Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
30 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Atmospheric Pollutant Advection-Diffusion Equation Modeling and Construction of Analytical Solutions
- : Represents the substantial derivative, capturing the rate of change in pollutant concentration from the perspective of a moving air parcel, embodying both the temporal and spatial variations due to airflow.
- : Stands for the total concentration of pollutants, which includes both the average concentration and the transient fluctuations attributable to atmospheric turbulence.
- : Denotes the total wind velocity vector represented by , where U indicates the east-west component, V the north-south component, and W the vertical component, encompassing both the average wind speed and its instantaneous fluctuations.
- : Indicates the partial derivative with respect to time, denoting how the concentration of pollutants changes at a fixed point as time progresses.
- ∇: Is the gradient operator, employed to calculate the spatial gradient of the pollutant concentration.
- : Describes the divergence of the wind velocity and pollutant concentration product, representing the net movement of pollutants carried by the wind across the spatial domain.
- S: Is the source term within the equation, quantifying the addition or removal of pollutants from the atmosphere via various processes such as industrial emissions, chemical reactions, or the deposition and uptake by terrestrial surfaces and vegetation.
- (i)
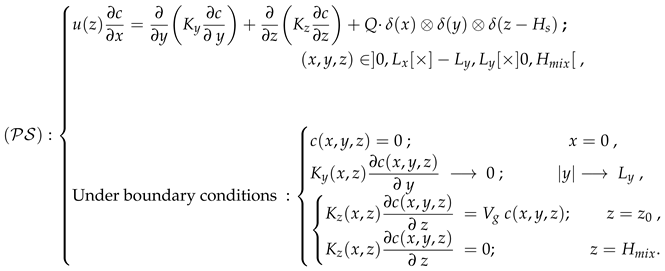
- The apex of the mixing or inversion layer functions as an impervious boundary preventing the diffusion of contaminants. Consequently, a reflective flux boundary condition is postulated at the height of the inversion layer, articulated mathematically as:
- (ii)
- Addressing the scenario where a pollutant is partially absorbed by the ground surface, Calder [2] delineates an applicable boundary condition in flux terms. It is posited that the ground surface may facilitate partial removal or absorption of the pollutant via deposition, characterized by a deposition velocity :where represents the surface roughness length.
- (iii)
- The lateral diffusive flux diminishes with increasing distance from the source, approaching zero as y extends towards the lateral boundary , formalized by:
- The system reaches a state of equilibrium dispersion ();
- Contributions from and are omitted, given that the x-axis aligns with the mean wind direction, rendering the w and v components of wind velocity minor;
- Turbulent diffusion along the mean wind direction is disregarded in comparison to advective transport, implying:
