1. Introduction
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver disease of unknown aetiology that preferentially affects women and is characterized by interface hepatitis on liver histology, hypergammaglobulinemia, circulating autoantibodies and a favourable response to immunosuppression [
1]. AIH is subdivided into type 1 and type 2: AIH-1 is more common and affects both children and adults, whereas AIH-2 is mainly a paediatric disease. Interestingly an increasing number of patients are diagnosed also at older ages. Some authors identify a third type, AIH-3, characterised by the presence of specific autoantibodies and a more severe course, while for others it is only a variant of AIH-1 [
1,
2]. The prevalence of AIH varies from 160 to 250 per 1million in Europe and North America. Even if the prevalence and incidence data are limited, the last 10 years have seen an increase of AIH not only in Northern Europe but also in the Mediterranean countries [
1,
2]. Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously named primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic cholestatic liver disease characterized by a specific bile duct pathology with progressive intrahepatic duct destruction leading to cholestasis. PBC is potentially fatal and can have both intrahepatic and extrahepatic complications [
3]. Its prevalence is estimated to be between 19 and 42 cases per million inhabitants, with higher peaks in the north of England. The incidence is also increasing, especially in Europe and North America [
1,
4] .
The early diagnosis is critical because, if untreated, those diseases progress to liver cirrhosis and death from liver failure [
2,
5]. The detection of autoimmune liver diseases-related antibodies is a prerequisite in the diagnosis of AIH and PBC and is part of the diagnostic scoring system in those pathologies [
6]. Type 1 AIH is associated with F-actin reactive smooth muscle autoantibodies (SMA) and autoantibodies to soluble liver antigen (SLA/LP). Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is associated with liver kidney microsome (LKM-1) and liver cytosol (LC-1) autoantibodies [
1]. Anti-LKM1 are considered more frequent in European patients and are typically unaccompanied by SMA [
7]. PBC is associated with a mitochondria-associated autoantibody (AMA) and PBC-specific anti-nuclear autoantibodies. These latter include: antibodies to the nuclear pore complex (NPC) that targets gp210 (glycoprotein of the nuclear pore complex) and nucleoporin p62 as well as antibodies to multiple nuclear dots that target Sp100 (nuclear body speckled 100KDa protein) and PML (promyelocytic leukemia protein), and are found in about 50% of patients with PBC [
5]. The reference method to test liver-related autoantibodies is still indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) on triple rodent tissue, i.e. liver, kidney, and stomach. This technique potentially allows the simultaneous detection of the main liver-related autoantibodies, including antinuclear antibodies (ANA), SMA, anti-LKM1, anti-LC1 , and AMA [
8]. For the detection of anti sp100 antibodies manifesting in a nuclear dots pattern on Hep2 cells) and anti gp210 (nuclear membrane pattern) ANA are not specific and could be detected in rheumatological diseases or in hepatitis of other origin [
6]. It must be emphasised that IIF method requires trained laboratory staff, is observer-dependent, and remains poorly standardized. Moreover, the quality of the substrates differs among laboratories/manufacturers and over time. Additionally, the detection of these antibodies must be confirmed by an antigen-specific technique, such as ELISA or dot-blot, among others [
6].
In Europe, there is consensus that solid-phase assays such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) or immunoblots should only be used to confirm the results of IIF, but not for initial screening. However, in the USA for instance, ELISA are frequently used for screening purposes [
6]. For the diagnostic workup of autoimmune liver diseases, anti-soluble anti-SLA/LP should already initially be tested for by ELISA or immunoblot since these autoantibodies cannot be detected by IIF and have high specificity for AIH [
6].
As for the ELISA, in our experience, since these diseases are rather rare, the confirmatory or the additional tests force our laboratory, from a practical point of view, to accumulate several samples for batch analysis in order not to waste controls and calibrations that would increase costs. This could also clearly delay results delivery to physicians and then diagnosis and treatment.
