Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Dataset
4. Feature Extraction Techniques
4.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4.1.1. Standardisation
4.1.2. Covariance Matrix Computation, ∑
4.1.3. Eigenvector and Eigenvalues Computation
4.2. Statistical Features: MRE
4.2.1. Mean,
4.2.2. Relative Amplitude, R
4.2.3. Entropy, E
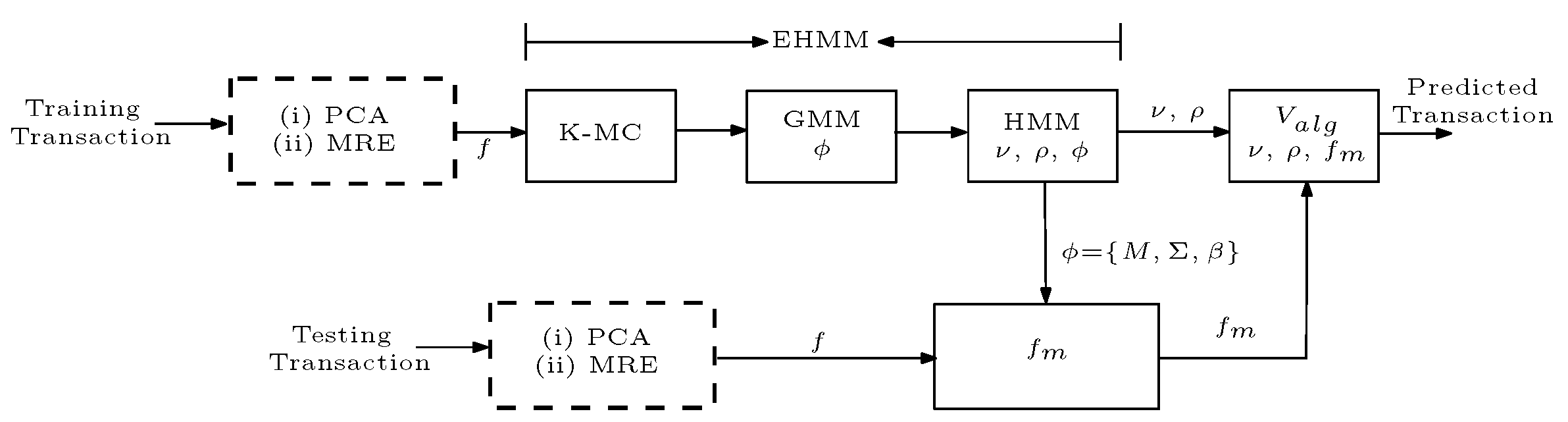
5. Ensemble Hidden Markov Model (EHMM)
5.1. EHMM Training
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Test Parameter
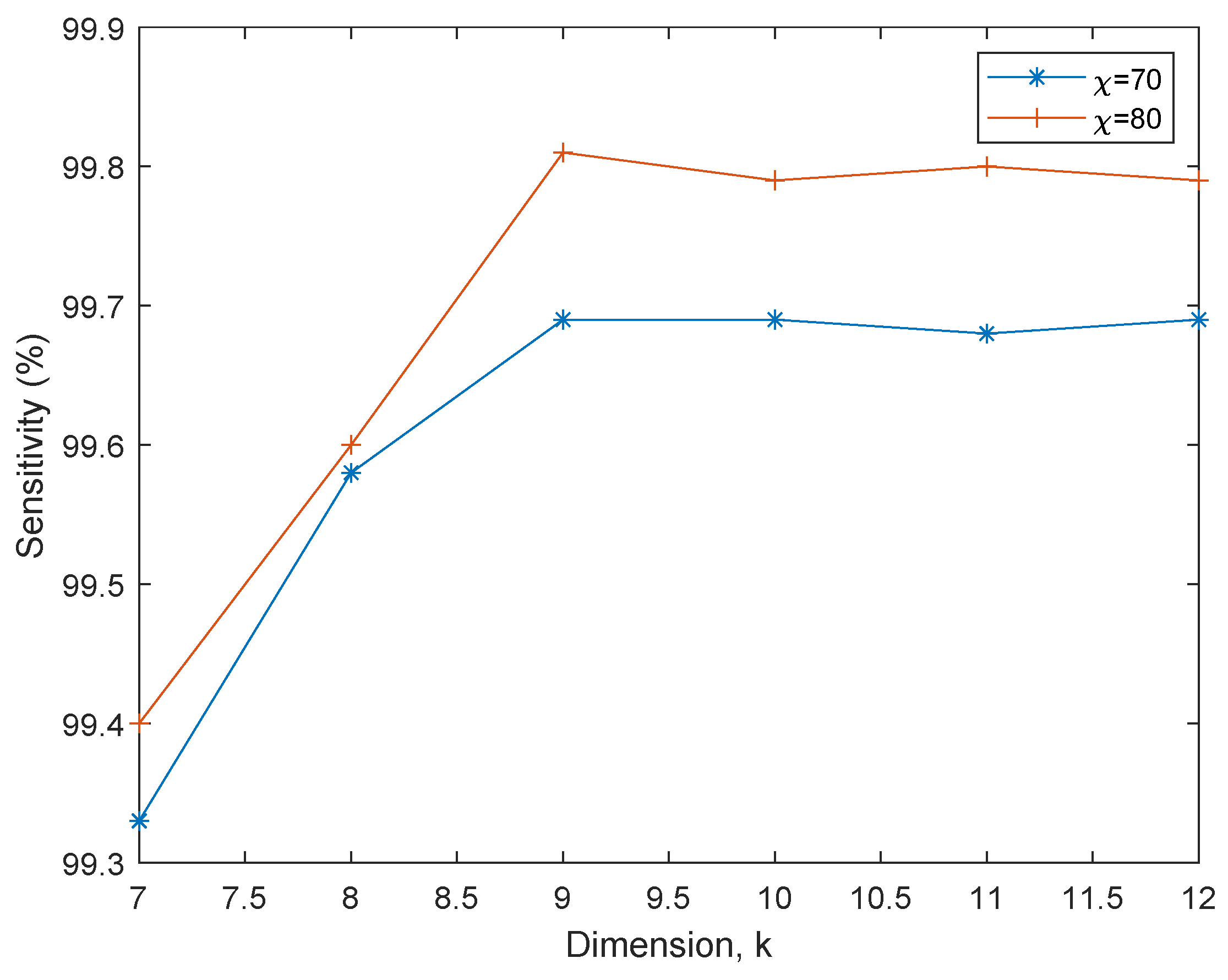
- Recall/Sensitivity, : The measures the ability of the models to correctly predict the non-fraudulent transactions; that is `0’. It is expressed as:where true positives (TP) refer to the number of accurately predicted non-fraudulent transaction and false negatives (FN) refer to the number of times the models miss a manually identified non-fraudulent transactions.
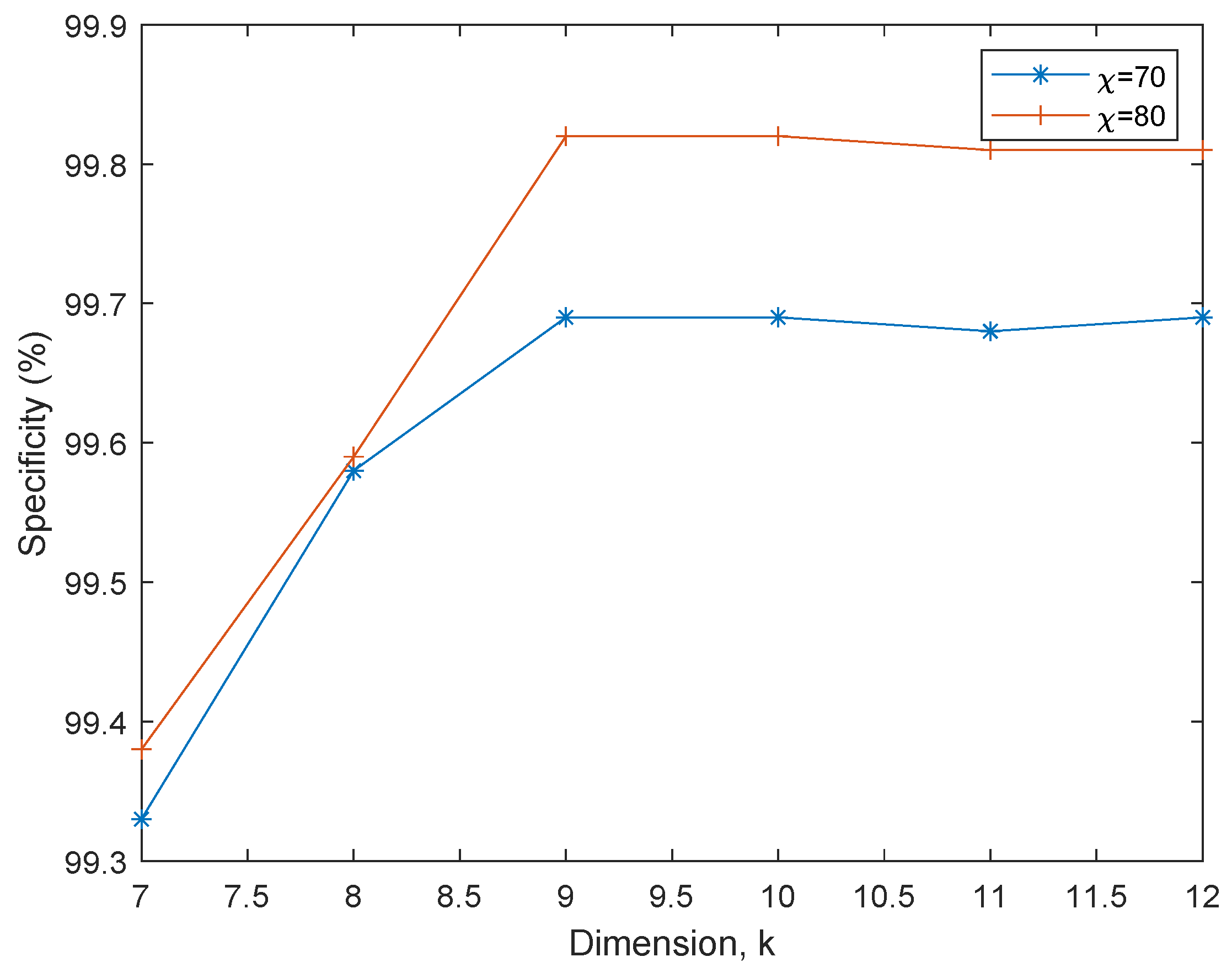
- Specificity, (): The measures the ability of the models to correctly predict the fraudulent transactions; that is, class `1’. It is expressed as:where true negatives (TN) refer to the number of accurately predicted fraudulent transactions and false positives (FP) refer to the number of times the models miss the manually identified fraudulent transactions.
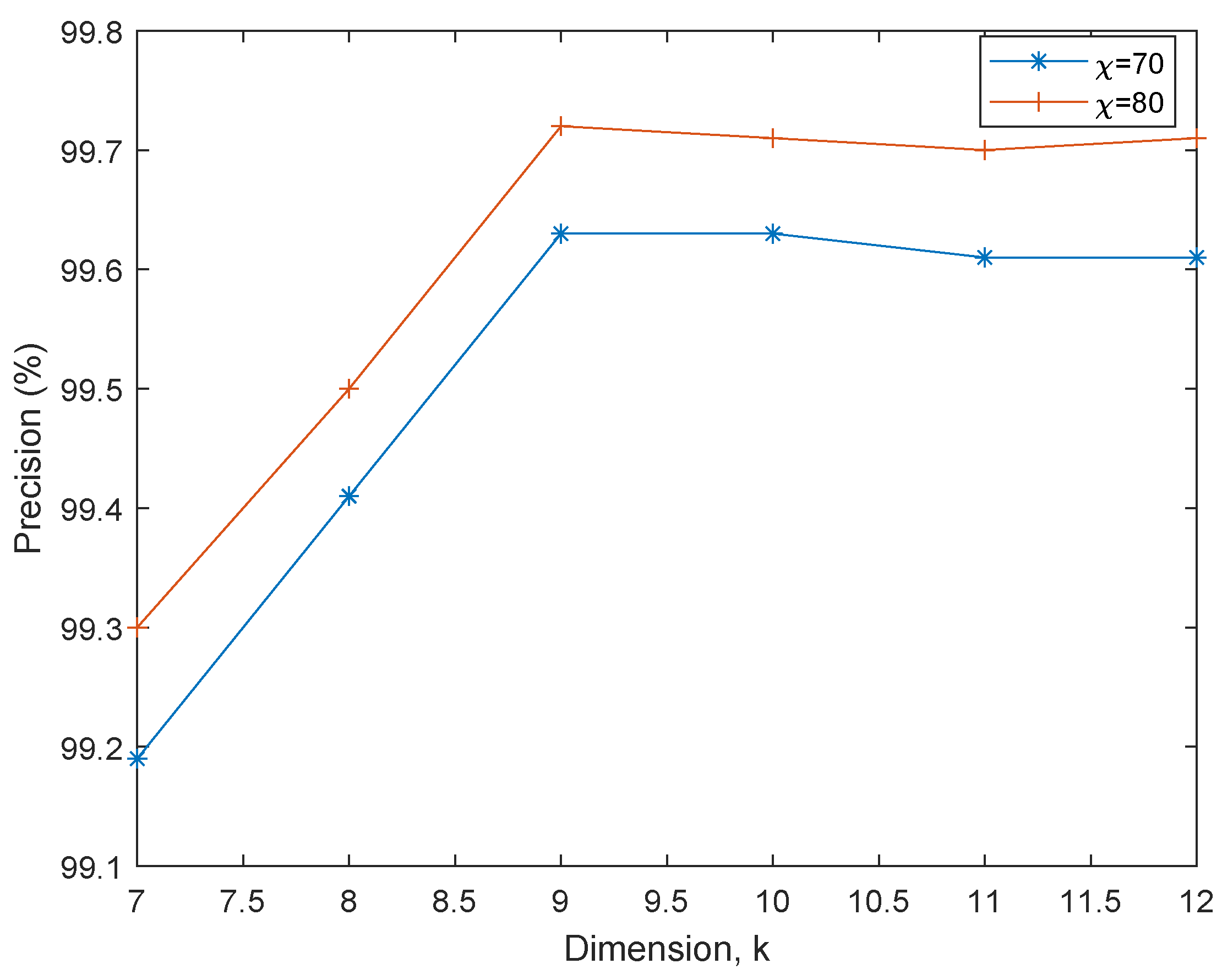
- Precision, : The is defined as the capacity of the model to accurately predict the class of the card transaction; that is `0’ of `1’. It is expressed as:where true positives (TP) refer to the number of accurately predicted transaction and false negatives (FP) refer to the number of times the models miss a manually identified transaction class. A high value of indicates a good model performance.
- F1-score, : The is a measure that combines precision and recall. It is commonly known as the harmonic mean of the two. It is expressed as:
6.2. PCA-EHMM Results and Discussion
6.3. MRE-EHMM Results and discussion
