1. Introduction
Optical design consists in finding the right sets of parameters to allow an instrument to perform a specific function. These parameters include finding relevant combinations of optical surfaces, reflective or refractive, and fine-tuning the shape, position and orientation of these surfaces using non-linear numerical optimization algorithms. The optimization of a combination of optical surfaces is usually performed using dedicated optical design software, such as CodeV of ANSYS-ZEMAX OpticStudio (OpticStudio). An appropriate solution is generally a compromise between performance metrics such as Modulation Transfer Function or geometric spot diameter and practical constraints, like the volume, cost and weight for example.
It is becoming increasingly common to use freeform surfaces in optical design [
1]. A freeform optical surface is typically defined as a non-rotationally symmetric surface which cannot be described as an off-axis section of a conicoid. These surfaces enable to outperform previous off-axis solutions on many of the afore-mentioned metrics thanks to an increased number of degrees of freedom (DOFs) [
2]. However, these added DOFs can be a real impediment for the optical designer to find an optimal system, as they can induce saddle points in the merit function topology. A saddle point is characterized by having a gradient equal to zero in all directions, but isn’t a local extremum of a function. This especially impacts local optimization algorithms, which rely on gradient descent to find the local minimum of a merit function. New design methods are being developed to deal with these added challenges, and can be sorted into starting point generation methods, the development of optimizers and the choice of a surface representation. This article aims at providing some insights on the latter.
Starting point generation methods generally leverage solving partial differential equations typically based on the Fermat path principle [
3]. These equations can be solved close to the on-axis chief ray (sometimes called parabasal ray) such as in the First-Time-Right (FTR) method [
4] or extended to the construction of 3D surfaces by numerically integrating higher order derivatives of these equations [
5]. Other methods rely on the direct construction of the surfaces, such as the SMS method [
6],which generalizes the Cartesian oval principle, allowing to design monochromatic systems with a number of rigorously stigmatic field points equal to the number of surfaces. A design method based on this approach was developed by Mayeur et al. in the context of dioptric systems in the infrared [
7]. Additionally, other construction methods were developed such as iterative construction using the Point-by-Point method [
8,
9,
10] or methods leveraging Artificial Intelligence [
11].
The methods mentioned above allow to design a freeform system directly, however they are generally well corrected over one or several discrete field points. As such, they also require to be optimized. The most common method relies of understanding and mathematically describing the behavior of the geometrical aberrations. This was the objective of the Nodal Aberration Theory (NAT), extended to freeform systems [
12]. However, optimization algorithms still need to be used [
13,
14]. The development of evolutionary algorithms, that allow to bypass the problems caused by the presence of local minima and saddle points in the merit function topology, is another area of interest [
15,
16]. An optical design tool using the Covariance Matrix Adaptation – Evolution Strategy (CMA-ES) algorithm was developed and allows to explore an entire landscape of solution and converge quickly in one optimization step [
17,
18].
Finally, a major aspect of freeform optical design is choosing a surface representation, and is something that has been subject to debate [
19,
20,
21]. The most common way to represent a freeform surface relies on describing the sag of a surface with an analytical formula using 2D-polynomials. Several bases are typically used, and an extensive summary can be found in [
22]. On the other hand, Chrisp [
23] pioneered the use of Non-Uniform Rational Basis-Splines (NURBS) in optical design of imaging systems. NURBS are well-suited for representing freeform surfaces compared to polynomials because they exhibit interesting mathematical properties, such as local control of the surface shape. They also allow to remove any prior knowledge of the surface, and are already commonly used in Computer Assisted Design (CAD) software, which is interesting from an opto-mechanical standpoint. NURBS use a grid of weighted control points to influence the surface over a limited area. This contrasts with polynomials surfaces, where every polynomial term affects the entire surface. The requirements to optimize a NURBS system are different from those used in commercial optical design software, mainly due to the high number of degrees of freedom involved. For that reason, commercial design software empirically show poor performances in optimizing NURBS, and require to use custom-made software. Fast accurate NURBS optimization (FANO) [
24] is an example of such software. FANO utilizes parallelized ray tracing to trace a large number of rays (over 50 000). Moreover, FANO uses about
grid points to sample the surfaces. Given the large number of rays being traced, FANO was designed to perform fast ray trace and to communicate with other programs, such as CodeV, FRED and DIFFSYS. In this article, we use the Freeform Optics Raytracer with Manufacturable Imaging Design cApaBiLitiEs (FORMIDABLE) software [
25], under ESCL license [
26] and available at [
27] to optimize NURBS surfaces. This software uses differential ray tracing (described in the following section), which allows to optimize complex surfaces such as NURBS with a number of rays similar to those used in commercial optical design software. This makes FORMIDABLE a much less resource-heavy software than FANO.
