1. Introduction
Functional neurological disorder (FND) is a complex condition at the intersection of neurology and psychiatry, involving a dynamic interplay between body and mind (Hallett et al., 2022). A key explanation is the Bayesian model (Edwards et al., 2012), which describes perception as a process of combining prior expectations and sensory input to minimize prediction errors. FND symptoms arise when these prediction errors are not properly updated, leading to dysfunction. Abnormal, highly weighted prior expectations, influenced by attention, are central to this process. Empirical evidence supports this model, such as studies on predictive processing abnormalities in functional gait disorder. Functional movement disorders (FMD) are movement abnormalities altered by distraction or non-physiologic maneuvers, distinct from neurologic disease-related movement disorders. They are a subset of functional neurologic disorders, which are common in neurology, accounting for 15% of new referrals, second only to headaches. Despite their prevalence, FMDs have a poor prognosis, with 39% of patients remaining the same or worsening over time, often experiencing high physical disability and psychological issues (Pringsheim and Edwards, 2017). These disorders present a clinical paradox: while the movements appear voluntary, patients experience them as involuntary and uncontrollable. The prevalence of FMD in neurology clinics underscores the need for effective therapeutic interventions to address the significant disability associated with these disorders. Recent research has highlighted the role of sensory attenuation and the sense of agency in the pathophysiology of FMD (Pringsheim and Edwards, 2017). Sensory attenuation refers to the brain’s ability to predict the sensory consequences of voluntary movement, i.e., efference copy, that suppress the actual sensory feedback, i.e., reafference, a process that is crucial for distinguishing self-produced sensations from external stimuli. This predictive mechanism (Wolpert and Ghahramani, 2000) is where a duplicate of the motor command, known as an efference copy, is sent to a forward model that integrates the efference copy with an estimate of the body’s state to predict the sensory consequences of the movement. This predictive mechanism is impaired in FMD patients (Pareés et al., 2014) leading to a reduced ability to predict the sensory consequences thereby leading to a reduced sense of agency over their self-generated movement. This reduced sense of agency could explain why these patients perceive their movements as involuntary despite their voluntary appearance (Brown et al., 2013). Sensory attenuation process is primarily mediated by forward models within the motor control system (Wolpert and Ghahramani, 2000), which predict the sensory consequences of an action and modulate the sensory response accordingly (Hughes et al., 2013). When an action is self-generated, the forward model predicts the resulting sensory input and attenuates the sensory experience to prevent self-caused sensations from interfering with the processing of external stimuli. Sensory attenuation can be measured using the force matching task, where participants match a force applied to their finger either directly using their opposite hand (direct condition) or indirectly using a potentiometer and a torque motor (slider condition) (McNaughton et al., 2023). Healthy individuals typically overestimate the force in the direct condition, producing greater matched force due to sensory attenuation. This phenomenon is reduced in individuals with schizophrenia and FMD, potentially due to altered predictive mechanisms affecting their sense of agency (McNaughton et al., 2023).
The force-matching task needs a well-designed haptics device following transparent methodological considerations (McNaughton et al., 2023) that can be combined with brain imaging for brain-behavior analysis. Primary motor cortex (M1) is involved in the execution of voluntary movements as well as plays a critical role in sensory attenuation process (Voss et al., 2007). Using theta-burst stimulation (TBS) approach, Voss et. al. (Voss et al., 2007) applied continuous TBS (cTBS) and intermittent TBS (iTBS) over M1 to alter its excitability. They found that cTBS, which decreases cortical excitability, reduced sensory attenuation and improved performance in a force-matching task, suggesting a disruption in the predictive process using efference copy signals. In contrast, iTBS had no effect on sensory attenuation. Then, the cerebellum is crucial for fine-tuning motor actions and predicting their sensory consequences (Blakemore et al., 2001). The study by Blakemore et al. (Blakemore et al., 2001) demonstrated that the cerebellum predicts sensory outcomes of motor actions and signal discrepancies between expected and actual (reafferent) sensory feedback. PET scans of participants performing a delayed tactile task showed increased cerebellar activity with longer delays, confirming its role in fine-tuning motor actions and motor learning by comparing intended and achieved movements. The thalamus is a subcortical structure that acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals (Sherman and Guillery, 2006). Thalamus exhibits reduced activity during self-generated sensations, indicating its involvement in sensory attenuation process (Hua et al., 2023). Hua et al. applied dynamic causal modelling (DCM) analysis that indicated top-down modulation from the right inferior parietal lobe during sensory attenuation of auditory stimulus. Here, sensory attenuation is evident not only in somatosensory domains but also in auditory and visual modalities. For instance, self-generated sounds and visual stimuli are perceived as less intense compared to externally generated ones, highlighting the broad applicability of sensory attenuation mechanisms across different sensory modalities. In FMDs, there is a notable disruption in sensory attenuation, leading to a diminished sense of agency and control over self-generated movements (Maurer et al., 2016). The comparator model posits that self-agency depends on monitoring if an action’s outcomes match predictions. The right temporo-parietal junction (rTPJ) acts as a mismatch detector, comparing predicted movements with actual feedback. The coordinates of the mean peak of activity in the TPJ have varied across studies (Zito et al., 2020), showing activation in the angular gyrus, middle temporal gyrus, parietal operculum, and supramarginal gyrus. This variation reflects the multidimensional processes contributing to the sense of agency, such as mismatch detection, action awareness, and sensory-motor conflicts. The angular gyrus is involved in inter-sensory mismatch detection, action awareness, and multisensory integration, while the supramarginal gyrus processes sensory-motor conflicts. Changes in perspective, mentalizing, and deception specifically activate the TPJ and posterior superior temporal sulcus, highlighting the role of perspective in assigning motor actions to oneself or others. Overall, different neural mechanisms and specific brain areas within the TPJ contribute to the formation of agency when motor control is disrupted. Functional neuroimaging has shown reduced activity and impaired connectivity of the rTPJ during functional tremor, indicating that altered rTPJ connectivity may contribute to impaired self-agency to be tested via intentional binding (motor intention is temporally matched with sensory feedback (Kühn et al., 2013)) and sensory attenuation paradigms (Maurer et al., 2016). Maurer et. al. (Maurer et al., 2016) found decreased functional connectivity in patients with FMD between the rTPJ, crucial for self-agency, and bilateral sensorimotor regions, including the right sensorimotor cortex, bilateral cerebellum, bilateral supplementary motor area (SMA), and right insula.
