1. Introduction
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a foam-like material with low density and high malleability, making it ideal for creating a variety of shapes . It is microbe and impact-resistant, with low thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for packaging and construction [
1]. Free radical vinyl polymerization in a suspension is used to produce EPS, which is then foamed with n-pentane. Once the styrene has reached the desired conversion point, steam heating transforms it into boiling foam, resulting in an eightfold increase in volume. After the maturation period is complete, the molds are filled with polymer and heated further with steam. This causes the polymer to expand and form the final cellular foam structure. During this process, air replaces the foaming agent, accounting for approximately 98% of the EPS volume [
2]. Because of its thermal and biological stability, this material is frequently used to make trays, cups, and disposable food packaging . Furthermore, due to its mechanical properties, it is used as packaging for the transportation of electronic and household appliances, as well as a structural component that provides thermal and acoustic insulation in the construction industry [
3].
Storing EPS is difficult because it takes up a large amount of space. A metric ton of waste EPS can occupy up to 200 cubic meters. Traditional treatment methods are unsuitable for the final arrangement of EPS, such as use as a material in sanitary landfills, because the compacting process requires significant effort due to its configuration and mechanical strength. Some companies are now using thermal compacting and pellet formation to create new EPS for non-food applications [
4]. Because of its low density, EPS must be compressed to reduce volume, complicating the recycling process [
5].
In the past, scientists suggested diluting EPS with fossil solvents like benzene or toluene [
6,
7,
8]. However, it is important to note that these substances are hazardous to human health and the environment [
9]. Given the preceding information, it is recommended to choose a solvent with a low environmental impact.
A viable alternative to fossil solvents is to use molecules derived from plants or microorganisms, such as ethyl acetate or the terpene family [
10,
11]. Researchers have investigated several commercial oils, including limonene, nard, violet, lavender, and orange blossom [
12], star anise, eucalyptus, thyme, and chamomile [
13], as environmentally friendly solvents for EPS. Both studies successfully recovered PS by adding alcohol but did not quantify the solubility limit. Other authors used commercial Omega 3 to dissolve PS and precipitate it by adding alcohol [
14]. Nevertheless, the study did not provide a specific value for the solubility limit. The effect of temperature on the time it takes for EPS to dissolve in limonene and eucalyptus oil had been investigated [
9]. However, we did not interpret these results as quantification of solubility limits. The studies aimed to characterize the polyester produced during the dilution-precipitation process using various essential oils.
Limonene is the predominant component of citrus oils, giving them their distinct aroma. Limonene accounts for 98% of the essential oil extracted from orange skin or peel [
15]. It has long been used in fragrances and flavorings, and it serves a variety of functions as a solvent and cleanser. It is classified as a terpene, specifically a limonoid, and is part of a large group of functional foods and phytonutrients known for their antioxidant properties, which protect polymer chains and facilitate PS recycling [
16]. Citrus oils are industrially produced by cold pressing the peel, steam distilling the pulp and rinds after juice extraction, and removing terpenes from essential citrus oils [
17,
18].
Ethanol, on the other hand, is a clear, rapidly evaporating liquid with a distinct odor and flavor. Industrial applications include the production of acetaldehyde, vinegar, butadiene, ethyl chloride, and nitrocellulose. Ethanol is widely used as a solvent in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, plastics, lacquers, perfumes, and cosmetics. Furthermore, it serves as a source of energy, a surgical disinfectant, and an essential component in chemical production. It is also useful in the preservation of both normal and abnormal biological samples.
Because of their biodegradability, these molecules are attractive for developing green chemistry processes, as reported in the literature [
19,
20,
21]. The goal of this research is to feature a chemical process for recycling EPS by dissolving it in D-limonene and then recovering it in solid form by insolubilizing it with ethanol [
13]. We calculated the maximum amount of PS that can dissolve in a solution of D-limonene and ethanol and expressed it as an empirical equation. Finally, we proposed a preliminary scheme for recycling EPS, which includes determining the necessary solvents, energy requirements, and fundamental equipment design characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Used
This study utilized waste PS derived from laboratory material packaging. The PS was thoroughly cleaned to eliminate any non-polystyrene particles, such as dust. The D-limonene employed was a commercially available product from the Econoclear brand, boasting a purity level of 99%, as stated by the manufacturer. Absolute ethanol from the Meyer brand, with a purity of 99.5%, was utilized without undergoing any further purification procedures.
To characterize PS, we utilized the Mark-Houwink-Sakurada correlation to determine its average molecular weight through viscosity measurements. Benzene was employed as the solvent, and a Cannon-Fenske capillary viscometer model 9721-F59 CFOF-100, immersed in a thermostatic bath at 298.15 K, was utilized. Once the intrinsic viscosity was determined, we referred to the literature to obtain the necessary parameters [
22].
