Submitted:
29 July 2024
Posted:
30 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Motor Coordination
1.2. Motor Coordination Training
1.3. Evaluation Methods
1.4. Purpose of This Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
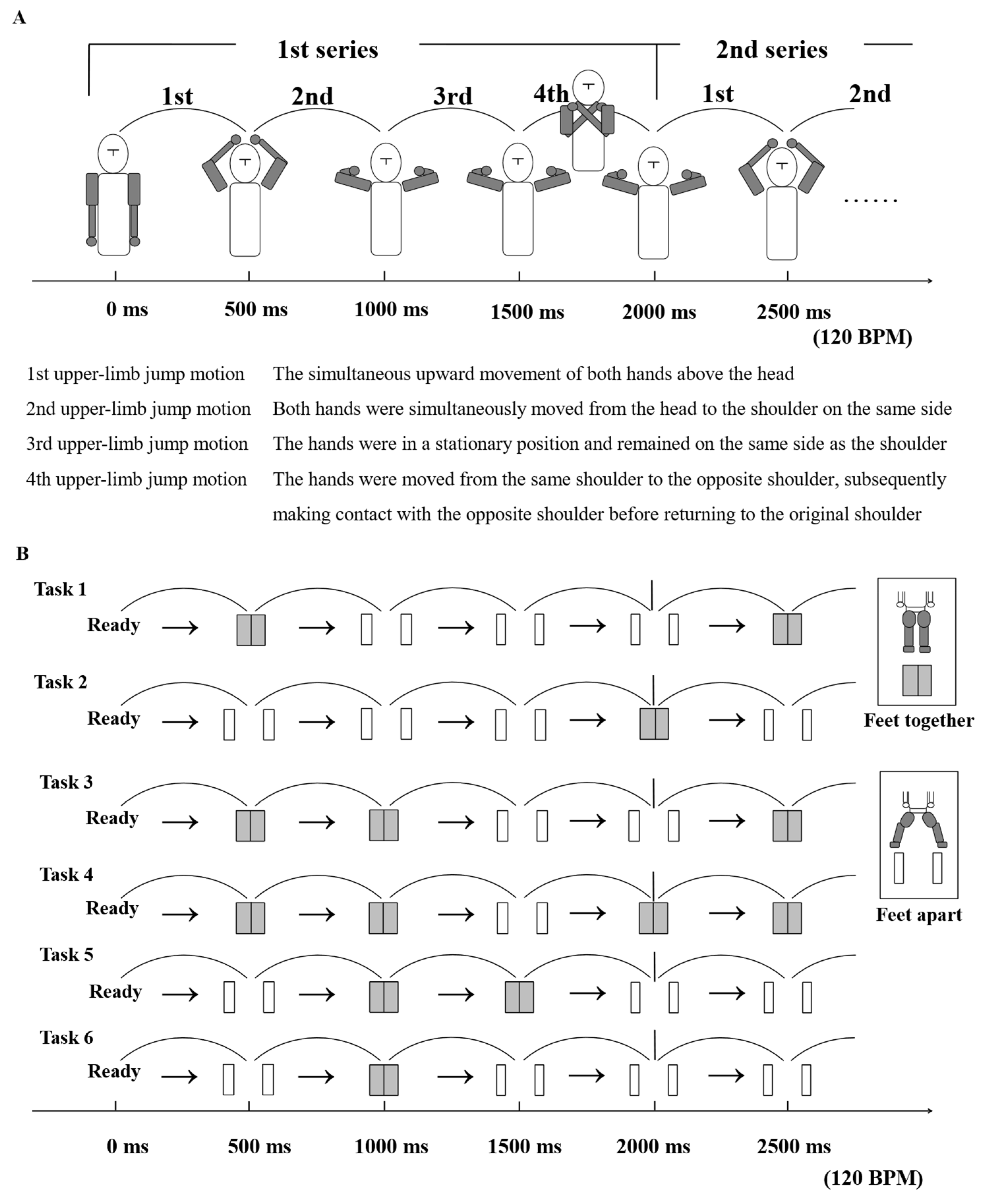
2.2. Explanation of the Motions and Tasks
2.3. Implementation Procedure
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
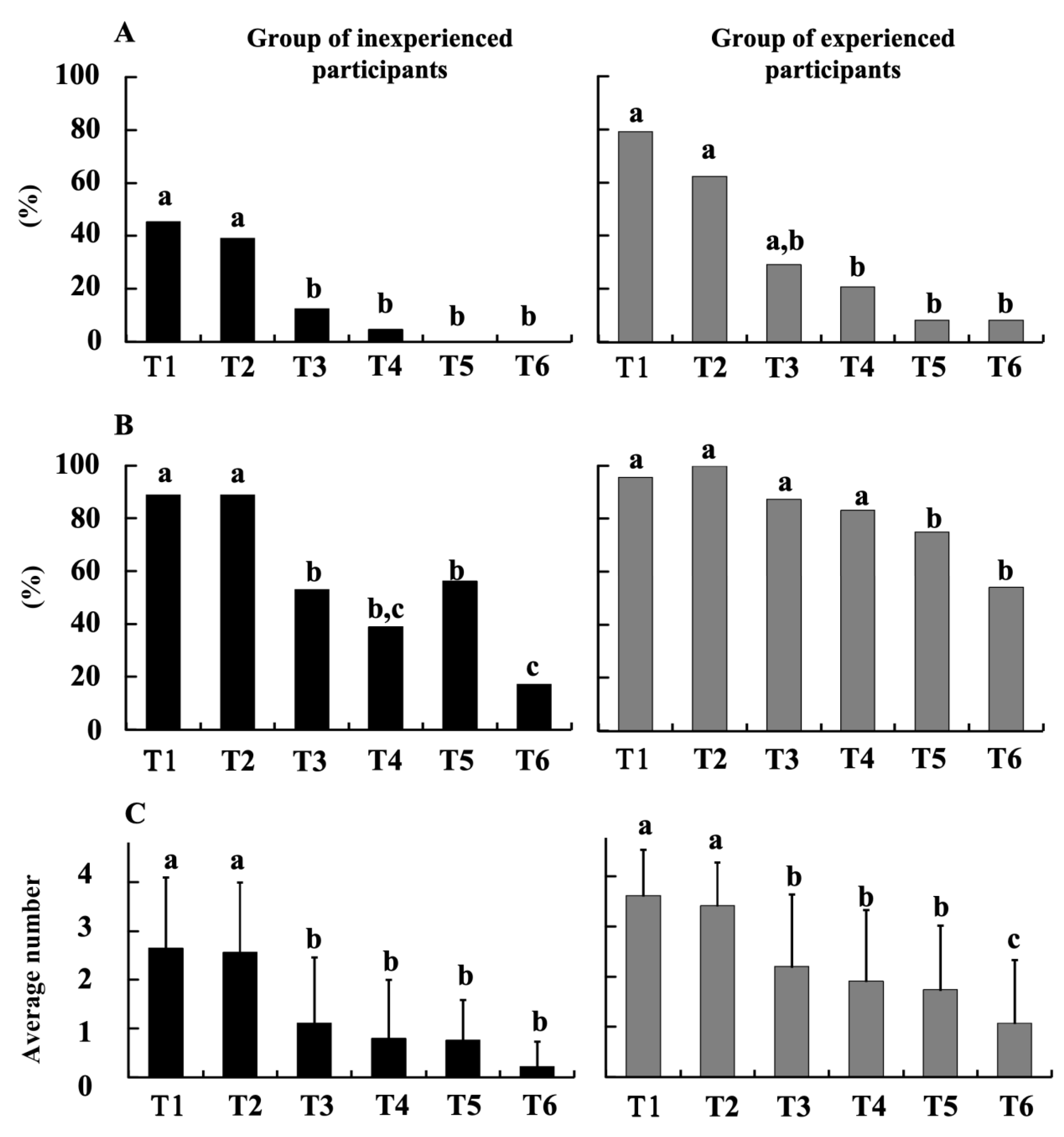
3.1. Comparison of Motions
3.2. Comparison between Six Tasks
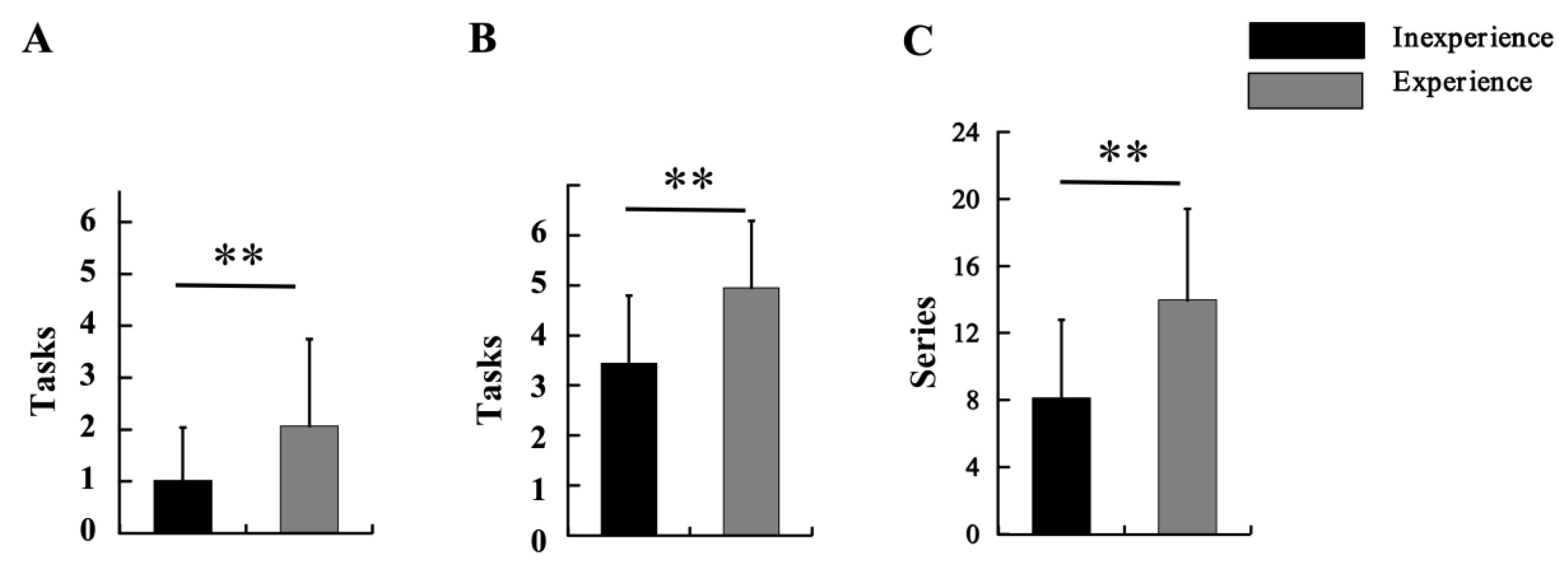
3.3. Comparison of Inexperienced and Experienced Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Motions
4.2. The Difficulty and Characteristics of the Six Tasks
4.3. Validity of the Test
4.4. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vandorpe, B.; Vandendriessche, J.; Vaeyens, R.; Pion, J.; Matthys, S.; Lefevre, J.; …; Lenoir, M. Relationship between sports participation and the level of motor coordination in childhood: A longitudinal approach. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2012, 15, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, J.; Lech, G.; Ambroży, T.; Żak, M. Identification of coordination motor abilities determining the sports skill level in elite male badminton players. Human Movement 2021, 22, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorga, A.; Jianu, A.; Gheorghiu, M.; Crețu, B.D.; Eremia, I.A. Motor Coordination and Its Importance in Practicing Performance Movement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S. Kokannsetsushuhenbuukosetsunorigakuryouhou. Japanese Physical Therapy Association 2012, 39, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin-Lang, A.; Luft, A.R.; Sawaki, L.; Burstein, A.H.; Sohn, Y.H.; Cohen, L.G. Modulation of human corticomotor excitability by somatosensory input. The Journal of physiology 2002, 540, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Rothwell, J.C. Modulation of proprioceptive integration in the motor cortex shapes human motor learning. Journal of Neuroscience 2012, 32, 9000–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, V.P.; Rodrigues, L.P.; Maia, J.A.; Malina, R.M. Motor coordination as predictor of physical activity in childhood. