Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- a.
- Safety Concerns: UVC light can cause damage to skin and eyes upon direct exposure. Implementing proper safeguards, like protective equipment, engineering controls (enclosed systems), and training for workers is essential.
- b.
- Limited Penetration Depth: UVC light has limited ability to penetrate through materials. This means that for effective disinfection, waste needs to be spread out in a thin layer or the UVC source needs to be strategically placed to ensure all areas are exposed.
- c.
- Efficacy for Complex Waste Streams: The effectiveness of UVC LEDs may vary depending on the type of waste and the presence of organic matter that can shield microorganisms from the UVC light. Further research is needed to optimize UVC LED application for different waste compositions.
- d.
- Long-Term Performance and Maintenance: The long-term effectiveness of UVC LEDs can be impacted by factors like aging and dust accumulation. Regular maintenance and monitoring of UVC LED systems are crucial to ensure consistent disinfection performance.
- e.
- Regulatory Landscape: Regulations governing the use of UVC LEDs for waste disinfection may vary by region. Staying updated on relevant regulations and obtaining necessary approvals is essential.
2. Relevant Literature
2.1. Global disease Threat of C. auris
2.1.1. Vulnerable Populations
2.1.2. Economic Impact
2.2. Public Health Pandemonium – AMR and Nosocomial Spread of C. auris
2.2.1. Public Health Prevention
2.3. Current Healthcare Environmental Infection Control Standard Procedures
2.3.1. Water
2.3.2. Air
2.3.3. Surface
2.3.4. Waste Management
- The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Waste and Their Disposal minimizes the generation of hazardous wastes, the treatment of waste close to where it was generated, and the transboundary movement of hazardous waste.
- The Bamako Convention is a treaty with well over a dozen signatories that bans the importation of hazardous wastes into Africa.
- Polluter Pays Principle - the producer of waste is legally and financially liable for disposing of waste in a manner safe for people and the environment.
- Precautionary Principle - When risk is uncertain, it must be regarded as significant.
- Proximity Principle - Hazardous waste must be treated and disposed of as close as possible to where it was produced.
2.4. UVC LED Disinfection of C. auris in Healthcare Settings
2.4.1. Water
2.4.2. Air
2.4.3. Surface
2.4.4. Waste Management
2.4.5. UVC LED Disinfection Critical Factors
2.5. Case Studies of UV-C in Reducing C. auris
2.5.1. Water
2.5.2. Air
2.5.3. Surface
2.5.3. Waste Management
3. Discussion
3.1. Benefits, Feasibility, & Challenges of Implementing UVC Disinfection in Healthcare Settings
3.1.1. Challenges
3.1.2. Benefits
3.2. Recommendations for the use of UVC Disinfection in Healthcare Settings to Reduce Transmission of C. auris
- 1.
- Determine the UVC application (i.e., water, air, surface, and/or waste) needed and how it will be integrated into the current infection prevention and control infrastructure.
- 2.
- Ensure the UVC LED device meets all regional, national, and international disinfection standards.
- a.
- Ensure all regulations put forth by the CDC or other regulating bodies are followed. We suggest using UVC LED disinfection as an adjunct to currently accepted chemical disinfection until nationally and internationally recognized regulations are amended to consider UVC LED technology a first-line defense for the disinfection of C. auris.
- 3.
- Research all available devices with a cross-tabulated list of specific needs. Then, find the device that most closely aligns with the facility’s size and disinfection challenges.
- a.
- Consider the necessary operating parameters and associated critical factors across application areas that are necessary for effective disinfection.
- b.
- Assess the time and space requirements for effective disinfection in contrast to the available time and space for implementation.
- c.
- If the budget allows layer UVC LED disinfection technology (e.g., water, air, surface, and waste; however, given C. auris’s primary transmission route, a minimum of surface disinfection devices are strongly suggested.
- 4.
- Consider the human capacity and technical expertise required to implement and operate each type of device.
- a.
- Determine if the current infection prevention team will be sufficiently trained to augment disinfection with UVC LED or if new training or staff will be required.
- i.
- Any new training or personnel requirement should be factored into the budget assessment for the device.
- 5.
- Ensure the UVC LED technology adopted meets all required industry disinfection standards specific to the application.
- a.
- b.
- c.
- Water - NSF/ ANSI 55 Class A certification [244]
- 6.
- Establish robust evaluation protocols
- a.
- Accurate data collection and disease surveillance are necessary to determine the efficacy of C. auris inactivation and reduce colony spread.
- 7.
- Develop and implement routine maintenance schedules for all UVC LED systems to ensure their proper function and efficacy in disinfection.
- 8.
- Educate all healthcare system staff and administrators on the new infection prevention and control protocols, device safety, and disinfection procedures.
- 9.
- Write all policies and procedures in language the entire staff can understand and operationalize.
- 10.
- Establish a routine schedule for the evaluation of emerging UVC LED technology applications and device updates or upgrades.
4. Future Directions, in the Collection, Analyses, or Interpretation of Data, in the Writing of the Manuscript,
5. Conclusions
Appendices
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed consent statement
Data Availability statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Air: Environmental Guidelines. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/environmental/appendix/air.html (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Founou, R.C.; Founou, L.L.; Essack, S.Y. Clinical and Economic Impact of Antibiotic Resistance in Developing Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0189621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Multifaceted Phenomenon. Pathog Glob Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, Md.A.; Al-Amin, Md.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare (Basel) 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. The Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect Drug Resist 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajic, I.; Jovicevic, M.; Popadic, V.; Trudic, A.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Ilic, A.; Klasnja, S.; Hadnadjev, M.; Popadic, D.J.; et al. The Emergence of Multi-Drug-Resistant Bacteria Causing Healthcare-Associated Infections in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Multi-Centre Study. Journal of Hospital Infection 2023, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripartite Monitoring Global Progress on Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO, FAO, OIE: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-5-130800-4.
- US Department of Agriculture NVAP Reference Guide - WOAH and International Standards. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/nvap/reference-guide/emergency-management/woah (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Sikora, A.; Zahra, F. Nosocomial Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo Ruiz, G.; Lorenz, A. What Do We Know about the Biology of the Emerging Fungal Pathogen of Humans Candida Auris? Microbiological Research 2021, 242, 126621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatchanamoorthy, N.; Rukumani Devi, V.; Chandramathi, S.; Tay, S.T. Candida Auris: A Mini Review on Epidemiology in Healthcare Facilities in Asia. Journal of Fungi 2022, 8, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Business Today Desk Deadly Fungus, Candida Auris, Emerges in US: All You Need to Know. Business Today 2024.
- Haas, G. Hospital Infections from ‘Superbug’ Hit New High in January; Sunrise Hospital Cases up Again. KLAS: Local News, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Putka, S. Candida Auris: What to Know About the Fungal Infection Spreading Across the U.S. MedPage Today Special Reports 2024.
- Sisson, P. Kaiser Working to Contain Spread of Fungal Infection at Zion Medical Center. San Diego Union-Tribune, 2024.
- Spokane Regional Health District Candida Auris Advisory for Healthcare Providers - Feb 1 2024; Washington, 2024.
- Dall, C. New York Hospital Reports Spike in Candida Auris during COVID-19. CIDRAP 2024.
