1. Introduction
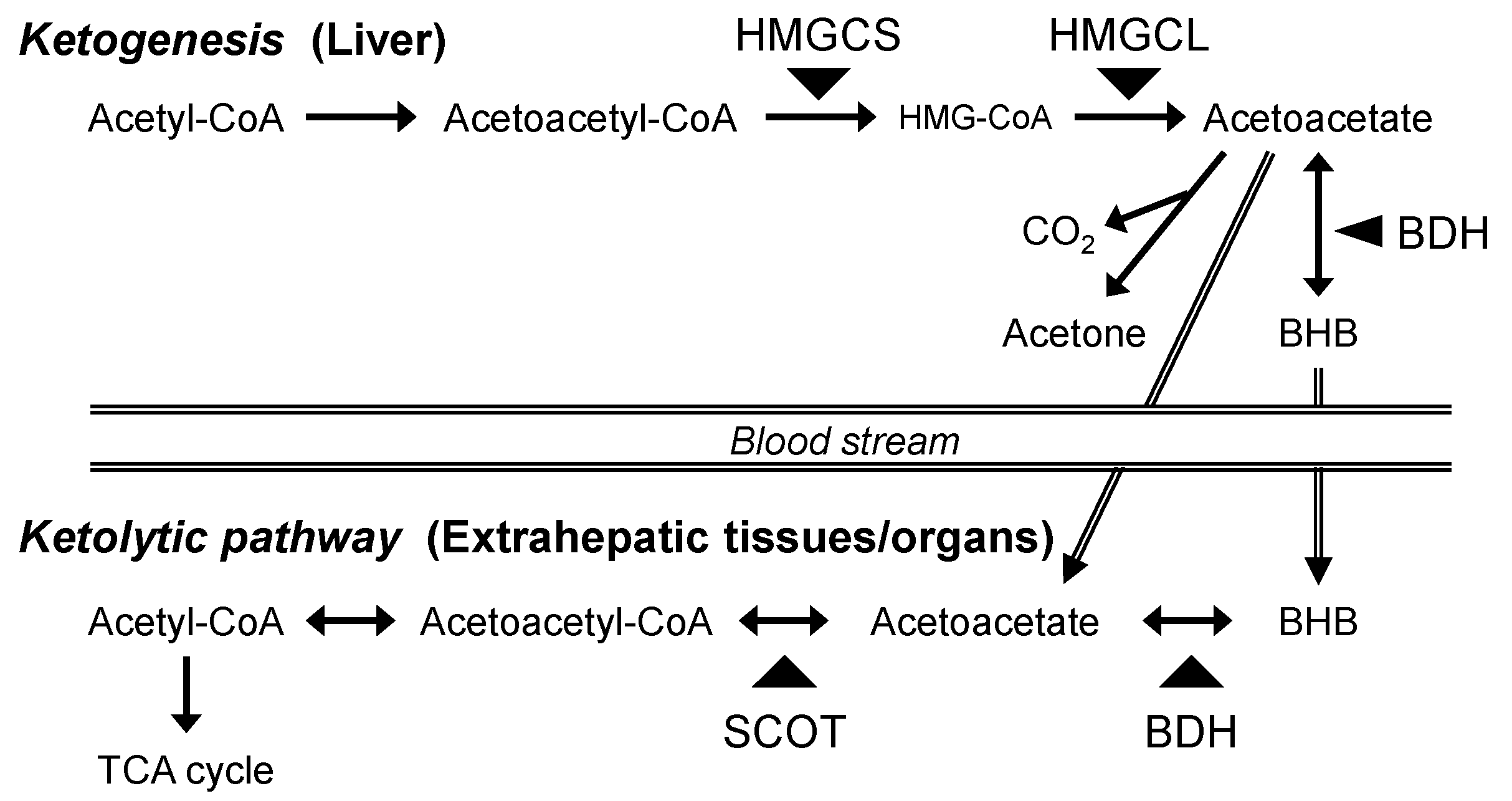
Ketone bodies, acetoacetate, acetone, and β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) are water-soluble substrates generated in the liver under fasted and hypoglycemic conditions. In the ketogenic process, acetyl-CoA derived from fatty acids is converted into acetoacetyl-CoA, from which acetoacetate is generated with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGCS) and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase (HMGCL) (
Figure.1). Thereafter, BHB is generated with BHB dehydrogenase (BDH), with acetone also generated by non-enzymatic decarboxylation. In extrahepatic tissues/organs, BHB is metabolized to acetoacetate, and this compound is subsequently re-converted into acetoacetyl-CoA, followed by acetyl-CoA formation. These ketolytic processes contribute to ATP production in mitochondria as an alternative energy source. In post-hatch chicks, plasma BHB concentration is higher as it is generated from residual egg yolk. The BHB levels is dramatically reduced with time after hatching [
1,
2]. It has also been reported that serum BHB concentration was not changed by 12 h of feed withdrawal, while the level was increased by the 24 h treatment and maintained constantly up to the next 24 h in young chickens [
3]. These reports suggest that BHB could be used as an energy substrate in response to physiological conditions.