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011, 21, 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- Krasovsky, T.; Levin, M.F. Toward a better understanding of coordination in healthy and poststroke gait. Neurorehabilitation and neural repair 2010, 24, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semjen, A.; Summers, J.J.; Cattaert, D. Hand coordination in bimanual circle drawing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 1995, 21, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, S.P.; Vangheluwe, S.; Wagemans, J.; Coxon, J.P.; Goble, D.J.; Van Impe, A.; …; Wenderoth, N. Shared neural resources between left and right interlimb coordination skills: the neural substrate of abstract motor representations. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 2570–2580. [Google Scholar]
- Candra, O. The contribution of eye-hand coordination to basketball lay up shoot skills. 1st Progress in Social Science, Humanities and Education Research Symposium (PSSHERS 2019); Atlantis Press, August 2020; pp. 864–869. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.H.; Langridge, R.W.; Marotta, J.J. Eye–hand coordination: memory-guided grasping during obstacle avoidance. Experimental brain research 2022, 240, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitrianto, A.T.; Prayoga, H.D. Comparison of physical fitness levels and hand-eye coordination of students aged 10-12 years. Journal Activator 2023, 1, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Suryadi, D.; Suganda, M.A.; Samodra YT, J.; Wati ID, P.; Rubiyatno, R.; Haïdara, Y.; …; Saputra, E. Eye-hand coordination and agility with basketball lay-up skills: A correlation study in students. JUMORA: Jurnal Moderasi Olahraga 2023, 3, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulos, A.; Magill, R.; Gordon, A. Coordination of the upper and lower limbs during walking in children with cerebral palsy. Gait & Posture 2021, 86, 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, Q.; Meng, W.; Ai, Q.; Xie, S.Q. An attention-based cnn-lstm model with limb synergy for joint angles prediction. 2021 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM); IEEE, July 2021; pp. 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Biino, V.; Giustino, V.; Gallotta, M.C.; Bellafiore, M.; Battaglia, G.; Lanza, M.; … Schena, F. Effects of sports experience on children’s gross motor coordination level. Frontiers in Sports and Active Living 2023, 5, 000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, S.; Zaffagnini, S.; Pizza, N.; Grassi, A.; Bragonzoni, L. Poor motor coordination elicits altered lower limb biomechanics in young football (soccer) players: implications for injury prevention through wearable sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trecroci, A.; Cavaggioni, L.; Caccia, R.; Alberti, G. Jump rope training: Balance and motor coordination in preadolescent soccer players. Journal of sports science & medicine 2015, 14, 792. [Google Scholar]
