Submitted:
29 July 2024
Posted:
29 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
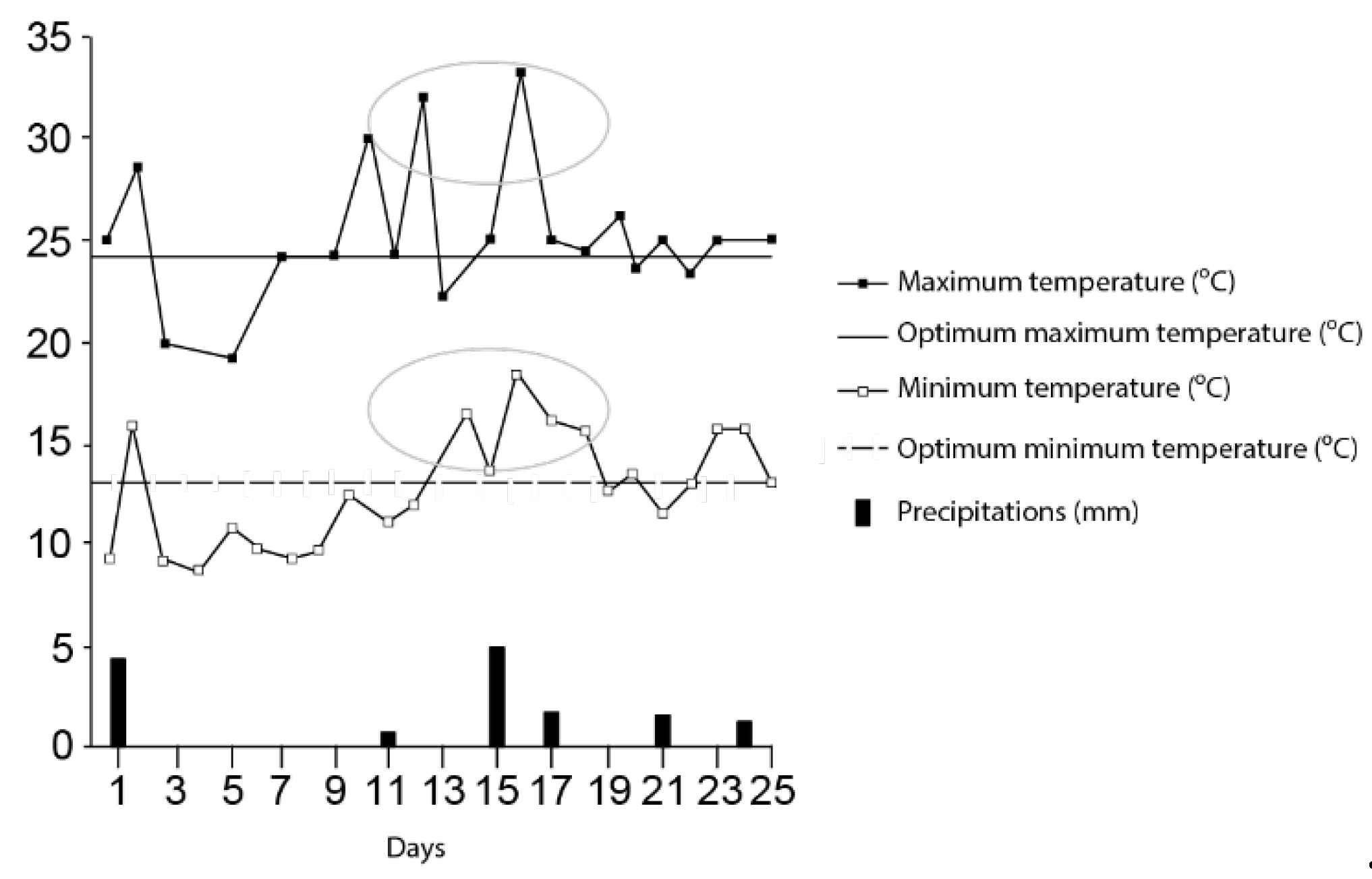
2.1. Field Experimental Design and Treatments
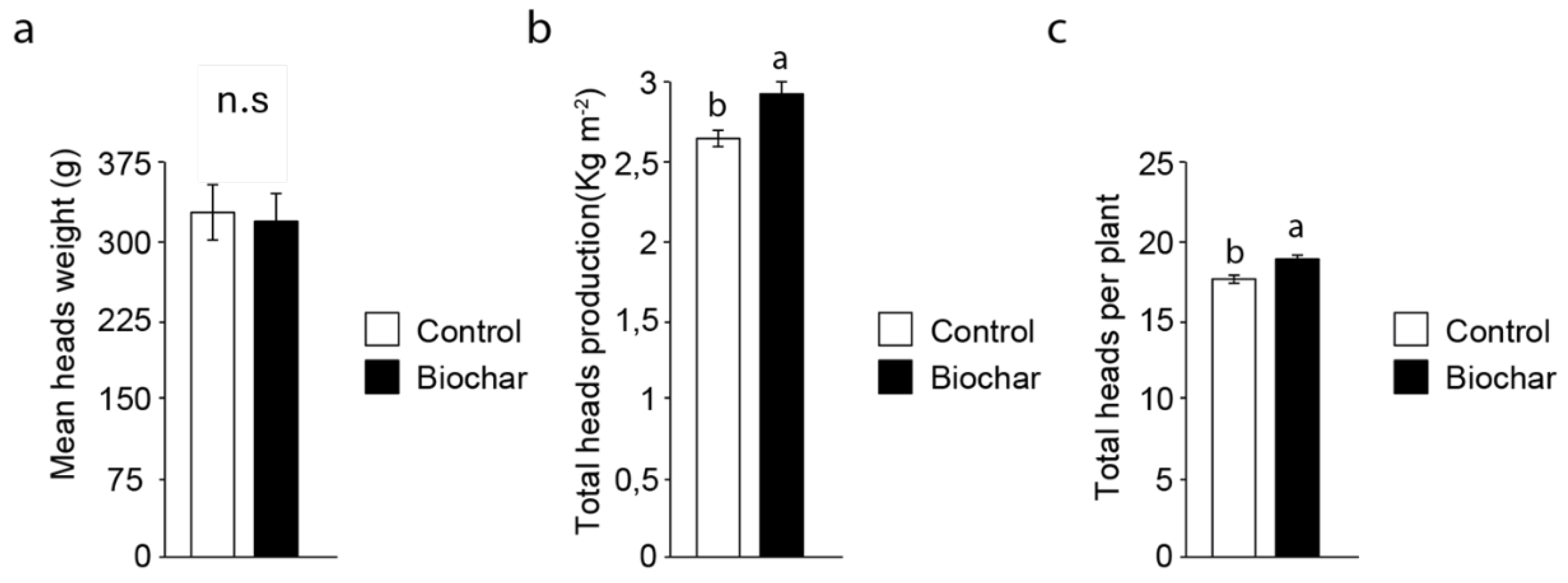
2.2. Crop Yield and Production
2.3. Cations Determination in the Plant and Soils
2.4. Organic Matter (OM) and Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in the Soils
2.5. Extraction and Determination of Fatty Acids
2.6. Extraction and Determination of Phenolic Compounds and Flavonoids.
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Crop Yield and Production
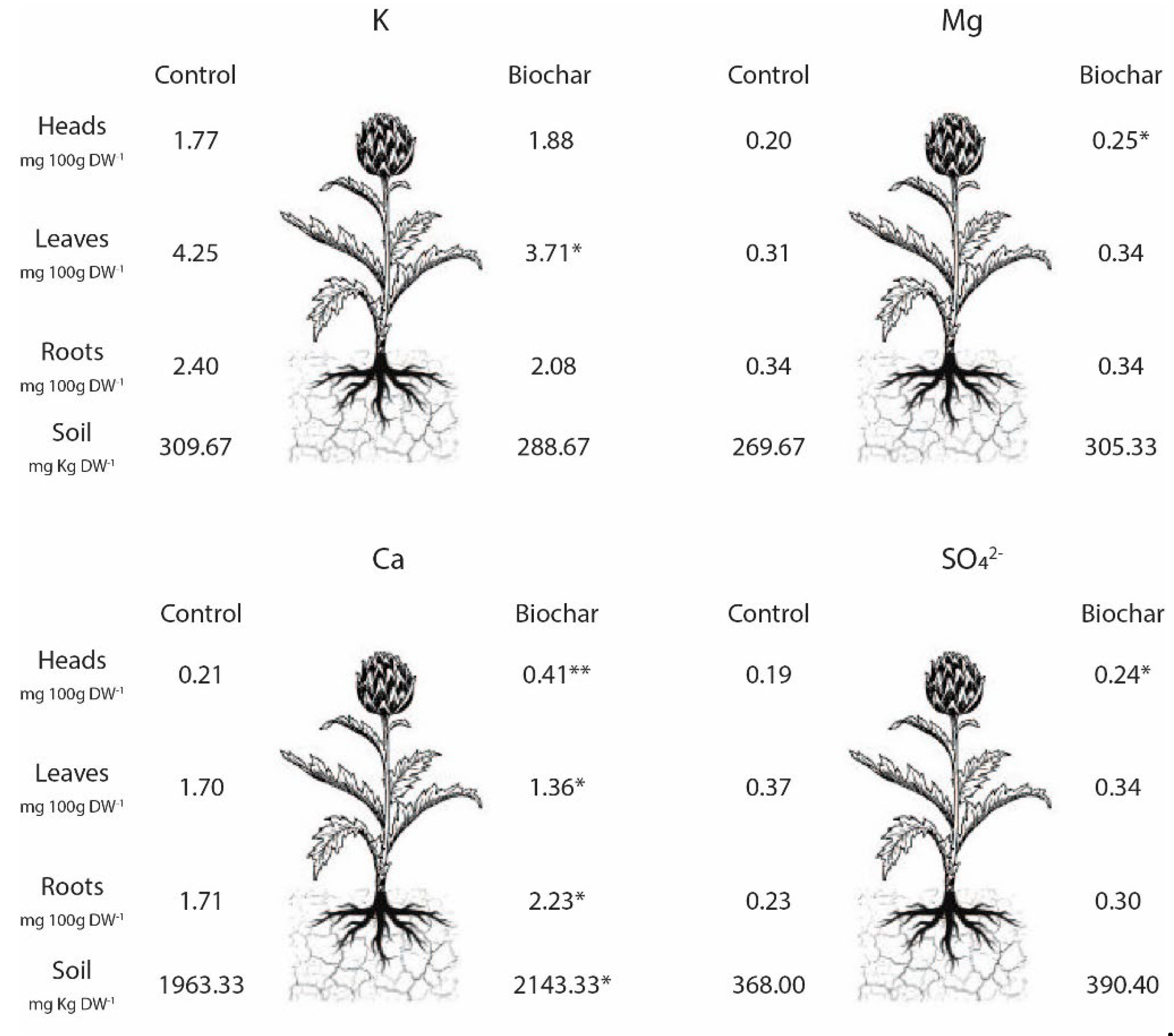
3.2. Mineral Content in Plant and Soils. Organic Matter and Total Organic Carbon in the Soil
| Micronutrients (mg kg-1 DW) | Control | Biochar |
|---|---|---|
| Mn | 91.3±2,11a | 104.8 ±4,60b |
| Co | 1.3±0.15a | 0.90±0.02b |
| Zn | 305.0±7.30a | 225.5±7.75b |
| Fe | 314.5±17.61 n.s | 310.2±6.27 n.s |
| Cu | 42.9±1.30a | 30.5±0.60b |
| Control | Biochar | ||
| CEC (meq 100g-1 ) | 9,99 b | 11,6a | |
| OM (%) | 1,88 b | 1,98a | |
| TOC (%) | 1,0 b | 1,2a | |
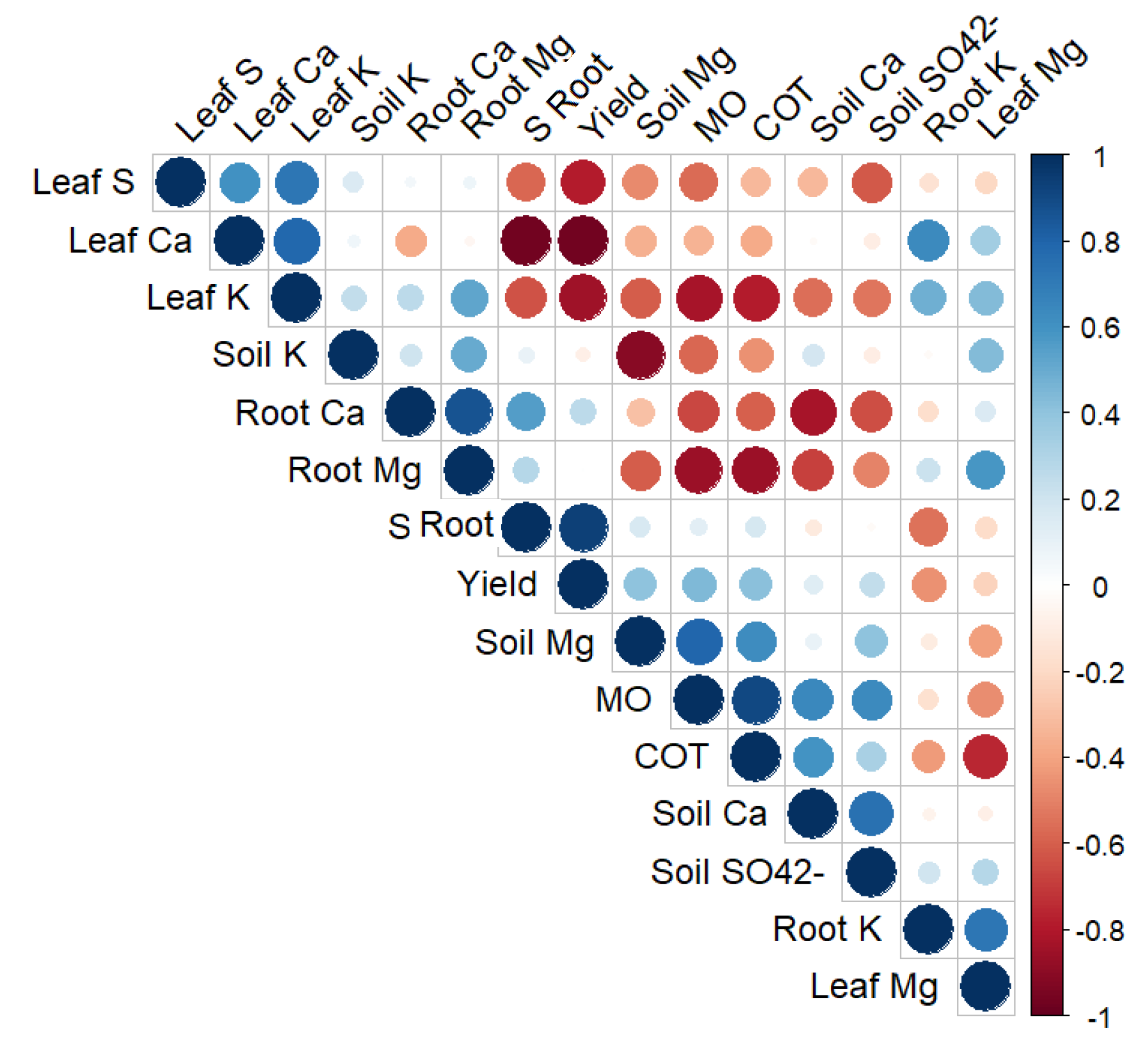
3.3. Relationship between Soil Fertility and Plant Parameters
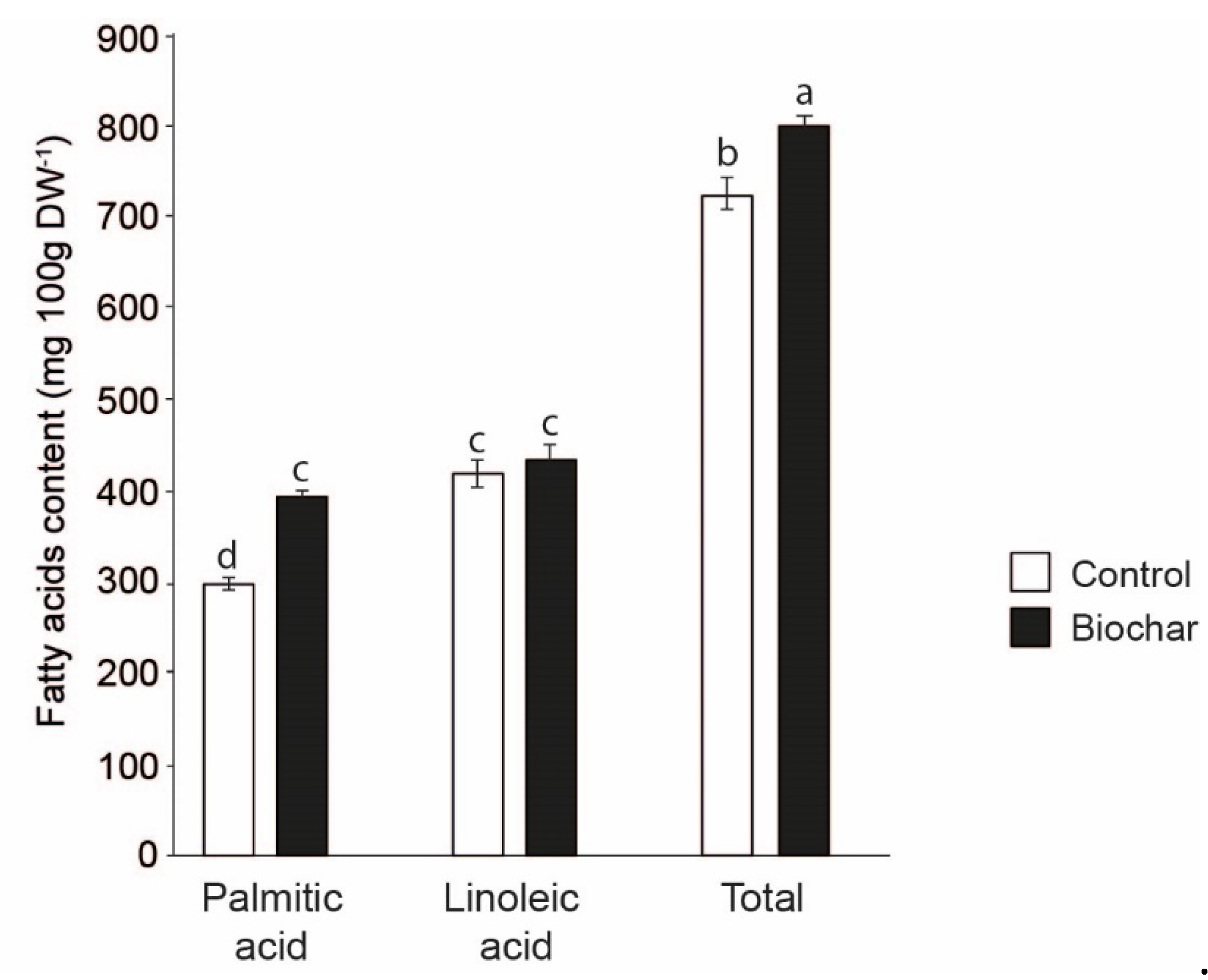
3.4. Fatty acid Content
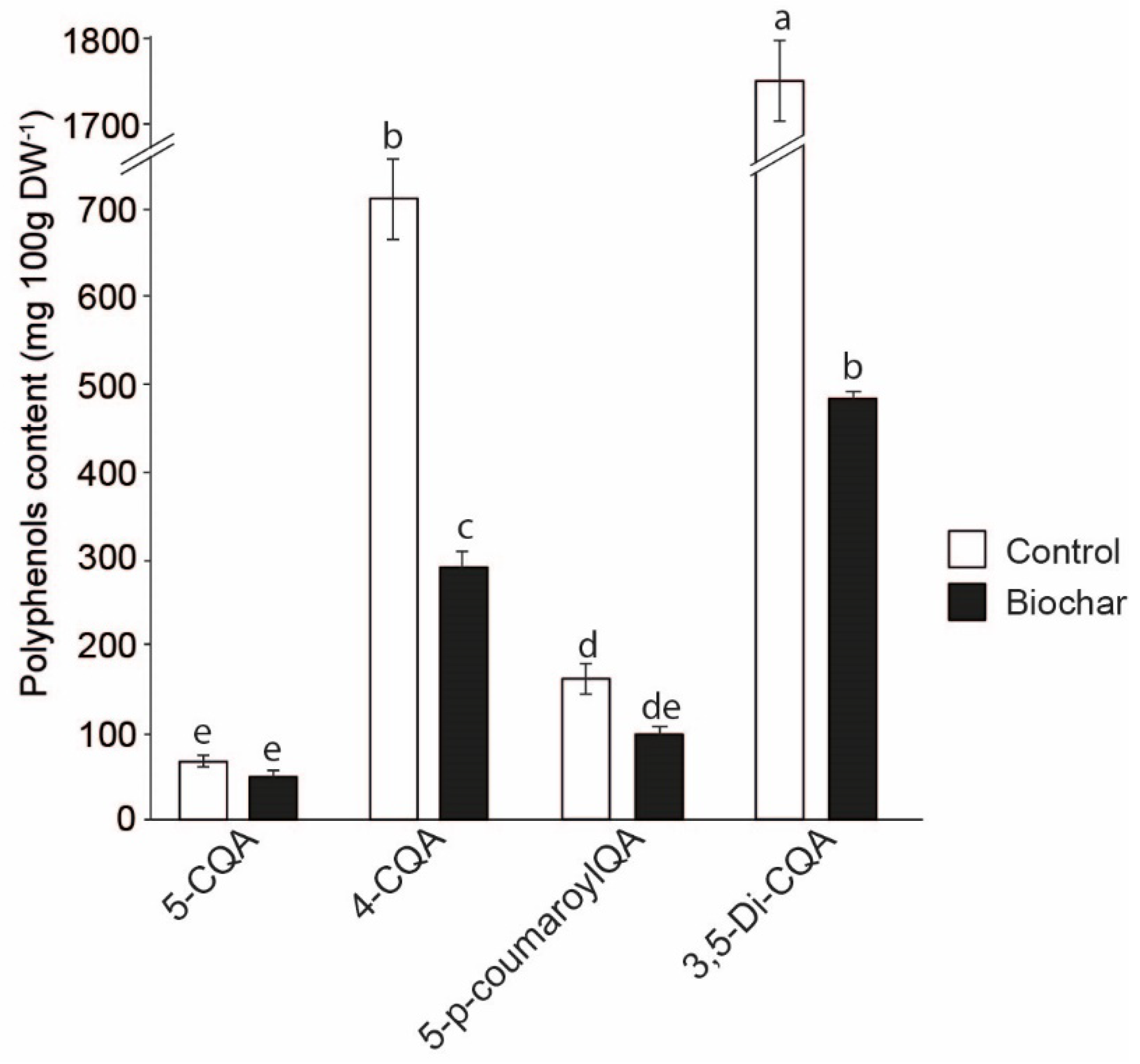
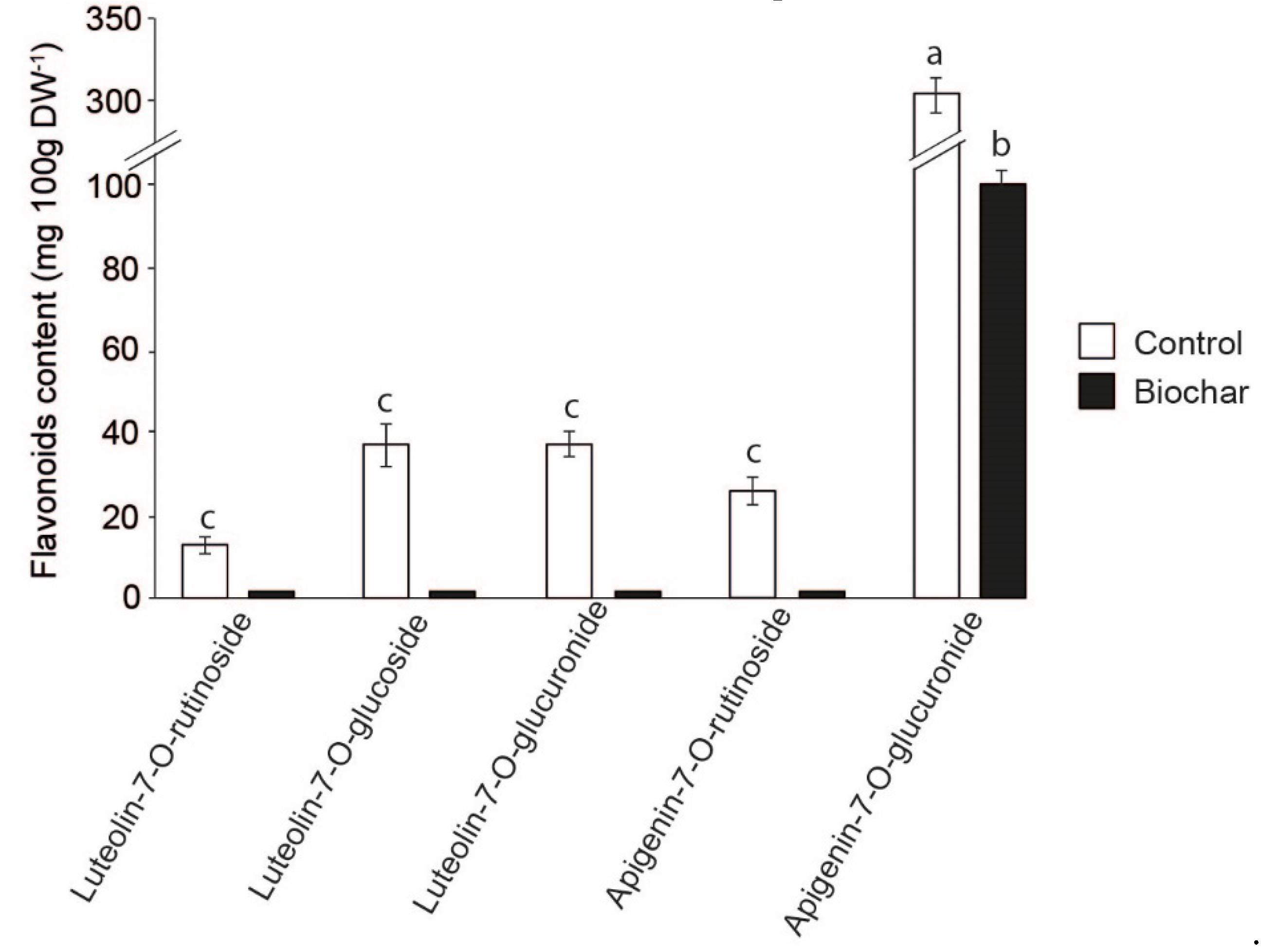
3.5. Phenolic Compounds Content.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sani, M.N.H.; Hasan, M.; Uddain, J.; Subramaniam, S. Impact of Application of Trichoderma and Biochar on Growth, Productivity and Nutritional Quality of Tomato under Reduced N-P-K Fertilization. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoung, O.C.N.; Figueiredo, C.C. de; Ramos, M.L.G. A Scoping Review on Biochar-Based Fertilizers: Enrichment Techniques and Agro-Environmental Application. Heliyon 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Pyne, S.; Chaturvedi, S. Effect of Enriched Biochar Based Fertilizers on Growth, Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Direct-Seeded Rice (Oryza Sativa). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 91, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-J.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z.-B.; Xu, S.-G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yi, S.-Y. Biochar Preparation and Its Effects with Reduced Compound Fertilizer on Nutrients, Phenolic Acid and Fungal Community in Tobacco Rhizosphere Soil. Mater. Express 2023, 13, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Wen, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Qiao, G. Tobacco Straw Biochar Improved the Growth of Chinese Cherry (Prunus Pseudocerasus) via Altering Plant Physiology and Shifting the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam). 2022, 303, 111244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, D.; Fernández, J.A.; Franco, J.A.; del Carmen Martínez Ballesta, M. Enriched-Biochar Application Increases Broccoli Nutritional and Phytochemical Content without Detrimental Effect on Yield. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 7353–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, J. Biochar-Enhanced Composts Reduce the Potential Leaching of Nutrients and Heavy Metals and Suppress Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Excessively Fertilized Cucumber Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7589–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Cole, A.J.; Paul, N.A.; de Nys, R. Algal Biochar Enhances the Re-Vegetation of Stockpiled Mine Soils with Native Grass. J. Environ. Manage. 