Introduction
Bowel obstruction (BO) represents one of the most common acute abdominal conditions requiring emergency surgery, accounting for approximately 15% of hospital admissions for acute abdominal pain in the United States, and 20% of cases needing acute surgical care [
1].
Small bowel obstruction is caused in 90% of cases by adhesions, hernias, and neoplasms, whereas large bowel obstruction is provoked by cancer in about 60% of cases; volvulus and diverticular disease are responsible for the other 30% [
2,
3].
Bowel obstruction represents a significant burden on healthcare systems, characterized by its high incidence, considerable disease severity, substantial morbidity and mortality rates, and associated economic costs [
4,
5].
Most patients presenting with bowel obstruction require urgent evaluation, primarily relying on contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography (CT) imaging [
6]. Recent research has explored the utility of serum procalcitonin as a potential biomarker for predicting the failure of conservative management in small bowel obstruction cases, as well as an indicator of intestinal ischemia - a particularly challenging complication to diagnose [
7]. Despite the development of numerous clinical scoring systems aimed at predicting bowel ischemia, this aspect of bowel obstruction management remains a significant challenge in clinical practice [
8].
These clinical scoring systems’ validity across diverse clinical contexts and geographical regions remains unestablished, thus restricting their generalizability. Alternative scoring methodologies have been developed with the aim of identifying patients with more severe diseases who require emergency surgical intervention or those at high risk of non-operative management failure. These approaches typically integrate a combination of clinical and laboratory data or incorporate radiological findings. However, the efficacy and reliability of these integrated scoring systems also warrant further investigation and validation [
9,
10].
Currently, the decision-making process regarding the necessity and timing of surgical intervention for bowel obstruction (BO), as well as the prediction of stoma creation or bowel resection, largely relies on clinicians’ subjective assessments, often characterized as "gut-feeling" judgments. Reliable and objective predictive tools would enhance patient counseling and optimize postoperative care strategies, potentially reducing the variability in patient outcomes [
11].
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used in other fields, such as radiology [
12] or clinical trial design [
13]. In emergency settings, several applications are being tested where AI-based solutions can assist, e.g., in triaging patients or in predicting disease progression, [
14] but little research has been conducted data exist on its implementation in bowel obstruction. The present study aims to analyze the role of machine learning algorithms in bowel obstruction and their ability to predict postoperative complications.
Materials and Methods
Study Design
This investigation is a component of an international collaborative research program involving undergraduate students from Italian and French universities. The study design is observational and retrospective, utilizing data from a prospectively maintained database focused on Emergency and Trauma Surgery at the Sant’Andrea Sapienza University teaching hospital in Rome, Italy. The establishment and maintenance of this database were conducted in accordance with previously approved research protocols and studies by the relevant Ethical Committee [
15,
16]
This adherence to established ethical guidelines ensures the integrity and validity of the data used in the current study. This research framework allows for the analysis of real-world clinical data while fostering international academic collaboration at the undergraduate level. For this study, a formal Institutional Review Board approval was not required due to the study design; however, we obtained a signed consent for the storage and analysis of data for scientific purposes from all patients at admission.
Population and Data
Medical records of patients who underwent surgery for bowel obstruction between January 2019 and December 2022 were retrieved. The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) patients over 18 years of age; 2) admission through the Emergency Department; 3) intraoperative confirmed diagnosis of bowel obstruction; 4) procedures performed or directly supervised by senior surgeons. Patients were excluded if: 1) they were already hospitalized; 2) they were already scheduled for elective surgery; 3) patients with intra-abdominal sepsis such as appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, or acute diverticulitis; 4) patients with peritoneal free air; or 5) patients participating in other randomized or interventional clinical trials.
To reduce bias, we excluded the procedures that were not performed or tutored by two senior surgeons (PA, NP). After the identification of eligible patients, we collected data including demographic characteristics and clinical variables, level and type of obstruction, procedure details, and outcomes. Demographics variables and clinical data included: age, gender, weight, height, body mass index (BMI), heart rate, systolic blood pressure, medical and surgical history (comorbidities), common preoperative biochemical blood examination (including C-Reactive Protein [CRP], and arterial blood gas analysis). Cause of bowel obstruction were divided as neoplastic, adhesions, sigmoid volvulus, and abdominal wall hernia either primary or incisional. Comorbidity was recorded if the condition was present at the admission. Preoperative risk was assessed with the American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) score. The Age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index (age-CACI) was also calculated [
17].
