1. Introduction
Almost 10% of all children are at increased risk for long term sequelae due to preterm birth prematurely [
1,
2]. The medical care required for survival of premature babies often lasts for months and constant monitoring using conventional techniques can cause pain and skin irritation [
3,
4,
5]. In the context of intensive care, it is necessary to observe vital parameters regularly over a longer period of time. In the search for better ways to monitor such vulnerable infants without causing distress, contactless measurement methods are becoming increasingly important [
4,
6]. Pulse oximetry (PO) is a standard technique used to continuously measure the proportion of hemoglobin molecules that are loaded with oxygen in arterial blood [
7,
8]. Common pulse oximeters (PO-meter) are poorly suited for preterm neonates, since they usually require a circular bandaid for the sensor and a wire with a diameter of approximately 4 mm. The circular bandaid can disturb the perfusion of extremities and skin lesions during removal, and the wire can cause entanglements or decubitus once the infants move. Moreover, motion artefacts are very frequent [
5,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The aim of this project is to close the gap for premature infants in vital monitoring by developing a sensor that measures the infant’s vital signs (heartbeat and oxygen saturation) by means of a camera without requiring any skin contact.
Here we demonstrate the functionality of the system on an animal model to pave the way for its use in neonatal intensive care units (NICU).
2. Materials and Methods
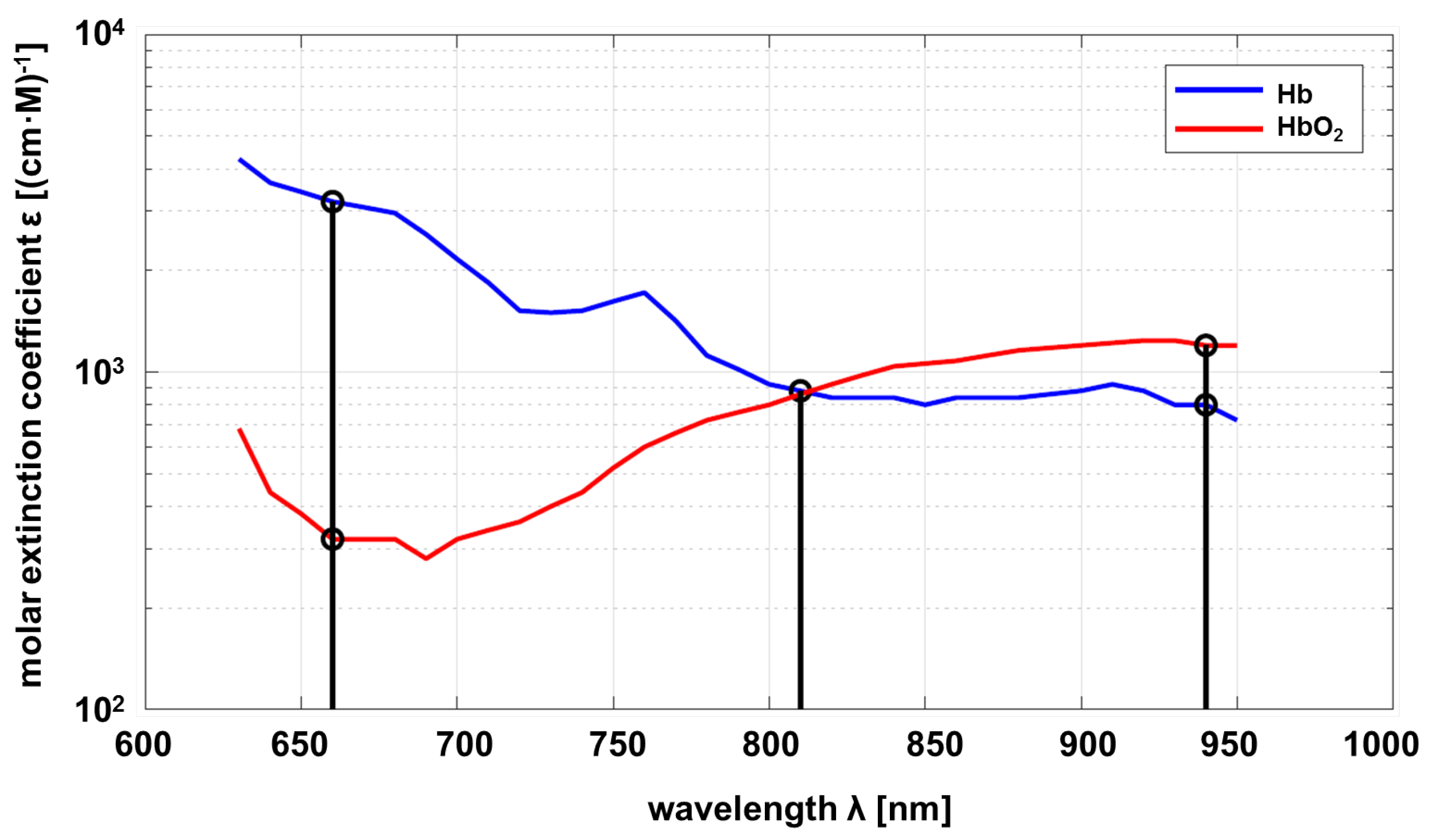
For the Lambert-Beer law, the optical properties of the substance to be investigated must be known as a function of the wavelength. In this project, the relevant substance is circulating blood, in particular hemoglobin, which is responsible for oxygen transport. As a consequence, the properties of deoxyhemoglobin (Hb) and oxyhemoglobin (HbO
) are of interest. The molar absorbtion of Hb and HbO
depending on the wavelength is shown in
Figure 1.
Common pulse oximeters are using two wavelengths approximately
nm and
nm. The sensor developed within this project uses an additional wavelength at
nm as proposed by Wieringa et al. [
13]. The maximum difference in absorption of Hb compared to HbO
, is at
, and vice versa at
. Both substances show the same absorption at
(adiabatic point). The linear independence of the transmission at different wavelengths allows a statement about the composition ratio of Hb and HbO
, if measurements with different wavelengths are carried out. The mathematical principles are described below [
14,
15].
2.1. Pulse Oximetry
The calculation of the oxygen saturation of the blood is based on the principles of Lambert-Beer’s law (eq.
1), which describes the absorbance of blood, in particular hemoglobin. This depends on the density
c, (decadic) extinction coefficient
and the path length
l at which the light passes through an artery.
means the intensity or power of the incident light and
means the intensity of transmitted light escaping from the measuring medium.
It can also be written in exponential form for the transmittance with extinction coefficient
(natural base) written in the following as
.
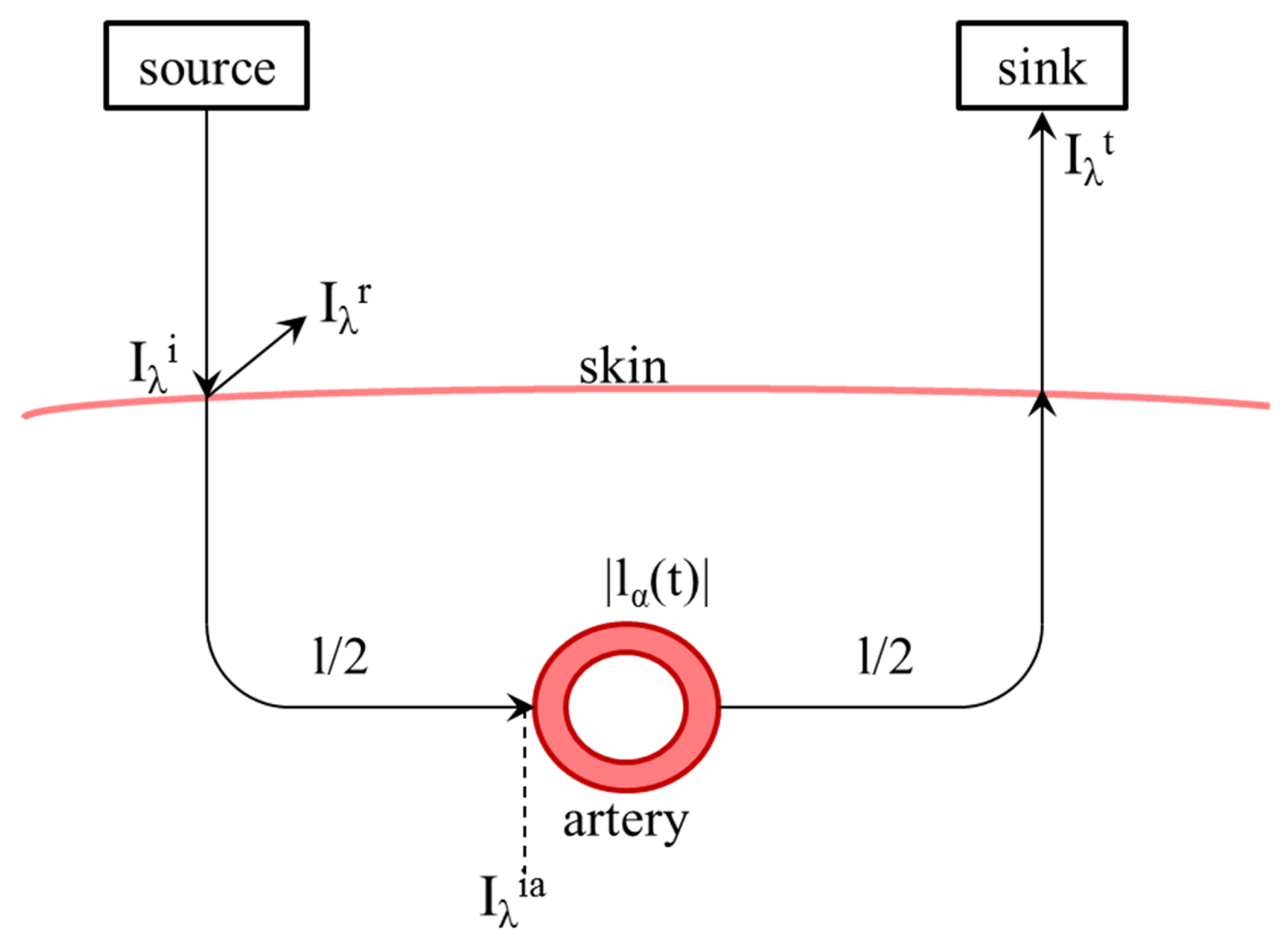
This equation is intended to describe one measuring medium with a constant path length. For real application to measure oxygen saturation, different attenuations caused by skin, bone and other non-pulsating elements lead to a constant part
l, as well as in an alternating
caused by the pulse wave in artery and vessels, shown in
Figure 2.