2015, 161, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnan, S.; Deenik, J.L.; Toomsan, B.; Antal, M.J.; Vityakon, P. Biochar Characteristics and Application Rates Affecting Corn Growth and Properties of Soils Contrasting in Texture and Mineralogy. Geoderma 2015, 237, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszyk, D.M.; Shiroyama, T.; Novak, J.M.; Cantrell, K.B.; Sigua, G.; Watts, D.W.; Johnson, M.G. Biochar Affects Essential Nutrients of Carrot Taproots and Lettuce Leaves. HortScience 2020, 55, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kosma, D.K.; Lü, S. Functional Role of Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetases in Plant Development and Stress Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, H.; Khalesro, S.; Mokhatssi-Bidgoli, A.; Sharifi, Z. Biochar and Conservation Tillage Affect the Agronomic Performance and Fatty Acid Composition of Nigella Sativa L. under Both Irrigated and Dryland Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.A.A.; Muddathir, A.M.; Abdalla, A.H. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Growth, Yield, Seed Fixed Oil Content, and Fatty Acids Profile of Garden Cress (Lepidium Sativum L.). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, A.; Poudyal, S.; Singh, S.; Coldren, C.; Moustaid-moussa, N.; Simpson, C. Biochar Influences Phytochemical Concentrations of Viola Cornuta Flowers. 2023, 1–12.
