Submitted:
26 July 2024
Posted:
27 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. The Collectin Subfamily
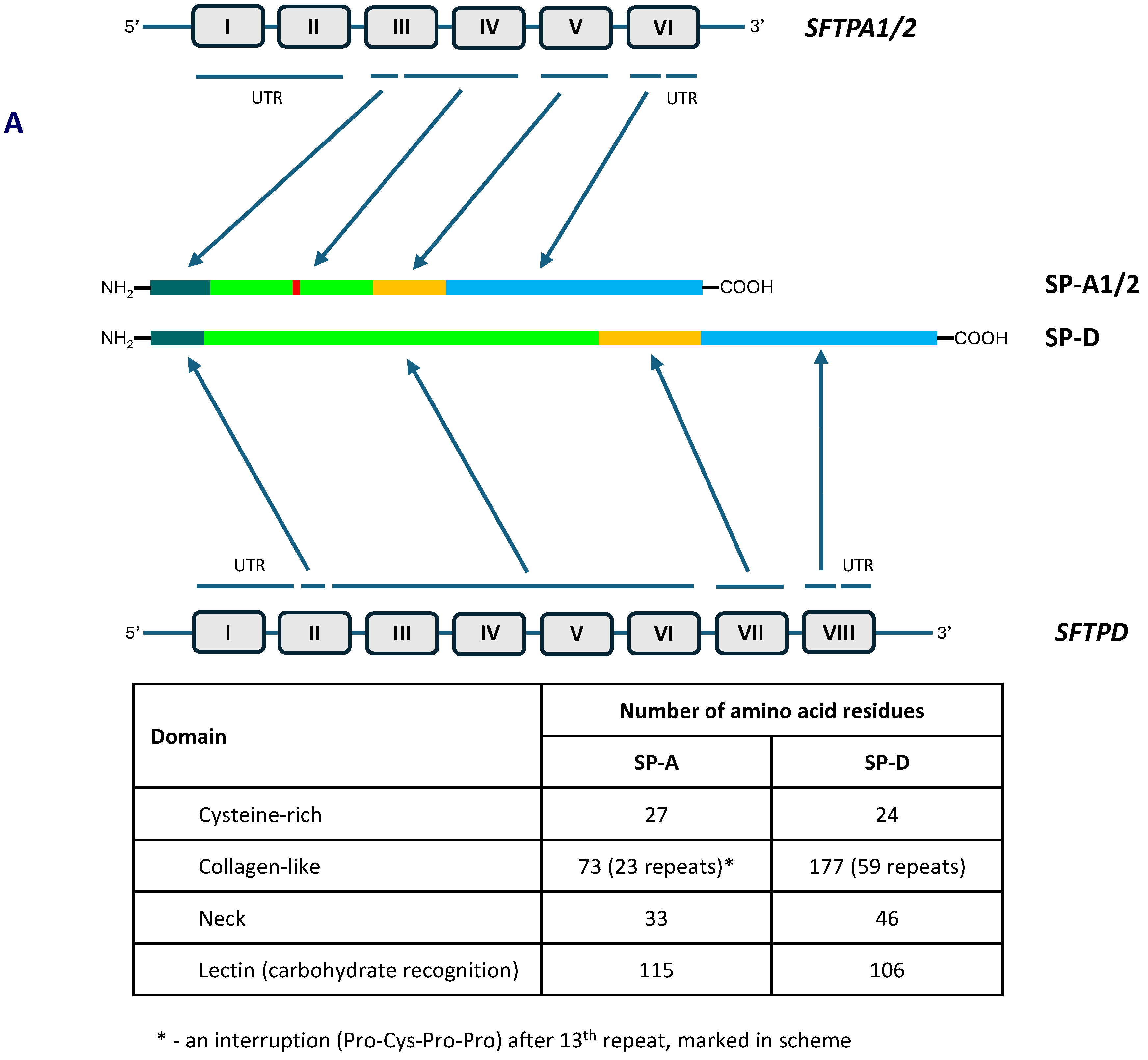
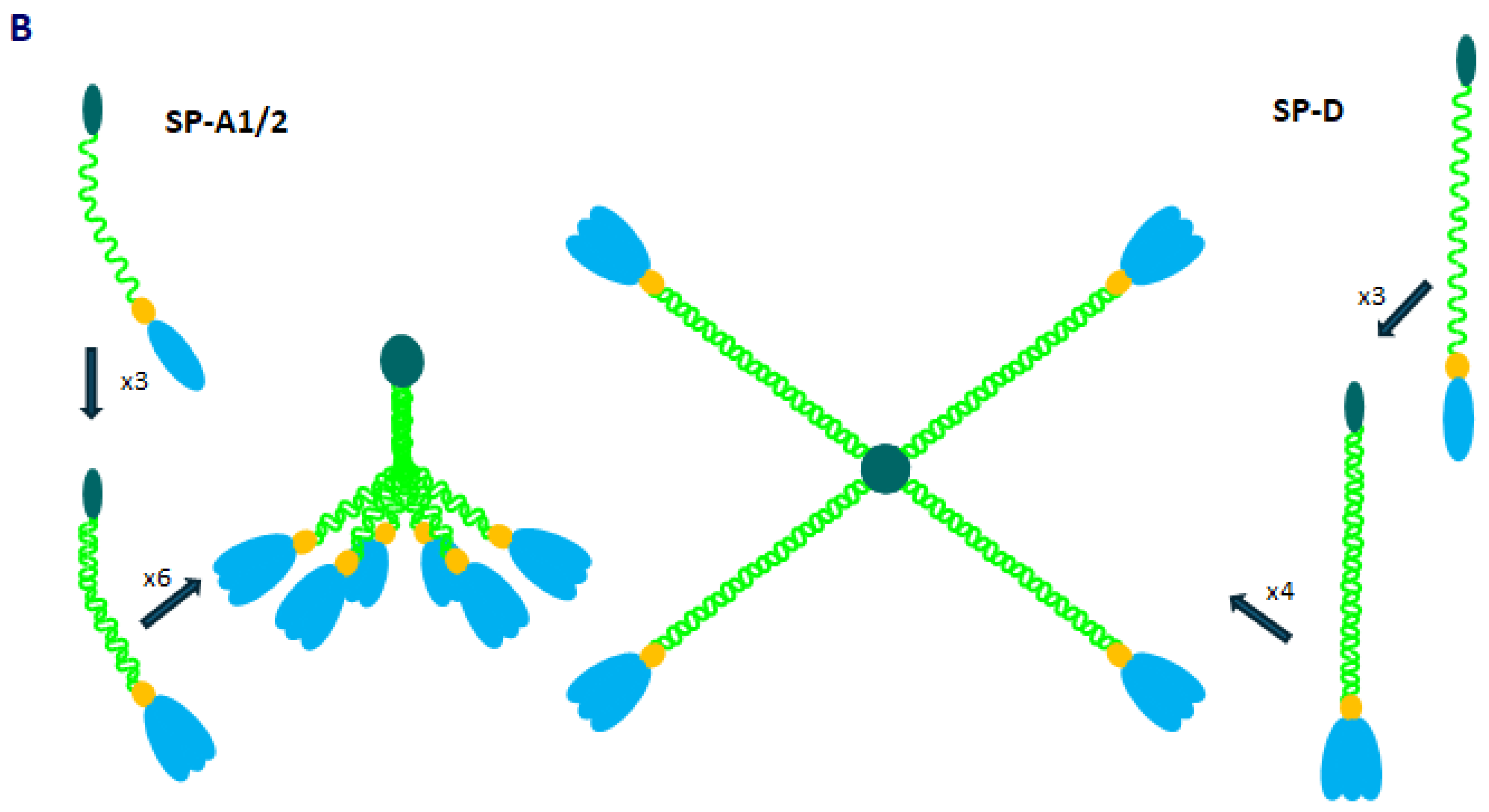
2. Pulmonary Surfactant Collectins: SP-A and SP-D
3. The Role of SP-A and SP-D in Cancer
3.1. Lung Cancers
3.2. Cancers of Other Organs
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casals, C.; Garcia-Fojeda, B.; Minutti, C.M. Soluble defense collagens: sweeping up immune threats. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedzyński, M.; Świerzko, A.S. Collectins and ficolins in neonatal health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1328658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveyra, P.; Floros, J. Genetic variant associations of human SP-A and SP-D with acute and chronic lung injury. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, F.; Kung, J.W.; Bhatti, F. Structure, genetics and function of the pulmonary associated surfactant proteins A and D: The extra-pulmonary role of these C type lectins. Ann. Anat. 2017, 211, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
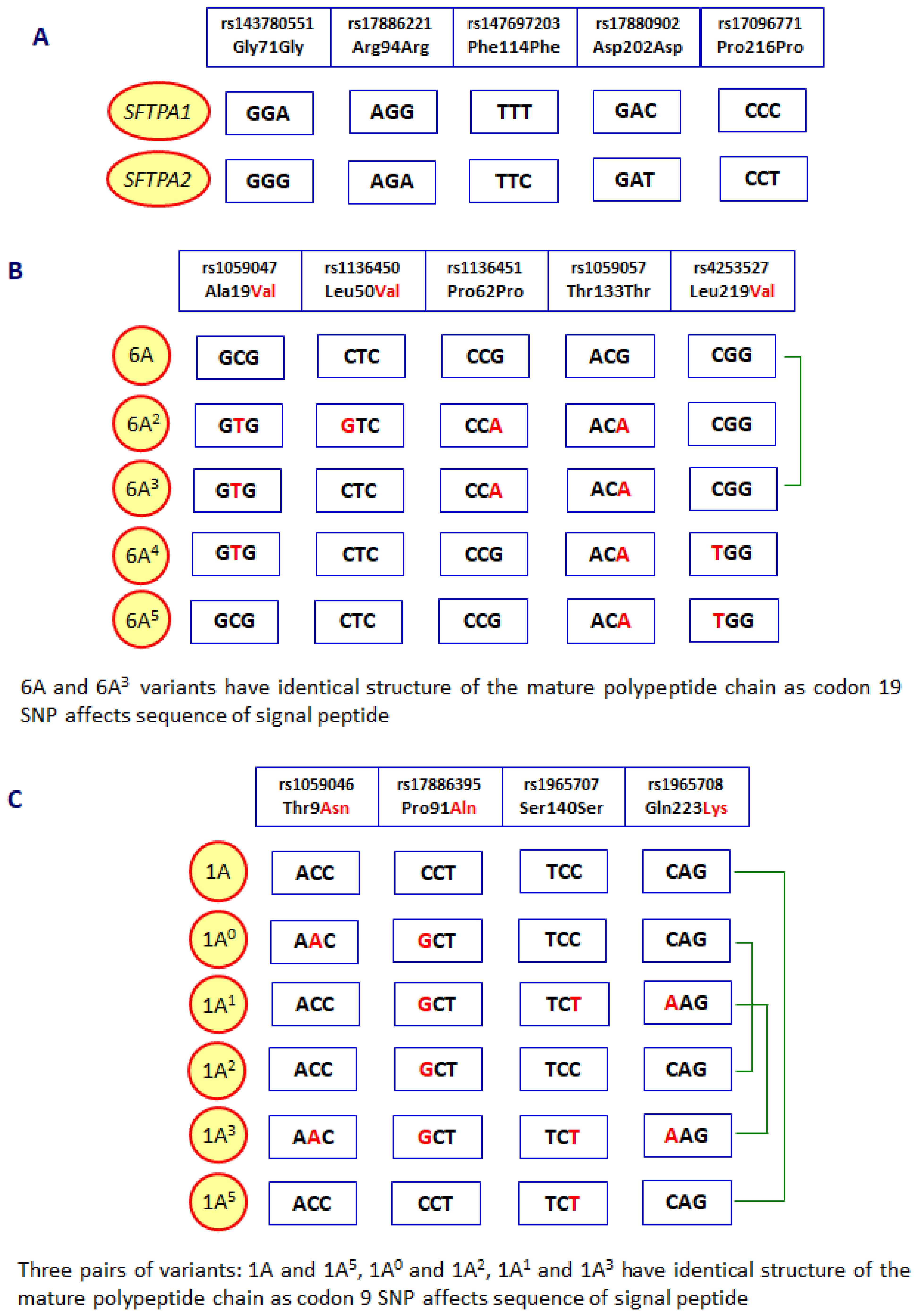
- Silveyra, P.; Floros, J. Genetic complexity of the human surfactant-associated proteins SP-A1 and SP-A2. Genes. 2013, 531, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floros, J.; Thorenoor, N.; Tsotakos, N.; Phelps, D.S. Human surfactant protein SP-A1 and SP-A2 variants differentially affect the alveolar microenvironment, surfactant structure, regulation and function of the alveolar macrophage, and animal and human survival under various conditions. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 681639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, F.X. Structure, processing and properties of surfactant protein A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998, 1408, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakel, A.; Qaseem, A.S.; Kishore, U.; Sim, R.B. Ligands and receptors of lung surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D. Front. Biosci. 2013, 18, 1129-1140. [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, K.; Konig, I.R.; Bohnert, A.; Kleinsteiber, A.; Hilgendorff, A.; Gortner, L,; Ziegler, A. ; Chakraborty, T.; Bein, G. Polymorphisms in the human surfactant protein-D (SFTPD) gene: strong evidence that serum levels of surfactant protein-D (SP-D) are genetically influenced. Immunogenetics. 2005, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, G.L.; Hjelmborg, J.v.B.; Kyvik, K.O.; Fenger, M.; Hoj, A.; Bendixen, C.; Sorensen, T.I.; Holmskov, U. Genetic and environmental influences of surfactant protein D serum levels. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L1010–L1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haagsman, H.P.; Diemel, R.V. Surfactant-associated proteins: functions and structural variations. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 129, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, U.; Greenhough, T.J.; Waters, P.; Shrive, A.K.; Ghai, R.; Kamran, M.F.; Bernal, A.L.; Reid, K.B.; Madan, T.; Chakraborty, T. Surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D: structure, function and receptors. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1293–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujma, S.; Horsnell, W.G.C.; Katz, A.A.; Clark, H.W.; Schafer, G. Non-pulmonary immune functions of surfactant proteins A and D. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Dodagatta-Marri, E.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Kishore, U. An insight into the diverse roles of surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D in innate and adaptive immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12-49. [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, T.B.; Bandi, P.; Freedman, N.D.; Smith, R.A.; Travis, W.D.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Lung cancer statistics, 2023. Cancer. 2024, 130, 1330–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-small lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Trans. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Mitsuhashi, A.; Nishyoka, Y. Role of surfactant protein A in non-infectious lung diseases. J. Med. Invest. 2014, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, O.; Takahashi, H.; Hirasawa, M.; Chiba, H.; Shiratori, M,; Kuroki, Y.; Abe, S. Surfactant protein gene expressions for detection of lung carcinoma cells in peripheral blood. Resp. Med. 2005, 99, 1164-1174. [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, A.; Goto, H.; Kuramoto, T.; Tabata, S.; Yukishige, S.; Abe, S.; Hanibuchi, M.; Kakiuchi, S.; Saijo, A.; Aono, Y.; Uehara, H.; Yano, S.; Ledford, J.G.; Sone, S.; Nishioka, Y. Surfactant protein A suppresses lung cancer progression by regulating the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Lagiedo, M. , Masztalerz, A.; Kozłowska, M.; Nowicka, A.; Brajer, B.; Batura-Gabryel, H.; Sikora, J. Concentrations of SP-A and HSP70 are associated with polarization of macrophages in pleural effusions of non-small cell lung cancer. Immunobiology. 2018; 223, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijubo, N.; Tsutahara, S.; Hirasawa, M. , Takahashi H.; Honda, A.; Suzuki, E.; Kuroki, Y.; Akino, T. Pulmonary surfactant protein A in pleural effusions. Cancer. 1992, 69, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijubo, N.; Honda, Y.; Fujishima, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kodama, T.; Kuroki, Y.; Akino, T.; Abe, S. Lung surfactant protein-A and carcinoembryonic antigen in pleural effusions due to lung adenocarcinoma and malignant mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 1995, 8, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, C.; Takahashi, H.; Fujishima, T.; Shiratori, M.; Morita, Y.; Sano, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Abe, S. Assessment of differentiation in adenocarcinoma cells from pleural effusion by peripheral airway cell markers and their diagnostic values. Lung Cancer. 