The transmission
is the ratio of received (AC, numerator) light, which has penetrated the artery at a certain point in time, to incident light (DC, denominator).
Consequently, the transmission ratio
can be calculated from the AC (numerator) and the DC (denominator) value.
Using two different wavelengths and the ratios the definition of the so-called ratio-of-ratio
R is possible to be calculated directly out of the measurement by applying the logarithm.
The relative saturation
S describes the ratio of oxyhemoglobin
to total hemoglobin
.
The ratio-of-ratio can also be described by the extinction coefficients and the relative saturation of the blood, see equation
11.
If now converted to saturation, it is possible to calculate the relative saturation
S including
R as described previously.
Since equation
12 is a simplification which does not take into account all the constituents of the blood, this formula should be considered only as an approximation. In practice, the measurement system must be calibrated or use more wavelengths to resolve more components [
14,
16,
17,
18,
19].
2.2. Signal Processing
The implementation of a camera-based method of pulse oximetry requires various considerations in reference to the physical conditions, mathematical methods and the resulting signal processing, which will be regarded below. Commercial PO-meters are contact based, which means that both the transmitter light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and the receiver unit are located directly on the skin. For newborns, the foot, palm or wrist is usually used as fingers are too small for correct probe placement [
20,
21]. A circular band-aid ensures the probe is fastened securely in place and simultaneously forms a shield against extraneous light. The transmitter and receiver are located opposite one other to allow measurement through transmission.
The developed method of camera-based contactless pulse oximetry shows some significant differences compared to the conventional method. The following physical differences have to be considered: The light source and light-sensitive receiver are located next to each other and on one side of the object, so that the reflection and transmission is measured [
22]. The distance between the sensor and the object of interest is variable and generally further away when compared to that of the commercial PO-meter. The vital parameters of premature infants must be monitored continuously in an incubator. These incubators set a distance of approximately 0.3 m between the neonate and the sensor, which is located on top of the incubator. Various methods use the passive ambient light as a source and realize the differentiation of wavelengths by spectral filters, for example RGB bayer-filter or two cameras [
19,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27]. The method presented here, however, uses active lighting, which guarantees constant illumination.
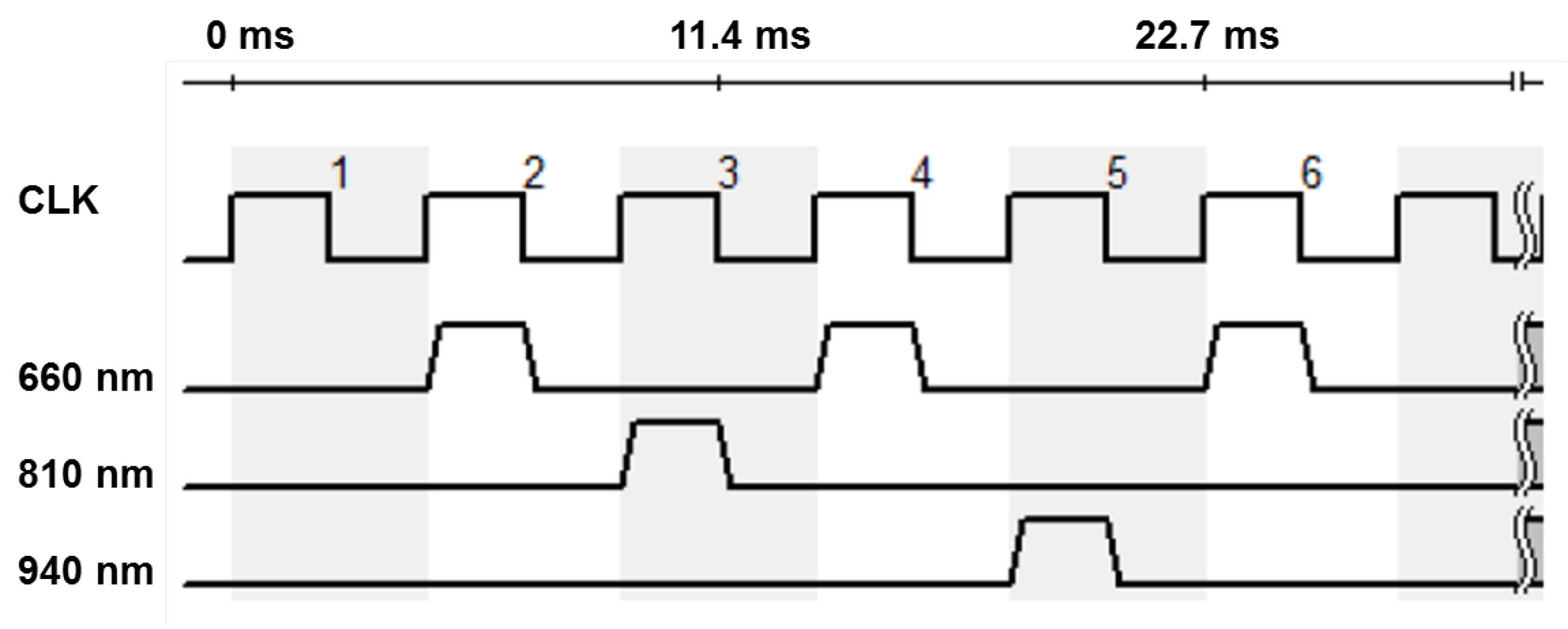
The involved monochrome camera (IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH, Obersulm, Germany) does not allow any spectral distinctions. In order to achieve a spectral resolution, the lighting is operated in a synchronous time-division multiplex process. The three available types of LEDs are operated alternately. In the following considerations and evaluations, the multiplex scheme shown in
Figure 3 is preferred. The sampling rate of the camera is decisive for the selection of the sequence. For the intended application in the incubator, it is important that the light emitted does not flicker visibly, as this is unpleasant and can cause distress in premature infants.
At the selected area of interest (AOI) of 250x250 px, the maximum frame rate of the camera is about 220 fps. This results in an effective sampling rate of 110 Hz for a given multiplex time scheme for 660 nm, so that the strobe light is no longer visible to the human eye.
All other wavelengths alternate at approximately 36 Hz. This illumination of the measuring object must be strong enough to ensure sufficient signal strength and quality as well as to dominate over extraneous background (bg) light. The incubator is not shielded from ambient light. The following condition applies:
If this condition is fulfilled, a large part of the light radiating to the skin is reflected (remission,
). The light penetrating the skin is attenuated, penetrates arteries and is captured as a signal in the camera/receiver when it leaves the skin. Thus, a combination of transmission and reflection are measured, see equations
15 and
16. With these properties, the system is described as a time-dependent signal
and background light
.
The reflected and transmitted intensity
and
shown in
Figure 2 can be described by the reflection factor
and the transmission factor
, too.
and
It is to be assumed that
is constant. This supposition describes the phenomenon in which reflected light behaves independently of the pulse wave and thus independently of the time. The recorded signal can therefore be described as follows
The signal term influenced by the background light can be separated into varying two parts, one part called
influenced by the time-varying transmission of a static background light and one signal part called
from a time-varying background light with constant background illumination.
