal of Endocrinology, 2012, 167, 327–335.
- C. Sági, A. Gézsi, B. Egyed, Z. Jakab, N. Benedek, A. Attarbaschi, S. Köhrer, J. Sipek, L. Winkowska, M. Zaliova, S. Anastasopoulou, B. O. Wolthers, S. Ranta, C. Szalai, G. T. Kovács, Á. F. Semsei and D. J. Erdélyi, Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13, 2333.
- G. L‘Huillier, K. Ing Lorenzini, P.-A. Crisinel, M. C. Rebsamen, J. Fluss, C. M. Korff, R. P. Barbe, C.-A. Siegrist, P. Dayer, K. M. Posfay-Barbe and J. A. Desmeules, Pharmacogenomics, 2011, 12, 1493–1501.
- Y. Yamasaki, T. Moriwaki, S. Ogata, S. Ito, S. Ohtsuki, G. Minegishi, S. Abe, Y. Ohta, K. Kazuki, K. Kobayashi and Y. Kazuki, Pharmacogenetics and Genomics, 2022, 32, 288–292.
- M. Hitzl, E. Schaeffeler, B. Hocher, T. Slowinski, H. Halle, M. Eichelbaum, P. Kaufmann, P. Fritz, M. F. Fromm and M. Schwab, Pharmacogenetics, 2004, 14, 309–318.
- D. M. van Assema, M. Lubberink, P. Rizzu, J. C. van Swieten, R. C. Schuit, J. Eriksson, P. Scheltens, M. Koepp, A. A. Lammertsma and B. N. van Berckel, EJNMMI Res, 2012, 2, 57–57.
- Magliulo, M.-L. Dahl, G. Lombardi, S. Fallarini, L. M. Villa, A. Biolcati and M. G. Scordo, European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2010, 67, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Noetzli, M. Guidi, K. Ebbing, S. Eyer, L. Wilhelm, A. Michon, V. Thomazic, I. Stancu, A.-M. Alnawaqil, C. Bula, S. Zumbach, M. Gaillard, P. Giannakopoulos, A. von Gunten, C. Csajka and C. B. Eap, Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2014, 78, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- A. Levran, K. O’Hara, E. Peles, D. Li, S. Barral, B. Ray, L. Borg, J. Ott, M. Adelson and M. J. Kreek, Hum Mol Genet, 2008, 17, 2219–2227.
- H. -Y. Lee, J.-H. Li, Y.-L. Sheu, H.-P. Tang, W.-C. Chang, T.-C. Tang, Y.-C. Yeh, S.-Y. Wang and R.-H. Liu, Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013, 741403–741403.
- J. Coller, D. Barratt, K. Dahlen, M. Loennechen and A. Somogyi, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2006, 80, 682–690.
- C. -C. Hung, M.-H. Chiou, Y.-N. Teng, Y.-W. Hsieh, C.-L. Huang and H.-Y. Lane, PLoS One, 2013, 8, e59419–e59419.
- C. -C. Hung, M.-H. Chiou, B.-H. Huang, Y.-W. Hsieh, T.-J. Hsieh, C.-L. Huang and H.-Y. Lane, Pharmacogenomics, 2011, 12, 1525–1533.
- D. Kreutzwiser and Q. A. Tawfic, CNS drugs, 2020, 34, 827–839.
- G. Nikisch, C. Eap and P. Baumann, Pharmacological Research, 2008, 58, 344–347.
- Gex-Fabry, C. B. Eap, B. Oneda, N. Gervasoni, J.-M. Aubry, G. Bondolfi and G. Bertschy, Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 2008, 30, 474–482. [Google Scholar]
- Z. Vancova, M. Cizmarikova, J. Dragasek, S. Zofcakova, P. Kolarcik and J. Mojzis, Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24, 3136–3145.
- L. M. Geers, I. V. Pozhidaev, S. A. Ivanova, M. B. Freidin, A. F. Schmidt, D. Cohen, A. S. Boiko, D. Z. Paderina, O. Y. Fedorenko, A. V. Semke, N. A. Bokhan, B. Wilffert, J. G. W. Kosterink, D. J. Touw and A. J. M. Loonen, Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 86, 1827–1835.
- H. Y. Cho, H. D. Yoo and Y. B. Lee, Neuroscience, 2010, 169, 378–387.
