Submitted:
23 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal and Treatments
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Exercise Function Measurement
2.4. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Measurement
2.5. Histological Tissue Staining
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
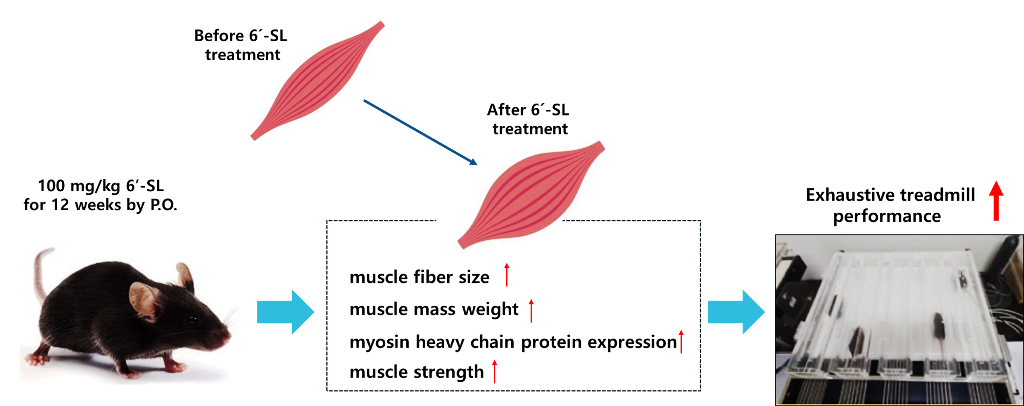
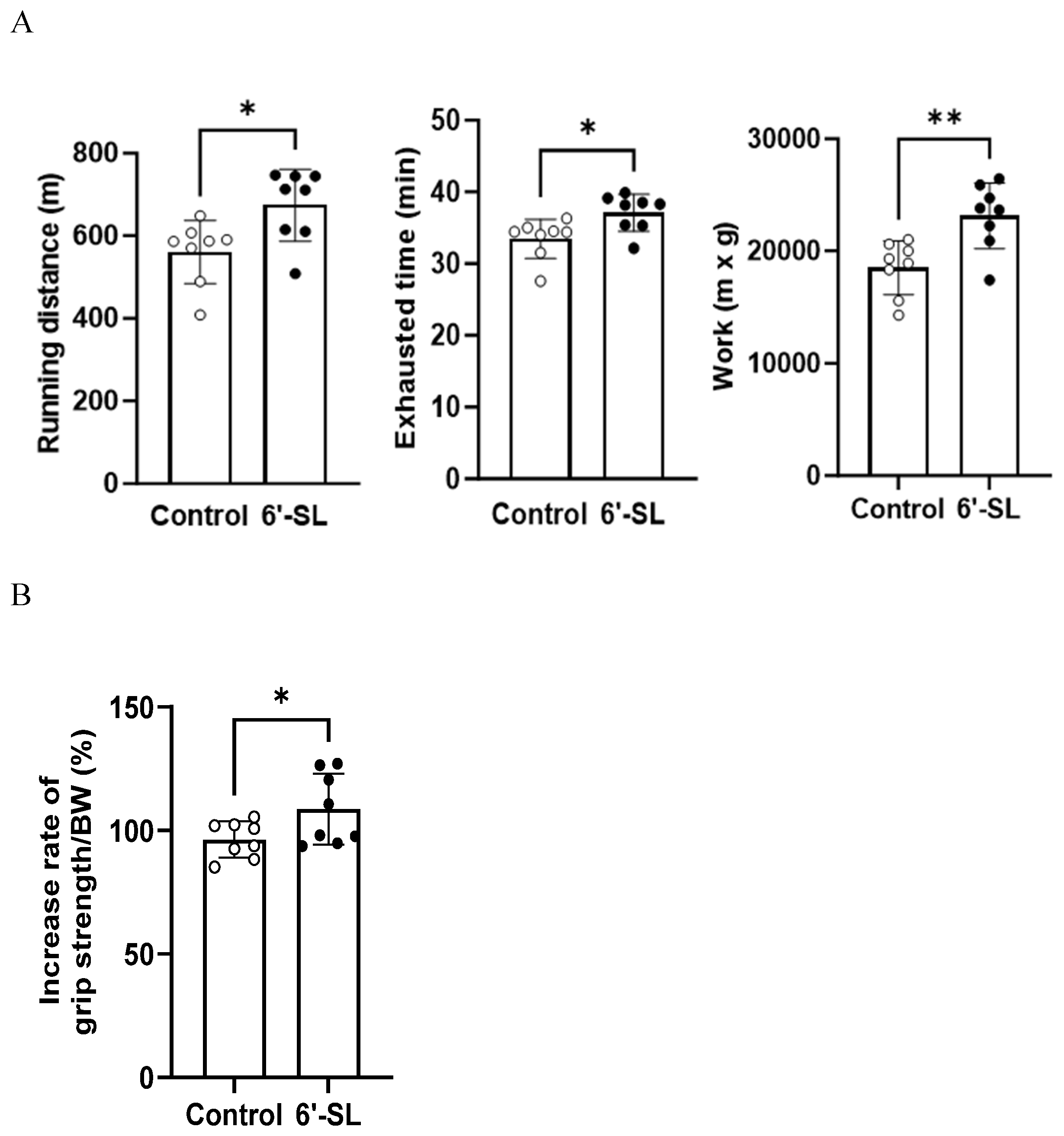
3.1. 6′-SL Enhances Muscle Function
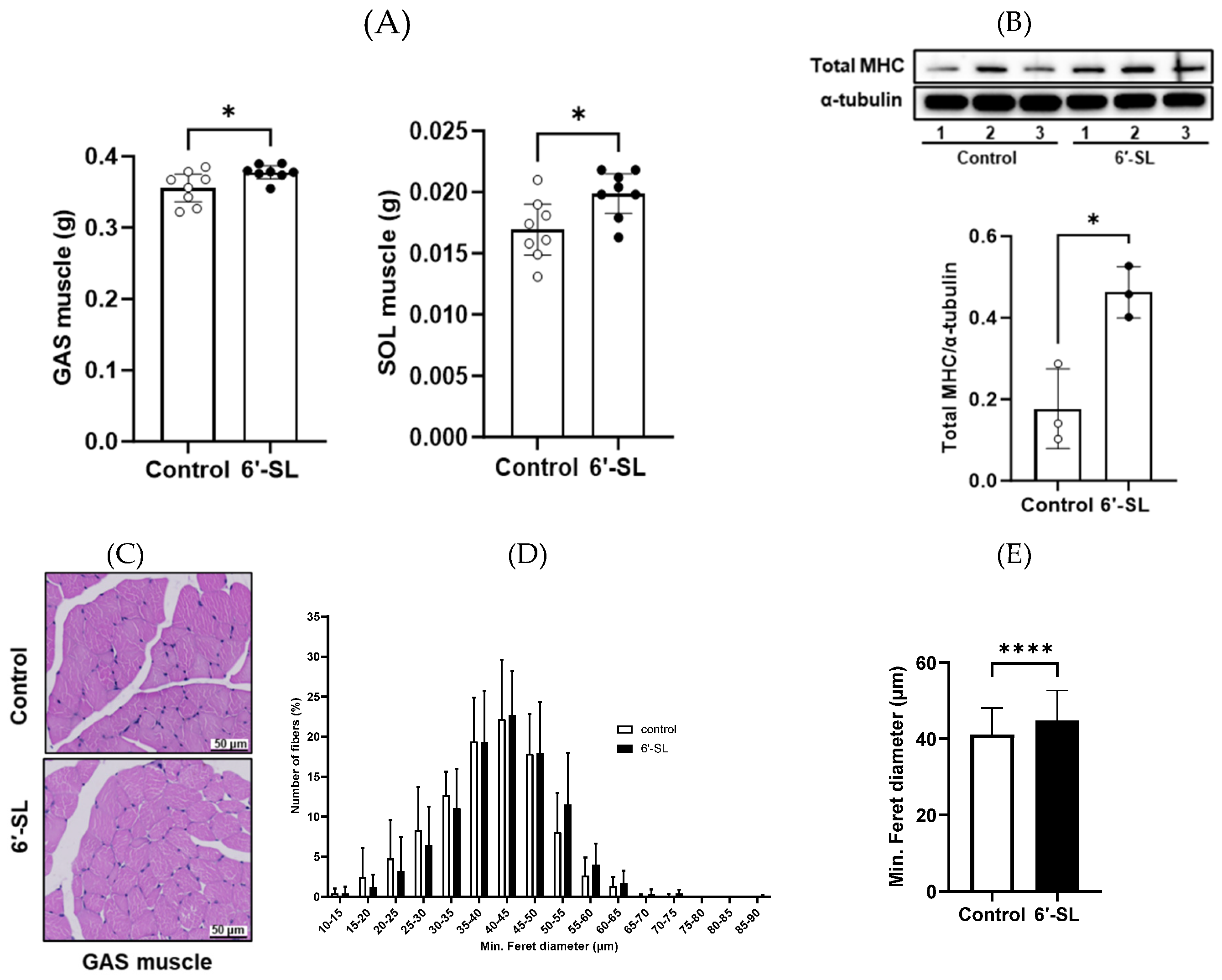
3.2. 6′-SL Increases the Volume and Size of GAS Muscles
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Acknowledgments
References
- Zierath, J. R.; Hawley, J. A. Skeletal muscle fiber type: influence on contractile and metabolic properties. PLoS Biol 2004, 2, e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanis, G. C. Effects of physical activity and inactivity on muscle fatigue. Front Physiol 2012, 3, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Soh, K. G.; Jazaily Mohd Nasiruddin, N.; Bashir, M.; Cao, S.; Soh, K. L. Effects of neuromuscular training on athletes physical fitness in sports: A systematic review. Front Physiol 2022, 13, 939042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchomel, T. J.; Nimphius, S.; Stone, M. H. The Importance of Muscular Strength in Athletic Performance. Sports Med 2016, 46, 1419–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, Y.; Usumoto, Y.; Takeshita, Y. The Effects of Regional Muscle Strength and Mass on Standing Long Jump Performance. Muscles 2024, 3, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, M.; Khosravy, T.; Azadbakht, L.; Rezaei, M.; Mosafaghadir, M.; Kamari, N.; Bagheri, A.; Pasdar, Y.; Najafi, F.; Hamze, B.; Soleimani, D. Major dietary patterns in relation to muscle strength status among middle-aged people: A cross-sectional study within the RaNCD cohort. Food Sci Nutri 2021, 9, 6672–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.; Depiesse, F.; Geyer, H. The use of dietary supplements by athletes. J Sports Sci 2007, 25 Suppl 1, S103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, E. S.; Miles, M. P.; Larson-Meyer, D. E. Dietary Supplements for Health, Adaptation, and Recovery in Athletes. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2018, 28, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreider, R. B. Dietary supplements and the promotion of muscle growth with resistance exercise. Sports Med 1999, 27, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Rabenda, V.; Simmons, M.; Geerinck, A.; Araujo de Carvalho, I.; Reginster, J. Y.; Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan, J.; Bruyère, O. Effects of Protein, Essential Amino Acids, B-Hydroxy B-Methylbutyrate, Creatine, Dehydroepiandrosterone and Fatty Acid Supplementation on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older People Aged 60 Years and Over. A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Nutr