1. Introduction
The incidence of complications after cardiac surgery has been reducing due to the development of new technologies and treatment methods, as well as improved qualifications of surgeons. However, the development of various complications still remains a serious problem that can lead to an increasing expense for treatment, mortality or deterioration in the patient’s quality of life after surgery [
1]. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons identifies five major postoperative complications: stroke, renal failure, prolonged intubation, unplanned reoperation, and deep sternal wound infection. The frequency of complications may vary depending on the type of operation, the patient’s condition before surgery and the professionalism of the operating team of cardiac surgeons [
2]. To reduce the risks of postoperative complications, various measures are used, such as careful planning of the operation, preparing the patient before the operation, strict monitoring in the postoperative period.
The use of biomarkers is a powerful tool that can improve the quality of the diagnostics and treatment of patients, help to understand the patient’s condition and promptly identify possible complications. These biomarkers are lactate [
3], procalcitonin, interleukin-6, NT-proBNP, protein S100 [
4], high-sensitivity troponin T [
5]. They have different sensitivity and specificity for the prognosis of the post-cardiosurgical complications, however, none of them is an excellent biomarker with 100% sensitivity and specificity.
Various metabolites have increasingly been used in clinical practice and actively studied for early diagnosis [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. The value of metabolites lies in their ability to mark not only changes in the human body. The gut microbiota is known to influence host physiology, including through the production of multiple metabolites [
11]. There is a concept about the relationship between the gut microbiota and the heart, so-called the gut-heart axis, which led to novel treatment and prevention strategies by studying and targeting the composition of gut microbiome and its metabolites [
4,
12,
13].
One of our recent single-center study on aortic prosthetics highlighted the importance of the assessment of the serum metabolic profile in patients on admission and in the early postoperative period. Increased concentrations of the sepsis-associated aromatic microbial metabolites were detected in patients (n=79) compared to healthy donors (p < 0.05) before the surgery. In addition, aromatic metabolites were increased in the early postoperative period (6 hours after the end of the surgery) in the group of patients both with all types of postoperative complications (n=43) and in particular in patients with infectious complications (n=26) [
14].
Another previous single-center pilot study included patients undergoing cardiac surgery where we analyzed the composition of the gut microbiome in patients (n=24) before and after surgery. Patients who developed infectious complications (n=12) in the early postoperative period had a distinct gut microbiota taxonomy, with a predominance of potentially pathogenic species even before surgery. This change in microbiome composition may be associated with an increased risk of developing infectious complications [
15]. In the current study, we decided to further analyze certain metabolites in all cardiac surgery patients from this study, as well as examine known biomarkers to try to predict complications that may occur. Therefore, the aim of this study was to identify the value of metabolite and biomarker monitoring for predicting postoperative complications in cardiac surgery in comparison with clinical data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study was performed in the N. Pirogov National Medical Surgical Center, Moscow, Russian Federation. The local Ethics Committee approved the study (no. 04 from 22/05/2018), which was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. An informed consent for participation in this study was also obtained from each patient or his/her legal representative.
Patients (n = 62 including 44 males and 18 females) had different types of planned cardiovascular surgery. All patients had coronary artery bypass grafting – CABG (n = 62, 100%); some patients had combined operations – CABG and plastics of aortic or mitral valve – PAMV (n = 12, 19%), CABG and post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm resection (n = 2, 3%). All surgeries were performed with cardiopulmonary bypass. Some patients had following concomitant diseases: chronic heart failure (n = 54, 87%), chronic gastritis (n = 45, 73%), hypertension (n = 44, 71%), diabetes (n = 10, 16%), atrial fibrillation (n = 7, 11%), obesity (n = 5, 8%), gastric ulcers (n = 4, 7%), and chronic pancreatitis (n = 4, 7%). Median (interquartile range 25, 75%) age was 62 (57, 68) years, ejection fraction (EF) was 60 (49, 64) %. All patients used perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis using cefazolin 2 g three times within 24 hours.