Apart from the properties of BHB as energy fuel, recent studies have demonstrated that BHB exerts inflammatory effects due to a modulation of the signaling cascade [
4,
5]. It has been reported that BHB induces forkhead box protein O1 and its target gene, heme oxygenase-1 gene expression [
6], reinforcing the anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin (IL)-10 [
7]. Moreover, BHB has been reported to block the formation and activation of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome [8-10] and stimulate GPR109A receptor [
11], promoting anti-inflammation. Moreover, BHB administration has been reported to ameliorate renal inflammation, in which nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2), a master regulator of antioxidative gene’s transcription [
12], was activated with enhanced metabolic flux of TCA intermediates, acetoacetate, succinate, fumarate [
13]. These lines of evidence suggest that BHB alleviates inflammation through various molecular signaling transduction pathways, and metabolic alterations could also be involved in the effects.
Administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a cell-wall constituent of Gram-negative bacteria, is often used as a pathogenic inflammation model [
14,
15,
16,
17]. However, there is no available information on the effects of BHB on innate immune response of LPS-treated chickens. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of BHB on LPS-treated chickens by measuring plasma inflammatory parameters, cytokine expression. The study also examined ketolytic enzymes’ gene expression to seek a possible mechanism exhibiting the BHB effects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
Twenty day-old Ross 308 male broiler chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) were obtained from a local commercial hatchery (Matsumoto Poultry Farms & Hatcheries Co., LTD., Zao, Miyagi, Japan). The chicks were bred according to the breeding manuals and were provided ad libitum access to water and feed, a corn/soybean-based standard diet for broiler chickens at the grower phase (crude protein, 22%; metabolizable energy, 3,200 kcal/kg) until 25 days of age. The chickens were randomly allocated to the following treatment groups with similar average body weight (BW): sterile 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride solution (saline, control, n = 7), LPS [1.5 mg/kg (BW), Escherichia coli O127:B8 (#L3129; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), n = 6], or LPS plus BHB sodium [3 mmol/kg BW (#H0231; Tokyo Chemical industry, Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), n = 7]. The LPS and BHB solutions were prepared using saline on the day of use. The chickens were intraperitoneally injected with saline and LPS for 3 h, with BHB injected for 2 h before euthanasia. Feed was withdrawn in all groups during the treatment. Birds were euthanized by decapitation, and the spleen, liver, and gastrocnemius muscles were then excised and immediately frozen/powdered in liquid nitrogen. For isolation of PBMC, whole blood was collected in a heparinized centrifuge tube from the wing vein. The blood was gently transferred onto Lymphoprep™ solution (#ST-07811; STEMCELL Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada) and thereafter centrifuged at 800 ×g for 30 min at 20 °C. The organs, tissues, and PBMC was stored at -80 °C until use.