2.1. Solubility Limit
Various blends of EPS and D-limonene were created with precise mass ratios ranging from 5% to 40% (w/w). These mixtures were then allowed to settle at room temperature for a period of two days to ensure that complete dissolution occurred. In order to separate any solid particles that were evenly distributed in the solution, the mixtures underwent centrifugation at a speed of 4500 rpm for a duration of 10 minutes. A 3 ml sample was introduced into a test tube, and the weight of the PS solution in the tube was measured. Ethanol was then added gradually using a burette until the cloud point was reached [
23,
24]. At this moment, the weight of the added alcohol was measured. Finally, the sample was centrifuged at 4500 rpm for 10 minutes. We evaporated the solvents by placing one milliliter of the supernatant in a porcelain capsule. Finally, we quantified the amount of PS in the solution using a gravimeter. The masses were determined using a VeLab model VE-204 analytical balance, while the centrifuge employed was a clinical type DM0412S from Science Med.
2.2. Modeling of Continuous Stirred Tank (CST)
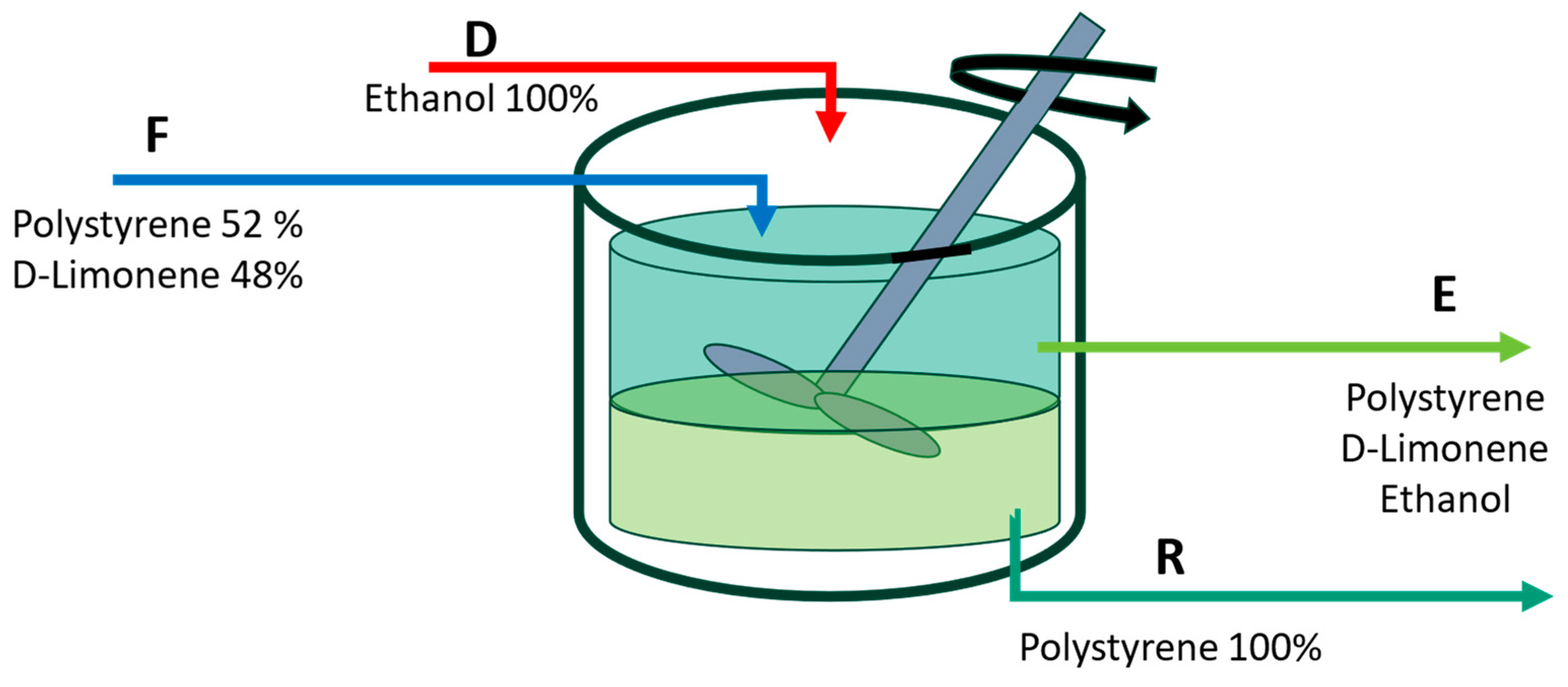
Figure 1 shows the intended application of a continuous stirred tank as a means of separation. Enough time is supposed to be allocated to achieve equilibrium in the solution.
The goal is to process a mixture of PS with D-limonene, with a polymer concentration of 52% (w/w), at a rate of 100 kg/s. The ethanol supply is intended to be fresh, and the quantity of alcohol required to extract a minimum of 99% of the PS in the raffinate stream is computed. According to the previously provided information, the material balances are presented as follows:
where F represents the feed containing a mixture of PS and limonene, D is the incoming ethanol stream, E corresponds to the extract, and R indicates the raffinate. The number in the subindex corresponds to the following substances: (1) polystyrene, (2) D-limonene, and (3) ethanol. The solubility is denoted by the symbol S and represents a ratio between the mass of PS and the weight of the solvent mixture of ethanol with D-limonene.