- TikTok Candida Auris Fungus 2024 Pandemic. Available online: https://www.tiktok.com/discover/candida-auris-fungus-2024-pandemic (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of Foodborne, Waterborne, and Environmental Diseases (DFWED) Tracking Candida Auris. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/candida-auris/tracking-c-auris.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Irfan, H.; Ahmed, A.; Hafeez, H.; Tatsadjieu, N.L.S. Multidrug-Resistant Candida Auris Outbreak: A New Challenge for the United States. IJS Global Health 2023, 6, e0223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortegiani, A.; Misseri, G.; Fasciana, T.; Giammanco, A.; Giarratano, A.; Chowdhary, A. Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, Resistance, and Treatment of Infections by Candida Auris. Journal of Intensive Care 2018, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei Sekyere, J. Candida Auris: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Current Updates on an Emerging Multidrug-resistant Pathogen. Microbiologyopen 2018, 7, e00578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettadili, H.; Vural, C. Current Global Status of Candida Auris an Emerging Multidrug-Resistant Fungal Pathogen: Bibliometric Analysis and Network Visualization. Braz J Microbiol 2024, 55, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caceres, D.H.; Forsberg, K.; Welsh, R.M.; Sexton, D.J.; Lockhart, S.R.; Jackson, B.R.; Chiller, T. Candida Auris: A Review of Recommendations for Detection and Control in Healthcare Settings. Journal of Fungi 2019, 5, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Infection Prevention and Control for Candida Auris. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/candida-auris/c-auris-infection-control.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Weber, D.J.; Rutala, W.A.; Anderson, D.J.; Sickbert-Bennett, E.E. ....úNo Touch..Ñ Methods for Health Care Room Disinfection: Focus on Clinical Trials. American Journal of Infection Control 2023, 51, A134–A143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.E.; Ryu, H.; Boczek, L.A.; Cashdollar, J.L.; Jeanis, K.M.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Lawal, O.R.; Linden, K.G. Evaluating UV-C LED Disinfection Performance and Investigating Potential Dual-Wavelength Synergy. Water Res 2017, 109, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, T.; Vrahas, M.S.; Murray, C.K.; Hamblin, M.R. Ultraviolet C Irradiation: An Alternative Antimicrobial Approach to Localized Infections? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2012, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeiszadeh, M.; Adeli, B. A Critical Review on Ultraviolet Disinfection Systems against COVID-19 Outbreak: Applicability, Validation, and Safety Considerations. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedy, J.M.; Pousty, D.; Waliaula, B.W.; Maniga, J.; Mamane, H.; Mariita, R.M. Enhancing Quality of Life, Public Health, and Economic Development in the Global South through Waterborne Disease Prevention with Ultraviolet C Light-Emitting Diode Technology. GHES 2024, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różańska, A.; Walkowicz, M.; Bulanda, M.; Kasperski, T.; Synowiec, E.; Osuch, P.; Chmielarczyk, A. Evaluation of the Efficacy of UV-C Radiation in Eliminating Microorganisms of Special Epidemiological Importance from Touch Surfaces under Laboratory Conditions and in the Hospital Environment. Healthcare 2023, 11, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Griffith, T.M.; Nyangaresi, P.O.; Qin, Y.; Pang, X.; Chen, G.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, B. Efficacy of UVC-LED in Water Disinfection on Bacillus Species with Consideration of Antibiotic Resistance Issue. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2020, 386, 121968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Mechanisms Investigation on Bacterial Inactivation through Combinations of UV Wavelengths. Water Research 2019, 163, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Sun, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Study on the Inactivation and Reactivation Mechanism of Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquaculture by UVC-LED. Frontiers in Marine Science 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterley, C.; Linden, K. Demonstration and Evaluation of Germicidal UV-LEDs for Point-of-Use Water Disinfection. J Water Health 2010, 8, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Kumar, A.; Schweizer, H.P. A 10-Min Method for Preparation of Highly Electrocompetent Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Cells: Application for DNA Fragment Transfer between Chromosomes and Plasmid Transformation. J Microbiol Methods 2006, 64, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cai, M.; Wang, L.; Niu, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, G. Evaluation Survey of Microbial Disinfection Methods in UV-LED Water Treatment Systems. Sci Total Environ 2019, 659, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, N.; Samaranayake, L. Emerging Strategies for Environmental Decontamination of the Nosocomial Fungal Pathogen Candida Auris. J Med Microbiol 2022, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottani, C.; Barraza, G.F.; Frigerio, F.; Corica, G.; Cuna, F.S.R. della; Cottica, D.; Grignani, E. Effectiveness of a Combined UV-C and Ozone Treatment in Reducing Healthcare-Associated Infections in Hospital Facilities. Journal of Hospital Infection 2023, 139, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariita, R.M.; Davis, J.H.; Lottridge, M.M.; Randive, R.V. Shining Light on Multi-Drug Resistant Candida Auris: Ultraviolet-C Disinfection, Wavelength Sensitivity, and Prevention of Biofilm Formation of an Emerging Yeast Pathogen. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11, e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss, A.; Emmanuel, J.; Stringer, R.; Pieper, U.; Townend, W.; Wilburn, S.; Chantier, Y. ; World Health Organization Safe Management of Wastes from Health-Care Activities / Edited by A. Prüss …[et Al]; 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2014; ISBN 978-92-4-154856-4. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization Health-Care Waste. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/health-care-waste (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Sansom, S.E.; Gussin, G.M.; Schoeny, M.; Singh, R.D.; Adil, H.; Bell, P.; Benson, E.C.; Bittencourt, C.E.; Black, S.; Del Mar Villanueva Guzman, M.; et al. Rapid Environmental Contamination With Candida Auris and Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens Near Colonized Patients. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2024, 78, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Chain of Infection Components. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/learning/safetyculturehc/module-2/3.html (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- World Health Organization Global Analysis of Healthcare Waste in the Context of COVID-19: Status, Impacts and Recommendations; Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-92-4-003961-2.
