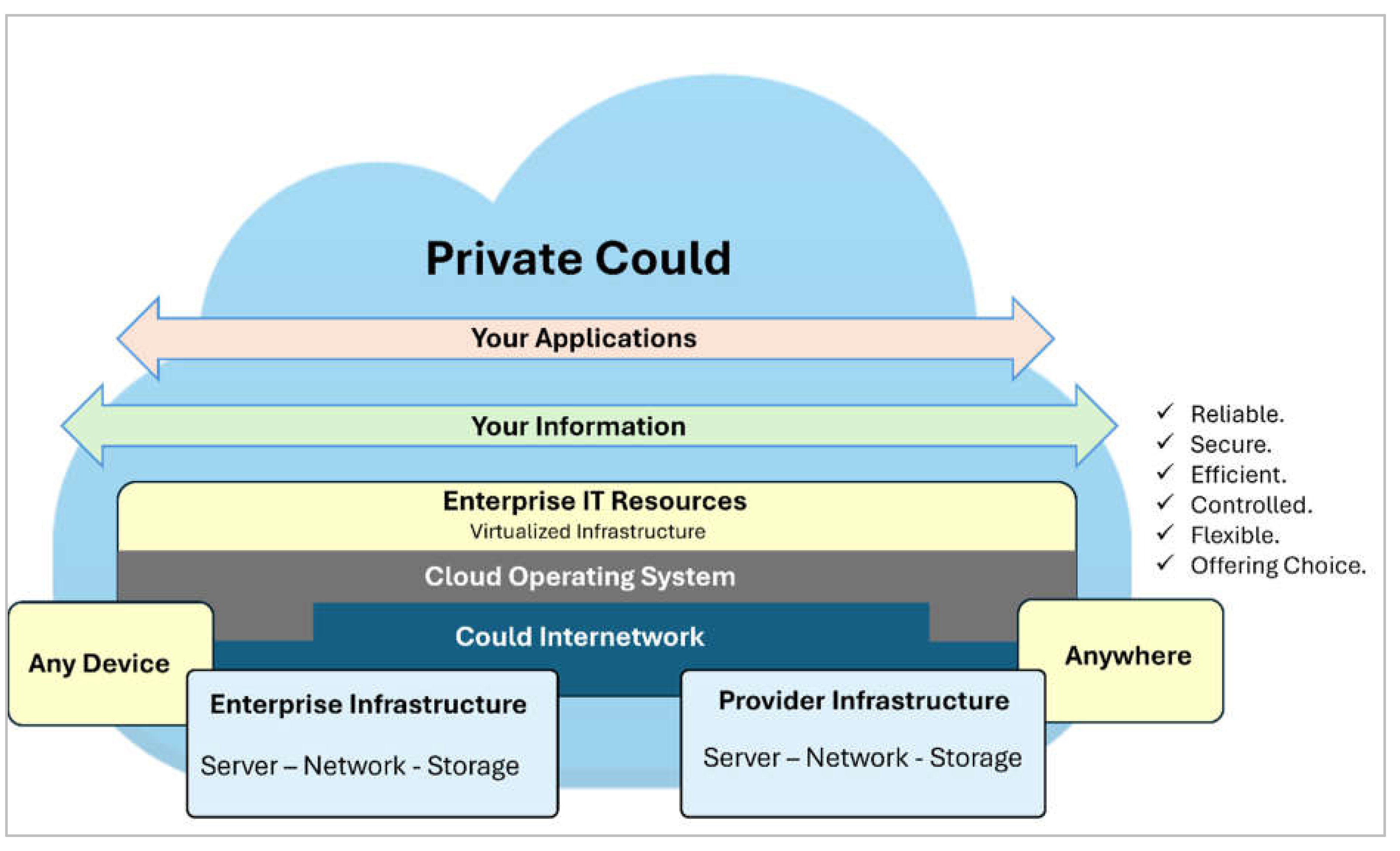
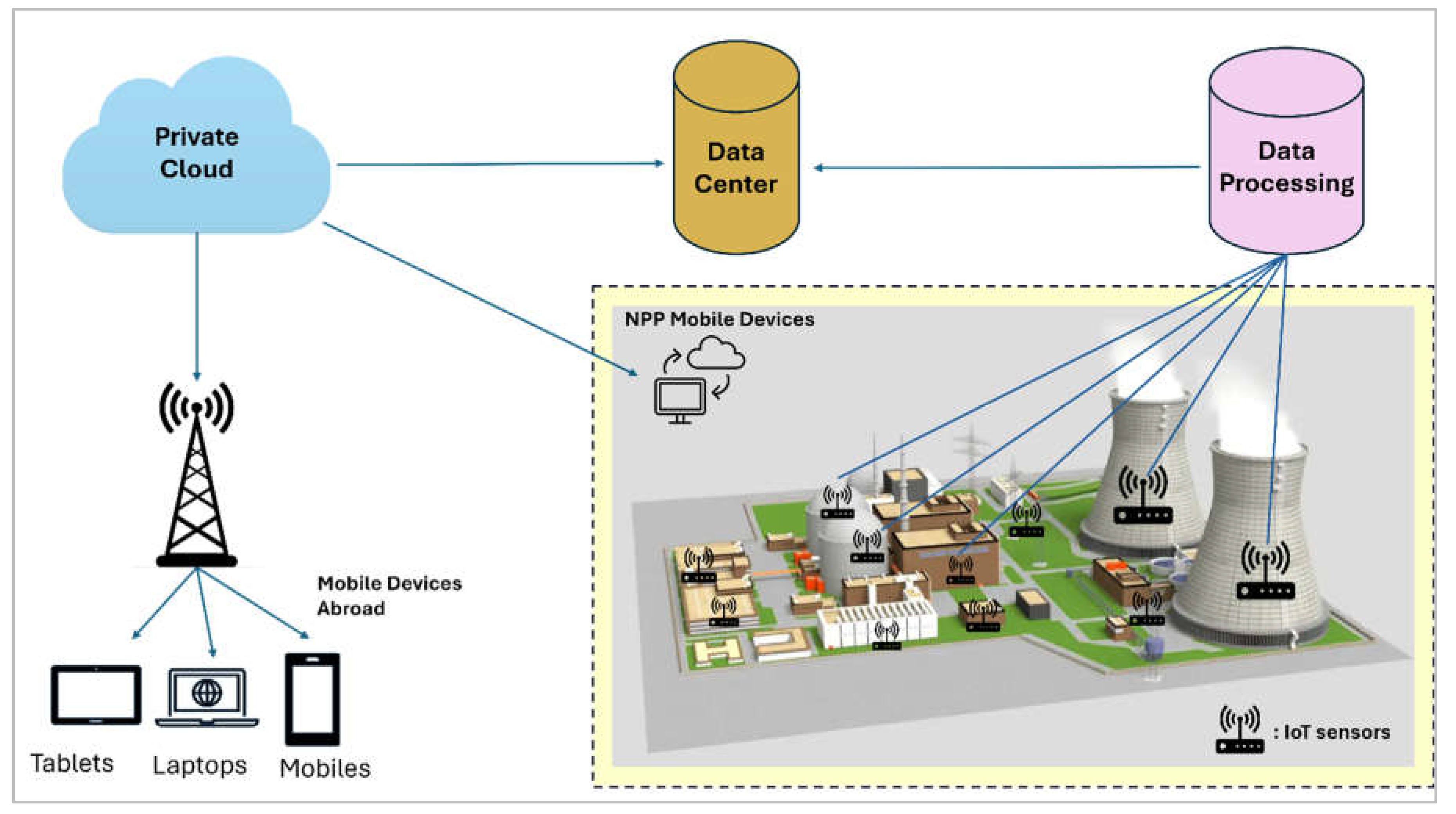
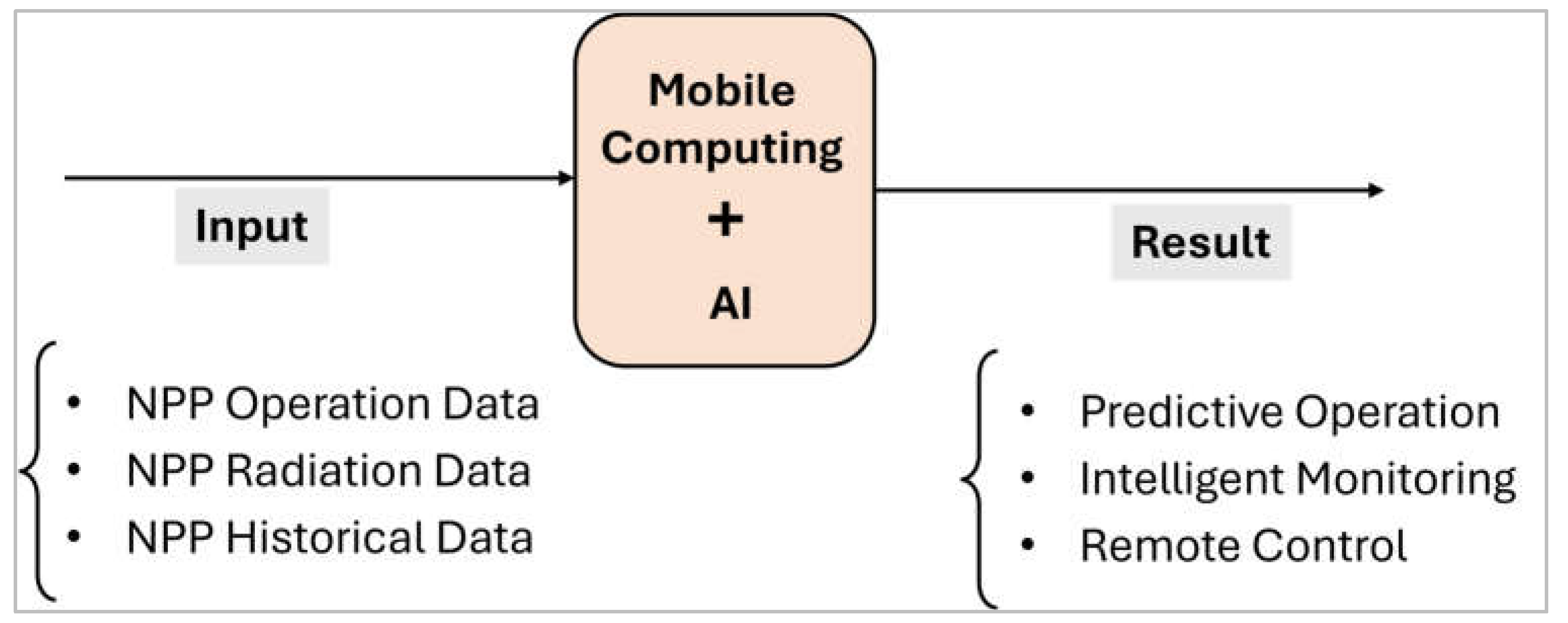
1. Introduction
Nuclear power plants (NPP) are highly complex, interconnected systems of large numbers of critical subsystems and components. The malfunction of any one of these components could initiate the accident event that may be propagating through a plant and causing serious consequences. Safety and optimal performance during operational life have paramount importance and demand full understanding of the nonlinear dynamic behavior of the plant. The lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi accident pointed to the futility of the used monitoring systems, which triggered generally poor operation and management prior to the accident [
1]. Real-time coordination and early warning systems are therefore essential, because they offer much more than monitoring functions, instead they also offer an effective predictability of nonlinear dynamic behavior of nuclear power systems components, subsystems, and the full system under normal and transient operating conditions [
1]. The fast transmission of early warning information through mobile networking can drive effective risk mitigation strategies, taking complex considerations into high consideration to act as a very valuable decision support system for plant operators. Decision-making within the dynamic and highly interdependent environment of NPPs can be challenging, necessitating the adoption of intelligent and adaptive, plant-specific predictive systems to ensure the safety of the plant, environment, and the public [
1]. Predictive intelligent systems are designed for collecting overflow data, organizing them, and analyzing them with the target of making informed decisions during emergency situations. Such data, however, may have difficult meanings to extract, and more sophisticated tools are required in predicting a system's response under various operating conditions [
