1. Introduction
The insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP; oxytocinase; placental leucine aminopeptidase) is part of the M1 aminopeptidase family and is highly expressed in many tissues, including the neocortex and hippocampus of the brain [
1,
2,
3,
4]. In 1995, IRAP was discovered in fat and muscle cells by Keller et al. [
5] and has since been associated with various physiological functions, although the exact role of this peptidase remains unknown. It is involved in the degradation of several endogenous substrates, such as oxytocin, vasopressin, cholecystokinin-8 and somatostatin [
3,
6,
7,
8,
9], and in the immune system where IRAP is involved in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen presentation and T cell activation [
10,
11]. IRAP can be found in glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) vesicles, and is thought to mediate GLUT4 trafficking to the plasma membrane, indicating a potential role in regulating cellular glucose uptake [
12,
13,
14,
15]. Although IRAP has been shown to be involved in many different physiological functions, the evaluation of IRAP as a pharmaceutical target has mainly been focused on its role in the brain, more specifically in cognition [
16,
17]. In the beginning of the century, IRAP was identified as the receptor for the hexapeptide Angiotensin IV (Ang IV) [
7,
18]. Ang IV and related analogues have demonstrated enhanced memory effects in several behavior models, as first demonstrated by Brazko et al. [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26] and bind to the active site of the protein and thereby causing inhibition of its enzymatic activity. This inhibition is suggested to increase levels of peptides such as vasopressin and oxytocin, and also modulate glucose uptake, leading to improved cognitive functions [
6,
7,
12,
14,
15,
27,
28]. Reported data has initiated the search for new ligands with capacity to inhibit IRAP in a pursuit for cognitive enhancers that are more suitable as pharmaceuticals compared to the endogenous Ang IV and related peptides [
16,
29,
30,
31]. A series of macrocyclic compounds were synthesized and confirmed as IRAP inhibitors and among those compound 9 (C9) [
32], exhibiting a similar inhibitory capacity as the structurally related HA08 [
33], attracted our interest. Compound C9 and HA08 combine structural elements from Ang IV and the physiological substrates oxytocin and vasopressin (
Figure 1). A crystal structure of HA08 reveals that the macrocycle binds in the catalytic site in a near canonical substrate-like configuration and inhibits IRAP by a competitive mechanism [
34]. Compound C9 encompasses a primary amide in the C-terminal rather than the acidic carboxylic acid function present in HA08. Despite the loss of the negative charge by replacement of the carboxyl group, the binding mode of C9 to IRAP seems unaltered as compared with HA08, according to a molecular dynamics analysis [
32,
33].
We have previously demonstrated that HA08 increases dendritic spine density and can reverse cellular viability in rat primary hippocampal cells [
35,
36]. Dendritic spines are small membrane protrusions on the neuronal dendrites and play an important role in synaptic connectivity by receiving and transmitting neuronal signals. Alterations in synaptic strength are linked to cognitive performance and different memory processes, and deviations in spine morphology or density is observed in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44]. One important protein for defining and upholding the dendritic structure and synaptic transmission is the neuronal specific marker microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) [
45]. MAP2 regulates cytoskeleton dynamics and intracellular trafficking and has been directly linked to the initiation of long-term potentiation by increasing its translocation to dendritic spines [
46]. This microtubule protein is involved in many important physiological processes and closely related to the neurodegeneration-related MAP Tau, although the pathological role of MAP2 remains to be determined [
45]. In contrast to the neuronal marker MAP2, the astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) has been linked to several types of brain disorders and injuries [
47]. Increased levels of GFAP in cerebral spinal fluid and plasma can be seen in patients with traumatic brain injuries, neuroinflammatory- and neurodegenerative diseases. This astrocytic protein is therefore suggested as a potential biomarker and prognostic tool for some of the most common brain disorders, including Alzheimer’s - and Parkinson’s disease [
47,
48].
To further evaluate potent IRAP inhibitors suitable for future pharmaceutical development, we have examined the macrocycle inhibitor compound C9 and its impact on cognitive markers, including the dendritic spine related protein drebrin, neuronal marker MAP2, and astrocytic marker GFAP, in rat primary hippocampal and cortical cells.
2. Results
2.1. The IRAP Receptor is Expressed Differently in Hippocampal and Cortical Cell Cultures
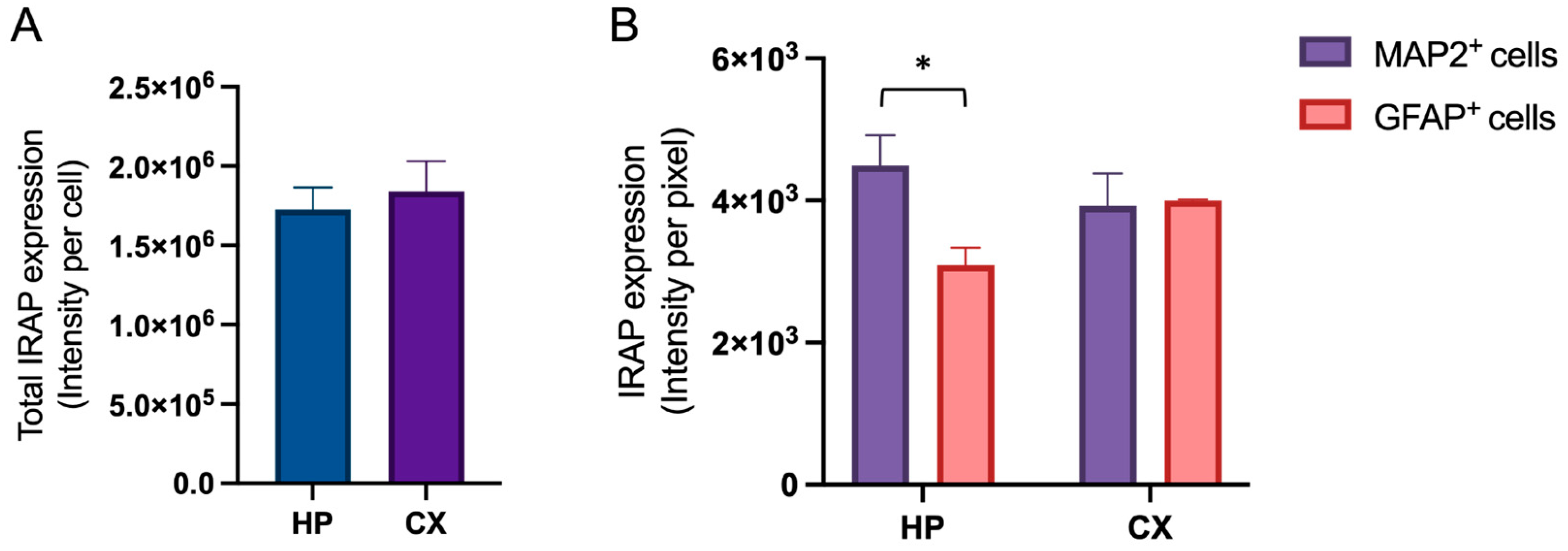
Untreated hippocampal and cortical cell cultures were analysed for the expression of IRAP at in vitro day 18. There was no difference in the total amount of expressed IRAP between hippocampal and cortical cultures (
Figure 2A). However, the distribution of IRAP expression between neurons (MAP2 positive cells) and astrocytes (GFAP positive cells) was different between hippocampal and cortical cultures (
Figure 2B). The IRAP intensity was significantly higher in the neurons compared to the astrocytes in the hippocampal cultures (p-value 0.0482). There was no significant difference between the two cell types in cortical cultures. See
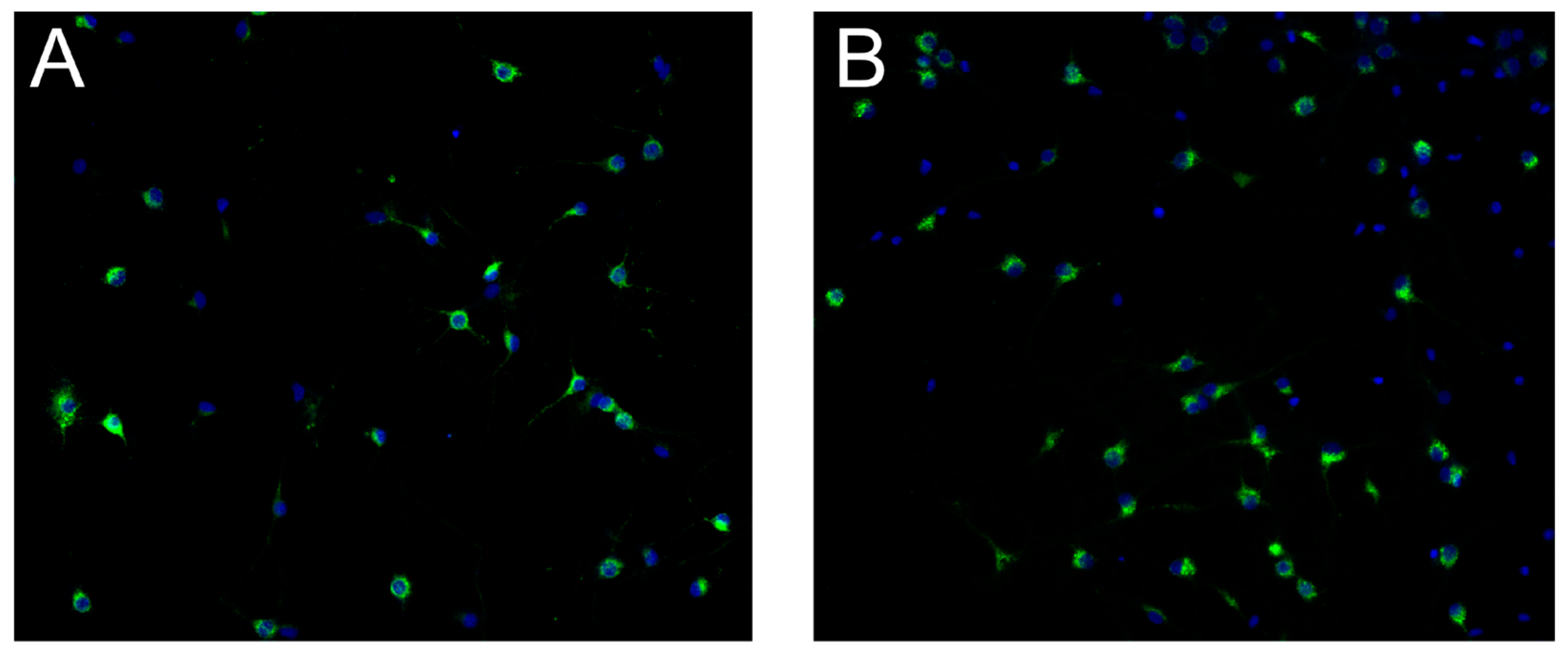
Figure 3 for representative images of the IRAP expression in hippocampal and cortical cultures.