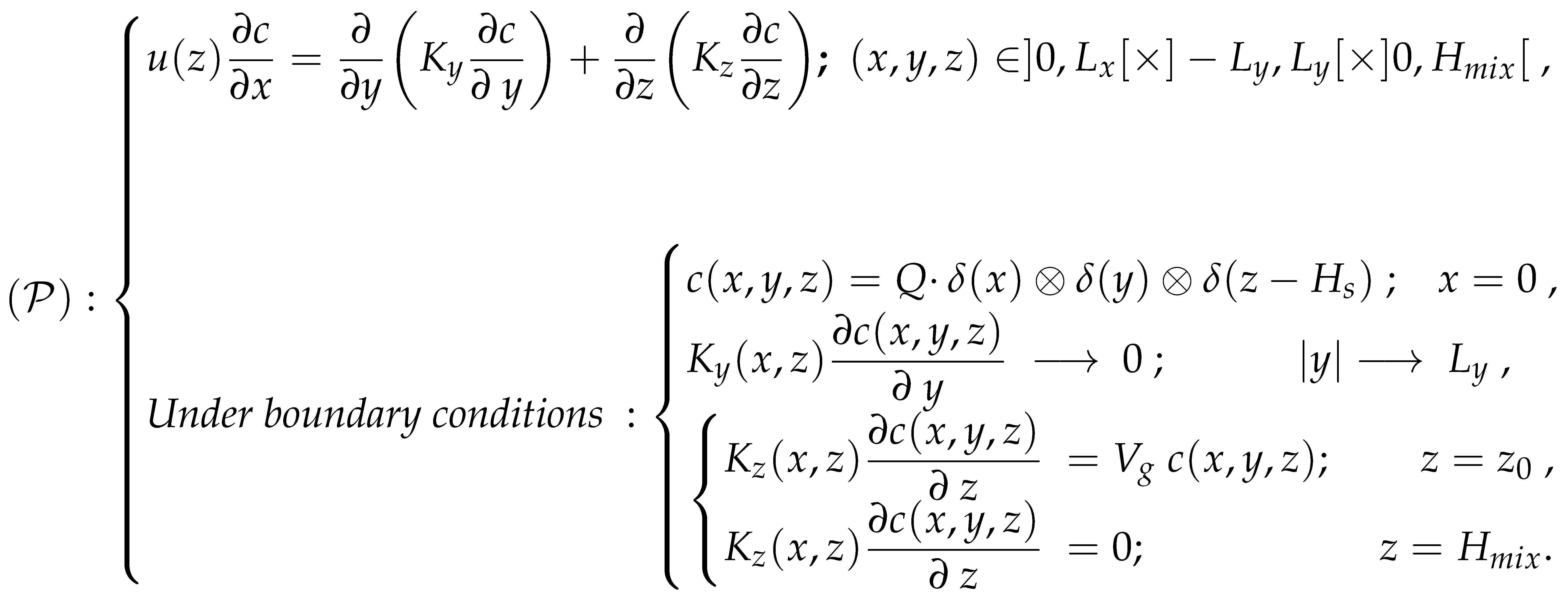
-
Consider as the solution for of the system , and define as follows:We will establish that satisfies the requirements of system .
- To improve solution regularity, we apply mollifiers , as referenced in [11], over , defined as follows:with and using the Heaviside function , which is 1 for and 0 otherwise, where * denotes convolution.
- We differentiate with respect to x, leading to:
-
Integrating the advection and diffusion terms, we find:This confirms that corresponds to the system when n approaches infinity, thus completing the proof of equivalence between the systems and .
- The concentration at the end of a sub-layer must equal the concentration at the beginning of the subsequent sub-layer to ensure the continuity of concentration across sub-layer interfaces, as denoted by the equation
- The concentration flux, which is the product of diffusivity () and the concentration gradient with respect to the vertical axis (z), must also be continuous across the interfaces between sub-layers. This continuity is captured by the equation
- The coefficient is determined by the following relationship:
- The coefficient is determined by the following relationship:
- The norm is defined as:
- The parameter is characterized by the equation:with the associated eigenvalues the eigenvalues , for , associated with this problem are real and discrete. Additionally, the corresponding eigenfunctions are mutually orthogonal.
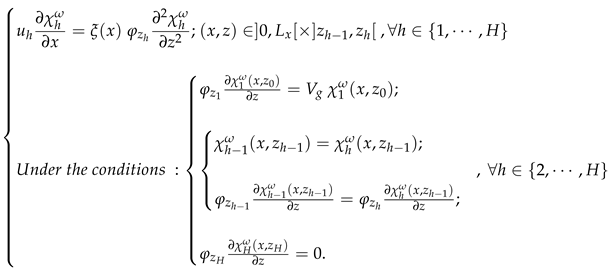
- We begin by applying the Fourier transform with respect to the lateral coordinate y, as presented in Eqt 16, to the problem. The resulting equation is:
- We calculate the derivative of with respect to x, obtaining:
- We multiply both sides of Eqt 17 by the exponential term . Given that and remain constants within each sub-layer, it simplifies to:
- We apply the same method to the boundary conditions, expressing them in terms of to ensure consistency with the transformed system.
- Applying the lemma 1, we transform the problem into a formulation that depends on ;
- Representing as a series, we express it in a separated variables form:
- Verifying that the functions and satisfy their respective differential equations. We must therefore confirm that satisfies the equationand adheres to the system
- Determining the specific forms of and ensures that they are respectively expressed as:where is an arbitrary function depending on , andwhere is expressed in Eqt 14. This formulation must meet the system’s criteria, resulting in the determination of and , as specified in Eqts 11 and 12 respectively.