In contrast to sensory attenuation, sensory amplification occurs when the perceived intensity of a sensory stimulus is enhanced due to the influence of selective attention (Hillyard et al., 1998) e.g., following error commission (Maier et al., 2011). This effect is particularly noticeable when an individual directs their visual attention to a specific touch event, thereby increasing the perceived intensity of the touch. This phenomenon is related to the visual enhancement of touch effect, where simply viewing a body part can improve tactile acuity for that part. Frontal and parietal cortices are involved in the modulation of sensory precision by attention that involves neural hierarchies (Hillyard et al., 1998). Increased activity in the posterior parietal cortex is associated with enhanced sensory perception when visual attention is directed towards a stimulus, supporting the idea of optimizing sensory precision through attention. Empirical studies have shown that visual attention to a touch event, whether active or passive, amplifies the perceived intensity of the touch. This sensory amplification effect is significantly larger than the sensory attenuation effect, underscoring the powerful influence of attention on sensory perception. Overall, the interplay between sensory attenuation and amplification highlights the complex nature of sensory processing, where the brain dynamically adjusts the perceived intensity of stimuli based on predictive models and attentional focus (Hillyard et al., 1998),(Hughes et al., 2013). Understanding these mechanisms provides valuable insights into how sensory experiences are modulated in various contexts, including during the observation of others’ actions and in conditions involving altered sensory processing, such as FMD (Pareés et al., 2014). We aim to utilize the interplay between sensory attenuation and amplification through an operant conditioning approach, which has demonstrated potential as a therapeutic method for addressing learned non-use, believed to result from a maladaptive forward model, in individuals with chronic stroke (Kumar et al., 2019). This behavioral technique involves reinforcing desired motor behaviors through visual feedback, thereby encouraging patients to regain control over their movements by visual attention and sensory amplification. Kumar et al. (Kumar et al., 2019) showed the feasibility of the virtual reality (VR)-based balance training system that used operant conditioning by re-weighting feedback (Dutta et al., 2014) of the center of pressure from each limb to encourage hemiplegic stroke patients to use their paretic leg more during weight-shifting tasks. The system adjusted the weight given to the paretic leg during normal trials, rewarding increased use with better performance scores and motivational feedback. Intermediate catch trials provided unbiased measures of standing balance capability. Our approach incorporated individualized weight distribution, VR tasks, and subtle reinforcement mechanisms, including suggestions as an operant factor that influences behavior (Turner and Chapman, 1982). This method effectively promoted the use of the paretic leg, addressing learned nonuse and improving overall balance in the stroke patients (Kumar et al., 2019).
2. Hypothesis for Operant Conditioning Sense of Agency in FMD
Sensory attenuation refers to the brain’s ability to reduce the perceived intensity of sensory inputs resulting from self-generated actions compared to externally generated ones. This mechanism is critical for differentiating between self and non-self-actions, thereby contributing to the sense of agency and control during motor tasks. Following Maurer et al. (Maurer et al., 2016) study on impaired self-agency, we propose portable functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) brain imaging (Kamat et al., 2022) of intentional binding and sensory attenuation paradigms of task-specific functional connectivity (FC) between the rTPJ and the sensorimotor cortex to test any disrupted sensory feedback signaling in FMD. Additionally, any decreased FC between the rTPJ and the SMA, which contributes to intentional binding, may also impair the sense of agency in these patients. Then, the postulated information flow model for sense of agency (Nahab et al., 2011) involves a leading network for mismatch detection, including the right supramarginal gyrus, left anterior inferior parietal lobule (IPL), anterior insula, and rTPJ. Mismatch information is relayed through intermediate areas before reaching the lagging network, which includes bilateral prefrontal cortex (PFC), cingulate, and bilateral posterior IPL. The PFC’s role in the lagging network suggests its later involvement in sense of agency processing. Our hypothesis for operant conditioning sense of agency processing in FMD is based on our prior brain-behavior research on motor learning (Walia et al., 2022) where successful skill acquisition involves creating an internal forward model that predicts the perceptual outcomes of motor commands, relying heavily on the cerebellum for error-based learning. Other brain areas involved include the parietal cortex, striatum, and anterior cingulate cortex. Skill learning progresses along the frontal lobe’s rostro caudal axis, with the dorsolateral PFC aiding visual guidance in novices and the ventrolateral PFC assisting recognition in experts. The SMA and premotor cortex are key for coordinating complex movements, while the medial frontal cortex, including the anterior portions of the cingulate gyrus, is central to performance monitoring and cognitive flexibility. Error-related cortical activation and corrective action, crucial for operant conditioning, can be enhanced with non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) and explicit error feedback, aiding skill learning and rehabilitation. For example, subjects may lack error perception in the lagging network (Nahab et al., 2011) leading to low medial frontal cortex activation disrupting skill learning (Walia et al., 2022). Here, electroencephalogram (EEG) topography in conjunction with fNIRS can guide subject-specific motor control interventions to improve perception and action integration via intentional binding in virtual reality (Kumar et al., 2019) that is postulated to be feasible for FMD rehabilitation.