1]. Artificial intelligence provides us with faster and more efficient tools that can learn by themselves from the patterns in the data, hence having the potential to predict the behavior of complex systems through intelligent algorithms. Mobile computing provides real-time data transmission to different remote locations and as a result has the advantage to warn a big numbers of nuclear power plant operator and different stakeholders such as regulatory authorities around the world. The integration of artificial intelligence feature with the mobile computing feature into nuclear power plant system is innovative idea that aims to increase the safety and reliability of the nuclear power as well as enhance the decision-making process through intelligent predictive systems. The present work is the first scientific paper that examines the integration of AI and mobile computing together in the nuclear power plant systems.
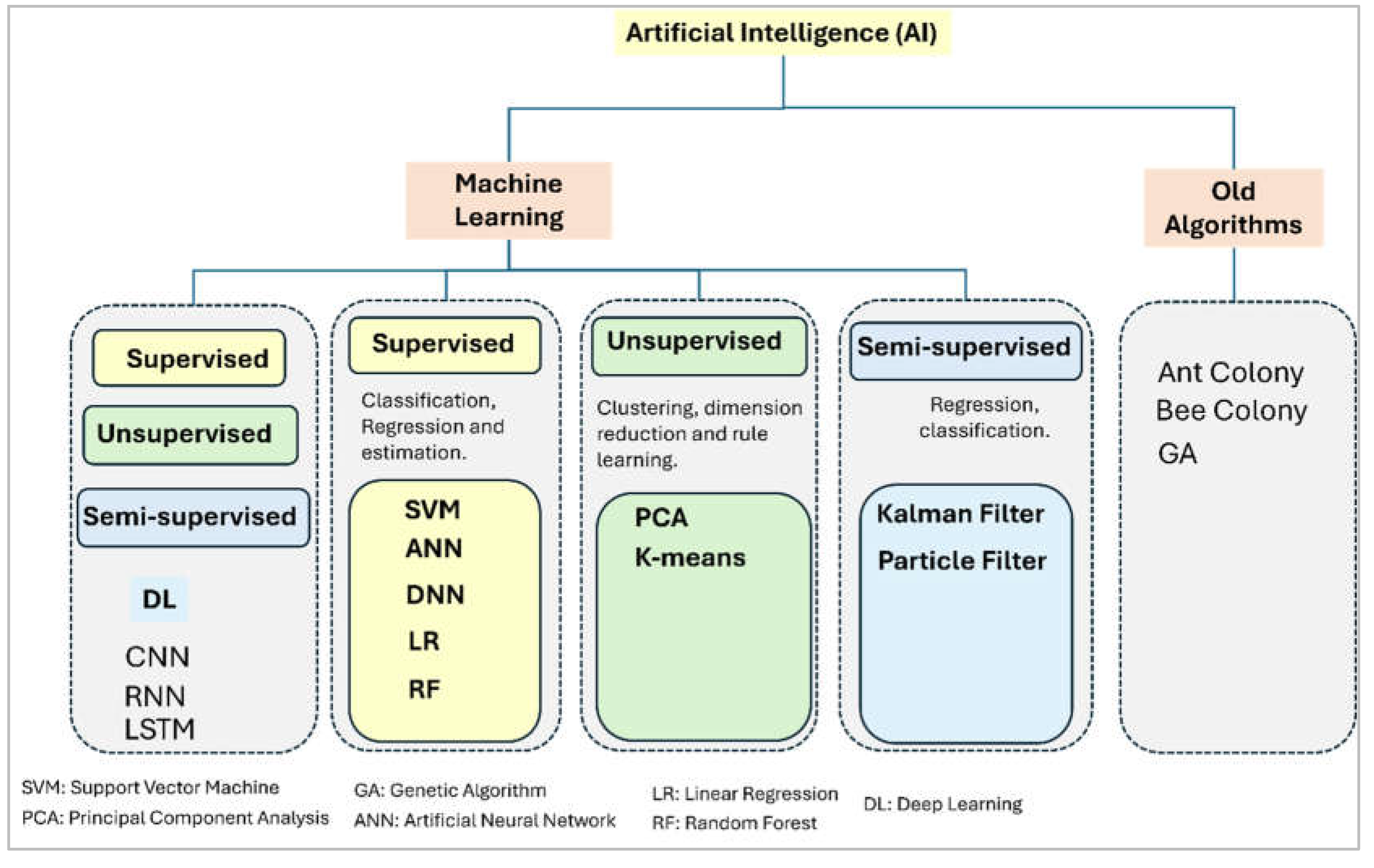
Figure 1 illustrates the structure of this article and highlights the main application of mobile computing and artificial intelligence in nuclear power plant. The first part of this paper highlights the nuclear power plant data sources, and the different modern AI algorithms used in the context of NPP, such as Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Genetic Algorithm (GA), etc. The second part focuses on the history of using smart devices in nuclear systems, and the architecture of AI powered mobile computing networks. The third part emphasis the application of artificial intelligence and mobile computing in nuclear power plants. Subsequently, the last part of this paper delves into the features and challenges associated with the integration of AI and mobile computing into future application within the nuclear power plant systems.
