Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Patients
3.2. Changes in Metabolic Parameters by the 3-Year-SGLT2is Treatment
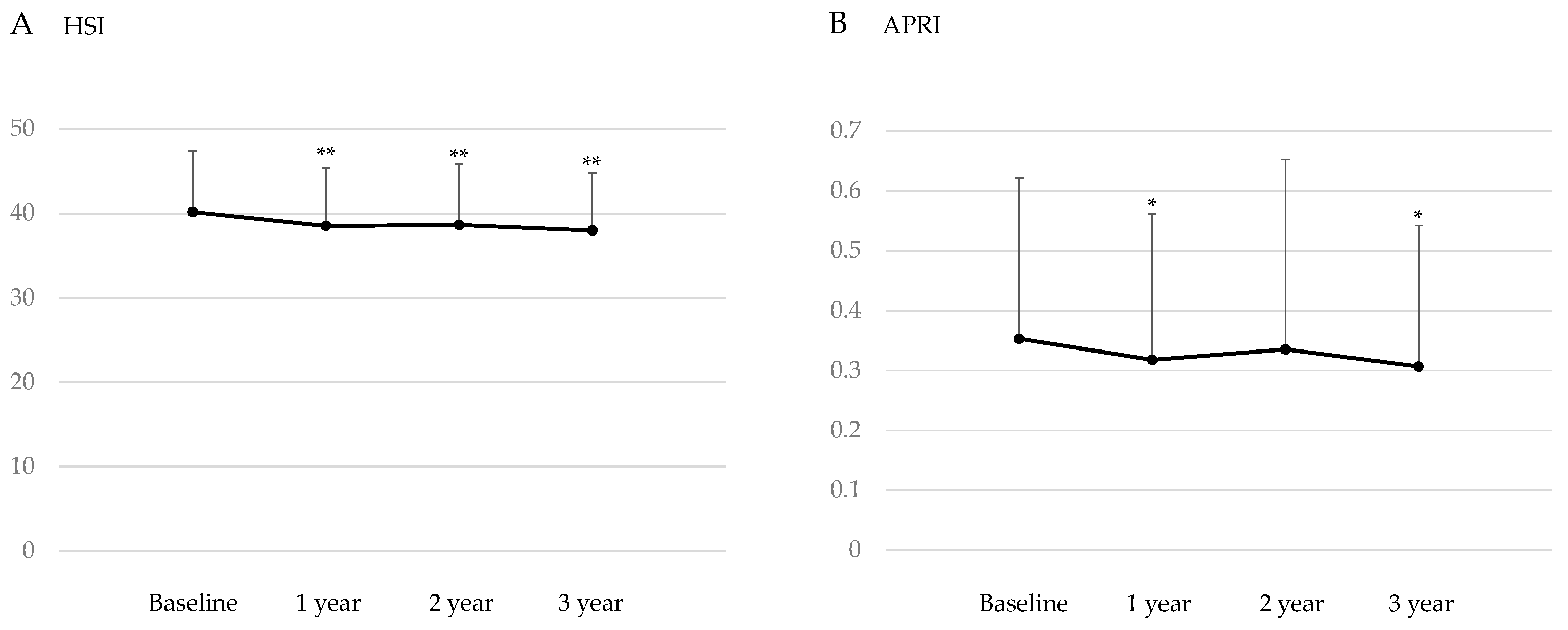
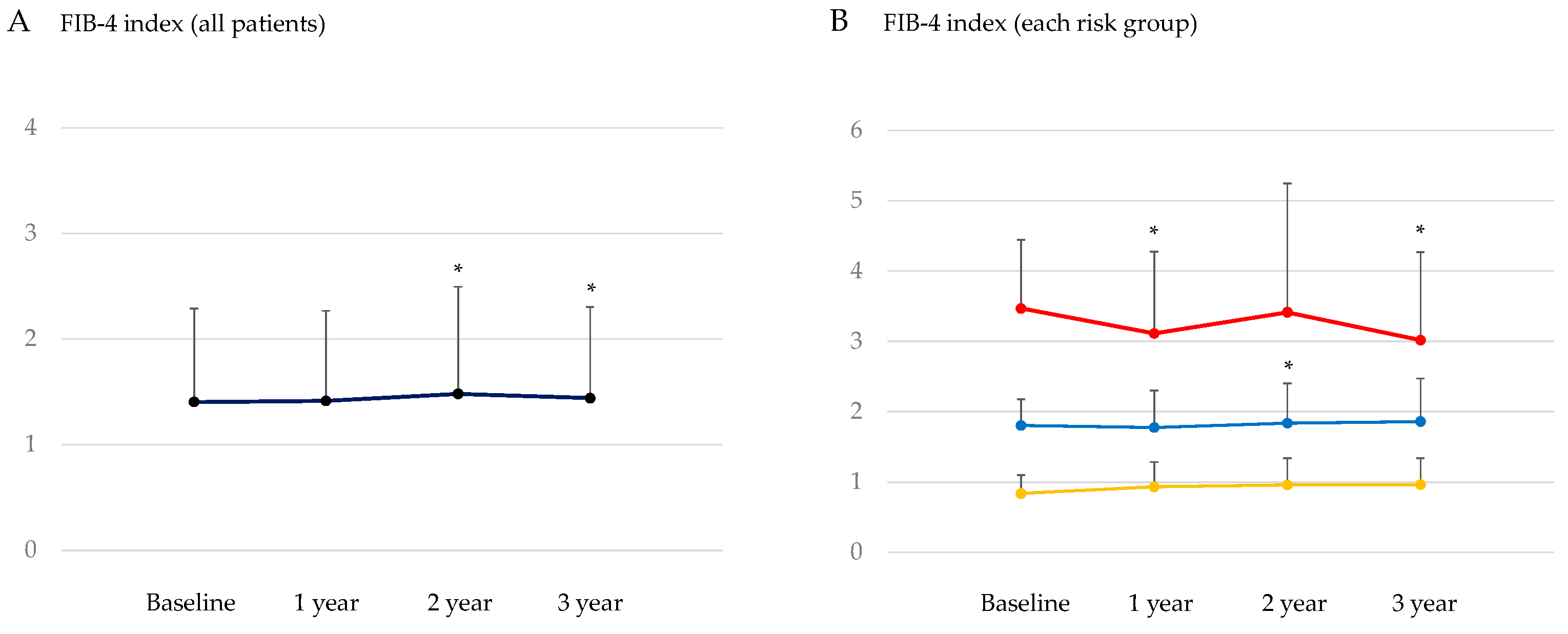
3.3. Changes in the Markers for Hepatic Steatosis and Hepatic Fibrosis after the Start of SGLT2is
3.4. Correlations between Changes in Metabolic Parameters by the 3-Year-SGLT2is Treatment
3.4.1. Correlation of Changes in Serum Lipids with Changes in Metabolic Parameters at 3 Years after the Start of SGLT2is
3.4.2. Correlation of Changes in the Markers for Hepatic Steatosis And Hepatic Fibrosis with Changes in Metabolic Parameters by the 3-Year-SGLT2is Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, J.V.; Mark, H.E.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; Batterham, R.L.; Castera, L.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Crespo, J.; Cusi, K.; Dirac, M.A.; et al. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: a consensus statement. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2015, 149, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iida, S.; Katsuyama, H. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-Its Pathophysiology, Association with Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease, and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Song, S.D.; Qu, K.; Xu, X.S.; Liu, S.S.; Liu, C. Central obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease risk after adjusting for body mass index. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Platt, K.A.; Cunard, R.; Schroth, J.; Whaley, J.; Thomson, S.C.; Koepsell, H.; Rieg, T. SGLT2 mediates glucose reabsorption in the early proximal tubule. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, S.A.; Goldstein, B.J. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: blocking renal tubular reabsorption of glucose to improve glycaemic control in patients with diabetes. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, S.; Yoshikawa, R.; Sako, A. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Possible Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects Beyond Glucose Lowering. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, N.; Sun, C.; Jin, D.; Lu, H. Effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, S.; Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Nitta, K.; Yamagata, K.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Hishida, A.; et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, S.H.; Sung, M.W.; et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2010, 42, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Xin, Y.N.; Dong, Q.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhan, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Xuan, S.Y. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: An updated meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011, 53, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Lydecker, A.; Murray, K.; Tetri, B.N.; Contos, M.J.; Sanyal, A.J.A. Use of the Fib4 index for non-invasive evaluation of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Itoh, Y.; Ono, M.; Fujii, H.; Eguchi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Aoki, N.; Kanemasa, K. Validation of the FIB4 index in a Japanese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease population. BMC. Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztalryd, C.; Kraemer, F.B. Regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Metabolism. 1995, 44, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, D.E.; Goodpaster, B.H. Skeletal muscle triglyceride. An aspect of regional adiposity and insulin resistance. Diabetes. Care. 2001, 24, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.A. The degradation of apolipoprotein B100: Multiple opportunities to regulate VLDL triglyceride production by different proteolytic pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 1821, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghibiglou, C.; Carpentier, A.; Van Iderstine, S.C.; Chen, B.; Rudy, D.; Aiton, A.; Lewis, G.F.; Adeli, K. Mechanisms of hepatic very low density lipoprotein overproduction in insulin resistance. Evidence for enhanced lipoprotein assembly, reduced intracellular ApoB degradation, and increased microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in a fructose-fed hamster model. J. Biol. Chem. 2000; 275, 8416–8425. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Breslow, J.L.; Li, W.; Leff, T. Transcriptional regulation of the apoC-III gene by insulin in diabetic mice: Correlation with changes in plasma triglyceride levels. J. Lipid. Res. 1994, 35, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramoglu, R.K.; Basciano, H.; Adeli, K. Lipid and lipoprotein dysregulation in insulin resistant states. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2006, 368, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H. Atherogenic Lipoproteins for the Statin Residual Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkila, E.A.; Huttunen, J.K.; Ehnholm, C. Postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in diabetes mellitus. Relationship to plasma triglyceride metabolism. Diabetes. 1977, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkila, E.A.; Taskinen, M.R.; Kekki, M. Relation of plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to lipoprotein-lipase activity in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle of man. Atherosclerosis. 1978, 29, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, N.C. A comprehensive account of insulin and LDL receptor activity over the years: A highlight on their signaling and functional role. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, S.; Owens, D.; Tomkin, G.H. Genes that affect cholesterol synthesis, cholesterol absorption, and chylomicron assembly: The relationship between the liver and intestine in control and streptozotosin diabetic rats. Metabolism. 2007, 56, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Guo, D.L.; Zuo, H. The impact of sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 inhibitors on lipid profile: A meta-analysis of 28 randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 959, 176087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, L.E.; Emanuelsson, F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Benn, M. SGLT2-inhibition increases total, LDL, and HDL cholesterol and lowers triglycerides: Meta-analyses of 60 randomized trials, overall and by dose, ethnicity, and drug type. Atherosclerosis. 