2.2. IRAP Inhibitor C9 Increases Drebrin Intensity
The effect of repeated treatment with 1 nM to 10 µM C9 on the dendritic spine density was determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of expressed drebrin in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures. The acquired images were analysed for total drebrin intensity, soma drebrin intensity, and axonal drebrin intensity. There was no overall effect of treatment on the total amount of drebrin intensity or the axonal drebrin intensity in the hippocampal cell cultures (
Figure 4A and 4C). However, the soma drebrin intensity was significantly altered by the treatment (ANOVA p-value 0.0052) and post-hoc analysis revealed that 10
-8, 10
-7, 10
-6, and 10
-5 M C9 increased the amount of drebrin in the soma ROI of hippocampal cells when compared to vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) treated group (p-values 0.0136, 0.0029, 0.0030, and 0.0141, respectively), see
Figure 4B. The results of the C9 treatment in cortical cell cultures showed an overall treatment effect for total drebrin intensity (ANOVA p-value 0.0161), soma drebrin intensity (ANOVA p-value 0.0192), as well as the axonal drebrin intensity (ANOVA p-value 0.0132), see
Figure 4D-F. Post-hoc analysis revealed that the total amount of drebrin in the cells was significantly increased at concentrations 10
-9 and 10
-8 M C9 when compared to the vehicle treated cells (p-values 0.0073 and 0.0062), see
Figure 4D. The soma drebrin amount was significantly increased for all concentrations of C9; 10
-9, 10
-8, 10
-7, 10
-6, and 10
-5 M, when compared to vehicle (p-values 0.0352, 0.0120, 0.0365, 0.100, and 0.0141, respectively), see
Figure 4E. The amount of drebrin located in the axons of the cortical cells was significantly increased at concentrations 10
-9 and 10
-8 M C9 when compared to vehicle (p-values 0.0103 and 0.0259), as shown in
Figure 4F. See
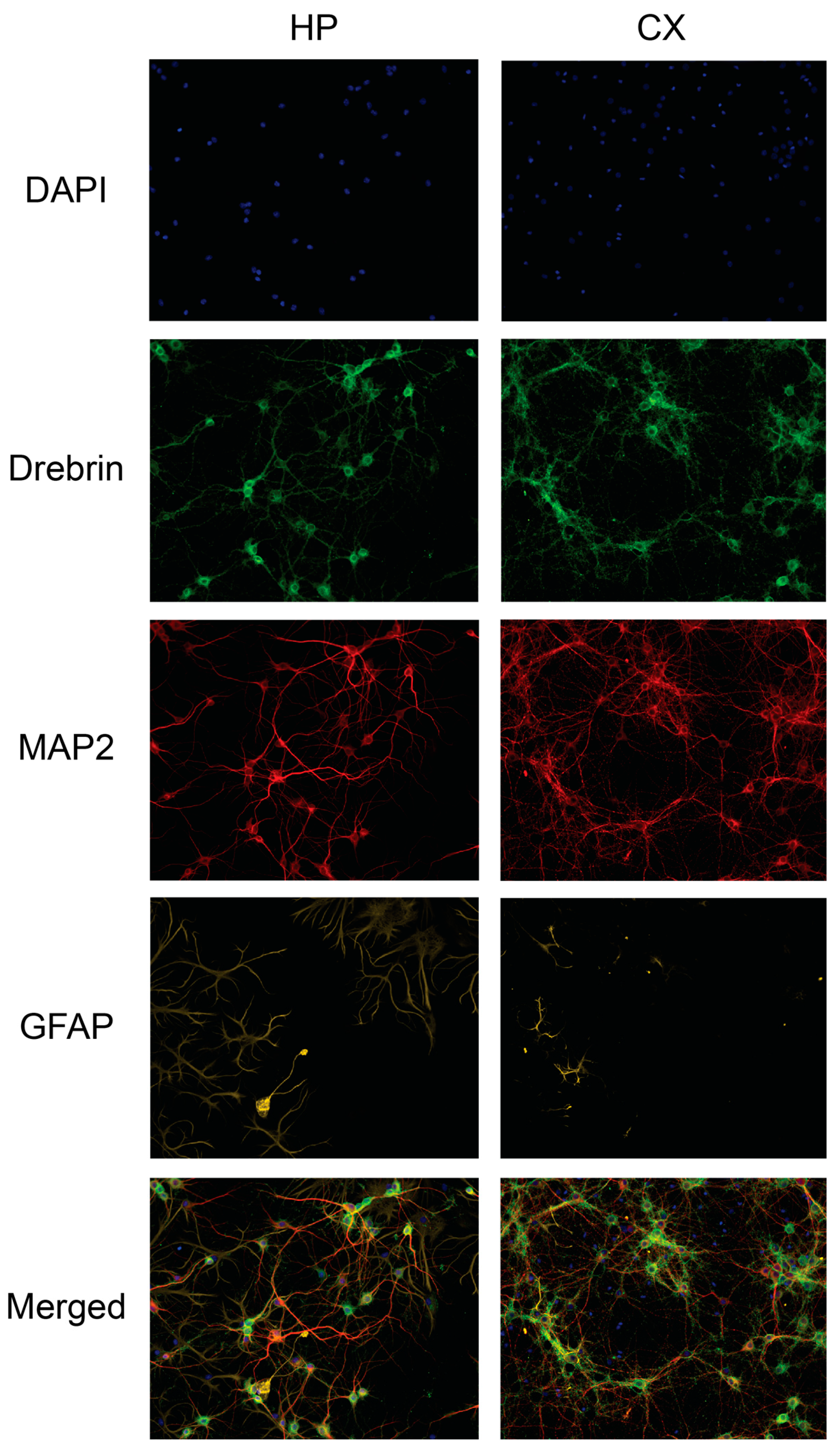
Figure 5 for representative images of drebrin expression in hippocampal and cortical cell cultures.
2.3. Treatment with C9 Alters the Ratio of Neurons and Astrocytes
The ratio of neurons and astrocytes following treatment with 1 nM to 10 µM C9 in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures was determined using ICC. The acquired images were analysed for total number of DAPI nuclei (total number of cells), total area of MAP2 positive cells (neurons), and total area of GFAP positive cells (astrocytes). In the hippocampal cell cultures, there was no overall effect of C9 on the total number of cells (
Figure 6A), however, there was an overall treatment effect on the MAP2 cell area (ANOVA p-value 0.0003), see
Figure 6B. Further post-hoc analysis revealed that all tested concentrations of C9; 10
-9, 10
-8, 10
-7, 10
-6, and 10
-5 M, significantly increased the total area of cells positive for MAP2 when compared to vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) treatment (p-values 0.0083, 0.0004, 0.0001, 0.0019 and 0.0008, respectively). The total area of cells positive for GFAP was not significantly altered by treatment with C9 in the hippocampal cultures (
Figure 6C). In the cortical cultures, there was an overall effect of C9 treatment on the total number of cells (ANOVA p-value 0.0005), along with the amount of MAP2 positive cells (ANOVA p-value 0.0206) and GFAP positive cells (ANOVA p-value 0.0230), see
Figure 6D-F. Further post-hoc analysis revealed that all concentrations of C9; 10
-9, 10
-8, 10
-7, 10
-6, and 10
-5 M, significantly increased the total number of cells when compared to vehicle (p-values 0.0019, 0.0011, 0.0014, 0.0003, and 0.0004). The area of MAP2 positive cells was also significantly increased after 10
-9, 10
-8, and 10
-6 M C9 treatment compared to the vehicle treated cells (p-values 0.0195, 0.0096, and 0.0105). The area of cells positive for GFAP was significantly decreased by C9 treatment at concentrations 10
-7 and 10
-5 M (p-value 0.0468 and 0.0072).
2.4. GLUT4 Expression Is Increased in Cortical Astrocytes
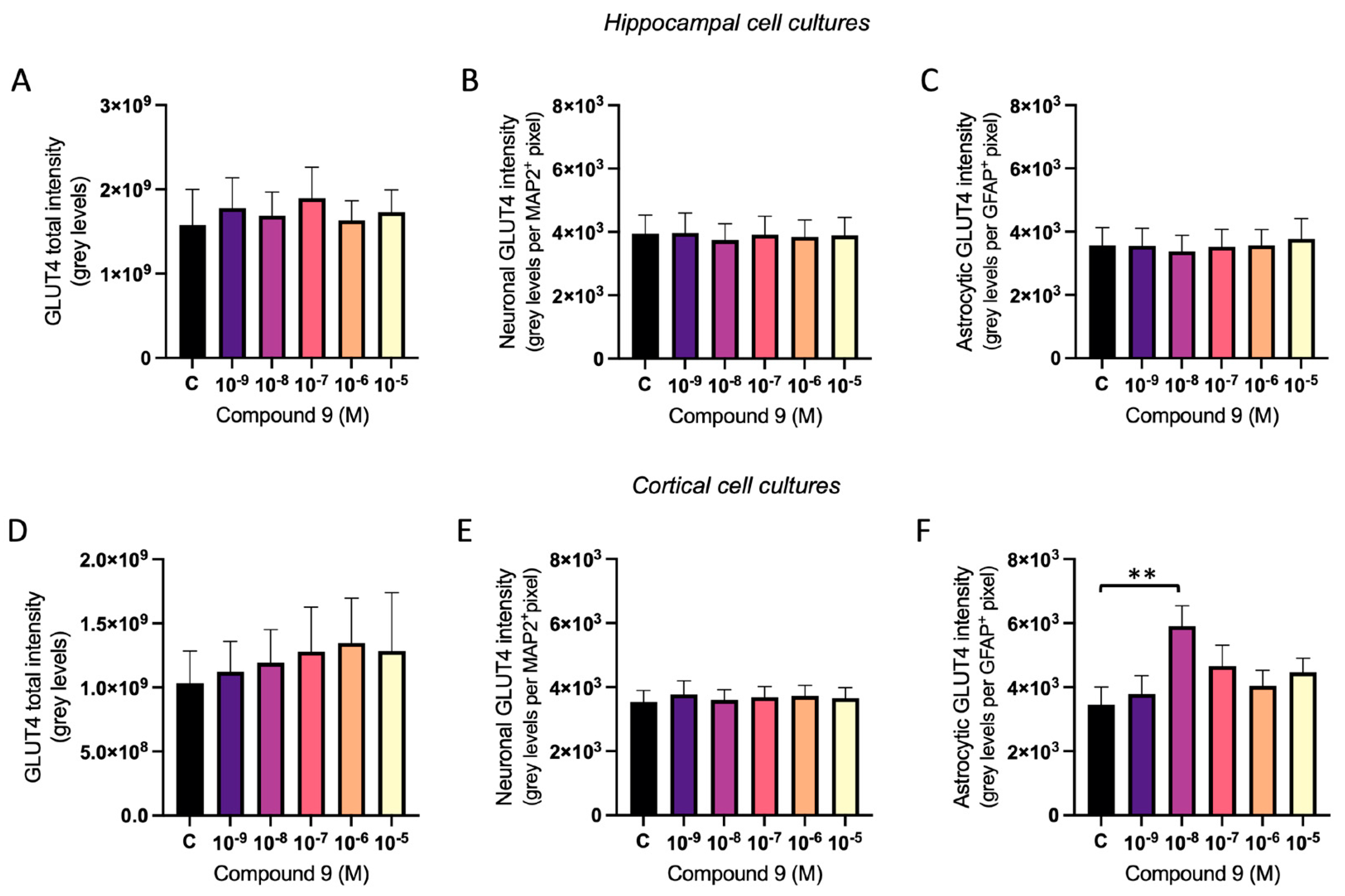
The effect of repeated treatment with 1 nM to 10 µM C9 on GLUT4 was determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of expressed GLUT4 in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures. The acquired images were analysed for total GLUT4 intensity, GLUT4 intensity in MAP2 positive cells (neuronal GLUT4), and GLUT4 intensity in GFAP positive cells (astrocytic GLUT4). There was no overall effect of treatment on the total amount of GLUT4 intensity, the neuronal GLUT4 intensity divided with the total pixel area of MAP2 positive cells, nor on the astrocytic GLUT4 intensity divided with the total pixel area of GFAP positive cells in hippocampal cultures (
Figure 7A-C). In cortical cell cultures, there was no overall effect of treatment on the total GLUT4 intensity or the neuronal GLUT4 intensity per pixel area of MAP2 positive cells (
Figure 7D-E). However, there was a treatment effect of C9 for the astrocytic GLUT4 intensity per pixel area of GFAP positive cells (ANOVA p-value 0.0341). Further post-hoc analysis revealed that 10
-8 M C9 increased the amount of GLUT4 intensity per GFAP positive pixel (astrocyte area) in cortical cell cultures when compared to vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) treatment (p-value 0.0092), see
Figure 7F.