It is obvious that the useful signal is strongly influenced by the background light. The active illumination is presumed to be constant in amplitude, otherwise a further modulation is added which falsifies the measurement. As shown in
Figure 3, one frame per multiplex sequence is a zero frame when the light source is switched off. It is utilized to reduce the influence of background light. The constant included in the ‘bg’-calculation can be reduced by subtracting the zero image as long as it remains unchanged over time. It follows
The superimposed signal
now consists of the time-varying signal background [
14,
17,
18,
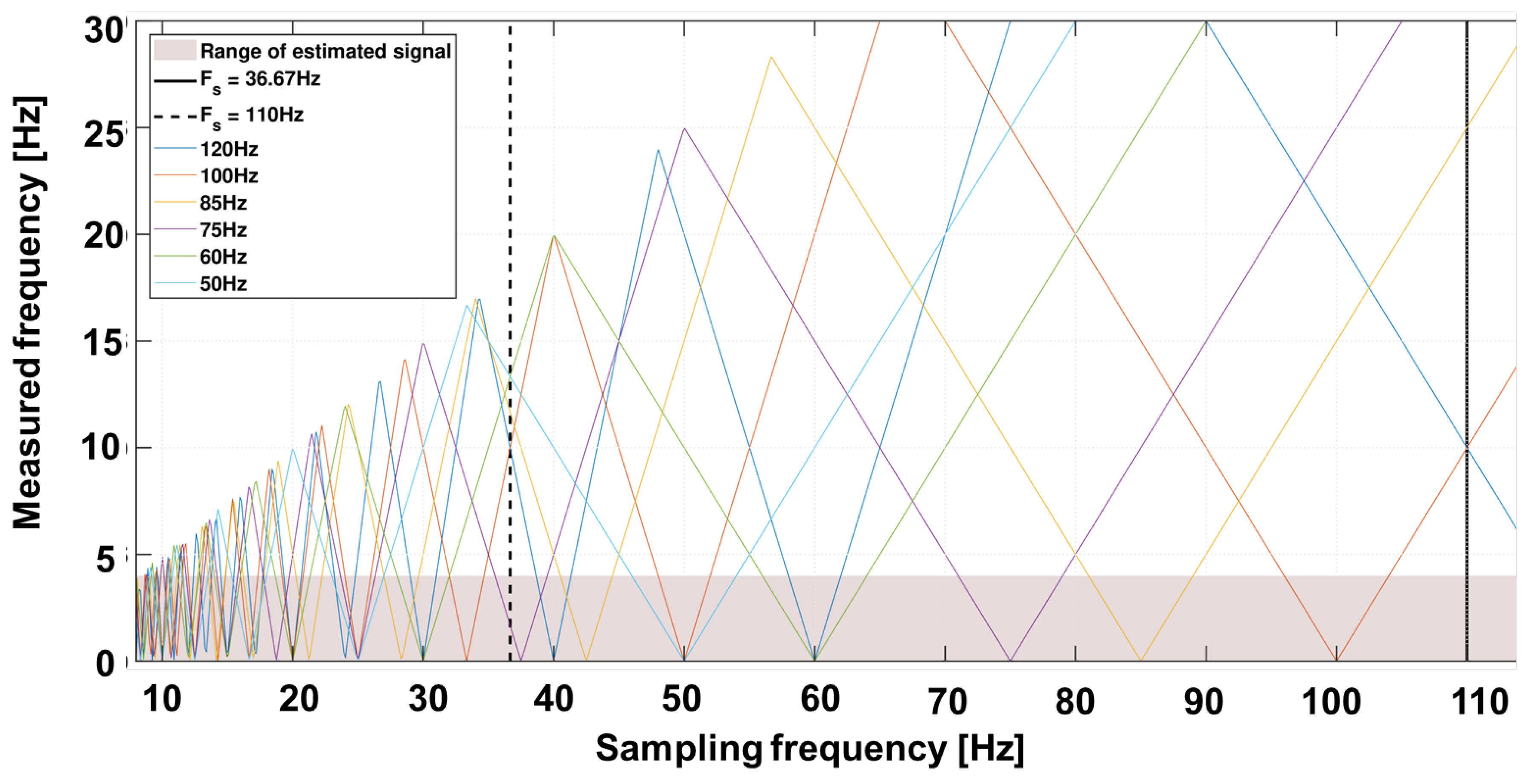
19]. The frequencies to be expected are above the useful signal band. However, the previously described sampling rate of the camera leads to sub-sampling and thus to allowing for aliasing. The expected external sources including mains frequency at 50 Hz, tubes at 100 Hz or screens with 75 Hz, can lie within the useful bandwidth.
Figure 4 shows an example of the spectrum to be expected with various background artefacts. The variability of frame rate allows a suitable selection in which the useful bandwidth contains no or as few artefacts as possible.
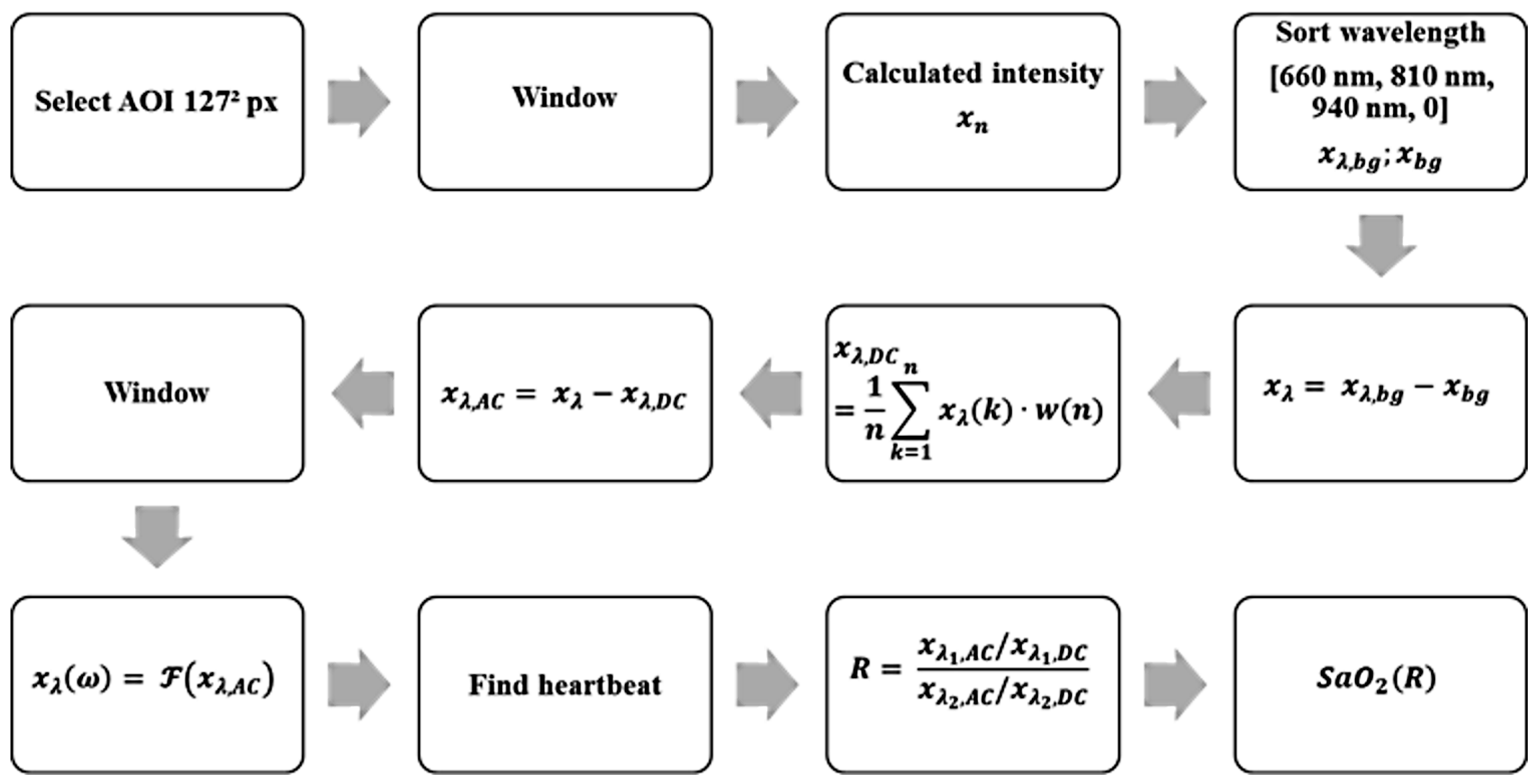
Using these parameters and properties, an algorithm for the detection of a heartbeat and calculation of the oxygen saturation could be designed. The block diagram in
Figure 5 shows the algorithm explained below.
Display a default image of the recorded scene, in which a suitable place for the Sub-AOI (125px)² is selected.
Rework of each image with a 2D Hann window to filter light movements. Edge pixels are weighted less than in the center.
Averaging of all pixels to one intensity value. Thus, the given quantization is increased from 10 bit by to 17 bit (compare oversampling effect). Without this virtual increase, the pulse signal cannot be reliably detected because it is in the range of noise level.
Sorting the discrete time values to match the corresponding spectral component.
Subtraction of the black value from each signal to remove constant background lighting.
-
(A) Averaging the weighted window of a length of 12 seconds to obtain DC.
(B) Subtraction of the DC value in the current time window and thus determining the AC part of the signal.
Adjusting spectral components in the phase by multiplying with . With corresponds to and n the corresponding timestamp in each multiplex phase starting with zero.
Rework the last 12 seconds of the signal with a window function to obtain a periodic signal.
Transformation of each window (12 seconds) from time domain into frequency domain by a fast Fourier transformation including zero padding to obtain a length of 8192 points.
Classification of the pulse signal in .
Calculation of the ratio-of-ratio.
Calculate oxygen saturation according to equation
12.
Steps one through seven are repeated for each multiplex phase, steps eight through twelve are repeated every 22 multiplex phases to reduce computational effort.
2.3. Camera
In order to continuously improve these algorithms, the development of a modular and dynamic system was necessary. The most important components are the cameras, which were selected based on different parameters. These include resolution, quantization, quantum efficiency and the possibility of communication/software integration. Two IDS cameras were used for the described system. A monochrome UI-3240ML-NIR-GL and an RGB camera UI-3240ML-M-GL. Both have the option of multi AOI, which makes it possible to increase the sampling frequency when reducing the recorded scene. This provides advantages in signal processing, such as an increase in 10-bit quantization as described in
Section 2.2.
Both sensors are equipped with redundant electronics so that they can be operated as master or slave. The master is used to record the vital data, while the slave can be used to synchronously record the scene to identify artefacts such as movements during an offline evaluation. Both cameras have a USB 3.0 port for communication and data transfer as well as General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) pins to control the exposure electronics.
2.4. Microcontroller and Illumination
The GPIO outputs of the master, control a STM8 microcontroller (C) of the driver board by means of a software SPI. It is not mandatory that the camera serves as a clock, it is also possible to use the C as a clock source. The board also has GPIO’s, which allows stacking of any number of these drivers to increase the light output.
Variants of the multiplex methods are predefined in the software and can be freely selected. In addition to switching on additional lighting boards, the intensity can be adjusted by switching LEDs for each wavelength on and off. The intensity of the illumination is set for each wavelength that the maximum value (white image) is not exceeded at a certain exposure time. This increases the signal-to-noise ratio.