2.3. Conceptual Design and Process Simulation
After calculating the specific amount of ethanol required to recover 99% of PS, we devised a conceptual design for a more complete procedure that encompassed the retrieval and reutilization of solvents. The proposal entails the combination of PS and D-limonene, the introduction of ethanol, the retrieval of PS in solid form, the preparation of the solvent stream for separation in a plate distillation column, and ultimately, the recycling of the solvents. The PS was simulated using the Compound Creator Wizard, which incorporated data regarding its melting point, normal boiling temperature, and solid density. The design of the distillation column incorporated heuristic rules [
25], beginning with the simulation of a column using a short-cut method. Following that, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to ascertain the precise number of stages and the optimal feeding plate. Ultimately, a rigorous distillation column model was employed, utilizing the Naphtali-Sandholm simultaneous correction method. The process simulation was conducted using DWSIM [
26].
3. Results
3.1. Polystyrene Molecular Weight
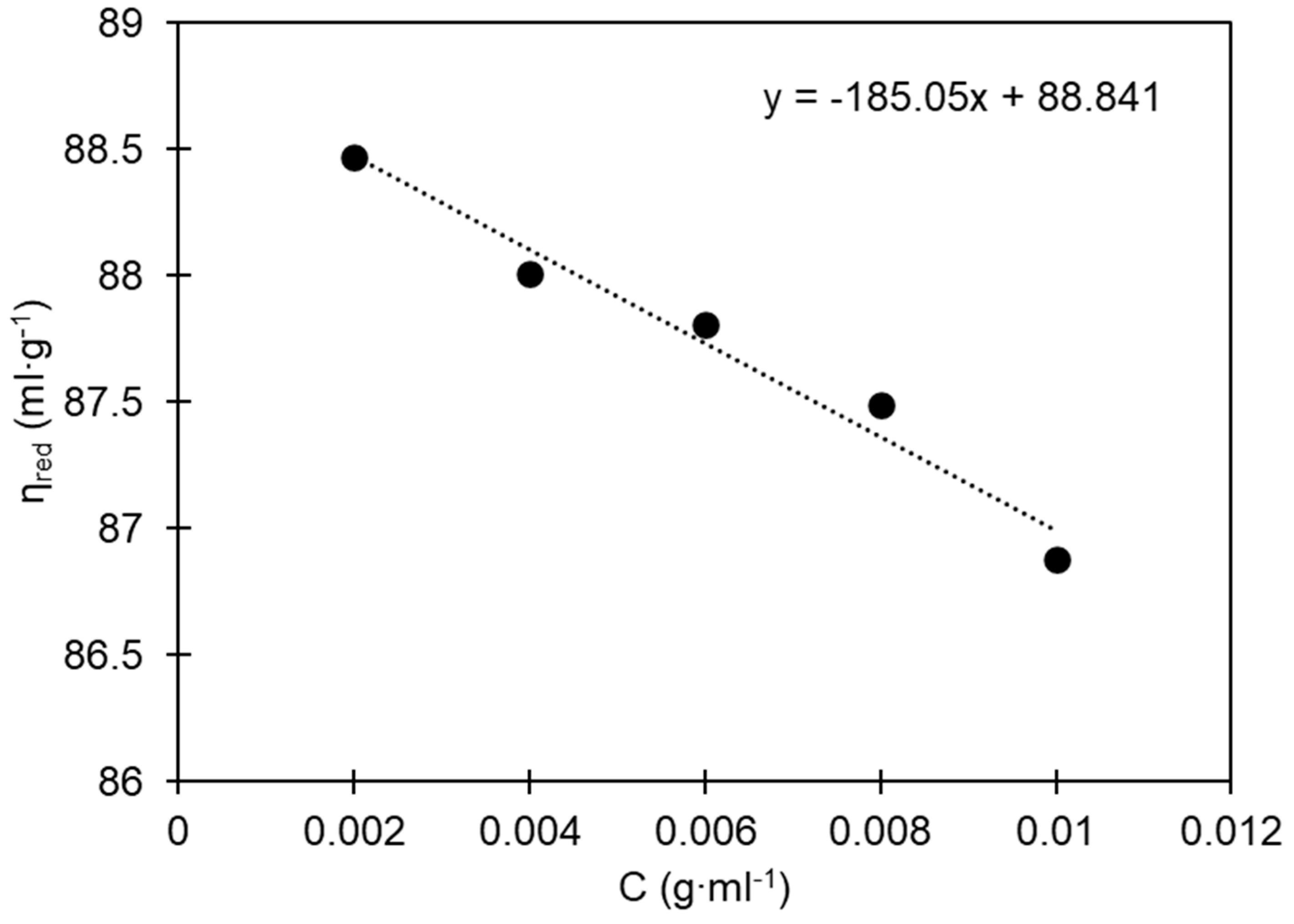
Figure 2 illustrates the relationship between the concentration of PS in benzene and the corresponding reduced viscosity (
). The intrinsic viscosity (
) represents the intercept of the regression line at the origin, specifically when the concentration of the solution approaches zero.