2.5. C9 Has an Overall Treatment Effect on Synaptic Markers vGluT1 and Synapsin I
The vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGluT1) and synapsin I expression were analysed in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after treatment with 1 nM to 10 µM C9. The acquired images after ICC were analysed for total number of cells (DAPI positive nuclei) and total amount of vGluT1 or synapsin I fluorescence intensity. The total intensity was divided with the total number of cells to normalise for differences in cell amount. There was an overall treatment effect on the vGluT1 intensity per cell in hippocampal and cortical cultures (ANOVA p-value 0.0357 and p-value 0.0115, respectively). However, further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference in intensity for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to the vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) treated cells (
Figure 8A-B). Similarly, the treatment of C9 had an overall effect on the synapsin I expression in cortical cultures (ANOVA p-value 0.0327), but further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle (
Figure 8D). There was no effect on the synapsin I expression in the hippocampal cultures (
Figure 8C).
2.6. IRAP Inhibitor C9 Decreases the mRNA Levels in Hippocampal Cells
The effect of repeated treatment with 1 nM to 10 µM compound C9 on the gene expression of
Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and
Map2 was determined in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures by using qPCR. There was an overall treatment effect of C9 on the mRNA levels of
Dbn1 (ANOVA p-value 0.0083)
, Gfap (ANOVA p-value 0.0011)
, Glut1 (ANOVA p-value <0.0001)
, Glut3 (ANOVA p-value 0.0319)
, Glut4 (ANOVA p-value 0.0168), and
Map2 (ANOVA p-value 0.0379) in hippocampal cells (
Table 1). Further post-hoc testing revealed that 10
-8 and 10
-6 M C9 decreased the gene expression of
Dbn1 when compared to vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) treated cells (p-value 0.0440 and 0.0035). There was also a significant decrease of
Gfap, Glut1 and
Glut4 mRNA levels after treatment with 10
-8, 10
-7 and 10
-6 M C9 (
Gfap p-values 0.0085, 0.0126, and 0.0005;
Glut1 p-values <0.0001, 0.0008, and <0.0001;
Glut4 p-values 0.0364, 0.0179, and 0.0296). The
Glut3 and
Map2 mRNA levels were significantly decreased at concentration 10
-6 M C9 (
Glut3 p-value 0.0170;
Map2 p-value 0.0278). There was no overall treatment effect on the mRNA levels of
Lnpep, the gene coding for IRAP, in hippocampal cells. However, in the cortical cell cultures there was no overall treatment effect of C9 on any of the genes. See
Table 1 for results of standardised mRNA levels of
Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and
Map2 in hippocampal and cortical cell cultures.
2.7. Treatment with C9 Does Not Impact Viability of Primary Cell Cultures
The mitochondrial metabolism, the membrane integrity, and the calcein metabolism was measured to assess the viability of the cell cultures after treatment with 1 nM to 10 µM C9. There was no overall treatment effect of IRAP inhibitor C9 in primary hippocampal or cortical cell cultures on the mitochondrial metabolism (
Figure 9A and 9D). To determine the membrane integrity, the amount of LDH in the cell media was measured and for hippocampal cultures there was an overall treatment effect of C9 (ANOVA p-value 0.0475). Further post-hoc analysis revealed that cells treated with the highest concentration of C9, 10
-5 M, had significantly lower amount of LDH leakage compared to vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) treatment (p-value 0.022), see
Figure 9B. For the cortical cell cultures there was no overall treatment effect on the release of LDH in the cell media (
Figure 9E). The level of calcein metabolism in the cells was analysed by dividing the total calcein intensity with the number of cells (DAPI positive nuclei). There was no overall treatment effect of C9 in the hippocampal cultures (
Figure 9C), nor in the cortical cultures (
Figure 9F).
3. Discussion
The results of the present study demonstrate that compound C9 increases the protein expression of drebrin as well as alters the distribution of neurons (MAP2 positive cells) and astrocytes (GFAP positive cells) in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures from rat. The effects on drebrin protein expression differed between hippocampal and cortical cultures, where the main effect in hippocampal cells was an overall increase of drebrin localized in the vicinity of the cell nuclei (soma ROI), and an increase of MAP2 positive neurons. In cortical cell cultures, the number of cells was significantly increased following treatment with all concentrations of compound C9, and also the amount of MAP2 positive cells increased. Interestingly, there was also an increase of drebrin in the soma ROI as well as for the axonal drebrin expression in these cells. The image analysis method for measuring drebrin intensity in the vicinity of the cell nuclei was based on first identifying MAP2 positive cell nucleus, and then measuring drebrin in the nuclei area as well as an expanded area around it (soma ROI). This also meant that an increased amount of MAP2 positive cells would result in a greater area for the soma ROI, thus resulting in an increased drebrin amount. MAP2 is a neuronal specific marker that plays a key role in defining and upholding the dendritic structure. By influencing the microtubule cytoskeleton dynamics and intracellular trafficking, MAP2 regulates neuronal structure and synaptic transmission. It has also been directly linked to induction of long-term potentiation, where MAP2 translocation to dendritic spines increased [
46]. There is also evidence suggesting that MAP2 is closely linked to the NMDA receptor, more specifically, NMDA receptor activation induces degradation of this microtubule protein [
49]. Additionally, phosphorylation of MAP2 has been linked to activation of insulin secretion upon glucose stimulation of CaM kinase II [
50,
51]. Both IRAP and MAP2 seem to be linked to the cellular processes of insulin signaling, as IRAP is located in GLUT4 vesicles in insulin responsive cells, and is translocated and co-expressed with GLUT4 on the plasma membrane upon insulin stimulation [
7,
13]. Although MAP2 is involved in many important physiological processes as well as closely related to MAP Tau, which is highly associated to neurodegenerative disorders, the pathological involvement of MAP2 is still unclear [
45]. The findings from our study suggests that IRAP can regulate MAP2 in primary hippocampal cell cultures from rat, indicating an involvement in the function and processes of dendritic spines and synaptic plasticity which confirms previous studies were inhibition of IRAP increased dendritic spines [
14,
35,
52]. Interestingly, the impact on MAP2 positive cells after treatment with compound C9 seem to be more prominent in hippocampal cells than in cortical cells. Although there was a significant increase of MAP2 positive cells in the cortical cultures, there was also an overall increase in the total number of cells after C9 treatment, which could explain the MAP2 effect. However, there was a significant decrease of GFAP positive cells in the cortical cultures which suggest that there is an impact on the neuron to astrocyte ratio in these cultures as well. GFAP is suggested as a potential biomarker for different brain disorders, including neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease [
47,
48]. Decreased levels of this protein could therefore implicate an improved, or protective, effect on the cellular health.
The GLUT4 expression differed to some extent between treated hippocampal and cortical cultures. GLUT4 is believed to play a role in the mechanism behind memory improvement induced by IRAP inhibition [
7,
13,
14]. The main effect on the amount of GLUT4 in this study was linked to the GFAP positive cells, the astrocytes, in the mixed primary cortical cultures. There was a significant increase of this glucose transporter in cortical astrocytes at 10 nM C9 and the total amount of GLUT4 showed a slight increasing trend with higher concentrations of C9. However, this effect was not seen in the hippocampal cultures where the GLUT4 expression seemed to remain the same in all treatment groups. Interestingly, the amount of astrocytes in the cortical cultures had a decreasing trend with increased C9 concentrations, where 0.1 µM and 10 µM had a significantly lower amount of astrocytes, along with a significant increase of the total number of cells at all C9 concentrations. The neuronal MAP2 positive cells showed no difference in GLUT4 expression after C9 treatment in neither hippocampal nor cortical cell cultures.
Surprisingly, the results of the gene expression analysis showed a slightly opposing trend to what was seen from the protein expression analysis. The expression of the genes encoding for drebrin, GFAP, GLUT1, GLUT3, GLUT4, and MAP2 was downregulated in hippocampal cells after treatment with compound C9. There was no significant decrease of mRNA levels for the gene encoding for IRAP, but a downward trend was seen for concentration 1 µM. There was less effect on gene expression in cortical cells after C9 treatment. Although no significant difference was detected, there was a minor downward trend of the expression of genes encoding proteins drebrin, GLUT3, GLUT4, MAP2 and IRAP and an upward trend for the expression of genes encoding GFAP. The fact that MAP2 protein expression was significantly increased in hippocampal cells for all concentrations of C9 (highest at 0.1 µM) but the mRNA levels of the same protein, and the gene encoding for drebrin, were significantly decreased at 1 µM suggest that there might be negative feedback induced by the inhibition of IRAP. The same theory could be reasoned for the glucose transporters, the genes might be downregulated as a consequence of higher protein activity. Glucose transporter deficiencies has been linked to disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury and stroke [
53] and in an IRAP knockout mice, the level of GLUT4 was markedly decreased [
54]. The effects on gene and protein expression in this study could be dependent on the timing of the analysis. If the effect of IRAP inhibitor C9 has peaked during the treatment period, negative feedback could have been induced after four consecutive days of treatment and may not yet be seen on the actual cellular protein expression. As for the results of the C9 treatment in cortical cells, the
Gfap mRNA levels follows the same pattern as
Map2 and
Dbn1 levels in relation to the corresponding protein expression. The amount of GFAP positive cells was decreased in cortical cultures at higher C9 concentrations (significant decrease for 0.1 µM and 10 µM) and the mRNA levels of
Gfap showed a strong upward trend at 1 µM, the highest concentration that was analysed for gene expression, which also indicates a possible feedback effect.
The results of the viability analyses, MTT, LDH and calcein metabolism, did not demonstrate any toxic effect on hippocampal or cortical cell cultures after administration of compound C9. On the contrary, there was a significant decrease in LDH release in hippocampal cells at 10 µM C9, suggesting that the membrane integrity was improved at this concentration. This suggests that some of the obtained data regarding an increased number of cells or a change in distribution ratio between neurons and astrocytes after compound C9 treatment could be a result of an overall improved cellular health. This would be similar to previous findings, where we have seen that IRAP inhibition with HA08 can restore cell viability in rat primary hippocampal cultures after ROS induced damage [
36].