Health Aging 2018, 22, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, K. L.; Thomson, J. S.; Swift, R. J.; von Hurst, P. R. Role of nutrition in performance enhancement and postexercise recovery. Open Access J Sports Med 2015, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Candow, D. G.; Forbes, S. C.; Gualano, B.; Jagim, A. R.; Kreider, R. B.; Rawson, E. S.; Smith-Ryan, A. E.; VanDusseldorp, T. A.; Willoughby, D. S.; et al. Common questions and misconceptions about creatine supplementation: what does the scientific evidence really show? J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ten Bruggencate, S. J.; Bovee-Oudenhoven, I. M.; Feitsma, A. L.; van Hoffen, E.; Schoterman, M. H. Functional role and mechanisms of sialyllactose and other sialylated milk oligosaccharides. Nutr Rev 2014, 72, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Xiao, M.; Lu, L. Enzymatic Synthesis of 6'-Sialyllactose, a Dominant Sialylated Human Milk Oligosaccharide, by a Novel exo-alpha-Sialidase from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC9343. Appl Environ Microbiol 2018, 84, e00071–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E. Y.; Jin, B. R.; Chung, T. W.; Bae, S. J.; Park, H.; Ryu, D.; Jin, L.; An, H. J.; Ha, K. T. 6-sialyllactose ameliorates dihydrotestosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia through suppressing VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. BMB Rep 2019, 52, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S. X.; He, J. H.; Mi, Y. J.; Shen, H. F.; Schachner, M.; Zhao, W. J. A mimetic peptide of alpha2,6-sialyllactose promotes neuritogenesis. Neural Regen Res 2020, 15, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, C. P.; Wipf, O.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fulton, W. B. ; K., M.; Niño, D. F.; Zhou, Q.; Banfield, E.; Werts, A. D.; Ladd, M. R.; Buck, R. H.; Goehring, K. C.; Prindle Jr, T.; Wang, S.; Jia, H.; Lu, P.; Hackam, D. J. The human milk oligosaccharides 2'-fucosyllactose and 6'-sialyllactose protect against the development of necrotizing enterocolitis by inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Pediatr Res, 2021; 89, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yonekawa, T.; Malicdan, M. C.; Cho, A.; Hayashi, Y. K.; Nonaka, I.; Mine, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Nishino, I.; Noguchi, S. Sialyllactose ameliorates myopathic phenotypes in symptomatic GNE myopathy model mice. Brain 2014, 137, 2670–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y. E.; Park, E.; Choi, J.; Go, H.; Park, D. B.; Kim, M. Y.; Sung, N. J.; Kim, L.; Shin, J. H. Pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of 6'-sialyllactose in patients with GNE myopathy: Randomized pilot trial. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 168, 115689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. A.; Oh, S. H.; Lee, G. H.; Hoa, P. T.; Jin, S. W.; Chung, Y. C.; Lee, Y.C.; Jeong, H. G. Platycodon grandiflorum-derived saponin attenuates the eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Food Chem Toxicol 2018, 112, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menalled, L. B.; Patry, M.; Ragland, N.; Lowden, P. A.; Goodman, J.; Minnich, J.; Zahasky, B.; Park, L.; Leeds, J.; Howland, D.; Signer, E.; Tobin, A. J.; Brunner, D. Comprehensive behavioral testing in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington's disease shows no benefit from CoQ10 or minocycline. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, N.; Soibam, B.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Byers, L. A.; Liu, Y.; Schwartz, R. J.; Stewart, M. D. HIRA deficiency in muscle fibers causes hypertrophy and susceptibility to oxidative stress. J Cell Sci 2017, 130, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murru, C.; Duvert, L.; Magdinier, F.; Casanova, A.; Alloncle, A.-P.; Testa, S.; Al-Kattan, A. Assessment of laser-synthesized Si nanoparticle effects on myoblast motility, proliferation and differentiation: towards potential tissue engineering applications. Nanoscale Adv 2024, 6, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuok Ho, D. T. A Review of the Association between Environmental Factors and Athletic Performance. Sport Sci 2021, 1, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnolo, A.; Klug, S.; Schenkl, C.; Schwarzer, M. Links between Exercise Capacity, Exercise Training, and Metabolism. Compr Physiol 2023, 13, 5115–5155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pourreza, S.; Shahinfar, H.; Bazshahi, E.; Gholami, F.; Djafarian, K.; Shab-Bidar, S. Association of the Mediterranean Dietary Quality Index with handgrip strength and muscle endurance: A cross-sectional study. Food Sci Nutr 2022, 10, 2749–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schytz, C. T.; Ørtenblad, N.; Birkholm, T. A.; Plomgaard, P.; Nybo, L.; Kolnes, K. J.; Andersen, O. E.; Lundby, C.; Nielsen, J.; Gejl, K. D. Lowered muscle glycogen reduces body mass with no effect on short-term exercise performance in men. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2023, 33, 1054–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, P. M.; Rawson, E. S. Nutritional supplements to increase muscle mass. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1999, 39, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Iemitsu, M. The Role of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in Skeletal Muscle. Vitam Horm 2018, 108, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G. J.; Wilson, J. M.; Manninen, A. H. Effects of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) on exercise performance and body composition across varying levels of age, sex, and training experience: A review. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2008, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktaviana, J.; Zanker, J.; Vogrin, S.; Duque, G. The Effect of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) on Sarcopenia and Functional Frailty in Older Persons: A Systematic Review. J Nutr Health Aging 2019, 23, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wax, B.; Kerksick, C. M.; Jagim, A. R.; Mayo, J. J.; Lyons, B. C.; Kreider, R. B. Creatine for Exercise and Sports Performance, with Recovery Considerations for Healthy Populations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M. Dietary supplements and sports performance: amino acids. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2005, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C. T. A.; Ochala, J. Myosin Heavy Chain as a Novel Key Modulator of Striated Muscle Resting State. Physiology (Bethesda) 2023, 38, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C. Y.; Wu, C. H.; Huang, W. J.; Lo, Y. M.; Lin, S. X.; Wu, J. S.; Huang, W. C.; Shen, S. C. Alleviative effects of α-lipoic acid on muscle atrophy via the modulation of TNF-α/JNK and PI3K/AKT pathways in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Food Sci Nutr 2023, 11, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willoughby, D. S.; Rosene, J. Effects of oral creatine and resistance training on myosin heavy chain expression. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001, 33, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Luo, Y.; Chen, H.; Yan, H.; Huang, Z. Dihydromyricetin alters myosin heavy chain expression via AMPK signaling pathway in porcine myotubes. Food & Function 2022, 13, 10525–10534. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Sung, B.; Kang, Y. J.; Kim, D. H.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, S. Y.; Yoon, J. H.; Yoo, M. A.; Kim, C. M.; Chung, H. Y.; Kim, N. D. The combination of ursolic acid and leucine potentiates the differentiation of C2C12 murine myoblasts through the mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 2015, 35, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, K. R.; Baldwin, N. J.; Lynch, B.; Stannard, D. R.; Šoltésová, A.; Gilby, B.; Mikš, M. H.; Röhrig, C. H. Toxicological safety evaluation of the human-identical milk oligosaccharide 6'-sialyllactose sodium salt. J Appl Toxicol 2019, 39, 1444–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H.; Yong, S. Y.; Kim, S. H.; Baek, A.; Go, T. H.; Kang, D. R. Randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety of 6'-Sialyllactose in healthy adults. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2022, 129, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, R.; Sutkus, L.; Bauer, L.; Donovan, S.; Dilger, R. Determining the safety and efficacy of dietary supplementation with 3ˊ-sialyllactose or 6ˊ-sialyllactose on growth, tolerance, and brain sialic acid concentrations. Front Nutr 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, D.; Negro, M.; Arcelli, E.; Marzatico, F. Anti-inflammatory Dietary Interventions and Supplements to Improve Performance during Athletic Training. J Am Coll Nutr 2015, 34 Suppl 1, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therdyothin, A.; Phiphopthatsanee, N.; Isanejad, M. The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Sarcopenia: Mechanism of Action and Potential Efficacy. Mar Drugs 2023, 21, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnfield, M. M.; Carey, K. A.; Gran, P.; Trenerry, M. K.; Cameron-Smith, D. Whey protein ingestion activates mTOR-dependent signalling after resistance exercise in young men: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2009, 1, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.; Yoshida, N.; Maekawa, D.; Kitakaze, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kitano, T.; Fujita, T.; Okuwa-Hayashi, H.; Harada, N.; Nakano, Y.; Yamaji, R. 5-Hydroxy-7-methoxyflavone derivatives from Kaempferia parviflora induce skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Food Sci Nutr 2018, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Castellanos, B.; Martínez-López, P.; Bailón-Moreno, R.; Esquius, L. Effect of Ginseng Intake on Muscle Damage Induced by Exercise in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochet, C.; Belloni, G.; Buondonno, I.; Chiara, F.; D'Amelio, P. The Role of Nutrition in the Treatment of Sarcopenia in Old Patients: From Restoration of Mitochondrial Activity to Improvement of Muscle Performance, a Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J. Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, G.; Shin, H. J.; Lee, E. J.; Lee, C. S.; Yoon, S.; Lee, E.; Lim, A.; Kim S., H. Ameliorating effect of 2'-Fucosyllactose and 6'-Sialyllactose on lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammation. J Dairy Sci 2024, 107, 4147–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano Spadaro, J.; Hishida, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; van Es-Remers, M.; Korthout, H.; Kim, H. K.; Poppelaars, E.; Keizer, H.; Iliopoulou, E.; van Duijn, B.; Wildwater, M.; van Rijnberk, L. 3'sialyllactose and 6'sialyllactose enhance performance in endurance-type exercise through metabolic adaptation. Food Sci Nutr 2023, 11, 6199–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| . | Control (n = 8) |
6′-SL (n = 8) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Body weight (g) Fat mass (g) |
34.15 ± 1.40 6.67 ± 1.13 |
35.92 ± 1.00* 6.83 ± 1.10 |
0.0164 0.7987 |
| Fat mass (%) | 19.97 ± 3.24 | 19.43 ± 3.08 | 0.7542 |
| BMC (g) | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 0.78 ±0.08 | 0.4361 |
| BMD (g/cm2) | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.9153 |
| Bone area (cm2) | 11.33 ± 0.40 | 11.72 ± 0.71 | 0.2328 |
| Bone volume (cm2) | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 0.4358 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