2002, 38, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnoilla, R.I.; Mulshine, J.L.; Steiberg, S.M.; Gazdar, A.F. Expression of surfactant-associated protein in non-small-cell lung cancer: a discriminant between biologic subsets. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 1992, 13, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tsutahara, S.; Shijubo, N.; Hirasawa, M.; Honda, Y.; Satoh, M.; Kuroki, Y,; Akino, T. Lung adenocarcinoma with type II pneumocyte characteristics. Eur. Resp. J. 1993, 6, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Morinaga, S.; Gotoh, M.; Shimosato, Y.; Akino, T.; Suzuki, A. Immunohistochemical localization of pulmonary surfactant apoproteins in various lung tumors. Special reference to nonmucus producing lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer. 1988, 61, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Nakajima, T.; Hirohashi, S.; Akiba, T.; Shimosato, Y. Immunohistochemical distinction of malignant mesothelioma from pulmonary adenocarcinoma with anti-surfactant apoprotein, amti-Lewis-a, and anti-Tn antibodies. Hum. Pathol. 1989, 20, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamecnik, J.; Kodet, R. Value of thyroid transcription factor-1 and surfactant apoprotein A in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary carcinomas; a study of 109 cases. Virchows Arch. 2002, 440, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumida, H.; Goto, M.; Kitajima, S.; Kubota, I.; Hirotsu, Y.; Yonezawa, S. Combined status of MUC1 mucin and surfactant apoprotein A expression can predict the outcome of patients with small-size lung adenocarcinoma. Histopathology. 2004, 44, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Shijubo, N.; Yamada, G.; Ichimiya, S.; Satoh, M.; Abe, S.; Sato, N. Napsin A is useful to distinguish primary lung adenocarcinoma from adenocarcinomas of other organs. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2005, 201, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Nonaka, D. A study of immunohistochemical differential expression in pulmonary and mammary carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Ma, J.; Chen, L.J.; Hu, X.F. Genotype-phenotype correlation in Chinese patients with pulmonary mixed type adenocarcinoma: relationship between histologic subtypes, TIFF-1/SP-A expressions and EGFR mutations. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, D.D.; Man, S.F.P.; McWilliams, A.; Lam, S. Surfactant protein D and bronchial dysplasia in smokers at high risk of lung cancer. Chest. 2008, 134, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Soda, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Takasu, M.; Tomonaga, N.; Nakano, H.; Doi, S.; Nakatomi, K.; Nagashima, S.; Takatani, H.; Fukuda, M.; Hayashi, T.; Tsukamoto, K.; Kohno, S. Serum levels of surfactant protein D predict the anti-tumor activity of gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Ariki, S.; Takamiya, R.; Saito, A.; Uehara, Y.; Saijo, H.; Kuronuma, K.; Chiba, H.; Ohnishi, H.; Sakuma, Y,; Takahashi, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Takahashi, M. Surfactant protein D inhibits activation of non-small lung cancer-associated mutant EGFR and affects clinical outcomes of patients. Oncogene. 