In the present study IRAP is expressed differently in hippocampal cultures compared to cortical cultures, which could be one explanation to the different effects seen between these cell cultures. There was no difference in the total amount of expressed IRAP between hippocampal and cortical cultures. However, the results presented above demonstrate that more prominent effects were observed in the hippocampal cell cultures after IRAP inhibition. Interestingly, the distribution of IRAP between neurons and astrocytes was different between the hippocampal and cortical cultures. In hippocampal cultures, there was a higher density of IRAP in the neurons compared to the astrocytes. In cortical cultures there was no difference between the two cell types. IRAP is believed to be co-expressed with GLUT4 [
2,
13] and according to the results in this study the amount of expressed GLUT4 remain approximately at the same level in untreated (vehicle treatment) hippocampal and cortical cells, which is also the case for the total amount of IRAP expressed. However, the amount of expressed GLUT4 distributed in neurons and astrocytes remains the same in both hippocampal and cortical cultures (vehicle treated cells), in contrast to the IRAP expression in the same type of untreated cells. A previous study on mouse hippocampus and cerebellum slices suggests that IRAP and GLUT4 are not always densely co-expressed, and that this expression pattern might determine the function of IRAP and ligand inhibition [
55]. They found that in hippocampus, the co-expression was high and here Ang IV treatment induced an increase in glucose uptake, whereas in the cerebellum where the co-expression was minor this effect on glucose uptake was not seen.
The results of this study provide additional insight into the mechanisms behind inhibition of IRAP and its cognitive enhancing effects. The present study demonstrates a strong relation between IRAP and the microtubule variant MAP2, and furthermore the neurodegenerative disease marker GFAP is also altered by IRAP inhibition. Additionally, the impact of IRAP inhibition is proposed to be dependent on brain region and cell type. Further studies are needed to fully unravel the complex processes of cognitive functions and the role of IRAP in this. In conclusion, the IRAP inhibiting compound C9 increases the expression of the pro-cognitive markers drebrin and MAP2, further confirming IRAP as a promising pharmaceutical target and compound C9 as a potent candidate for further investigation.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
All animal experiments were in accordance with Swedish rules and guidelines for animal experiments (Animal Welfare Act SFS: 2018:1192) and the European Union directive on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes (Directive 2010/63/EU). The animal experiment protocol was approved by the local animal ethics committee in Uppsala (permit number 5.8.18-18550/2018; 5.8.18-16657/2023). Foetuses of pregnant Sprague Dawley dams were used to set up primary cortical and hippocampal cell cultures.
4.2. Rat Primary Cell Cultures
The rat primary cell cultures were collected from embryonic day 17 Sprague Dawley foetuses by harvesting part of the cortex and the hippocampus, as described earlier [
36]. Briefly, the tissue was digested and dissociated into a homogenous cell suspension and dissolved in Gibcos neurobasal plus media (NBM; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 0.25% glutaMAX™ (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 4% Gibcos B27 plus (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The cells were seeded on poly-D-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) coated plates and kept in an incubator at 37°C and 5% CO
2.
4.3. IRAP Inhibitor Compound C9
The IRAP inhibitor used for treatment in the experiment was the synthetic macrocyclic substance compound C9 [
32]. The IRAP inhibitor was dissolved in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to a concentration of 10
-2 M and stored in - 20°C. The stock solution was thawed and diluted into 10
-3, 10
-4, 10
-5, 10
-6, and 10
-7 M solutions in 10% (v/v) DMSO for each experiment. During cell treatment, the inhibitor was further diluted 1:100 in cell media to final concentrations 10
-5, 10
-6, 10
-7, 10
-8 or 10
-9 M in 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. The cells were grown for 13 days in vitro before C9 or vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) was added on day 14, 15, 16, and 17.
4.4. Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) was used to visualize different cellular components after treatment with 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6 and 10-5 M C9. The dendritic spine related protein drebrin was targeted to determine the effect on dendritic spines, along with the neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) and astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). The glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) was targeted in a separate ICC along with MAP2 and GFAP. ICC was also performed for synaptic markers vGluT1 and synapsin I. The cells were fixed with 4% PFA on in vitro day 18 and then permeabilized using 0.2% Triton-X. Normal donkey serum (10%) in 0.1% Triton-X was added for 1h in room temperature (RT) to block unspecific binding before incubating the cells with primary antibody for the target of interest, also for 1h in RT. Primary antibodies rabbit anti-drebrin (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), mouse anti-MAP2 (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA), and rat anti-GFAP (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) were added in concentration 1:500. Primary antibodies rabbit anti-GLUT4 (Abcam), rabbit anti-vGluT1 (Abcam), and rabbit anti-synapsin I (Abcam) were added in concentration 1:250. The cells were then incubated for 1h in RT with a secondary antibody (Alexa 488 anti-rabbit for drebrin, GLUT4, vGluT1, and synapsin I, Alexa 647 anti-mouse for MAP2, and Alexa 568 anti-rat for GFAP; Invitrogen) at concentration 1:500 and kept away from light from this point forward. This was followed by cell nuclei staining with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Sigma-Aldrich) at concentration 2.5:500 for 25 min in RT. Additionally, untreated cells were fixed on in vitro day 18 to visualize the IRAP receptor along with MAP2 and GFAP markers. For this ICC the procedure was the same as described above, except Tween-20 was used instead of Triton-X. Primary antibody rabbit anti-IRAP (Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MS, USA) was added in concentration 1:250 and antibodies mouse anti-MAP2 and rat anti-GFAP were added in concentration 1:500. Secondary antibodies used were Alexa 488 anti-rabbit for IRAP, Alexa 647 anti-mouse for MAP2, and Alexa 568 anti-rat for GFAP (Invitrogen). All plates analysed with immunocytochemistry had a cell density of 1.5x104 cells per well.
4.5. Image Analysis
Fluorescently stained (ICC) 16-bit high resolution images were acquired using a high-content screening device, ImageXpress (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) mounted with a 10x objective. Images were analysed using an automated macro in ImageJ (version 1.52p), developed by the group. For all image analyses, the automated macros measured both intensity levels (grey levels) and area (pixels) of specific region of interests (ROI). Images containing debris or other anomalies were removed from the analysis. Individual threshold values for each cell culture were set up in the beginning of the analysis using randomized images from the cell plate. Intensity was measured as integrated intensity (sum of all pixel intensities in a given ROI) if not stated otherwise. To ensure macro validity, the automated workflow was visually inspected during the first five minutes. For the dendritic spine analysis, images containing cell nuclei (DAPI), spine density (drebrin), and neuronal maturity (MAP2) was used. First, cells were detected and counted using the ImageJ built-in function “analyse particles”. Each cell was assigned a unique cell-ROI using the DAPI channel. The number of MAP2-positive cells was reported and cells with low MAP2-intensity were considered non-neuronal cells and were removed from further analysis. Second, the cell-ROI was dilated to capture the cell cytoplasm and this new ROI (soma-ROI) was used to measure the intensity of drebrin in and around the cell nuclei, in which drebrin is more densely expressed. To avoid repeated measurement from cells located in close proximity to each other, the content within each soma-ROI was deleted after intensity measurement. Third, the axonal drebrin intensity was measured by subtracting the soma-ROI drebrin intensity from the total intensity of drebrin. For the GLUT4 image analysis, the total intensity of GLUT4 was measured in both neurons (MAP2 positive cells) as well as astrocytes (GFAP positive cells). First, a threshold was determined for channels MAP2 and GFAP and the total area of respective channels was assigned a ROI. Second, an overlay of the MAP2-ROI was created on the GLUT4 channel and the intensity of GLUT4 in neurons was determined. Similarly, an overlay of the GFAP-ROI was created on the GLUT4 channel and the intensity of GLUT4 in astrocytes was determined. The area of these three channels was also reported. The data for total cell area of the MAP2 and GFAP channels (collected from multiple ICC rounds) was also used to analyse the ratio of neurons and astrocytes in the cultures. For the calcein, vGluT1, and synapsin I analysis, images containing cell nuclei (DAPI) and either of the mentioned protein markers were used. These macros measured number of cell nuclei and integrated intensity of thresholded images.
4.6. mRNA Expression
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was used to determine the gene expression (mRNA levels) after treatment with 10
-8, 10
-7, and 10
-6 M C9. The primary cell cultures were lysed and homogenized on in vitro day 18 so that RNA could be extracted according to instructions of Qiagen RNeasy® Plus Mini Kit (Cat.no 74134; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The RNA concentration was measured using a NanoDrop® ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA) and diluted to 20 ng/µl. The RNA samples were converted to cDNA using iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). Every reaction sample contained 250 ng RNA, 5x iScript reaction mix, iScript reverse transcriptase and Rnase free water in a total volume of 20 µl. Negative control reactions were also included and contained no iScript reverse transcriptase. The samples were run according to following protocol: 25°C for 5 min, 46°C for 20 min, and 95°C for 1 min. The gene expression (mRNA levels) of
Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and
Map2 was determined using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) with SYBR® Green (Bio-Rad).
Actb, Rplp0, and
Rpl19 were used as reference genes. Primers for each analysed gene was purchased from Thermo Fischer Scientific, see
Table 2 for primer sequences.
The samples, including negative controls, were analysed in duplicates using a 96 well PCR plate. Each reaction sample contained 5 ng cDNA, 20 µM forward primer, 20 µM reverse primer, 1x iQ SYBR® Green supermix (hippocampal cultures) or 1x SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR® Green supermix (cortical cultures), and RNase free water in a total volume of 25 µl. The samples were run on the CFX96 Real-time PCR detection system version 3.1 (Bio-Rad) according to the following amplification protocol: 95°C for 3 min, then 40 cycles of 95°C for 15s, 60°C for 20s, 72°C for 10s. Each run ended with a melt curve to ensure specific amplification. The amplification efficiency of each primer set was obtained using linRegPCR software (version 2020.2) and the Cq-value of each sample was then obtained using qbase+ software version 3.4 (BioGazelle).
4.7. Mitochondrial Metabolism
To determine the mitochondrial activity in the cells after treatment with 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6 and 10-5 M C9, tetrazolium bromide salt (MTT; Sigma-Aldrich) was used. On in vitro day 18 the cells were incubated with MTT (0.8mg/ml) for 30 min in 37°C in the dark after which the cells were lysed with 100% DMSO and then incubated in the dark for 15 min in RT. Triton-X was used as a negative control for mitochondrial metabolism. Active mitochondria metabolise the added MTT to a purple formazan product and the amount of developed formazan product corresponds to the amount of metabolised MTT. The plate was measured in a plate reader (FLUOstar Omega, Ortenberg, Germany) for absorbance at 570 nm. All plates analysed for mitochondrial activity had a cell density of 5x104 cells per well.