- Boichuk, R.; Iermakov, S.; Kovtsun, V. Influence of motor coordination indicators on efficiency of game activity of volleyball players at the stage of specialized basic training. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H. Cho enryoku toreeningu no sonnzaironn wo tou. Denshou 2007, 7, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tokairin, Y. A study on resistance training for handball teams of high school boys : A case of the champion team of inter-high school athletic championship. The Japan Journal of Coaching Studies 2007, 20, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami, K. Examination of posture evaluation feedback method during lower limb muscle strength training. Journal of Life Support Engineering 2022, 34, 25–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeoka, Y.; Nishimoto, T. Immediate Effects of Short Coordination Training. Kawasaki journal of medical welfare 2020, 30, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kochanowicz, K.; Boraczynska, L.B.; Boraczynski, T. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of motor coordination abilities in gymnast girls aged 7–9 years. Baltic Journal of Health and Physical Activity 2009, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, A.; Tamashiro, Y.; Yonehara, K.; Morita, A. Rehabilitation therapists’ assessment and intervention methods for children needing professional support during after-school day service. Memoirs of Osaka Shin-ai College 2023, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shimura, M.; Kariyama, Y.; Ogata, M. Development of an index for evaluation of rhythm adjustment ability when combining running jumping movements: Focusing on the long jump as performed by elementary school students Jpn. J. Phys. Educ. Health Sport Sci. 2022, 67, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, D.A.; Neagu, N.; Sopa, I.S. Research regarding the development and evaluation of agility (balance, coordination and speed) in children aged 9-10 years. Health, Sports & Rehabilitation Medicine 2020, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wulf, G.; Töllner, T.; Shea, C.H. Attentional focus effects as a function of task difficulty. Research quarterly for exercise and sport 2007, 78, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, Y. Effect