The relationship between intrinsic viscosity and average molecular weight (
) for the PS + benzene system can be described by an empirical correlation [
22]
In this paper, the intrinsic viscosity of the analyzed sample was found to be 88.841 ml∙g
-1, indicating a molecular weight of 232,476 g∙mol
-1. This value corresponds to the expected molecular weight for commercially available PS [
2]. The Newton-Raphson method was employed to numerically solve Eq 5.
3.2. Solubility Limit
D-limonene is a natural solvent for PS and can be easily mixed with ethanol, regardless of the presence of the hydroxyl group in the alcohol's structure. However, the lack of polarity in the polymer is unsuitable for the polarity of ethanol, resulting in the precipitation of the PS and its conversion into a solid form. This phenomenon is referred to as the solubility limit, which was assessed in this study using gravimetric analysis. The solubility limit was determined using the equation
where
represents the remaining mass of PS after the solvent has been evaporated, and
is the initial mass of the mixture consisting of PS, D-limonene, and ethanol, which was placed in the porcelain capsule before evaporation.
We establish a relationship between solubility and the ethanol composition in the solvent mixture free of PS, using the equation
here,
represents the mass of ethanol added during the insolubility experiment,
represents the mass composition of PS in the mixture of PS + D-limonene before the precipitation experiment, and
represents the mass of the PS + D-limonene mixture used in the precipitation experiment.
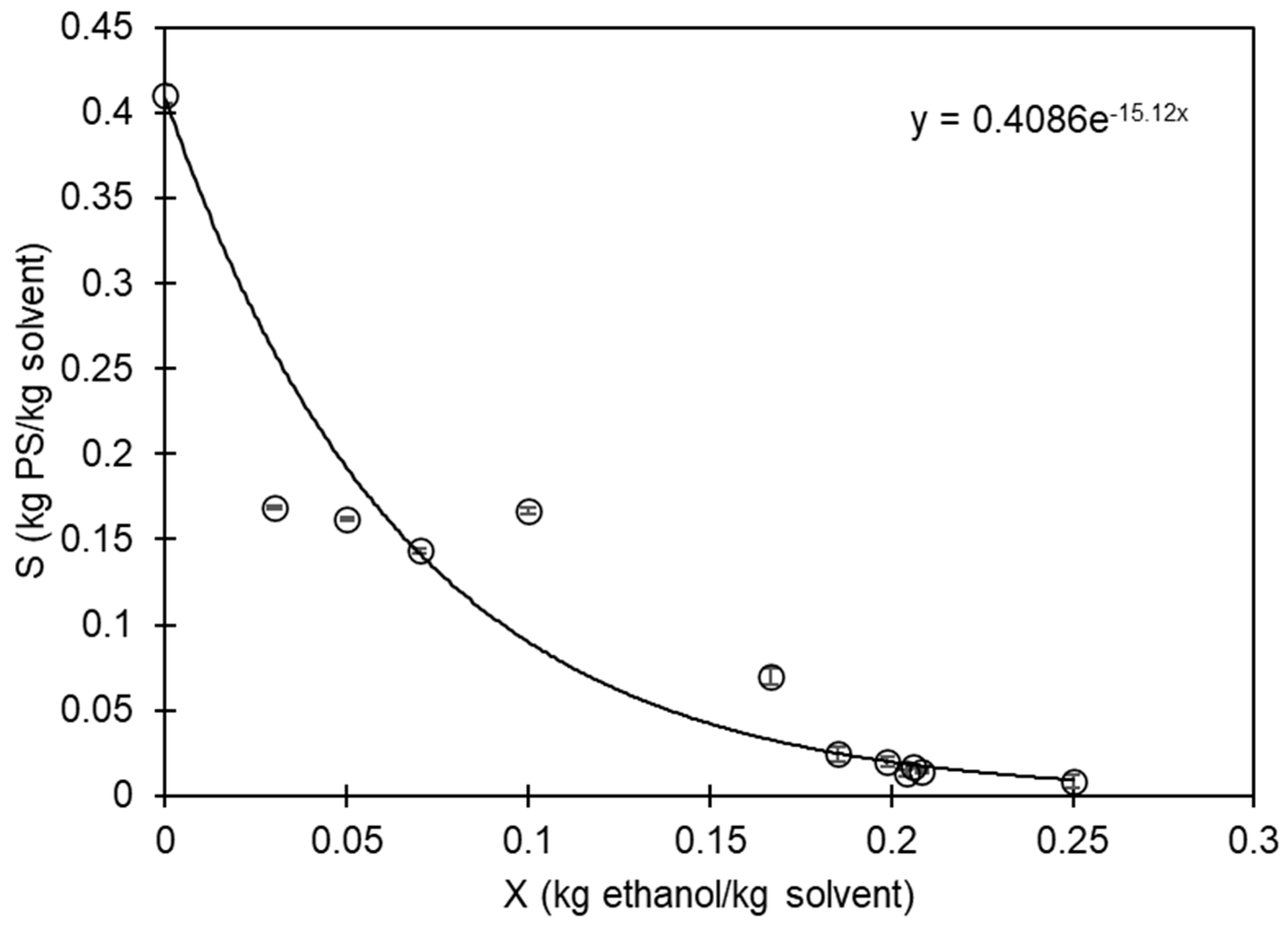
Figure 3 displays the empirical data regarding the maximum amount of PS that can dissolve in the mixture of D-limonene and ethanol. It is evident that as the concentration of ethanol in the mixture increases, the solubility of PS in D-limonene decreases. The data was adjusted to an exponential-type equation using the least square method
Figure 3 depicts the solubility limit, which can be utilized to recover and utilize EPS waste. By dissolving it in D-limonene, the trapped air that makes it voluminous is eliminated. Furthermore, by adding ethanol, the PS can be recovered as a solid. The D-limonene + ethanol mixture can then be separated through distillation to recover the solvents.