- D. V. Ivashchenko, S. Z. Khoang, B. V. Makhmudova, N. I. Buromskaya, P. V. Shimanov, R. V. Deitch, K. A. Akmalova, G. N. Shuev, I. V. Dorina, M. I. Nastovich, E. N. Shagovenko, E. A. Grishina, L. M. Savchenko, Y. S. Shevchenko and D. A. Sychev, Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions, 2020, 35.
- R. Kuzman, V. Medved, N. Bozina, L. Hotujac, I. Sain and H. Bilusic, Psychiatry Research, 2008, 160, 308–315.
- E. Skogh, I. Sjödin, M. Josefsson and M.-L. Dahl, Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 2011, 31, 4–9.
- G. Consoli, M. Lastella, A. Ciapparelli, M. C. Dell‘Osso, L. Ciofi, E. Guidotti, R. Danesi, L. Dell‘Osso, M. Del Tacca and A. Di Paolo, Pharmacogenomics, 2009, 10, 1267–1276.
- Rafaniello, M. Sessa, F. F. Bernardi, M. Pozzi, S. Cheli, D. Cattaneo, S. Baldelli, M. Molteni, R. Bernardini, F. Rossi, E. Clementi, C. Bravaccio, S. Radice and A. Capuano, The Pharmacogenomics Journal, 2017, 18, 422–430. [Google Scholar]
- T. Suzuki, K. Mihara, A. Nakamura, S. Kagawa, G. Nagai, K. Nemoto and T. Kondo, Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 2014, 36, 651–655.
- Belmonte, D. Ochoa, M. Román, M. Saiz-Rodríguez, A. Wojnicz, C. I. Gómez-Sánchez, S. Martín-Vílchez and F. Abad-Santos, Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 2018, 122, 596–605. [Google Scholar]
- S. Hattori, A. Suda, I. Kishida, M. Miyauchi, Y. Shiraishi, M. Fujibayashi, N. Tsujita, C. Ishii, N. Ishii, T. Moritani, M. Taguri and Y. Hirayasu, BMC Psychiatry, 2018, 18, 231–231.
- Koller, C. Belmonte, R. Lubomirov, M. Saiz-Rodríguez, P. Zubiaur, M. Román, D. Ochoa, A. Carcas, A. Wojnicz and F. Abad-Santos, Journal of Psychopharmacology, 2018, 32, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Q. Xing, R. Gao, H. Li, G. Feng, M. Xu, S. Duan, J. Meng, A. Zhang, S. Qin and L. He, Pharmacogenomics, 2006, 7, 987–993.
- Yasui-Furukori, S. Tsuchimine, M. Saito, T. Nakagami, Y. Sato and S. Kaneko, Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 2007, 31, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimprich, R. Sunder-Plassmann, E. Stogmann, A. Gleiss, A. Dal-Bianco, A. Zimprich, S. Plumer, C. Baumgartner and C. Mannhalter, Neurology, 2004, 63, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar]
- C. -C. Hung, J. J. Tai, C.-J. Lin, M.-J. Lee and H.-H. Liou, Pharmacogenomics, 2005, 6, 411–417.
- S. A. Vahab, S. Sen, N. Ravindran, S. Mony, A. Mathew, N. Vijayan, G. Nayak, N. Bhaskaranand, M. Banerjee and K. Satyamoorthy, Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 2009, 24, 255–260.
- Sun, B.-Q. Cao, B. Wang, S.-Q. Wu and D.-H. Jiang, Exp Ther Med, 2016, 12, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Lovrić, N. Božina, S. Hajnšek, M. R. Kuzman, D. Sporiš, Z. Lalić, T. Božina and P. Granić, Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 2012, 34, 518–525.
- B. Smolarz, D. Skalski, A. Rysz, A. Marchel, H. Romanowicz and M. Makowska, Acta Neurologica Belgica, 2017, 117, 849–855.
- M. Chouchi, H. Klaa, I. Ben-Youssef Turki and L. Hila, Dis Markers, 2019, 2019, 1343650–1343650.
- D. Escalante-Santiago, I. A. Feria-Romero, R. M. Ribas-Aparicio, D. Rayo-Mares, P. Fagiolino, M. Vázquez, C. Escamilla-Núñez, I. Grijalva-Otero, M. A. López-García and S. Orozco-Suárez, Front Neurol, 2014, 5, 184–184.
