1. Introduction
Approximately two million dental implants are implanted each year, with that number expected to increase by 2035 when the number of older adults (65 years and older) surpasses the number of children in the United States [
1,
2].With over 700 different bacterial species populating the oral cavity, implanted dental biomaterials are often susceptible to bacterial contamination because they provide a substrate for bacterial attachment [
3,
4,
5].
Porphyromonas gingivalis (
P. gingivalis) is a significant contributor to periodontal disease and biofilm-associated infections among these pathogens. P. gingivalis is a key pathogen implicated in periodontal disease and is commonly found in biofilms on dental implants and natural teeth. If biofilm-associated infections are not addressed, there can be loss of gum tissue and bone, and bacteria can enter the bloodstream, traveling throughout the body and potentially causing cancers and chronic diseases including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis [
6,
7]. Metallic implants are widely used due to high tensile strength, ductility, toughness, wear resistance, fatigue resistance, and creep resistance [
7]. Still, metal implants also have limited biocompatibility and high corrosion in the biological environment, with failure occurring in 5-11% of dental implants [
2,
8,
9,
10,
11]. Peri-implantitis is the primary reason for late-stage dental implant failure, accounting for 81.9% of late-stage failures [
12]. Opposingly, ceramic coatings for implants have high biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and inertness; however, these materials also have low impact resistance, reproducibility, and susceptibility to peri-implantitis [
8].
Hydroxyapatite (HAp) is a naturally occurring and non-toxic bioceramic making up 70% of human bone weight and constituting dental enamel and dentin [
13]. HAp is also the most widely used calcium phosphate for metal implant coatings [
8,
14]. Coating titanium implant surfaces with HAp has shown enhanced integration with bone, improved corrosion and wear resistance, and decreased metallic ion release, compared to commercial titanium alloy implant surfaces [
15,
16]. Previous research has suggested that unsaturated fatty acids like
cis-2-decenoic acid (C2DA) and
trans-2-decenoic acid (T2DA) disperse and inhibit biofilm formation [
17,
18]. Diffusible signaling factors such as these fatty acids also cause biofilm dispersal, increasing the effect of antibiotics through synergy and preventing implant removal, tissue debridement, and patient trauma [
19]. Many DSF molecules become less effective when exposed to light, radiation, and other sterilization methods, but a synthetic DSF that is stable and resistant to isomerization by light, radiation, and sterilization has been developed: 2-heptylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (2CP) is a medium chain fatty acid and is useful for biomaterials due to its structural stability, cell compatibility, and antimicrobial activity [
20]. Overall, the use of unsaturated
cis isomers of fatty acids could be used to reduce oral biofilm formation.
The overall goal of this work is to develop a simple 2CP loading strategy for teeth and HAp-coated dental implants to prevent dental plaque formation and subsequent occurrence of caries, gingivitis, and peri-implantitis. It was hypothesized that 2CP-loaded HAp would inhibit biofilm formation of dentally relevant bacteria while remaining cytocompatible with osteoblast cells.
2. Materials and Methods
To assess the qualities of 2CP-loaded HAp and the interaction of 2CP with commercial oral rinse, a 2CP coating for HAp was fabricated, the release profile of 2CP from HAp coupons with and without the presence of oral rinse was evaluated, the antimicrobial activity of 2CP released from HAp coupons, alone and in combination with oral rinse, against P. gingivalis was determined, and the cellular response of Saos-2 cells to 2CP released from Hap coupons, alone and in combination with oral rinse, was determined.