2024, 394, 117236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.; Siddiqi, A.K.; Alabduladhem, T.O.; Rashid, A.M.; Sarfraz, S.; Maniya, T.; Menezes, R.G.; Almas, T. Effects of novel glucose-lowering drugs on the lipid parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg (Lond). 2022, 77, 103633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, A.; Simental-Mendía, M.; Millán-Alanís, J.M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E. Effect of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 48 randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Sako, A.; Mishima, S.; Yanai, H. Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Chart-Based Analysis. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Adachi, H.; Kawaguchi, A.; Waragai, Y.; Harigae, T.; Masui, Y.; Kakuta, K.; Hamasaki, H.; Katsuyama, H.; et al. Effects of Six Kinds of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters, and Summarized Effect and Its Correlations With Baseline Data. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotto, A.M. Jr. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides as therapeutic targets for preventing and treating coronary artery disease. Am. Heart. J. 2002, 144(6 Suppl), S33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iijima, T.; Adachi, H.; Yanai, H. Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Chart-Based Analysis. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, M.; Kakazu, E.; Sano, A.; Katsuyama, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Yanai, H.; Aoki, Y.; Imamura, M.; Yamazoe, T.; Mori, T. , et al. Effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and pioglitazone on FIB-4 index in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2023; 53, 618–628. [Google Scholar]
- Obata, A.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Sato, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Takamoto, I.; Katsuyama, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; et al. Tofogliflozin Improves Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle and Accelerates Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue in Male Mice. Endocrinology. 2016, 157, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhong, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Xiao, X. The effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on biomarkers of inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1045235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randle, P.J.; Garland, P.B.; Hales, C.N.; Newsholme, E.A. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963, 1, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Nagata, N.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhuge, F.; Ni, Y.; Chen, G.; Mayoux, E.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. SGLT2 inhibition by empagliflozin promotes fat utilization and browning and attenuates inflammation and insulin resistance by polarizing M2 macrophages in diet-induced obese mice. EBioMedicine. 2017, 20, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical characteristics | ||