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admission, length of ICU stays, and length of hospital stay (LOS) were recorded. Morbidity and mortality have been considered as the 30-day standard period definition. Any adverse outcomes have been also considered regardless of the time elapsed if occurred during the hospitalization following the index emergency procedure. Postoperative complications were classified according to Clavien-Dindo system [
18]. Grade IIIa or higher were considered as major complication. No enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocol was adopted, but in the postoperative period the patients were managed following the same standardized pathways of care both for uneventful and complicated courses. Data about the postoperative outcome was available for all patients.
All pre-operative characteristics, such as clinical and demographic, level of occlusion and radiological bowel findings along with post-operative data, including minor and major complications, were blind reviewed and coded by two expert surgeons (MM, TD). Any disagreements were discussed and resolved through a consensus meeting with a third senior emergency surgeon (GC). Finally, data was entered in a new specific worksheet crafted with LibreOffice (Vers. 7.6.7 for Windows).
Table 1 shows all the list of investigated variables and their description.
Machine Learning Methodology
The machine learning study was done by A.O and T.P, leveraging models that include algorithms based on supervised learning. A sample of 70% of the cohort generated randomly using a seed was applied for the training set; the remaining 30% was used for testing. Based on the predictive factors selected, 3 models were constructed including support K-nearest neighbor (KNN), XgBoost and logistic regression. During training, the algorithm iteratively learns the optimal path from root nodes to leaves by minimizing prediction errors. This path signifies the classification rules guiding the decision model’s predictions for new patients. KNN builds a robust predictive model by aggregating information from multiple neighbors, thus mitigating the risk of overfitting associated with highly complex models.
KNN has the capability to handle missing values by defining default directions for each node in case of missing data. o train and validate the performance of the KNN algorithm, we employed repeated stratified ten-fold cross-validation, repeating the process five times. This method ensures each patient appears at least once in the testing set, cycling the dataset into ten equally sized folds for training and validation. In our study, we optimized KNN hyperparameters through grid-search and fivefold cross-validation. The grid-search space included parameters such as ’n_neighbors’ and the distance metric, allowing us to identify systematically the optimal configuration for the KNN algorithm. The models were evaluated and compared by sensitivity, specificity, and the Area Under the Curve (AUC) of the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve. The analyses were performed using software from the Python Software Foundation