2.2. Analyses of Plasma Inflammation Markers
Plasma was obtained from heparinized-whole blood by centrifugation at 825 ×g for 10 min at 4 °C. The following inflammation markers were measured using each commercial kit: aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities (#431-30901; FUJIFILM-Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan), albumin and total protein concentration (#274-24301; FUJIFILM-Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan). The study also measured plasma interleukin (IL)-6 concentration using a commercial kit (#MBS2021018; MyBioSource, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3. Quantification of Gene Expression Levels
Real-time reverse transcript polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to quantify gene expression levels of inflammatory cytokines and ketogenic and ketolytic enzymes. Isolation of tissue RNA from the spleen, PBMC, skeletal muscle, and liver. Synthesis of complementary DNA and real-time RT-PCR analysis were conducted as previously described [18, 19]. Inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18), and ketogenic and ketolytic enzymes (HMGCL, HMGCS2, BDH1, SCOT) were amplified using each specific primer (
Table 1). The values were normalized to the expression levels of ribosomal protein S9 (RPS9) as an internal standard.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as the mean + standard error (SE) of 6-7 individuals. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni's method, with values of P < 0.05 considered to indicate statistical significance in each test.
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Inflammatory Parameters
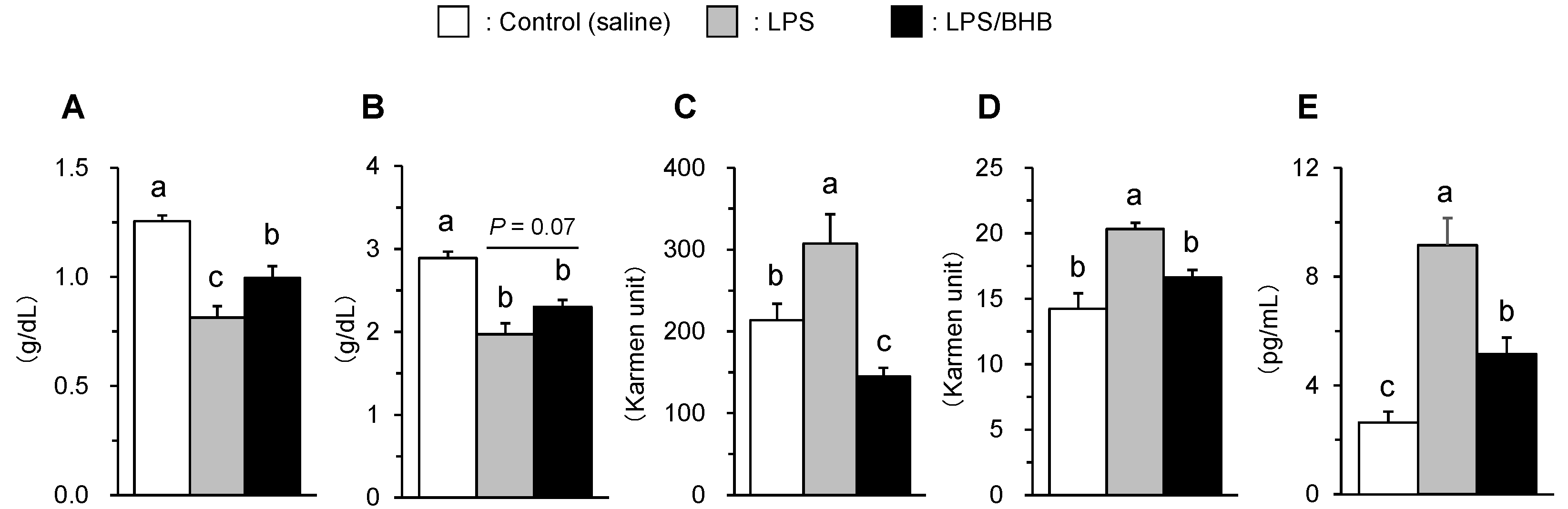
Plasma albumin and total protein concentration were significantly reduced by LPS administration, while the effects were partially inhibited in the BHB co-treated group (
P < 0.05 in albumin;
P = 0.07 in total protein) (
Fig. 2A, 2B). The LPS treatment significantly increased plasma AST and ALT activities, and the increases did not occur in the BHB co-treated group (
Fig. 2C, 2D), and similar results were obtained in plasma IL-6 concentration (
Fig. 2E). These results suggest that BHB intraperitoneal administration may have a suppressive effect on LPS-induced acute inflammation in broiler chickens.