| Gender (male/female) | 188/136 58.9±14.2 163.0±10.0 74.3±18.2 28.1±5.9 133.3±17.9 76.8±12.1 |
|
| Age (years) | ||
| Body height (cm) | ||
| Body weight (kg) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | ||
| Diastolic blood pressure | ||
| Laborarory characteristics | ||
| Data at baseline | Normal range | |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dl) | 192±83 | < 110 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.3±1.7 | 4.9~6.0 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 13.9±1.8 | Male 13.7~16.8 Female 11.6~14.8 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 41.9±5.0 | Male 40.7~50.1 Female 35.1~44.4 |
| Platelets (x 104/ml) | 24.0±7.5 | 158~348 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dl) | 16.5±6.2 | 8~20 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 0.8±0.3 | Male 0.65~1.07 Female 0.46~0.79 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73m2) | 78±28 | 60 < |
| UA (mg/dl) | 5.5±1.4 | < 7 |
| TP (g/dl) | 7.2±0.5 | 6.6~8.1 |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 4.2±0.5 | 4.1~5.1 |
| T-Bil | 0.7±0.3 | 0.4~1.5 |
| AST (IU/l) | 30±20 | 13~30 |
| ALT (IU/l) | 38±32 | Male 10~42 Female 7~23 |
| GGT (IU/l) | 58±69 | Male 13~64 Female 9~32 |
| TC (mg/dl) | 187±40 | < 220 |
| HDL-C (mg/dl) | 50±13 | < 40 |
| LDL-C (mg/dl) | 105±32 | < 140 |
| TG (mg/dl) | 185±126 | Non-fasting value < 175 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dl) | 138±39 | < 170 |
| Kind of SGLT2is | n (%) |
| Dapagliflozin | 98 (30%) |
| Luseogliflozin | 96 (30%) |
| Tofogliflozin | 36 (11%) |
| Ipragliflozin | 34 (10%) |
| Canagliflozin | 34 (10%) |
| Empagliflozin | 30 (9%) |
| Baseline | After 3 years | p values | |
| Body weight (kg) | 74.3±18.2 | 70.9±17.6 | < 0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 28.1±5.9 | 26.8±5.5 | < 0.001 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dl) | 192±83 | 162±69 | < 0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.3±1.7 | 7.4±1.2 | < 0.001 |
| TC (mg/dl) | 187±40 | 177±33 | < 0.001 |
| HDL-C (mg/dl) | 50±13 | 53±14 | < 0.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dl) | 105±32 | 98±27 | 0.023 |
| TG (mg/dl) | 185±126 | 161±103 | 0.001 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dl) | 138±39 | 124±32 | < 0.001 |
| AST (IU/l) | 30±20 | 26±17 | 0.004 |
| ALT (IU/l) | 38±32 | 31±32 | 0.009 |
| GGT (IU/l) | 58±69 | 53±101 | 0.014 |
| Δ HDL-C | Δ LDL-C | Δ TG | Δ Non-HDL-C | |
| Δ Body weight | -0.073 | -0.099 | -0.032 | -0.029 |
| Δ BMI | -0.098 | -0.152 | -0.022 | -0.013 |
| Δ HbA1c | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.165** | 0.151* |
| Δ AST | 0.079 | 0.079 | 0.093 | 0.025 |
| Δ ALT | -0.044 | 0.037 | 0.119* | -0.011 |
| Δ GGT | -0.021 | 0.119 | 0.285** | 0.217** |
| Δ HSI | Δ APRI | |
| Δ Body weight | 0.583** | 0.273** |
| Δ BMI | 0.593** | 0.258** |
| Δ HbA1c | 0.291** | 0.143* |
| Δ TG | 0.007 | 0.054 |
| Δ HDL-C | -0.228** | 0.063 |
| Δ LDL-C | -0.121 | 0.063 |
| Δ Non-HDL-C | -0.086 | -0.049 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