2. Nuclear Power Plant Data Source
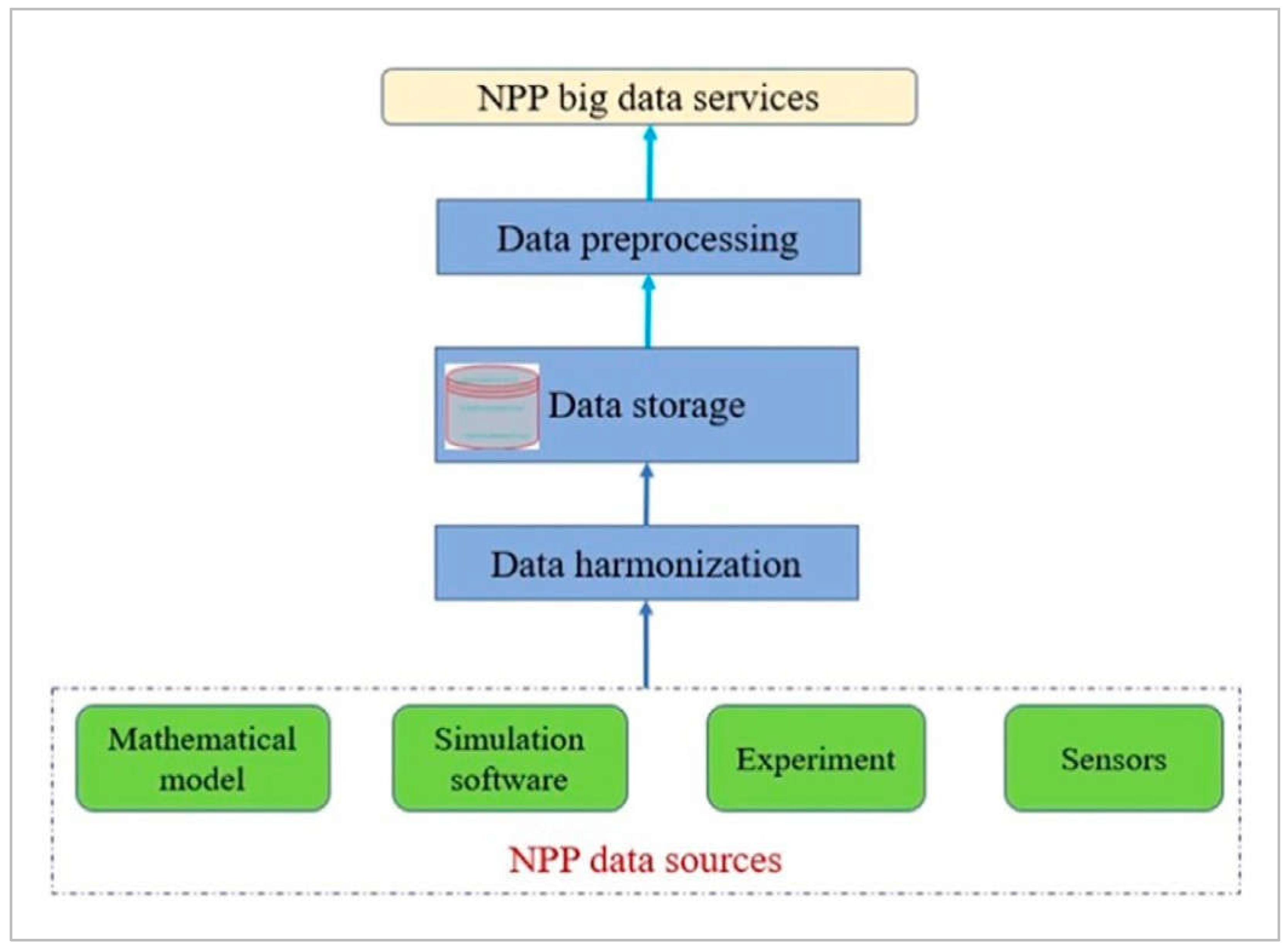
The data of nuclear power plants (NPPs) comes from mathematical modelling software, experiments, and plant sensors and it is divided into four main categories, as mentioned in
Figure 2. Nuclear power NPPs, in which the first-principles approach based on fundamental physical laws is used in mathematical modelling, provides the necessary important and easily accessible data, especially when real-world observations are limited. In this case, the models can reproduce the behaviour of NPP during the safe operation and the accident scenarios and the operator training and plant safety analysis are the results of these models. However, the challenges of this process are the accuracy and simplicity of the development of mathematical models of NPPs due to their nonlinearity [
2].
The data of NPPs can also be retrieved from software platforms, such as the RELAP5 thermal-hydraulics code, which is used to model the coupled behavior of primary and secondary systems under different operational conditions. These applications facilitate the prediction, assessing, and monitoring of NPPs, however, the availability and accessibility of the data may be affected by security restrictions, regulations, and user permissions. The NPP data also come from the experimental data collected in nuclear engineering laboratories by creating a robust and comprehensive dataset with their specialized equipment. Experiments are flexible and can be used in various research areas and for the nuclear industry as well [
2]. Furthermore, in NPPs, sensors are installed, and they are able to generate data in real-time and hence they continuously provide a great volume of it. The sensor data helps to provide mathematical models that are based on sub-systems that include feedback loops and continuously fed by the real-time data and make it possible to estimate and control such reactor variables like core outlet temperature and control rod position [
2].
Through merging AI and mobile computing within the NPP data sources, the operators and researchers are able to have a better apprehension of the system’s behaviour, which is a stepping stone to making correct decisions by predicting and monitoring the overall plant behavior in real-time.
5. Mobile Computing and AI Application in NPP
The concept of using artificial intelligence and mobile computing in nuclear power plant is based on the predictive capabilities of AI algorithms and the real-time data transmission capabilities of mobile computing as mentioned if
Figure 7.
All the reviewed applications of artificial intelligence and AI in nuclear power plant are summarized by AI algorithm used, suggested mobile computing architecture and reference in
Table 1.
Nuclear Fuel Management
Artificial intelligence and mobile computing are two powerful tools that are able to enhance nuclear fuel management during the operation of the nuclear reactors. While AI can analyse and predict high level fuel parameters from the embedded sensors in the reactor core, mobile computing offers the opportunity for real-time monitoring and remote access for these data. Several applications involve a promising AI and mobile computing tool in the field of fuel management. For instance, [
9,
10,
11,
12] used genetic algorithm to optimize nuclear fuel management and loading patterns, whereas, [
13,
14] used ant colony algorithm to optimize and predict fuel burnup in Boiling Water Reactor (BWR). In [
15,
16,
17], the authors demonstrated the use of AI algorithms to predict the critical heat flux and the temperature values at the wall using artificial neural network (ANN) and physics-informed machine learning-aided framework (PIMLAF). The fuel optimization provides an AI based prediction for burnup pattern based on previous data, and the mobile computing feature provides an enhanced reloading schedules reminder. This typical feature might be of more interest in the developing countries which new nuclear installed nuclear facilities and less experience in licensing and regulations, thus, AI and mobile computing in fuel management would serve as a very helpful tolls for the nuclear agencies to monitor the operation of these facilities and receive an instant notification for any predicted fuel issues. Added to that the AI based mobile computing enhances the security of nuclear fuel by enabling remote monitoring for nuclear fuel storage especially at remote location, such as small modular reactor (SMR), which increase the safety and the security of the nuclear fuel and decrease the non-proliferation risk.
Control Rod Position Monitoring
Control rod plays a crucial role in the safety and operation of the nuclear reactor. In the meantime, the measurement of the control rod position is conducted by the control rod position measurement sensor (CRMS), which concerns the start-up, power regulation and shutdown of the nuclear reactor. However, there still lacks research on comprehensive reviewing the state of art progress on the CRMS of the nuclear reactor [
18].
The application of AI together with mobile computing offers a tremendous opportunity to enhance the monitoring of the position of the control rod. In [
19], the author used radial basis function neural network, Levenberg–Marquardt and a group method of data handling to monitor the position of the rod from the in-core neutron flux measurements. The implementation involve AI algorithm and mobile computing to monitor the control rod in the nuclear reactor would involves IoT sensors, data collection, wireless data transmission and AI algorithm to monitor and predict the control rod position. This feature is very important in an operated nuclear power plant not only because it increases the safety, but it also increased the reliability of the plant with continuous production by avoiding control rod position issues.
Operating Parameters Trend Prediction
The use of AI and mobile computing in normal operation of nuclear facilities, provides the possibility to detect the failure of any equipment or any incorrect sensor measurement when the prediction results deviate from the actual measurement results [
20]. In his paper, [
20] used neuro-fuzzy technique to predict the operating parameters of nuclear power plant, whereas [
21] used dynamic Back-propagation neural network (BPNN) as an AI algorithm. These parameters include different operating data such as temperature, pressure, radiation levels, coolant flow rates, etc. which are very crucial for the safety of the plant an for its availability.
By implementing AI algorithms, the system can predict trends in operating parameters by learning from historical and operating experience data. For instance, forecasting potential equipment failures or deviations from normal operating conditions. The integration of mobile computing with the AI would provide an opportunity for alert systems that notify operators whenever the AI algorithm detects abnormal trends in the parameters. Thus, mobile computing plays a crucial role here by delivering alerts to smart devices, allowing quick response and informative decision-making.