3.2. The Effects of LPS and BHB Administration on Inflammatory Gene Expression
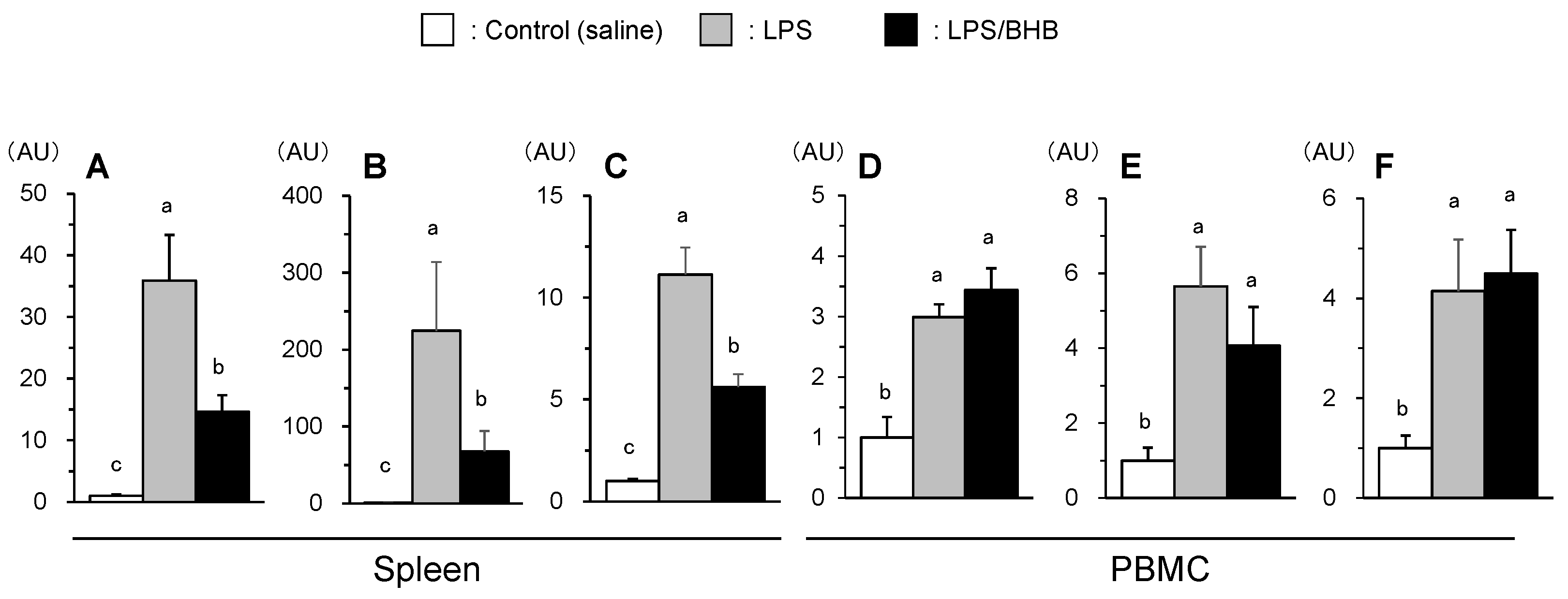
Gene expression levels of inflammatory cytokines were measured. As illustrated in
Fig. 3, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-18 gene expression levels were significantly increased by LPS administration in spleen and PBMC, with the greater up-regulation was observed in spleen than in PBMC. The above changes were partially inhibited in BHB co-treated group in spleen (
P < 0.05); however, the suppression did not occur in PBMC (
Fig. 3).