3.3. The Continuos Stirred Tank
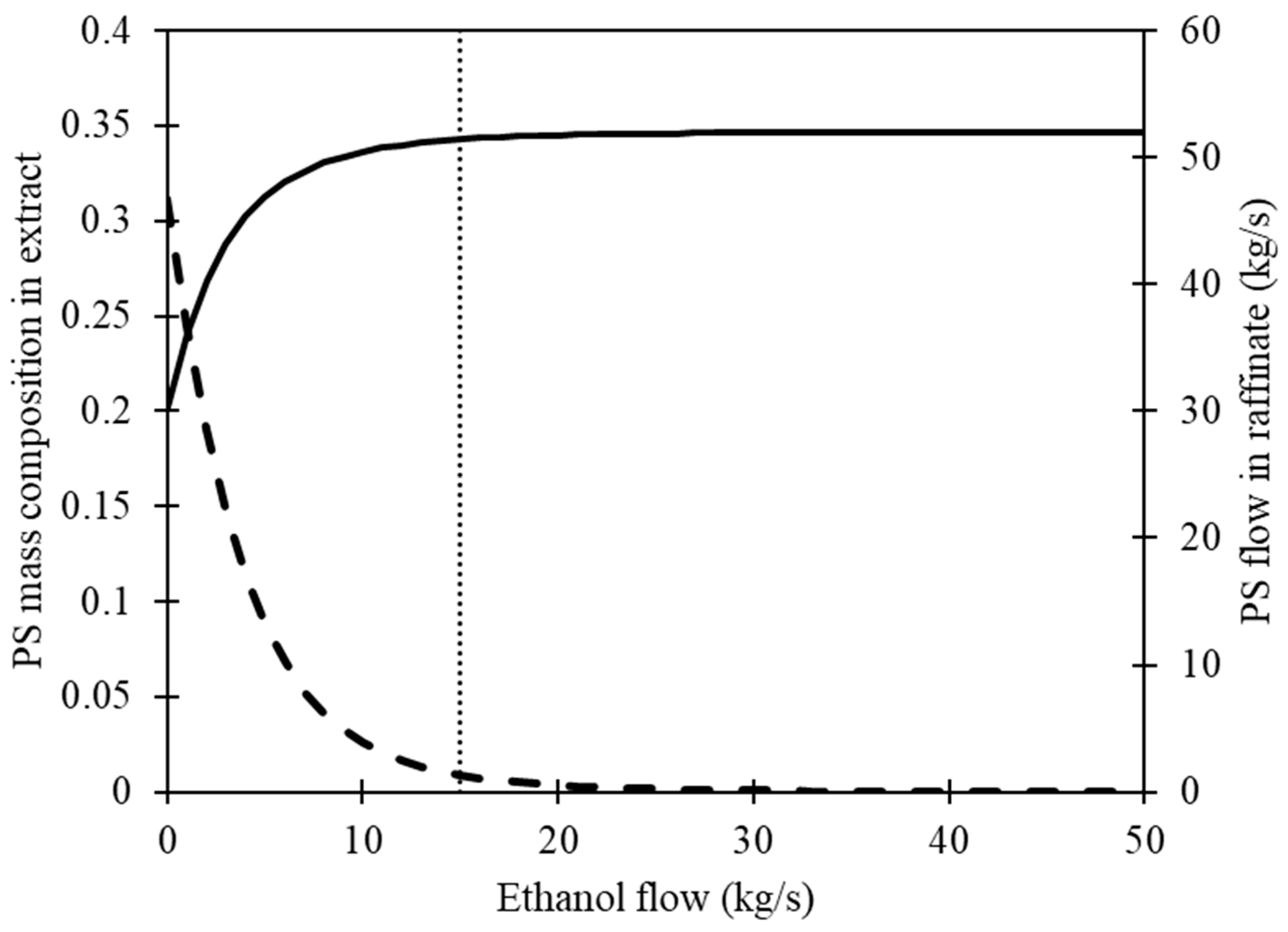
Equations 1 – 4 were solved simultaneously using algebraic methods, with the flow of fresh ethanol in stream D as a variable. The findings are presented in
Figure 4. As the ethanol flow to the stirred tank increases, the concentration of PS in the extract decreases, resulting in an increase in the amount of PS recovered in the raffinate. The objective of recovering 99% of the fed PS can be accomplished by using a 15 kg ethanol flow. However, it is important to note that regardless of the amount of ethanol added to the polymer mixture, there will still be some PS residue present in the extract stream due to the inherent characteristics of the process. The obtained results were utilized as an initial step in the development of the conceptual design for the PS recovery process.