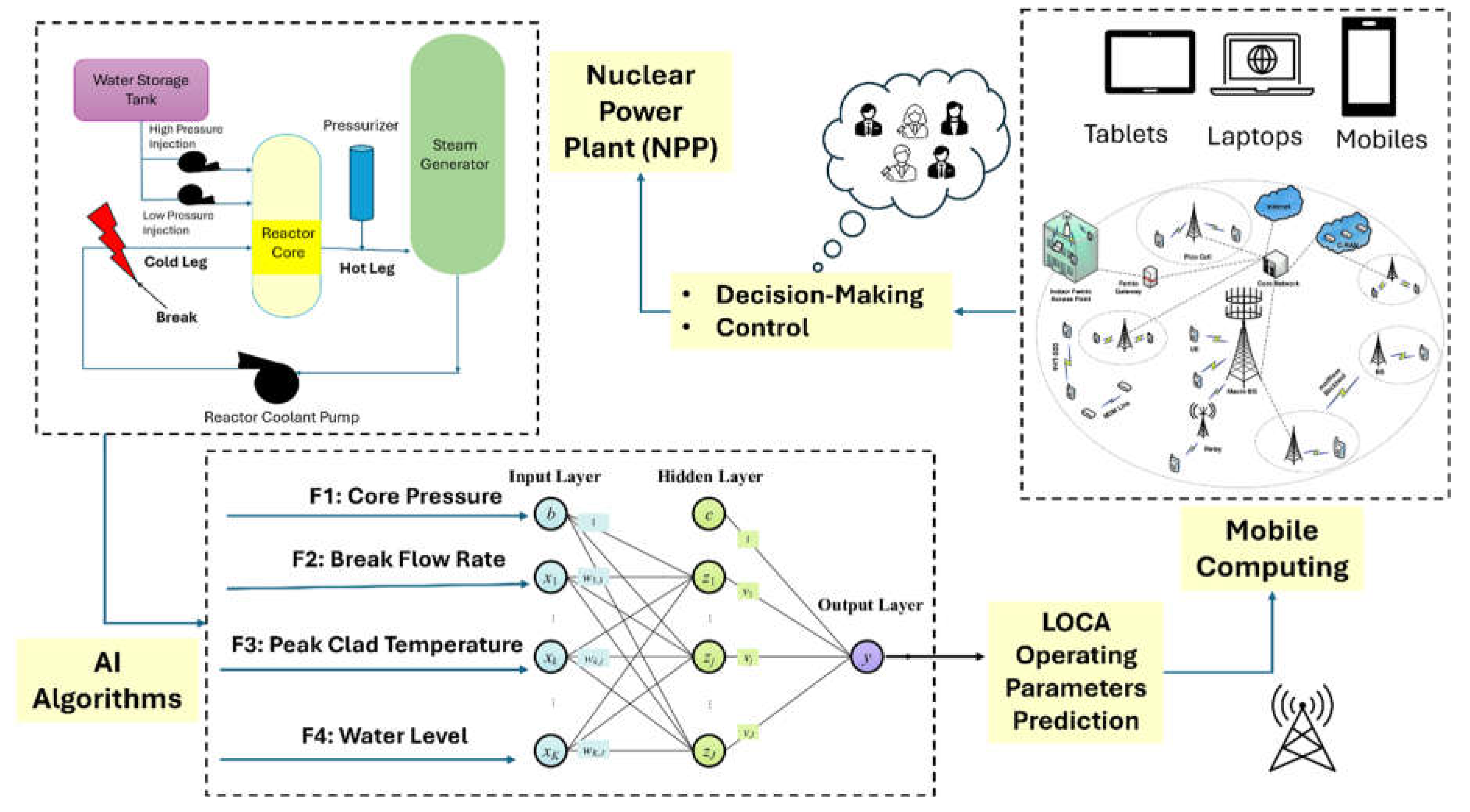
Operating Parameters Prediction During LOCA
Loss of coolant accident (LOCA) is a design-based accident in nuclear power plants. This accident includes a break in the cold leg of the reactor which induces loss of the coolant and increase in the temperature of the fuel which constitutes an increased risk to melt the fuel and threaten the safety of the plant. Artificial intelligence and mobile computing can be used in this context to predict LOCA scenarios before it happens and send real-time data to the operator and to the regulator authority to help prepare response strategies beforehand. As the mobile computing feature allows a transmission of data, the international nuclear authority overseas would have the opportunity to receive the LOCA scenario data on real-time which allow them full control and contain of any LOCA related incident. This feature is very helpful especially in countries operating NPP for the first time with less experience.
At the moment of this article, few works have been conducted on the use of artificial intelligence algorithm in LOCA scenario.
Figure 8 illustrates and models the concept of using AI and mobile computing to predict the operating parameters during loss of coolant accident in nuclear power plant. In his paper, the author [
22] used feedforward deep neural network and long-short memory to train and predict the LOCA scenario in nuclear power plant using four different parameters, peak clad temperature, core pressure, break flow rate and water level.
Reactor Vessel Water Level Prediction
Obtaining data generated from NPP is crucial to preserve reactor integrity and mitigate normal operating incidents and severe accident. Nevertheless, several safety-critical data signals from the nuclear power plant cannot be perfectly measured due to sensor degradation or failure under severe accident circumstances. One crucial reactor data is the reactor vessel (RV) water level, which is very important in case of an accident because it is directly related to reactor cooling and prevention of core exposure [
23].
Sometimes, during severe conditions, this parameter is hard to monitor for several reasons, hence, the use of artificial intelligence and mobile computing in this area would enable a real time RV water level prediction and transmission to multiple smart devices. Therefore, in case of failure to get data of the RV eater level directly from the sensor, the AI algorithm would predict and send the measurement based on the accident circumstances. The use of mobile computing offers the opportunity of this parameter to be interpreted and analyzed by different nuclear authority. Added to that, it will help in keeping a record of this data for future training and accident mitigation strategies implementation.
In his paper [
23] has predicted the RV water level using deep neural networks where the data were gotten by simulating the postulated loss-of-coolant accidents at hot- and cold-legs, and steam generator tube rupture using modular accident analysis program code. The author used also another AI algorithm, genetic algorithm, to optimize the DNN model for RV water level prediction by optimizing the selection of the numbers of hidden layers and nodes [
23].
Neutron Flux and Power Distribution Prediction
The nuclear reactor is a complex physical system to generate electricity. The generation of nuclear energy is realized under very high safety standards where constricted criteria must be fulfilled at the design level and operation level. What is fundamentally required is the precise knowledge of important quantities, such as temperature, neutron flux, power, radiation level, etc. The quantities can be overall outputs, e.g., maximum temperature, average temperature, total generated power, etc. but the knowledge of more complete information such as temperature, flux, power maps in the whole reactor might also be required, for reliable NPP operation [
24].
This knowledge can be attained through measurements, simulation and recently through Artificial Intelligence. The use of AI algorithm and mobile computing can significantly improve the measurement of neutron flux and lower distribution within the reactor core. Furthermore, while AI algorithm can collect data from various sensor within the reactor, e.g., neutron detectors, temperature, pressure gauges, etc., mobile computing can facilitate real-time data collection and transmission from the sensor.
Some technique can be used to reduce the dimensionality and extract the features from these data to improve the data set quality and relevance. The deployment of AI models and mobile devises allow for real-time neutron flux and power distribution prediction which allow in return a quick decision making by the designated authorities as well as a remote monitoring capabilities of these two parameters. This AI and mobile computing feature of the neutron flux and power distribution offers a tremendous opportunity for the regulator authority to inspect the nuclear facilities at any-time at any place in the world to ensure that the operation of the plant aligns perfectly with the safety regulations and the operational guidelines of their license. Different AI algorithm was proposed to predict the neutron flux and the power distribution in nuclear reactor core. In his paper [
24], the author has used ROM-ML to predict with high-dimensional outputs the neutron flux and the distribution of the power in a simulated reactor core.
Pressurizer and Steam Generator Fault Diagnosis
The pressurizer is very important component in the nuclear power plant operation, as it regulates the heat transport system. Any deviation or incorrect data from this component will result in variation of the operating conditions for reliable plant. Artificial Intelligence such as machine learning could be employed in the detection of any deviation or anomalies in the operating condition of the pressurizer. Data collection and training through the historical data involve a great potential for predicting the faults that may happen within the pressurizer in nuclear power plant. The integration of mobile computing within the AI feature allows for mobile devices connection which can receive the prediction for AI algorithm and then alert the maintenance personnel in real-time, resulting in a proactive pressurizer control.
Different AI methodologies can be used for fault detection within the pressurizer. In his paper [
25], the author used unsupervised clustering methodology for pressurizer transient prediction, as well as Fuzz C-Means algorithm to optimize the interpretation and the determination of fault causes and origins.
The steam generator (SG) is the heat sink of the nuclear reactor, and it generates the steam that rotate the turbine for power generation. A deviation in one of the steam generator parameters result in anomalies within the reactor core as well as anomalies in the balance of plant (BOP). The use of artificial intelligence and mobile computing to monitor and predict the steam generator anomalies would result in an increased plant safety and a stable power generation. IoT sensors can be employed to collect real-time data on temperature and pressure from the steam generator. AI algorithms can be trained to detect and diagnose any fault within the SG parameters, isolate it and propose alternative components. The use of mobile computing within the AI feature for SG fault diagnosis, provide the opportunity for remote assistance and quick decision support.