4.8. Membrane Integrity
To determine the membrane integrity of the cells after treatment with 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6 and 10-5 M C9, the amount of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the cell media was measured using a cytotoxicity detection kit (Sigma-Aldrich). When the cell membrane is damaged, the cytoplasmic LDH leaks out in the cell media. The LDH reagent mix was added to the cell media on in vitro day 18 and then incubated for 30 min in the dark at RT. Triton-X was used as a positive control for cell toxicity. A red formazan product is produced when there is LDH present in the cell media and the amount of formazan product developed corresponds to the amount of LDH. The plate was measured in a plate reader (FLUOstar Omega) for absorbance at 492 nm. All plates analysed for membrane integrity had a cell density of 5x104 cells per well.
4.9. Calcein metabolism
The amount of metabolised calcein was measured in the cells as part of the viability assessment of treatment with 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6 and 10-5 M C9. Calcein (Invitrogen, Thermo Fischer Scientific), 1 µM, was added to the cells together with fresh media on in vitro day 18 and incubated for 40 min in 37°C in the dark. The calcein media was then removed and 5 µg/ml Hoescht (Invitrogen, Thermo Fischer Scientific) was added to the cells together with 1x PBS and incubated for 15 min in 37°C in the dark before images were acquired of the fluorescent metabolised calcein and the cell nuclei. Images were acquired using ImageXpress (Molecular Devices). All plates analysed for calcein metabolism had a cell density of 1.5x104 cells per well.
4.10. Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism (version 10.2.3) was used to perform all statistical analysis. Tissues collected from foetuses of one individual Sprague Dawley dam was considered as one primary cell culture (n=1). Raw data comparing multiple groups (>2) was analysed using two-way ANOVA with treatment and culture as factors. If there was a significant overall treatment effect, further post-hoc testing was performed using Dunnett’s post-hoc test with comparison to the vehicle treated group (0.1% (v/v) DMSO). Data converted to percentage comparing multiple groups (>2) was analysed using one-way ANOVA. If there was a significant overall treatment effect, the one-way ANOVA was followed by a Dunnett’s post-hoc test with comparison to the vehicle treated group. Data where two groups were compared was analysed using unpaired t-test. All data is visualized as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) and statistical significance was defined as p-value <0.05.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S., E.N., A.G., and M.H.; Methodology, F.S., S.B., E.N., E.O.H., N.B., J.G., L.R.O., and A.G.; Software, F.S. and E.N.; Validation, F.S., E.N., A.G., and M.H.; Formal analysis, F.S.; Investigation, F.S.; Resources, M.L., L.R.O., and M.H.; Data curation, F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S; writing—review and editing, F.S., S.B., E.N., E.O.H., N.B., J.G., M.L., L.R.O., A.G., and M.H.; Visualization, F.S.; Supervision, E.N., A.G., and M.H.; Project administration, F.S., E.N., A.G., and M.H.; Funding acquisition, A.G. and M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Kjell and Märta Beijer Foundation.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this article are not readily available because the data are part of an ongoing study and due to technical limitations. The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article can be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| Ang IV |
Angiotensin IV |
| ANOVA |
Analysis of variance |
| DAPI |
4’, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DMSO |
Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| GFAP |
Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GLUT |
Glucose transporter |
| ICC |
Immunocytochemistry |
| IRAP |
Insulin regulated aminopeptidase |
| LDH |
Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MAP2 |
Microtubule associated protein 2 |
| MTT |
Tetrazolium bromide salt |
| ROI |
Region of interest |
| SEM |
Standard error of the mean |
| vGluT1 |
Vesicular glutamate transporter 1 |
References
- Chai SY, Bastias MA, Clune EF, Matsacos DJ, Mustafa T, Lee JH, et al. Distribution of angiotensin IV binding sites (AT4 receptor) in the human forebrain, midbrain and pons as visualised by in vitro receptor autoradiography. J Chem Neuroanat. 2000, 20, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando RN, Larm J, Albiston AL, Chai SY. Distribution and cellular localization of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 2005, 487, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto H, Nagasaka T, Hattori A, Rogi T, Tsuruoka N, Mizutani S, et al. Expression of placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase in neuronal cells and its action on neuronal peptides. Eur J Biochem. 2001, 268, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto M, Hattori A. The oxytocinase subfamily of M1 aminopeptidases. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA - Proteins Proteomics. 2005, 1751, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller SR, Scott HM, Mastick CC, Aebersold R, Lienhard GE. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Insulin-regulated Membrane Aminopeptidase from Glut4 Vesicles (∗). J Biol Chem. 1995, 270, 23612–23618. [CrossRef]
- Albiston AL, Mustafa T, McDowall SG, Mendelsohn FAO, Lee J, Chai SY. AT4 receptor is insulin-regulated membrane aminopeptidase: potential mechanisms of memory enhancement. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003, 14, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai SY, Fernando R, Peck G, Ye SY, Mendelsohn F a. O, Jenkins TA, et al. The angiotensin IV/AT4 receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. 2004, 61, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogi T, Tsujimoto M, Nakazato H, Mizutani S, Tomoda Y. Human Placental Leucine Aminopeptidase/Oxytocinase: A NEW MEMBER OF TYPE II MEMBRANE-SPANNING ZINC METALLOPEPTIDASE FAMILY (∗). J Biol Chem. 1996, 271, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst JJ, Ross SA, Scott HM, Bobin SA, Morris NJ, Lienhard GE, et al. Insulin stimulates cell surface aminopeptidase activity toward vasopressin in adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1997, 272, E600–E606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveanu L, Carroll O, Weimershaus M, Guermonprez P, Firat E, Lindo V, et al. IRAP identifies an endosomal compartment required for MHC class I cross-presentation. Science. 2009, 325, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evnouchidou I, Chappert P, Benadda S, Zucchetti A, Weimershaus M, Bens M, et al. IRAP-dependent endosomal T cell receptor signalling is essential for T cell responses. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant NJ, Govers R, James DE. Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 267–277. [CrossRef]
- Keller, SR. The insulin-regulated aminopeptidase: a companion and regulator of GLUT4. Front Biosci J Virtual Libr. 2003, 8, s410–s420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyer B, Diwakarla S, Burns P, Hallberg A, Grӧnbladh A, Hallberg M, et al. Insulin-regulated aminopeptidase inhibitor-mediated increases in dendritic spine density are facilitated by glucose uptake. J Neurochem. 2020, 153, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters SB, D’Auria M, Martin SS, Nguyen C, Kozma LM, Luskey KL. The amino terminus of insulin-responsive aminopeptidase causes Glut4 translocation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272, 23323–23327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson H, Hallberg M. Discovery of Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase as Cognitive Enhancers. Int J Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 789671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis D, Ziotopoulou A, Kaloumenou E, Lelis A, Papasava A. The Discovery of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase (IRAP) Inhibitors: A Literature Review. Front Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 585838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiston AL, McDowall SG, Matsacos D, Sim P, Clune E, Mustafa T, et al. Evidence That the Angiotensin IV (AT4) Receptor Is the Enzyme Insulin-regulated Aminopeptidase*. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276, 48623–48626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszko JJ, Kupryszewski G, Witczuk B, Wiśniewski K. Angiotensin II-(3-8)-hexapeptide affects motor activity, performance of passive avoidance and a conditioned avoidance response in rats. Neuroscience. 1988, 27, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson ES, Harding JW, Wright JW. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced spatial learning impairments by an angiotensin IV analog. Regul Pept. 1998, 74, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright JW, Stubley L, Pederson ES, Kramár EA, Hanesworth JM, Harding JW. Contributions of the brain angiotensin IV-AT4 receptor subtype system to spatial learning. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3952–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee J, Albiston AL, Allen AM, Mendelsohn F a. O, Ping SE, Barrett GL, et al. Effect of I.C.V. injection of AT4 receptor ligands, NLE1-angiotensin IV and LVV-hemorphin 7, on spatial learning in rats. Neuroscience. 2004, 124, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiston AL, Pederson ES, Burns P, Purcell B, Wright JW, Harding JW, et al. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced learning deficits by LVV-hemorphin-7 in rats in the passive avoidance and water maze paradigms. Behav Brain Res. 2004, 154, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royea J, Martinot P, Hamel E. Memory and cerebrovascular deficits recovered following angiotensin IV intervention in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2020, 134, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic A, Ustunova S, Elibol B, Bulut H, Meral I, Sahin G. Angiotensin IV improves spatial memory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by reducing oxidative stress and altering BDNF levels. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Warsz). 2021, 81, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- De Bundel D, Smolders I, Yang R, Albiston AL, Michotte Y, Chai SY. Angiotensin IV and LVV-haemorphin 7 enhance spatial working memory in rats: Effects on hippocampal glucose levels and blood flow. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2009, 92, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gard, PR. Cognitive-enhancing effects of angiotensin IV. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew RA, Mustafa T, Ye S, McDowall SG, Chai SY, Albiston AL. Angiotensin AT4 ligands are potent, competitive inhibitors of insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP). J Neurochem. 2003, 86, 344–350. [CrossRef]
- Albiston AL, Morton CJ, Ng HL, Pham V, Yeatman HR, Ye S, et al. Identification and characterization of a new cognitive enhancer based on inhibition of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2008, 22, 4209–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axén A, Lindeberg G, Demaegdt H, Vauquelin G, Karlén A, Hallberg M. Cyclic insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP)/AT4 receptor ligands. J Pept Sci Off Publ Eur Pept Soc. 2006, 12, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, M. Targeting the insulin-regulated aminopeptidase/AT4 receptor for cognitive disorders. Drug News Perspect. 2009, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow N, Vanga SR, Sävmarker J, Sandström A, Burns P, Hallberg A, et al. Macrocyclic peptidomimetics as inhibitors of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP). RSC Med Chem. 2020, 11, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson H, Demaegdt H, Vauquelin G, Lindeberg G, Karlén A, Hallberg M, et al. Disulfide Cyclized Tripeptide Analogues of Angiotensin IV as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase (IRAP). J Med Chem. 2010, 53, 8059–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpakali A, Saridakis E, Giastas P, Maben Z, Stern LJ, Larhed M, et al. Structural Basis of Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by a Macrocyclic Peptidic Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020, 11, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwakarla S, Nylander E, Grönbladh A, Vanga SR, Khan YS, Gutiérrez-de-Terán H, et al. Binding to and Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Macrocyclic Disulfides Enhances Spine Density. Mol Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam F, Florén Lind S, Schroff A, Zelleroth S, Nylander E, Gising J, et al. Hydrogen Peroxide Induced Toxicity Is Reversed by the Macrocyclic IRAP-Inhibitor HA08 in Primary Hippocampal Cell Cultures. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022, 44, 5000–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajal, SR. Estructura de los centros nerviosos de las aves. Rev Trim Histol Norm Patol. 1888, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fiala JC, Spacek J, Harris KM. Dendritic spine pathology: cause or consequence of neurological disorders? Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2002, 39, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering H, Sheng M. Dentritic spines : structure, dynamics and regulation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001, 2, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai H, Matsuzaki M, Noguchi J, Yasumatsu N, Nakahara H. Structure-stability-function relationships of dendritic spines. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy MB, Beale HC, Carlisle HJ, Washburn LR. Integration of biochemical signalling in spines. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005, 6, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuner B, Falduto J, Shors TJ. Associative memory formation increases the observation of dendritic spines in the hippocampus. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 2003, 23, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Spronsen M, Hoogenraad CC. Synapse pathology in psychiatric and neurologic disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2010, 10, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuste, R. The discovery of dendritic spines by Cajal. Front Neuroanat. 1: 21;9. [CrossRef]
- DeGiosio RA, Grubisha MJ, MacDonald ML, McKinney BC, Camacho CJ, Sweet RA. More than a marker: potential pathogenic functions of MAP2. Front Mol Neurosci [Internet]. 2022 Sep 16 [cited 2024 Jun 22];15. [CrossRef]
- Kim Y, Jang YN, Kim JY, Kim N, Noh S, Kim H, et al. Microtubule-associated protein 2 mediates induction of long-term potentiation in hippocampal neurons. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2020, 34, 6965–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhak A, Foschi M, Abu-Rumeileh S, Yue JK, D’Anna L, Huss A, et al. Blood GFAP as an emerging biomarker in brain and spinal cord disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022, 18, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu T, Zuo H, Ma D, Song D, Zhao Y, Cheng O. Cerebrospinal fluid GFAP is a predictive biomarker for conversion to dementia and Alzheimer’s disease-associated biomarkers alterations among de novo Parkinson’s disease patients: a prospective cohort study. J Neuroinflammation. 2023, 20, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddle M, Eberhardt E, Ciminello LH, Levin T, Wing R, DiPasquale K, et al. Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) associates with the NMDA receptor and is spatially redistributed within rat hippocampal neurons after oxygen-glucose deprivation. Brain Res. 2003, 978, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhê GF, Torrão AS, Nogueira TCA, Caperuto LC, Amaral MEC, Medina MC, et al. ERK3 associates with MAP2 and is involved in glucose-induced insulin secretion. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006, 251, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easom, RA. CaM kinase II: a protein kinase with extraordinary talents germane to insulin exocytosis. Diabetes. 1999, 48, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwakarla S, Nylander E, Grönbladh A, Vanga SR, Khan YS, Gutiérrez-de-Terán H, et al. Aryl Sulfonamide Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase Enhance Spine Density in Primary Hippocampal Neuron Cultures. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepsell, H. Glucose transporters in brain in health and disease. Pflüg Arch - Eur J Physiol. 2020, 472, 1299–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller SR, Davis AC, Clairmont KB. Mice Deficient in the Insulin-regulated Membrane Aminopeptidase Show Substantial Decreases in Glucose Transporter GLUT4 Levels but Maintain Normal Glucose Homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277, 17677–17686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando RN, Albiston AL, Chai SY. The insulin-regulated aminopeptidase IRAP is colocalised with GLUT4 in the mouse hippocampus – potential role in modulation of glucose uptake in neurones? Eur J Neurosci. 2008, 28, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of IRAP inhibitors Angiotensin IV, HA08, and Compound 9 [
32,
33].