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using IBM Corp. Released 2013. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp. Dichotomous data and counts were presented in frequencies, whereas continuous data was presented as mean values ± standard deviations (SD). Differences between means were compared using the independent sample Student’s t-test, the Mann–Whitney U test or the Kruskall-Wallis test when indicated. Fisher’s exact test or χ2 test, with or without Yates correction, were used to compare differences in frequencies. Variables significantly associated with major postoperative morbidity were identified using Cox univariate and multivariate analysis. The level of significance to allow inclusion of a variable in the logistic regression multivariate model was 0.05 for major complications. Any statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
Results
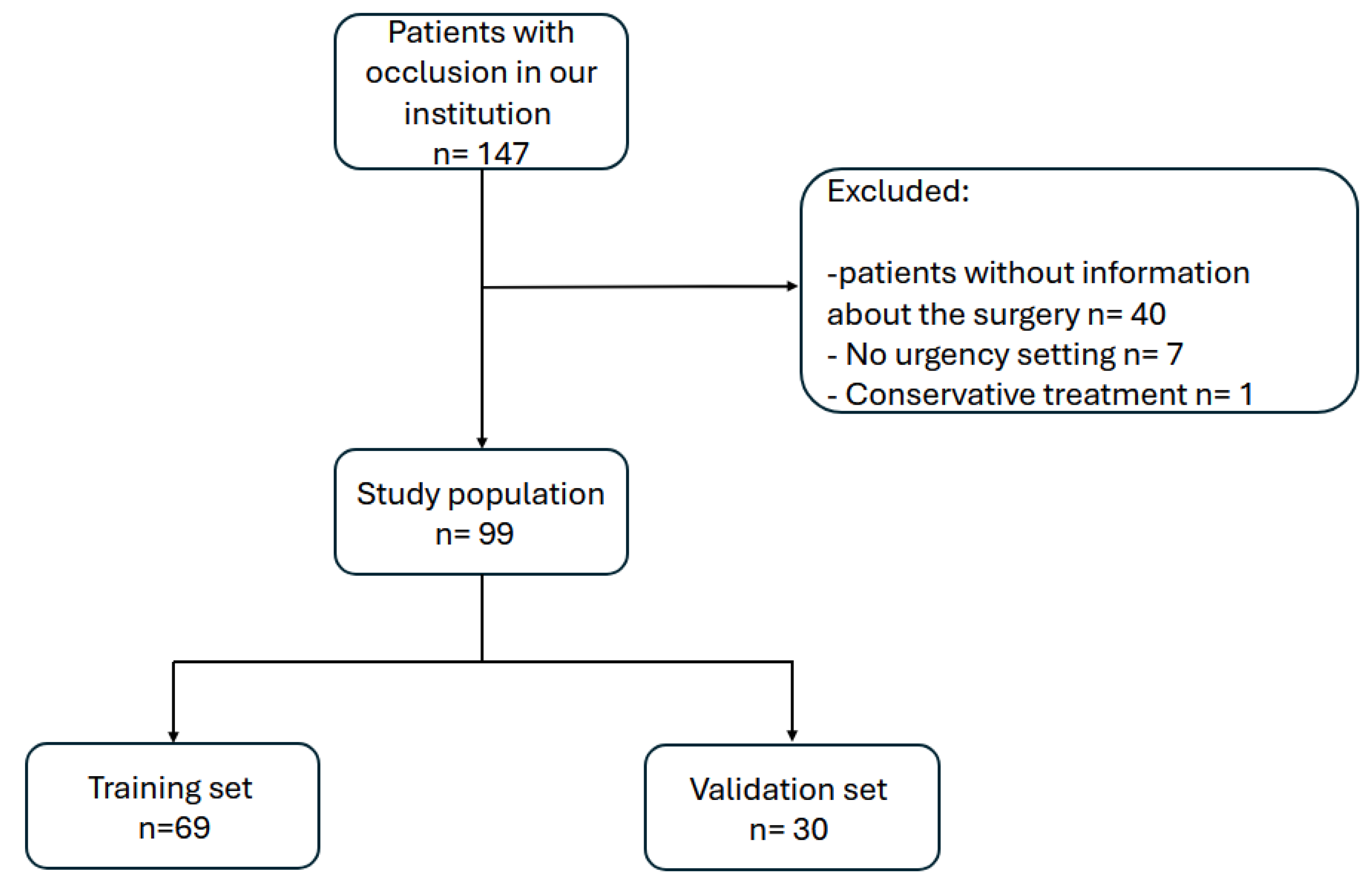
Ninety-nine patients undergoing emergency surgery for bowel obstruction were included.
Figure 1 illustrates the participant selection and allocation process for the AI algorithm training and validation datasets .
Table 1 reports the general characteristics of the population; data are reported for the overall population and according to the benign or malignant etiology of the obstruction. The majority of patients had small bowel obstruction (63.6%), whereas colonic obstruction was present in 32% of patients. The majority of patients had previous abdominal surgery (62.3%). The median BMI was 23.6 [20.7-27.6]. C-reactive protein was above normal values (> 1.0 mg/100 ml) in 60% of cases. Average waiting time between admission and abdominal CT scan was 10 hours. At CT scan, fluid effusion was detected in 59.2% of patients, bowel ischemia in 12.2% of cases.
A laparoscopic approach was attempted in 34 patients, 18 of which were converted to open surgery. Mean operative time was 105 minutes. Histological exams were performed in 43 cases, and in 24 cases, the diagnosis of malignant disease was confirmed.
Table 2 reports intraoperative and postoperative outcomes. The major complication rate was 27.3% for all patients with a significant difference between benign obstruction and malignant obstruction (20% vs 41%, respectively). Postoperative death occurred in 7 patients. Mean hospital stay was 10 days.
Univariate and multivariate analysis showed that PCR (OR 1.18, CI 1.05-1.3, p=0.003) and cancer-related obstruction (OR 4.2, CI 1.2-14.0, p=0.02) were independent risk factors for major complications. (
Table 3).