Several AI algorithms can be used to predict faults within the steam generator in nuclear power plant. In his paper, [
26], the author used Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) to predict and diagnose the steam generator transient within the nuclear power plant, by predicting data for steam outlet pressure, steam generator water level and rupture pressure severity.
Balancing False and Missed Alarms
In nuclear power plant, balancing the false alarms and missed alarms is vital for the continued safety of the plant as well as for efficient operation. The integration of artificial intelligence and mobile computing would play a significant role in attaining this balance. Furthermore, AI algorithms can be trained using the historical plant data for false alarms in a manner to be able to recognize the different patterns of normal operations versus anomalies with real issues. Additionally, by employing AI models within the nuclear power plant systems, the detection of any deviation would be easily predicted and recognized which reduces the false alarms. AI models are also able to predict the equipment or sensor failures before they happen which results in reducing the likelihood of false alarms triggered due to equipment deterioration. The integration of mobile computing with the AI, enable a real-time monitoring and collaborative decision making with regards to the alarms, by involving different team members remotely and ensuring efficient response to the alarm and so reduce the risk of missed alarms.
Various AI algorithms can be used to balance the false and missed alarms within the nuclear power plants. In his paper [
27], the author used Auto-Associative Kernel Regression (AAKR) algorithm as well as a hybrid approach based on Correlation Analysis (CA) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) as an AI algorithm to balance the alarms occurrence in NPP.
Predictive Maintenance
Nuclear power plant operates under high requirements of safety and reliability, and they integrate critical infrastructure systems that require collection of real-time data to ensure effective and secure operations. Furthermore, in order to be cost effective, NPP have to run at maximum capacity and minimal interruption. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain plant equipment in optimal condition so that NPP can achieve higher availability and reliability. However, maintaining the equipment increased the operating cost considerably, and solution to this problem is to implement corrective and predictive maintenance of the NPP components [
28].
Artificial intelligence and mobile computing can be employed to address this issue by involving IoT sensors on equipment to collect real-time data on different nuclear power plant parameters such as the temperature on the pressure tube to avoid creep and other temperature and pressure related issues. The AI algorithm can be utilized to analyze the collected data and predict effective maintenance needs and schedules based on the generative AI model. The integration of mobile devices allows the maintenance staff to receive alerts for timely intervention. Different machine learning can be employed in the predictive maintenance, such as support vector machine (SVM) and logistic regression (LR) model [
28].
Monitoring Radiation Levels and Predictive Nuclear Releases
Nuclear energy includes a significant promise however it also poses significant security risks, therefore efficient radiation detection technology with support from Artificial Intelligence (AI) system is vital [
29]. Furthermore, there is an increasing concern that act of terrorism may attempt to detonate a nuclear weapon. For those reasons, there is a continuous quest of inventing novel analyses and systems (i.e., Artificial Intelligence Driven Detection and Tracking) that can find nuclear materials being produced or being transported between facilities/to their destinations [
29].
By the mean of AI technology (i.e., Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), it is possible to develop radiation detection algorithms that leverage cutting edge technology in multimode data fusion, machine learning, sensor networks, mobile computing and big-data analytics [
29]. The implication of radiation detection technology becomes apparent in this complex environment as a key protector against the nuclear threat [
29]. Primarily, radiation detection is the observant guard responsible for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation. This radiation involves neutrons, gamma rays, and alpha and beta particles and has the potential to have both positive and negative effects [
29].
Radiation detection technology plays a fundamental role in nuclear threat reduction, acting as a crucial tool to safeguard against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and materials, avoid acts of nuclear terrorism, and monitor potential environmental risks [
29]. Furthermore, AI algorithms can process vast amounts of radiation data from sensors and detectors with unparalleled speed and accuracy. This enables real-time analysis of radiation levels, identifying anomalies or potential threats more effectively than manual monitoring [
29]. Additionally, AI algorithm based on machine learning and artificial neural network models, can predict equipment failures in radiation detectors by analyzing historical data and sensor performance. This ensures that detectors are always operational and reliable [
29].
Likewise, AI-powered robots can autonomously inspect and maintain radiation detectors in hazardous or hard to reach areas, reducing human exposure to ionizing radiation [
29]. Moreover, AI algorithms can identify unusual radiation patterns or signatures, which may indicate tampering or the presence of illicit nuclear materials. This early warning system is essential for nuclear security [
29].
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and mobile computing could revolutionize Radiation Detection. AI systems, powered by advanced algorithms and machine learning can predict radiation levels for normal and safe operation. In case of deviation or anomalies, the shift between the measured radiation levels and the levels predicted by the AI model would indicate potential issues that require an immediate intervention. The use of mobile computing with the AI feature, makes this intervention effective and quick as the mobile devices allow to send the real-time radiation levels to different team members which allows for virtual assistance and a collaborative decision-making.
Nuclear Spent Fuel Monitoring and Safeguarding
Nuclear fuel is defined as the fissionable nuclear material in the form of fabricated elements for loading into the reactor core of a nuclear power plant, and the nuclear spent fuel is classified as radioactive waste and it is constituted of uranium, TRU (transuranic actinides) and fissions products [
30].
Artificial intelligence and mobile computing can be employed to ensure safe monitoring and storage of the nuclear spent fuel. AI can assist in monitoring spent fuel storage and transportation by analyzing data from security cameras, access logs, and environmental sensors. It can detect unusual activities or breaches in security protocols [
29]. Furthermore, AI-driven predictive maintenance models can optimize the upkeep of spent fuel storage facilities, ensuring they meet safety and security standards [
29].
On the other hand, mobile computing feature can assist in handling and inspecting spent fuel casks, improving the efficiency and safety of storage and transport operations, while AI technology detects irregularities in spent fuel storage conditions, such as temperature fluctuations or unauthorized access, triggering immediate response protocols [
29].
Additionally, AI can play a pivotal role in monitoring nuclear spent fuel storge facilities by combining data from security systems, environmental sensors, and access control logs and creating a holistic security overview of spent fuel facilities [
29]. The combined feature of mobile computing, allow monitoring of all the spent fuel storage facilities around the world, by the means of smart remote devices and IoT sensors and cameras, which enhance the containing of the nuclear material and decrease the non-proliferation risk related to nuclear waste weaponizing.
Remote Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
In the perspective of nuclear power plants, incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and mobile computing can considerably advance regulatory compliance monitoring and inspection systems. AI algorithms can process widespread datasets collected from different sensors, control systems, and inspection reports, applying machine learning algorithms to detect glitches, predict equipment failures, and ensure firm adherence to regulatory safety standards. These intelligent models can recognize emerging patterns and trends indicative of potential compliance concerns, facilitating timely and practical interventions. Mobile computing improves these capabilities by permitting real-time data collection, transmission, and analysis directly on-site, thus raising the precision and efficiency of regulatory inspections.
Regulatory authorities benefit from this integration by obtaining the ability to continuously monitor all critical parameters of nuclear power plants, validating that operations conform to the safety guidelines specified in their licenses. Mobile computing permits inspectors equipped with advanced devices to access AI-driven diagnostics and analytics tools, streamlining the identification of non-compliance areas and enabling immediate corrective actions, thereby minimizing risks associated with delayed responses.
Furthermore, the mobile computing feature and real-time data transmission capabilities extend the reach of regulatory oversight, permitting authorities to remotely monitor and inspect nuclear facilities across the globe. This global oversight confirms that facilities maintain compliance with international safety standards irrespective of their geographic location. AI-generated reports, available on a daily, monthly, and yearly basis, provide comprehensive insights into the operational status and safety compliance of nuclear facilities. These reports facilitate regulatory committees to track adherence to protocols continuously, promptly address deviations, and maintain a high level of safety assurance. Therefore, the combination of AI and mobile computing not only improves the effectiveness of regulatory compliance monitoring but also improves the overall safety and operational reliability of nuclear power plants worldwide.
Revolutionizing Remote Decision-Making
One of the most exciting things that the coupling of the AI and computing technology of mobile devices can make possible is to support the nuclear power plant monitoring and decision-making processes remotely. The AI algorithm, in essence, consists of data analytics programs and programs that provide the plant with the critical data needed to have the plant perform as expected all of the time. Its deep learning component aids in the real-time analysis of vast amounts of data generated by sensors and monitoring devices at the plant, thus, enables early detection of problems and ensures the necessary preventive maintenance of the equipment. Moreover, the highly developed machine learning techniques can discern hidden trends and correlations in the data that can throw human detection off course, thereby making it possible for them to give their teammates a compatible analysis of the plant conditions and potential problems. Through the use of these AI capabilities, decision-makers can make both quicker and positive responses given that they have all valid information, thus providing the environment of better decision-making being created. Adding on to this, mobile computing supports the idea by enabling the people who operate, manage and maintain the plant to have access to the critical information and AI-driven insights remotely. With the help of secure mobile applications, plant owners, employees, and decision-makers can visor plant conditions from anywhere and get commands from the system, all through their mobile devices. The technology that encourages online access to the plant conditions finally can be considered a real-time technology with online surveillance systems, which will help in the dissemination of information, course reconfiguration, and the support of content expertise between geographically distributed teams. At the same time, electronic devices with digital reality might be used to visualize things like the location of objects personnel have to inspect which in turn would be displayed on the physical objects thus enabling the best precision and the greatest efficiency.