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of IRAP inhibitors Angiotensin IV, HA08, and Compound 9 [
32,
33].
Figure 2.
The expression of insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP) in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures. Untreated hippocampal and cortical primary cells were fixed at in vitro day 18 to visualise the expression of IRAP. A) There was no significant difference in the total IRAP expression, measured as intensity per cell, when comparing hippocampal (HP) and cortical (CX) cultures (n=3). B) Hippocampal culture data (HP) and cortical culture data (CX) was analysed separately for the expression of IRAP in MAP2 positive cells (neurons) compared to the IRAP expression in GFAP positive cells (astrocytes), using unpaired t-test. The expression of IRAP in neurons compared to the IRAP expression in astrocytes was significantly different in hippocampal cultures, there was a lower expression in astrocytes (n=3). There was no significant difference in IRAP expression between neurons and astrocytes in cortical cultures (n=3). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05.
Figure 2.
The expression of insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP) in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures. Untreated hippocampal and cortical primary cells were fixed at in vitro day 18 to visualise the expression of IRAP. A) There was no significant difference in the total IRAP expression, measured as intensity per cell, when comparing hippocampal (HP) and cortical (CX) cultures (n=3). B) Hippocampal culture data (HP) and cortical culture data (CX) was analysed separately for the expression of IRAP in MAP2 positive cells (neurons) compared to the IRAP expression in GFAP positive cells (astrocytes), using unpaired t-test. The expression of IRAP in neurons compared to the IRAP expression in astrocytes was significantly different in hippocampal cultures, there was a lower expression in astrocytes (n=3). There was no significant difference in IRAP expression between neurons and astrocytes in cortical cultures (n=3). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05.
Figure 3.
Insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP) expression at 18 days in vitro in primary cell cultures from rat. Untreated primary hippocampal and cortical cells were fixed at in vitro day 18 for evaluation of IRAP expression. Immunocytochemistry was used to visualise IRAP along with the cell nuclei (DAPI). A) IRAP expression (green) and cell nuclei (blue) in untreated hippocampal cell cultures. B) IRAP expression (green) and cell nuclei (blue) in cortical cell cultures. The images were acquired using ImageXpress (Molecular Devices) with a 20x objective.
Figure 3.
Insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP) expression at 18 days in vitro in primary cell cultures from rat. Untreated primary hippocampal and cortical cells were fixed at in vitro day 18 for evaluation of IRAP expression. Immunocytochemistry was used to visualise IRAP along with the cell nuclei (DAPI). A) IRAP expression (green) and cell nuclei (blue) in untreated hippocampal cell cultures. B) IRAP expression (green) and cell nuclei (blue) in cortical cell cultures. The images were acquired using ImageXpress (Molecular Devices) with a 20x objective.
Figure 4.
The effect of compound C9 on drebrin intensity in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures. The results of the dendritic spine density analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) The total drebrin intensity in hippocampal cells showed no significant overall treatment effect (n=8). B) The drebrin intensity in soma regions was significantly increased after treatment with 10-8, 10-7, 10-6, and 10-5 M C9 in hippocampal cells (n=8). C) The drebrin intensity in axons showed no significant overall treatment effect in hippocampal cells (n=8). D) The total drebrin intensity was significantly increased after treatment with 10-9 and 10-8 M C9 in cortical cells (n=4). E) The drebrin intensity in soma regions was significantly increased after treatment with 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6, and 10-5 M C9 in cortical cells (n=4). F) The drebrin intensity in axons was significantly increased after treatment with 10-9 and 10-8 M C9 in cortical cells (n=4). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05, **p-value <0.01.
Figure 4.
The effect of compound C9 on drebrin intensity in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures. The results of the dendritic spine density analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) The total drebrin intensity in hippocampal cells showed no significant overall treatment effect (n=8). B) The drebrin intensity in soma regions was significantly increased after treatment with 10-8, 10-7, 10-6, and 10-5 M C9 in hippocampal cells (n=8). C) The drebrin intensity in axons showed no significant overall treatment effect in hippocampal cells (n=8). D) The total drebrin intensity was significantly increased after treatment with 10-9 and 10-8 M C9 in cortical cells (n=4). E) The drebrin intensity in soma regions was significantly increased after treatment with 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6, and 10-5 M C9 in cortical cells (n=4). F) The drebrin intensity in axons was significantly increased after treatment with 10-9 and 10-8 M C9 in cortical cells (n=4). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05, **p-value <0.01.
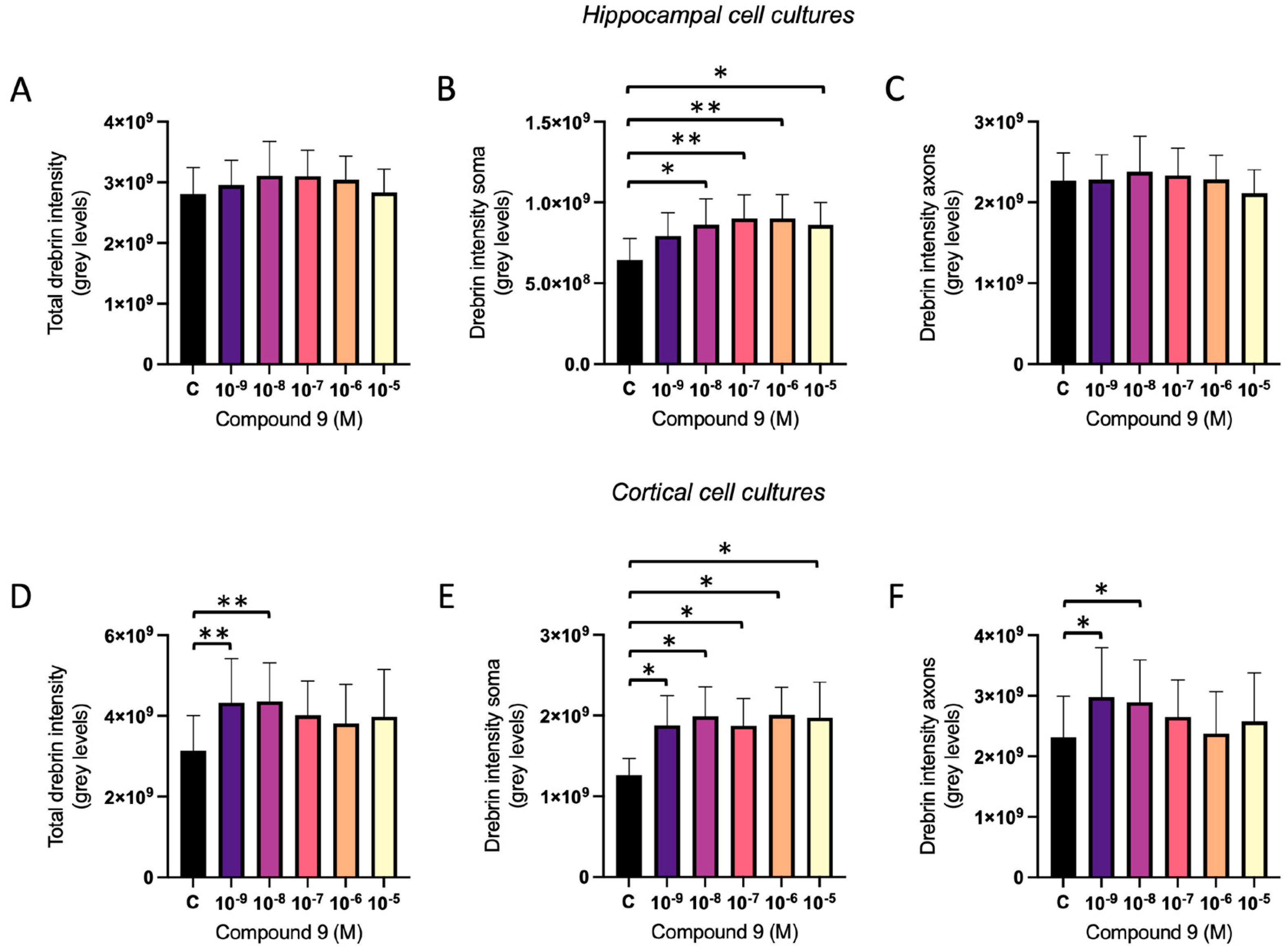
Figure 5.