Loading and Characterization
2-heptylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (2CP) was fabricated in a chemistry laboratory at the University of Memphis. Hydroxyapatite Disc Coupons were purchased from BioSurface Technologies Corporation (Bozeman, Montana, USA). The manufacturer measures the composition of the coupons through x-ray diffraction to guarantee a minimum composition of 95% hydroxyapatite. Coupons are machine-pressed to achieve 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) diameter and 0.15-inch (3.8 mm) thickness. Based on methods from a study with alumina particles and long chain alcohols,20 an immersion loading method was developed for loading hydroxyapatite with fatty acids. HAp coupons were immersed in 2CP in EtOH for 3 hours at 40°C and 50 rpm in capped vials. Loaded coupons were then dried overnight in a fume hood. Commercial dental rinse containing chlorhexidine was obtained to compare its effect on 2CP elution as well as to compare its antimicrobial properties to 2CP alone. The dental rinse chosen was 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse (Xtrrium, Madrid Dental Supply), which is commonly prescribed for twice daily use after dental implant surgeries. For loading HAp with 2CP+oral rinse, HAp coupons were immersed in 2.5 mg/ml 2CP in 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) oral rinse solution for 3 hours at 40°C in capped vials. Loaded coupons were then dried overnight in a fume hood.
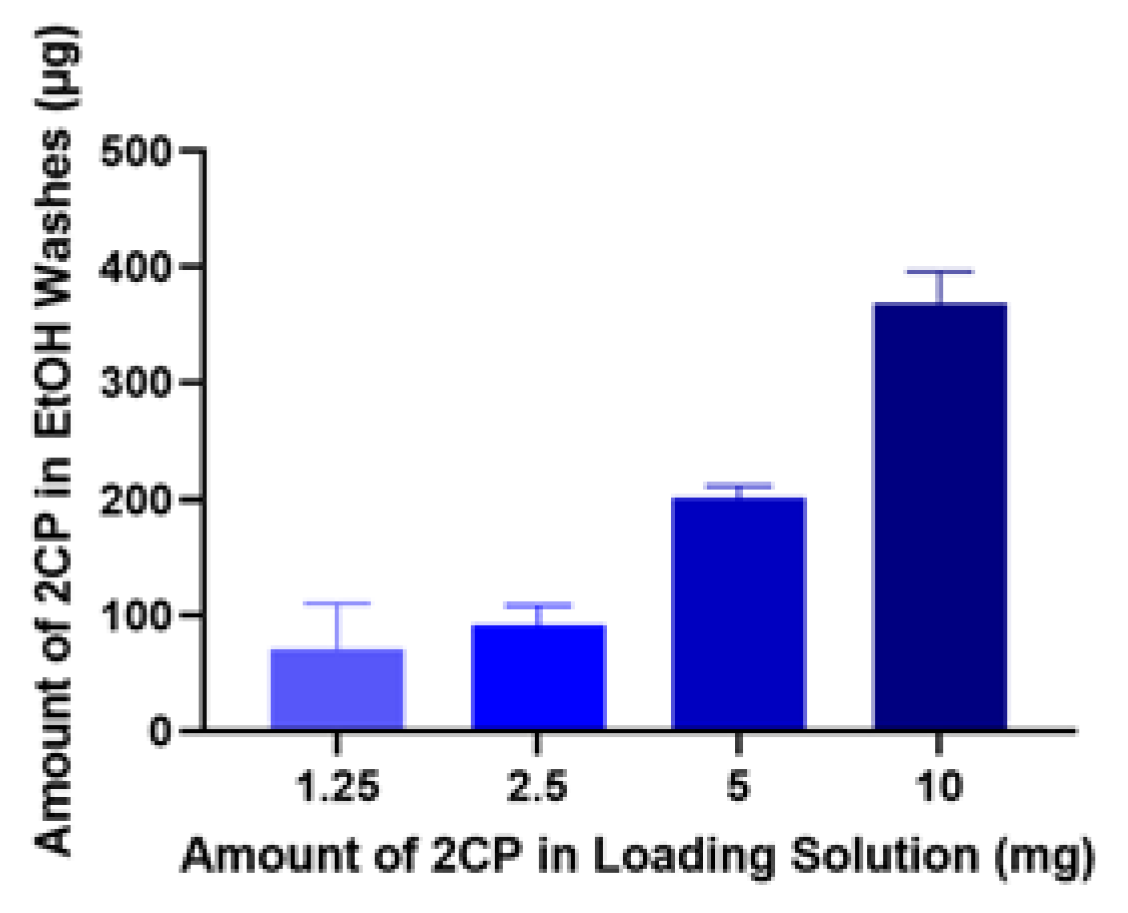
To determine actual amount loaded, HAp coupons were soaked in four different concentrations of 2CP-100% ethanol solution: 30 mg 2CP/3 ml ethanol, 15 mg 2CP/3 ml ethanol, 7.5 mg 2CP/3 ml ethanol, and 3.75 mg 2CP/3 ml ethanol. Loaded coupons (n=3) were washed with 100% ethanol and the wash-off solution was analyzed with HPLC-UV. This washing procedure was repeated until minimal amount of fatty acid was present in the wash-off samples.