of rhythm-trianing on elementary school children’s physcical strength, their exercise capacity, and the number of visit to the school health center. Mimasaka University Departmental Bulletin Pape 2017, 50, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Semjen, A.; Summers, J.J.; Cattaert, D. Hand coordination in bimanual circle drawing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 1995, 21, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R.G.; Thomas, J.; Summers, J.J.; WaltersAndras Semjen, M.R. The dynamics of bimanual circle drawing. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology: Section A 1997, 50, 664–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byblow, W.D.; Summers, J.J.; Semjen, A.; Wuyts, I.J.; Carson, R.G. Spontaneous and intentional pattern switching in a multisegmental bimanual coordination task. Motor control 1999, 3, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temprado, J.J.; Swinnen, S.P.; Carson, R.G.; Tourment, A.; Laurent, M. Interaction of directional, neuromuscular and egocentric constraints on the stability of preferred bimanual coordination patterns. Human movement science 2003, 22, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Muraoka, T.; Kanosue, K. Factors that determine directional constraint in ipsilateral hand–foot coordinated movements. Physiological reports 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Kawashima, S.; Mizuguchi, N.; Kanosue, K. Difference in activity in the supplementary motor area depending on limb combination of hand–foot coordinated movements. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2016, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesen RL, J.; Wenderoth, N.; Temprado, J.J.; Summers, J.J.; Swinnen, S.P. The coalition of constraints during coordination of the ipsilateral and heterolateral limbs. Experimental Brain Research 2006, 174, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, R.; Tokumaru, M. Rhythm correction system for promoting motivation towards exercise. In Proceedings of the 38th Fuzzy System Symposium, Japan Society for Fuzzy Theory and Intelligent Informatics; 2022; pp. 722–727. [Google Scholar]