The drebrin expression in rat primary hippocampal and cortical neuronal cultures. Primary hippocampal and cortical cells were fixed at in vitro day 18 and immunocytochemistry was used to visualise drebrin along with the neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and cell nuclei (DAPI). The fluorescent images represent the expression of drebrin (green), MAP2 (red), GFAP (yellow) and cell nuclei (blue) in untreated hippocampal (HP) and cortical (CX) cell cultures. The last row shows all channels merged. The images were acquired using ImageXpress (Molecular Devices) with a 20x objective.
Figure 5.
The drebrin expression in rat primary hippocampal and cortical neuronal cultures. Primary hippocampal and cortical cells were fixed at in vitro day 18 and immunocytochemistry was used to visualise drebrin along with the neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and cell nuclei (DAPI). The fluorescent images represent the expression of drebrin (green), MAP2 (red), GFAP (yellow) and cell nuclei (blue) in untreated hippocampal (HP) and cortical (CX) cell cultures. The last row shows all channels merged. The images were acquired using ImageXpress (Molecular Devices) with a 20x objective.
Figure 6.
The effect of compound C9 on the distribution of cell types in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the cell type analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the total number of cells in hippocampal cells (n=8). B) There was a significant increase of MAP2 cell area after treatment with all concentrations of C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in hippocampal cells (n=8). C) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the GFAP positive cell area in hippocampal cells (n=6). D) The total number of cells was significantly increased by all concentrations of C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in cortical cells (n=5). E) There was a significant increase of MAP2 cell area at 10-9, 10-8, and 10-6 M C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in cortical cells (n=5). F) The amount of GFAP cell area was significantly increased after treatment with 10-7 and 10-5 M C9 compared to vehicle group in cortical cells (n=5). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05, **p-value <0.01, ***p-value <0.001.
Figure 6.
The effect of compound C9 on the distribution of cell types in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the cell type analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the total number of cells in hippocampal cells (n=8). B) There was a significant increase of MAP2 cell area after treatment with all concentrations of C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in hippocampal cells (n=8). C) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the GFAP positive cell area in hippocampal cells (n=6). D) The total number of cells was significantly increased by all concentrations of C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in cortical cells (n=5). E) There was a significant increase of MAP2 cell area at 10-9, 10-8, and 10-6 M C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in cortical cells (n=5). F) The amount of GFAP cell area was significantly increased after treatment with 10-7 and 10-5 M C9 compared to vehicle group in cortical cells (n=5). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05, **p-value <0.01, ***p-value <0.001.
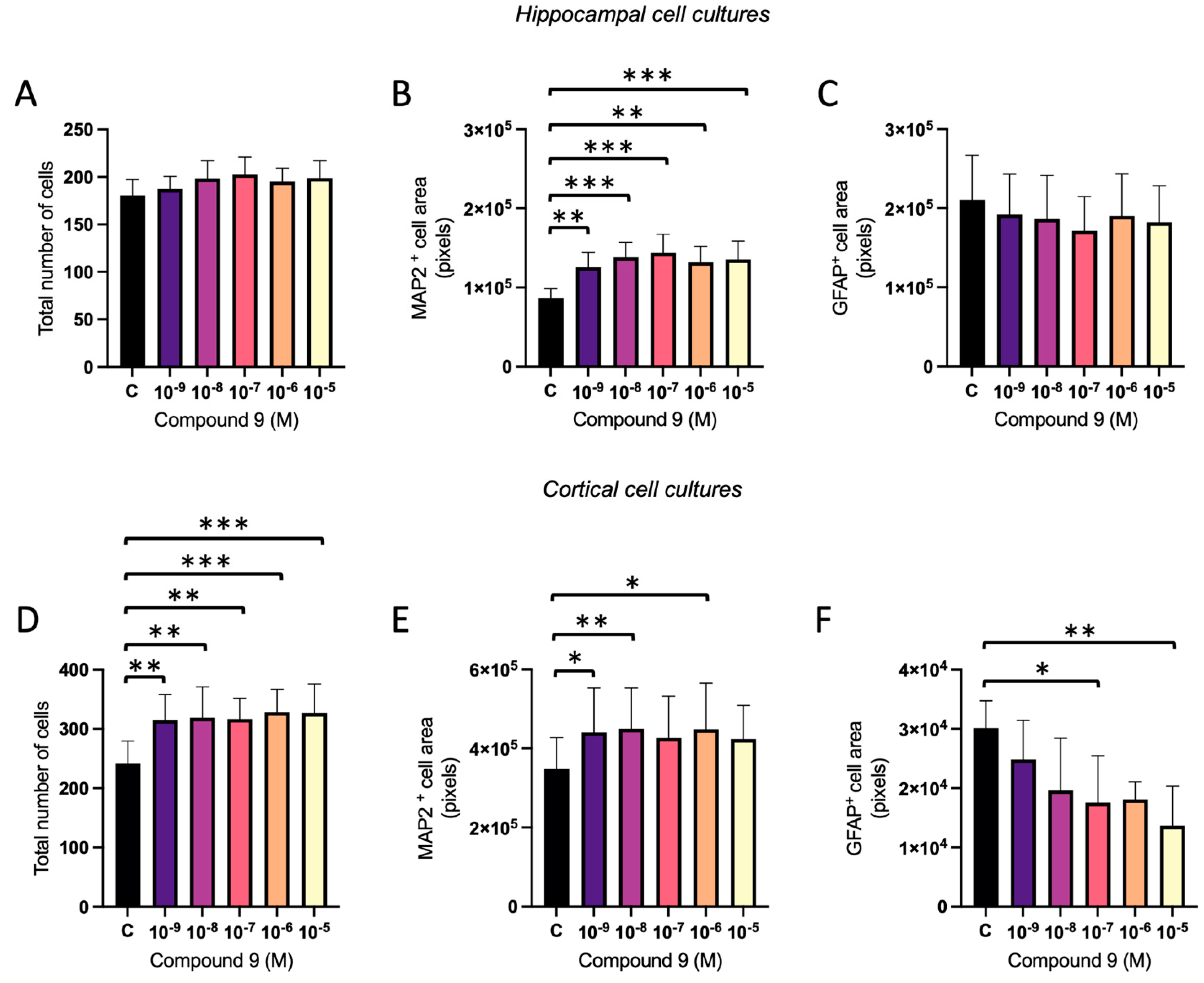
Figure 7.
The effect of compound C9 on the expression of GLUT4 in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the GLUT4 analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on A) the total GLUT4 intensity (n=4-5); B) the neuronal expression of GLUT4 (n=5); or C) the astrocytic expression of GLUT4 (n=3) in hippocampal cells. There was also no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on D) the total GLUT4 intensity (n=5) and E) the neuronal expression of GLUT4 (n=6) in cortical cells. F) There was a significant increase of astrocytic expression of GLUT4 after treatment with 10-8 M C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in the cortical cells (n=5). All data are presented as means ± SEM, **p-value <0.01.
Figure 7.
The effect of compound C9 on the expression of GLUT4 in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the GLUT4 analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on A) the total GLUT4 intensity (n=4-5); B) the neuronal expression of GLUT4 (n=5); or C) the astrocytic expression of GLUT4 (n=3) in hippocampal cells. There was also no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on D) the total GLUT4 intensity (n=5) and E) the neuronal expression of GLUT4 (n=6) in cortical cells. F) There was a significant increase of astrocytic expression of GLUT4 after treatment with 10-8 M C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in the cortical cells (n=5). All data are presented as means ± SEM, **p-value <0.01.
Figure 8.
The effect of compound C9 on the expression of vGluT1 and synapsin I in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the vGluT1 and synapsin I analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) There was a significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the vGluT1 intensity per cell in hippocampal cells, however further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle treated cells (n=5). B) There was a significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the vGluT1 intensity per cell in cortical cells, however further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle treated cells (n=4-5). C) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the synapsin I intensity per cell in hippocampal cultures (n=4). D) There was a significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the synapsin I intensity per cell in cortical cells, however further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle treated cells (n=4). All data are presented as means ± SEM.
Figure 8.
The effect of compound C9 on the expression of vGluT1 and synapsin I in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the vGluT1 and synapsin I analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) There was a significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the vGluT1 intensity per cell in hippocampal cells, however further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle treated cells (n=5). B) There was a significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the vGluT1 intensity per cell in cortical cells, however further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle treated cells (n=4-5). C) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the synapsin I intensity per cell in hippocampal cultures (n=4). D) There was a significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the synapsin I intensity per cell in cortical cells, however further post-hoc analysis revealed no significant difference for any of the C9 concentrations when compared to vehicle treated cells (n=4). All data are presented as means ± SEM.
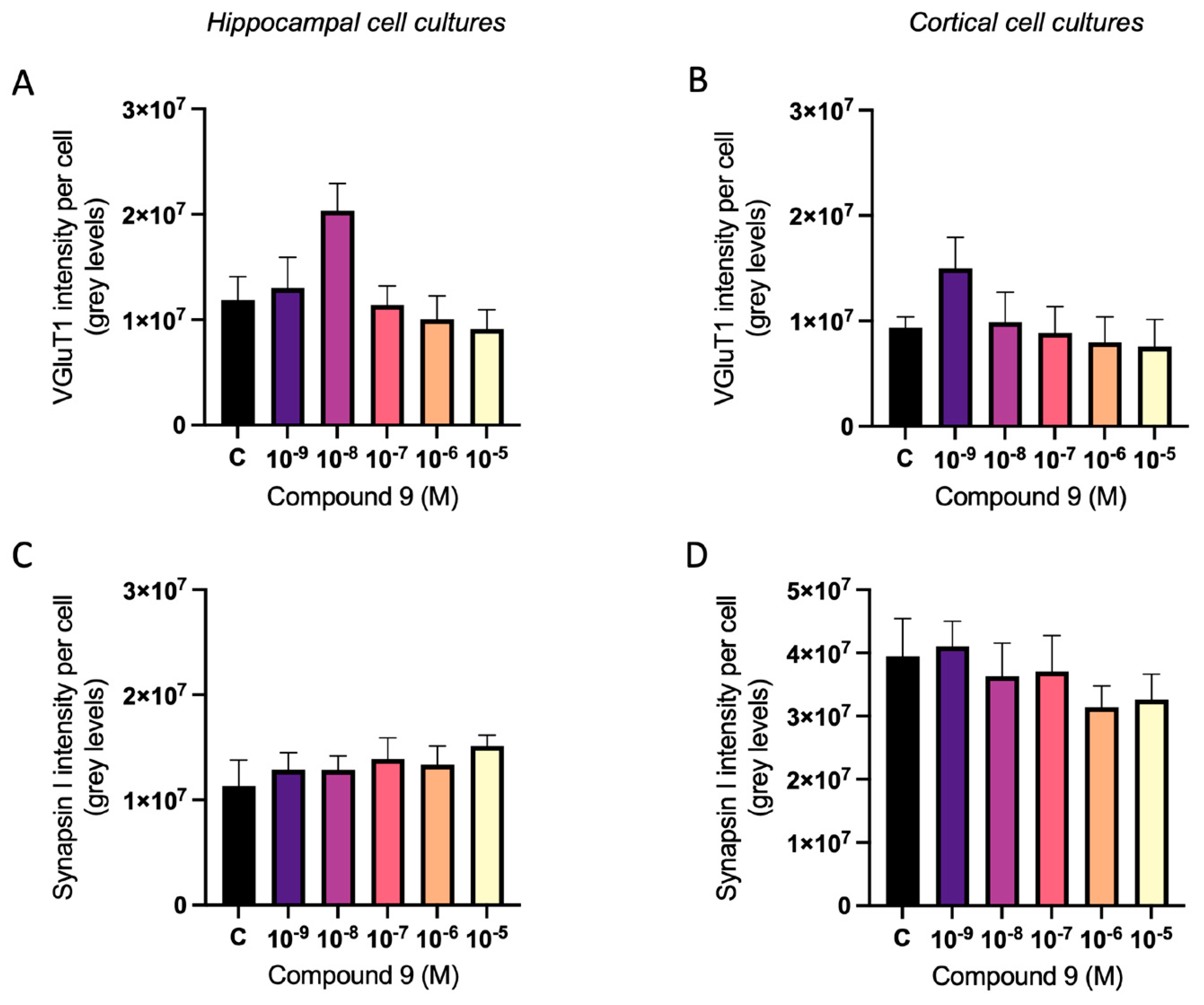
Figure 9.