2. Materials and Methods
In this paper, we compare how the optimization of systems using NURBS surfaces performs against polynomial descriptions. NURBS surfaces are optimized with FORMIDABLE, while polynomial surfaces are optimized with OpticStudio, a commercial optical design software. The FORMIDABLE software capabilities are detailed in [
25]. We will simply remind some of the most interesting features of the software:
Differential Ray Tracing consisting in simultaneously computing the rays and their derivatives when doing a ray trace. A ray is defined as a line that is perpendicular to a wavefront and can be represented by a point and a normalized direction vector. Rays being reflected and refracted by the optical surfaces form the ray path, which does not necessarily have an explicit analytical expression. In FORMIDABLE, differential ray tracing is implemented in two ways: implicit differentiation applied to the calculation of the intersection between a ray and a surface and differentiating the offense to the Fermat path principle [
25].
Merit function differentiation using Automatic Differentiation (AD) [
28].
Projected apertures, allowing to define an aperture on NURBS surfaces, whereas optical design software usually only consider surfaces that are defined with a sag. The projected aperture is defined on a plane in front of the NURBS that is projected on it.
Ray aiming allowing to place the stop at any desired location. This is implemented using black-box algorithms in commercial optical design software, and might not be considered in FANO. FORMIDABLE performs ray aiming using a three-step algorithm. The algorithm finds the on-axis chief ray (OAR), computes the physical pupil of the system which then allows to compute a raymap through backward propagation. These points intersect the pupil at the correct position, but do not originate from the correct points in the FOV. Ray tracing from the correct field points is done through direct propagation, and uses the raymap as guesses to find the ray that intersect the pupil at the correct location. Then, non-physical rays are eliminated.
Use of external optimizers. Tests have shown that the Levenberg-Marquart algorithm performed well on optical systems. We used the open source implementation in SciPy library [
29].
For reference, OpticStudio documentation can be found in the OpticStudio User Manual.
The starting point for the off-axis Three Mirror Anastigmat (TMA) presented here was first designed under OpticStudio with spherical surfaces. It is illustrated in
Figure 1 and its characteristics are presented in
Table 1. As can be expected from using spherical mirrors in fast, wide field of view (FOV) off-axis telescopes, the aberrations are not well corrected.
We use this starting point in both FORMIDABLE and OpticStudio. To ensure a fair comparison between both software, the Merit Functions (MFs) were defined on the same parameters, and arranged to be as similar as possible. It was not possible to define strictly the same Merit Functions however. The Merit Function is defined using five main parameters, that are explained below:
Pupil sampling corresponds to the number and repartition of rays used to sample the pupil of the system. We used a rectangular array sampling with points for FORMIDABLE, which needs to use odd value to sample the center of the pupil as well. The closest we could get with OpticStudio was either or . Both were tested and the one yielding the best optimization results was kept (). The difference between both these settings was marginal.
Field sampling corresponds to the number and repartition of point sources in the FOV. We used a rectangular array sampling with points.
The optimization criterion corresponds to the OpticStudio Default Merit Function Start (DMFS) operand, which can be set in the Optimization Wizard. Common criteria include spot radius or wavefront error. We chose to optimize over RMS spot radius. In FORMIDABLE, the equivalent setting is called “TransverseAberration”.
We also chose to use two types of constraints operands.
The first one allows to maintain the focal length of the system. In OpticStudio, for centered optical systems, the EFFL operand can be used. However, it cannot be used for off-axis systems, and such an operand was not implemented in FORMIDABLE. We thus minimize the distance between the real centroids position and those given by the following equation, for 8 points at the edges of the FOV and the central field:
In this equation is the centroid position on the image plane of a system with a focal length of a point source at an angle .
In OpticStudio, this can be done using the CENX and CENY operands and simple mathematical operations. In FORMIDABLE, we use the “centroid_goals” parameter within the “TransverseAberration” operand.
The second operand allows to define the ray clearance of the system and avoid vignetting. The implementation of the RayClearance operand in FORMIDABLE is based on the JMRCC operand in CodeV [
30]. The geometry of the NURBS system is frozen by ensuring that the ray clearances keep their respective value at the beginning of the optimization. A similar implementation was done in OpticStudio using the RAGY, RAGX, RAGB and RAGC operands as well as simple mathematical operations. In the systems optimized with OpticStudio, the surfaces’ position and orientation were not used as variables.