Overall, the combination of AI and mobile computing technologies can significantly enhance remote decision-making processes in nuclear power plant operations.AI algorithm can analyze vast amounts of data from plant sensors and monitoring equipment in real-time, enabling the early detection of anomalies, predictive maintenance, and optimization of operational performance. The training mechanism for AI, therefore, is based on dimensions like data analytics programs and programs required that supply the demands of the plant that the plant operates at a highly efficient level. The synergy between AI and mobile computing acts as a firm foundation for improving security, reliability, and efficiency in nuclear power plants. This technology plays a role in the adoption of quicker, data-based decision-making and the influencing of communication and collaboration, which leads to risk reduction and plant operation profit. This methodology of action is bringing not only fast and short-term operating needs but also strategic planning and continuous improvement in nuclear power plant management in the near future.
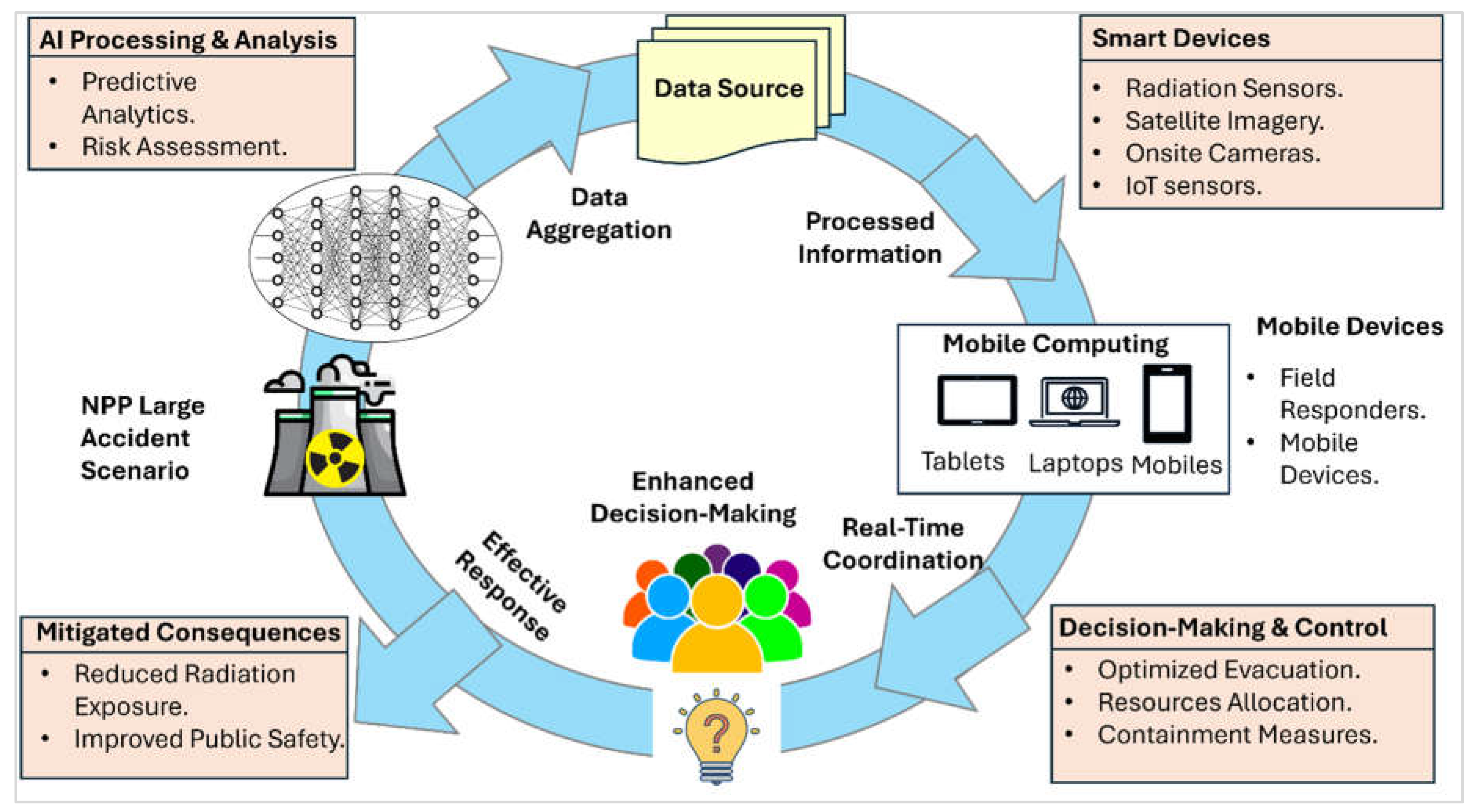
Remote Real-Time Coordination During Large Nuclear Accident
AI and mobile computing integrating to deal with large-scale nuclear accidents from remote areas is an innovative feature that has really never been done anywhere. AI is capable to process and analyse a huge amount of data coming from many sources, sensors, radiation detectors, satellite imaging that in return will give real-time status of the situation and predictive analytics. As a result, it will be possible to immediately recognize the risks and to make the right decisions. Further, as for mobile computing, its advantages should include the possibility for the first responders to reach out, share, and upgrade key data by using their mobile phones, tablets and other handheld devices, thus, guaranteeing smooth communication and coordination.
For instance, a similar problem emerged during the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 [
31], where real-time data processing and mobile phone coordination was not integrated. Among the issues experienced, the failure in quick information collection, analysis, and dissemination was the leading factor, while such issues resulted in problems like missing evacuations, wrongful allocation of available resources and failure of the containment measures. In an alternative reality, where AI and mobile computing were present, short-burning AI programs would have measured radiation doses and radiation spread and estimated the amount of damage to reactors in seconds. Simultaneously, mobile computing could have provided emergency responders and decision-makers with real-time updates, interactive maps, and coordination tools, enhancing situational awareness and enabling more effective and timely actions.
During such incidents, AI could use the data to produce dynamic risk maps and thus optimize the routes of evacuation, while the mobile applications could offer the direct communication between field teams and command centers. This union is not limited to the proliferation of disaster management but also the reduction of human exposure to radiation and the realization of protection measures, and, eventually, lessening the consequences of the disaster. The above dissemination of technology will make a smart, educated, and flexible response to the disaster, which will play a major part in safety, re-direction of resources, and encasement of the disaster, eventually taking into care the public health and the environment in the case of a nuclear emergency.
Figure 9 models the employment of AI and mobile computing during large nuclear accident.