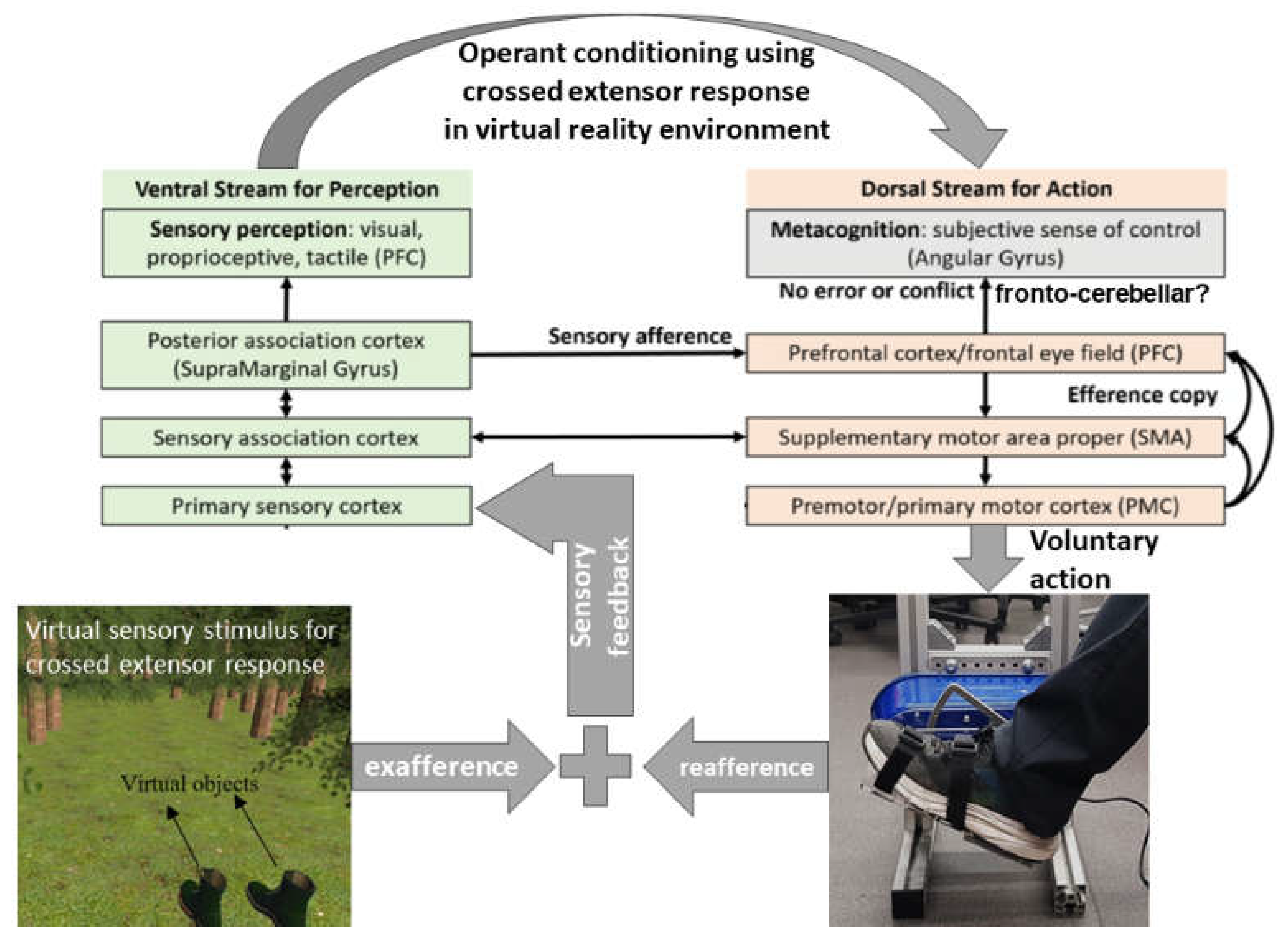
Prior studies on intentional binding (Moore et al., 2012) suggest that repeated operant experience can strengthen associations automatically, linking it to lower-level implicit aspects of the sense of agency through automatic associative learning. This finding also highlighted a distinction between implicit and explicit aspects of the sense of agency. Here, the conscious expectancy in an explicit sense of agency can be developed by showing patients with functional motor symptoms their physical signs such as Hoover sign or tremor entrainment (Stone and Edwards, 2012). Then, automatic link formation in associative learning in an implicit sense of agency can be developed via repeated operant experience (Kumar et al., 2019). While implicit and explicit aspects of the sense of agency are separable, they interact through top-down and bottom-up mechanisms (Moore et al., 2012) that can be artificially modulated in the virtual reality (VR) through exafference – see
Figure 1. Therefore, VR with exafference in an augmented reality setting holds significant potential for advancing the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of FMD. The recent review by Brouwer et al. (Brouwer et al., 2024) highlighted how VR can be utilized to explore neurocognitive mechanisms, such as sense of agency, attention, and suggestibility, and proposed VR-based interventions that could offer novel therapeutic avenues. The premise is that VR can manipulate and study predictive coding abnormalities to uncover the mechanisms of FMD where the key concepts include attention, sense of agency, and suggestibility.
3. Human Machine Interface for Testing and Operant Conditioning Sense of Agency in FMD
To better understand the neural mechanisms underlying the sense of control during motor tasks, analyzing directed information flow using fNIRS-EEG can provide insights (Kamat et al., 2022),(Walia et al., 2022). Directed information flow analysis can reveal how different brain regions communicate and how this communication is altered in FMDs. This technique can help identify specific disruptions in the sensory-motor integration processes e.g., disrupted sensory feedback signaling (rTPJ and sensorimotor cortex) and intentional binding (rTPJ and SMA). The force-matching task utilizes a specialized haptic ankle device (HRX-1, Humanrobotix Ltd., London, UK)(Otaran and Farkhatdinov, 2022) that includes a high-precision torque sensor and a motor system to deliver controlled torques. Participants are required to match a target force applied to their affected leg under two conditions: Direct and Indirect. Perceptual noise distorts the participant’s tactile perception of both the target force and the matching force. Furthermore, once the participant feels the target force, they need to remember that sensation for comparison with the matching force. This memory process can introduce variability and bias. In the Direct condition, an efference copy from the active leg predicts the tactile sensation resulting in an attenuated sensation in neurotypical controls. In the Indirect condition, where the relationship is unnatural, the sensation is not attenuated in neurotypical controls.
Condition Direct: Participants use their leg to apply directly on the haptic ankle device to match the target torque – see
Figure 1. This condition involves self-generated force, which typically leads to sensory attenuation, resulting in an overestimation of the required torque in neurotypical controls.
Condition Indirect: Participants use an ankle goniometer on one leg to control the motor in the haptic ankle device that applies the ankle torque to their other leg. This condition removes direct tactile feedback, leading to a more accurate torque estimation as it reduces sensory attenuation.