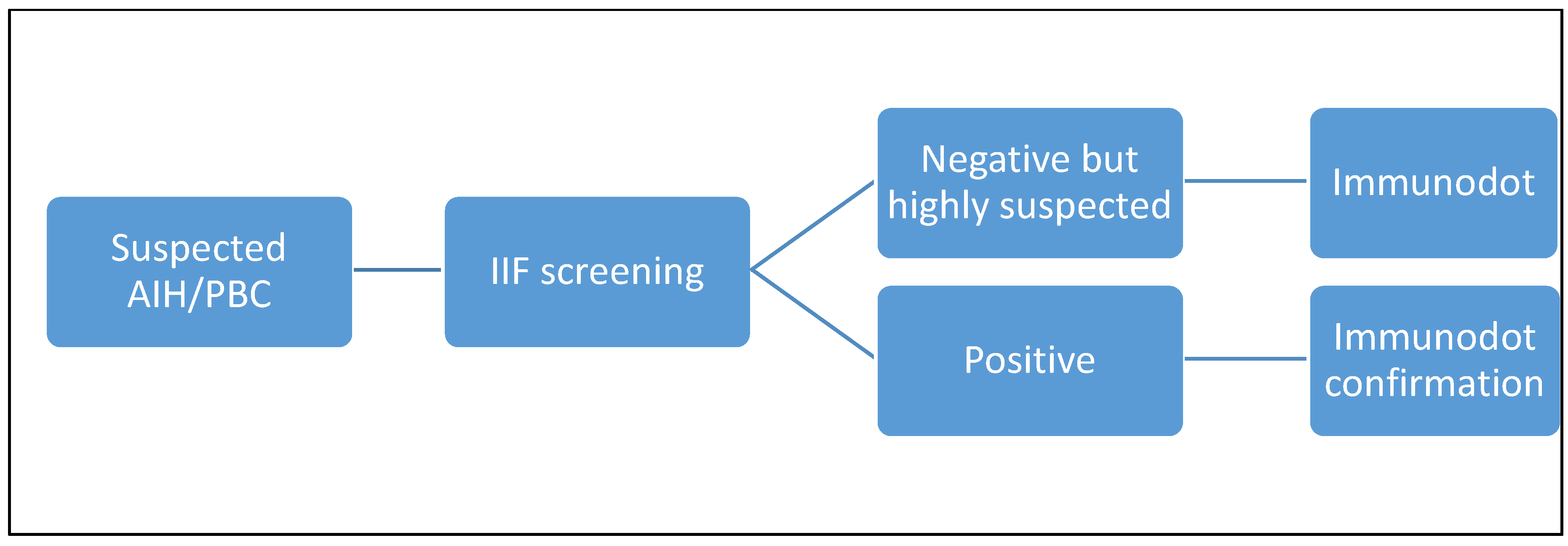
Therefore, in our laboratory, if there is a suspicion of autoimmune pathology of the liver or biliary tract, we perform a screening with IIF (AMA, ASMA or LKM according to the clinician's request) and, in the case of a positive result, we confirm with an ELISA method. If the screening is negative, but the clinical suspicion remains important, the laboratory, in agreement with the clinician, decides whether to expand the panel and add ELISA tests (e.g. in the case of anti-SLA) or ANA (if not requested). We didn’t have tests to confirm anti-sp100 and gp210 antibodies, so we sent them to an external laboratory in case of a specific request or positive screening with a likely ANA pattern and a clinical suspicion.
There is therefore a clear need, firstly, for an unambiguous screening algorithm and, secondly, for a test that is as comprehensive and complete as possible for confirmation and, in selected cases, for first-line use. Dot-line immunoassays have been proven very useful for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and systemic sclerosis, conditions in which multiple autoantibodies are relevant for a correct diagnosis [
9]. We therefore decided to evaluate the contribution of using a comprehensive immunodot test for liver in our laboratory, where we receive more than 2500 test requests per year. The purpose of our study was to compare the results obtained with the immunodot “10 antigens liver profile” with those obtained with the reference technique in use (IIF + ELISA) to determine the performance of this technique and assess its impact on the completeness of the examination and the time taken for diagnosis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
In this retrospective study, we analysed 111 samples received at the laboratory of the Cliniques universitaires Saint Luc, Brussels, Belgium, from June to September 2023. Those samples were sent as screening or follow-up tests in the context of suspected autoimmune pathology of the liver or biliary tract, a previous diagnosis or in the context of a screening post hepatic transplantation (for detection of de novo AIH). No additional sampling was required, and the same serum sample provided for the routine test was used. For these samples, in addition to the ordinary tests already done, we performed the liver profile test with 10 antigens.
Clinical data including comorbidities, biopsy results and other laboratory assays were collected for correlation with auto-antibodies results. The data were collected using our institutional database (Epic electronic health record).
2.2. Laboratory Assays
2.2.1. Indirect Immunofluorescence Screening Test
The kits for indirect immunofluorescence were obtained from Inova Diagnostics and distributed by Werfen. The samples were prepared by QUANTA-Lyser® (Inova Diagnostics Inc, San Diego, USA).
They consisted of rat’s kidney stomach and liver sections assessing, AMA, SMA, LC-1 and LKM and Hep-2 cells for ANA detection, when requested. The initial dilution for ANA is 1/80 and 1/40 for AMA, SMA, LC1 and LKM, following manufacturer’s instructions. Each run included a positive and a negative antibody control provided by the manufacturer. All analyses were performed and firstly interpreted with the NOVA View® microscope (Inova Diagnostics Inc, San Diego, USA) and then reviewed and checked by a specialized technologist and a medical supervisor.
2.2.2. Confirmation Tests
Depending on the results of the screening or, of our own agreement or on special request, we proceeded with a confirmatory test: Quanta lite® Actin IgG, M2 EP (MIT3), LKM-1 and SLA are enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative detection of Ig antibodies (Inova Diagnostics). Normally we perform ELISA confirmation after a positive or equivocal result with IIF. The antigens used are a purified F-actin antigen for Actin IgG, an affinity-purified recombinant antigen containing parts of PDC-E2, BCOADC-E2 and OGDC-E2 for M2, a partially purified recombinant human cytochrome P450 2D6 for LKM-1 and a partially purified recombinant human SLA antigen.