The interested reader may refer to FORMIDABLE’s SpaceCodev repository for more details on the implementation of the TMA and the merit function in FORMIDABLE [
27]. The parameters used are summarized in
Table 2, and the corresponding operands and settings for both FORMIDABLE and OpticStudio are provided as well.
The optimization was made using either OpticStudio’s local optimization tool or SciPy’s implementation of Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm for optimizations in FORMIDABLE. The optimization was performed over the surface shape, while maintaining surface position and orientation fixed with respect to the starting point. When using OpticStudio, we chose to work with XY polynomials (also called ‘Extended Polynomials’ in OpticStudio). We made this choice arbitrarily on the basis that the choice of a polynomial surface description was not of major importance compared to imaging quality criteria and parameters, as was suggested by several studies
[20,31,32]. The surface sag can thus be described by:
In this equation, represent the local pupil coordinate in a cartesian coordinate system, is the surface curvature and are weight coefficients affected to the XY polynomial indexed by Polynomial surfaces were initially described up to order 5 () and increased to order 7 () to compare lower and higher order surfaces with NURBS. As the systems share a planar-symmetry along the YZ plane, only the radius of curvature and polynomial coefficients with even powers of X were optimized. In addition, the term needs to be kept to zero, as it is redundant with the radius of curvature. The term is not redundant and must be kept. Thus, we set the coefficient to zero as well.
In FORMIDABLE, NURBS surfaces are described using order 3 splines with a grid of
control points. For a fixed number of control points, using splines of higher order reduces the locality of the NURBS and generate more extreme local curvatures. Therefore, using 3rd order splines is a usual default setting when representing freeform surfaces with NURBS as higher order might generate more extreme local curvatures [
33]. This allows to have high locality without drastically increasing the number of control points. The choice of the number of control points was chosen as a compromise between number of degrees of freedom and computational speed. The number of degrees of freedom used in each optimization case is given in
Table 3. It is clearly apparent that NURBS require a lot more degrees of freedom than polynomial descriptions (8 to 15 times more in this case), which justifies needing to use differential ray tracing. This allows to directly compute the Jacobian matrix of the optimization problem and feed it directly to the optimizer instead of numerically computing it, which saves time and computational resources.
We ran several optimizations iterating over various cycle numbers, ranging from 5 to 200. To sample the 5-20 cycles range with steps of 5 cycles to generate more data points in the earlier stages of optimization We chose to optimize between 20 and 200 cycles with a step of 10 iterations. We added an optimization with “Automatic” stop condition for XY5 and XY7 systems. The duration of each optimization cycle was also retrieved.
To compare our results, we use the RMS Field Map, which corresponds to the RMS radius of the spot-diagram as a function of FOV. We use more specifically the average value of this RMS Field Map () as the major figure of merit for our comparison, but we also plot the standard deviation across the FOV with respect to as well as the minimum and maximum values. The diffraction limit in the Long Wave Infrared (LWIR, ) is given as well, along with the minimum wavelength that results in a diffraction limited system for each system. We also used the total optimization duration as a comparison criterion. Then, we compared one of the results obtained in each of the optimization case. We perform a full RMS spot diagram comparison as well as a comparison of the mirror shapes to assess differences in manufacturability. All the results are provided in the following section.
3. Results
In this section, we provide the results of the study described above. This section is divided in two main subsections. In the first section, we present the results obtained from the systematic comparative study. Then, we zoom in a single iteration of each system to make a detailed comparison.
3.1. Systematic Approach
This study aims at highlighting mainly two things. The first is the impact of surface representation on optical imaging quality post-optimization and the second is computing time.