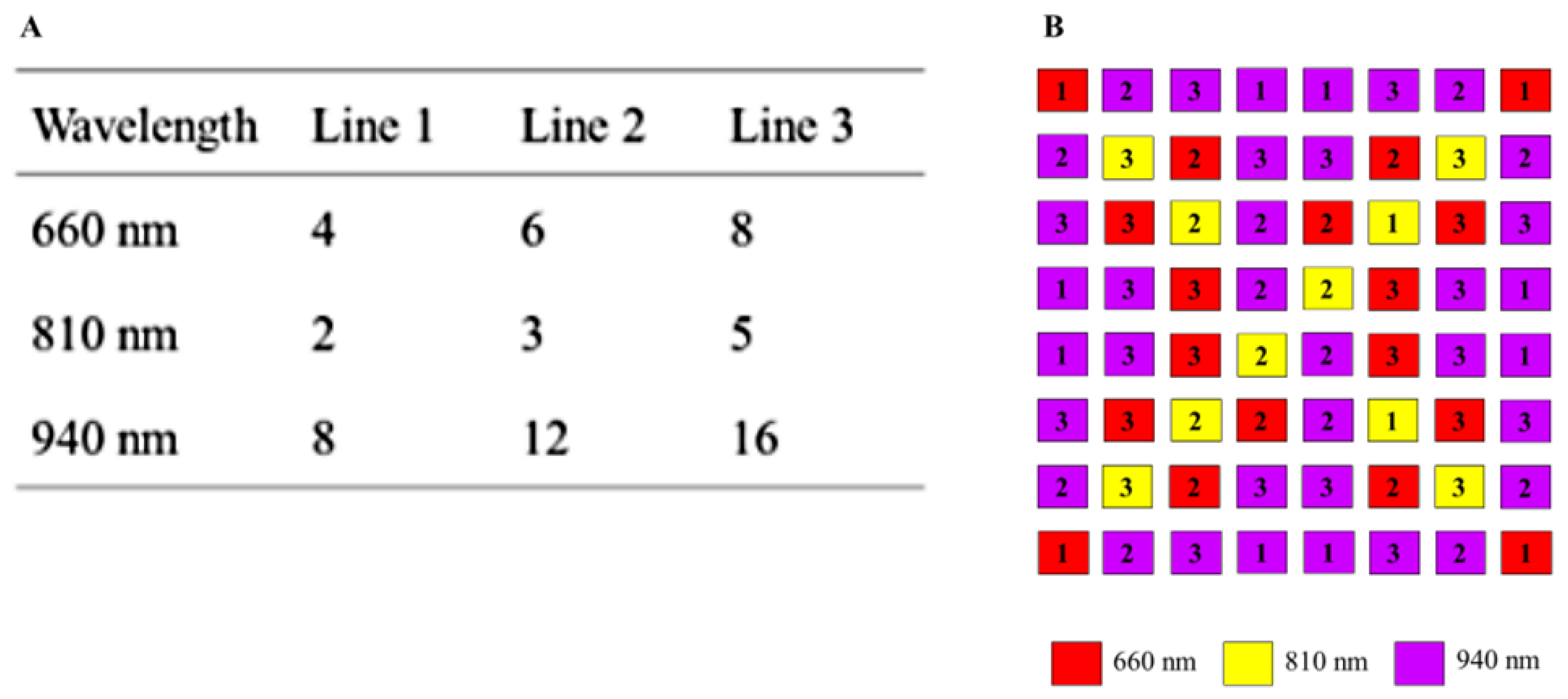
Figure 6A shows the possibilities of respective lines. The pattern of each line is normally distributed so that a homogeneous illumination is achieved. Thus, up to six intensity states per line are possible. The number of LEDs per wavelength compensates the spectral quantum efficiency of the sensor.
Figure 6B shows the arrangement of the illumination board. At a distance of 0.3 m between ceiling and floor of the incubator, even a bright field illumination is guaranteed.
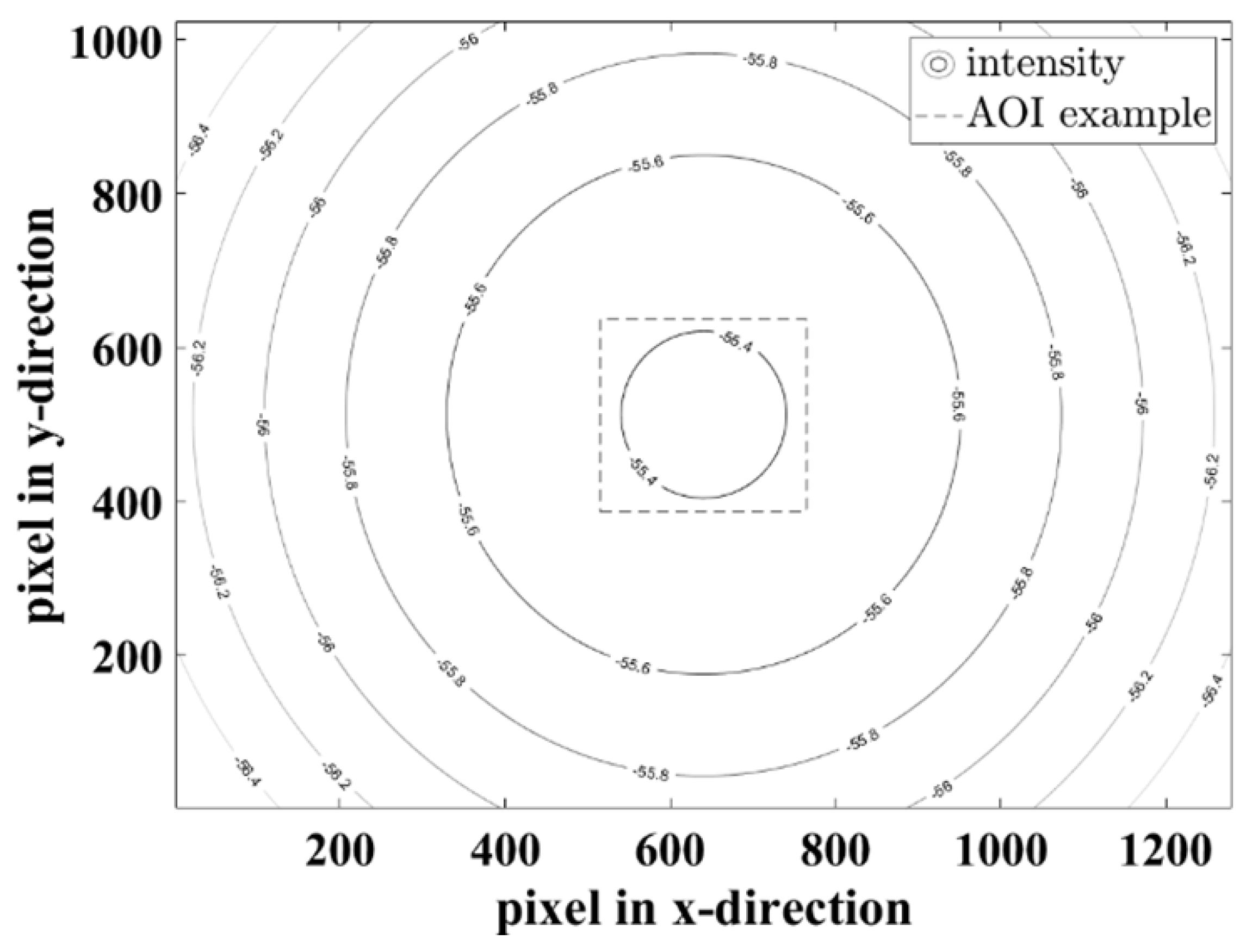
Figure 7 shows the simulated radiant power for the 940 nm LEDs on a plane object as an example. For other wavelengths the distribution is similar, with different attenuations caused by the number of LEDs.
The minimum attenuation for 660 nm is -58.98 dB, for 810 nm -60.93 dB and for 940 nm -55.37 dB. In the entire scene (1280 x 1024 px), the maximum attenuation difference is 1.9 dB, so that diffuse lighting is created.
After setting up all of the hardware components, a storage system for the raw data was required, as the data evaluation was to be carried out offline. Furthermore, due to the high data rates in the range of 26.3 MByte/s, caused by the sampling rates and resolutions, online data evaluation including storage is currently not possible. The software is comprised of two programs: First, the “Record GUI”, which handles all camera settings and data storage, and the second “Analysis GUI” for offline evaluation.
The “Record GUI” uses a USB 3.0 standard to set the camera, which in turn uses a software SPI to set the lighting unit. For an optimal adjustment of the measurement area, it is necessary to view the entire scene in which the AOI to be examined is placed at (250px)² before starting the recording. The whole AOI is divided into four sub-AOIs with 125 x 125 px each, these are each freely selectable. Each window can be viewed live for analysis and evaluation of the extraneous light. Thus, artefacts and their frequencies are detectable at an early stage. To reduce the artefacts in the useful signal bandwidth, see
Section 2.2, the frame rate is adjusted. The optimal exposure is selected by switching LEDs on or off. Recording begins with the settings selected by the multiplex method.
At the beginning of analysis, a sub-AOI (125px)² is selected on an illuminated preview image. These windows as well as the data of the reference monitor (CARESCAPE B650, GE healthcare, Chicago, Illinois, United States) are synchronized, processed and evaluated as described in section sec:SigProc. The vital signs heartbeat and SpO are then stored alongside the comparison data from the reference monitor.