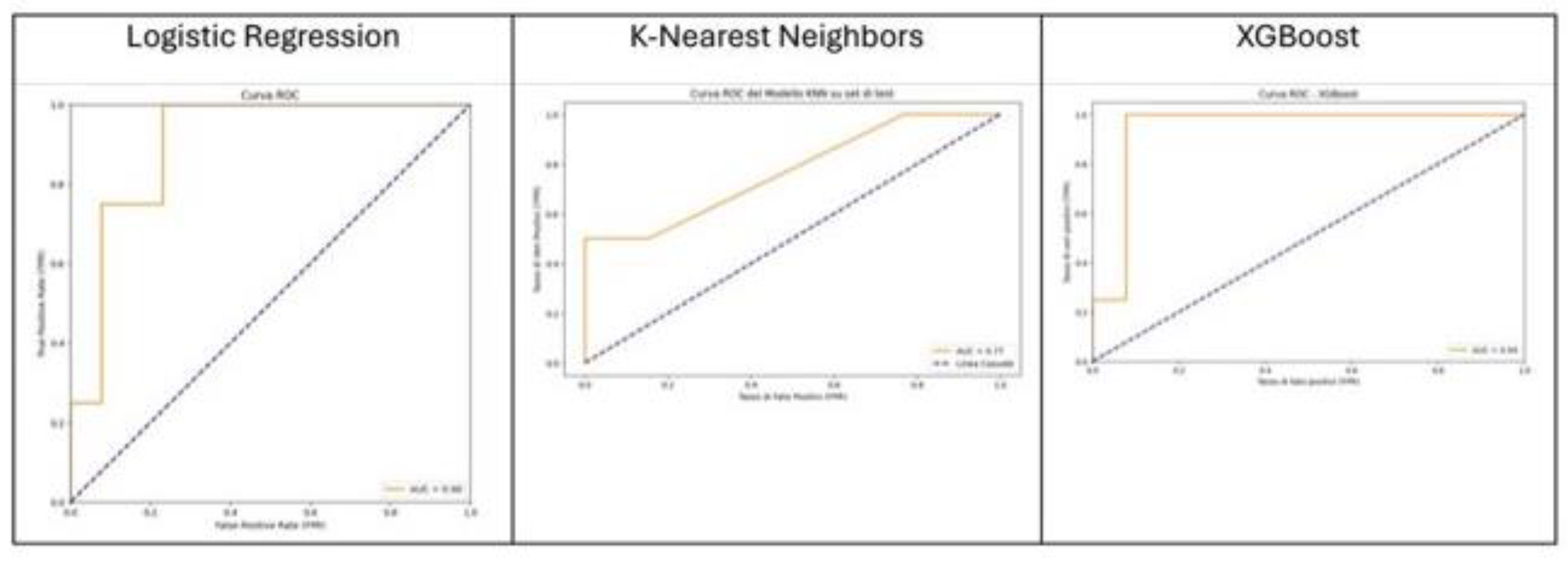
We compared XGBOOST, KNN and logistic regression capacity to predict the outcome with good performance, as shown in
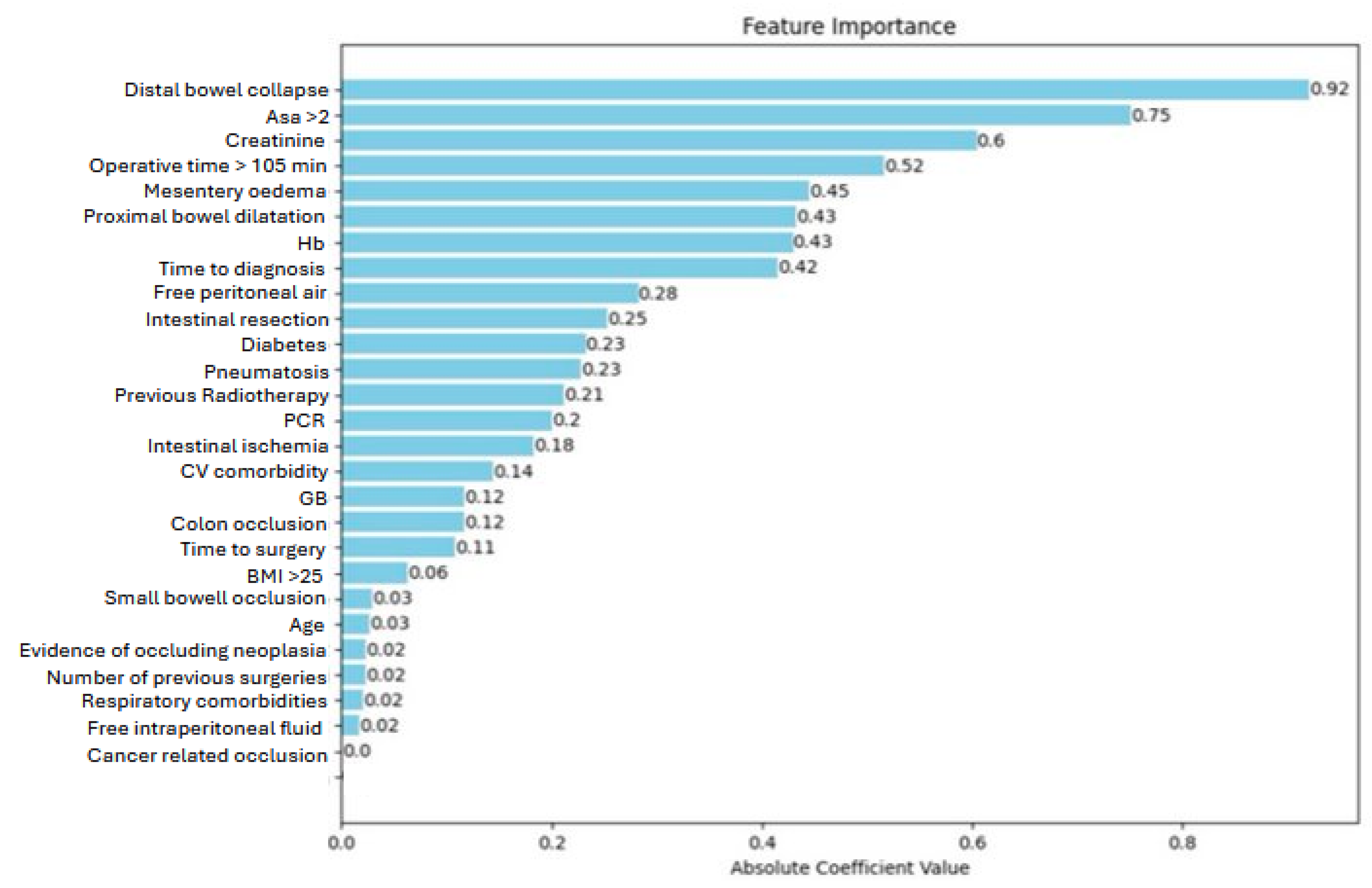
Figure 2. KNN was considered the best algorithm with an Area under the Curve (AUC) of 0.77 and overall accuracy of 0.88. The most significant features are distal bowel collapse with an importance value of 0.92, followed by ASA >2 at 0.75, and creatinine at 0.6. Operative time >105 min and mesentery oedema are also notable, with importance values of 0.52 and 0.45 respectively.
Figure 3 shows a gradual decrease in importance for subsequent features.
Discussion
Bowel obstruction represents a significant challenge for the health systems worldwide. It causes 15% of emergency department access for abdominal pain [
1], with different causes and possibly presenting as heterogeneous clinical scenarios. Morbidity and mortality rates are elevated, particularly in patients who need emergency surgery [
19,
20,
21]. The complexity and heterogeneity of bowel obstruction makes the prediction of the outcomes very difficult for clinicians. Even patients undergoing surgery for bowel obstruction due to adherences (one of the less “severe” scenarios) may experience intraoperative complications such as bowel effractions and postoperative major complications. A rapid analysis of patients’ characteristics and preoperative exams is the responsibility of the on-call surgeons to assess the need of surgery, type of approach [
22] to predict potential outcomes in order to correctly inform the patient and eventually its family and program the more appropriate setting for the postoperative surveillance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) represents a promising tool to facilitate physicians’ complex tasks. In the setting of small bowel obstruction, previous research has shown the ability of neural networks to identify small bowel obstruction on plain radiographs with a high degree of accuracy [
23,
24].
AI could represent a valid tool to integrate a large amount of clinical and radiological information and predict postoperative complications, to facilitate the decision-making process of surgeons giving the indication for surgery and correct patients’ counseling. The World Society of Emergency Surgery has included bowel obstructions among the clinical scenarios where neural networks may support clinical decisions [
24].
The present study demonstrated that machine learning was able to predict the occurrence of postoperative complications with an overall accuracy of 0.88, performing better than available clinical risk score. As shown in
Figure 2, the AI based model was able to classify the different variables according to their importance in predicting the outcomes. Among the variables with higher predictive value for postoperative major morbidity, preoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) and malignant obstruction were identified. C-reactive protein represents nowadays a useful tool for early detection of postoperative complications after several abdominal procedures [
23,
25].