- Muraoka, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Kato, K.; Qi, W.; Kanosue, K. Interlimb coordination from a psychological perspective. The Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine 2016, 5, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, G.; Lauterbach, B.; Toole, T. Learning benefits of an external focus of attention in golf. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology 1998, 20, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Filoteo, J.V.; Maddox, W.T. Quantitative modeling of visual attention processes in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Effects of stimulus integrality on selective attention and dimensional integration. Neuropsychology 1999, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulf, G.; McNevin, N.H.; Fuchs, T.; Ritter, F.; Toole, T. Attentional focus in complex skill learning. Research quarterly for exercise and sport 2000, 71, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Wulf, G. Golf skill learning: An external focus of attention enhances performance and motivation. Psychology of Sport and Exercise 2024, 70, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva LA, D.; Doyenart, R.; Henrique Salvan, P.; Rodrigues, W.; Felipe Lopes, J.; Gomes, K.; …; Silveira, P. C. Swimming training improves mental health parameters, cognition and motor coordination in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. International journal of environmental health research 2020, 30, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymoshenko, O.; Arefiev, V.; Domina, Z.; Malechko, T.; Bondar, T.; Tymchyk, M.; …; Prontenko, K. Exercise machines in speed and coordination development among students playing basketball. International Journal of Human Movement and Sports Sciences 2021, 9, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, E.; Gerber, M.; Pühse, U.; Vaezmosavi, M.; Brand, S. Combined virtual reality and physical training improved the bimanual coordination of women with multiple sclerosis. Neuropsychological rehabilitation 2021, 31, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Han, J. Muscle strength coordination training for athletes in mountaineering sports. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte 2022, 29, e2022_0289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 | Task 5 | Task 6 | |||||||
| % | % | % | % | % | % | |||||||
| M1-S1 | 100.0 | a | 100.0 | a | 100.0 | a | 100.0 | a | 100.0 | a | 100.0 | a |
| M2-S1 | 96.9 | a | 95.3 | a | 96.9 | a | 92.2 | a | 71.9 | b | 70.3 | b |
| M3-S1 | 98.4 | a | 96.7 | a | 62.9 | b | 47.5 | b | 95.7 | a | 35.6 | b |
| M4-S1 | 77.0 | a | 86.4 | a | 82.1 | a | 78.6 | a | 79.5 | a | 75.0 | a |
| M1-S2 | 100.0 | a | 88.2 | a | 90.6 | a | 100.0 | a | 31.4 | b | 33.3 | b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