- Adler, C.; Agyei, K.; Danquah, A.; Asare, A.T.; Aggor-woananu, S. Heliyon Application of Biochar and Inorganic Phosphorus Fertilizer in Fl Uenced Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics, Nodule Formation and Phytoconstituents of Cowpea Grown on Tropical Soil. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, F.P.; Maienza, A.; Miglietta, F.; Baronti, S.; Di Lonardo, S.; Giagnoni, L.; Lagomarsino, A.; Pozzi, A.; Pusceddu, E.; Ranieri, R.; et al. Biochar Stimulates Plant Growth but Not Fruit Yield of Processing Tomato in a Fertile Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 207, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M. Ben; Affes, H.; Ksouda, K.; Dhouibi, R.; Sahnoun, Z.; Hammami, S.; Zeghal, K.M. Pharmacological Studies of Artichoke Leaf Extract and Their Health Benefits. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, H.O.; Bueno, A.A.; Mota, J.F. The Effect of Artichoke on Lipid Profile: A Review of Possible Mechanisms of Action. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 137, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sałata, A.; Nurzyńska-Wierdak, R.; Kalisz, A.; Kunicki, E.; Ibáñez-Asensio, S.; Moreno-Ramón, H. Effects of Organic Cropping on Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Globe Artichoke Herbs. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, D.; Kiefer, E.; Drouet, A.; Sandermann, H. A Simple Method of DNA Extraction from Soil for Detection of Composite Transgenic Plants by PCR. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 1996, 14, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Fallon, J.V.; Busboom, J.R.; Nelson, M.L.; Gaskins, C.T. A Direct Method for Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Synthesis: Application to Wet Meat Tissues, Oils, and Feedstuffs. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-belchí, M.D.; Caamaño, E.F.; Pascual, G.; Noriega, F.; Fierro-morales, P.; Romero-román, M.E.; Jara, P.; Schoebitz, M.; Serra, I.; Moreno, D.A. Spray-dried Formulations Rich in Malvidin from Tintorera Grape Wastes: Characterization, Stability, and Storage. Processes 2021, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.R.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A.; Silva, L.R. Valorisation of Prunus Avium l. By-Products: Phenolic Composition and Effect on Caco-2 Cells Viability. Foods 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramírez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological Nitrogen Fixation by Common Beans (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.) Increases with Bio-Char Additions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Bogomolova, I.; Glaser, B. Biochar Stability in Soil: Decomposition during Eight Years and Transformation as Assessed by Compound-Specific 14C Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.R.; Hall, W.; Box, P.O. Abiotic and Microbial Oxidation of Laboratory-Produced Black Carbon ( Biochar ). 2010, 44, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhai, B.; Shi, D.; Chen, A.; Liu, C. How Does Bio-Organic Fertilizer Combined with Biochar Affect Chinese Small Cabbage’s Growth and Quality on Newly Reclaimed Land? Plants 2024, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, I.; Paungfoo-Lonhienne, C.; Tahmasbian, I.; Hunter, B.; Smith, B.; Mayer, D.; Redding, M. Combination of Inorganic Nitrogen and Organic Soil Amendment Improves Nitrogen Use Efficiency While Reducing Nitrogen