| (%) | MRE-EHMM | PCA-EHMM | MRE-EHMM | PCA-EHMM | MRE-EHMM | PCA-EHMM | MRE-EHMM | PCA-EHMM |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |||||
| 70 | 99.68 | 99.69 | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.62 | 99.63 | 88.69 | 99.70 |
| 75 | 99.80 | 99.79 | 99.80 | 99.82 | 99.72 | 99.71 | 99.80 | 99.80 |
| 80 | 99.81 | 99.81 | 99.81 | 99.82 | 99.73 | 99.72 | 99.81 | 99.82 |
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 |
References
- Alkarkhi, A.F.M.; Alqaraghuli, W.A.A. Chapter 8 - Principal Components Analysis. In Easy Statistics for Food Science with R; Alkarkhi, A.F.M., Alqaraghuli, W.A.A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Aristov, V.V.; Buchelnikov, A.S.; Nechipurenko, Y.D. The Use of the Statistical Entropy in Some New Approaches for the Description of Biosystems. Entropy 2022, 24, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.P.; Usman, A.M.; Ogundile, O.O.; Versfeld, D.J.J. Detection of Bryde’s Whale Short Pulse Calls using Time Domain Features with Hidden Markov Models. South African Institute of Electrical Engineers 2021, 112, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, L.E.; Petrie, T.; Soules, G.; Weiss, N. A Maximization Technique Occurring in the Statistical Analysis of Probabilistic Functions of Markov Chains. Ann. Math. Statist. 1970, 41, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, M.L. The Role of Technology in Combating Bank Frauds: Perspectives and Prospects. Ecoforum Journal 2016, 5, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Dornadula, V.N.; Geetha, S. Credit Card Fraud Detection using Machine Learning Algorithms. Proc Comput Sci. 2019, 165, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.; Hart, P.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fashoto, S.G.; Owolabi, O.; Adeleye, O.; Wandera, J. Hybrid Methods for Credit Card Fraud Detection Using K-means Clustering with Hidden Markov Model and Multilayer Perceptron Algorithm. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgy, E.W. Cluster Analysis of Multivariate Data: Efficiency versus Interpretability of Classification. Biometrics 1965, 21, 768–780. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Singh, T.; Sinhal, A. Observation Probability in Hidden Markov Model for Credit Card Fraudulent Detection System. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem Solving (SocProS 2012) 2014, 236, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, N.; Sait, S.Y. Credit Card Fraud Detection using Machine Learning Models and Collating Machine Learning Models. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018, 118, 825–837. [Google Scholar]
- Ileberi, E.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z. A Machine Learning Based Credit Card Fraud Detection using the GA Algorithm for Feature Selection. J. Big Data 2022, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasokun, G.B.; Omomule, T.G.; Akinyede, R.O. Encryption and Tokenization-Based System for Credit Card Information Security. Int. J. Cyber Secur. Digit. Forensics 2018, 7, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, Y.; Portier, P.-E.; Laporte, L.; He-Guelton, L.; Caelen, O.; Granitzer, M.; Calabretto, S. Towards Automated Feature Engineering for Credit Card Fraud Detection Using Multi-Perspective HMMs. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 102, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Volume 1: Statistics; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA; 1967; pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Nalband, S.; Prince, A.; Agrawal, A. Entropy-Based Feature Extraction and Classification of Vibroarthographic Signal Using Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2018, 12, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundile, O.O.; Babalola, O.P.; Odeyemi, S.G.; Rufai, K.I. Hidden Markov Models for Detection of Mysticetes Vocalisations Based on Principal Component Analysis. Bioacoustics 2022, 31, 710–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundile, O.M.; Owoade, A.A.; Ogundile, O.O.; Babalola, O.P. Linear Discriminant Analysis Based Hidden Markov Model for Detection of Mysticetes’ Vocalisations. Sci. Afr. 2024, 24, e02128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundile, O.O.; Usman, A.M.; Babalola, O.P.; Versfeld, D.J.J. Dynamic Mode Decomposition: A Feature Extraction Technique Based Hidden Markov Model for Detection of Mysticetes’ Vocalisations. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundile, O.O.; Usman, A.M.; Versfeld, D.J.J. An Empirical Mode Decomposition Based Hidden Markov Model Approach for Detection of Bryde’s Whale Pulse Calls. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, EL125–EL131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundile, O.O.; Usman, A.M.; Babalola, O.P.; Versfeld, D.J.J. A Hidden Markov Model with Selective Time Domain Feature Extraction to Detect Inshore Bryde’s Whale Short Pulse Calls. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 57, 101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ololade, B.M.; Salawu, M.K.; Adekanmi, A.D. E-Fraud in Nigerian Banks: Why and How? J. Financ. Risk Manag. 2020, 9, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D. Gaussian Mixture Models. In Encyclopedia of Biometrics; Li, S.Z., Jain, A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Lake, D.E.; Moorman, J.R. Sample Entropy. In Numerical Computer Methods, Part E; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2004; Volume 384, pp. 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, W.N.; Aria, A. Sequential Fraud Detection for Prepaid Cards Using Hidden Markov Model Divergence. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 91, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushin, G.; Stancil, C.; Sun, S.; Adam, S.; Beling, P. Horse Race Analysis in Credit Card Fraud—Deep Learning, Logistic Regression, and Gradient Boosted Tree. In Proceedings of the 2017 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Syms, C. Principal Components Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Jørgensen, S.E., Fath, B.D., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2008; pp. 2940–2949. [Google Scholar]