3.3. Different Gene Expression of Ketogenic and Ketolytic Enzymes in Peripheral Tissues/Organs
Beta-hydroxybutyrate is metabolized to acetyl-CoA (
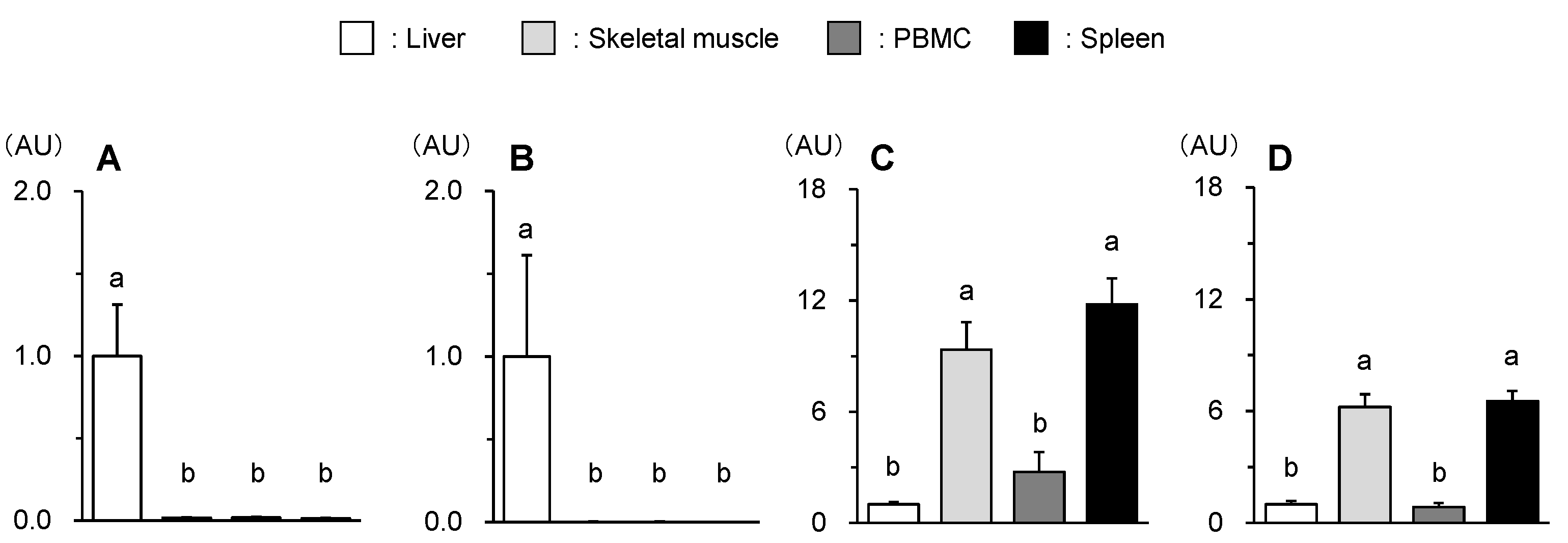
Fig. 1) and subsequently yields TCA-cycle intermediates. Therefore, the present study examined the gene expression levels of enzymes of ketone body metabolism to seek possible machinery associated with the different responses of BHB effects on LPS-induced inflammation between the spleen and PBMC. Gene expression levels of HMGCS2 and HMGCL were investigated as a rate-limiting enzyme of ketone body synthesis, each of which catalyzes the formation of acetoacetyl-CoA and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA from acetyl-CoA and acetoacetyl-CoA, respectively. The study also measured the gene expression levels of BDH1 and SCOT, each of which catalyzes a reversible reaction of BHB to acetoacetate and acetoacetate to acetoacetyl-CoA, respectively. The above four gene expression levels were also measured in the liver and skeletal muscle tissue as typical ketogenetic and ketolytic tissue/organ, respectively.