- Kwan, V. Wong, P. W. Ng, C. H. T. Lui, N. C. Sin, W. S. Poon, H. K. Ng, K. S. Wong and L. Baum, Pharmacogenomics, 2009, 10, 723–732. [Google Scholar]
- T. Zhao, H.-J. Li, J. Feng, H.-L. Zhang, W. Ting-Ting, L. Ma, J. Yu, W.-B. Zhao, L. Sun, L.-H. Yu and Y. Sun, Therapeutic drug monitoring, 2022, 44, 455–464.
- A. Macauda, E. Castelli, G. Buda, M. Pelosini, A. Butrym, M. Watek, M. Kruszewski, A. J. Vangsted, M. Rymko, K. Jamroziak, N. Abildgaard, E. K. Haastrup, G. Mazur, R. Ríos, A. Jurczyszyn, D. Zawirska, M. Dudziński, M. Raźny, M. Dutka, W. Tomczak, A. Suska, A. Druzd-Sitek, H. Marques, M. Petrini, M. Markiewicz, J. Martinez-Lopez, L. H. Ebbesen, E. Iskierka-Jażdżewska, J. Sainz, F. Canzian and D. Campa, British Journal of Haematology, 2018, 183, 375–384.
- A.J. de Luna, M. H. Cervera, I. S. Lázaro, L. A. Bonet, J. P. Andrés and S. A. Pellicer, 2011.
- J. L. Weissfeld, B. Diergaarde, T. Nukui, S. Buch, A. Pennathur, M. A. Socinski, J. M. Siegfried and M. Romkes, J Thorac Oncol, 2014, 9, 1264–1271.
- A. Krupoves, E. G. Seidman, D. Mack, D. Israel, K. Morgan, P. Lambrette, I. Costea, C. Deslandres, G. Grimard, L. Law, E. Levy and D. K. Amre, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 2009, 15, 900–908.
- A. Huebner, B. L. Browning, I. Petermann, D. Y. Han, M. Philpott, M. Barclay, R. Gearry, A. McCulloch, P. Demmers and L. R. Ferguson, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 2009, 15, 1784–1793.
- Ji, Y. Zhang, Y. Hu, L. Liu, S. Cao, L. Gao, B. Li, Y. Tian, L. Kong, S. Wu, J. Ling, P. Xiao, J. Lu, J. Li, Y. Yao, J. Qin and S. Hu, Blood, 2023, 142, 6960–6960. [Google Scholar]
- M. Margier, X. Collet, C. May, C. Desmarchelier, F. André, C. Lebrun, C. Defoort, A. Bluteau, P. Borel, A. Lespine and E. Reboul, The FASEB Journal, 2018, 33, 2084–2094.
- P. Moya, J. Salazar, M. J. Arranz, C. Díaz-Torné, E. del Río, J. Casademont, H. Corominas and M. Baiget, Pharmacogenomics, 2015, 17, 25–29.
- L. Gao, X. Yin, Y. Li, H. Xiao, L. Yang, H. Fan, H. Qi, J. Zhang, J. Feng and F. Zheng, Zhonghua yi xue yi Chuan xue za zhi= Zhonghua Yixue Yichuanxue Zazhi= Chinese Journal of Medical Genetics, 2019, 36, 1073–1076.
- A.Das, S. Balan, A. Mathew, V. Radhakrishnan, M. Banerjee and K. Radhakrishnan, Indian J Hum Genet, 2011, 17 Suppl 1, S41-S47.
- D. Campa, J. Sainz, B. Pardini, L. Vodickova, A. Naccarati, A. Rudolph, J. Novotny, A. Försti, S. Buch, W. von Schönfels, C. Schafmayer, H. Völzke, M. Hoffmeister, B. Frank, R. Barale, K. Hemminki, J. Hampe, J. Chang-Claude, H. Brenner, P. Vodicka and F. Canzian, PLoS One, 2012, 7, e32784–e32784.
- A. Rudolph, J. Sainz, R. Hein, M. Hoffmeister, B. Frank, A. Forsti, H. Brenner, K. Hemminki and J. Chang-Claude, Endocrine Related Cancer, 2011, 18, 371–384.
- J. m. L. Cousar, Y. P. Conley, F. A. Willyerd, A. A. Sarnaik, A. M. Puccio, P. E. Empey, P. M. Kochanek, M. J. Bell, D. O. Okonkwo and R. S. B. Clark, Neurocrit Care, 2013, 19, 192–198.
- Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 2009, 120, 727-736.
- Vaclavikova, M. Ehrlichova, I. Hlavata, V. Pecha, R. Kozevnikovova, M. Trnkova, J. Adamek, H. Edvardsen, V. N. Kristensen, I. Gut and P. Soucek, Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM), 2012, 50, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar]
- A. Ikediobi, B. Aouizerat, Y. Xiao, M. Gandhi, S. Gebhardt and L. Warnich, Hum Genomics, 2011, 5, 265–282.
- J. Ma, J. Divers, N. D. Palmer, B. A. Julian, A. K. Israni, D. Schladt, S. O. Pastan, K. Chattrabhuti, M. D. Gautreaux, V. Hauptfeld, R. A. Bray, A. D. Kirk, W. M. Brown, R. S. Gaston, J. Rogers, A. C. Farney, G. Orlando, R. J. Stratta, M. Guan, A. Palanisamy, A. M. Reeves-Daniel, D. W. Bowden, C. D. Langefeld, P. J. Hicks, L. Ma and B. I. Freedman, Kidney Int, 2015, 88, 584–592.
- J. McMahon, N. Akula, T. G. Schulze, P. Muglia, F. Tozzi, S. D. Detera-Wadleigh, C. J. M. Steele, R. Breuer, J. Strohmaier, J. R. Wendland, M. Mattheisen, T. W. Mühleisen, W. Maier, M. M. Nöthen, S. Cichon, A. Farmer, J. B. Vincent, F. Holsboer, M. Preisig, M. Rietschel and C. Bipolar Disorder Genome Study, Nat Genet, 2010, 42, 128–131.
- C. Dong, M. L. Wong and J. Licinio, Molecular psychiatry, 2009, 14, 1105–1118.
- A. Martino, D. Campa, G. Buda, J. Sainz, R. García-Sanz, K. Jamroziak, R. M. Reis, N. Weinhold, M. Jurado, R. Ríos, Z. Szemraj-Rogucka, H. Marques, J. Szemraj, A. Stein, R. Kumar, E. Orciuolo, F. Gemignani, S. Landi, H. Goldschmidt, M. Petrini, C. Dumontet, F. Canzian and A. M. Rossi, Leukemia, 2011, 26, 1419–1422.
- P. Thompson, H. E. Wheeler, S. M. Delaney, R. Lorier, U. Broeckel, M. Devidas, G. H. Reaman, K. Scorsone, L. Sung, M. E. Dolan and S. L. Berg, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2014, 74, 831–838.
- I. Woo, S. R. Kim, W. Huh, J.-W. Ko and S.-Y. Lee, Drug Des Devel Ther, 2017, 11, 1135–1146.
- Y. Yang, J. Jia, Z. Sun, C. Liu, Z. Li, Y. Xiao, J. Yu, F. Du, Y. Shi, J. Sun, J. Shui and X. Zhang, Future Oncology, 2021, 17, 2351–2363.
- Z. Sun, X. Yang, F. Du, Y. Shi, J. Sun, J. Jia, C. Liu, Y. Xiao, J. Yu, X. Zhang and Y. Yang, The Journal of Gene Medicine, 2022, 24.
- G. K. Boora, R. Kanwar, A. A. Kulkarni, A. Abyzov, J. Sloan, K. J. Ruddy, M. S. Banck, C. L. Loprinzi and A. S. Beutler, Cancer Med, 2016, 5, 631–639.
- E. Abraham, Q. Guo, L. Dorling, J. Tyrer, S. Ingle, R. Hardy, A.-L. Vallier, L. Hiller, R. Burns, L. Jones, S. J. Bowden, J. A. Dunn, C. J. Poole, C. Caldas, P. P. D. Pharoah and H. M. Earl, Clinical Cancer Research, 2014, 20, 2466–2475.
- Louis, R. M. Busch, D. Lal, J. Hockings, O. Hogue, M. Morita-Sherman, D. Vegh, I. Najm, C. Ghosh, P. Bazeley, C. Eng, L. Jehi and D. M. Rotroff, Front Neurol, 2022, 13, 942643–942643. [Google Scholar]
- D. Caronia, A. Patiño-Garcia, A. Peréz-Martínez, G. Pita, L. T. Moreno, M. Zalacain-Díez, B. Molina, I. Colmenero, L. Sierrasesúmaga, J. Benítez and A. Gonzalez-Neira, PLoS One, 2011, 6, e26091–e26091.