- Tharwat, A. Principal Component Analysis - A Tutorial. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2009, 7, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.M.; Ogundile, O.O.; Versfeld, D.J.J. Review of Automatic Detection and Classification Techniques for Cetacean Vocalization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 105181–105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viterbi, A. Error Bounds for Convolutional Codes and an Asymptotically Optimum Decoding Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Yi, Z. Research on Bank Anti-fraud Model Based on K-means and Hidden Markov Model. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; 2018; pp. 780–784. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, S.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C. Random Forest for Credit Card Fraud Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC); IEEE: Zhuhai, China; 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]

| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 70 | 99.33 | 99.27 | 99.19 | 99.30 |
| 75 | 99.39 | 99.39 | 99.31 | 99.39 |
| 80 | 99.40 | 99.38 | 99.30 | 99.39 |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 70 | 99.58 | 99.49 | 99.41 | 99.54 |
| 75 | 99.60 | 99.61 | 99.52 | 99.61 |
| 80 | 99.60 | 99.59 | 99.50 | 99.60 |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 70 | 99.69 | 99.70 | 99.63 | 99.70 |
| 75 | 99.79 | 99.82 | 99.71 | 99.80 |
| 80 | 99.81 | 99.82 | 99.72 | 99.82 |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 70 | 99.69 | 99.71 | 99.63 | 99.70 |
| 75 | 99.80 | 99.81 | 99.70 | 99.81 |
| 80 | 99.79 | 99.82 | 99.71 | 99.81 |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 70 | 99.68 | 99.70 | 99.61 | 99.69 |
| 75 | 99.79 | 99.79 | 99.71 | 99.79 |
| 80 | 99.80 | 99.81 | 99.70 | 99.81 |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 70 | 99.69 | 99.71 | 99.61 | 99.70 |
| 75 | 99.79 | 99.80 | 99.72 | 99.80 |
| 80 | 99.79 | 99.81 | 99.71 | 99.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