We first compare the imaging performance of the NURBS system optimized with FORMIDABLE versus that of systems optimized in OpticStudio and described by XY polynomials. In
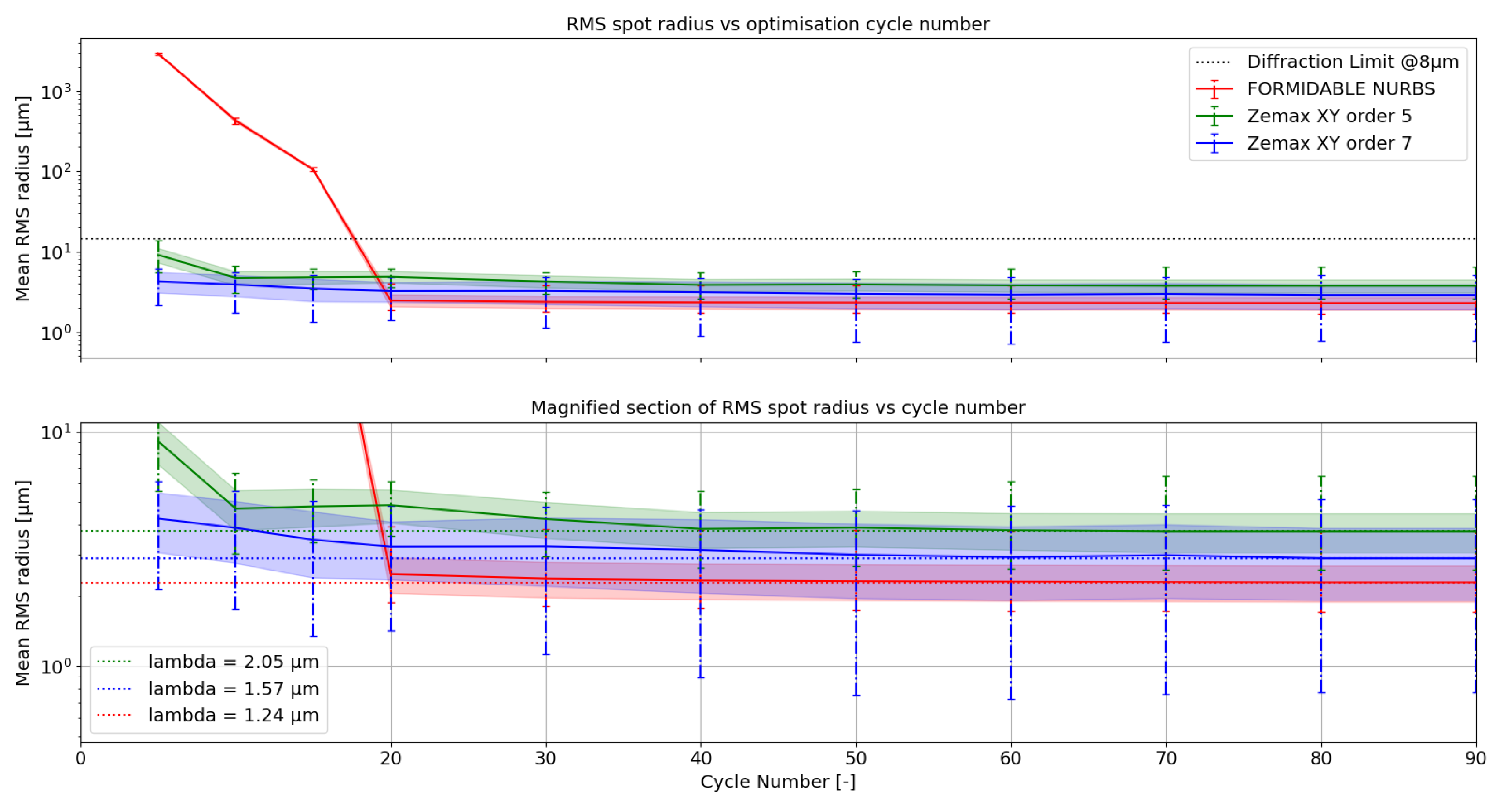
Figure 2 the RMS spot radii are averaged over the FOV and represented in full line for each optimization case as a function of the number of iteration cycle. The standard deviation of the RMS spot radii variation across the FOV is represented by the colored ribbon and gives an estimate of the uniformity over the whole FOV. Finally, the minimum and maximum values are represented with the vertical error bar. We chose a step of 10 iteration cycles, except between 0 and 20 cycles, where a step of 5 cycles was chosen to determine how the optimization behaves before reaching a threshold.
As can be seen on the top panel, each system can be optimized well below the diffraction limit (in the LWIR, at
) after a few optimization cycles, although it takes a little more optimization cycles with FORMIDABLE to achieve the same level of correction than with OpticStudio. After 40 cycles, a plateau is reached and subsequent improvement in optical quality are marginal. This behavior is maintained through the maximum number of cycles used (
), and with OpticStudio systems even when after pushing the local optimization in “Automatic” mode. For clarity of representation, we only plot up to 90 cycles on this graph. The bottom panel is a magnified view around the imaging performance plateau to better showcase the differences between each system. The dotted lines represent the asymptotic average RMS spot radius and can be linked to the Airy radius of a diffraction limited system at a wavelength indicated in the legend of the bottom panel. It appears that the NURBS TMA provides an image quality as good as those of the polynomials one in the LWIR, albeit with a smaller deviation in the spot radii field distribution. The image uniformity is also much better in the NURBS TMA, which suggests a better opto-mechanical tolerancing as shown in Kopon’s article [
34]. More advanced studies on the tolerancing of NURBS systems in FORMIDABLE will be performed in the future, upon later releases of the feature. For shorter wavelengths however, these results suggest than NURBS allow to reach diffraction limited performance at lower wavelengths than polynomial systems. In this case, taking the average RMS spot radius as a reference, the NURBS TMA can achieve diffraction limited performance down to
, while the polynomial TMAs may only be diffraction limited to
and
at orders 7 and 5 respectively. As a result, and combined with the spot radii uniformity in the FOV, a NURBS TMA might be more interesting for multispectral applications. The main challenge is to have a small enough aperture ratio to be able to use an uncooled microbolometer, while maintaining an image quality sufficient to image other spectral bands.