2.2.3. Liver Profile 10 Ag Dot for BDI
Liver Dot kits were provided by D-tek and distributed by Alphadia (Mons, Belgium). The test is able to detect autoantibodies against the following antigens: M2/nPDC (subunits E1,E2 and E3 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, purified bovine), M2/OGDC-E2 (subunit E2 of oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, recombinant), M2/BCOADC-E2 (E2 subunit of branched-chain oxoacid dehydrogenase complex, recombinant), M2/PDC-E2 (subunit E2 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, recombinant), gp210 (recombinant), sp100 (recombinant), LKM1 (formiminotransferase cyclodeaminase, recombinant) LC1 (cytochrome oxydase P450 2D6, recombinant), SLA (purified rat) and F-actin (in vitro polymerized actin filaments, purified rabbit). The test is based on the principle of an enzyme immunoassay. Test strips are composed of a membrane fixed on a specific plastic support. The strips are firstly incubated with patients’ sera. Human antibodies, if present, bind to the corresponding specific antigen on the membrane. Unbound or excess antibodies are then removed by washing. Upon further incubation into conjugated goat antibodies against human IgG, the enzyme conjugate binds to the antigen-antibody complexes. After removal of excess conjugate, the strips are finally incubated into a substrate solution. If enzyme activity is present, purple dots develop on the membrane pads and the intensity of coloration is directly proportional to the number of antibodies present in the sample. Each strip contains two controls: the reaction one, for the validity of the test, and the cut-off control, necessary for the qualitative interpretation of the test. All the steps were performed by the BlueDiver I instrument ( D-tek). The strips are read using the BlueDiver scanner and the DrDOT software, which also gives us a semi-quantitative evaluation of the result (from zero to 100). Signal strength >10 arbitrary units are considered positive, and score between 5 and 10 are considered borderline as recommended by the manufacturer. To ensure intra-observer agreement the results were checked by two independent operators.
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis and Curve Fittings
GraphPad version 4.0.3 (GraphPad Prism Software, San Diego, CA) was used. Data were expressed as median (range) or n (%), as appropriate. Diagnostic performance was analysed using the following indices: sensitivity (SE) = true positives/(true positives + false negatives) , specificity (SP) = true negatives/(true negatives + false positives),positive predictive value (PPV) = true positives/(true positives + false positives), negative predictive value (NPV) = true negatives/(true negatives + false negatives) and accuracy = (true positives + true negatives)/(true negatives + true positives + false positives + false negatives). Statistical significance between groups (Dot vs IFI+ELISA) was assessed using McNemar's Chi-squared test with continuity correction for categorical variables. P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
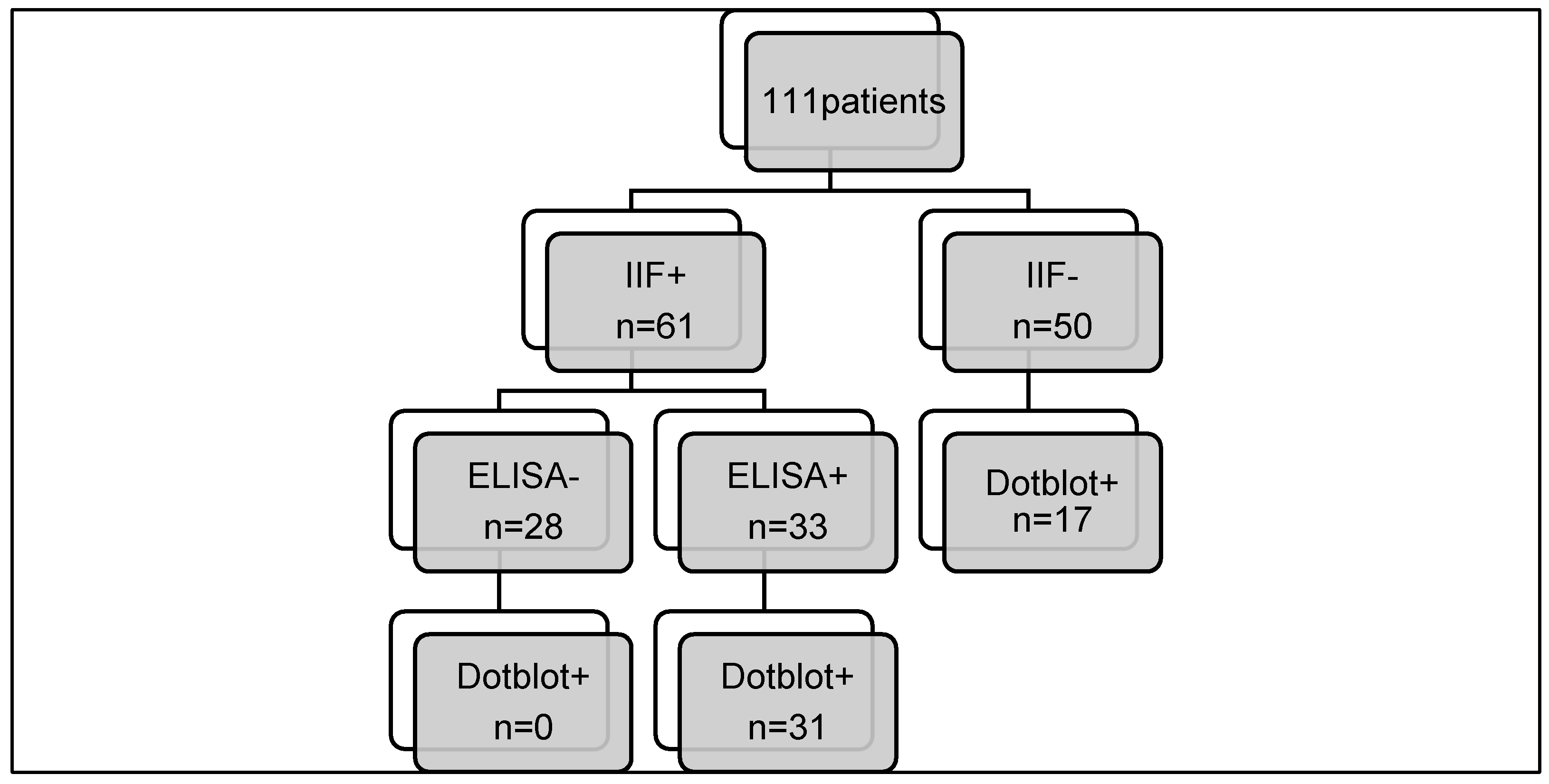
Of the 111 selected patients, 61 were positive on triple tissue screening and 50 were negative. Within this group, more than 70% were women. The mean age was 37 years (
Table 1).