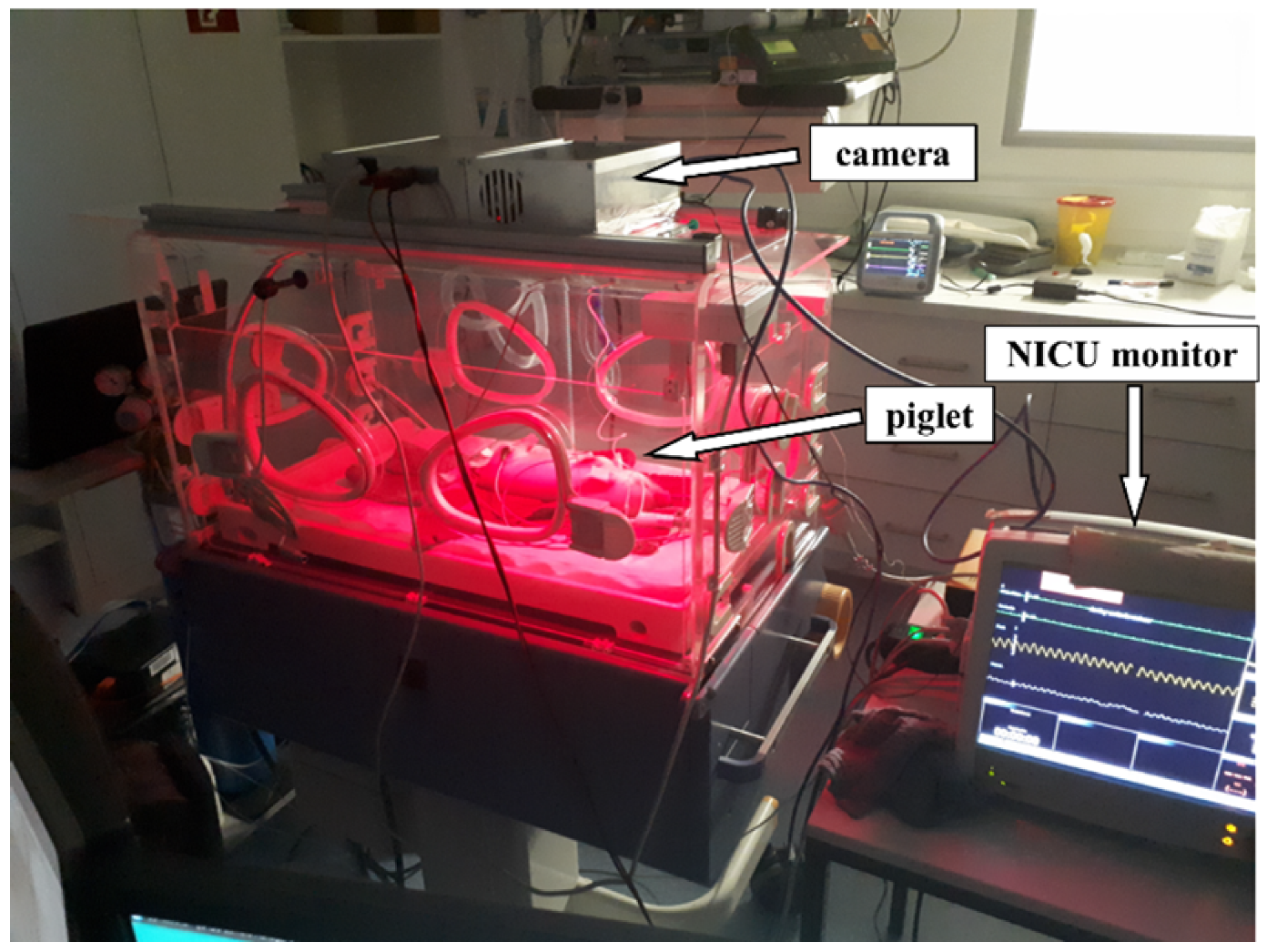
3. Experimental Setup
The various hardware components described above have been integrated into an incubator 8000 IC (Drägerwerk AG & Co KGaA, Lübeck, Germany). To evaluate the camera-based contactless pulse oximeter with time-division multiplex lightning as a novel tool in the NICU, a series of measurements were carried out. The vital parameters data should correspond as closely as possible to those of the later target group, premature infants. Similar to human preterm neonates, newborn piglets have a heart rate that ranges between 100 and 180 bpm [
28]. For this reason, the measurement series was carried out on a piglet aged between one and four weeks.
In preparation for the experiments, the pregnant sow (Aachen Minipig, Heinrichs Tierzucht GmbH, Heinsberg, Germany) was housed in the animal husbandry with special litter bay three weeks before the expected date of delivery. After spontaneous birth, the weaning piglets had constant access to water and a warming lamp. Piglets (Aachen Minipig) from one litter were included in the study at the age of one to three weeks. Sedation was induced with 4% isoflurane in oxygen via a face mask to place a peripheral venous catheter in one of the ear veins. Blood was drawn from the catheterized vein through a three-way stopcock for blood gas analysis. Anesthetic maintenance was achieved by anesthetic depth controlled IV administration of propofol (2-3 mg/kg/h). The spontaneously breathing piglet was placed in the center of the temperature-regulated incubator. The study was carried out in compliance with ARRIVE guidelines. All measurements were taken under constant supervision of physicians and veterinarians.
Data collection for the piglet involved four to five separate measurements in one day. For the measurements, the piglet was anesthetized and placed in the center of the temperature-regulated incubator. During a period of 5 minutes to 25 minutes, the piglet was simultaneously monitored using both the contactless camera-based method described above and a conventional wired NICU monitor. To ensure optimal signals, we tested the contactless monitoring system using different locations of the sensor.
The optimum conditions of the above-mentioned time-division multiplex method are measurements taken in a relatively darkened room, so that condition eq.
13 is fulfilled. Thus, the adjustment of the sampling rate was not necessary; the maximum rate was selected. With the multiplex procedure used, all other procedures can be reproduced. To validate the data collected by the contactless monitoring, the vital parameters were measured additionally by an independent monitor (GE healthcare CARESCAPE B650), which is commonly used in neonatal intensive care units. The monitor was connected to the piglet legs via a pulse oximeter sensor, which uses red and infrared light to measure oxygen saturation (SpO
) together and with a three-channel electrocardiograph (ECG).
Figure 8 shows the setup during measurements.
4. Results
Firstly, we generated an extensive number of data using the contactless monitoring system with a high variation in the parameters. Using this as a base, error detection and improvement was possible. Thus, measurement data can be provided in case of a subsequent change of the algorithm. During the evaluation of the contactless monitoring system, the skin pulse rate was first extracted and compared to the heart rate measured by the ECG, for reference, as this has a significant influence on the accuracy of the saturation reading. Here we present the selected data collected from measurements of a single piglet concerning detection of heart-beat, skin pulse rate, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation using contactless monitoring.
4.1. Skin Pulse Rate and Respiratory Rate
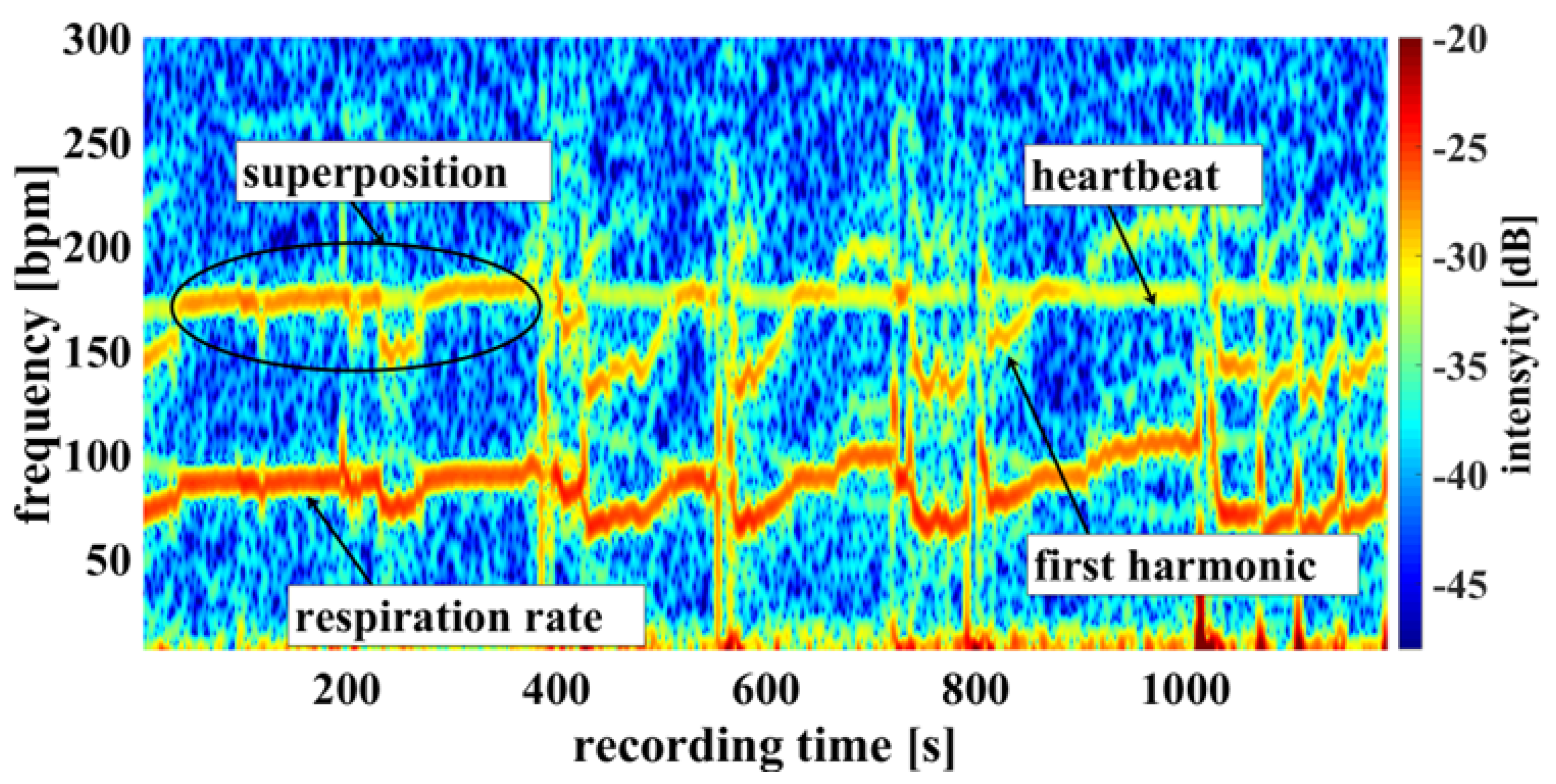
Using the camera system, measurement of respiratory rate was also possible. Some of the challenges encountered are demonstrated in
Figure 9, an example of a cumulated spectrum. The respiratory rate of the piglet is around 90 bpm. Since respiration rate is a side effect of heart beat measurement and not an ideal sinus rhythm, the harmonics can superimpose upon the heartbeat. This may lead to a misinterpretation, depicted in
Figure 9 between 0 and 400 seconds.