The present study showed that both HMGCS2 and HMGCL gene levels were markedly higher in the liver compared to those of skeletal muscle, PBMC, and spleen (
abP < 0.01) (
Fig. 4A, 3B) since the liver is a major ketogenic organ. Next, As seen in
Fig 4C and 4D, BDH1 and SCOT gene levels were relatively higher in skeletal muscle and spleen because they use ketone bodies as an alternative energy substrate. Meanwhile, these gene expressions in PBMC were lower than the above extrahepatic tissues/organs and comparable to those observed in the liver. These results suggest that PBMC may be unable to utilize BHB, which could explain the little effect of BHB on LPS-induced inflammatory response.
4. Discussion
There was little information regarding the effects of BHB on chicken’s innate immune response to our knowledge. One study has shown a possible involvement of BHB in chicken inflammation; serum BHB concentration was increased with ingestion of anti-inflammatory plant polysaccharides in pathogen-challenged laying hens [
20]. This report suggests that BHB could participate in suppressing pathogen-induced inflammation, although it is not evident that BHB directly suppresses inflammation. Therefore, the present study was the first to demonstrate that BHB administration may alleviate LPS-induced inflammation in chickens. While the present study did not address the precise mechanism of the BHB effects, one could suggest that expression levels of ketolytic enzymes, BDH1 and SCOT, could participate in the occurrence of the therapeutic effects of BHB in chickens.
It has been reported that intraperitoneal BHB injection mitigated kidney and placental injury [9, 21, 22]. In the present study, BHB was administered intraperitoneally to avoid the interference of altered intestinal functions and microbial compositions to inflammatory status. Oral BHB administration was reported to alleviate the intestinal integrity of mice [
23], and poly-BHB administration was reported to activate intestinal butyrate production, probably through production of BHB and its proliferating effect on butyrate-producing bacteria [
24]. From these findings, it could be considered that the oral BHB administration model could not precisely evaluate the BHB effects because other factors, such as short-chain fatty acid or prevention of pathogen incorporation, may be associated with the inflammatory status. Thus, the present study using an intraperitoneal BHB injection model indicates that BHB may directly contribute to improving inflammatory status.
The study found that the effects could depend on the gene expression levels of the ketolytic enzymes, BDH1 and SCOT. It has been reported that BDH1 plays a pivotal role in the suppression of diabetic kidney injury [
13]. The study proposed the suppression machinery based on the interaction of metabolites with transcriptional factor; fumarate yielded from BHB catabolism induces a nuclear translocation of Nrf2, suppressing inflammation/oxidative stress in the kidney. Given the findings, it could be considered that BDH1-meditated BHB metabolism participate in the BHB effects in chickens. It should be noted that the liver does not express BDH1 and SCOT. Therefore, it could be considered that BHB had little effect on hepatic inflammation. However, the present study showed that BHB alleviated inflammatory cytokine expression and ALT activity, which mainly depends on hepatic inflammatory/injury status, in LPS-treated birds. A few studies have demonstrated that BHB administration alleviated hepatic inflammation in postnatal piglets exhibiting growth retardation [
25] and human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells [
26]. The latter report suggests that AMP-activated protein kinase activation may be involved in the anti-inflammatory effects. These findings suggest that the BHB effects on hepatic inflammation could be independent of the ketolytic enzymes.
The present and previous studies showed the therapeutic effects of BHB in several inflammation models. However, a few investigations have reported the toxin-like or inflammatory effects of BHB. It has been reported that BHB exacerbates LPS/d-galactosamine-induced inflammatory response in mice [
27], and promotes inflammatory gene expression in calf hepatocytes [
28]. Moreover, acetoacetate derived from BHB as one of the ketone bodies has been reported to trigger NLRP3 inflammasome activation in bovine PBMC. The administration dosage, exposure time, and inflammation model or animals used differ between the studies. Therefore, it could be difficult to obtain a consistent result for BHB effects, considering these reports and the present results. Increased ketone bodies in circulation due to metabolic disorders often induce ketoacidosis. From these lines of findings, one could suggest that the physiological conditions prior to BHB administration are an important factor in exerting the therapeutic/anti-inflammatory effects of BHB.