In the setting of emergency surgery, preoperative CRP was associated with higher incidence of difficult cholecystectomies and perforated appendicitis [
26,
27] but its role on predicting the outcomes after surgery for bowel obstruction was not yet reported.
The other significant factors were the malignant nature of the obstruction, confirming the results of previous studies showing the worst prognosis of malignant obstructions in terms of postoperative complications and need of stoma creation [
28]. Out of 20 stomas created, 14 were done in patients with cancer and only 3 of them have been reconstructed during follow-up. In addition, the use of laparoscopy was concordant with previous reports [
29,
30]. In our series, the laparoscopic approach was effective in 16 cases only, whereas in 18 cases open conversion was needed. Laparoscopic approach reduces the overall morbidity and length of stay and facilitate postoperative recovery [
31,
32,
33] but segments the lacking surgical pace due to overdistended colon or small bowel and the difficult manipulation of the dilated segments often limit its feasibility. The analysis of large quantities of data with AI could allow in the future identifying patients at greater risk of major complications and modulating the clinical approach by dedicating greater resources and establishing dedicated paths for patients at greater risk of major complications. The detailed collection of international multicenter data that flows into a single dataset is desirable.
Limitations
This study has several limitations to consider when interpreting the results. Its retrospective design introduces potential biases in data collection and analysis. Being a single-center experience from Sant’Andrea Sapienza University teaching hospital in Rome, Italy, the findings may have limited generalizability to other healthcare settings or regions. The relatively small sample size of 99 patients, particularly when divided into subgroups, may limit statistical power and the ability to detect smaller effect sizes. The study’s time span from 2019 to 2022 could introduce variability due to evolving clinical practices. The exclusion of certain patient groups limits the applicability of findings to those populations. The machine learning models, while promising, lack external validation, which is crucial for assessing their true predictive performance and generalizability. There was limited direct comparison with specific, widely used clinical risk scores for bowel obstruction. Given the small dataset and complex machine learning models, there is a risk of overfitting, potentially leading to optimistic performance estimates. Lastly, the focus on 30-day morbidity and mortality may not capture longer-term outcomes relevant to bowel obstruction patients, particularly those with cancer-related obstructions. These limitations highlight the need for larger, multi-center prospective studies with external validation to confirm the predictive value of the machine learning approaches in patients undergoing surgery for bowel obstruction.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the potential of machine learning approaches, particularly the K-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm, in predicting major postoperative complications for patients undergoing emergency surgery for bowel obstruction. Our model achieved an overall accuracy of 0.88 and an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.77, outperforming traditional clinical risk scores. The analysis identified preoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and cancer-related obstruction as significant independent risk factors for major complications. The ability to rapidly integrate multiple clinical and radiological variables could enhance the precision of predicting postoperative complications, facilitating more informed surgical decisions and appropriate postoperative care planning.
Author Contributions
ADM and NP conceived the idea and wrote the manuscript. EB, SM, ML, TD, GC, and MM contributed to data collection and analysis. AO and TP performed the machine learning analysis. FAC contributed to the organization and final revision of the study. GC designed the project methodology and handled the paper. PA supervised the study. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Catena, F. et al. Bowel obstruction: a narrative review for all physicians. World J Emerg Surg 14, (2019). [CrossRef]
- Frago, R. et al. Current management of acute malignant large bowel obstruction: a systematic review. Am J Surg 207, 127–138 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Richard, P. G. et al. Burden of adhesions in abdominal and pelvic surgery: systematic review and met-analysis. BMJ 347, (2013).
- Behman, R. et al. Population-based study of the impact of small bowel obstruction due to adhesions on short- and medium-term mortality. Br J Surg 106, 1847–1854 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, E. J. et al. Costs of Care for Operative and Nonoperative Management of Emergency General Surgery Conditions. Ann Surg 279, 684–691 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Taghavifar, S. et al. Computed Tomography in Emergency Diagnosis and Management Considerations of Small Bowel Obstruction for Surgical vs. Non-surgical Approach. Curr Med Imaging 18, 275–284 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Cosse, C., Regimbeau, J. M., Fuks, D., Mauvais, F. & Scotte, M. Serum procalcitonin for predicting the failure of conservative management and the need for bowel resection in patients with small bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Surg 216, 997–1004 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Wassmer, C. H. et al. A new clinical severity score for the management of acute small bowel obstruction in predicting bowel ischemia: a cohort study. Int J Surg 109, 1620–1628 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Scrima, A. et al. Value of MDCT and Clinical and Laboratory Data for Predicting the Need for Surgical Intervention in Suspected Small-Bowel Obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 208, 785–793 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, M. D. et al. Small bowel obstruction-who needs an operation? A multivariate prediction model. World J Surg 34, 910–919 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, A. D. et al. Conditional cumulative incidence of postoperative complications stratified by complexity classification for laparoscopic liver resection: Optimization of in-hospital observation. Surgery (2022). [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A., Parmar, C., Quackenbush, J., Schwartz, L. H. & Aerts, H. J. W. L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat Rev Cancer 18, 500–510 (2018).