A human-machine interface using a haptic ankle device (HRX-1, Humanrobotix Ltd., London, UK)(Otaran and Farkhatdinov, 2022) is proposed in this paper for operant conditioning in FMD leveraging the force-matching task paradigm (McNaughton et al., 2023). In this task, individuals are asked to match a force applied to their effector, either directly using their own effector or indirectly using a device. Healthy individuals typically overestimate the force in the direct condition due to sensory attenuation, whereas this effect is diminished or absent in FMD patients (Pareés et al., 2014). This finding indicates a fundamental disruption in the predictive mechanisms that underpin motor control in FMD. Here, motor learning is proposed (Sugiyama et al., 2023) that involves the continuous updating and refining of these internal models. As individuals perform motor tasks, they generate motor commands and compare the predicted sensory outcomes with the actual sensory feedback received (reafferent feedback). Discrepancies between the predicted and actual feedback are used to update the internal models, improving the accuracy of future predictions. Therefore, combining operant conditioning with modern technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and haptic feedback offers a novel and potentially more effective intervention (Dutta et al., 2014). Based on our prior works (Kumar et al., 2019),(Dutta et al., 2014), we will use a bipedal reaching VR task where foot position on a haptic ankle device is represented by a VR object (see
Figure 1). Initially, higher gain will be given to the unaffected limb, shifting to the affected limb as its involvement increases. To investigate motor-related processing, we will occasionally perturb the VR object introducing errors during a rewarding biped reaching task against haptic virtual spring by changing either the visual feedback of the position or the virtual spring stiffness i.e., the exafference in the VR haptic ankle device. Motor responses to such perturbations are postulated to be automatic and cannot be voluntarily suppressed (Franklin and Wolpert, 2008). The strength of feedback correction thus will serve as a sensitive measure of visuomotor control (Franklin and Wolpert, 2011). The primary motor cortex is involved in both fast feedback responses and feedforward control (Franklin and Wolpert, 2011) and the same neural circuitry handles both processes, highlighting the importance of feedback modulation in sensorimotor control. Operant conditioning in VR (Kumar et al., 2019) aims to recruit neural structures responsible for motor control without conscious interaction; however, it remains unclear whether the sensory information originates from local pathways within the motor cortex or from other structures like the cerebellum or somatosensory areas since we did not perform brain imaging in our prior work (Kumar et al., 2019).
Neuroimaging techniques, particularly functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and electroencephalography (EEG), can be employed to monitor brain activity and assess the effectiveness of these interventions. Macerollo et al. (Macerollo et al., 2015) examined sensory attenuation in patients with FMD by comparing sensory evoked potentials (SEPs) at rest and during self-paced movement. Seventeen patients with FMD and seventeen healthy controls participated. The results showed that healthy controls exhibited significant sensory attenuation, marked by reduced SEPs amplitude (N30 at frontal electrode and N20 at central and parietal electrodes) during movement, whereas FMD patients did not, indicating impaired sensory attenuation. This lack of sensory attenuation in FMD patients suggests a disrupted sense of agency for movement. A neuroimaging meta-analysis study (Zito et al., 2020) explored the neural mechanisms underlying the sense of agency during motor control. Through a comprehensive meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies, the paper identifies key brain regions that included the SMA, premotor cortex (PMC), parietal lobes, and insula. The study highlights that the integration of motor and sensory information is crucial for predicting the sensory consequences of actions, which contributes to the sense of agency with the rTPJ confirmed to play a crucial role in detecting sensory-motor discrepancies. The analysis also underscored the importance of the motor system areas (ventral premotor cortex, supplementary motor areas, and cerebellum) and cognitive regions (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, posterior parietal cortex, and insula) in sense of agency processing. Here, fNIRS measures changes in cortical oxygenation and can provide insights into the neural mechanisms underlying sense of agency in motor control (Kamat et al., 2022). Fusing fNIRS with EEG provides a comprehensive wearable approach to studying brain function by combining the high temporal resolution of EEG with the better spatial resolution of fNIRS (Li et al., 2022). This multi-modal integration (Walia et al., 2022) enhances the monitoring of neural and hemodynamic responses, improves signal interpretation, and reduces artifacts. It also enables detailed functional connectivity analysis and is versatile for point of care applications (Kamat et al., 2022).