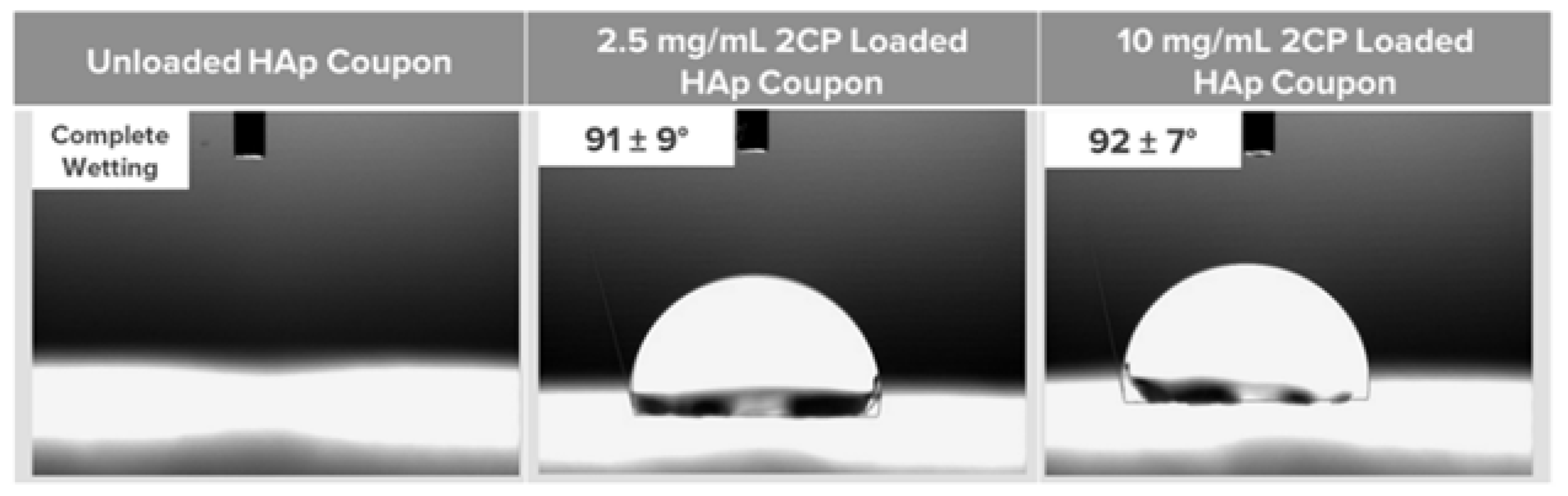
Contact angle measurements were collected for unloaded and 2CP-loaded HAp coupons (n=3) using a VCA Optima measurement machine (AST products, INC, USA) to determine the hydrophobicity of the coupon surface as a representation of whether 2CP was present. Water droplets (5 μL) were placed carefully onto the coupon surfaces, and after approximately one minute to allow any water to absorb, a digital camera recorded photographs of the droplets and the VCA OptimaXE goniometry software calculated the angle measurements.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Nova NANOSEM 650 FEI™, Hillsboro, OR, USA) was performed to characterize the HAp coupons and observe any differences in the surfaces of unloaded and 2CP-loaded coupons. Unloaded and 2CP-loaded HAp coupons (n=1) were mounted on metal SEM stubs and an Au 80 Pt 20 sputter coating with 5 nm thickness was applied using a Q150T ES Plus turbomolecular pumped coater (EMS Quorum). SEM images were taken at multiple magnifications.