3.4. Conceptual Design and Process Simulation
The thermodynamic model used for this design was the Non-Random Two Liquids (NRTL). The binary interaction parameters for the ethanol and D-limonene mixture were adjusted based on experimental data using the regression analysis tool included in the process simulator. The Interior Point Optimizer (IPOPT) method was employed, and the Objective Function (OF) was [
27]:
Two isobaric databases for the ethanol + D-limonene mixture have been found in the literature, one at a pressure of 40 kPa [
28] and another at a pressure of 101.3 kPa [
29]. The parameter values are presented in
Table 1. The Root-Mean-Square Deviation (RMSD) for the vapor composition was 0.017 at 40kPa and 0.038 at 101.3 kPa. The RMSD for temperature was 2.3 K at 40kPa and 3.7 K at 101.3 kPa.
The DWSIM process simulator does not have specific features for polymer processes, but it is still possible to utilize the Compound Creator wizard for this purpose. The PS was defined by incorporating data on the molecular weight determined in this study, he standard boiling point was supposed to be 673.15 K, considering that polymers start to boil before decomposition [
30], the melting temperature (513.15 K) [
31], and the density of the solid phase (0.92 g/cm
3) [
30].
The conceptual design of the process considered the results from the previous section, which included a flow of a mixture consisting of 100 kg/s of PS (52% w/w) and D-limonene (48% w/v), as well as a fresh ethanol feed of 15 kg/s.
The initial scheme examined consisted of a mixer to merge the feed streams and a compound separator. The design variable for the separator was set to achieve a recovery rate of 99%. The resulting solvent mixture consists of 75.6% w of D-limonene, 23.6% w of ethanol, and 0.8% w of PS. A distillation column was designed using the shortcut method module, with ethanol selected as the light key component and D-limonene as the heavy key component. A proposal was made to achieve a recovery rate of 99.99% for the key components located in both the dome and bottom. The specified pressure for the condenser was 206.8 kPa (30 psia), while for the reboiler it was 241.3 kPa (35 psia), with the utilization of a total condenser. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to determine the minimum reflux ratio (
). The reflux ratio was varied from 1.2 to 20 times
. It was found that a reflux ratio of 1.5 reduces the number of stages without impacting the quality of the distillate. The findings are displayed in
Table 2.
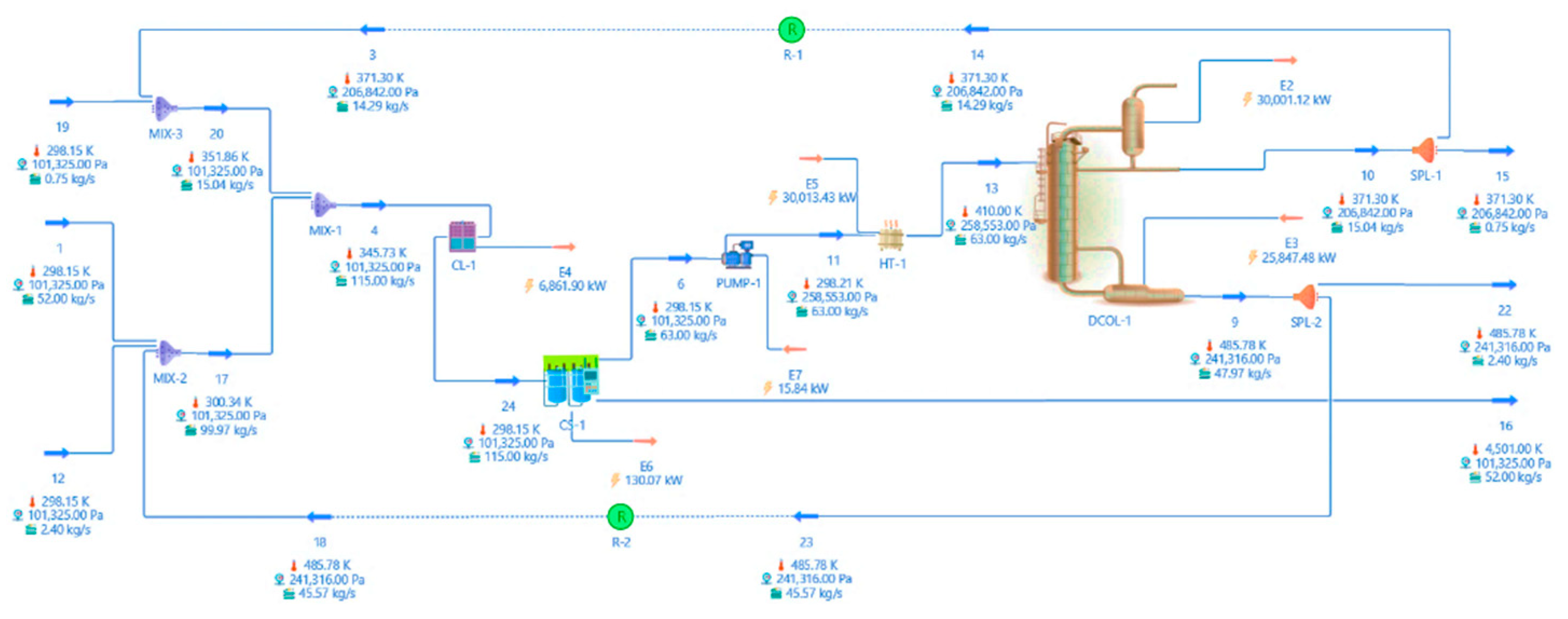
The final design of the distillation column was determined using the rigorous method, which involved six equilibrium stages and feeding on plate four. After achieving convergence, the proposal for the recirculation of solvents was presented, as depicted in
Figure 5. The temperature in Stream 16 is extremely high. This is because the property dataset for PS is not sufficient. Because the amount of PS in other currents is insignificant, this does not affect the thermodynamic properties of other streams.