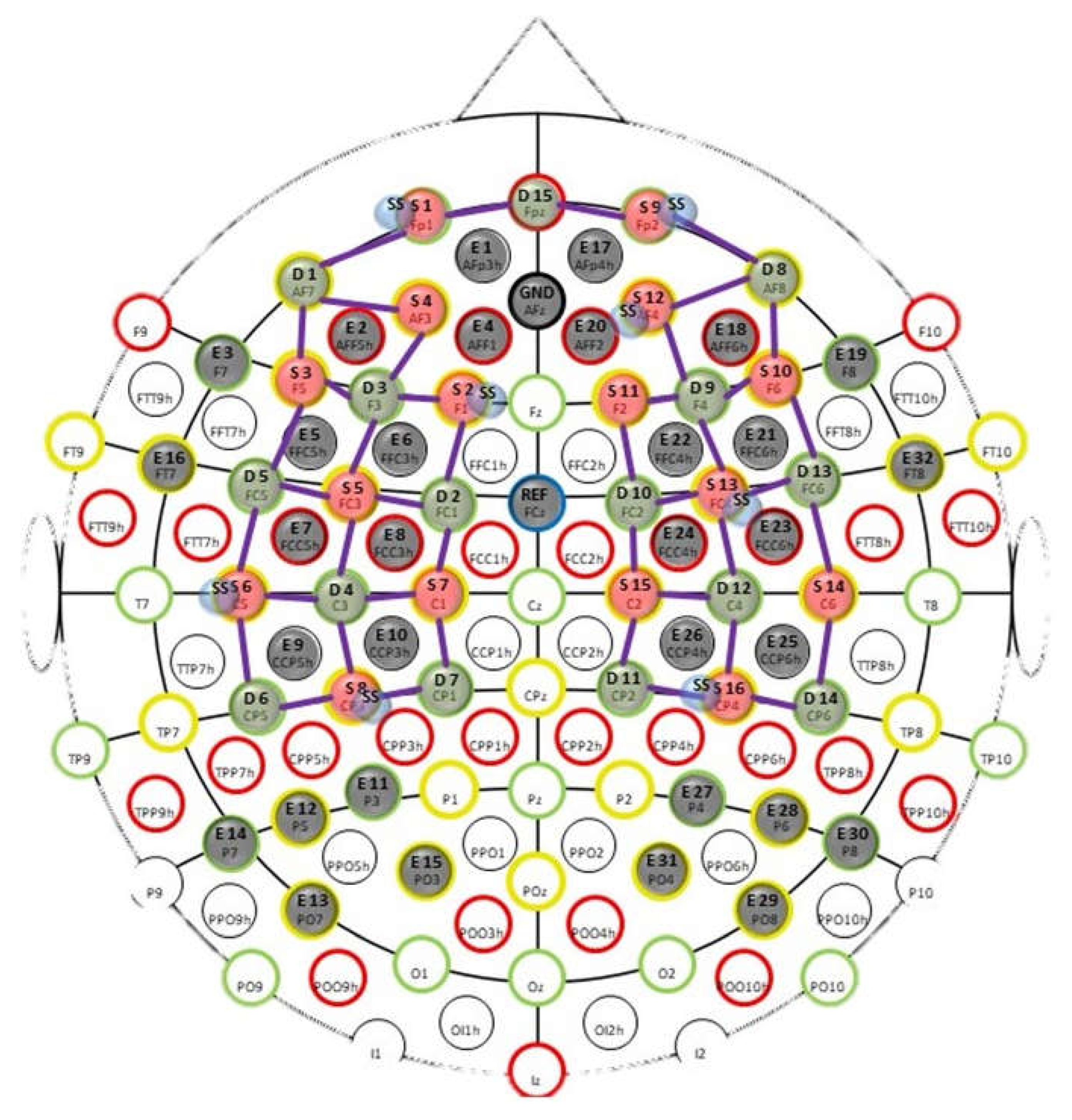
Figure 2 shows the fNIRS-EEG montage from our related study on error-related brain state analysis (Walia et al., 2022). A customized setup consisting of EEG electrodes and fNIRS optodes was employed to record synchronized multimodal brain activation signals. 32-channel EEG signals were recorded using a wireless LiveAmp system (Brain Vision, USA) at 500 Hz with active gel-electrodes. Simultaneously, 32-channel fNIRS signals and 8-channel short-separation channels were recorded at a 5 Hz sampling rate using NIRSPORT2 (NIRx, USA). A 1 Hz hardware trigger synchronized the fNIRS and EEG data, which were aligned and segmented into 1-second epochs. The optical probes and electrodes were positioned according to the standard 10-5 montage – see
Figure 1. Probes were placed carefully to avoid hair interference and not restrict the subject’s mobility during the study. The simultaneously recorded EEG and fNIRS signals were preprocessed and analyzed offline. EEG signals were processed using the open-source EEGlab toolbox (Delorme and Makeig, 2004) for microstate analysis (Poulsen et al., 2018). Data were down sampled to 250 Hz, high pass filtered at 1 Hz, and cleaned of line noise using the ‘cleanline’ function. Bad channels were rejected with the ‘clean_rawdata’ function and interpolated using spherical splines, followed by re-referencing to the global average. Artifact Subspace Reconstruction (ASR) was performed to remove transient EEG artifacts, using a default parameter value of 20 for optimal balance between removing non-brain signals and retaining brain activities. Preprocessed EEG data were used for microstate analysis. A Laplacian spatial filter removed volume conduction from subcortical sources while preserving cortical sources postulated to correspond with the hemodynamic response measured with fNIRS. fNIRS data were processed using the HOMER3 package (Huppert et al., 2009), involving conversion to optical density, motion artifact detection and filtering with the Savitzky-Golay method, bandpass filtering (0.01-0.1 Hz), and conversion to HbO concentration. Microstate analysis performed using the EEGlab toolbox, aggregated EEG data from the motor task. EEG microstate prototypes were identified using modified K-means clustering based on the global field power (GFP). The prototypes were extracted with a high signal-to-noise ratio and clustered topographically. Hierarchical clustering methods delivered similar performance, but modified K-means was chosen based on the goodness of fit determined by global explained variance (GEV) and cross-validation (CV) criteria. Microstate labels were applied to EEG samples based on topographical similarity (‘backfitting’) to quantify dynamic brain states during task initiation and error epochs. Error epochs, defined as the 10 seconds following error commission, captured the hemodynamic response corresponding to EEG band power changes. Statistical properties of EEG microstates, including GFP, GEV, spatial correlation, occurrence, duration, and coverage, were computed to compare error-related cortical activations. Correspondence between fNIRS HbO changes and EEG band power changes was determined using the General Linear Model (GLM) and regularized Canonical Correlation Analysis with temporal embedding in HOMER3. The design matrix included all regressors for GLM, solved with least-squares for each regressor’s contribution. Short separation fNIRS channels served as nuisance regressors for systemic artifacts. The HbO response was reconstructed from multi-channel EEG band power signals using selected regressors with high canonical correlation. The hemodynamic response (HbO) during the motor task and error epochs (due to perturbations here) analyzed using t-tests for each fNIRS channel controlling for false discovery rate (FDR). Visualization of HbO responses performed using AtlasViewer (Aasted et al., 2015). The duration of backfitted microstates during task and error epochs can be analyzed with a two-way ANOVA, considering microstate types, after testing for normality with the Shapiro-Wilk Test.