The criteria for inclusion in the study were the following: the patient was over 18 years old, had a planned cardiovascular surgery that corresponded to one of the following categories of cardiac surgery – CABG or combination surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Also, serum samples should be collected in dynamics, at least before the surgery (point 0) and in a day after the surgery (point 1). Additionally, the patient gave an informed consent to participate in the study. Initially 72 patients were included in the study, however, only 62 of them met the necessary criteria for inclusion, i.e. had cardiopulmonary bypass during the cardiac surgery and had serum samples in both points 0 and 1.
Exclusion criteria included the presence of active infectious endocarditis, emergency surgery, previous bacterial infectious diseases in the past three months, antibiotic use within the past three months and refusal to participate in the study.
All patients were divided into two groups retrospectively: with postsurgical complications (n = 26) and without postsurgical complications (n = 36). Complications included postoperative bleeding (n = 9, 14.5%), respiratory disorders (n = 7, 11%), atrial fibrillation (n = 5, 8%), myocardial ischemia (n = 5, 8%), delirium (n = 2, 3%). Some patients had multiple organ failure (n = 3, 5%). Demographic and perioperative information, comorbidity, scales and laboratory parameters were retrospectively analyzed from medical documentation.
2.2. Blood Sample Collection
Collection of patients’ blood samples was performed before the surgery (point 0) and in a day after the surgery (point 1). There were also 48 blood samples from healthy donors (n=48), which were used to reveal reference values for aromatic and dicarboxylic acid concentrations [
14]. Serum samples were obtained by blood centrifuging at 1500×g for 10 min on the same day. The total number of serum samples (n = 172) included 124 ones from patients and 48 ones from healthy volunteers.
Data on the following parameters was taken from the medical documentation: EF% before surgery, hemoglobin (Hb), leucocytes, the highest value of lactate for the first day (lactate max), pH max, pH min, infusion volume, on-pump time, number of erythrocytes transfusions, and total blood loss. Additionally, some specific analyses were conducted in the Federal Research and Clinical Center of Intensive Care Medicine and Rehabilitology in Moscow, Russia. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses using a Trace GC 1310 gas chromatograph and ISQ LT mass spectrometer from Thermo Electron Corporation (Santa Clara, CA, USA) were conducted to measure the concentration of various aromatic and dicarboxylic acids (benzoic acid – BA, phenylacetic acid – PhAA, phenylpropionic acid – PhPA, phenyllactic acid – PhLA, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid – p-HBA, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid – p-HPhAA, 4-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid – p-HPhPA, homovanillic acid – HVA, 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid – p-HPhLA, succinic acid – SA, and fumaric acid – FA). The limit of quantitation for all acids was 0.5 µmol/l with a relative standard deviation of 10-30% and the calibration curve was linear for all metabolites within the clinically significant concentration range (0.5-15 µmol/l). The sample preparation for the analytes and the details on the GC-MS analysis were previously described [
16]. Several biomarkers were measured (interleukin-6 – IL6, procalcitonin – PCT, N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide – NT-proBNP, protein S100 and high-sensitive troponin T – HST-T) by electrochemiluminescence (Cobas e411, Roche, Basel, Switzerland).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to assess the normality of the data distribution. Continuous variables were described in tables using median and interquartile ranges; categorial variables were described using number of cases and percentage. The Mann-Whitney U-test (two-sided) and Chi-square test used for primary descriptive statistics in
Section 3.1, p-value < 0.05 was chosen as significant. All statistical tests performed with Scipy, Python. To achieve dimensional reduction for visualization and machine learning PLS was used (
Section 3.2). VIP-scores were computed to evaluate the importance of variables. Finally, the data used for fitting of PLS-DA model for binary classification. Predictive models performed with Sklearn (Python) and metrics (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC), sensitivity, specificity) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) computed and evaluated with k-fold cross-validation (k = 7).
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Uncomplicated and Complicated Patient Groups
Table 1 describes the medical and demographic characteristics, intraoperative parameters, serum concentrations of metabolites and biomarkers in all patients (n=62), which could be compared to corresponding reference values or donors’ concentration for metabolites, and the differences between uncomplicated (n=36) and complicated (n=26) patients before (point 0) and in a day after the surgery (point 1).