- Marsh, J. Hazardous Waste Incineration: A Closer Look at Environmental Solutions. Available online: https://environment.co/hazardous-waste-incineration-closer-look-at-environmental-solutions/ (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Beck, S.E. Wavelength-Specific Effects of Ultraviolet Light on Microorganisms and Viruses for Improving Water. Disinfection. Dissertation, University of Colorado Boulder: Boulder, Colorado, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, P.; Choi, H.; Ochoa, B.; Garmon, G.; Coppin, J.D.; Allton, Y.; Lukey, J.; Williams, M.D.; Navarathna, D.; Jinadatha, C. Clade-Specific Variation in Susceptibility of Candida Auris to Broad-Spectrum Ultraviolet C Light (UV-C). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2020, 41, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frongillo, E.; Amodeo, D.; Nante, N.; Cevenini, G.; Messina, G. A Novel Technology for Disinfecting Surfaces Infested with Candida Auris: The UVC Chip. European Journal of Public Health 2022, 32, ckac131–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Le, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Hu, J. Different Efficacies of Common Disinfection Methods against Candida Auris and Other Candida Species. J Infect Public Health 2020, 13, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutras, C.; Wade, R.L. Ultraviolet-C Mediated Inactivation of Candida Auris, a Rapid Emerging Health Threat. American Journal of Infection Control 2024, 52, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, A.R.; McClelland, T.; Martin, S.B.; Lindsley, W.G.; Green, B.J. Susceptibility of Candida Auris to Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) Correlates with Drug Resistance to Common Antifungal Agents. American Journal of Infection Control 2019, 47, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariita, R.M.; Davis, J.H.; Lottridge, M.M.; Randive, R.V. Shining Light on Multi-drug Resistant Candida Auris: Ultraviolet-C Disinfection, Wavelength Sensitivity, and Prevention of Biofilm Formation of an Emerging Yeast Pathogen. Microbiologyopen 2022, 11, e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslo, C.; du Plooy, M.; Coetzee, J. The Efficacy of Pulsed-Xenon Ultraviolet Light Technology on Candida Auris. BMC Infect Dis 2019, 19, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omardien, S.; Teska, P. Skin and Hard Surface Disinfection against Candida Auris – What We Know Today. Front. Med. 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutala, W.A.; Kanamori, H.; Gergen, M.F.; Sickbert-Bennett, E.E.; Weber, D.J. Inactivation of Candida Auris and Candida Albicans by Ultraviolet-C. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2022, 43, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases—Estimate Precision. Journal of Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Roudbary, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Černáková, L.; Rodrigues, C.F. Overview on the Infections Related to Rare Candida Species. Pathogens 2022, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Types of Fungal Diseases. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/index.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Abbasi, A.F.; Prakash, S.; Mangat, J.; Hosein, Z.; Haider, N.; Chan, J. Candida Auris: An Overview of the Emerging Drug-Resistant Fungal Infection. Infect Chemother 2022, 54, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Invasive Candidiasis. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/invasive/index.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Du, H.; Bing, J.; Hu, T.; Ennis, C.L.; Nobile, C.J.; Huang, G. Candida Auris: Epidemiology, Biology, Antifungal Resistance, and Virulence. PLOS Pathogens 2020, 16, e1008921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikora, A.; Hashmi, M.F.; Zahra, F. Candida Auris. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2024. [Google Scholar]
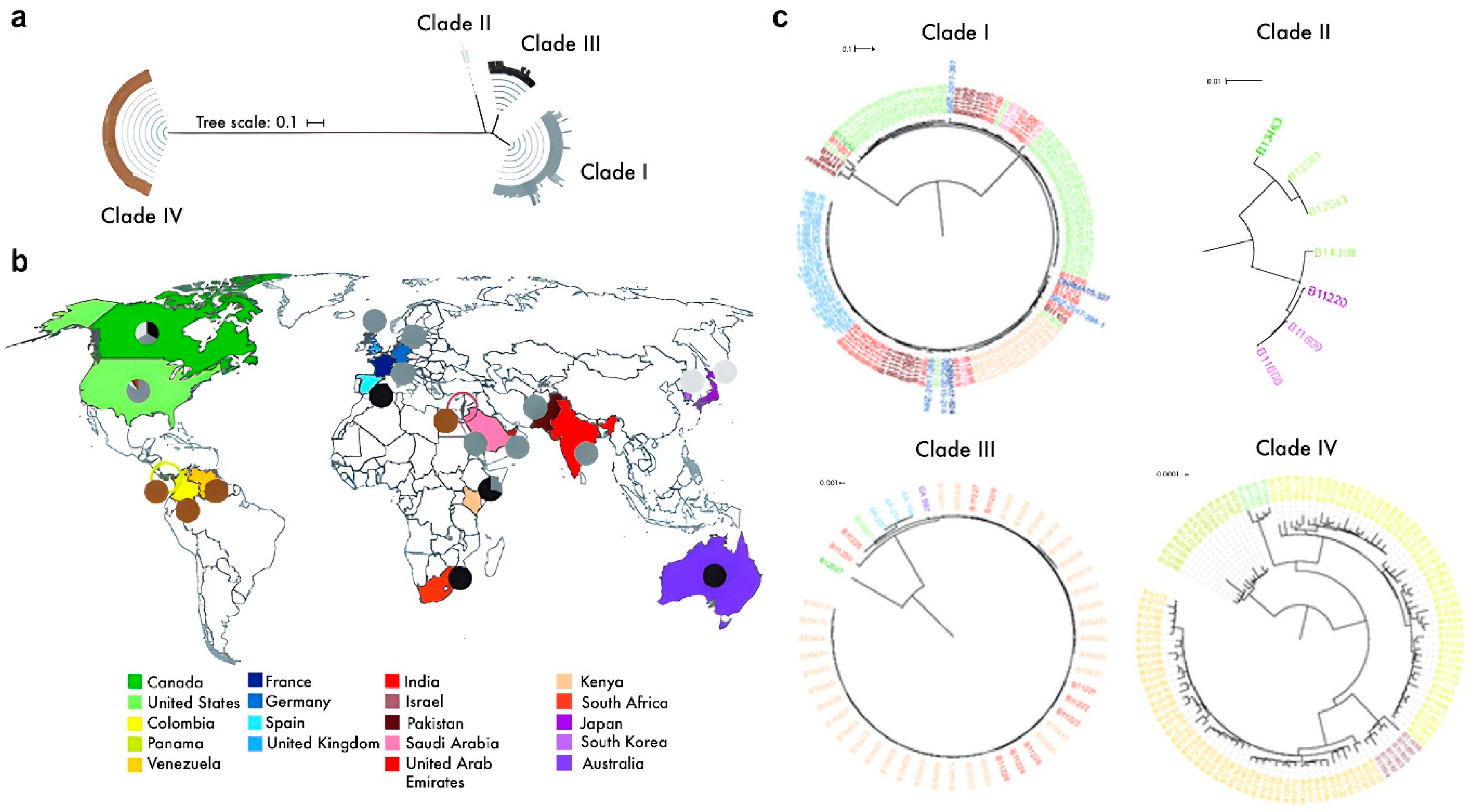
- Chow, N.A.; Muñoz, J.F.; Gade, L.; Berkow, E.L.; Li, X.; Welsh, R.M.; Forsberg, K.; Lockhart, S.R.; Adam, R.; Alanio, A.; et al. Tracing the Evolutionary History and Global Expansion of Candida Auris Using Population Genomic Analyses. mBio 2020, 11, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, P.A.; Rivera, S.M.; Escandon, P.; Caceres, D.H.; Chow, N.; Stuckey, M.J.; Díaz, J.; Gomez, A.; Vélez, N.; Espinosa-Bode, A.; et al. Hospital-Associated Multicenter Outbreak of Emerging Fungus Candida Auris, Colombia, 2016. Emerg Infect Dis 2019, 25, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Sood, P. On the Emergence, Spread and Resistance of Candida Auris: Host, Pathogen and Environmental Tipping Points. J Med Microbiol 2021, 70, 001318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, A.; Sharma, C.; Duggal, S.; Agarwal, K.; Prakash, A.; Singh, P.K.; Jain, S.; Kathuria, S.; Randhawa, H.S.; Hagen, F.; et al. New Clonal Strain of Candida Auris, Delhi, India. Emerging Infectious Diseases journal 2013, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, N.P.; Magobo, R.E.; Mpembe, R.; Mhlanga, M.; Matlapeng, P.; Corcoran, C.; Govind, C.; Lowman, W.; Senekal, M.; Thomas, J. Candida Auris in South Africa, 2012–2016. Emerg Infect Dis 2018, 24, 2036–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.A.; Ahmad, A. Candida Auris-the Growing Menace to Global Health. Mycoses 2019, 62, 620–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R. Emergence of Resistant Candida Auris. The Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.; Abdolrasouli, A.; Farrer, R.A.; Cuomo, C.A.; Aanensen, D.M.; Armstrong-James, D.; Fisher, M.C.; Schelenz, S. Genomic Epidemiology of the UK Outbreak of the Emerging Human Fungal Pathogen Candida Auris. Emerg Microbes Infect 2018, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, A.; Rasheed, Z.; Alghsham, R.S.; Abdulmonem, W.A. Candida Auris: An Emerging Fungus That Presents a Serious Global Health Threat. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 2023, 17, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Schalkwyk, E.; Mpembe, R.S.; Thomas, J.; Shuping, L.; Ismail, H.; Lowman, W.; Karstaedt, A.S.; Chibabhai, V.; Wadula, J.; Avenant, T.; et al. Epidemiologic Shift in Candidemia Driven by Candida Auris, South Africa, 2016–20171. Emerg Infect Dis 2019, 25, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, N.A.; Gade, L.; Tsay, S.V.; Forsberg, K.; Greenko, J.A.; Southwick, K.L.; Barrett, P.M.; Kerins, J.L.; Lockhart, S.R.; Chiller, T.M.; et al. Multiple Introductions and Subsequent Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Candida Auris in the USA: A Molecular Epidemiological Survey. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2018, 18, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.K.; Yasir, M.; Willcox, M. Candida Auris: An Emerging Antimicrobial-Resistant Organism with the Highest Level of Concern. The Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e482–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, A.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Robert, V. On the Emergence of Candida Auris: Climate Change, Azoles, Swamps, and Birds. mBio 2019, 10, e01397–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization WHO Fungal Priority Pathogens List to Guide Research, Development and Public Health Action; Geneva, 2022.
- Satoh, K.; Makimura, K.; Hasumi, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Uchida, K.; Yamaguchi, H. Candida Auris Sp. Nov., a Novel Ascomycetous Yeast Isolated from the External Ear Canal of an Inpatient in a Japanese Hospital. Microbiol Immunol 2009, 53, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, S. epiTrends. July 2021 .