Recent investigations proposed that metabolic intermediates and enzymes potentiate anti-inflammation [
29] and that ketogenesis favors oxidative phosphorylation to promote disease tolerance [
30]. Therefore, the BHB utilization may be one of the determinants of the anti-inflammatory effects. Further investigation using other tissues/organs, such as the kidney, brain, and intestine, is needed to precisely evaluate the involvement of ketolytic enzymes in BHB effects. Nonetheless, the present study is the first to demonstrate that BHB alleviated LPS-induced inflammation, in which the ketolytic enzyme’s gene expression could be involved in extrahepatic cells/organs in chickens.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, TH, MK; methodology, TH, KF, MK ; Formal analysis, TH, KF, MK; Funding acquisition/resources, MK; Investigation/methodology, TH, KF, MK; writing—original draft preparation, KF, MK; writing—review and editing, TH, KF, MK; visualization, TH, MK; supervision/project administration, MK. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 20H03123 (MK).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Animal Care and Use Committee of the Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University, approved all procedures, and every effort was made to minimize pain or discomfort to the animals (approval ID: 2014AgA-033).
Data Availability Statement
There is no available data from the investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ohtsu, H.; Sato, K.; Nishida, H.; Akiba, Y. High β-hydroxybutyrate concentration in liver and skeletal muscle of newly hatched chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2003, 134, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahagna, M.; Nir, I. Comparative development of digestive organs, intestinal disaccharidases and some blood metabolites in broiler and layer-type chicks after hatching. Br Poult Sci. 1996, 37, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Yan, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Yuan, J. The duration of food withdrawal affects the intestinal structure, nutrients absorption, and utilization in broiler chicken. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neudorf, H.; Little, J. P. Impact of fasting & ketogenic interventions on the NLRP3 inflammasome: A narrative review. Biomed J. 2024, 47, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendridi, N.; Selmi, A.; Balcerczyk, A.; Pirola, L. Ketone bodies as metabolites and signalling molecules at the crossroad between inflammation and epigenetic control of cardiometabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 14564, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, T.; Uchida, Y.; Kadono, K.; Hirao, H.; Kawasoe, J.; Watanabe, T.; Ueda, S.; Okajima, H.; Terajima, H.; Uemoto, S. Up-regulation of FOXO1 and reduced inflammation by β-hydroxybutyric acid are essential diet restriction benefits against liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019, 116, 13533–13542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T. S.; Chau, L. Y. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 in mice. Nat Med. 2002, 8, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y. H.; Nguyen, K. Y.; Grant, R. W.; Goldberg, E. L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D'Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T. D.; Kang, S.; Horvath, T. L.; Fahmy, T. M.; Crawford, P. A.; Biragyn, A.; Alnemri, E.; Dixit, V. D. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, Y.; Shimazaki, S.; Suzuki, S.; Henmi, Y.; Komiyama, H.; Kuwayama, T.; Iwata, H.; Karasawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Shirasuna, K. β-hydroxybutyrate suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated placental inflammation and lipopolysaccharide-induced fetal absorption. J Reprod Immunol. 2021, 148, 103433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Lin, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Q. Ketone metabolite β-Hydroxybutyrate ameliorates Inflammation after spinal cord injury by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurochem Res. 2021, 46, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, M. A.; Chen, H.; Ridder, D. A.; Müller-Fielitz, H.; Pokorná, B.; Vollbrandt, T.; Stölting, I.; Nadrowitz, R.; Okun, J. G.; Offermanns, S.; Schwaninger, M. The β-hydroxybutyrate receptor HCA2 activates a neuroprotective subset of macrophages. Nat Commun. 2014, 5, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazian, S. M.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S. M.; Barzegari, A.; Pavon-Djavid, G.; Razi Soofiyani, S.; Hassannejhad, S.; Ahmadian, E.; Ardalan, M.; Zununi Vahed, S. Nrf-2 as a therapeutic target in acute kidney injury. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S. R.; Teng, F. Y.; Fan, W.; Xu, B. T.; Li, X. Y.; Tan, X. Z.; Guo, M.; Gao, C. L.; Zhang, C. X.; Jiang, Z. Z.; Xu, Y. BDH1-mediated βOHB metabolism ameliorates diabetic kidney disease by activation of NRF2-mediated antioxidative pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2023, 15, 13384–13410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Du, L.; Shao, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Cao, L.; Chen, H.; Bi, S. Molecular and metabolic responses to immune stress in the jejunum of broiler chickens: transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis. Poult Sci. 2024, 103, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Li, Y.; Ying, S.; Yan, J.; Shi, Z. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide with different administration routes affects intestinal mucosal morphological, immunological, and microbial barrier functions in goslings. Poult Sci. 2023, 102, 102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ogaili, A. S.; Hameed, S. S.; Noori, N. LPS-induced NLRP3 gene expression in chicken. Open Vet J. 2022, 12, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Ji, P.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. Study on the hepatoprotective effect mechanism of polysaccharides from charred Angelica sinensis on the layer chickens based on the detection of the intestinal floras and short-chain fatty acids of cecal contents and association analysis. Vet Sci. 2023, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muroi, H.; Hori, K.; Tokutake, Y.; Hakamata, Y.; Kawabata, F.; Toyomizu, M.; Kikusato, M. Oleuropein suppresses mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation possibly via an activation of transient receptor potential V1 and sirtuin-1 in cultured chicken muscle cells. Anim Sci J. 2021, 93, e13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikusato, M.; Nanto, F.; Mukai, K.; Toyomizu, M. Effects of trehalose supplementation on the growth performance and intestinal innate immunity of juvenile chicks. Br Poult Sci. 2016, 57, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, P.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Huang, Y.; Bai, R.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, L.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; He, B.; Zeng, J.; Zeng, X. Gut microbiota and serum metabolome reveal the mechanism by which TCM polysaccharides alleviate salpingitis in laying hens challenged by bacteria. Poult Sci. 2024, 103, 103288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M. J.; Kim, Y. S.; Kim, S. R.; Lee, D. W.; Lee, S. B.; Kim, I. Y. Pre-treatment with β-hydroxybutyrate mitigates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024, 695, 149482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M. J.; Kim, Y. S.; Kim, S. R.; Lee, D. W.; Lee, S. B.; Kim, I. Y. β-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Mol Biol Rep. 2023, 50, 8915–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhuang, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, K.; Li, Y. D-β-hydroxybutyrate up-regulates Claudin-1 and alleviates the intestinal hyperpermeability in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Tissue Cell. 2024, 87, 102343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T. Ketobiotics by poly-3-hydroxybutyrate: a novel prebiotic activation of butyrate-producing bacteria through 3-hydroxybutyrate donation to the microbiota. Journal of Biotechnology and Biomedicine. 2023, 5, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, N.; Deng, Y.; Zha, A.; Li, J.; Tan, B.; Qi, M.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y. β-hydroxybutyrate administration improves liver injury and metabolic abnormality in postnatal growth retardation piglets. Front Vet Sci. 2023, 10, 1294095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, H. R.; Kim, D. H.; Park, M. H.; Lee, B.; Kim, M. J.; Lee, E. K.; Chung, K. W.; Kim, S. M.; Im, D. S.; Chung, H. Y. β-Hydroxybutyrate suppresses inflammasome formation by ameliorating endoplasmic reticulum stress via AMPK activation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66444–66454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shao, R.; Jiang, R.; Zhu, M.; Tang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. β-Hydroxybutyrate exacerbates lipopolysaccharide/ d-galactosamine-induced inflammatory response and hepatocyte apoptosis in mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2019, 33, e22372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Deng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Yin, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G. β-Hydroxybutyrate activates the NF-κB signaling pathway to promote the expression of pro-inflammatory factors in calf hepatocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014, 33, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pålsson-McDermott, E. M.; O'Neill, L. A. J. Targeting immunometabolism as an anti-inflammatory strategy. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, K.; Moita, L. F. Ketogenesis favors oxidative phosphorylation to promote disease tolerance. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2024, 35, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).