4. Discussion
Our proposed model integrates concepts from cognitive neuroscience regarding how actions are controlled and monitored by the brain, including the role of expectations and feedback in shaping behavior. The model illustrates the closed-loop control system of motor function, emphasizing the role of corollary discharge and efferent copy mechanisms, potentially observable through fNIRS (Kamat et al., 2022) during such therapeutic interventions. Our hypothesis suggests that in cases of FMD, while the brain’s controller functions (Brain as Controller) remain operational, the issue may lie within its observational capabilities (Brain as Observer) that can lead to ‘feedback decoupling’ (Boven et al., 2023). Bayesian state estimation is a crucial methodology for predicting hidden dynamic states, which can be used to model the Brain as Observer. The process sequentially constructs a posterior probability density function (PDF) of the state, considering all sensor observations. It predicts a state from the state transition model and refines it using the sensor observation model. The Kalman filter (Kalman, 1960), introduced by R.E. Kalman in 1960, is a prominent Bayesian filtering strategy that analytically estimates the state to minimize the estimation error, making it theoretically optimal for linear Gaussian models. Despite its limitation to linear Gaussian models, the Kalman filter remains prevalent in state estimation applications, including physiological model (Paulin, 1989). Here, Bayesian models are heralded as normative constructs that articulate the optimal actions an agent should take considering specific observations and objectives. Concurrently, they are recognized as process models that elucidate the internal representations and procedural pathways an observer might undertake in response to sensory input (Bayesian Models of Perception and Action, n.d.). In the book (Bayesian Models of Perception and Action, n.d.), Ma, Kording, and Goldreich explore the intricate ways in which our brain harnesses noisy and ambiguous sensory data, apply probabilistic reasoning, and generate interpretations of our environment that inform our decisions. The book (Bayesian Models of Perception and Action, n.d.) delves into perception as a multifaceted problem of inference. It posits that the brain’s interpretive function in deciphering sensory inputs is not a straightforward task but one fraught with uncertainty and multiple possible outcomes that may go awry, e.g., in FND (Edwards et al., 2012). Even with high-quality sensory feedback, ambiguity remains, prompting the necessity for a probabilistic framework—namely Bayesian inference—to navigate the labyrinth of potential world states. This framework is not merely an abstract concept; it is grounded in empirical evidence, underpinning many observed behaviors in experimental settings (Körding and Wolpert, 2006).
Multiple mathematical interpretations of the Kalman filter exist, ranging from least square estimation to minimum variance estimation under Gaussian assumptions to minimize mean square error (MSE) in estimations. Its foundational principles are based on least squares estimation and have been adapted for sequential estimation problems (Kalman, 1960), e.g., in recursive application of Bayesian prediction and correction that optimizes the estimated error covariance during trial-by-trial error correction (Dutta et al., 2014),(Porrill et al., 2013). Here, we formulate the theoretical underpinnings for a discrete-time state-space model based upon the methodology of Bayesian state estimation. The evolving state of a system at any discrete time point
, symbolized by
, is indicative of the system’s dynamic properties such as position and velocity in case of center of pressure (Dutta et al., 2014). This state is a function of a Markovian process:
Here,
represents a Markov function detailing the state’s progression from time
to
, and
is the noise associated with this transition. The observation of this state,
, arises from an observation model and is formulated as:
where
denotes the observation function, and
is the observational noise.
The objective of Bayesian state estimation is to sequentially deduce the probability density function (PDF) of the hidden state conditioned upon all sensor data up to that point:
At any discrete timestep , the goal is to compute the posterior PDF .
Bayesian filtering posits that if the PDF at time
,
, is known, the PDF at time
,
, can be determined through the equation:
This follows the Bayesian paradigm where the state estimation is a two-step process of prediction and update. If posterior PDF at a discrete time point is accessible, then the predicted PDF at a discrete time point is computed as an integral of the joint probability of previous state PDF, and state transition PDF, , with the assumption that is conditionally independent of given . Then, the updated posterior PDF (called the Belief) at a discrete time point is derived using Bayes’ theorem, relating the measurement or observation likelihood PDF at that time point to the predicted state PDF (called the Prior or Expectation) at that time point , normalized by the evidence PDF at that time point (Körding and Wolpert, 2006),(Körding, 2007).
The Kalman filter comes into play when assuming Gaussian PDFs in the Bayesian framework for linear state-space models (Barker et al., 1995). Under these conditions, the filter, recognized as a minimum mean square error estimator, provides an optimal solution by striking a balance between the prediction and the measurement, modulated by a factor known as the Kalman gain – see
Figure 2. Given the Gaussian assumptions, the Kalman filter iterations project the mean and covariance of the system’s state forward in time. Specifically, if the covariance
and expectation
at a discrete time point
are known, one can predict the state’s mean and covariance at next discrete time point
using the state transition and control matrices, as well as the associated noise characteristics. Therefore, the Kalman filter presents an optimal estimator for linear Gaussian models, elegantly solving for the PDFs and offering a practical approach to Bayesian state estimation (Barker et al., 1995).
In our previous research on an operant approach to post-stroke balance rehabilitation (Kumar et al., 2019), we modified the visual biofeedback related to the outcomes of actions to motivate individuals to better utilize their weaker leg while performing weight-shifting activities. This strategy to modulate the prediction error of the weaker leg using a human machine interface could help tackle the problem of acquired disuse of the affected leg in stroke survivors. Then, VR environment (Kumar et al., 2019) via suggestions modulated the motivation likely via basal ganglia circuit (Ikemoto et al., 2015) to facilitate the learning rate (which may not always be optimal Kalman gain (Beers, 2012))(Herz et al., 2022). Here, neural regulation of vigor is known to be partially influenced by structures within the basal ganglia (Yoon et al., 2018) while cerebellum creates predictions about cerebral feedback based on the activity in the cerebrum, utilizing error signals from the inferior olive for learning, i.e., the involvement of the Cortico-Basal Ganglia-Cerebellar Network (Doya, 1999),(Bostan et al., 2010). However, in case of ‘feedback decoupling’ (Boven et al., 2023), which is postulated in case of functional motor disorders, if the action feedback is not accessible; then, the cerebellum relies on its own predictions for learning. In such situations, the inferior olive evaluates previous predictions made by the cerebellum against the latest ones to produce signals that facilitate cerebellar learning via action imagery (Miall, 2024) without real motor action. Therefore, if the sense of control guiding the higher-level cerebral executive functions or the anticipated motor states influencing the cerebral sensorimotor regions are not functioning properly, it is suggested that the suggestion and motor imagery (Apelian et al., 2023) (non-invasive brain stimulation in low suggestibility individuals (Faerman et al., 2024)) for top-down facilitation be integrated with the bottom-up adjustment of prediction errors through the use of motor-imagery driven human-machine interfaces.