For all patients, toxic or infectious hepatitis (HAV, HBV, HCV, HEV, CMV, and EBV) had been previously excluded.
Among this group, 29 patients had histologically confirmed autoimmune hepatitis (26%), 16 patients had PBC (14%) and 7 (6.3%) had an overlap syndrome (AIH combined with PBC).
Similarly to many other autoimmune conditions, autoimmune liver diseases are associated with a variety of other illnesses thought to have an autoimmune pathogenesis [
4,
9,
10]: 30.6% of our total study population and 48.8% of our positive population presented with another autoimmune/autoinflammatory disease, the most frequent being autoimmune thyroiditis and diabetes (
Table 2).
3.2. Comparison of the “Gold Standard” with immunodots
Of the 61 positive triple-tissue screening tests routinely performed, 33 were confirmed by ELISA (54.1%): 4 LKM, 11 M2 and 18 F-actin. All but two results were consistent with the patient's clinical history, laboratory and histology findings. We then compared the combined positive IIF + ELISA results with those obtained with the immunodot (
Table 3), and no difference was observed (p-value = 0.184).
All the positive results were confirmed with the dot panel, except for two samples. As far as antibodies to LC1 and SLA are concerned, we do not have a confirmatory test and they are therefore not included in this table and will be discussed later. A perfect agreement between IIF+ELISA and immunodot method was observed for AMA/M2 and LKM. As far as SMA/F-actin is concerned, by comparing IIF+ELISA combined technique with immunodot, we theoretically lose 2 actin positive samples. However, neither of the two patients was diagnosed with AIH based on the biopsy and other tests, so the positive result obtained with IIF and ELISA is highly questionable. It will be interesting to follow these two patients over time.
3.3. Immunodot positive with negative IIF screening
On the other hand, when we compared the negative IIF screening results with the immunodot ones, we noticed that there were 23 discrepant results (
Table 4).
For these samples we successively performed confirmatory ELISA tests or ANA IIF, if not done, stressing the fact that these tests would not have been performed routinely, if not requested by the clinician or added expressly by the laboratory.
By performing the immunodot test, we were able to detect the additional presence of the following auto-antibodies, sometimes more than one type present in the same sample:
3 anti-LC1, one of which was masked by the presence of anti-LKM antibodies with IIF method. All of them have been confirmed by ELISA and matched with the diagnosis.
One positive anti-LKM in a patient who already had a diagnosis of AIH type 2 with anti-LKM antibodies and had been on therapy since 2018; IIF is completely negative.
9 positive anti-sp100: for those patients only 4 samples had a simultaneous ANA screening result, for the others it was not routinely requested and therefore not done. We retrospectively performed an IIF on Hep2 cells to highlight the eventual presence of nuclear dots and all but one were positive; for all of them there was a diagnosis of PBC and in three of them the known presence of anti-mitochondria autoantibodies.
9 F-actin positive or borderline, all confirmed retrospectively by ELISA and 6 of which corresponded to patients with a diagnosis of AIH type 1. For the other three cases, it will be necessary to follow up over time to determine whether the result is significant or not.
A SLA-positive sample (also sp100 positive), confirmed by ELISA,
2 anti-gp210, both masked by the presence of anti-mitochondrial antibodies on Hep2 cells.
All immunofluorescence images were reviewed in the light of these results, and we were able to confirm our initial observations.
To summarise our results, we noticed that with the dot-blot as a first approach, we would have lost two samples positive for anti-F-actin but we recovered nine, as well as cases of anti-LKM, anti-SLA, anti-sp100 and anti-gp210 (
Figure 1).
4. Discussion
The present study confirms the good overall performance of the 10 antigens immunodot panel in confirming the results of the gold standard test in use (IIF+ELISA). Moreover, the blot panel can provide important diagnostic information when the current routine diagnostic approach has failed to detect the presence of certain auto-antibodies. In our study, we found a significant number of disagreements in favour of the dot-blot-test as a first-line test. This could be explained by several factors. First, the reading and interpreting of IIF images is obviously linked to the operator who performs it. For example, AMA IIF may be confused with other cytoplasmic antibodies [
12,
13], not directly associated with PBC. Some false positives may be in fact misinterpretations. A second re-reading of the images should always be performed, either by a second operator or by a medical supervisor. This check is not always carried out in all the laboratories, mostly due to time or staffing constraints. Despite these measures, there will always remain a subtle difference in the sensitivity and perception of different operators, even if they are properly trained and experienced.