We also compared the time required to perform each optimization, which is represented on
Figure 3. Cumulative optimization time is represented as a function of the number of optimization cycles by a stepped function. We noticed that there are no significant differences between the optimization of the NURBS TMA and a polynomial TMA at order 7. The polynomial TMA at order 5 was however much faster to optimize under similar machine workload.
3.2. Detailed Comparison between NURBS and Polynomial TMA
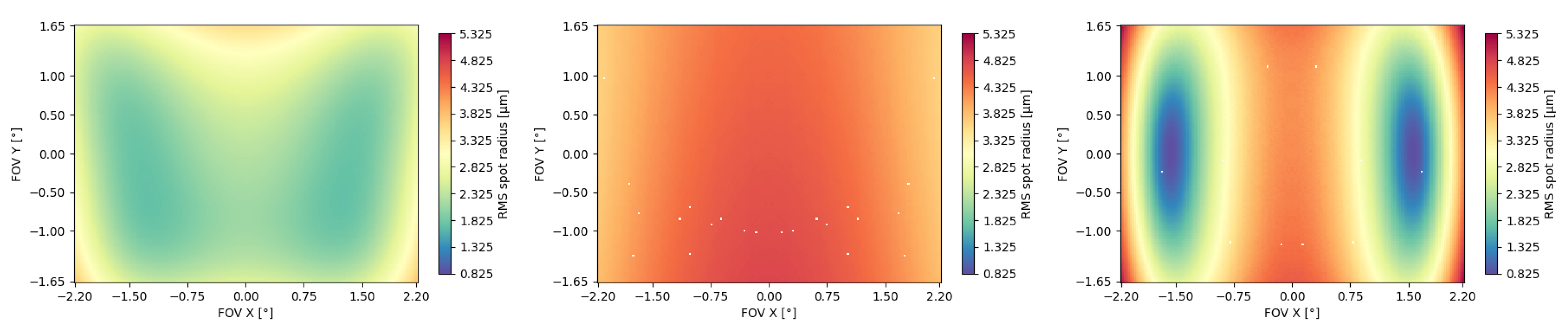
In addition to the previous analyses, we compare an iteration of the NURBS TMA and polynomial TMA at order 5 and 7. We chose to compare the systems optimized with 80 cycles since according to
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 it is a good compromise between the optimally achieved imaging quality and optimization duration. The optical imaging quality comparison was made using the RMS Field Maps. These were plotted using FORMIDABLE’s algorithm in order to be able to accurately compare each system
. Figure 4 represents the RMS Field Map of each of these systems on the same scale. On the left is represented the NURBS TMA and on the right the polynomial one. As Error! Reference source not found. suggested, the NURBS TMA displays a much more uniform RMS Field Map compared to the polynomial one. This is especially true when comparing the NURBS and the XY7 systems. The XY5 exhibits are smoother RMS Field Map than the XY7 system, but with significantly higher spot radii than the NURBS TMA.