FMD rehabilitation starting with the action imagery suggests the use of mental practice to prepare and simulate motor actions, drawing on internal models of action stored in the brain, potentially within structures like the cerebellum. This imagery may predict states of the body that can be compared with actual states for error correction, contributing to motor learning. Then, motor action represents the actual execution of movement. The process begins with a top-down intent from the prefrontal cortex, which serves as an executive control center, and translates into motor commands in the sensorimotor cortices. The motor plant, likely the musculoskeletal system, then carries out the command, with the resulting action being fed back to the ‘Brain as Controller,’ possibly through the parietal cortex as multi-sensory integrator. The influence of operant conditioning methods, which modulate the consequences of actions to shape future behaviors can be applied through human-machine interfaces, providing external feedback (exafference) that can enhance the learning process. A Kalman filter process, a mathematical algorithm of ‘Brain as Observer,’ used for estimating body and environment states over time. In our context, the Kalman filter process might be used to continuously refine predictions about the state of the motor system by integrating new sensory information and correcting for any differences between predicted and actual motor output. The Kalman gain, typically computed in such filtering, optimizes the estimation process, and may here be related to brain structures like the basal ganglia for setting the learning rate. Overall, this framework implies a closed-loop system where the brain predicts, executes, and then learns from actions, adjusting future predictions and actions based on feedback from both internal and external sources. This kind of model could be useful to understand the effects of operant conditioning where VR suggestion is postulated to affect the executive control center while the motor imagery is postulated to affect the action imagery part at the initial stages of rehabilitation.
Author Contributions
AnD: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Project administration; AbD: Writing – review & editing.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available upon request. Researchers interested in accessing the data should contact the corresponding author. Data will be shared in accordance with relevant data protection and privacy regulations and may require a data use agreement.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Farkhatdinov for renting the HRX-1 haptic platform (
https://www.humanrobotix.co.uk/) for our bench testing, funded by pump-priming funding by the school of engineering at the University of Lincoln. Additionally, Dr. Dutta’s summer intern, Takahiro Manabe, funded by pump-priming funding by the school of engineering at the University of Lincoln interfaced the HRX-1 in collaboration with Dr. Buchanan from Nudge Reality (
https://nudgereality.com/) for bench testing that is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Aasted, C. M. , Yücel, M. A., Cooper, R. J., Dubb, J., Tsuzuki, D., Becerra, L., et al. (2015). Anatomical guidance for functional near-infrared spectroscopy: AtlasViewer tutorial. Neurophotonics 2. [CrossRef]
- Apelian, C., De Vignemont, F., and Terhune, D. B. (2023). Comparative effects of hypnotic suggestion and imagery instruction on bodily awareness. Consciousness and Cognition 108, 103473. [CrossRef]
- Barker, A. L. , Brown, D. E., and Martin, W. N. (1995). Bayesian estimation and the Kalman filter. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 30, 55–77. [CrossRef]
- Bayesian Models of Perception and Action (n.d.). MIT Press. Available at: https://mitpress.mit.edu/9780262047593/bayesian-models-of-perception-and-action/. (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Beers, R. J. van (2012). How Does Our Motor System Determine Its Learning Rate? PLOS ONE 7, e49373. [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, S. J., Frith, C. D., and Wolpert, D. M. (2001). The cerebellum is involved in predicting the sensory consequences of action. Neuroreport 12, 1879–1884. [CrossRef]
- Bostan, A. C., Dum, R. P., and Strick, P. L. (2010). The basal ganglia communicate with the cerebellum. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107, 8452–8456. [CrossRef]
- Boven, E. , Pemberton, J., Chadderton, P., Apps, R., and Costa, R. P. (2023). Cerebro-cerebellar networks facilitate learning through feedback decoupling. Nat Commun 14, 51. [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, D. , Morrin, H., Nicholson, T. R., Terhune, D. B., Schrijnemaekers, M., Edwards, M. J., et al. (2024). Virtual reality in functional neurological disorder: a theoretical framework and research agenda for use in the real world. BMJ Neurology Open 6, e000622. [CrossRef]
- Brown, H., Adams, R. A., Parees, I., Edwards, M., and Friston, K. (2013). Active inference, sensory attenuation and illusions. Cogn Process 14, 411–427. [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A. , and Makeig, S. (2004). EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 134, 9–21. [CrossRef]
- Doya, K. (1999). What are the computations of the cerebellum, the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex? Neural Networks 12, 961–974. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A. , Lahiri, U., Das, A., Nitsche, M. A., and Guiraud, D. (2014). Post-stroke balance rehabilitation under multi-level electrotherapy: a conceptual review. Front Neurosci 8. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M. J. , Adams, R. A., Brown, H., Parees, I., and Friston, K. J. (2012). A Bayesian account of ‘hysteria.’ Brain 135, 3495–3512.
- Faerman, A. , Bishop, J. H., Stimpson, K. H., Phillips, A., Gülser, M., Amin, H., et al. (2024). Stanford Hypnosis Integrated with Functional Connectivity-targeted Transcranial Stimulation (SHIFT): a preregistered randomized controlled trial. Nat. Mental Health 2, 96–103. [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D. W. , and Wolpert, D. M. (2008). Specificity of Reflex Adaptation for Task-Relevant Variability. J. Neurosci. 28, 14165–14175. [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D. W. , and Wolpert, D. M. (2011). Feedback modulation: a window into cortical function. Curr Biol 21, R924-926. [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M. , Aybek, S., Dworetzky, B. A., McWhirter, L., Staab, J., and Stone, J. (2022). Functional Neurological Disorder: New Phenotypes, Common Mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 21, 537–550. [CrossRef]
- Herz, D. M. , Bange, M., Gonzalez-Escamilla, G., Auer, M., Ashkan, K., Fischer, P., et al. (2022). Dynamic control of decision and movement speed in the human basal ganglia. Nat Commun 13, 7530. [CrossRef]
- Hillyard, S. A. , Vogel, E. K., and Luck, S. J. (1998). Sensory gain control (amplification) as a mechanism of selective attention: electrophysiological and neuroimaging evidence. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 353, 1257–1270.