A second point of discussion could be around the search for sp100 and gp210 antibodies: over the last 20 years, several reports described the correlation of PBC-specific ANAs with more severe disease and worse outcome [
13,
15]. The importance of early detection of these antibodies is therefore clear and their presence can induce a much more severe and rapid progression of biliary pathology [
16,
17,
18]. Finding anti-sp100 and anti-sp210 is not always easy as they are sometimes not visible on Hep2 cells or because the ANA visualisation can be hindered by the AMA presence or other ANA specificities, often seen in patients with rheumatic disease [
17]. In an interesting study, Invernizzi et al demonstrated reactivity to NPC (nuclear pore complex, of which gp210 is a component) by immunoblotting in 22% of patients known to be ANA negative with IIF [
18]. In our series, 5 of the samples positive for sp100 or gp210 are equally positive for anti-mitochondria: the presence of the latter masked the other antibodies. Two samples, however, were completely negative in a retrospective control on Hep2 cells. This clearly shows that IIF is not ideal for the search for these autoantibodies, which is necessary for a correct prognosis. In a study by Villalta et al they also had higher positivity rate with a line blot than the corresponding ANA pattern positivity’s observed with IIF technique [
11].
A separate argument justifying the discrepancies found when comparing the two methods is the fact that ANAs are not systematically requested by clinicians or by external laboratories that send us samples: in this case there is no chance of even suspecting presence of autoantibodies such as anti-gp210 and/or anti-sp100. With immunofluorescence technique, anti LC1 stain hepatocytes but spares the centrilobular areas of the liver; by contrast anti-LKM1 stain hepatocytes throughout the lobule. When both antibodies are present, anti-LKM cover the areas of anti-LC1 that are not stained. That’s why anti LC1 was “invisible” in one of our samples using the IIF technique. As for anti-SLA antibodies, they are not visible with the IIF method and are eventually sought only in the absence of other positive results, when there is a very strong suspicion of hepatic autoimmune pathology. Consequently, there is a risk of missing a diagnosis or of wasting precious time.
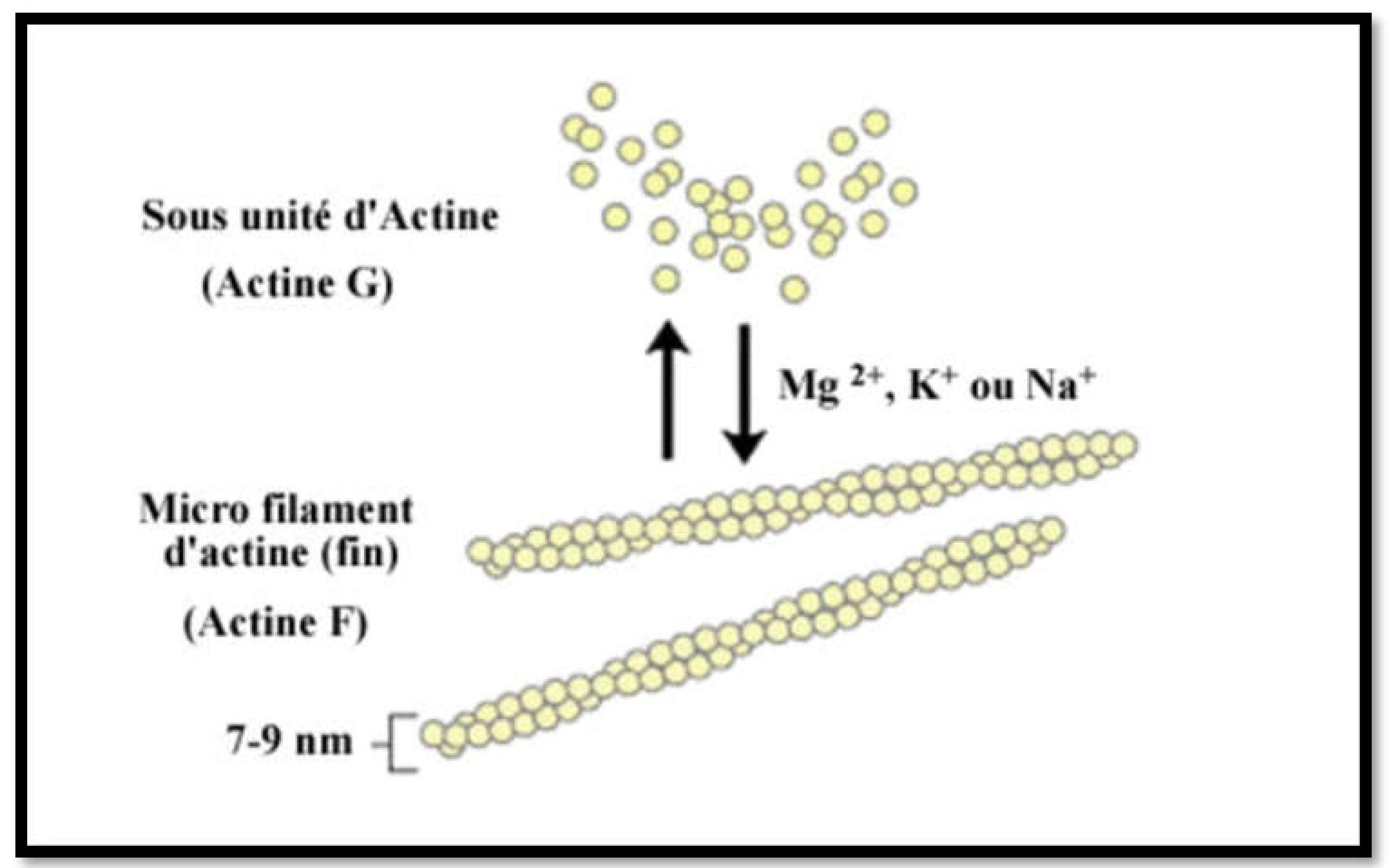
Lastly, using the immunodot technique, we recovered several F-actin positive or borderline patients who were IIF negative. How should we interpret these results? Are they false positives? But upon further investigation of those patients' files, we found that six out of nine of these reports were corroborated by clinical and laboratory history and other evidences such as biopsy, response to therapy and had a diagnosis of AIH 1. A possible explanation for this apparent increased sensitivity is provided by the test construction technique itself (
Figure 2): F-actin is an in-house preparation consisting of in-vitro polymerisation of G-actin using a specific polymerisation buffer and the addition of polymerisation-promoting elements and ATP. This F-actin is immobilised on nitrocellulose when it has reached its maximum degree of polymerisation, making the test particularly efficient.