A 5% purge is suggested for the distillation column's product streams to recover materials like residual PS in the solvents. Subsequent equipment, including pumps, heaters, and coolers, was installed to condition the streams before each treatment.
Table 3 presents a concise overview of the main results.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we present experimental data and empirical correlation for the solubility limit for the mixture PS + D-limonene + ethanol. We discovered that increasing the amount of polar molecules in the solvent resulted in the insolubilization of diluted PS. We used the experimental data from this work on the solubility limit to conceptually design a process that treats EPS and recovers it as a solid, ready for market reintroduction. We use D-limonene and ethanol instead of fossil solvents like benzene or toluene because we can obtain them from agro-waste. It is necessary to supplement experimental information on the properties of PS in order to improve the results for this material.
Author Contributions
A.I.H.G.: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – original draft; S.A.H.: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing; Z.B.C.C.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing; J.A.G.P.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing; J.M.V.R.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing; D.G.Z.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Supervision.
Funding
This research was funded by Consejo de Ciencia y Tecnología del Estado de Tabasco (CCYTET), project number PRODECTI- 2022-01/84.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Juárez Autonomous University of Tabasco for the facilities granted for the development of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- White, D. and Winchester, N. The Plastic Intensity of Industries in the USA: The Devil Wears Plastic. Environmental Modeling and Assessment 2023, 28, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gausepohl, H., Nießner, N. Polystyrene and Styrene Copolymers. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, Elsevier, 2001, pp. 7735–7741. [CrossRef]
- Lafond, C.; Blanchet, P. Technical Performance Overview of Bio-Based Insulation Materials Compared to Expanded Polystyrene. Buildings 2020, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, M. D.; Garcia-Sanoguera, D.; Parres, F.; López, J. Recycling of Expanded Polystyrene from Packaging. Progress in Rubber, Plastics and Recycling Technology 2010, 26, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, P. A. Plastic packaging sector: a contemporary and crucial challenge. Master of Science, Aalto University, Tokyo, Japan, 2020. Accessed: Jul. 19, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://aaltodoc.aalto.fi/server/api/core/bitstreams/6141d032-e3e9-4b64-b8e3-3861a7e59839/content.
- Achilias, D. S., Kanellopoulou, I., Megalokonomos, P., Lappas, A., Antonakou, E. Chemical Recycling of Polystyrene. In Proceedings of the international conference protection and restoration of the environment, Jul. 2006, pp. 3–7. Accessed: Jul. 19, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dimitris-Achilias/publication/266371180_CHEMICAL_RECYCLING_OF_POLYSTYRENE/links/54af9ac40cf2b48e8ed675f0/CHEMICAL-RECYCLING-OF-POLYSTYRENE.pdf.