- Hua, L. , Adams, R. A., Grent-‘t-Jong, T., Gajwani, R., Gross, J., Gumley, A. I., et al. (2023). Thalamo-cortical circuits during sensory attenuation in emerging psychosis: a combined magnetoencephalography and dynamic causal modelling study. Schizophr 9, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G. , Desantis, A., and Waszak, F. (2013). Mechanisms of intentional binding and sensory attenuation: the role of temporal prediction, temporal control, identity prediction, and motor prediction. Psychol Bull 139, 133–151. [CrossRef]
- Huppert, T. J. , Diamond, S. G., Franceschini, M. A., and Boas, D. A. (2009). HomER: a review of time-series analysis methods for near-infrared spectroscopy of the brain. Appl Opt 48, D280–D298.
- Ikemoto, S. , Yang, C., and Tan, A. (2015). Basal ganglia circuit loops, dopamine and motivation: A review and enquiry. Behav Brain Res 290, 17–31. [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R. E. (1960). A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Journal of Basic Engineering 82, 35–45. [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A. , Makled, B., Norfleet, J., Schwaitzberg, S. D., Intes, X., De, S., et al. (2022). Directed information flow during laparoscopic surgical skill acquisition dissociated skill level and medical simulation technology. npj Sci. Learn. 7, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Körding, K. (2007). Decision theory: what “should” the nervous system do? Science 318, 606–610. [CrossRef]
- Körding, K. P., and Wolpert, D. M. (2006). Bayesian decision theory in sensorimotor control. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 10, 319–326. [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S. , Brass, M., and Haggard, P. (2013). Feeling in control: Neural correlates of experience of agency. Cortex 49, 1935–1942. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. , Sinha, N., Dutta, A., and Lahiri, U. (2019). Virtual reality-based balance training system augmented with operant conditioning paradigm. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 18, 90. [CrossRef]
- Li, R. , Yang, D., Fang, F., Hong, K.-S., Reiss, A. L., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Concurrent fNIRS and EEG for Brain Function Investigation: A Systematic, Methodology-Focused Review. Sensors (Basel) 22, 5865. [CrossRef]
- Macerollo, A., Chen, J.-C., Pareés, I., Kassavetis, P., Kilner, J. M., and Edwards, M. J. (2015). Sensory Attenuation Assessed by Sensory Evoked Potentials in Functional Movement Disorders. PLoS One 10, e0129507. [CrossRef]
- Maier, M. E. , Yeung, N., and Steinhauser, M. (2011). Error-related brain activity and adjustments of selective attention following errors. Neuroimage 56, 2339–2347. [CrossRef]
- Maurer, C. W. , LaFaver, K., Ameli, R., Epstein, S. A., Hallett, M., and Horovitz, S. G. (2016). Impaired self-agency in functional movement disorders. Neurology 87, 564–570. [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, D. , Hope, R., Gray, E., Xavier, F., Beath, A., and Jones, M. (2023). Methodological considerations for the force-matching task. Behav Res 55, 2979–2988. [CrossRef]
- Miall, R. C. (2024). Motor imagery, forward models and the cerebellum: a commentary on Rieger et al., 2023. Psychological Research. [CrossRef]
- Moore, J. W., Middleton, D., Haggard, P., and Fletcher, P. C. (2012). Exploring implicit and explicit aspects of sense of agency. Consciousness and Cognition 21, 1748–1753. [CrossRef]
- Nahab, F. B. , Kundu, P., Gallea, C., Kakareka, J., Pursley, R., Pohida, T., et al. (2011). The Neural Processes Underlying Self-Agency. Cereb Cortex 21, 48–55. [CrossRef]
- Otaran, A., and Farkhatdinov, I. (2022). Haptic Ankle Platform for Interactive Walking in Virtual Reality. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 28, 3974–3985. [CrossRef]
- Pareés, I., Brown, H., Nuruki, A., Adams, R. A., Davare, M., Bhatia, K. P., et al. (2014). Loss of sensory attenuation in patients with functional (psychogenic) movement disorders. Brain 137, 2916–2921. [CrossRef]
- Paulin, M. (1989). A Kalman Filter Theory of the Cerebellum., in Dynamic Interactions in Neural Networks: Models and Data, eds. M. A. Arbib and S. Amari (New York, NY: Springer), 239–259. [CrossRef]
- Porrill, J. , Dean, P., and Anderson, S. R. (2013). Adaptive filters and internal models: multilevel description of cerebellar function. Neural Netw 47, 134–149. [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, A. T. , Pedroni, A., Langer, N., and Hansen, L. K. (2018). Microstate EEGlab toolbox: An introductory guide. [CrossRef]
- Pringsheim, T., and Edwards, M. (2017). Functional movement disorders. Neurol Clin Pract 7, 141–147. [CrossRef]
- Sherman, S. M. , and Guillery, R. W. (2006). Exploring the thalamus and its role in cortical function, 2nd ed. Cambridge, MA, US: MIT Press.
- Stone, J. , and Edwards, M. (2012). Trick or treat? Showing patients with functional (psychogenic) motor symptoms their physical signs. Neurology 79, 282–284. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T. , Schweighofer, N., and Izawa, J. (2023). Reinforcement learning establishes a minimal metacognitive process to monitor and control motor learning performance. Nat Commun 14, 3988. [CrossRef]
- Turner, J. A. , and Chapman, C. R. (1982). Psychological interventions for chronic pain: a critical review. II Operant conditioning, hypnosis, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. Pain 12, 23–46. [CrossRef]
- Voss, M. , Bays, P. M., Rothwell, J. C., and Wolpert, D. M. (2007). An improvement in perception of self-generated tactile stimuli following theta-burst stimulation of primary motor cortex. Neuropsychologia 45, 2712–2717. [CrossRef]
- Walia, P. , Fu, Y., Norfleet, J., Schwaitzberg, S. D., Intes, X., De, S., et al. (2022). Error-related brain state analysis using electroencephalography in conjunction with functional near-infrared spectroscopy during a complex surgical motor task. Brain Inform 9, 29. [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D. M., and Ghahramani, Z. (2000). Computational principles of movement neuroscience. Nat Neurosci 3, 1212–1217. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T., Geary, R. B., Ahmed, A. A., and Shadmehr, R. (2018). Control of movement vigor and decision making during foraging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115, E10476–E10485. [CrossRef]
- Zito, G. A. , Wiest, R., and Aybek, S. (2020). Neural correlates of sense of agency in motor control: A neuroimaging meta-analysis. PLOS ONE 15, e0234321. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).