-
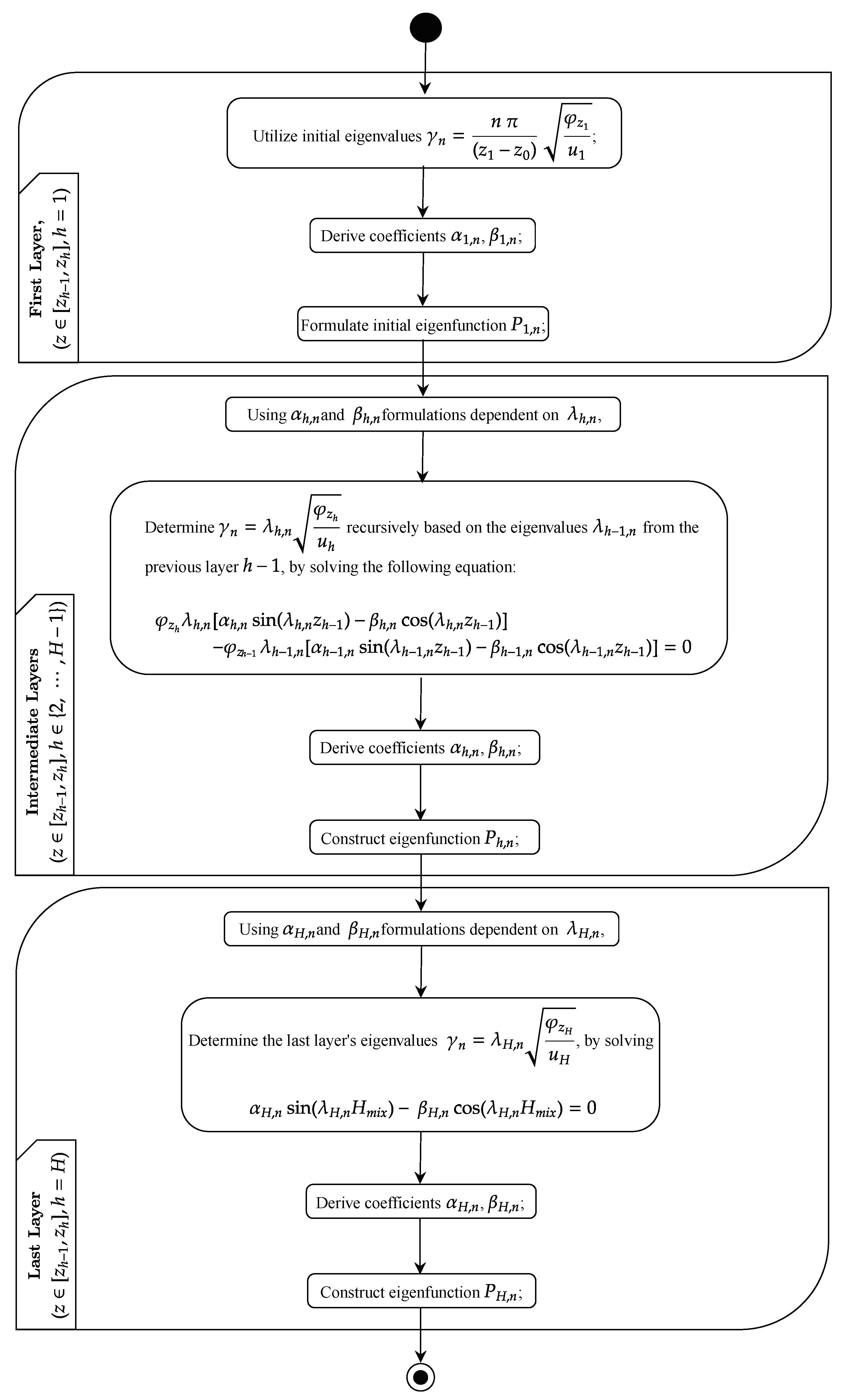
The continuity condition between sub-layers necessitates a recursion of eigenvalues and the eigenfunctions , for . This process begins by determining the eigenvalues associated with the first layer, , using the conditions related to . The resulting expressions are enumerated below:
- -
- The function is expressed as:where .
- -
- The norm of is given by:
The recursive generation of eigenvalues for the intermediate and final layers depends on the known values of the previous layers, in accordance with their respective conditions. This approach makes it possible to construct the associated eigenfunctions, succinctly maintaining continuity between the layers. For further details, please refer to Appendix Section A.1. - The Sturm-Liouville theorem [1] allows for the expanded representation of as:where the eigenfunctions form a complete and mutually orthogonal set. Consequently, is detailed as above. The coefficients are determined leveraging the orthogonality of , calculated as follows:
- Applying the inverse Fourier transform to from Equation (16), and considering that the inverse transform ofis given byleads to the final expression for the solution of the problem .
-
Single-Layer and Two-Dimensional Solution:
-
Multi-Layer and Three-Dimensional Solution:
- represents the average wind speed over the height of the mixing layer, calculated as
- denotes the average eddy diffusivity over the same height, expressed as
- Substitute Single-Layer Values into the CIC Equation: Begin by inserting the conditions of a single-layer setup into the original CIC formula from Eqt (27):where .