2017, 36, 6432-6445. [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Ito, F.; Hasegawa, K.; Saga, R.; Hosokawa, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Aoki, M. Identification of novel prognostic factors focused on clinical outcomes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after stereotactic body radiotherapy. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 23, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Imai, Y.; Fujishima, T.; Shiratori, M.; Murakami, S.; Chiba, H.; Kon, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Abe, S. Diagnostic significance of surfactant proteins A and D in sera from patients with radiation pneumonitis. Eur. Resp. J. 2001, 17, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Katki, H.A.; Gochuico, B.R.; Caporaso, N.E.; Engels, E.A. Circulating markers of interstitial lung disease and subsequent risk of lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2011, 20, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ariki, S.; Asakawa, D.; Tajiri, M.; Wada, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nishitani, C.; Takamiya, R.; Saito, A.; Uehara, Y.; Hashimoto, J.; Kurimura, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kuroki, Y. Surfactant protein D suppresses lung cancer progression by down-regulation of epidermal growth factor signaling. Oncogene. 2015, 34, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ariki, S.; Saito, A.; Uehara, Y.; Takamiya, R.; Kuronuma, K.; Chiba, H.; Sakuma, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kuroki, Y. Surfactant protein A down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor by mechanisms different from those of surfactant protein D. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 18565–18576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broers, J.L.; Jensen, S.M.; Travis, W.D.; Pass, H.; Whitsett, J.A.; Singh, G.; Katyal, S.L.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D.; Linnoila, R.I. Expression of surfactant-associated protein A and Clara cell 10 kilodalton mRNA in neoplastic and non-neoplastic human lung tissue as detected by in situ hybridization. Lab. Invest. 1992, 66, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Honda, Y.; Shijubo, N.; Hirasawa, M.; Fujishima, T.; Akino, T.; Abe, S. Lipid analysis and surfactant-associated protein expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells from pleural effusion. Respiration. 1996, 63, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, G.; Papadopoulos, T.; Buchwald, J.; Dammrich, J.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K. Surfactant protein gene expression in metastatic and micrometastatic pulmonary adenocarcinomas and other non-small lung carcinomas: detection by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 4283–4286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V. , Garcia, C.K. Genetic defects in surfactant protein A2 are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, N.; Giraud, V.; Picard, C.; Nunes, H.