In point 0 there were patients with following parameters that were out of the reference values: hemoglobin (n = 23, 37%), leucocytes (n = 58, 94%), lactate (n = 62, 100%), pH (n = 39, 63%), IL-6 (n = 33, 53%), NT-proBNP (n = 50, 81%,), S100 (n = 8, 13%), and HST-T (n = 48, 77%). According to the criterium that 95% CI of the parameter should not contain the minimum or maximum level of the corresponding reference range, the following parameters should be considered as significantly out of reference range: leukocytes in all patients – 95% CI (11.3-20.8)×109 (out of reference range (4-9)×109) and lactate in all patients – 95% CI 2.82-7.51 mmol/l (higher than the reference maximum level of 2 mmol/l).
Usage of vasopressors (p = 0.02), time of mechanic ventilation (p < 0.001), infusion volume (p < 0.001), on-pump time (p < 0.001), number of erythrocytes transfusions (p = 0.03), blood loss on the 1st day (p = 0.04), SOFA scores (p < 0.001), and HST-T after the surgery (p = 0.03) were significantly higher in complicated patients compared to uncomplicated ones.
In serum samples of donors and all patients before the surgery (in point 0) differences in concentrations of BA (p <0.001), PhAA (p < 0.001), p-HBA (p = 0.03), p-HPhAA (<0.001), sum of sepsis associated PhLA, p-HPhAA and p-HPhLA – Σ3AMM (p = 0.04), SA (p < 0.001), and FA (p < 0.001) were statistically significant. In a day after the surgery all metabolites statistically differed in all donors and patients.
The dynamics of the metabolites and biomarkers was evaluated as the difference (Δ) between their levels in points 1 and 0 (1-0). The differences in the level of Σ3AMM (p = 0.03), PCT (p = 0.01), NT-proBNP (p = 0.01), and HST-T (p = 0.01) were statistically significant.