- Apply Limits as Approaches 0 and Extends to : Evaluate the limits to reflect the shift to a single-layer framework that spans the entire mixing height :
Turbulent Parameters in Pollutant Dispersion Modeling
- (a)
-
Parameterizing the Wind Speed Profile,.The wind speed profile is principally derived using surface layer theory enhanced by Monin-Obukhov (M-O) similarity theory [23]. While traditionally limited to the surface layer, extending the M-O scaling across the entire Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) involves maintaining a constant wind speed profile above this initial layer, ensuring the model’s extended applicability and continuity.Gryning et al. [8] have refined this approach to create a comprehensive wind speed profile applicable over the entire ABL, particularly suited for homogeneous terrain. Their advanced model employs a local mixing length composed of three component scales, leading to a robust formulation that incorporates adjustments for atmospheric stability throughout the entire ABL:where is an empirically determined constant, and , the Monin-Obukhov length [23], plays a critical role in modeling stability within the boundary layer. The mid-boundary layer length, , crucial for stable conditions, is given by:In this formulation, represents the Coriolis parameter, is the von Karman constant, and and are resistance law functions, dependent on the stability parameter . Additionally, Gryning et al. proposed an empirical formula for that enhances the model’s ability to adapt to various atmospheric stability conditions:
- (b)
-
Parameterizing the Diffusivity Profiles
- (b.1)
-
Vertical Diffusivity:In atmospheric dispersion models, the parameterization of eddy diffusivity, , significantly influences model accuracy and performance. Traditionally, has been modeled as solely a function of height above the ground, z. However, recent advancements have extended this parameterization to include the downwind distance x, recognizing its impact on near-source dispersion dynamics.An innovative approach by Mooney and Wilson [20] introduced a composite model for , blending both spatial variables into a single expression:where represents the vertical eddy diffusivity as a function of height, and denotes the along-wind length scale. This scale delineates the transition across which diffusivity reaches its extensive field value. Here, signifies the Lagrangian time scale at the source height, reflecting the turbulence’s persistence in the atmosphere.The parameterization of at the source height is given by:with representing the vertical turbulent intensity. In stable atmospheric conditions, the formulation for is:demonstrating how stability affects turbulence characteristics.Mangia et al. [18] further refined based on local similarity and statistical diffusion theories, resulting in the following relation:where represents the local Obukhov length and is expressed as:utilizing constants and , derived from the second-order closure model by Nieuwstadt [22], which accounts for stationary turbulence under a constant cooling rate.
- (b.2)
-
Horizontal Diffusivity:In the realm of atmospheric dispersion modeling, lateral eddy diffusivity plays a crucial role in determining the spread of pollutants in the crosswind direction. This diffusivity is fundamentally expressed through a relationship that ties it to the wind speed profile and the variance in lateral dispersion:where represents the standard deviation of the pollutant’s distribution in the lateral or crosswind direction, and is predominantly a function of the downwind distance x. This formulation underscores the dependency of lateral diffusivity on both the vertical wind speed profile and the rate of change in lateral dispersion as pollutants travel away from the source.This parameterization, based on the foundational work cited from Huang’s theory [12], encapsulates the dynamic interactions between wind speed and atmospheric turbulence. By integrating the vertical wind profile with the derivative of the squared standard deviation with respect to x, the model effectively captures how lateral diffusion varies with both altitude and distance from the source.