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; Copin, B.; Galeron, L.; De Ligniville, A.; Kuziner, N.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Valeyre, D.; Couderc, J.-L.; Chinet, T.; Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Simansour, M.; Nau, V.; Tissier, S.; Duquesnoy, P.; Mansour-Hendili, L.; Legendre, M.; Kannengiesser, C.; Coulomb-L’Hermine, A.; Gouya, L.; Amselem, S.; Clement, A. Germline SFTPA1 mutation in familial idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and lung cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, M.; Butt, A.; Borie, R.; Debray, M.-P.; Bouvry, D.; Filhol-Blin, E.; Desroziers, T.; Nau, V.; Copin, B.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; Hery, M.; Duquesnoy, P.; Allou, N.; Bergeron, A.; Bermudez, J.; Cazes, A.; Chene, A.-L.; Cottin, V.; Crestani, B.; Dalphin, J.-C.; Dombret, C.; Doray, B.; Dupin, C.; Giraud, V.; Gondouin, A.; Gouya, L.; Israel-Biet, D.; Kannengiesser, C.; Le Borgne, A.; Leroy, S.; Longchampt, E.; Lorillon, G.; Nunez, H.; Picard, C.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Traclet, J.; de Vuyst, P.; Coulomb-L’Hermine, A.; Clement, A.; Amselem, S.; Nathan, N. Functional assessment and phenotypic heterogeneity of SFTPA1 and SFTPA2 mutations in interstitial lung diseases and lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Hagiwara, K.; Ikeda, S.; Arai, T.; Mieno, M.N.; Kumasaka, T.; Maramatsu, M.; Sawabe, M.; Gemma, A.; Kida, K. Association between genetic variations in surfactant protein D and emphysema, interstitial pneumonia, and lung cancer in a Japanese population. COPD. 2012, 9, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, H.; Li, B.; Jiang, P.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, S.; Jin, T.; Meng, Y. Effects of ALOX5, IL6R and SFTPD gene polymorphisms on the risk of lung cancer: A case-control study in China. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 79, 106155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grageda, M.; Silveyra, P.; Thomas, N.J.; DiAngelo, S.L.; Floros, J. DNA methylation profile and expression of surfactant protein A2 gene in lung cancer. Exp. Lung Res. 2015, 41, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Thomas, N.J.; Bibikova, M.; Seifart, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, G.; Vollmer, E.; Goldmann, T.; Garcia, E.W.; Zhou, L.; Fan, J.-B.; Floros, J. DNA methylation markers of surfactant proteins in lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Yin, Z.; Caraway, N.P.; Li, R.; Katz, R.L. Genomic profiles in stage I primary non small lung cancer using comparative genomic hybridization analysis of cDNA microarrays. Neoplasia. 2004, 6, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Caraway, N.P., Nebioyu Bekele, B.; Zhang, H.Z.; Kahnna, A.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Fernandez, R.L.; Zaidi, T.M.; Johnston, D.A.; Katz, R.L. Surfactant protein A gene deletion and prognosis for patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5417-5427. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Meng, N.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Lian, J.; Hu, C. Identification of crucial genes and signaling pathways in alectinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma using bioinformatic analysis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangogna, A.; Belmonte, B.; Agostinis, C.; Ricci, G.; Gulino, A.; Ferrara, I.; Zanconati, F.; Tipodo, C.; Romano, F.; Kishore, U.; Bulla, R. Pathological significance and prognostic value of surfactant protein D in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J. Collectins: collectors of microorganisms for the innate immune system. Bioessays. 1997, 19, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Kliem, A.; Tornoe, I.; Skjodt, K.; Koch, C.; Holmskov, U. Localization of lung surfactant protein D on mucosal surfaces in human tissues. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5866–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Tornoe, I.; Nielsen, O.; Koch, C.; Steinhilber, W.; Holmskov, U. Expression and localization of lung surfactant protein A in human tissues. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberley, R.E.; Goss, K.L.; Dahmoush, L.; Ault, K.A.; Crouch, E.C.; Snyder, J.M. A role for surfactant protein D in innate immunity of the human prostate. Prostate. 2005, 65, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herias, M.V.; Hogenkamp, A.; van Asten, A.J.A.M.; Tersteeg, M.H.G.; van Ejik, M.; Haagsman, H.P. Expression sites of the collectin SP-D suggest its importance in first line host defence: power of combining in situ hybridisation, RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3324–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beileke, S.; Claassen, H.; Wagner, W.; Matthies, C.; Ruf, C.; Hartmann, A.; Garrels, F.; Paulsen, F.; Schicht, M.; Brauer, L. Expression and localization of lung surfactant proteins in human testis. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0143058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankavi, O.; Baykara, M.; Karanis, M.I.E.; Bassorgun, C.I.; Ergin, H.; Ciftcioglu, M.A. Evidence of surfactant protein A and D expression decrement and their localizations in human prostate adenocarcinomas. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, G.; Prakash, G.; Murthy, V.; Sable, N.; Menon, S.; Alrokayan, S.H.; Khan, H.A.; Murugaiah, V.; Bakshi, G.; Kishore, U.; Madan, T. Human SP-D acts as immune surveillance molecule against androgen-responsive and androgen-resistant prostate cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, K.; Kishore, U.; Metkari, S.M.; Madan, T. Immunomodulatory role of surfactant protein-D in a transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate (TRAMP) model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, G.; Sathe, G.; Kundu, I.; Biswas, B,; Gautam, P.; Alkahtani, S.; Idicula-Thomas, S.; Sirdeshmukh, R.; Kishore, U.; Madan, T. Membrane interactome of a recombinant fragment of human surfactant protein D reveals GRP78 as a novel binding partner in PC3, a metastatic prostate cancer cell line. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 600660. [CrossRef]