- Fasciana, T.; Cortegiani, A.; Ippolito, M.; Giarratano, A.; Di Quattro, O.; Lipari, D.; Graceffa, D.; Giammanco, A. Candida Auris: An Overview of How to Screen, Detect, Test and Control This Emerging Pathogen. Antibiotics (Basel) 2020, 9, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spivak, E.S.; Hanson, K.E. Candida Auris: An Emerging Fungal Pathogen. J Clin Microbiol 2018, 56, e01588–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, N.; Samaranayake, L. Emerging and Future Strategies in the Management of Recalcitrant Candida Auris. Medical Mycology 2022, 60, myac008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escandón, P.; Chow, N.A.; Caceres, D.H.; Gade, L.; Berkow, E.L.; Armstrong, P.; Rivera, S.; Misas, E.; Duarte, C.; Moulton-Meissner, H.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Candida Auris in Colombia Reveals a Highly Related, Countrywide Colonization With Regional Patterns in Amphotericin B Resistance. Clin Infect Dis 2019, 68, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.M.; Doorley, L.A.; Nishimoto, A.T.; Barker, K.S.; Palmer, G.E.; Rogers, P.D. Abrogation of Triazole Resistance upon Deletion of CDR1 in a Clinical Isolate of Candida Auris. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2019, 63, e00057-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Prakash, A.; Sharma, C.; Kordalewska, M.; Kumar, A.; Sarma, S.; Tarai, B.; Singh, A.; Upadhyaya, G.; Upadhyay, S.; et al. A Multicentre Study of Antifungal Susceptibility Patterns among 350 Candida Auris Isolates (2009-17) in India: Role of the ERG11 and FKS1 Genes in Azole and Echinocandin Resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother 2018, 73, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, K.R.; Kordalewska, M.; Jiménez Ortigosa, C.; Singh, A.; Berrío, I.; Chowdhary, A.; Perlin, D.S. Limited ERG11 Mutations Identified in Isolates of Candida Auris Directly Contribute to Reduced Azole Susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2018, 62, e01427-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.M.; Sharma, C.; Doorley, L.A.; Barker, K.S.; Palmer, G.E.; Rogers, P.D. Delineation of the Direct Contribution of Candida Auris ERG11 Mutations to Clinical Triazole Resistance. Microbiol Spectr 2021, 9, e01585-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, N.B.; Kainz, K.; Schulze, A.; Bauer, M.A.; Madeo, F.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D. The Rise of Candida Auris: From Unique Traits to Co-Infection Potential. Microb Cell 2022, 9, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, M.C.; Moye-Rowley, W.S.; Krysan, D.J. Candida Auris: The Canary in the Mine of Antifungal Drug Resistance. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, S.R.; Etienne, K.A.; Vallabhaneni, S.; Farooqi, J.; Chowdhary, A.; Govender, N.P.; Colombo, A.L.; Calvo, B.; Cuomo, C.A.; Desjardins, C.A.; et al. Simultaneous Emergence of Multidrug-Resistant Candida Auris on 3 Continents Confirmed by Whole-Genome Sequencing and Epidemiological Analyses. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2017, 64, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, M.; Forsberg, K.; Reuben, J.; Dang, T.; Free, R.; Seagle, E.E.; Sexton, D.J.; Soda, E.; Jones, H.; Hawkins, D.; et al. Notes from the Field: Transmission of Pan-Resistant and Echinocandin-Resistant Candida Auris in Health Care Facilities ― Texas and the District of Columbia, January–April 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021, 70, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainer, M.A.; Kemble, S.; Black, S.; Blog, D.; Lutterloh, E.; Quinn, M.; VonBank, B.; Barrett, P.; Greeley, R.; Kratz, M.; et al. Standardized Case Definition for Candida Auris Clinical and Colonization/Screening Cases and National Notification of C. Auris Case, Clinical 2018.
- Gonzalez-Lara, M.F.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L. Invasive Candidiasis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2020, 41, 003–012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Khan, Z.; Al-Sweih, N.; Alfouzan, W.; Joseph, L. Candida Auris in Various Hospitals across Kuwait and Their Susceptibility and Molecular Basis of Resistance to Antifungal Drugs. Mycoses 2020, 63, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araúz, A.B.; Caceres, D.H.; Santiago, E.; Armstrong, P.; Arosemena, S.; Ramos, C.; Espinosa-Bode, A.; Borace, J.; Hayer, L.; Cedeño, I.; et al. Isolation of Candida Auris from 9 Patients in Central America: Importance of Accurate Diagnosis and Susceptibility Testing. Mycoses 2018, 61, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, B.; Melo, A.S.A.; Perozo-Mena, A.; Hernandez, M.; Francisco, E.C.; Hagen, F.; Meis, J.F.; Colombo, A.L. First Report of Candida Auris in America: Clinical and Microbiological Aspects of 18 Episodes of Candidemia. J Infect 2016, 73, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chybowska, A.D.; Childers, D.S.; Farrer, R.A. Nine Things Genomics Can Tell Us About Candida Auris. Front Genet 2020, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlenberg, A.; Monnet, D.L.; Plachouras, D.; Group, C. auris survey collaborative Increasing Number of Cases and Outbreaks Caused by Candida Auris in the EU/EEA, 2020 to 2021. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelenz, S.; Hagen, F.; Rhodes, J.L.; Abdolrasouli, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Hall, A.; Ryan, L.; Shackleton, J.; Trimlett, R.; Meis, J.F.; et al. First Hospital Outbreak of the Globally Emerging Candida Auris in a European Hospital. Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control 2016, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; O’Brien, B.; Leach, L.; Clarke, A.; Bates, M.; Adams, E.; Ostrowsky, B.; Quinn, M.; Dufort, E.; Southwick, K.; et al. Laboratory Analysis of an Outbreak of Candida Auris in New York from 2016 to 2018: Impact and Lessons Learned. J Clin Microbiol 2020, 58, e01503–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Sharma, C.; Meis, J.F. Candida Auris: A Rapidly Emerging Cause of Hospital-Acquired Multidrug-Resistant Fungal Infections Globally. PLOS Pathogens 2017, 13, e1006290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, M.; Forsberg, K.; Sexton, D.J.; Chow, N.A.; Lockhart, S.R.; Jackson, B.R.; Chiller, T. Worsening Spread of Candida Auris in the United States, 2019 to 2021. Ann Intern Med 2023, 176, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, T.S.N.; Walraven, C.J.; Lee, S.A. Candida Auris: Disinfectants and Implications for Infection Control. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, J.Q.; Jabeen, K.; Saeed, N.; Iqbal, N.; Malik, B.; Lockhart, S.R.; Zafar, A.; Brandt, M.E.; Hasan, R. Invasive Candidiasis in Pakistan: Clinical Characteristics, Species Distribution and Antifungal Susceptibility. J Med Microbiol 2013, 62, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Epidemiology of Invasive Candidiasis: A Persistent Public Health Problem. Clin Microbiol Rev 2007, 20, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smidt, M.C.F.; Meiring, S.; Mpembe, R.; Kularatane, R.; Govender, N. Factors Associated with Mortality among Patients with Candidaemia in South Africa, 2012. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2014, 21, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, A.M.; Pignatari, A.C.C.; Edmond, M.B.; Marra, A.R.; Camargo, L.F.A.; Siqueira, R.A.; da Mota, V.P.; Colombo, A.L. Epidemiology and Microbiologic Characterization of Nosocomial Candidemia from a Brazilian National Surveillance Program. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0146909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taori, S.K.; Khonyongwa, K.; Hayden, I.; Athukorala, G.D.A.; Letters, A.; Fife, A.; Desai, N.; Borman, A.M. Candida Auris Outbreak: Mortality, Interventions and Cost of Sustaining Control. J Infect 2019, 79, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention About Candida Auris (C. Auris) Available online:. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/candida-auris/candida-auris-qanda.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Ahmad, S.; Asadzadeh, M. Strategies to Prevent Transmission of Candida Auris in Healthcare Settings. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 2023, 17, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudramurthy, S.M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Paul, R.A.; Sood, P.; Kaur, H.; Capoor, M.R.; Kindo, A.J.; Marak, R.S.K.; Arora, A.; Sardana, R.; et al. Candida Auris Candidaemia in Indian ICUs: Analysis of Risk Factors. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2017, 72, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, A.; Sifri, Z.; Cennimo, D.; Horng, H. Global Contributors to Antibiotic Resistance. J Glob Infect Dis 2019, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance-the Need for Global Solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNICEF Neonatal Mortality. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-survival/neonatal-mortality/ (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- World Health Organization Newborns: Improving Survival and Well-Being. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/newborns-reducing-mortality (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Cook, A.; Ferreras-Antolin, L.; Adhisivam, B.; Ballot, D.; Berkley, J.A.; Bernaschi, P.; Carvalheiro, C.G.; Chaikittisuk, N.; Chen, Y.; Chibabhai, V.; et al. Neonatal Invasive Candidiasis in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Data from the NeoOBS Study. Medical Mycology 2023, 61, myad010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warris, A. Candida Auris, What Do Paediatricians Need to Know? Archives of Disease in Childhood 2018, 103, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrio, I.; Caceres, D.H.; Coronell R, W.; Salcedo, S.; Mora, L.; Marin, A.; Varón, C.; Lockhart, S.R.; Escandón, P.; Berkow, E.L.; et al. Bloodstream Infections With Candida Auris Among Children in Colombia: Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of 34 Cases. Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 2021, 10, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuping, L.; Mpembe, R.; Mhlanga, M.; Naicker, S.D.; Maphanga, T.G.; Tsotetsi, E.; Wadula, J.; Velaphi, S.; Nakwa, F.; Chibabhai, V.; et al. Epidemiology of Culture-Confirmed Candidemia Among Hospitalized Children in South Africa, 2012–2017. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2021, 40, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Sood, P.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Chen, S.; Jillwin, J.; Iyer, R.; Sharma, A.; Harish, B.N.; Roy, I.; Kindo, A.J.; et al. Characteristics, Outcome and Risk Factors for Mortality of Paediatric Patients with ICU-Acquired Candidemia in India: A Multicentre Prospective Study. Mycoses 2020, 63, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesini, A.; Saffioti, C.; Mariani, M.; Florio, A.; Medici, C.; Moscatelli, A.; Castagnola, E. First Case of Candida Auris Colonization in a Preterm, Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Newborn after Vaginal Delivery. Journal of Fungi 2021, 7, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, O.; Irwin, A.; Berthe, F.C.J.; Le Gall, F.G.; Marquez, P.V. Drug-Resistant Infections : A Threat to Our Economic Future (Vol. 2) : Final Report (English); HNP/Agriculture Global Antimicrobial Resistance Initiative; World Bank Group: Washington D.C, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, K.; Whitham, H.K.; Jackson, B.R. Economic Burden of Fungal Diseases in the United States. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2022, 9, ofac097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.; Jackson, B.R.; Chiller, T.; Beer, K.D. Estimation of Direct Healthcare Costs of Fungal Diseases in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2019, 68, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ismail, W.N.A.; Jasmi, N.; Khan, T.M.; Hong, Y.H.; Neoh, C.F. The Economic Burden of Candidemia and Invasive Candidiasis: A Systematic Review. Value in Health Regional Issues 2020, 21, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlin, D.S.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. The Global Problem of Antifungal Resistance: Prevalence, Mechanisms, and Management. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2017, 17, e383–e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Repository, S.; Basu, S. Antibiotic Resistance: A Threat to Global Health | Perils of Growing Antibiotic Resistance in Today’s World. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Valerio, M.; Vena, A.; Bouza, E. Antifungal Stewardship in Daily Practice and Health Economic Implications. Mycoses 2015, 58, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.K.; Chaturvedi, S.; Chaturvedi, V. So Many Diagnostic Tests, So Little Time: Review and Preview of Candida Auris Testing in Clinical and Public Health Laboratories. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, A.; Voss, A.; Meis, J.F. Multidrug-Resistant Candida Auris: ‘New Kid on the Block’ in Hospital-Associated Infections? Journal of Hospital Infection 2016, 94, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, M.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Jain, N.; Shamanth, A.S.; Sharma, D.; Jain, K.; Yaddanapudi, L.N.; Chakrabarti, A. Controlling a Possible Outbreak of Candida Auris Infection: Lessons Learnt from Multiple Interventions. Journal of Hospital Infection 2017, 97, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.J.; Chen, L.F.; Weber, D.J.; Moehring, R.W.; Lewis, S.S.; Triplett, P.F.; Blocker, M.; Becherer, P.; Schwab, J.C.; Knelson, L.P.; et al. Enhanced Terminal Room Disinfection and Acquisition and Infection Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Organisms and Clostridium Difficile (the Benefits of Enhanced Terminal Room Disinfection Study): A Cluster-Randomised, Multicentre, Crossover Study. The Lancet 2017, 389, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, L.; Ramage, G.; Kean, R.; Borman, A.; Johnson, E.M.; Richardson, M.D.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R. Biofilm-Forming Capability of Highly Virulent, Multidrug-Resistant Candida Auris. Emerg Infect Dis 2017, 23, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Alfouzan, W. Candida Auris: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antifungal Susceptibility, and Infection Control Measures to Combat the Spread of Infections in Healthcare Facilities. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černáková, L.; Roudbary, M.; Brás, S.; Tafaj, S.; Rodrigues, C.F. Candida Auris: A Quick Review on Identification, Current Treatments, and Challenges. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Eilertson, B.; Cadnum, J.L.; Whitlow, C.S.; Jencson, A.L.; Safdar, N.; Krein, S.L.; Tanner, W.D.; Mayer, J.; Samore, M.H.; et al. Environmental Contamination with Candida Species in Multiple Hospitals Including a Tertiary Care Hospital with a Candida Auris Outbreak. Pathog Immun 2019, 4, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhaneni, S. Investigation of the First Seven Reported Cases of Candida Auris, a Globally Emerging Invasive, Multidrug-Resistant Fungus — United States, May 2013–August 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, T.; Sultan, A.S.; Montelongo-Jauregui, D.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Candida Auris: A Fungus with Identity Crisis. Pathog Dis 2020, 78, ftaa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristina, M.L.; Spagnolo, A.M.; Sartini, M.; Carbone, A.; Oliva, M.; Schinca, E.; Boni, S.; Pontali, E. An Overview on Candida Auris in Healthcare Settings. Journal of Fungi 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.; Crank, K.; Papp, K.; Innes, G.K.; Schmitz, B.W.; Chavez, J.; Rossi, A.; Gerrity, D. Community-Scale Wastewater Surveillance of Candida Auris during an Ongoing Outbreak in Southern Nevada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Cuevas, S.; De la Obra, I.; Gualda-Alonso, E.; Soriano-Molina, P.; Casas López, J.L.; Sánchez Pérez, J.A. Simultaneous Disinfection and Organic Microcontaminant Removal by UVC-LED-Driven Advanced Oxidation Processes. Water 2021, 13, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangaresi, P.O.; Qin, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Shen, L. Comparison of the Performance of Pulsed and Continuous UVC-LED Irradiation in the Inactivation of Bacteria. Water Research 2019, 157, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Taghipour, F.; Mohseni, M. Microorganisms Inactivation by Wavelength Combinations of Ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diodes (UV-LEDs). Science of The Total Environment 2019, 665, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Kang, D.-H. UVC LED Irradiation Effectively Inactivates Aerosolized Viruses, Bacteria, and Fungi in a Chamber-Type Air Disinfection System. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2018, 84, e00944–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.C.K.; Nunayon, S.S. A New UVC-LED System for Disinfection of Pathogens Generated by Toilet Flushing. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunayon, S.S.; Zhang, H.H.; Lai, A.C.K. A Novel Upper-Room UVC-LED Irradiation System for Disinfection of Indoor Bioaerosols under Different Operating and Airflow Conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2020, 396, 122715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunayon, S.S.; Zhang, H.; Lai, A.C.K. Comparison of Disinfection Performance of UVC-LED and Conventional Upper-Room UVGI Systems. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, M.; Anglès d’Auriac, M.; Wennberg, A.C. Application of UV-LEDs for Antibiotic Resistance Genes Inactivation – Efficiency Monitoring with qPCR and Transformation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2021, 9, 105260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didik, T.; Yau, A.P.-Y.; Cheung, H.L.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chan, N.-H.; Wah, Y.-T.; Luk, H.K.-H.; Choi, G.K.-Y.; Cheng, N.H.-Y.; Tse, H.; et al. Long-Range Air Dispersion of Candida Auris in a Cardiothoracic Unit Outbreak in Hong Kong. J Hosp Infect 2023, 142, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghajari, A.; Lotfali, E.; Azari, M.; Fateh, R.; Kalantary, S. Fungal Airborne Contamination as a Serious Threat for Respiratory Infection in the Hematology Ward. Tanaffos 2015, 14, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.S.; Guy, R. National Public Health Response to Candida Auris in England. J Fungi (Basel) 2019, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dire, O.; Ahmad, A.; Duze, S.; Patel, M. Survival of Candida Auris on Environmental Surface Materials and Low-Level Resistance to Disinfectant. Journal of Hospital Infection 2023, 137, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobrega de Almeida, J.; Brandão, I.B.; Francisco, E.C.; de Almeida, S.L.R.; de Oliveira Dias, P.; Pereira, F.M.; Santos Ferreira, F.; de Andrade, T.S.; de Miranda Costa, M.M.; de Souza Jordão, R.T.; et al. Axillary Digital Thermometers Uplifted a Multidrug-susceptible Candida Auris Outbreak among COVID-19 Patients in Brazil. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutala, W.A.; Bolomey, A.C.; Cadnum, J.L.; Donskey, C.J. Inactivation and/or Physical Removal of Candida Auris from Floors by Detergent Cleaner, Disinfectants, Microfiber, and Ultraviolet C Light (UV-C). Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 2023; 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA, O. EPA’s Registered Antimicrobial Products Effective Against Candida Auris [List P]. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-registration/epas-registered-antimicrobial-products-effective-against-candida-auris-list (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Goulart, M.A.; El Itani, R.; Buchanan, S.R.; Brown, D.S.; Hays, A.K.; King, W.B.; Luciani, D.L.; Neilsen, C.D.; Verdecia, J.L. Identification and Infection Control Response to Candida Auris at an Academic Level I Trauma Center. American Journal of Infection Control 2024, 52, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestel, C.; Anderson, E.; Forsberg, K.; Lyman, M.; de Perio, M.A.; Kuhar, D.; Edwards, K.; Rivera, M.; Shugart, A.; Walters, M.; et al. Candida Auris Outbreak in a COVID-19 Specialty Care Unit — Florida, July–August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021, 70, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Gaitán, A.; Moret, A.M.; Tasias-Pitarch, M.; Aleixandre-López, A.I.; Martínez-Morel, H.; Calabuig, E.; Salavert-Lletí, M.; Ramírez, P.; López-Hontangas, J.L.; Hagen, F.; et al. An Outbreak Due to Candida Auris with Prolonged Colonisation and Candidaemia in a Tertiary Care European Hospital. Mycoses 2018, 61, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, M.V.; Johnson, C.J.; Kernien, J.F.; Patel, T.D.; Lam, B.C.; Cheong, J.Z.A.; Meudt, J.J.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Kalan, L.R.; Nett, J.E. Candida Auris Forms High-Burden Biofilms in Skin Niche Conditions and on Porcine Skin. mSphere 2020, 5, e00910–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, M.V.; Nett, J.E. Candida Auris Infection and Biofilm Formation: Going beyond the Surface. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep 2020, 7, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledwoch, K.; Maillard, J.-Y. Candida Auris Dry Surface Biofilm (DSB) for Disinfectant Efficacy Testing. Materials (Basel) 2018, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.J.; Rutala, W.A.; Sickbert-Bennett, E. Emerging Infectious Diseases, Focus on Infection Prevention, Environmental Survival and Germicide Susceptibility: SARS-CoV-2, Mpox, and Candida Auris. American Journal of Infection Control 2023, 51, A22–A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.; Ahmad, A. Abrogation of Pathogenic Attributes in Drug Resistant Candida Auris Strains by Farnesol. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0233102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salkin, I.F.; Krisiunas, E.; Turnberg, W.L. Medical and Infectious Waste Management. Journal of the American Biological Safety Association 2000, 5, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Overview of Technologies for the Treatment of Infectious and Sharp Waste from Health Care Facilities; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2019; ISBN 978-92-4-151622-8.
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Disinfection, Sterilization, and Control of Hospital Waste. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 2015; 3294–3309.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Omar, F.M.; Halim, H.A.; Hung, Y.-T. Health-Care Waste Management. In Solid Waste Engineering and Management: Volume 3; Wang, L.K., Wang, M.-H.S., Hung, Y.-T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 163–229. ISBN 978-3-030-96989-9. [Google Scholar]
- Street, A.; Vernooij, E.; Rogers, M.H. Diagnostic Waste: Whose Responsibility? Global Health 2022, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Committee of the Red Cross Medical Waste Management; Geneva, Switzerland, 2015;
- Sater, M.; Farrell, T.; Pangestu, F.; Herriott, I.; Anahtar, M.; Kwon, D.; Shenoy, E.; Hooper, D.; Huntley, M. Democratizing Sequencing for Infection Control: A Scalable, Automated Pipeline for WGS Analysis for Outbreak Detection. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2020, 41, s442–s443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselin, A.; Prasath, A.; Krishna, R.; Mohanarathinam, A. Clinical Waste Storage System with Contamination Prevention Mechanism Using UV and Arduino Microcontroller. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT); April 2023; pp. 1585–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Okethwengu, H.; Amisiri, B.; Ogwang, E. A TECHNICAL REPORT ON THE DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF A SMART WASTE BIN FOR MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT. SJ Engineering Africa 2024, 1, 21–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, T.; Gomes Filho, N.; Padrão, J.; Zille, A. A Comprehensive Analysis of the UVC LEDs’ Applications and Decontamination Capability. Materials (Basel) 2022, 15, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matafonova, G.; Batoev, V. Recent Advances in Application of UV Light-Emitting Diodes for Degrading Organic Pollutants in Water through Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. Water Res 2018, 132, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.Z.; Craik, S.A.; Bolton, J.R. Comparison of the Action Spectra and Relative DNA Absorbance Spectra of Microorganisms: Information Important for the Determination of Germicidal Fluence (UV Dose) in an Ultraviolet Disinfection of Water. Water Res 2009, 43, 5087–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, O.; Cosman, J.; Pagan, J. UVSolutions. 2018,.
- Giese, N.; Darby, J. Sensitivity of Microorganisms to Different Wavelengths of UV Light: Implications on Modeling of Medium Pressure UV Systems. Water Research 2000, 34, 4007–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.C.R.; Roque, J.L.A.; Sarmiento, D.B.; Suarez, L.E.G.; Sunio, J.T.P.; Tabungar, K.I.B.; Tengco, G.S.C.; Rio, P.C.; Hilario, A.L. Use of Ultraviolet-C in Environmental Sterilization in Hospitals: A Systematic Review on Efficacy and Safety. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 2020, 14, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gora, S.L.; Rauch, K.D.; Ontiveros, C.C.; Stoddart, A.K.; Gagnon, G.A. Inactivation of Biofilm-Bound Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Bacteria Using UVC Light Emitting Diodes (UVC LEDs). Water Research 2019, 151, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Stangl, F.; Hoenes, K.; Sift, M.; Hessling, M. Improved Drinking Water Disinfection with UVC-LEDs for Escherichia Coli and Bacillus Subtilis Utilizing Quartz Tubes as Light Guide. Water 2015, 7, 4605–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Kim, S.-J.; Kang, D.-H. Inactivation Modeling of Human Enteric Virus Surrogates, MS2, Qβ, and ΦX174, in Water Using UVC-LEDs, a Novel Disinfecting System. Food Research International 2017, 91, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, U.; Jang, E.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.-J.; Kang, C.-W.; Cho, M.; Lee, J. Near Dissolved Organic Matter Microfiltration (NDOM MF) Coupled with UVC LED Disinfection to Maximize the Efficiency of Water Treatment for the Removal of Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Water Research 2023, 233, 119731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariita, R.M.; Davis, J.H.; Randive, R.V. Illuminating Human Norovirus: A Perspective on Disinfection of Water and Surfaces Using UVC, Norovirus Model Organisms, and Radiation Safety Considerations. Pathogens 2022, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Cuevas, S.; De la Obra, I.; Gualda-Alonso, E.; Soriano-Molina, P.; Casas López, J.L.; Sánchez Pérez, J.A. Simultaneous Disinfection and Organic Microcontaminant Removal by UVC-LED-Driven Advanced Oxidation Processes. Water (20734441) 2021, 13, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangaresi, P.O.; Qin, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Shen, L. Effects of Single and Combined UV-LEDs on Inactivation and Subsequent Reactivation of E. Coli in Water Disinfection. Water Research 2018, 147, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Chu, X.N.; He, M.; Liu, X.C.; Hu, J.Y. Impact of UVA Pre-Radiation on UVC Disinfection Performance: Inactivation, Repair and Mechanism Study. Water Research 2018, 141, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Acosta, N.; Bautista, M.A.; McCalder, J.; Himann, J.; Pogosian, S.; Hubert, C.R.J.; Parkins, M.D.; Achari, G. Quantitative Evaluation of Municipal Wastewater Disinfection by 280 Nm UVC LED. Water 2023, 15, NA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariita, R.M.; Blumenstein, S.A.; Beckert, C.M.; Gombas, T.; Randive, R.V. Disinfection Performance of a Drinking Water Bottle System With a UV Subtype C LED Cap Against Waterborne Pathogens and Heterotrophic Contaminants. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 719578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, K.P.; Kanmani, S. Design and Evaluation of Zero-Energy UVC-LED Reactor Fitted with Hand Pump System for Disinfection. AQUA - Water Infrastructure, Ecosystems and Society 2020, 70, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitzilaiou, E.; Kuria, A.M.; Siegumfeldt, H.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Knøchel, S. The Impact of Bacterial Cell Aggregation on UV Inactivation Kinetics. Water Research 2021, 204, 117593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyangaresi, P.O.; Zhang, B.; Shen, L.; Nyangaresi, P.O.; Zhang, B.; Shen, L. Effects of UV-LED Irradiation on E. Coli in Water Disinfection. In E. Coli Infections - Importance of Early Diagnosis and Efficient Treatment; IntechOpen, 2020 ISBN 978-1-83962-524-4.