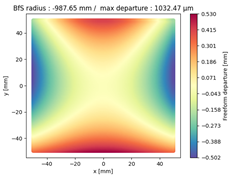
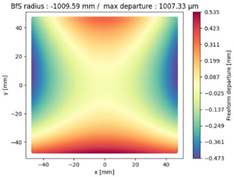
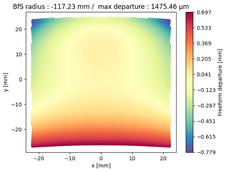
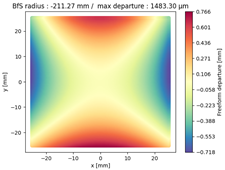
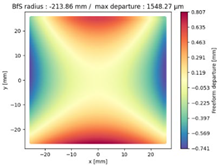
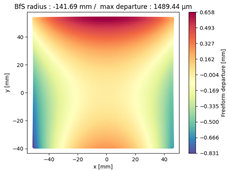
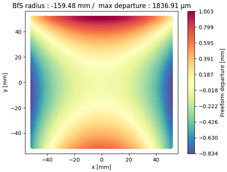
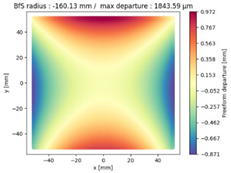
Finally, we compared the shape of the freeform mirrors. We plotted the deviation from the best fit sphere of each mirror computed on its clear aperture only. The results are displayed on
Table 4, which illustrates the freeform departure maps of each mirror, and in
Table 5, which indicates the radius of curvature of the best fit sphere (“BfS radius”) and the RMS freeform departure of each surface from that sphere. The maximum freeform departures of
in the NURBS TMA are smaller than those of the XY5 and XY7 ones by about
. Similarly, the Peak-to-Valley variation in freeform departures for the NURBS
is about 25% smaller than those of its XY counterparts. The secondary mirror (
) share similar freeform departures in each case. Furthermore, the average RMS freeform departure is the smaller for the NURBS TMA. This indicates that overall, the mirrors of the NURBS TMA are slightly easier to manufacture than those of the XY5 or XY7 ones. We can also notice that the freeform shapes of the mirrors in both XY5 and XY7 cases are similar, along with the RMS freeform departures. In addition, the NURBS mirrors are less symmetrical than the polynomial ones. This indicates that NURBS allow to achieve mirror shapes that freeform polynomial surfaces would not be able to achieve unless significantly increase the polynomial order.
4. Discussion
In this article, we compared the performance of a NURBS TMA optimized with FORMIDABLE versus polynomial TMAs designed with OpticStudio using XY polynomials. The design strategy and merit function were as similar as possible in each case, as well as optimization duration, to ensure that comparisons could be made. The results achieved in this study show that a NURBS TMA optimized with FORMIDABLE does not take longer to optimize than a polynomial one optimized with OpticStudio. In addition, the NURBS TMA exhibits slightly better average RMS spot radii and improves the uniformity of the spot radii across the FOV compared to its polynomial counterparts. As a result, the NURBS TMA can be diffraction limited over a larger spectral range, and seems to be a slightly better alternative for multispectral applications using a single optical path for each spectral channel. In addition, the better spot uniformity may indicate a better behavior of the system to opto-mechanical errors. A better spot uniformity can allow to not having to compromise between imaging performance at the edge of the FOV or at the center. This may allow to increase depth of field. This result is in accordance with Kopon et al.’s study, which compared a NURBS freeform TMA to conventional aspheric and Zernike freeform telescopes with similar designs, and concluded that the NURBS TMA was as sensitive to alignment errors, and half as sensitive to thermal changes than the conventional designs [
34]. The results we achieved suggest that 3rd degree NURBS can allow to performances better than or similar to higher order polynomials and with better uniformity without increasing the RMS freeform departures of the mirrors.
Additionally, we can compare our results to Chrisp’s [
35]. In this article, Chrisp used FANO to optimize a freeform TMA with NURBS surfaces and compared it to an aspherical and a freeform TMA using XY polynomials up to order 10. Compared to our study, Chrisp used the odd powers of
as variables as well. In addition, in FANO, the NURBS freeform design with optimized with about
control points (
for
,
for
and
for
). Due to the high number of control points, FANO also uses parallelized ray tracing to trace a large number of rays (over
). Chrisp’s results indicate a significantly better image correction with the NURBS TMA than with aspheres or XY polynomials, while the improvement we found is smaller. This could be partially due to the fact that, unlike in our study, Chrisp did not freeze the surfaces’ position and orientation, and that he used significantly more control points. The spot radii uniformity also seems better with NURBS. However, the TMA optimized with FANO exhibits significantly larger freeform departures compared to the polynomial TMA (twice larger on average and 33 times larger for
), while with FORMIDABLE we were able to maintain the RMS freeform departures at a similar level or better than with polynomial TMAs. Both studies seem to indicate that NURBS make interesting surface descriptors for freeform TMAs. However, some differences between FORMIDABLE and FANO are worth mentioning. Compared to FANO, that uses a large number of control points (about
) and rays) and uses parallelized ray tracing to increase the optimization speed, FORMIDABLE uses differential ray tracing in addition to raytracing parallelization in the merit operands and is able to achieve satisfying results with much less variables. In our study, we used grids of
control points for the NURBS surfaces and about
rays (
rays to sample the pupil for each of the
field points). This is 5 times less rays, and about 36 times less control points. In addition, although the optimization duration is not indicated in Chrisp’s article, we achieved optimization times of the same order than OpticStudio for a 7-th order XY polynomial TMA.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we optimized freeform TMAs with NURBS surfaces using FORMIDABLE, an optical design library with differential ray tracing capabilities. We then compared the RMS spot radii obtained against freeform TMAs designed using OpticStudio with XY polynomials up to order 5 and 7 respectively. The results show that the NURBS TMA exhibits a better uniformity in the distribution of the spot radii across the FOV, along with slightly better imaging performance on average. This is especially interesting for multispectral applications. Furthermore, the RMS freeform departure of the mirrors is not larger for the NURBS TMA than for the polynomial ones, indicating that both could be manufactured with similar methods.