The effect of compound C9 on the cellular viability in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the MTT, LDH, and calcein metabolism analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the MTT metabolism in hippocampal cells (n=7). B) There was a significant decrease of LDH released in the cell media after treatment with 10-5 M C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in hippocampal cells (n=7). C) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the calcein intensity per cell in hippocampal cultures (n=4). D) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the MTT metabolism in cortical cells (n=7). E) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the LDH release in cortical cells (n=6). F) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the calcein intensity per cell in cortical cultures (n=3). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05.
Figure 9.
The effect of compound C9 on the cellular viability in primary hippocampal and cortical cells. The results of the MTT, LDH, and calcein metabolism analysis for hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after four days of consecutive treatment with IRAP inhibitor C9. The vehicle group (C) was treated with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO. A) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the MTT metabolism in hippocampal cells (n=7). B) There was a significant decrease of LDH released in the cell media after treatment with 10-5 M C9, when compared to vehicle treatment, in hippocampal cells (n=7). C) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the calcein intensity per cell in hippocampal cultures (n=4). D) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the MTT metabolism in cortical cells (n=7). E) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the LDH release in cortical cells (n=6). F) There was no significant overall treatment effect of C9 on the calcein intensity per cell in cortical cultures (n=3). All data are presented as means ± SEM, * p-value < 0.05.
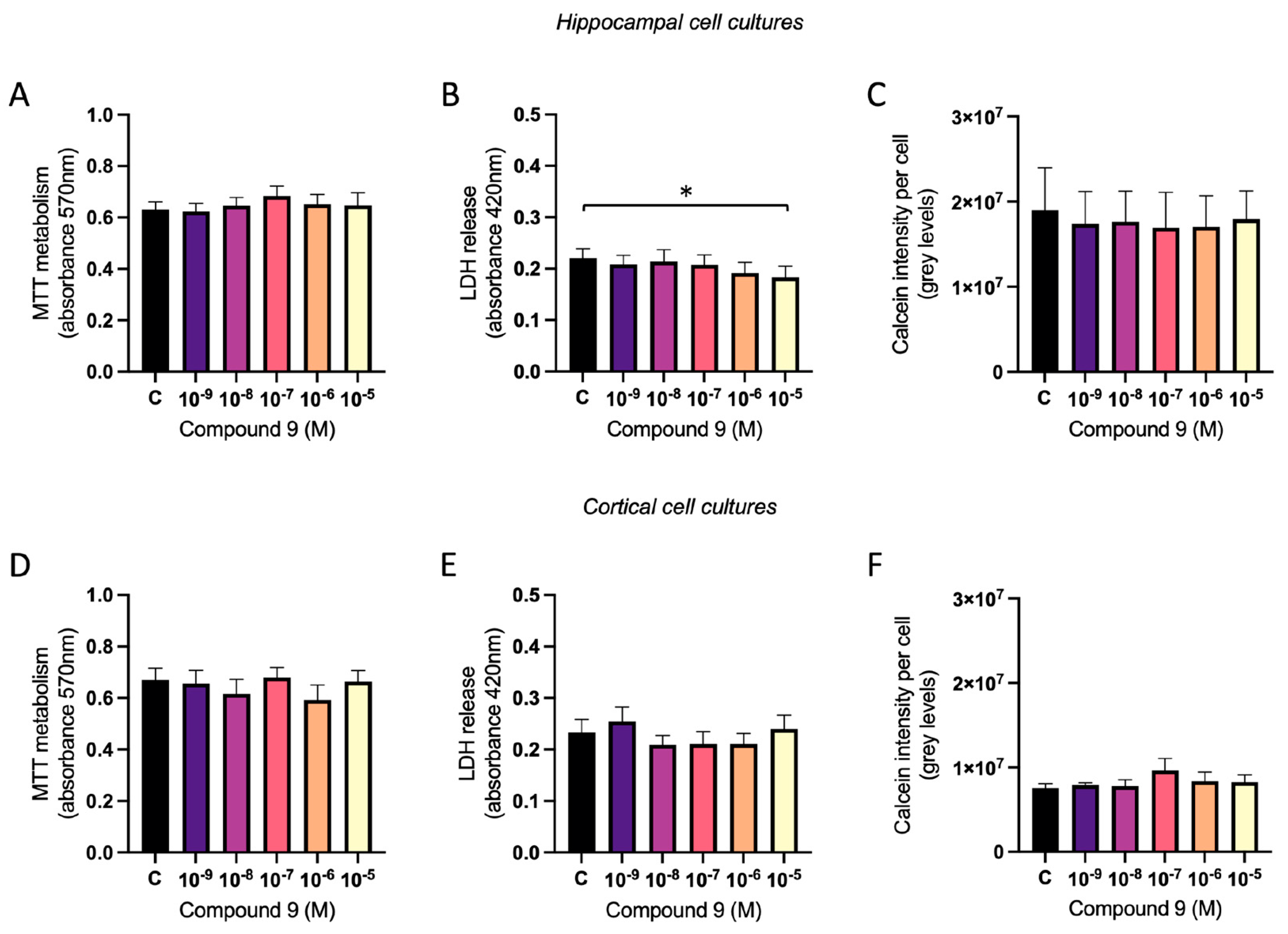
Table 1.
The mRNA levels of Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and Map2 in rat primary hippocampal (n=3-5) and cortical (n=3) cell cultures presented as mean of percentage of control (vehicle treated group). The cells were treated with C9 (0.01, 0.1, and 1 µM) for four consecutive days (vehicle treatment 0.1% DMSO) before analysed for mRNA levels using qPCR.
Table 1.
The mRNA levels of Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and Map2 in rat primary hippocampal (n=3-5) and cortical (n=3) cell cultures presented as mean of percentage of control (vehicle treated group). The cells were treated with C9 (0.01, 0.1, and 1 µM) for four consecutive days (vehicle treatment 0.1% DMSO) before analysed for mRNA levels using qPCR.
| Standardised mRNA levels of Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep and Map2 1 |
| Gene: |
Dbn1 |
Gfap |
Glut1 |
Glut3 |
Glut4 |
Lnpep |
Map2 |
Hippocampal cell
cultures
|
C9
0.01 µM |
61.1 *
± 18.4 |
70.2 **
±7.0 |
55.7 ****
±6.5 |
67.2
± 9.0 |
58.1 *
± 8.3 |
86.3
± 16.1 |
71.0
± 7.5 |
C9
0.1 µM |
70.5
±12.3 |
74.3 *
± 8.9 |
76.8 ***
± 4.4 |
72.1
± 15.2 |
56.3 *
± 11.2 |
104.7
± 15.1 |
92.5
± 16.3 |
C9
1 µM |
46.2 **
± 6.9 |
60.8 ***
± 4.4 |
62.4 ****
± 2.7 |
57.6 *
± 9.8 |
60.0 *
± 15.4 |
69.3
± 6.7 |
63.4 *
± 5.7 |
Cortical cell
cultures
|
C9
0.01 µM |
87.8
± 6.7 |
85.4
± 19.4 |
101.5
± 21.7 |
75.9
± 10.3 |
77.6
± 17.6 |
95.5
± 16.7 |
99.7
± 23.2 |
C9
0.1 µM |
103.3
± 19.0 |
102.2
± 12.6 |
99.1
± 13.7 |
84.6
± 3.1 |
88.0
± 12.0 |
84.1
± 7.2 |
82.7
± 7.3 |
C9
1 µM |
72.4
± 13.6 |
126.8 2
± 4.22 |
101.5
± 12.9 |
88.2
± 8.9 |
73.8
± 10.9 |
87.7
± 6.8 |
94.4
± 10.1 |
Table 2.
The mRNA levels of Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and Map2 was analysed using qPCR in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after treatment with IRAP inhibitor compound C9. Actb, Rplp0, and Rpl19 were used as reference genes. Forward (FW) and reverse (R) primer sequence for each gene is presented in the table below.
Table 2.
The mRNA levels of Dbn1, Gfap, Glut1, Glut3, Glut4, Lnpep, and Map2 was analysed using qPCR in primary hippocampal and cortical cell cultures after treatment with IRAP inhibitor compound C9. Actb, Rplp0, and Rpl19 were used as reference genes. Forward (FW) and reverse (R) primer sequence for each gene is presented in the table below.
| Protein |
Gene |
Primer sequence |
| Beta-actin |
Actb |
FW: CGTCCACCCGCGAGTACAACCT
R: ATCCATGGCGAACTGGTGGCG |
| Ribosomal protein lateral stalk subunit P0 |
Rplp0 |
FW: GGGCAATCCCTGACGCACCG
R: AGCTGCACATCGCTCAGGATTTCA |
| Drebrin |
Dbn1 |
FW: TCAGACAGCAGGAACGAGTG
R: TATGAAAGGGCAGTACGGACG |
| Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
Gfap |
FW: GTGGTATCGGTCCAAGTTTGC
R: GACTCAAGGTCGCAGGTCAA |
| Glucose transporter type 1 |
Glut1 |
FW: GAGCTAGGAGGCTTTACCGC
R: CCTAAATGGAGCCTGGACCC |
| Glucose transporter type 3 |
Glut3 |
FW: ATGGGGACAGCGAAGGTGAC
R: CCCCTCGCTTGGTAGGTCTT |
| Glucose transporter type 4 |
Glut4 |
FW: AGGCCGGGACACTATACCC
R: TAGCCAAACTGAAGGGAGCC |
| Insulin-regulated aminopeptidase |
Lnpep |
FW: GAGTGACAAAGACCGAGCCA
R: TCTGAAGAGGCACTTTGCCA |
| Microtubule-associated protein 2 |
Map2 |
FW: GACCACCAGGTCAGAACCAAT
R: TGGGCACCAAGATGCCAAAT |
| Large ribosomal subunit protein eL19 |
Rpl19 |
FW: GCGTCTGCAGCCATGAGTATGCTT
R: ATCGAGCCCGGGAATGGACAGT |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).