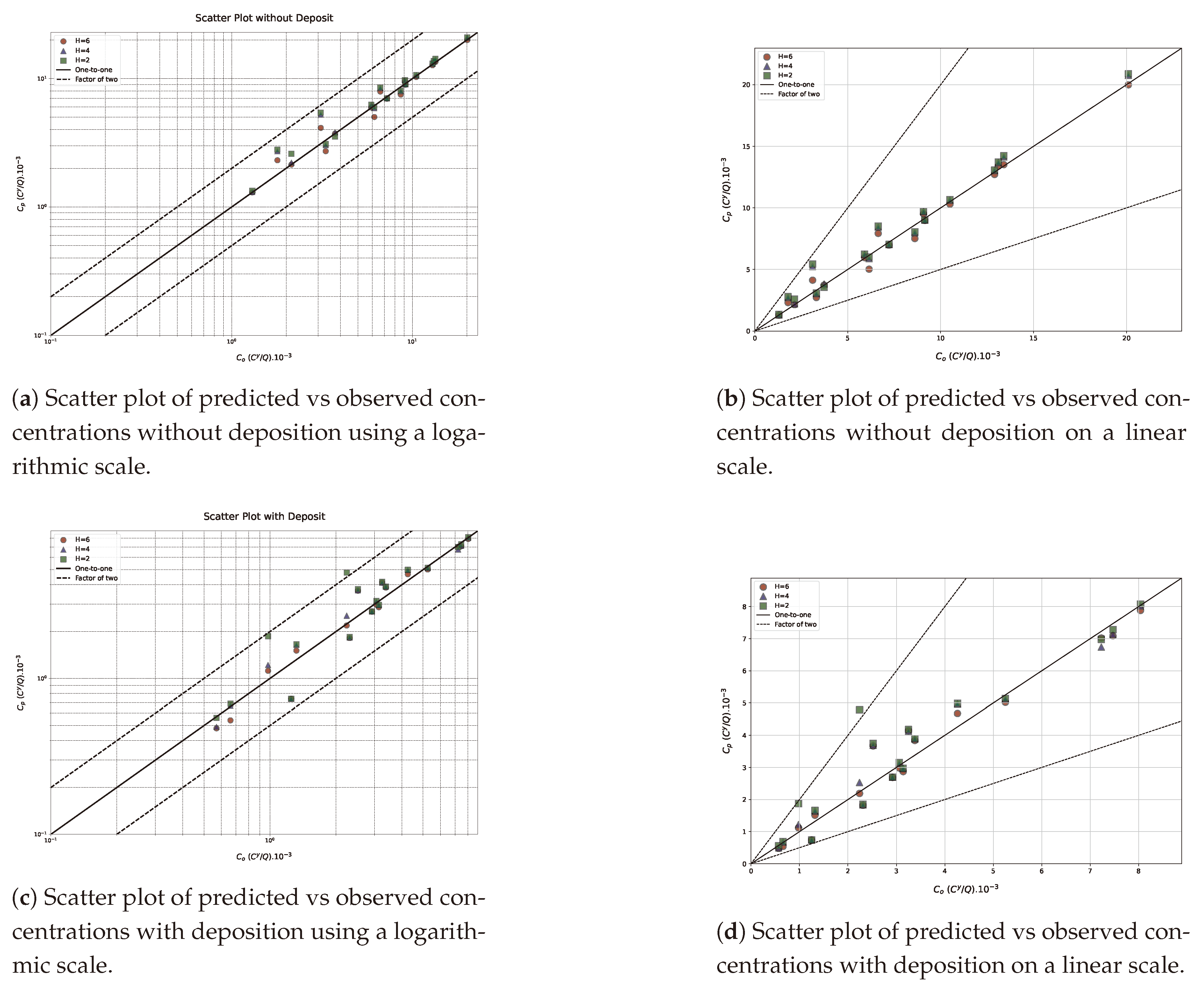
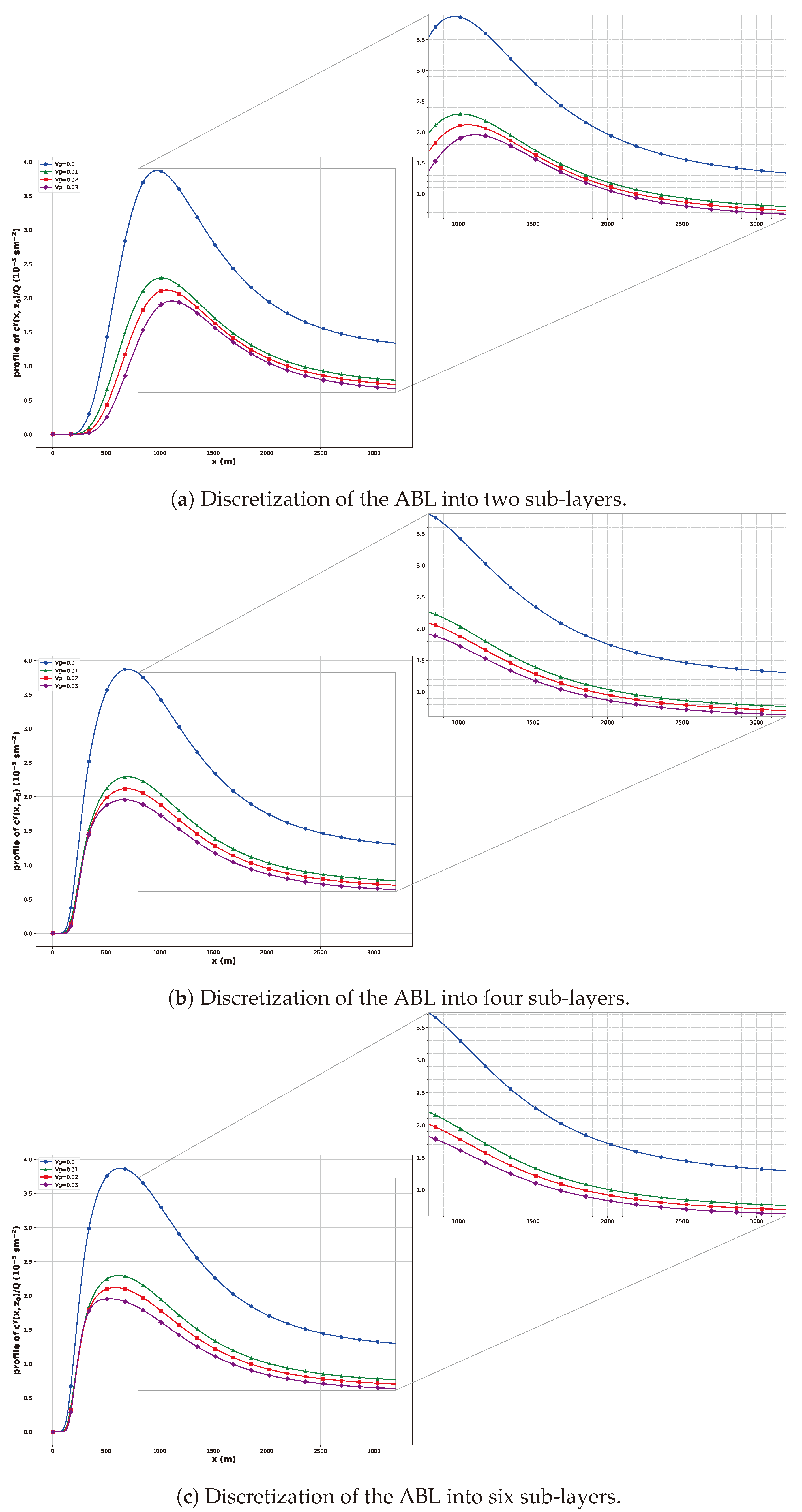
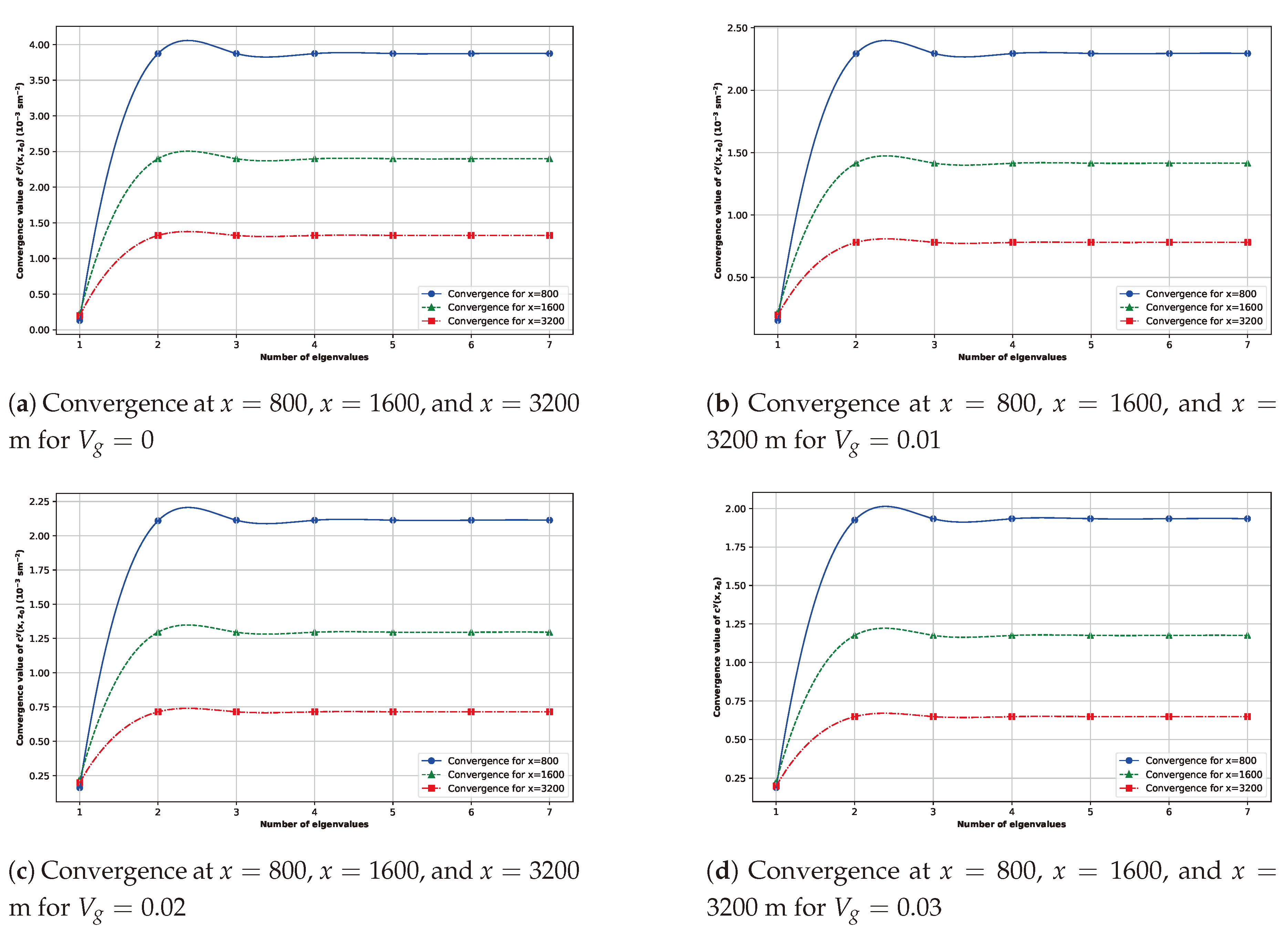
4. Results: Data Analysis and Model Validation
4.1. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusion
Abbreviations
| ABL | Atmospheric Boundary Layer |
| CIC | Crosswind-Integrated Concentration |
Appendix A. Construction of the Solution Associated with the First Sub-Layer and Eigenvalue Analysis of the Problem (21).
Appendix A.1. Construction of the Solution Associated with the First Sub-Layer of the Problem (21)
Appendix A.2. Eigenvalues Analysis of the Problem (21)
Appendix B. Derivation of Specific Solutions for
References
- Boyce, W., DiPrima, R. & Meade, D. Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems. (Wiley,2017).
- Calder, K. Atmospheric diffusion of particulate material, considered as a boundary value problem. Journal of Meteorology 1961, 18, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.C.; Horst, T.W. An evaluation of Gaussian plume-depletion models with dual-tracer field measurements. Atmospheric Environment 1985, 19, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.C.; Abbey, O.B.; Buck, J.W.; Glover, D.W.; Horst, T.W. Field Validation of Exposure Assessment Models. Data Environmental Science Research Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC, EPA/600/3-84/092A, p. 177.
- Ermak, D.L. An analytical model for air pollutant transport and deposition from a point source. Atmospheric Environment (1967). 11, 231-237 (1977,1).
- Farhane, M. & Souhar, O. A Novel Development in Three-Dimensional Analytical Solutions for Air Pollution Dispersion Modeling. Environmental Sciences. 9 (2023,9).
- Farhane, M. , Alehyane, O. & Souhar, O. Three-dimensional analytical solution of the advection-diffusion equation for air pollution dispersion. ANZIAM Journal 2022, 64, 40–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gryning, S.E.; Batchvarova, E.; Brümmer, B.; Jørgensen, H.; Larsen, S. On the extension of the wind profile over homogeneous terrain beyond the surface boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 2007, 124, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R. Applications in Air Pollution Modelling. In F. T. M. Nieuwstadt & H. van Dop (Eds.), Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling. Boston: Reidel (1982).
- Hewitt, C.N. , Jackson, A. Handbook of Atmospheric Science. Blackwell Publishing. p. 633.
- Hörmander, L. The analysis of linear partial differential operators. Springer-Verlag,1990.
- Huang, C. A Theory of Dispersion in Turbulent Shear Flow. Atmospheric Environment (1967) 1979, 13, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.S. A theoretical validation of the wind profile power law exponent as a function of surface roughness and stability. Atmospheric Environment 1979, 13, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadyri, A., Kandoussi, K., & Souhar, O. An approach on mathematical modeling of PV module with sensitivity analysis: a case study. Journal of Computational Electronics 2022, 21, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. & Sharan, M. A Generalized Analytical Model for Crosswind-Integrated Concentrations with Ground-Level Deposition in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Environmental Modeling & Assessment. 19, 487-501 (2014,12).