3.2. Models for the Prognosis of the Postoperative Complications
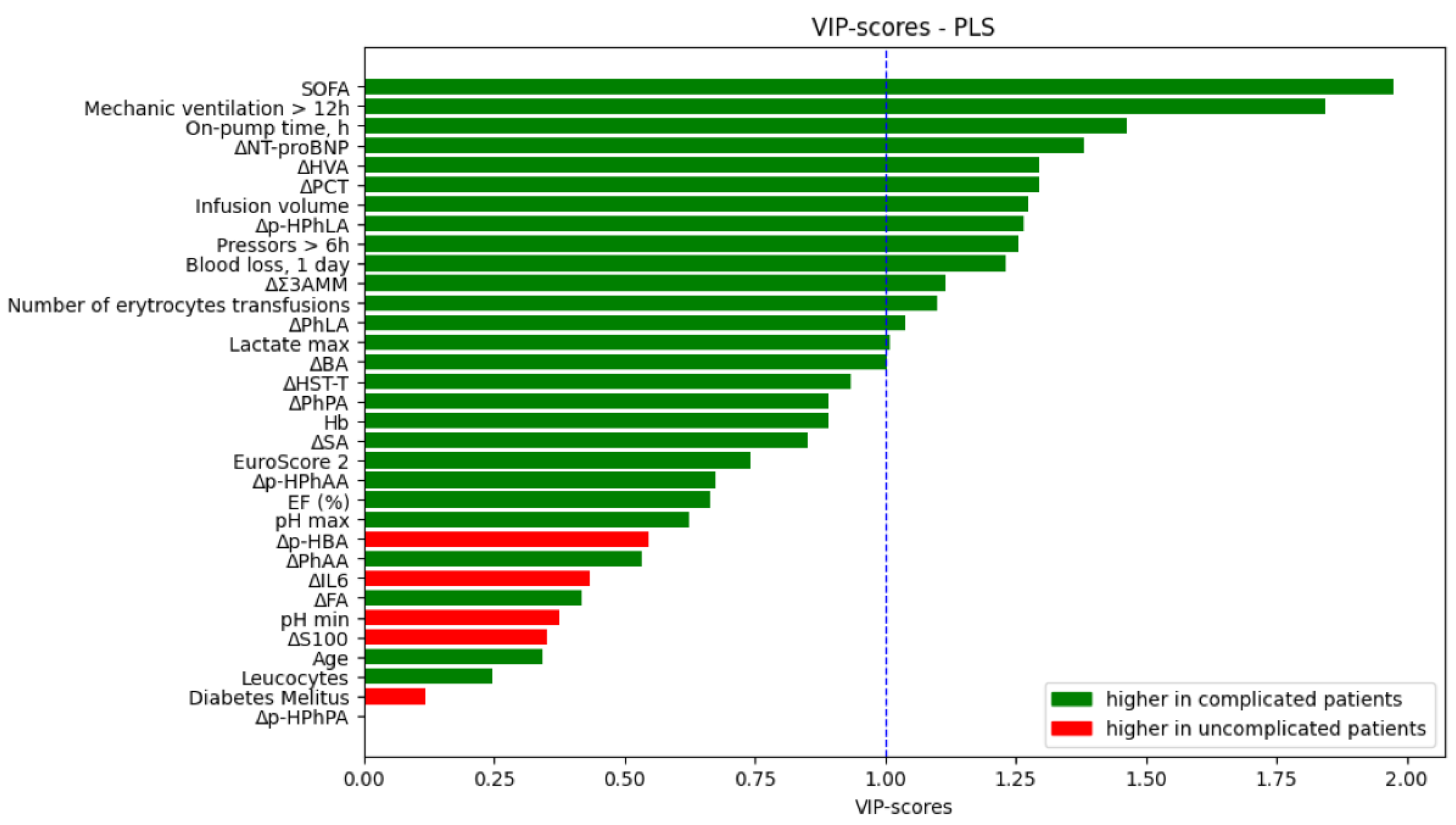
Data that was collected before and in a day after the surgery was used to fit models to predict if a patient will have complications or not. PLS analysis was performed for the importance evaluation of all parameters included in the model (
Figure 1). Threshold value for VIP-scores was chosen as 1. SOFA and time of mechanic ventilation > 12 h took leading positions in VIP-scores rating, also clinical parameters higher than the threshold were on-pump time, infusion volume, total blood loss, number of erythrocytes transfusions, and lactate. Differences in certain metabolites and biomarkers (NT-proBNP, HVA, PCT, p-HPhLA, Σ3AMM, PhLA, BA) were more than chosen threshold.
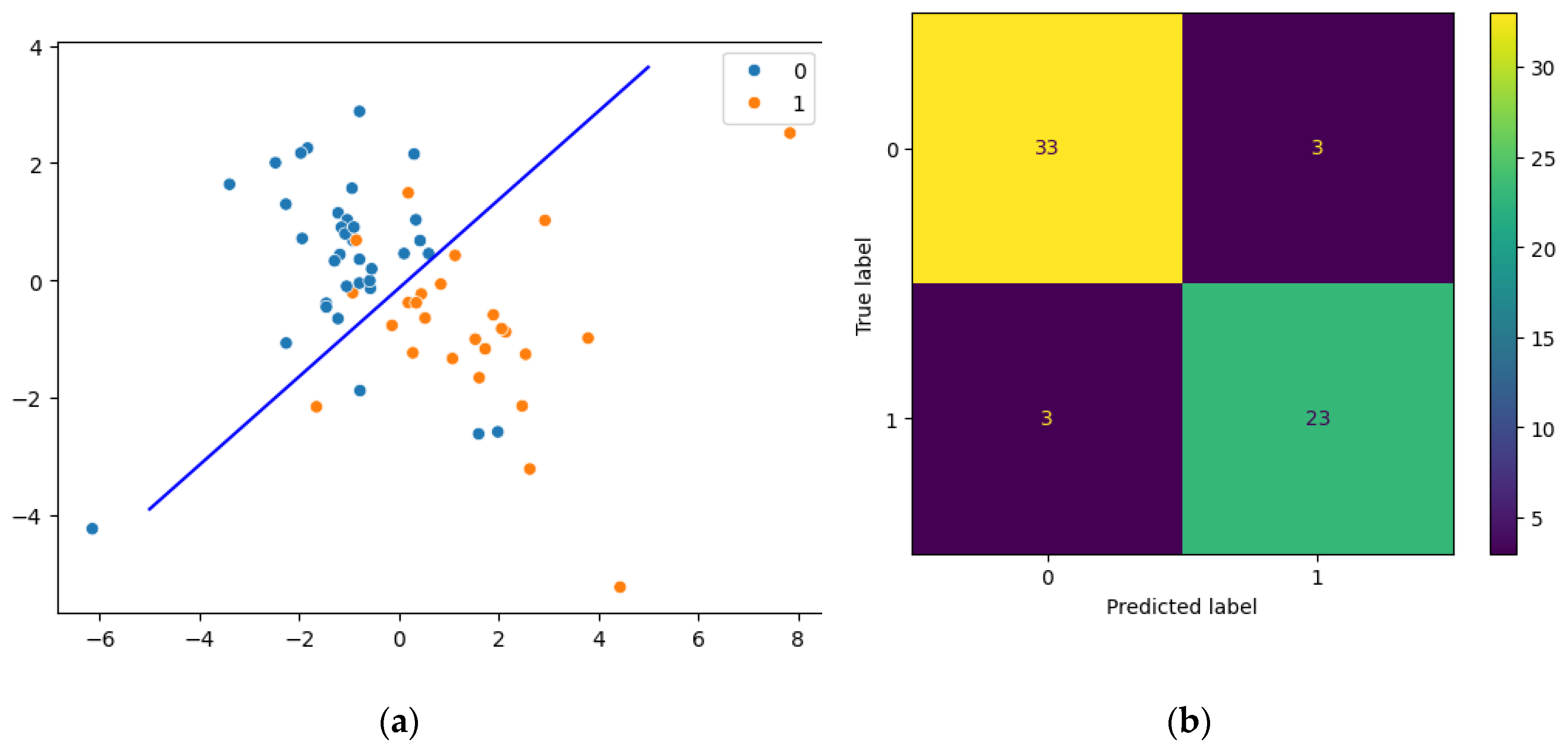
Resulting pipeline included transforming data with PLS and then predicting the development of complications by the logistic regression. Computed coordinates that are explained as scatter plot (
Figure 2 a) show linear discrimination between groups. A confusion matrix shows the quality of classification in all dataset (
Figure 2 b). Three samples were misclassified in the uncomplicated group of patients (false negative samples) and three samples were misclassified in the complicated group of patients (false positive samples).
Multivariate PLS-DA models were constructed. We built models fit on all data (ROC-AUC = 0.75); only on clinical data (ROC-AUC = 0.71), and only on metabolites and biomarkers (ROC-AUC = 0.60). We compared our models with univariate models built on SOFA (ROC-AUC = 0.76) and EuroScore 2 (ROC-AUC = 0.59) scores; lactate (ROC-AUC = 0.71); Δp-HPhLA (ROC-AUC = 0.69), and ΔΣ3AMM (ROC-AUC = 0.70). All data obtained were accumulated in
Table 2.
4. Discussion
Cardiac surgery remains one of the types of operations after which complications can arise, despite the development of medicine and the improvement in the quality of medical care provided. It is extremely important to try to predict the development of postoperative complications as early as possible. In early postoperative period either medical prophylaxis or simply more strict monitoring can be performed to effectively avoid undesirable consequences of invasive treatment [
17]. This was the main reason why we focused on data that was available in preoperative and early perioperative period in the current study.
Researchers have identified various risk factors for the developed of postoperative complications. They can be divided into three groups: patient characteristics (female sex, obesity, smoking), clinician characteristics (volume of infusion, duration of surgery, doses of assigned medications), and postoperative factors (clinical decisions and nursing) [
2,
18]. The use of cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery is considered to be one of the main risk factors that disrupts metabolic pathways mainly due to the activation of oxidative stress [
19]. This fact served as the basis for including in our study only those patients who had cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass to search for parameters that could distinguish complicated and uncomplicated patients. In our study clinical parameters that significantly differs in complicated and uncomplicated patients were infusion volume, on-pump time, SOFA, number of erythrocytes transfusion, and blood loss in the 1
st day (
Table 1). Data on pump-time correlated with other study where this parameter was also higher in complicated group of patients [
20].