Finally, we discussed the results obtained with FORMIDABLE against results found with FANO, another optical design library for optimizing NURBS surfaces. We report that FORMIDABLE is able to achieve satisfying results using less computational resources, thanks to the implementation of differential ray tracing. Differential ray tracing allows to trace a number of rays similar to those used in OpticStudio, and with significantly less control points than FANO uses. The duration of the optimization with FORMIDABLE is similar to what was achieved with OpticStudio. As we have determined that NURBS could be an interesting surface representation. The main perspectives of this work would be additional manufacturability figures of merit, such as orthogonal slopes, as well as tolerancing of NURBS systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.F. and G.D.; methodology, C.F., G.D. and S.B.; software, J-B.V. and S.B.; validation, C.F., G.D., A.F., T.L.; formal analysis, C.F.; investigation, C.F.; resources, C.F. and G.D.; data curation, F.K., C.B., T.A., A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, C.F.; writing—review and editing, C.F., A.F., G.D., T.L., S.B. ; visualization, C.F.; supervision, T.L. (director), G.D. (co-director), A.F., C.B., T.A., A.H., J-B.V.; project administration, F.K., G.D., P.J., S.B., J-B.V.; funding acquisition, ESA. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
FORMIDABLE development was funded by the European Space Agency under contract 4000136450/21/NL/AR. Clément Freslier’s doctoral scholarship has been funded by the European Space Agency under contract No. 4000137420/22/NL/GLC/my.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We kindly acknowledge Louis Duveau for providing the base material for the TMA used in this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rolland, J.P.; Davies, M.A.; Suleski, T.J.; Evans, C.; Bauer, A.; Lambropoulos, J.C.; Falaggis, K. Freeform optics for imaging. Optica 2021, 8, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiesser, E.M.; Bauer, A.; Rolland, J.P. Effect of freeform surfaces on the volume and performance of unobscured three mirror imagers in comparison with off-axis rotationally symmetric polynomials. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 21751–21766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Acuña, R.G. Design of a pair of aplanatic mirrors. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 1982–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerr, F.; Thienpont, H. "First time right" - calculating imaging systems from scratch -INVITED. EPJ Web Conf. 2021, 255, 02001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volatier, J.-B.; Druart, G. Differential method for freeform optics applied to two-mirror off-axis telescope design. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 1174–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, P.; Minano, J.C.; Blen, J.; Mohedano, R.; Chaves, J.; Dross, O.; Hernandez, M.; Alvarez, J.L.; Falicoff, W. SMS Design Method in 3D Geometry: Examples and Applications. In Proceedings of the Nonimaging Optics: Maximum Efficiency Light Transfer VII; SPIE, January 8 2004; Vol. 5185, pp. 18–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mayeur, T.; Volatier, J.-B.; Druart, G.; Cau, F.; Tartas, E.; Durand, A. Automatic Method of Exploring the Landscape of Freeform Dioptric Optical Problems, Working in the Infrared Region. Optics 2023, 4, 482–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, D.; Wang, A. Point-by-point fabrication and characterization of sapphire fiber Bragg gratings. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4219–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Jin, G. Direct design of freeform surfaces and freeform imaging systems with a point-by-point three-dimensional construction-iteration method. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 10233–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Yu, Y.-S.; Chen, C.; Zhu, C.-C.; Yang, R.; Liu, Z.-J.; Liang, J.-F.; Chen, Q.-D.; Sun, H.-B. Point-by-Point Dip Coated Long-Period Gratings in Microfibers. IEEE Photon- Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 2503–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Yang, T.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Cheng, D.; Wang, Y. FreeformNet: fast and automatic generation of multiple-solution freeform imaging systems enabled by deep learning. Photon- Res. 2023, 11, 1408–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.P.; Fuerschbach, K.; Schmid, T.; Rolland, J.P. Using Nodal Aberration Theory to Understand the Aberrations of Multiple Unobscured Three Mirror Anastigmatic (TMA) Telescopes; Sasián, J., Youngworth, R.N., Eds.; San Diego, CA, August 20 2009; p. 74330B. [Google Scholar]