- Laaouaoucha, D.; Farhane, M.; Essaouini, M.; Souhar, O. Analytical Model for the Two-Dimensional Advection-Diffusion Equation with the Logarithmic Wind Profile in Unstable Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 6825–6832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewelyn, R.P. An analytical model for the transport, dispersion and elimination of air pollutants emitted from a point source. Atmospheric Environment 1983, 17, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, C.; Moreira, D.M.; Schipa, I.; Degrazia, G.A.; Tirabassi, T.; Rizza, U. Evaluation of a New Eddy Diffusivity Parameterization from Turbulent Eulerian Spectra in Different Stability Conditions. Atmospheric Environment 2002, 36, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, E., Hubert, B., Patrice, E., Zarma, A. & Pierre, O. A Three-Dimensional Analytical Solution for the Study of Air Pollutant Dispersion in a Finite Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology. 155, 289-300 (2015,5).
- Mooney, C.J.; Wilson, J.D. Disagreements between gradient-diffusion and Lagrangian stochastic dispersion models, even for surface near the ground. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 1993, 64, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.M.; Tirabassi, T.; Vilhena, M.T.; Goulart, A.G. A Multi-layer Model for Pollutant Dispersion with Dry Deposition to the Ground. Atmospheric Environment 2010, 44, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwstadt, F.T.M.; van Ulden, A.P. A Numerical Study on the Vertical Dispersion of Passive Contaminants from a Continuous Source in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmospheric Environment 1978, 12, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhov, A. Turbulence in an Atmosphere with a Non-uniform Temperature. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 1971, 2, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquill, F. , Smith, F.B. Atmospheric Diffusion. John Wiley and Sons. p. 437.
- Seinfeld, J. Atmospheric chemistry and physics of air pollution. (1986,1), John Wiley and Sons.
- Sharan, M., Singh, M.P., & Yadav, A.K. A mathematical model for the atmospheric dispersion in low winds with eddy diffusivities as linear functions of downwind distance. Atmospheric Environment 1996, 30, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. A K-theory of dispersion, settling and deposition in the atmospheric surface layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 2008, 129, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirabassi, T. Operational advanced air pollution modeling. PAGEOPH 2003, 160, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viúdez-Moreiras, D. Editorial for the Special Issue “Atmospheric Dispersion and Chemistry Models: Advances and Applications”. Atmosphere. 14, 1275 (2023,8).
- Visscher, A. Air Dispersion Modeling: Foundations and Applications. Wiley–Blackwell,2013,11.
- Zannetti, P. Air Pollution Modeling: Theories, Computational Methods and Available Software. Springer Science & Business Media,2013,6.
| Run | Date | Distance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (DD/MM/YY) | (m) | () | (m) | (m) | () | () | () | |
| 800 | 3.73 | 2.24 | 4.21 | |||||
| 1 | 18-05-83 | 165 | 0.40 | 325 | 1600 | 2.14 | 0.98 | 4.05 |
| 3200 | 1.30 | 0.57 | 3.65 | |||||
| 800 | 12.90 | 7.47 | 1.93 | |||||
| 2 | 26-05-83 | 44 | 0.26 | 135 | 1600 | 9.08 | 3.25 | 1.80 |
| 3200 | 7.22 | 2.31 | 1.74 | |||||
| 800 | 5.91 | 3.06 | 3.14 | |||||
| 3 | 05-06-83 | 77 | 0.27 | 182 | 1600 | 3.31 | 1.32 | 3.02 |
| 3200 | 1.79 | 0.66 | 2.84 | |||||
| 800 | 20.10 | 8.04 | 1.75 | |||||
| 4 | 12-06-83 | 34 | 0.20 | 104 | 1600 | 13.10 | 4.26 | 1.62 |
| 3200 | 9.15 | 3.14 | 1.31 | |||||
| 800 | 10.50 | 5.25 | 1.56 | |||||
| 5 | 24-06-83 | 59 | 0.26 | 157 | 1600 | 8.61 | 3.38 | 1.47 |
| 3200 | 6.64 | 2.92 | 1.14 | |||||
| 800 | 13.40 | 7.23 | 1.17 | |||||
| 6 | 27-06-83 | 71 | 0.30 | 185 | 1600 | 6.15 | 2.52 | 1.15 |
| 3200 | 3.11 | 1.25 | 1.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