- M. Dhoro, B. Ngara, G. Kadzirange, C. Nhachi and C. Masimirembwa, Current HIV Research, 2014, 11, 481–490.
- M. Dhoro, S. Zvada, B. Ngara, C. Nhachi, G. Kadzirange, P. Chonzi and C. Masimirembwa, BMC Pharmacol Toxicol, 2015, 16, 4–4.
- P. M. Bet, E. C. Verbeek, Y. Milaneschi, D. B. Straver, T. Uithuisje, M. R. Bevova, J. G. Hugtenburg, P. Heutink, B. W. Penninx and W. J. Hoogendijk, The pharmacogenomics journal, 2016, 16, 202–208.
- R. Abduljabbar, T. D. Eid, A.-M. Yousef, S. R. Mukred and M. Zawiah, Journal of Medical Biochemistry, 2023, 42, 214.
- G. P. Consortium, A. Auton, L. Brooks, R. Durbin, E. Garrison and H. Kang, Nature, 2015, 526, 68–74.
- o. N. T. H. S. Center.
- Y. -O. Kim, S.-Y. Kim, D. H. Yun and S.-W. Lee, Exp Neurobiol, 2012, 21, 164–171.
- Wu, X. Wang, H. Chen, R. Yang, H. Yu, Y. Wu and Y. Hu, Metabolites, 2022, 12, 875. [Google Scholar]
- Y. Pan, W. Chen, Y. Wang, H. Li, S. C. Johnston, T. Simon, X. Zhao, L. Liu, D. Wang, X. Meng, Y. Wang and I. Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients With Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events, JAMA Neurol, 2019, 76, 552–560.
- L. White, R. A. Vierkant, Z. C. Fogarty, B. Charbonneau, M. S. Block, P. D. P. Pharoah, G. Chenevix-Trench, A. A. C. S. g. for, M. A. Rossing, D. W. Cramer, C. L. Pearce, J. M. Schildkraut, U. Menon, S. K. Kjaer, D. A. Levine, J. Gronwald, H. A. Culver, A. S. Whittemore, B. Y. Karlan, D. Lambrechts, N. Wentzensen, J. Kupryjanczyk, J. Chang-Claude, E. V. Bandera, E. Hogdall, F. Heitz, S. B. Kaye, P. A. Fasching, I. Campbell, M. T. Goodman, T. Pejovic, Y. Bean, G. Lurie, D. Eccles, A. Hein, M. W. Beckmann, A. B. Ekici, J. Paul, R. Brown, J. M. Flanagan, P. Harter, A. du Bois, I. Schwaab, C. K. Hogdall, L. Lundvall, S. H. Olson, I. Orlow, L. E. Paddock, A. Rudolph, U. Eilber, A. Dansonka-Mieszkowska, I. K. Rzepecka, I. Ziolkowska-Seta, L. Brinton, H. Yang, M. Garcia-Closas, E. Despierre, S. Lambrechts, I. Vergote, C. Walsh, J. Lester, W. Sieh, V. McGuire, J. H. Rothstein, A. Ziogas, J. Lubinski, C. Cybulski, J. Menkiszak, A. Jensen, S. A. Gayther, S. J. Ramus, A. Gentry-Maharaj, A. Berchuck, A. H. Wu, M. C. Pike, D. Van Denberg, K. L. Terry, A. F. Vitonis, J. A. Doherty, S. E. Johnatty, A. Defazio, H. Song, J. Tyrer, T. A. Sellers, C. M. Phelan, K. R. Kalli, J. M. Cunningham, B. L. Fridley and E. L. Goode, Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2013, 22, 987–992.
- P. Peethambaram, B. L. Fridley, R. A. Vierkant, M. C. Larson, K. R. Kalli, E. A. Elliott, A. L. Oberg, K. L. White, D. N. Rider and G. L. Keeney, International journal of molecular epidemiology and genetics, 2011, 2, 185.
- D. J. Christoffersen, P. Damkier, S. Feddersen, S. Möller, J. L. Thomsen, C. Brasch-Andersen and K. Brøsen, Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 2016, 119, 381–388.