- Sasián, J. Theory of sixth-order wave aberrations. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, D69–D95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasián, J. Theory of sixth-order wave aberrations: errata. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 6502–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houllier, T.; Lépine, T. Comparing optimization algorithms for conventional and freeform optical design. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 18940–18957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, F.E. Open-source optimization algorithms for optical design. Optik 2018, 178, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijkerk, M.D.; Gruber, J.M.; Boonacker, B. Freeform Optics Design Tool for Compact Spectrometers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Space Optics — ICSO 2018; SPIE, July 12 2019; Vol. 11180, pp. 780–788. [Google Scholar]
- Héron, S.; Semet, Y.; Barrère, R.; Lee, M.-S.-L.; Loiseaux, B. Automated Design of Freeform Off-Axis Three-Mirrors-Anastigmat. In Proceedings of the Imaging Systems and Applications; Optica Publishing Group; 2022; p. IW3C. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Muslimov, E.; Hugot, E.; Jahn, W.; Vives, S.; Ferrari, M.; Chambion, B.; Henry, D.; Gaschet, C. Combining freeform optics and curved detectors for wide field imaging: a polynomial approach over squared aperture. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 14598–14610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duveau, L. Freeform Mirror Designs for Aerospatial Multi Spectral Band Imaging Systems. phdthesis, Université de Lyon, 2022.
- Brömel, A. Development and Evaluation of Freeform Surface Descriptions, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, 2018.
- Houllier, T. Optical Imaging Systems with Freeform Surfaces : Optimization Algorithms Study and Freeform Surfaces Metrology. phdthesis, Université de Lyon, 2021.
- Chrisp, M.P. New Freeform NURBS Imaging Design Code. In Proceedings of the Classical Optics 2014 (2014), paper ITh3A.7; Optica Publishing Group, June 22 2014; p. ITh3A.7.
- Fast Accurate NURBS Optimization (FANO) - Sc22. Available online: https://sc22.mghpcc.org/project/fast-accurate-nurbs-optimization-fano/ (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Volatier, J.-B.; Beaussier, S.J.; Druart, G.; Jougla, P.; Keller, F. Implementation of FORMIDABLE: A generalized differential optical design library with NURBS capabilities. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Publ. 2024, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESSR - License European Space Agency Community License – v2.4 Strong Copyleft (Type 1). Available online: https://essr.esa.int/license/european-space-agency-community-license-v2-4-strong-copyleft-type-1 (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Formidable / Formidable · GitLab. Available online: https://gitlab.space-codev.org/formidable/formidable (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Baydin, A.G.; Pearlmutter, B.A.; Radul, A.A.; Siskind, J.M. Automatic Differentiation in Machine Learning: A Survey. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moré, J.J. The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory. In Numerical Analysis; Watson, G.A., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1978; Vol. 630, pp. 105–116. ISBN 978-3-540-08538-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, J.M. Control Of Packaging Constraints In The Optimization Of Unobscured Reflective Systems; Korsch, D.G., Ed.; Los Angeles, CA,, 10 June 1987; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Reshidko, D.; Sasian, J. Method for the design of nonaxially symmetric optical systems using free-form surfaces. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 101704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshidko, D.; Sasian, J. Method for the design of nonaxially symmetric optical systems using free-form surfaces (Erratum). Opt. Eng. 2021, 60, 119801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freslier, C.; Druart, G.; Fontbonne, A.; Lépine, T.; Keller, F.; Buisset, C.; Agocs, T.; Hélière, A.; Volatier, J.-B.; Beaussier, S.; et al. Optimization of a Freeform TMA with a Differential Ray Tracer with NURBS Capabilities. In Proceedings of the Optical Design and Engineering IX; Babington, J., Lépine, T., Gross, H., Eds.; SPIE: Strasbourg, France, June 172024; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Kopon, D.; Montague, J.; Primeau, B.; Krastev, P.; Cappiello, G.; Johnson, J. Sensitivity Comparison of a NURBS Freeform Telescope. In Proceedings of the Optomechanical Engineering 2023; SPIE, September 28 2023; Vol. 12669, pp. 122–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chrisp, M.P.; Primeau, B.; Echter, M.A. Imaging freeform optical systems designed with NURBS surfaces. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 071208–071208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).