Runoff. Nitrogen (Switzerland) 2022, 3, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavili, E.; Moosavi, A.A.; Moradi Choghamarani, F. Cattle Manure Biocty -40 Har Potential for Ameliorating Soil Physical Characteristics and Spinach Response under Drought. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; Velde, M. Van Der; Bastos, A.C. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment A Quantitative Review of the Effects of Biochar Application to Soils on Crop Productivity Using Meta-Analysis. "Agriculture, Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandino, G.; Lombardo, S.; Mauromicale, G. Mineral Profile in Globe Artichoke as Affected by Genotype, Head Part and Environment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Mauromicale, G. Minerals Profile of Two Globe Artichoke Cultivars as Affected by NPK Fertilizer Regimes. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormick, G.; Belizán, J.M. Calcium Intake and Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, L.; Manoni, M.; Ferrari, L.; Tretola, M.; Cazzola, R.; Givens, I. The Contribution of Dietary Magnesium in Farm Animals and Human Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laires, M.J. Biochemistry Laboratory, Faculty of Human Kinetics, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal, 2 Genetics Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine, University of Lisbon, Portugal. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azedo-Silva, J.; Osório, J.; Fonseca, F.; Correia, M.J. Effects of Soil Drying and Subsequent Re-Watering on the Activity of Nitrate Reductase in Roots and Leaves of Helianthus Annuus. Funct. Plant Biol. 2004, 31, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Nahar, K.; Hossain, M.S.; Al Mahmud, J.; Hossen, M.S.; Masud, A.A.C.; Moumita; Fujita, M. Potassium: A Vital Regulator of Plant Responses and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses. Agronomy 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland-Graves, J.H.; Mousa, T.Y.; Kim, S. International Variability in Diet and Requirements of Manganese: Causes and Consequences. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 38, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, D.B. Copper Intake and Assessment of Copper Status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyssens, L.; Vinck, B.; Van Der Straeten, C.; Wuyts, F.; Maes, L. Cobalt Toxicity in Humans—A Review of the Potential Sources and Systemic Health Effects. Toxicology 2017, 387, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbou, S.; Dabbou, S.; Flamini, G.; Peiretti, P.G.; Pandino, G.; Helal, A.N. Biochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activities of the Edible Part of Globe Artichoke Cultivars Grown in Tunisia. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S810–S819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouraei, S.; Rahimmalek, M.; Saeidi, G.; Bahreininejad, B. Variation in Seed Oil Content and Fatty Acid Composition of Globe Artichoke Under Different Irrigation Regimes. JAOCS, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Rajion, M.A.; Meng, G.Y.; Boo, L.J.; Ebrahimi, M.; Royan, M.; Sahebi, M.; Azizi, P.; Abiri, R.; Jahromi, M.F. Conjugated Linoleic Acid: A Potent Fatty Acid Linked to Animal and Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndiate, N.I.; Saeed, Q.; Haider, F.U.; Cai, L.Q.; Nkoh, J.N.; Mustafa, A. Co-Application