Biomarkers are wildly used in cardiac surgery. All of them generally explains one or few type of complications. NT-proBNP marks atrial wall distraction [
21]. There are also a lot of data revealing the role of cardiac troponins – biomarkers of ischemic processes in cardiac tissue [
5,
22], procalcitonin – marker of infectious process [
23], lactate – marker of tissue hypoxia [
24] in prediction of postoperative complications after cardiac surgery. Various studies were conducted to reveal metabolic changes after cardiac surgeries [
7,
8,
10]. In our previous study higher serum concentrations of metabolites of phenylalanine and tyrosine in complicated group of cardiac surgery patients were detected [
14]. In current study among metabolites and biomarkers only HST-T after the surgery differed significantly in two groups of patients, but differences between metabolites and biomarkers (point 1 – point 0) were statistically significant among few characteristics (ΔΣ3AMM, ΔPCT, ΔNT-pro-BNP, ΔHST-T). These facts show that dynamic changes are important for prediction of postoperative complications. In our previous study additionally statistically significant difference in ∆p-HPhAA and ∆p-HPhLA was obtained [
14] that we do not observe in current study, but we obtain statistically significant difference in the dynamics of the sum of p-HPhAA and ∆p-HPhLA together with PhLA – ΔΣ3AMM. These two studies repeatedly demonstrated the altered metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine in high-risk patients with a predominance of the sepsis-associated metabolites of microbial origin [
25].
Machine learning is a powerful tool that can be used for the prediction of the postoperative complications. In cardiac surgery it was successfully used for the prognosing of the postoperative atrial fibrillation [
12] or acute kidney injury [
26]. Although some studies described the results to apply predictive models built only on clinical data; they demonstrated different predictive ability. Zhang et al. reported predictive models with ROC-AUC = 0.94 for XGBoost and ROC-AUC = 0.75 for support vector machines built on records of monitoring during off-pump CABG [
27]. Li et al. demonstrated ROC-AUC for different models lower than 0.70 [
20]. Despite relatively good predictive ability of clinical data, prognostic models on metabolomic data show growing popularity in diagnostics because of its potential. In particular, in patients with aortic dissection there are results that mark impaired metabolic pathways and suggest potential biomarkers for different conditions and diseases [
10]. There are also attempts to use metabolites and biomarkers with clinical data in machine learning for prediction of postoperative delirium and acute kidney injury [
17,
28]. Our PLS-DA models fitted on metabolites and biomarkers demonstrated moderate predictive value with ROC-AUC = 0.60 and sensitivity/specificity 0.73/0.47. The model fitted only on clinical data demonstrated better predictive value with ROC-AUC = 0.71 and sensitivity/specificity 0.68/0.74. Finally, the best results were obtained for the model with entire set of data – ROC-AUC = 0.75 and sensitivity/specificity 0.74/0.77. This fact gives us opportunity to suppose that the use of metabolites and biomarkers in predictive models in cardiac surgery may improve their sensitivity and specificity for recognizing the postsurgical complications.
As additional data and for comparison, we built a series of univariate models. EuroScore2 scale is widely used by clinicians for evaluation of cardiosurgical risks [
29]. In current study EuroScore2 was weak for patients’ group discrimination (ROC-AUC = 0.59 and sensitivity/specificity 0.52/0.67). SOFA scale showed the best results in univariate models (ROC-AUC = 0.76 and sensitivity/specificity 0.69/0.83) despite the fact that it is usually used for mortality prediction and it may have different predictive ability for various pathologic conditions [
30]. We also examine model on lactate – ROC-AUC=0.71 and sensitivity/specificity 0.76/0.67, and it may be compared with data on predictive ability of this biomarker with that in other conditions despite the fact that lactate is not using as specific biomarker for cardiac surgery [
31,
32].
In our previous study we received ROC-AUC = 0.71 and sensitivity/specificity 0.81/0.56 for Σ3AMM and ROC-AUC = 0.69 and sensitivity/specificity 0.79/0.47 for p-HPhLA for the prediction of all types of postoperative complications after aortic prosthetics [
14]. In current study two univariate models using ΔΣ3AMM and Δp-HPhLA for the prediction of complications were built and demonstrated similar predictive ability with ROC-AUC = 0.70 and sensitivity/specificity 0.62/0.78 for ΔΣ3AMM and ROC-AUC = 0.69 and sensitivity/specificity 0.88/0.50 for Δp-HPhLA.