So, it should be regarded as an unwanted artifact because it can lead to an incorrect measurement. It has also been observed that the movements of the piglet led to modulation of light which can lie within the measuring bandwidth of the pulse wave, represented on
Figure 10 around 800 seconds.
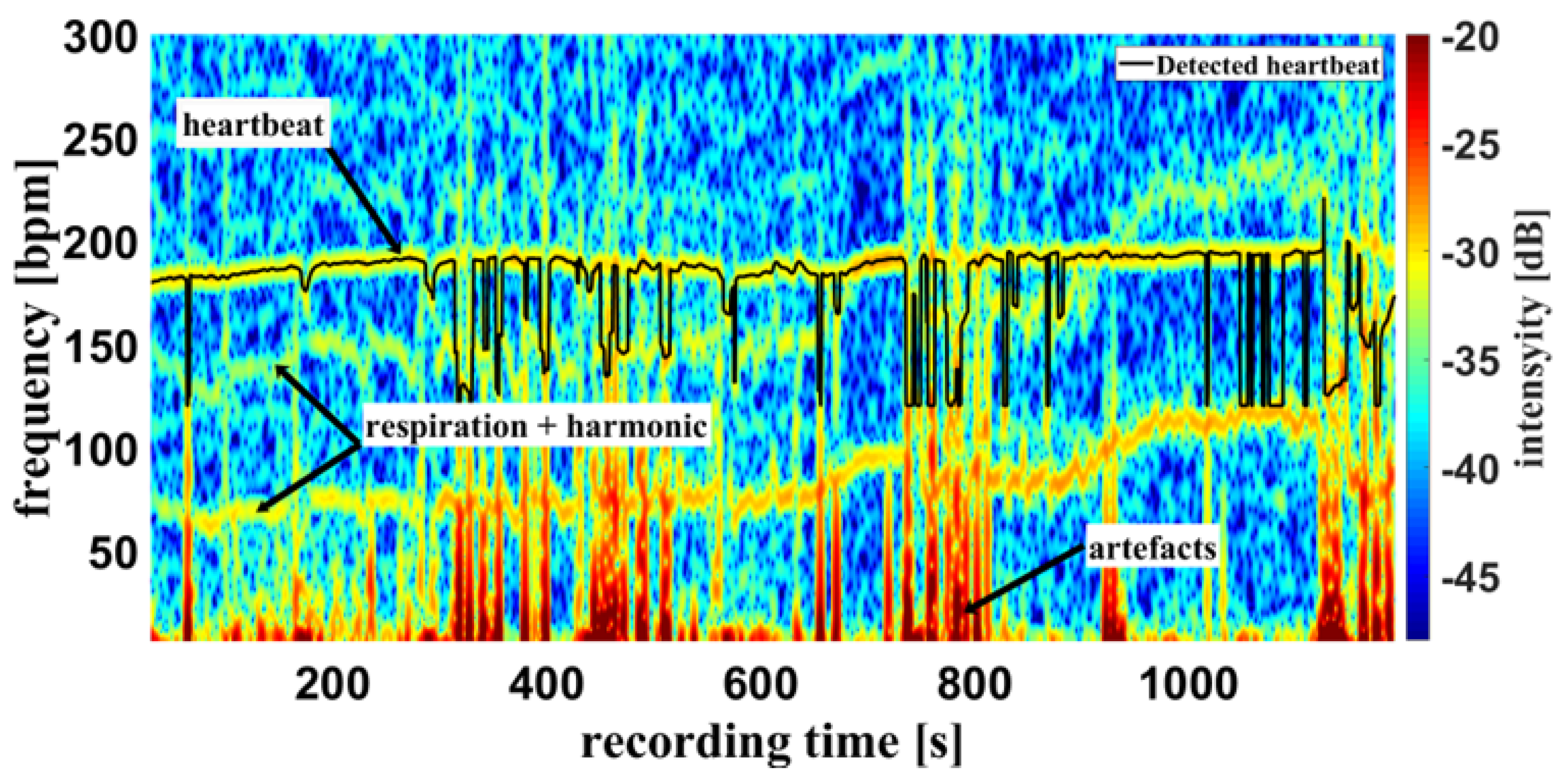
The respiratory rate, skin pulse rate and pulse waves were recorded by contactless monitoring.
Figure 10 shows a different measurement example of a cumulative spectrum with successful heartbeat detection. Heartbeat and respiration can be separated clearly during flat breathing and only minor intervention, caused by artefacts and respiratory interruptions (mean difference: -9.193 bpm). The peaks e.g. at 400 s, and 700 s are breathing interruptions.
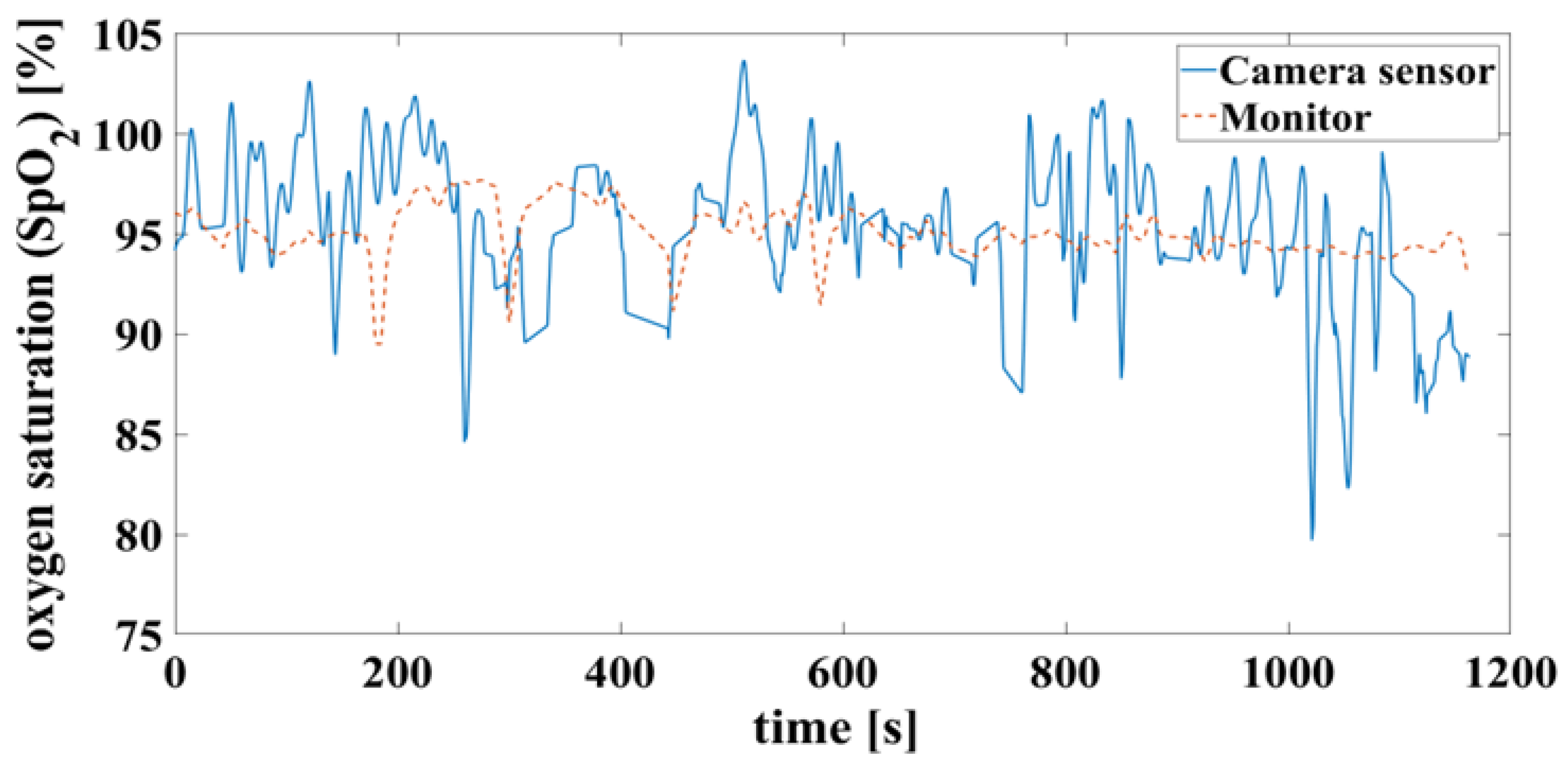
4.2. Oxygen Saturation
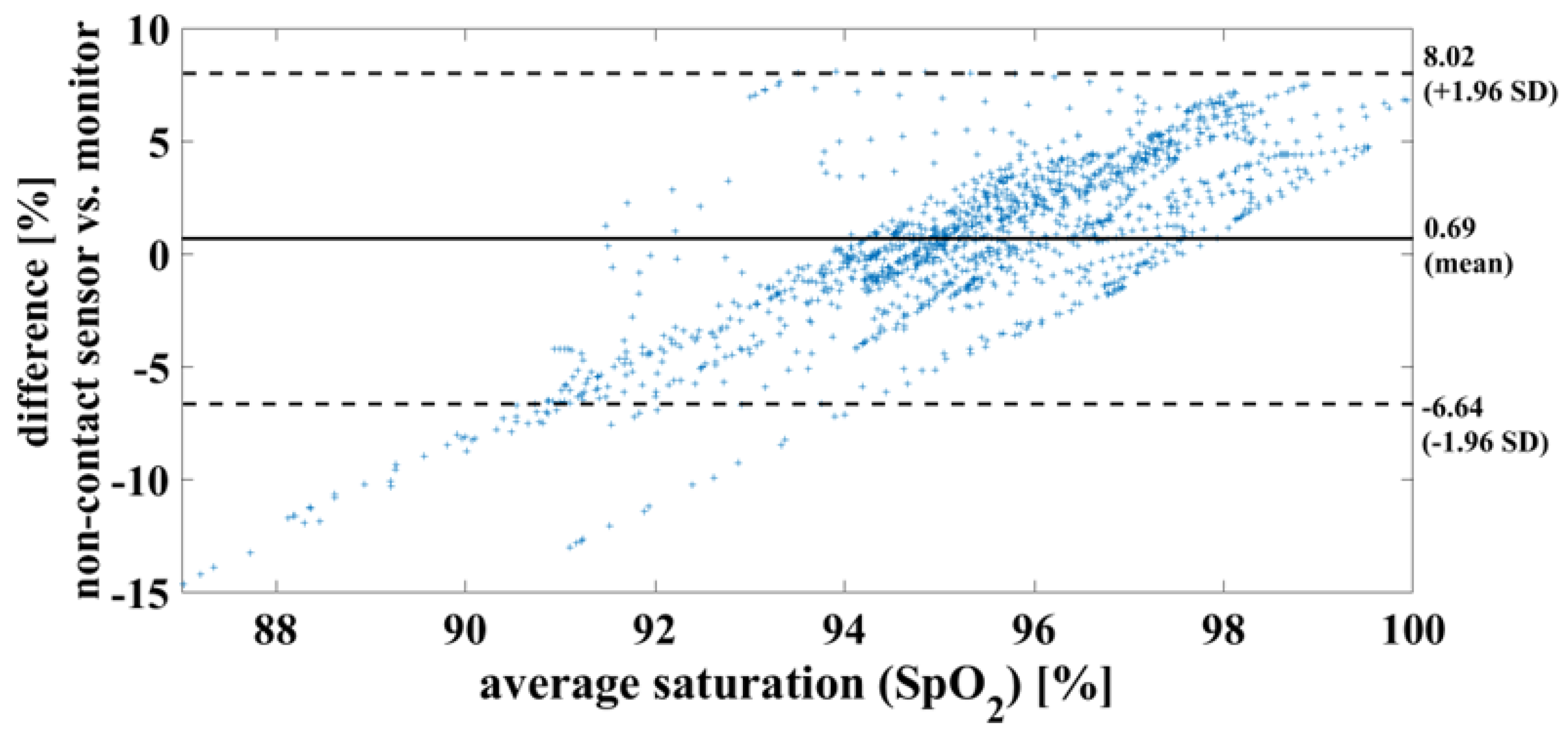
In the case of a successful contactless-monitoring measurement, in which heartbeat and respiration can be clearly separated (
Figure 10), the oxygen saturation can be determined with mean difference of 0.7%, RMSE of 3.8% and MAE of 2.93%. To compare the results using the measurement methods, on the one hand contactless monitoring and on the other hand wired pulse oximetry, the results are shown here as a Bland-Altman diagram in
Figure 11.
False detection of the heartbeat inevitably leads to an error in the oxygen saturation calculation. This can result in unrealistic saturation above 100% shown in
Figure 12, which are not yet filtered here.
5. Discussion
On average, every tenth child worldwide is born prematurely [
1,
2]. The enormous progress made in neonatological intensive care over the last two decades has significantly improved the survival prognosis for these children [
29]. However, the very immature brain of the premature neonate is exposed to unphysiological stimuli and impairments through birth and the necessary intensive care measures [
6,
30].
This includes the high susceptibility to infection [
31], which increases proportionally with the number and intensity of medical interventions and manipulation. Irritations such as pain, noise and handling can lead to functional and structural aberrations during this vulnerable development phase of the brain [
32]. By dispensing with the use of adhesive sensors, our newly developed contactless technology protects the sensitive skin of the premature babies and thus reduces the risk of infection and the formation of lifelong scars [
33,
34]. The possible pain involved when applying and removing the sensors is also avoided [
6]. It is important to seek to reduce stress factors for premature infants during their long stays in hospital and at the same time to improve the intensive medical treatment of these children.
For these reasons, an incubator that does not require wired sensors to record vital parameters is desired. This is intended allow a more ’hands-off approach’, leading to the avoidance of the aforementioned stimuli and thus to the prevention of the harmful acute and long-term consequences for the premature infant. A first step in the development of this technology is the establishment of a camera-based contactless pulse oximeter that monitors the pulse rate, respiratory rate (error term) and oxygen saturation of the blood. The initial testing should determine the ability of the camera-based contactless pulse oximetry sensor to validly determine the pulse rate.
5.1. Skin Pulse Rate and Respiratory Rate
The conventional monitor used by default in the NICU served as a reference to validate the measurements based on the contactless monitoring system. Throughout all recorded measurements, multiple deviations of the conventional and contactless monitoring were observed during the experiments. Multiple factors contributed to the deviations between the two measurement techniques. Respiration measurements of the contactless system (costal, as well as, abdominal) were caused by turbulent and extreme respiration leading to strong movements of the pig body. These, and also dislocation of the reference electrodes, do not allow reliable measurements with conventional algorithms. These errors cannot be detected, which leads to mistakes in the algorithm. A further error is the frequency which is modulated by the breathing of the pig: breathing modulation is the result of changing the distance between the skin and the camera during a breathing cycle. Under the simplified assumption of two isotropic emitters (LED, skin), a distance (r) change modulates the light intensity by .