- S. Sadhasivam, V. Chidambaran, X. Zhang, J. Meller, H. Esslinger, K. Zhang, L. J. Martin and J. McAuliffe, The Pharmacogenomics Journal, 2014, 15, 119–126.
- A. Ray, L. Tennakoon, J. Keller, J. E. Sarginson, H. S. Ryan, G. M. Murphy, L. C. Lazzeroni, M. H. Trivedi, J. H. Kocsis, C. DeBattista and A. F. Schatzberg, The Pharmacogenomics Journal, 2014, 15, 332–339.
- Sánchez-Lázaro, M. J. Herrero, C. Jordán-De Luna, V. Bosó, L. Almenar, L. Rojas, L. Martínez-Dolz, J. E. Megías-Vericat, L. Sendra, A. Miguel, J. L. Poveda and S. F. Aliño, Pharmacogenomics, 2015, 16, 971–979. [Google Scholar]
- G. Burgueño-Rodríguez, Y. Méndez, N. Olano, M. Schelotto, L. Castillo, A. M. Soler and J. da Luz, Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14, 1278769–1278769.
- B. Breitenstein, S. Scheuer, H. Pfister, M. Uhr, S. Lucae, F. Holsboer, M. Ising and T. M. Brückl, CNS Spectrums, 2013, 19, 165–175.
- A. L. de Klerk, I. M. Nolte, P. M. Bet, F. J. Bosker, H. Snieder, J. A. den Boer, R. Bruggeman, W. J. Hoogendijk and B. W. Penninx, The Pharmacogenomics Journal, 2012, 13, 349–353.
- M. Geers, T. Ochi, N. M. Vyalova, I. S. Losenkov, D. Z. Paderina, I. V. Pozhidaev, G. G. Simutkin, N. A. Bokhan, B. Wilffert, D. J. Touw, A. J. M. Loonen and S. A. Ivanova, Hum Psychopharmacol, 2022, 37, e2826–e2826.
- Magarbeh, C. Hassel, M. Choi, F. Islam, V. S. Marshe, C. C. Zai, R. Zuberi, R. S. Gammal, X. Men, M. Scherf-Clavel, D. Enko, B. N. Frey, R. Milev, C. N. Soares, S. V. Parikh, F. Placenza, S. C. Strother, S. Hassel, V. H. Taylor, F. Leri, P. Blier, F. Farzan, R. W. Lam, G. Turecki, J. A. Foster, S. Rotzinger, S. Kloiber, J. L. Kennedy, S. H. Kennedy, C. A. Bousman and D. J. Müller, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2023, 114, 88–117. [Google Scholar]
- L. R. Silberbauer, L. Rischka, C. Vraka, A. M. Hartmann, G. M. Godbersen, C. Philippe, D. Pacher, L. Nics, M. Klöbl, J. Unterholzner, T. Stimpfl, W. Wadsak, A. Hahn, M. Hacker, D. Rujescu, S. Kasper, R. Lanzenberger and G. Gryglewski, Molecular psychiatry, 2022, 27, 4502–4509.
- J. Bly, J. R. Bishop, K. L. H. Thomas and V. L. Ellingrod, J Sex Marital Ther, 2013, 39, 280–288.
- D. Tsuji, Y.-I. Kim, H. Nakamichi, T. Daimon, K. Suwa, Y. Iwabe, H. Hayashi, K. Inoue, M. Yoshida and K. Itoh, Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 2013, 28, 299–304.
- H. H. Chang, C.-H. Chou, Y. K. Yang, I. H. Lee and P. S. Chen, Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci, 2015, 13, 250–255.
- X. -X. Shan, Y. Qiu, W.-W. Xie, R.-R. Wu, Y. Yu, H.-S. Wu and L.-H. Li, Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10, 761–761.
| p-glycoprotein | Drug transport | Drug response and pharmacokinetics | Limited information | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs ID | rs3842, rs1045642 (C3435T), rs1922240, rs2032582 (G2677T/A), rs2235013, rs2235033, rs2235046 | rs17064, rs868755, rs1128503, rs1202168, rs1211152, rs1922242, rs2032588, rs2214102, rs2214103, rs2235018, rs2235020, rs2235035, rs2235074, rs3213619, rs10276036 | rs2888599, rs4148727, rs9282564, rs13237132 | rs2235015 (DRD2 Taq1A), rs55852620, rs58898486 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