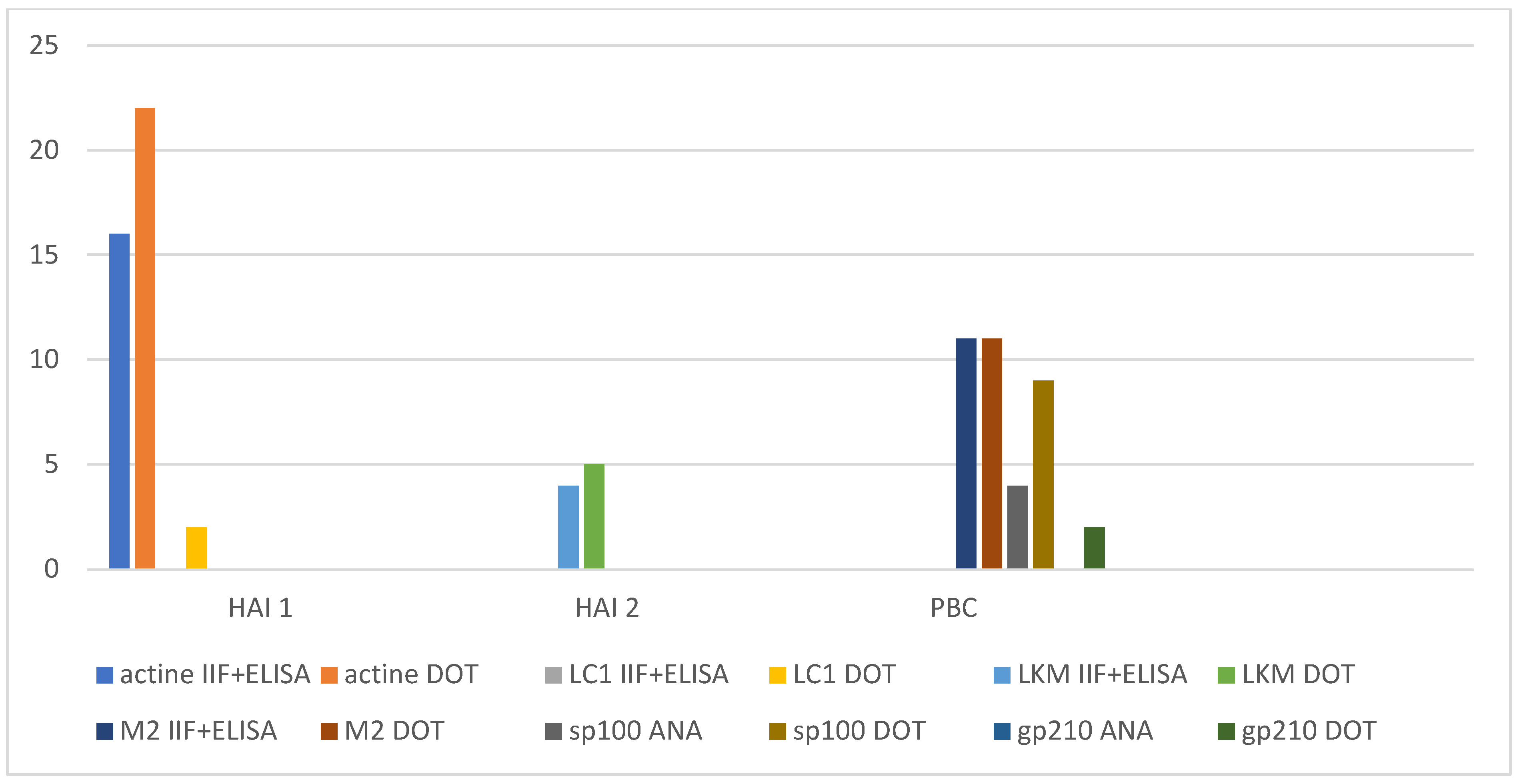
In our study, we found almost perfect agreement between the IIF positive samples and the dot-blot for the detection of AMA, LKM and F-actin. The only two positive samples with IIF method that were not found positive by immunoblots were from patients with other diseases who had never been diagnosed with an auto-immune disease. In contrast, relying solely on the use of immunofluorescence technique we would have missed approximately 20 positive results (
Figure 3).
IIF: indirect immunofluorescence; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays; AIH: autoimmune hepatitis; PBC: primary biliary cholangitis; SMA: F-actin reactive smooth muscle autoantibodies; LKM: Liver kidney microsome; LC: liver cytosol; M2: mitochondria-associated autoantibody; sp100: nuclear body speckled 100KDa protein; anti gp210: glycoprotein of the nuclear pore complex.