However, newborns physiologically have periodic modulations of the respiration rate due to an immature respiratory center. Apneas of up to 20 seconds are regarded as physiological in term neonates unless they are followed by consecutive bradycardia. Apnea of prematurity (AOP), which is characterized by apneas with consecutive bradycardia, are common among preterm neonates. Detection of AOP needs the continuous and precise measurement of breathing movements, heart rate and arterial oxygen saturation. The conventional monitoring of vital parameters using the wired NICU monitor is also subject to considerable artefacts. Artefacts are detected and defined on the conventional monitor by the fact that the ECG waves do not clearly indicate an R tick and that the pulse oximeter indicates a different pulse rate than the heart rate measured by the ECG. For respiration, there is no reliable method to identify artefacts.
5.2. Oxygen Saturation
In quiet, narcotized piglet, the contactless monitoring reliably yielded similar values for oxygen saturation as conventional pulse oximetry. However, the contactless measurement was subject to artefacts. For example, movements of the patient, pigmentation of the skin, poor blood circulation, and room brightness limit accurate measurements [
11,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39].
It is important to detect respiration and separate it from the useful signal. Estimating the heartbeat and its signal amplitude is the key to calculating arterial saturation. In addition, clinical calibration is required to eliminate constant errors, which is currently not possible due to cost and effort. This step makes sense if all other sources of error have been eliminated in the best possible way.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have successfully developed a novel sensor for the contactless measurement of heart rate, respiration and oxygen saturation. This novel sensor combines a monochrome camera with a time division multiplex controlled lightning with three different wavelengths in the red and infrared spectrum (660 nm, 810 nm, and 940 nm). Our proof of principle experiments in a neonatal piglet yielded highly reliable results when compared to conventional monitoring in a calm, motionless subject.
In our sensor, the measurement of the oxygen saturation requires the optical detection of the heart rate and breathing. As a result, the measurements of oxygen saturation and heart rate were prone to artefacts when the subject was agitated since movements of the whole body could interfere with the signals of breathing and heartbeat. Moreover, pigmentation of the skin, poor blood circulation, and excessive environmental light can reduce the accuracy of the measurements. Further experiments and adjustments of the detection algorithm are underway to optimize the camera-based contactless measurement of vital signs in preterm neonates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Zemlin, M. and Diewald, A.R.; Methodology, Goedicke-Fritz, S., Thull, R. and Schmiech, D.; Software, Thull, R. and Marnach, A.; Validation, Goedicke-Fritz, S., Thull, R. and Schmiech, D.; Formal analysis, Thull, R. and Diewald, A.R.; Investigation, Müller, S., Tutdibi, E. and Nourkami-Tutdibi, N., Körbel, C. and Laschke, M.W.; Writing—original draft preparation, Thull, R., Goedicke-Fritz, S., Kaiser, E. and Weber, R.; Writing—review and editing, Diewald, A.R.; Visualization, Thull, R.; Supervision, Goedicke-Fritz, S., Thull, R. and Schmiech, D.; Project administration, Zemlin, M. and Diewald, A.R.; Funding acquisition, Zemlin, M. and Diewald, A.R.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung - BMBF) with grant number 13GW0156G
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal procedures were approved by the Saarland State Office for Health and Consumer Protection and were conform to the guidelines from Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes as well as national guidelines and regulations.