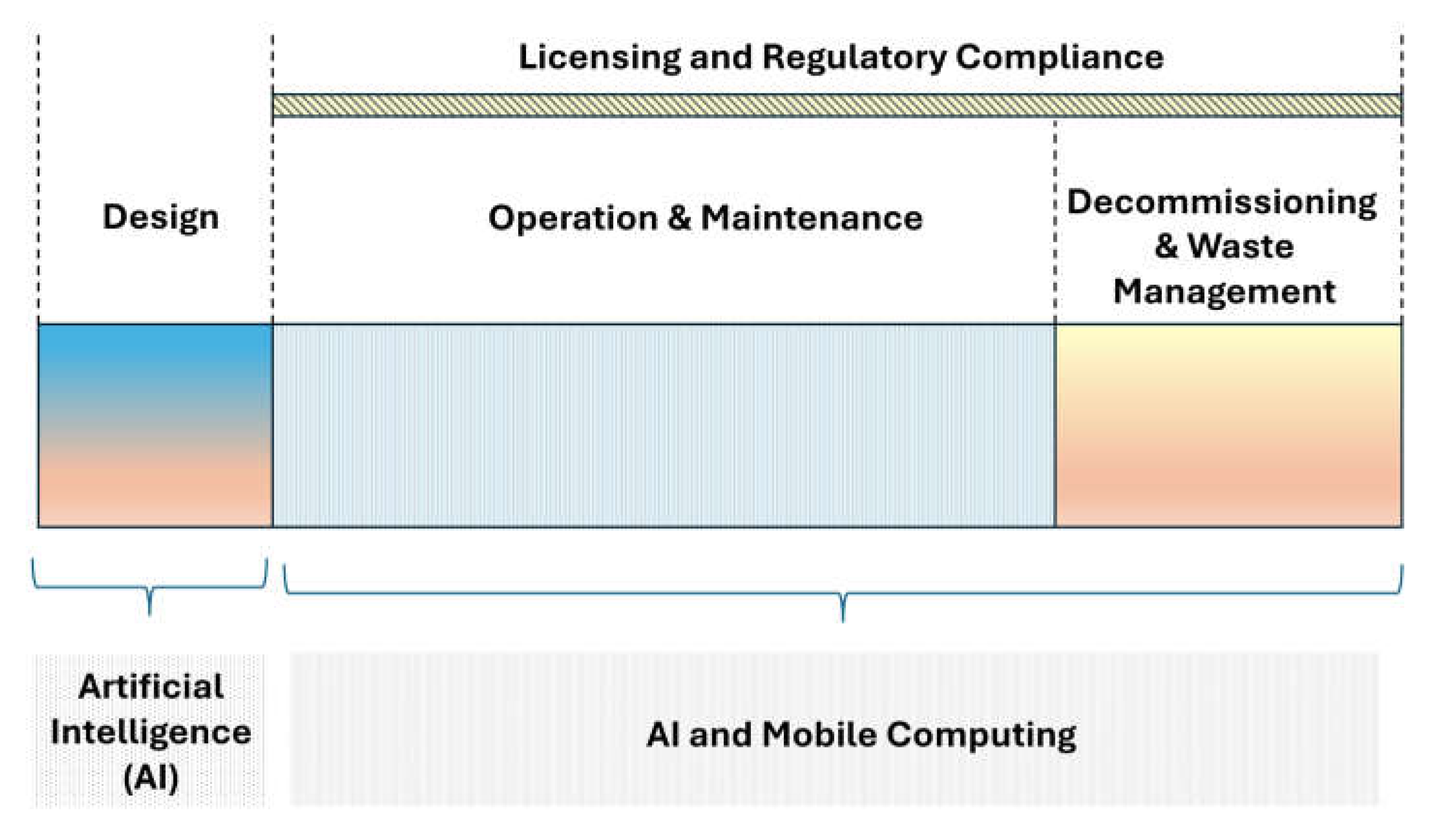
The literature reviewed here and summarized in
Table 1 shows that Artificial Intelligence can be applied to a nuclear power plant's entire life cycle. Contrasted with that, it seems that mobile computing is only used in operation phases and waste management. This is because during the design phase when the nuclear power plant is not under operation, no real-time data will be available that would warrant the use of mobile computing technologies. One major finding is that AI can be employed broadly throughout the whole life cycle of a nuclear power plant, from detailed design to decommissioning and waste management, as shown in
Figure 10. In contrast, mobile computing technologies apply only to operational and waste management stages since these stages involve the generation and transmission of real-time data that can be effectively tapped through mobile computing platforms.
7. Mobile Computing and AI features in NPP Future Application
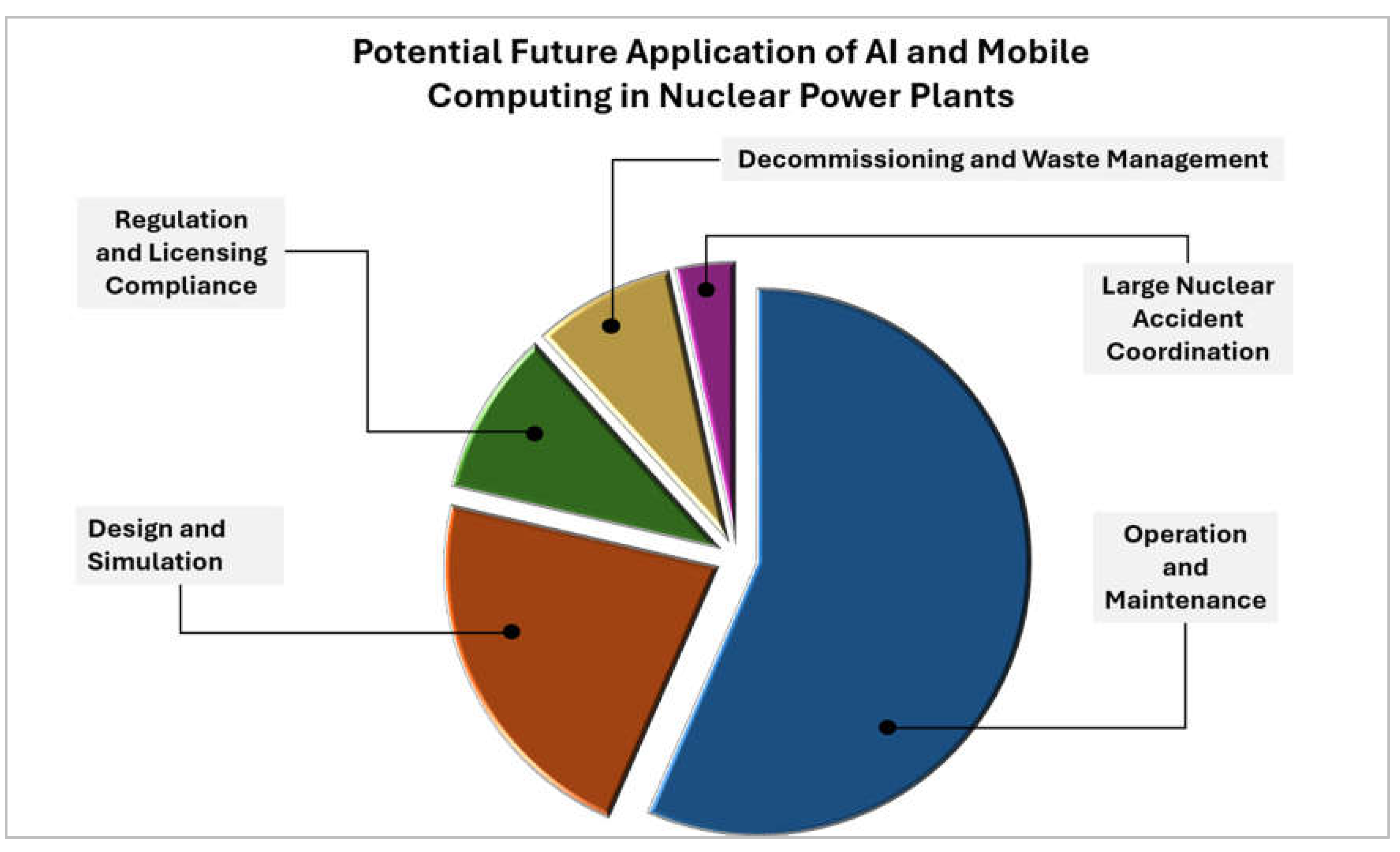
The integration of artificial intelligence and mobile computing technologies holds significant potential for enhancing the safety, efficiency, and reliability of nuclear power plants.
Figure 12 illustrates the potential areas of application of AI and mobile computing in the nuclear industry, based on the literature review in the present article. AI algorithms can serve as efficient data processing mechanisms, enabling intrinsically safe operation and effective accident investigation. By leveraging AI and mobile computing, NPPs can improve their performance and move towards more environmentally friendly and cost-effective operations. The artificial intelligence algorithms allow for the autonomous construction and calibration of virtual representations of the NPP core, enabling advanced parameter identification, state estimation, and anomaly detection capabilities. Furthermore, the integration of AI and IoT can transform NPP control systems, facilitating enhanced communication, information sharing, and decision-making processes among stakeholders. The collaboration between nuclear experts, AI specialists, and regulatory bodies is crucial to ensure the effective and safe implementation of these cutting-edge technologies within the nuclear industry, while maintaining the highest standards of operational safety. As the nuclear sector continues to digitize and accumulate vast amounts of operational data, the application of AI and mobile computing offers promising solutions to address the complex challenges faced by NPPs, ultimately contributing to their enhanced safety, efficiency, and long-term sustainability [
2]. The integration of the advanced technologies of AI and mobile computing, when implemented thoughtfully and with a focus on safety, can revolutionize the nuclear industry, unlocking new possibilities for clean, reliable, and cost-effective energy production.