of Biochar and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Improves Salinity Tolerance, Growth and Lipid Metabolism of Maize (Zea Mays L.) in an Alkaline Soil. PLANTS-BASEL 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Micha, R.; Wallace, S. Effects on Coronary Heart Disease of Increasing Polyunsaturated Fat in Place of Saturated Fat : A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, A.; Imperlini, E.; Nigro, E.; Montagnese, C.; Daniele, A.; Orrù, S.; Buono, P. Biological and Nutritional Properties of Palm Oil and Palmitic Acid: Effects on Health. Molecules 2015, 20, 17339–17361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murru, E.; Manca, C.; Carta, G.; Banni, S. Impact of Dietary Palmitic Acid on Lipid Metabolism. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandino, G.; Lombardo, S.; Mauromicale, G.; Williamson, G. Characterization of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids in Leaves, Stems, Bracts and Edible Parts of Globe Artichokes. Acta Hortic. 2012, 942, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Mauromicale, G. The Nutraceutical Response of Two Globe Artichoke Cultivars to Contrasting NPK Fertilizer Regimes. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandino, G.; Lombardo, S.; Lo Monaco, A.; Mauromicale, G. Choice of Time of Harvest Influences the Polyphenol Profile of Globe Artichoke. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalbert, A.; Williamson, G. Chocolate: Modern Science Investigates an Ancient Medicine Dietary Intake and Bioavailability of Polyphenols 1. J. Nutr 2000, 130, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