- Faretra, G. The Power of UV Treatment for Wastewater. Wastewater Digest 2023.
- Rossi, A.; Chavez, J.; Iverson, T.; Hergert, J.; Oakeson, K.; LaCross, N.; Njoku, C.; Gorzalski, A.; Gerrity, D. Candida Auris Discovery through Community Wastewater Surveillance during Healthcare Outbreak, Nevada, USA, 2022. Emerging Infectious Diseases journal 2023, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Griffith, T.M.; Nyangaresi, P.O.; Qin, Y.; Pang, X.; Chen, G.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, B. Efficacy of UVC-LED in Water Disinfection on Bacillus Species with Consideration of Antibiotic Resistance Issue. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2020, 386, 121968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Gole, V.L.; Sharma, J.; Yadav, R.K. Biologically Treated Industrial Wastewater Disinfection Using Synergy of US, LED-UVS, and Oxidants. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification 2021, 169, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowndarya, S.; Kanmani, S.; Amal Raj, S. Disinfection of Biologically Treated Sewage Using AlGaN-Based Ultraviolet-C Light-Emitting Diodes in a Novel Reactor System. DWT 2021, 212, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.; Chen, H.-B.; Wang, G.-S. Application of UVC-LED/H2O2 in Wastewater Treatments: Treatment Efficacy on Disinfection Byproduct Precursors and Micropollutants. Sustain Environ Res 2023, 33, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Shin, M.; Kang, J.-W.; Kim, D.-K.; Kang, D.-H. Application of the 222 nm Krypton-Chlorine Excilamp and 280 nm UVC Light-Emitting Diode for the Inactivation of Listeria Monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium in Water with Various Turbidities. LWT 2020, 117, 108458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Jo, D.-M.; Kang, M.-G.; Khan, F.; Hong, S.D.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, Y.-M.; Ryu, U.-C. Bactericidal Effect of Ultraviolet C Light-Emitting Diodes: Optimization of Efficacy toward Foodborne Pathogens in Water. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 2021, 222, 112277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzalel, Y.; Gerchman, Y.; Cohen-Yaniv, V.; Mamane, H. Multiwell Plates for Obtaining a Rapid Microbial Dose-Response Curve in UV-LED Systems. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 2020, 207, 111865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Mechanisms Investigation on Bacterial Inactivation through Combinations of UV Wavelengths. Water Research 2019, 163, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.; Kim, S.-S.; Kang, D.-H. Combined Treatment with a 222-Nm Krypton-Chlorine Excilamp and a 280-Nm LED-UVC for Inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria Monocytogenes. LWT 2020, 131, 109715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gora, S.L.; Rauch, K.D.; Ontiveros, C.C.; Stoddart, A.K.; Gagnon, G.A. Inactivation of Biofilm-Bound Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Bacteria Using UVC Light Emitting Diodes (UVC LEDs). Water Research 2019, 151, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, W.J.; Kubon, J.; Regner, N.; Haiser, K.; Schrader, T.E.; Zinth, W.; Clivio, P.; Gilch, P. Thymine Dimerization in DNA Model Systems: Cyclobutane Photolesion Is Predominantly Formed via the Singlet Channel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5038–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullotto, C.; Dragoni, L.; Amodeo, D.; Cevenini, G.; Nante, N.; Messina, G. Air Purifiers, Comparison between Real and Declared Surface for Use: Fake It or Make It? European Journal of Public Health 2022, 32, ckac131–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, K.; Mariita, R.M. Quantifying the Impact of Ultraviolet Subtype C in Reducing Airborne Pathogen Transmission and Improving Energy Efficiency in Healthy Buildings: A Kahn–Mariita Equivalent Ventilation Model. Front. Built Environ. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, W. Airstream Disinfection. In Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation Handbook: UVGI for Air and Surface Disinfection; Kowalski, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; pp. 177–209. ISBN 978-3-642-01999-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, W. Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation Handbook: UVGI for Air and Surface Disinfection; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; ISBN 978-3-642-01998-2. [Google Scholar]
- Muramoto, Y.; Kimura, M.; Kondo, A. Verification of Inactivation Effect of Deep-Ultraviolet LEDs on Bacteria and Viruses, and Consideration of Effective Irradiation Methods - IOPscience. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 2021, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, T.; Gomes Filho, N.; Padrão, J.; Zille, A. A Comprehensive Analysis of the UVC LEDs’ Applications and Decontamination Capability. Materials 2022, 15, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.P.; Archer, J.; Calfee, M.W.; Serre, S.; Mickelsen, L.; Mikelonis, A.; Oudejans, L.; Hu, M.; Hurst, S.; Rastogi, V.K. Inactivation of Bacillus Anthracis and Bacillus Atrophaeus Spores on Different Surfaces with Ultraviolet Light Produced with a Low-pressure Mercury Vapor Lamp or Light Emitting Diodes. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2021, 131, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kang, D.-H. Effect of Surface Characteristics on the Bactericidal Efficacy of UVC LEDs. Food Control 2020, 108, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivellin, N.; Buffolo, M.; Onelia, F.; Pizzolato, A.; Barbato, M.; Orlandi, V.T.; Del Vecchio, C.; Dughiero, F.; Zanoni, E.; Meneghesso, G.; et al. Inactivating SARS-CoV-2 Using 275 Nm UV-C LEDs through a Spherical Irradiation Box: Design, Characterization and Validation. Materials 2021, 14, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Are Room Decontamination Units Needed to Prevent Transmission of Environmental Pathogens? Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2011, 32, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlmutter, B.S.; Haq, M.F.; Cadnum, J.L.; Jencson, A.L.; Carlisle, M.; Donskey, C.J. Efficacy of Relatively Low-Cost Ultraviolet-C Light Devices against Candida Auris. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2022, 43, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, A.R.; McClelland, T.L.; Martin, S.B.; Lindsley, W.G.; Green, B.J. Inactivation of the Multi-Drug-Resistant Pathogen Candida Auris Using Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation. Journal of Hospital Infection 2020, 105, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadnum, J.L.; Shaikh, A.A.; Piedrahita, C.T.; Jencson, A.L.; Larkin, E.L.; Ghannoum, M.A.; Donskey, C.J. Relative Resistance of the Emerging Fungal Pathogen Candida Auris and Other Candida Species to Killing by Ultraviolet Light. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2018, 39, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, T.; Chowdhary, A.; Meis, J.F.; Voss, A. Killing of Candida Auris by UV-C: Importance of Exposure Time and Distance. Mycoses 2019, 62, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karidis, A. Waste Management Pros Build UV Sanitizer for Health Providers. Waste 360 2020.