- García, M. T. , Gracia, I., Duque, G., de Lucas, A., Rodríguez, J. F. Study of the solubility and stability of polystyrene wastes in a dissolution recycling process. Waste Management 2009, 29, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskander, S. B. , Tawfik, M. E. Polymer–cement composite based on recycled expanded polystyrene foam waste. Polym Compos 2011, 32, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo Mendoza, I. D. , León Pulido, J. Efecto de la concentración y temperatura en la disolución de poliestireno expandido usando solventes naturales. Avances Investigación en Ingeniería 2021, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C. , Chase, G. G. Nanofibers from recycle waste expanded polystyrene using natural solvent. Polymer Bulletin 2005, 55, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K. Recycling of Expanded Polystyrene Using Natural Solvents. In Proceedings of Recycling Materials Based on Environmentally Friendly Techniques, InTech, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Gil-Jasso, N. D. , Giles-Mazón, E. A., Soriano-Giles, G., Reinheimer, E. W., Varela-Guerrero, V., Ballesteros-Rivas, M. F. A methodology for recycling waste expanded polystyrene using flower essential oils. Fuel 2022, 307, 121835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Jasso, N. D., Segura-González, M. A., Soriano-Giles, G., Neri-Hipolito, J., López, N., Mas-Hernández, E., Barrera-Díaz, C. E., Varela-Guerrero, V., Ballesteros-Rivas, M. F. Dissolution and recovery of waste expanded polystyrene using alternative essential oils. Fuel 2019, 239, 611–616. [CrossRef]
- García-Barrera, L. V. , Ortega-Solís, D. L. Soriano-Giles, G., Lopez, N., Romero-Romero, F., Reinheimer, E., Varela-Guerrero, V., Ballesteros-Rivas, M. F. A Recycling Alternative for Expanded Polystyrene Residues Using Natural Esters. J Polym Environ 2022, 30, 3832–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngema, P. T. , Matkowska, D., Naidoo, P., Hofman, T., Ramjugernath, D. Vapor-liquid equilibrium data for binary systems of 1-methyl-4-(1- methylethenyl)-cyclohexene + {ethanol, propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, pentan-1-ol, or hexan-1-ol} at 40 kPa. J Chem Eng Data 2012, 57, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyns, Z. O. G. , Shaver, M. P. Mechanical Recycling of Packaging Plastics: A Review. Macromol Rapid Commun 2021, 42, 2000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, C. , Badgujar, P. C., Gundev, P., Upadhyay, A. Review of toxicological assessment of d-limonene, a food and cosmetics additive. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2018, 120, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C. , Theodoropoulos, C., Scrutton, N. S. Techno-economic assessment of microbial limonene production. Bioresour Technol 2020, 300, 122666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata-Boada, S. , Gonzalez-Miquel, M., Jobson, M., Cuéllar-Franca, R. M. Life Cycle Environmental Evaluation of Alternative Solvents Used in Lipid Extraction─The Case of Algae Biodiesel. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2023, 11, 11934–11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. , Cheng, H., Qi, Z. Experimental and Molecular Insights into Efficient Deterpenation of Essential Oil Intensified by Extraction with Deep Eutectic Solvent. Ind Eng Chem Res 2024, 63, 10761–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, S. H. , Hussain, A. A., Yansaneh, O. Y., Jalil, A. A. Modelling and Simulation of Dissolution/Reprecipitation Technique for Low-Density Polyethene Using Solvent/Non-Solvent System. Processes 2022, 10, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H. L. The Mark–Houwink–Sakurada Equation for the Viscosity of Atactic Polystyrene. J Phys Chem Ref Data 1985, 14, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G. , Vesely, D. Equilibrium solubility of alcohols in polystyrene attained by controlled diffusion. Eur Polym J 2007, 43, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L. H. , Pinto, R. R., Monteiro Filho, E. S., Aznar, M. Density, Refractive Index, pH, and Cloud Point Temperature Measurements and Thermal Expansion Coefficient Calculation for PPG 400, PE62, L64, L35, PEG 400, PEG 600, or PEG 1000 + Water Systems. J Chem Eng Data 2021, 66, 2959–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, E.J.; Seader, J.D. Equilibrium Stage Separation Operations in Chemical Engineering, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, United States of America, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, D. DWSIM – Open Source Process Simulation, Modeling and Optimization version 8.8.0 2024. URL: https://dwsim.org, accessed in July 2024.
- López, J. A. , Trejos, V. M., Cardona, C. A. Objective functions analysis in the minimization of binary VLE data for asymmetric mixtures at high pressures. Fluid Phase Equilib 2006, 248, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngema, P. T. , Matkowska, D., Naidoo, P., Hofman, T., Ramjugernath, D. Vapor–Liquid Equilibrium Data for Binary Systems of 1-Methyl-4-(1-methylethenyl)-cyclohexene + {Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, Propan-2-ol, Butan-1-ol, Pentan-1-ol, or Hexan-1-ol} at 40 kPa. J Chem Eng Data 2012, 57, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, D. , Shinobu, Y., Miyakoshi, Y., Kato, M. Vapor-Liquid Equilibria for Ethanol + Limonene and 1-Propanol + Limonene. Netsu Bussei 2003, 17, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathiba, R. , Shruthi, M., Miranda, L. R. Pyrolysis of polystyrene waste in the presence of activated carbon in conventional and microwave heating using modified thermocouple. Waste Management 2018, 76, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasztor, A. J. , Landes, B. G., Karjala, P. J. Thermal properties of syndiotactic polystyrene. Thermochim Acta 1991, 177, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).