- Cascini, F. et al. Scoping review of the current landscape of AI-based applications in clinical trials. Frontiers in Public Health vol. 10 Preprint at https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.949377 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Causio, F. A. et al. Big data and ICT solutions in the European Union and in China: A comparative analysis of policies in personalized medicine. Digital Health vol. 8 Preprint at https://doi.org/10.1177/20552076221129060 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Costa, G. et al. Gastro-intestinal emergency surgery: Evaluation of morbidity and mortality. Protocol of a prospective, multicenter study in Italy for evaluating the burden of abdominal emergency surgery in different age groups. (The GESEMM study). Front Surg 9, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Costa, G. et al. Frailty and emergency surgery in the elderly: protocol of a prospective, multicenter study in Italy for evaluating perioperative outcome (The FRAILESEL Study). Updates Surg 70, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M. E., Pompei, P., Ales, K. L. & MacKenzie, C. R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40, 373–383 (1987). [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P. A. et al. The clavien-dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann Surg 250, 187–196 (2009).
- Falola, A. F., Dada, O. S., Ndong, A. & Akande, D. G. Etiology and management outcomes of adult mechanical bowel obstruction in Nigeria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg 48, 29–39 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Xu, N., Sun, B. J., Yue, T. M. & Lee, B. Factors Predicting Readmission and Mortality in Patients Admitted for Malignant Bowel Obstruction. Am Surg (2024). [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, U. F. et al. Don’t Let the Sun Rise on Small Bowel Obstruction Without Surgical Consultation-Redefining Nonoperative Management Pathways. Am Surg (2024). [CrossRef]
- Hoi, H. et al. Surgeon and patient-specific factors influencing the decision for minimally invasive or open surgery in acute bowel obstruction: a retrospective single-center analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 407, 3747–3754 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. Y., Yim, H. W., Park, C. H. & Song, K. Y. C-reactive protein can be an early predictor of postoperative complications after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Surg Endosc 31, 445–454 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Litvin, A. et al. WSES project on decision support systems based on artificial neural networks in emergency surgery. World J Emerg Surg 16, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Yeung, D. E., Peterknecht, E., Hajibandeh, S., Hajibandeh, S. & Torrance, A. W. C-reactive protein can predict anastomotic leak in colorectal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis 36, 1147–1162 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S. et al. Predictive factors of perforated appendicitis: Impact of the C-reactive protein level. Surg Open Sci 6, 1–4 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Ng, H. J., Ahmed, Z., Khan, K. S., Katbeh, T. & Nassar, A. H. M. C-reactive protein level as a predictor of difficult emergency laparoscopic cholecystectomy. BJS Open 3, 641–645 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Capona, R. et al. Surgical intervention for mechanical large bowel obstruction at a tertiary hospital: Which patients receive a stoma and how often are they reversed? Am J Surg 221, 594–597 (2021).
- Zimmermann, M. et al. Laparoscopy for bowel obstruction--a contradiction? Results of a multi-institutional survey in Germany. Int J Colorectal Dis 31, 1011–1019 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, T., Mentula, P., Leppäniemi, A. & Sallinen, V. Laparoscopic versus Open Surgery for Acute Adhesive Small-Bowel Obstruction: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Scand J Surg 106, 28–33 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Darbyshire, A. R., Kostakis, I., Pucher, P. H., Toh, S. & Mercer, S. J. The impact of laparoscopy on emergency surgery for adhesional small bowel obstruction: prospective single centre cohort study. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 103, 255–262 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, P. & Maharjan, S. Adhesive Small Bowel Obstruction: A Review. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc 61, 390–396 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S. H. et al. Is Laparoscopy Underutilized for Sigmoid Volvulus? Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 32, 564–570 (2022).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).