- Manda, V.; Balachandran, S.; Danaboina; Roopak; Batchu, S. R.S.; Raj, S.; Kumar, janagam; Govindu, S.; Mahesh, D.; Houji, R.; et al. UV Sterilizing Dustbin. International Journal for Modern Trends in Science and Technology 2021, 7, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, N.M.; Herold, W.H.; Linden, K.G. UV LED Water Disinfection: Validation and Small System Demonstration Study. AWWA Water Science 2019, 1, e1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, M.; Tong, D.; Finkelstein, Z.; Hoek, E.M.V. A Critical Review of Point-of-Use Drinking Water Treatment in the United States. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Suwan, P.; Koottatep, T.; Beck, S.E. Application of a Novel, Continuous-Feeding Ultraviolet Light Emitting Diode (UV-LED) System to Disinfect Domestic Wastewater for Discharge or Agricultural Reuse. Water Res 2019, 153, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, P.; Das, S.; Adhikary, A.; Chaudhuri, C.R.; Bhattacharyya, A. Design and Implementation of Water Purification System Based on Deep Ultraviolet Light Emitting Diodes and a Multi-Pass Geometry Reactor. Journal of Water and Health 2020, 18, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, K.P.; Kanmani, S. Design and Evaluation of Zero-Energy UVC-LED Reactor Fitted with Hand Pump System for Disinfection. AQUA - Water Infrastructure, Ecosystems and Society 2020, 70, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkilima, T.; Sabitov, Y.; Shakhmov, Z.; Abilmazhenov, T.; Tlegenov, A.; Jumabayev, A.; Turashev, A.; Kaliyeva, Z.; Utepbergenova, L. Exploring the Potential of Biofunctionalized Agricultural Waste Adsorbents Integrated with UV-LED Disinfection for Enhanced Wastewater Treatment. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering 2024, 9, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethington, T.; Newsome, S.; Waugh, J.; Lee, L.D. Cleaning the Air with Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation Lessened Contact Infections in a Long-Term Acute Care Hospital. American Journal of Infection Control 2018, 46, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, D.W.; Finley, C.; Brown, D. UV-C Light and Infection Rate in a Long Term Care Ventilator Unit: Canadian Journal of Infection Control / Revue Canadienne de Prévention Des Infections. CAN J INFECT CONTROL 2018, 33, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Astrid, F.; Beata, Z.; Van den Nest Miriam; Julia, E. ; Elisabeth, P.; Magda, D.-E. The Use of a UV-C Disinfection Robot in the Routine Cleaning Process: A Field Study in an Academic Hospital. Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Schnugh, D.; Thomas, T. Effectiveness of Ultraviolet-C vs Aerosolized Hydrogen Peroxide in ICU Terminal Disinfection. Journal of Hospital Infection 2022, 121, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.J.; Knelson, L.P.; Moehring, R.W.; Lewis, S.S.; Weber, D.J.; Chen, L.F.; Triplett, P.F.; Blocker, M.; Cooney, R.M.; Schwab, J.C.; et al. Implementation Lessons Learned From the Benefits of Enhanced Terminal Room (BETR) Disinfection Study: Process and Perceptions of Enhanced Disinfection with Ultraviolet Disinfection Devices. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2018, 39, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeersseman, N.; Saegeman, V.; Cossey, V.; Devriese, H.; Schuermans, A. Shedding a Light on Ultraviolet-C Technologies in the Hospital Environment. Journal of Hospital Infection 2023, 132, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullotto, C.; Sparacino, M.; Amodeo, A.; Cevenini, G.; Nante, N.; Messina, G. Which One to Choose? A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis between Different Technologies of Air Purifiers. European Journal of Public Health 2022, 32, ckac131–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A: Health Organization Energizing Health, 2023.
- United Nations Development Programme Solar for Health. Available online: https://www.undp.org/energy/our-flagship-initiatives/solar-for-health (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- R-Zero How UV-C Light Can Help Combat the Spread of Candida Auris. R-Zero, 2023.
- Peasah, S.; McKay, N.; Harman, J.; Al-Amin, M.; Cook, R. Medicare Non-Payment of Hospital-Acquired Infections: Infection Rates Three Years Post Implementation. MMRR 2013, 3, E1–E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, C.C.; Liu, J.; Cohen, B.; Larson, E.L.; Glied, S. Financial Incentives to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections Under Alternative Payment Arrangements. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2018, 39, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insero, B. How to Calculate Cleaning Times. ISSA 2022.
- 2024.
- ASHRAE ASHRAE Standards and Guidelines. Available online: https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/ashrae-standards-and-guidelines (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 15858:2016(En), UV-C Devices — Safety Information — Permissible Human Exposure 2016.
- NSF International NSF/ANSI 55-2022 - Ultraviolet Microbiological Water Treatment Systems 2022.
- Zollner, C.J.; DenBaars, S.P.; Speck, J.S.; Nakamura, S. Germicidal Ultraviolet LEDs: A Review of Applications and Semiconductor Technologies. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Country | Mortality Rate (estimated) | Date | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | 52% | 2009 | (Farooqi et al., 2013) [105] |
| India | 50%* | 2009-2011 | (Chowdhary et al., 2013) [68] |
| 44% | (Pfaller & Diekema, 2007) [106] | ||
| South Africa | 46% | 2012 | (Smidt et al., 2014) [107] |
| Panama | 78%* | 2017 | (Araúz et al., 2018) [96] |
| Venezuela | 28%* | 2012 – 2013 | (Calvo et al., 2016) [97] |
| Brazil | 72% | 2007 – 2010 | (Doi et al., 2016) [108] |
| Columbia | 43% | 2015 – 2016 | (Armstrong et al., 2019) [66] |
| England (3 London hospitals) | 14.5%* | 2015 – 2018 | (Taori et al., 2019) [109] |
| India, US, UK (combined systematic review) | 30%* | _____ | (Osei Sekyere, 2018) [23] |
| Economic Burden | Cost Estimate ($USD)* | Cost Type | Source | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMR disease burden | ||||
| Europe | $9.77 billion | Total burden | (Prestinaci et al., 2015) [3] | |
| United States | $55 billion | Total Burden | CDC | (Dadgostar, 2019) [6] |
| $20 billion | Direct healthcare costs | |||
| $35 billion | Loss of productivity | |||
| Fungal Disease Burden | ||||
| $11.5 billion | Total burden | CDC | (Benedict et al., 2019, 2022; Kumar et al., 2022) [59,124,125] | |
| $7.5 billion | Direct healthcare costs | |||
| $870 million | Loss of productivity | |||
| $3.2 billion | Premature death | |||
| Candidiasis & Candidemia Burden | ||||
| Noninvasive Candidiasis | $2.5 billion | Total Cost Burden | CDC | (Benedict et al., 2019, 2022) [124,125] |
| Invasive Candidiasis | $1.7 billion | Total Cost Burden | ||
| $1.2 billion | Direct medical costs | |||
| $75 million | Loss of productivity | |||
| $450 million | Premature death | |||
| Western Developed Countries | Range: $48,487 - $157,574 | Cost per patient | Systematic Review | (Wan Ismail et al., 2020) [126] |
| Western Developed Countries | Range: $10,216 -$37,715 | Cost per hospitalization | Systematic Review | |
| London Outbreak | $1.2 million | At time of outbreak | Institutional Report | (Taori et al., 2019) [109] |
| $73,000 per month | Year to year post-outbreak | |||
| Peak wavelength (nm) | Time (s) | Dose (mJ/cm−2) | Controls (CFU ml−1 ) | UVC treated (CFU ml−1 ) | Log Reduction Value (LRV) | % Reduction | Susceptibility constant (k) (cm2 mJ) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 252 | 5 10 20 40 |
5 10 20 40 |
8.60E + 05 8.60E + 05 8.60E + 05 8.60E + 05 |
3.67E + 05 2.43E + 05 7.67E + 04 9.33E + 02 |
0.37 0.55 1.05 2.96 |
57.336 71.744 91.081 99.892 |
0.0691 | (Mariita et al., 2022) [54] |
| 261 | 5 10 20 40 |
5 10 20 40 |
8.60E + 05 8.60E + 05 8.60E + 05 8.60E + 05 |
5.47E + 05 2.03E + 05 5.50E + 04 5.21E + 03 |
0.20 0.63 1.20 2.22 |
36.617 76.477 93.627 99.396 |
0.0565 | (Giese & Darby, 2000) [178] |
| 267 | 5 10 20 40 |
5 10 20 40 |
6.40E + 05 6.40E + 05 6.40E + 05 6.40E + 05 |
2.50E + 05 4.33E + 04 2.33E + 02 1.00E + 01 |
0.41 1.17 3.44 4.81 |
60.938 93.234 99.964 99.998 |
0.1294 | (Mariita et al., 2022) [54] |
| 270 | 5 10 20 40 |
5 10 20 40 |
9.53E + 05 9.53E + 05 9.53E + 05 9.53E + 05 |
3.33E + 05 6.33E + 04 3.33E + 02 2.33E + 01 |
0.46 1.18 3.46 4.61 |
65.058 93.358 99.965 99.998 |
0.126 | (Giese & Darby, 2000) [178] |
| 273 | 5 10 20 40 |
5 10 20 40 |
8.00E + 05 8.00E + 05 8.00E + 05 8.00E + 05 |
3.27E + 05 1.07E + 05 2.03E + 03 3.67E + 01 |
0.39 0.88 2.59 4.34 |
59.125 86.625 99.746 99.995 |
0.111 | (Mariita et al., 2022) [54] |
| 280 | 5 10 20 40 |
5 10 20 40 |
4.07E + 05 4.07E + 05 4.07E + 05 4.07E + 05 |
2.07E + 05 1.70E + 05 2.87E + 04 4.00E + 01 |
0.29 0.38 1.16 4.01 |
49.140 58.537 93.000 99.990 |
0.0889 | (Mariita et al., 2022) [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