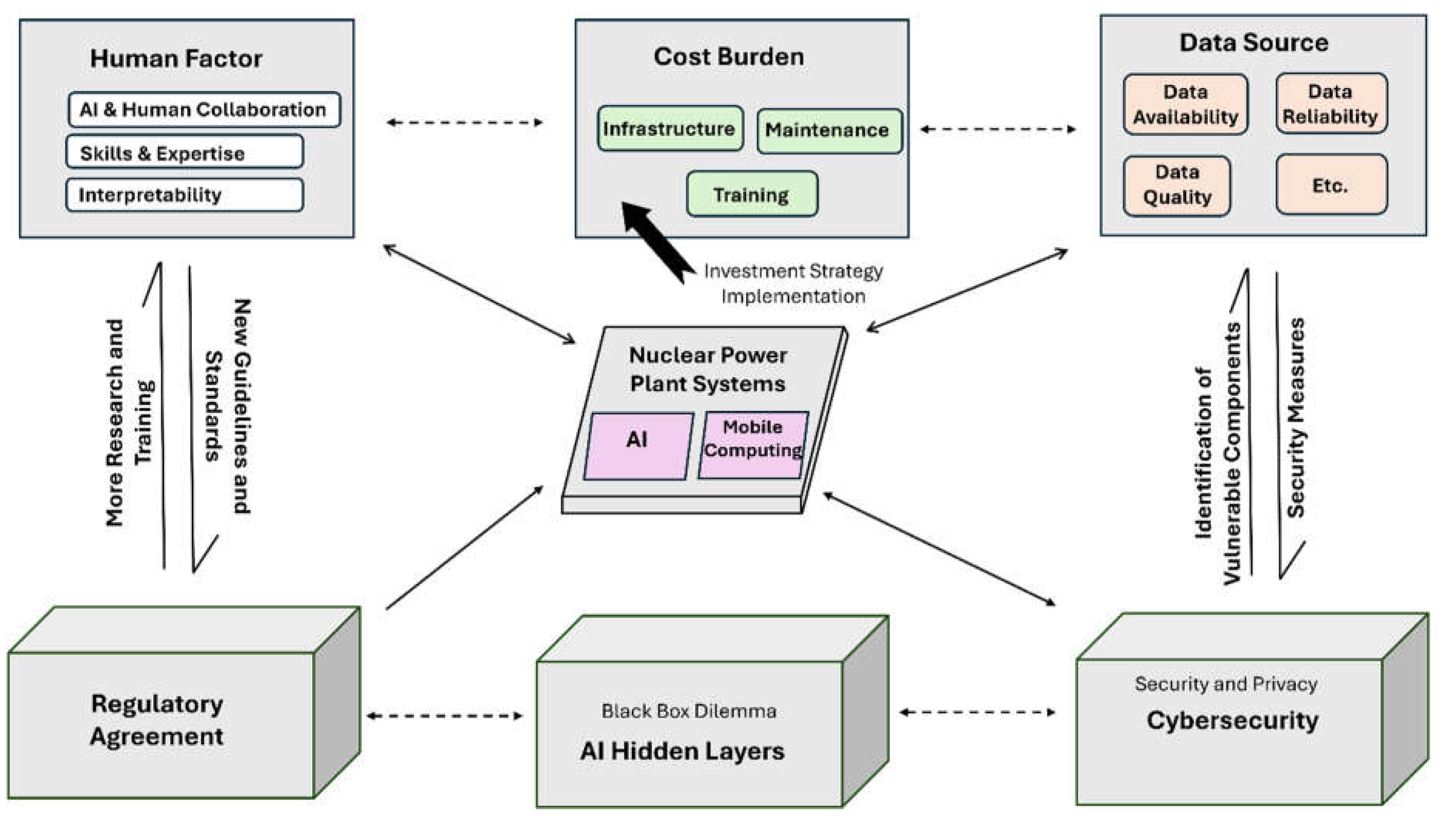
8. Future Work Directions
The integration of AI and mobile computing in nuclear power plants (NPPs) is an evolving field with vast potential. Future work should focus on enhancing safety, efficiency, and reliability while addressing regulatory and security concerns. One key area is advanced predictive features in nuclear power plant which involves improving AI algorithms for real-time data integration and anomaly detection to enable more accurate and proactive predictivity. Furthermore, AI-driven risk assessment coupled with mobile computing features for sending early warning via mobile devices is recommended area of research for future direction because it enhances the overall plant safety and increase reliability of nuclear power. Remote monitoring and inspection are also an important direction for future work recommendation in the field of AI and mobile computing, because sending the nuclear power plant real-time data allows for autonomous inspection and continuous remote monitoring which are very important for safe operation of the plant. Therefore, AI-powered drones and robots, mobile control interfaces, and advanced image/sensor data analysis are recommended to focus on in future work in this evolving area. Additionally, AI and mobile computing integration to enhance the decision-making within the nuclear power plant is another crucial recommended area of research in the upcoming years. This is because AI-based algorithms provide a prediction of different case scenarios based on real-time data and historical data, which make it a powerful tool in nuclear industry. Added to that, the feature of mobile computing allows different stakeholders to be involved in the decision which enhance the plant response, hence the safety. For those reasons, more research in this field is recommended to optimize the decision-making process in NPP.
It is also very recommended to include different parties during the application of AI and mobile computing, such as Lawyers and legal authorities, because as this is a novel field, then we would need new regulation and guidelines for sending the nuclear power plant data from the plant to another mobile devices in different location. Hence, we recommend more research on assigning new regulatory compliance to meet the requirements of AI and mobile computing safety standards, to ensure safe use of the nuclear material around the world. Lastly, the most important area that need to be researched more in the context of application of AI and mobile computing in nuclear power plant is the cybersecurity. This is a crucial feature for ensuring the continuity of real-time data transmission safely. However, this presents many challenges related to cyber-attacks and hackers. For those reasons, a sophisticated cybersecurity measures and new protocols are recommended to be addressed in future work and research.
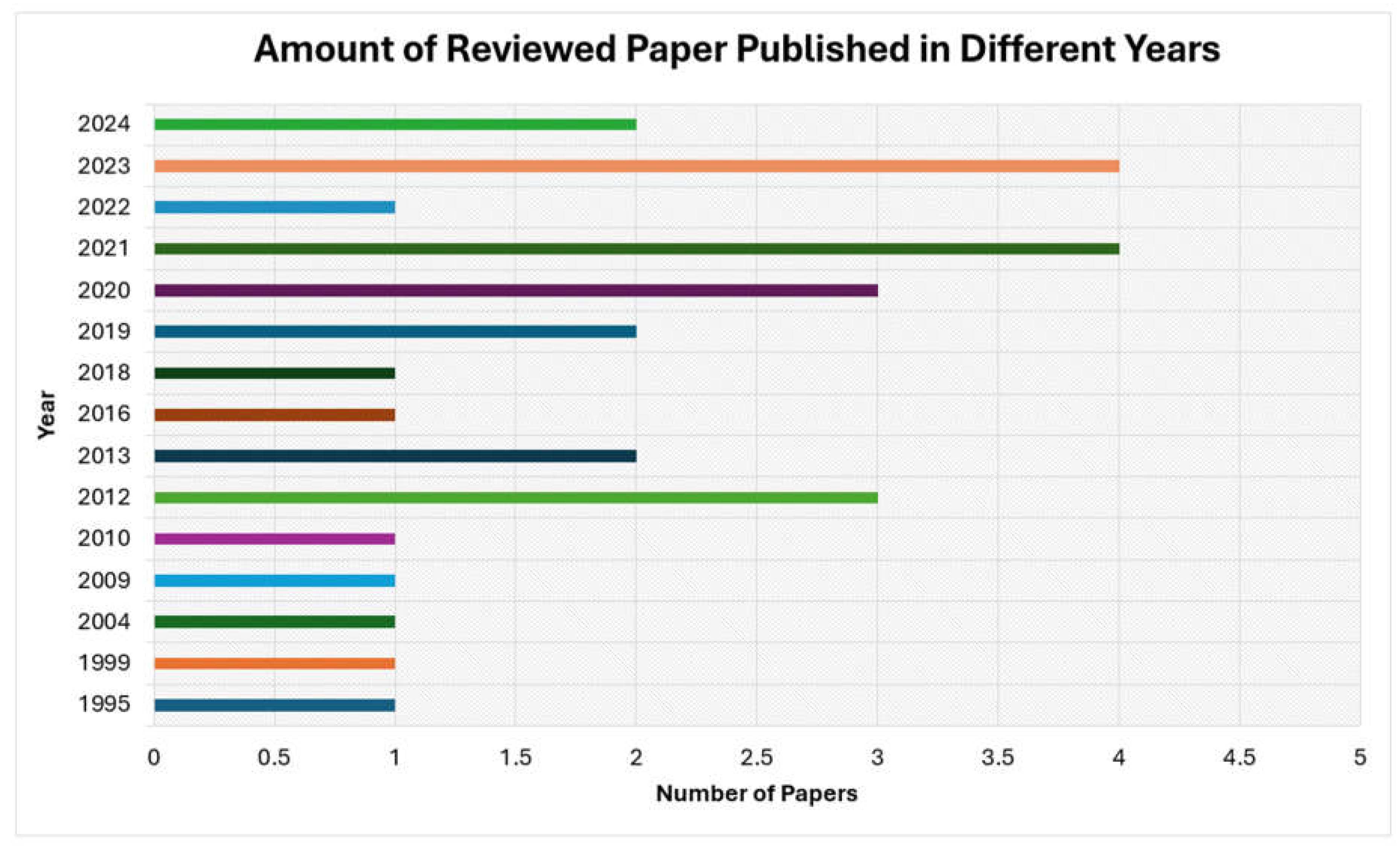
Figure 13 represents the amount of paper reviewed in this article. From this figure, we can conclude that not much work was done in the area of artificial intelligence in the industry of nuclear power plants, and there are significant gaps between the papers from 1995 to 2024. Therefore, we recommend more work on the overall topic of implementing artificial intelligence in nuclear power plants.
Underlying all of these efforts should be initiatives to integrate data, enable advanced analytics, and foster cross-industry collaboration and continuous innovation. By prioritizing these future work recommendations, nuclear power plants can harness the full potential of AI and mobile computing to operate more safely, efficiently, and sustainably.