- Murugaiah, V.; Agostinis, C.; Varghese, P.M.; Belmonte, B.; Vieni, S.; Alaql, F.A.; Alrokayan, S.H.; Khan, H.A.; Kaur, A.; Roberts, T.; Madan, T.; Bulla, R.; Kishore, U. Hyaluronic acid present in the tumour microenvironment can negate the pro-apoptotic effect of a recombinant fragment of human surfactant protein D on breast cancer cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberley, R.E.; Goss, K.L.; Ault, K.A.; Crouch, E.C.; Snyder, J.M. Surfactant protein D is present in the human female reproductive tract and inhibits Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 10, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Murugaiah, V.; Sotiriadis, G.; Kaur, A.; Jeyaneethi, J.; Sturniolo, I.; Alhamian, F.S.; Chatterjee, J.; Hall, M.; Kishore, U.; Karteris, E. Surfactant protein D as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaya, D.S.; Jalal, A.S.; Alburae, N.A.; Aljarba, N.H.; Murugaiah, V.; Kishore, U.; Al-Qahtani, A.A. Carbon nanotube-coated recombinant human surfactant protein D reduces cell viability in an ovarian cancer cell line, SKOV3, and modulates mTOR pathway and pro-inflammatory cytokine response. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, Y.; Tsuruta, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Okabayashi, K.; Ishida, T.; Yahagi, M. , Makino, A.; Koishikawa, K.; Akimoto, S.; Sin, D.D.; Kitagawa, Y. Association of surfactant protein D with pulmonary metastases from colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Riaz, M.S.; Murugaiah, V.; Varghese, P.M.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. A recombinant fragment of human surfactant protein D induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cell lines via Fas-mediated pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Riaz, M.S.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. Human surfactant protein D suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating TGF-β. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griese, M.; Neumann, M.; von Bredow, T.; Schmidt, R.; Ratjen, F. Surfactant in children with malignancies, immunosuppression, fever and pulmonary infiltrates. Eur. Resp. J. 2002, 20, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, L.; Pandit, H.; Madan, T.; Gautam, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Warke, H.; Sundaram, C.S.; Sirdeshmukh, R.; Sarma, P.U.; Kishore, U.; Surolia, A. Human surfactant protein D alters oxidative stress and HMGA1 expression to induce p53 apoptotic pathway in eosinophilic leukemic cell line. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e85046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, L.; Gautam, P.; Dodagatta-Marri, E.; Madan, T.; Kishore, U. Surfactant protein SP-D modulates activity of immune cells: proteomic profiling of its interaction with eosinophilic cells. Expert Rev. Proteomics. 2014, 11, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