Even if the IIF method have been considered for a long time the gold standard for the detection of most of auto-antibodies implicated in autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune biliary disease, this technique can be time consuming, observer dependent and often fails to provide information for some autoantibodies (especially in the presence of other concurrent IIF pattern) [
18]. Reading of the IIF slides is a constant concern, while the results obtained by immunodot are objective as the blots are analyzed by a software including a well-defined cut-off [
9].
Diagnosis is still challenging and there is currently no common algorithm for the detection of autoantibodies and this leads to a variability in the management of the patients [
14]. This also manifests itself in a variability in the way clinicians prescribe tests and sometimes, the need arises to expand the test panel by adding different techniques to fill in the gaps. This approach obviously slows down the diagnostic process and may cause the clinician to lose the overview of the patient .
Liver profile 10 Ag Dot appeared to be a quick, sensitive and specific method with a very good overall accuracy (
Table 6).
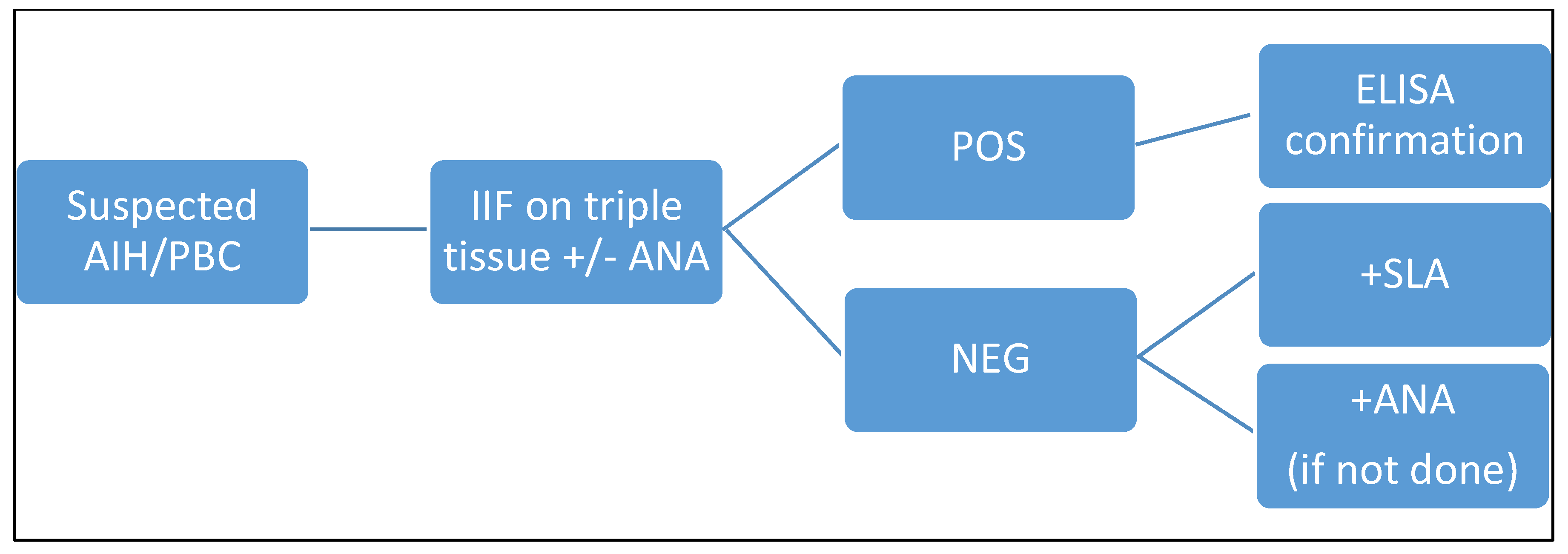
Considering these promising results obtained with the dot-line test, we propose a different algorithm (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5), which we will reconsider over time and adjust if necessary.
We have seen that other studies [
10,
11,
20,
21] have suggested immunodot in cases of IIF negativity but high clinical suspicion; we propose the use of the dot technique as a confirmation test or as an alternative test in case the IIF technique is negative despite a high suspicion of autoimmune pathology. In some cases we will propose it in the first instance as a screening test in naïve patients with or without IIF. The only difficulty in implementing this test as a first line diagnostic technique in our country is the fact that it is not reimbursed, and the test is charged to the patient; we hope that this obstacle can be overcome quickly in the future. On the other hand, we would like to point out that this technique is of no use in the case of follow-up firstly, because it provides semi-quantitative results and secondly, because therapy and time may lead these autoantibodies to become negative.
However our manuscript has some limitations In general, this paper proposes a new diagnostic algorithm and discusses some problems with existing diagnostic methods, but there are still some shortcomings in data interpretation, consistency of results and cost-effectiveness, which need further improvement and in-depth research.