Our pilot single center study has a number of limitations. Firstly, the number of patients was relatively low that did not allow us to evaluate the contribution of sex, age and comorbidity on statistics and quality of predictive models. Secondly, we consider all types of complications despite the fact that different types of complication have different developmental pathophysiology. However, we suppose that the microbiota disruption, indirectly assessed by the level of microbial metabolites, can affect the development of all types of complications. In addition, we considered only a few metabolites, biomarkers and clinical parameters in a plane of our interests and did not explain other substances and metabolic pathways. Finally, there were data on patients with off-pump surgery and some serum samples in latest days (the 3rd and 6th ) after surgery that was not analyzed.
5. Conclusions
Using levels of certain metabolites and biomarkers circulating in the blood in combination with clinical data can help improve the predictive ability of diagnostic algorithms. It is essential to explore methods to regulate microbiota metabolism to improve surgical outcomes in the future by finding alternatives to compensate for its functions. For these purposes, it is important to organize and conduct multicenter studies in which it would be possible to study various approaches to preoperative influences on the microbiota of patients in order to reduce the incidence of any type of postoperative complications in cardiac surgery.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.Z. and N.B.; methodology, E.Z., A.P., E.C.; formal analysis, P.M.; investigation, E.Z., A.P., E.S., E.C.; resources, E.Z. and N.B.; data curation, E.Z. and N.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P., P.M., E.S.; writing—review and editing, E.Z., N.B., E.C.; visualization, P.M.; supervision, A.P., N.B., E.C.; project administration, A.P., E.Z.; funding acquisition, N.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the local Ethics Committee of N. Pirogov National Medical Surgical Center, Moscow, Russian Federation (protocol no. 04 from 22/05/2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
not applicable
Acknowledgments
not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Crawford, T.C.; Magruder, J.T.; Grimm, J.C.; Suarez-Pierre, A.; Sciortino, C.M.; Mandal, K.; Zehr, K.J.; Conte, J. V.; Higgins, R.S.; Cameron, D.E.; et al. Complications After Cardiac Operations: All Are Not Created Equal. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montrief, T.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. Coronary artery bypass graft surgery complications: A review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzeri, C.; Valente, S.; Chiostri, M.; Gensini, G.F. Clinical significance of Lactate in acute cardiac patients. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.-Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.-Y. Current understanding of gut microbiota alterations and related therapeutic intervention strategies in heart failure. Chin. Med. J. (Engl). 2019, 132, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavsak, P.A.; Belley-Cote, E.P.; Whitlock, R.P.; Lamy, A. Cardiac troponin testing in cardiac surgery. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2023, 21, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, G.N.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Shu, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Plasma Metabolites-Based Prediction in Cardiac Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, B.A.; Dillon, S.T.; Yuan, M.; Asara, J.M.; Vasunilashorn, S.M.; Fong, T.G.; Metzger, E.D.; Inouye, S.K.; Xie, Z.; Ngo, L.H.; et al. Targeted metabolomics analysis of postoperative delirium. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, A.J.; Noss, C.D.; Chun, R.; Gysel, M.; Prusinkiewicz, C.; Webb, N.; Raymond, M.; Cogan, J.; Rousseau-Saine, N.; Lam, W.; et al. Perioperative Optimization of the Cardiac Surgical Patient. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; Cheng, L.; Yu, B.; Liu, H. Analysis of differential metabolites in serum metabolomics of patients with aortic dissection. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, D.; Spitzer, M.H.; Van Treuren, W.; Merrill, B.D.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Le, A.; Cowan, T.M.; Nolan, G.P.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature 2017, 551, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Mei, F.; Luo, J.; Cui, Y. Microbial metabolites and heart failure: Friends or enemies? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernevskaya, E.A.; Getsina, M.L.; Cherpakov, R.A.; Sorokina, E.A.; Shabanov, A.K.; Moroz, V. V.; Beloborodova, N. V. Sepsis-Associated Metabolites and Their Biotransformation by Intestinal Microbiota. Gen. Reanimatol. 2023, 19, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloborodova, N.; Pautova, A.; Grekova, M.; Yadgarov, M.; Grin, O.; Eremenko, A.; Babaev, M. Microbiota Metabolism Failure as a Risk Factor for Postoperative Complications after Aortic Prosthetics. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernevskaya, E.; Zuev, E.; Odintsova, V.; Meglei, A.; Beloborodova, N. Gut Microbiota as Early Predictor of Infectious Complications before Cardiac Surgery: A Prospective Pilot Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautova, A.K.; Burnakova, N.A.; Beloborodova, N. V.; Revelsky, A.I. Simultaneous Determination of Aromatic, Short-Chain Fatty and Dicarboxylic Acids in Blood Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 78, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiredu, K.; O’Connor, S.; Naseem, H.; Brauer, B.L.; Kettenbach, A.N.; Frost, H.R.; Shaefi, S.; Gerber, S.A. Intraoperative plasma proteomic changes in cardiac surgery: In search of biomarkers of post-operative delirium. PROTEOMICS – Clin. Appl. 2023, 17, e2200066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslyakova, I.A.; Belyakov, K.S.; Abdulrazakov, A.A.; Marinin, V.A. Predictors of Complications Related to Cardiac Ablation for Atrial Arrhythmias. Gen. Reanimatol. 2024, 20, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonenc, A.; Hacışevki, A.; Griffiths, H.R.; Torun, M.; Bakkaloglu, B.; Simsek, B. Free radical reaction products and antioxidant capacity in beating heart coronary artery surgery compared to conventional bypass. Biochem. 2011, 76, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lv, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Shi, J.; Zhou, C. Development and validation of a machine learning predictive model for perioperative myocardial injury in cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turagam, M.K.; Mirza, M.; Werner, P.H.; Sra, J.; Kress, D.C.; Tajik, A.J.; Jahangir, A. Circulating Biomarkers Predictive of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 24, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, J.; Schupp, T.; Weidner, K.; Rusnak, J.; Jawhar, S.; Dulatahu, F.; Brück, L.M.; Behnes, M.; Hoffmann, U.; Bertsch, T.; et al. Cardiac Troponin I Reveals Diagnostic and Prognostic Superiority to Aminoterminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Sepsis and Septic Shock. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavare, A.; Rissmiller, B.; Devaraj, S.; Guffey, D.; Rajapakshe, D.; Weiner, H.; Caldarone, C.; Shekerdemian, L. Perioperative Procalcitonin in Predicting Infection in Children Undergoing Surgical Procedures. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 258, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, E.H.; Epting, C.L.; Backer, C.L.; Wald, E.L. Hyperlactatemia: An Update on Postoperative Lactate. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Hear. Surg. 2020, 11, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhizhin, K.Y.; Turyshev, E.S.; Pautova, A.K.; Beloborodova, N. V.; Kuznetsov, N.T. Methodology for the determining aromatic monocarboxylic acids as products of phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism: current advances and trends. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2024, 93, RCR5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Xu, K.; Bai, Y.; Lv, M.; Shan, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; et al. Machine-learning predictions for acute kidney injuries after coronary artery bypass grafting: a real-life muticenter retrospective cohort study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z. Machine learning model-based risk prediction of severe complications after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 32, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Yao, G.; Yang, W.; Yang, K.; Xiong, C. Novel Blood Cytokine-Based Model for Predicting Severe Acute Kidney Injury and Poor Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, 18004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, W.B.; Leeuwenberg, A.M.; Grobbee, D.E.; Siregar, S.; Houterman, S.; Daeter, E.J.; de Vries, M.C.; Groenwold, R.H.H.; Schuit, E.; Bramer, S.; et al. Dynamics in cardiac surgery: trends in population characteristics and the performance of the EuroSCORE II over time. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2023, 64, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoe, A.; Bakhshi-Raiez, F.; de Keizer, N.; van Dissel, J.T.; de Jonge, E. Mortality prediction by SOFA score in ICU-patients after cardiac surgery; comparison with traditional prognostic–models. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Z.C.; Schreinemakers, J.M.J.; de Waal, R.A.L.; van der Laan, L. Searching for predictors of surgical complications in critically ill surgery patients in the intensive care unit: a review. Surg. Today 2015, 45, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Jung, J.-Y.; Yoon, H.-K.; Yang, S.-M.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, W.H.; Jung, C.-W.; Suh, K.-S. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and lactate level during surgery predict acute kidney injury and early allograft dysfunction after liver transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).