Data Availability Statement
The program code used in this study cannot be disclosed as it is proprietary to ELABS AG, Germany and is subject to confidentiality agreements. The data utilized is owned by CUBICAL GmbH, Germany; it is not available for public disclosure. Both ELABS AG and CUBICAL GmbH were participants in the BMBF-funded project.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ellen Maurer (Saarland University) for excellent technical assistance. We thank Oliver Simons from the company CUBICAL GmbH, München for the fruitful discussion and the support by his company.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AC |
Alternating current, here: the time-varying signal part |
| AOI |
Area-of-interest |
| AOP |
Apneo of prematurity |
| bpm |
Beats per minute |
| CLK |
Clock |
| ECG |
Electrocardiography |
| DC |
Direct current, here: the time-constant signal part |
| dB |
Decibel |
| GE |
General Electric |
| GUI |
Graphical User Interface |
| GPIO |
General Purpose Input Output |
| Hb |
Deoxyhemoglobin |
| HbO
|
Oxyhemoglobin |
| IDS |
Imaging Development Systems GmbH |
| LED |
Light emitting diode |
| MAE |
Mean Absolute Error |
|
C |
Microcontroller |
| NICU |
Neonatal intensive care units |
| PO |
Pulse Oximetry |
| px |
Pixel |
| RGB |
red-gree-blue colour space |
| RMSE |
Root Mean Squared Error |
| SpO
|
Oxygen saturation |
| USB |
Universal serial bus |
References
- Purisch, S. E.; Gyamfi-Bannerman, C. Epidemiology of preterm birth. Semin Perinatol 2017, 41, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedicke-Fritz, S.; Hartel, C.; Krasteva-Christ, G.; Kopp, M. V.; Meyer, S.; Zemlin, M. Preterm Birth Affects the Risk of Developing Immune-Mediated Diseases. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, H. C.; Costarino, A. T.; Stayer, S. A.; Brett, C. M.; Cladis, F.; Davis, P. J. Outcomes for extremely premature infants. Anesth Analg 2015, 120, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H. U.; Kim, B. H.; Lee, J. Y.; Lee, J.; Xie, Z. Q.; Ibler, E. M.; Lee, K.; Banks, A.; Jeong, J. Y.; Kim, J.; Ogle, C.; Grande, D.; Yu, Y.; Jang, H.; Assem, P.; Ryu, D.; Kwak, J. W.; Namkoong, M.; Park, J. B.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D. H.; Ryu, A.; Jeong, J.; You, K.; Ji, B. W.; Liu, Z. J.; Huo, Q. Z.; Feng, X.; Deng, Y. J.; Xu, Y. S.; Jang, K. I.; Kim, J.; Zhang, Y. H.; Ghaffari, R.; Rand, C. M.; Schau, M.; Hamvas, A.; Weese-Mayer, D. E.; Huang, Y. G.; Lee, S. M.; Lee, C. H.; Shanbhag, N. R.; Paller, A. S.; Xu, S.; Rogers, J. A. Binodal, wireless epidermal electronic systems with in-sensor analytics for neonatal intensive care. Science 2019, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartlidge, P. H.; Fox, P. E.; Rutter, N. The scars of newborn intensive care. Early Hum Dev 1990, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranger, M.; Grunau, R. E. Early repetitive pain in preterm infants in relation to the developing brain. Pain Manag 2014, 4, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T. Improvement of the earpiece oximeter. Abstracts of the Japanese Society of Medical Electronics and Biological Engineering 1974, 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Poets, C. F.; Southall, D. P. Noninvasive monitoring of oxygenation in infants and children: practical considerations and areas of concern. Pediatrics 1994, 93, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, L. A.; Jeanne, V.; Cleary, J. P.; Lieber, C.; Nelson, J. S.; Bambang Oetomo, S.; Verkruysse, W. Non-contact heart rate monitoring utilizing camera photoplethysmography in the neonatal intensive care unit - a pilot study. Early Hum Dev 2013, 89, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Correia, R.; Ballaji, H. K.; Korposh, S.; Hayes-Gill, B. R.; Morgan, S. P. Optical Fibre-Based Pulse Oximetry Sensor with Contact Force Detection. Sensors (Basel) 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S. J. "Motion-resistant" pulse oximetry: a comparison of new and old models. Anesth Analg 2002, 95, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prahl, S. Tabulated Molar Extinction Coefficient for Hemoglobin in Water. Available: https://omlc.org/spectra/hemoglobin/summary.html.
- Wieringa, F. P.; Mastik, F.; van der Steen, A. F. Contactless multiple wavelength photoplethysmographic imaging: a first step toward "SpO2 camera" technology. Ann Biomed Eng 2005, 33, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, T. Pulse oximetry: its invention, theory, and future. J Anesth 2003, 17, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severinghaus, J. W. Takuo Aoyagi: discovery of pulse oximetry. Anesthesia & Analgesia 2007, 105, S1–S4. [Google Scholar]
- Verkruysse, W.; Bartula, M.; Bresch, E.; Rocque, M.; Meftah, M.; Kirenko, I. Calibration of Contactless Pulse Oximetry. Anesth Analg 2017, 124, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, K. G. An investigation of remote non-contact photoplethysmography and pulse oximetry. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Electronic Engineering Faculty of Science and Engineering, National University of Ireland Maynooth, Ireland 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hülsbusch, M. Ein bildgestütztes, funktionelles Verfahren zur optoelektronischen Erfassung der Hautperfusion. Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät für Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik, Rheinisch-Westfälische Tehnische Hochschule Aachen, Germany 2008.
- Wieringa, F. P. Pulse Oxigraphy: And other new in-depth perspectives through the near infrared window. Ph.D. Thesis, Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam, Netherlands 2007.
- Phattraprayoon, N.; Sardesai, S.; Durand, M.; Ramanathan, R. Accuracy of pulse oximeter readings from probe placement on newborn wrist and ankle. J Perinatol 2012, 32, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar, H.; El-dash, H. Pulse Oximetry: Could Wrist and Ankle Be Alternative Placement Sites? Clinical Pediatrics 2015, 54, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijland, R.; Nierlich, S.; Jongsma, H. W.; Nijhuis, J. G.; Oeseburg, B.; Springer, K.; Mannheimer, P. Validation of reflectance pulse oximetry: an evaluation of a new sensor in piglets. J Clin Monit 1997, 13, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarassenko, L.; Villarroel, M.; Guazzi, A.; Jorge, J.; Clifton, D. A.; Pugh, C. Non-contact video-based vital sign monitoring using ambient light and auto-regressive models. Physiological Measurement 2014, 35, 807–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Papin, C.; Azorin-Peris, V.; Kalawsky, R.; Greenwald, S.; Hu, S. Use of ambient light in remote photoplethysmographic systems: comparison between a high-performance camera and a low-cost webcam. J Biomed Opt 2012, 17, 037005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jian, Y.; Jin, X.; Li, B.; Feng, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, H. Non-contact detection of oxygen saturation based on visible light imaging device using ambient light. Opt Express 2013, 21, 17464–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlen, W.; Lim, J.; Ansermino, J. M.; Dumont, G.; Scheffer, C. Design challenges for camera oximetry on a mobile phone. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2012, 2448–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kellicut, D. C.; Weiswasser, J.; Arora, S.; Freeman, J.; Lew, R.; Shuman, C.; Mansfield, J.; Sidawy, A. Emerging technology: hyperspectral imaging. Perspectives in vascular surgery and endovascular therapy 2004, 16, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, C. L.; Matsuda, L. S.; Uyehara, C. Normal physiologic values of neonatal pigs and the effects of isoflurane and pentobarbital anesthesia. Laboratory animal science 1994, 44, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, M.; Wittwer-Backofen, U.; Scholz, R.; Schneider, K. T.; Straube, S.; Olbertz, D.; Hesse, V.; Rochow, N. Analysis of the German perinatal survey of the years 2007-2011 and comparison with data from 1995-1997: neonatal characteristics and duration of pregnancy. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol 2013, 217, 211–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brew, N.; Walker, D.; Wong, F. Y. Cerebral vascular regulation and brain injury in preterm infants. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2014, 306, R773–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, V.; McFadden, D. E.; Poskitt, K. J.; Miller, S. P. Chorioamnionitis in the pathogenesis of brain injury in preterm infants. Clin Perinatol 2014, 41, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, K. C.; Pimentel Filho, Jda C.; Tristao, R. M.; Jesus, J. A.; Campos Junior, D. Sleep deprivation, pain and prematurity: a review study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2015, 73, 147–54.
- Onyeama, C. O.; Srinivasan, H.; Lotke, M.; Vickers, D. L. Subgaleal abscess and E. coli septicemia following scalp electrode in a preterm newborn: a case report. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2009, 22, 1201-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogdo, B.; Kahlert, C.; Diener, P. A.; Micallef, J. Primary cutaneous aspergillosis in a preterm neonate. BMJ Case Rep 2014, Sep 1.
- Langton, J. A.; Hanning, C. D. Effect of motion artefact on pulse oximeters: evaluation of four instruments and finger probes. Br J Anaesth 1990, 65, 564–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severinghaus, J. W.; Spellman, M. J. Pulse oximeter failure thresholds in hypotension and vasoconstriction. Anesthesiology 1990, 73, 532–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, R.; Bell, C.; Kain, Z. N.; Colingo, K. A. Effect of peripheral perfusion on accuracy of pulse oximetry in children. J Clin Anesth 1999, 11, 317–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J. N.; Hughes, L. A.; Vivilecchia, R.; Camargo, C. A. Effect of skin pigmentation on pulse oximetry accuracy in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 1998, 5, 965–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, D.; Neidzwski, J.; Wald, A.; Finck, A. D. Fluorescent light interferes with pulse oximetry. J Clin Monit 1989, 5, 135–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).