5. Conclusions
The choice of the best option for the detection of autoantibodies in liver /biliary tract pathologies depends on many factors such as the centre expertise, the technologies available to laboratories, the local prevalence, the level of diagnostic accuracy needed and the overall expenditure [
12]. Nevertheless in a specialized referral laboratory where the prevalence of patients with liver and biliary tract auto-immune pathologies is assumed to be higher, the ability to test for simultaneously all relevant antibodies could lead to prefer a multiple immunodot profile for a first-line assay
In the present study we have evaluated the performance of the Liver profile 10 Ag Dot (D-tek, Mons, Belgium) for the detection of autoantibodies in relation with autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cholangitis and our results showed an overall sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 95.2% respectively, compared to IIF which showed lower sensitivity and same specificity. Based on these results, we propose the use of this assay as confirmation to the IIF method and as a first-line test in certain situations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: G.Z.; methodology: G.Z.and P.N.P.; validation, G.Z. and D.G.; data curation: G.Z., P.N.P.; formal analysis: P.N.P., G.Z.; Investigation: G.Z., S.J., C.A.; Resources: G.Z. G.D., B.D., N.L., P.S., Y.H.; Data curation: G.Z. P.N.P. Writing – Original Draft Preparation, G.Z; P.N.P, Writing – Review & Editing, G.Z., P.N.P., G.D., B.D., N.L., P.S., Y.H.; visualization, D.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Comité d’Ethique Hospitalo-Facultaire (CEHF 2023/20AVR/195).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective design of the study and the analysis of the anonymized data.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request to the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
G.Z., P.N.P., A.C, S.J, G.D, B.D, P.S., Y.H. and D.G. declare no conflict of interest. N.L. acts as a consultant for Ipsen, receives speaker fees from Fresenius Kabi, Gilead Sciences and Orphalan; receives travel grants from Abbvie, Gilead Sciences and Norgine and receives research grants from FNRS, UCLouvain, Echosens, Gilead Sciences and Horizon Europe.
References
- Gatselis, N.K.; Zachou, K.; Koukoulis, G.K.; Dalekos, G.N. Autoimmune hepatitis, one disease with many faces: Etiopathogenetic, clinico-laboratory and histological characteristics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 2015, 63, 971–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, J.S.; Grandhe, S.; Matsukuma, K.; Bowlus, C.L. Primary Biliary Cholangitis: A Brief Overview. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 15, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.; Heathcote, E. Epidemiology of autoimmune liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, B. Diagnostic autoantibodies for autoimmune liver diseases. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebode, M.; Weiler-Normann, C.; Liwinski, T.; Schramm, C. Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Liver Disease—Clinical and Diagnostic Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, M.P.; Czaja, A.J.; Gorham, J.D.; Krawitt, E.L.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Vierling, J.M. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2193–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergani, D.; Alvarez, F.; Bianchi, F.B.; Cançado, E.L.; Mackay, I.R.; Manns, M.P.; Nishioka, M.; Penner, E. Liver autoimmune serology: a consensus statement from the committee for autoimmune serology of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderlocht, J.; van der Cruys, M.; Stals, F.; Bakker-Jonges, L.; Damoiseaux, J. Multiplex autoantibody detection for autoimmune liver diseases and autoimmune gastritis. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 448, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, D.; Sorrentino, M.C.; Girolami, E.; Tampoia, M.; Alessio, M.G.; Brusca, I.; Daves, M.; Porcelli, B.; Barberio, G.; Bizzaro, N. Autoantibody profiling of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis using a multiplexed line-blot assay. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 438, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, D.; Bizzaro, N.; Da Re, M.; Tozzoli, R.; Komorowski, L.; Tonutti, E. Diagnostic accuracy of four different immunological methods for the detection of anti-F-actin autoantibodies in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis and other liver-related disorders. Autoimmunity 2008, 41, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaguri, C.; Melegari, A.; Picanza, A.; Russo, A.; De Santis, E.; Trenti, T.; Parmeggiani, M.; Belloni, L.; Savi, E.; De'Angelis, G.L.; et al. Association of solid-phase assays to the indirect immunofluorescence in primary biliary cholangitis diagnosis: Results of an Italian multicenter study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiani, F.; Minerba, R.; Picanza, A.; Russo, A.; Melegari, A.; De Santis, E.; Trenti, T.; Belloni, L.; Peveri, S.; Aloe, R.; et al. Optimization of Laboratory Diagnostics of Primary Biliary Cholangitis: When Solid-Phase Assays and Immunofluorescence Combine. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Sánchez, G.; Pérez-Isidro, A.; de Landazuri, I.O.; López-Gómez, A.; Bravo-Gallego, L.Y.; Garcia-Ormaechea, M.; Julià, M.R.; Viñas, O.; Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Participants, O.B.O.T. 2.G.-S.W. Working Algorithms and Detection Methods of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Nationwide Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotte, H.; Willeke, P.; Schmalhorst, J.; Schlüter, B. Diagnostic Performance of an Anti-Actin Autoantibody Binding Enzyme Immunodot Blot in Autoimmune Hepatitis Type 1. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2014, 30, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Miao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Wei, Y.; Bian, Z.; Sheng, L.; Chen, X.; et al. The risk predictive values of UK-PBC and GLOBE scoring system in Chinese patients with primary biliary cholangitis: the additional effect of anti-gp210. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Rigopoulou, E.; Bogdanos, D.P. Role of autoantibodies in the clinical management of primary biliary cholangitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 1795–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invernizzi, P.; Podda, M.; Battezzati, P.M.; Crosignani, A.; Zuin, M.; Hitchman, E.; Maggioni, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Penner, E.; Wesierska-Gadek, J. Autoantibodies against nuclear pore complexes are associated with more active and severe liver disease in primary biliary cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta-Piccoli, B.T.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Autoimmune Hepatitis: Serum Autoantibodies in Clinical Practice. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 63, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejdoub, S.; Hamza, Z.; Hachicha, H.; et al. Les anticorps anti-mitochondries en pratique: concordance des techniques de détection et confrontation clinico-biologique. La Revue de Médecine Interne 2024, 43, A208–A209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, N.; Tozzoli, R.; Villalta, D. Autoimmune diagnostics: the technology, the strategy and the clinical governance. Immunol. Res. 2014, 61, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).