A fatty acid pre-column derivatization method was used to express 2CP in samples before HPLC analysis. After plating 100 µL of samples and standards in 50:50 PBS:methanol, 67 µL of 50 mM 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride in 10% pyridine and 24 µL of 100 mM indole-3-acetic acid hydrazide were added. To start the reaction, 10 µL of 100 mM hydrochloric acid was added before incubating at 50°C for 3 hours. After incubation, 10 µL of 200 mM sodium hydroxide was added to samples and standards to terminate the reaction. The concentration of 2CP in samples was measured with high-performance liquid chromatography–ultraviolet spectroscopy (HPLC–UV) using a reverse phase Hypersil GOLD Column with dimensions 150×4.6 mm. The mobile phase system was 80:20 ratio of methanol:0.1% o-phosphoric acid at a flow rate of 0.800 mL/min for 8 minutes per sample, and the injection volume was 5 µL. The column was maintained at a temperature of 30°C, and UV spectra were recorded at 220 and 280 nm.
Elution
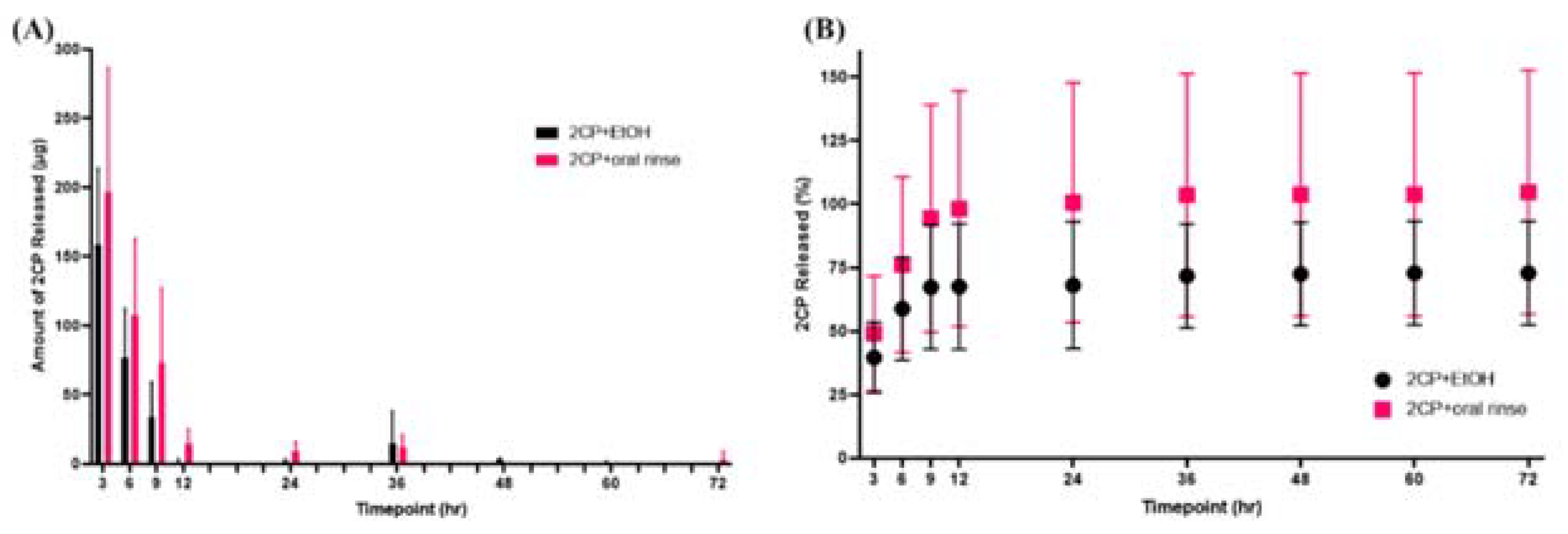
Elution studies were performed to determine the release profile of 2CP from HAp coupons. Groups included 2.5 mg/ml 2CP-loaded (5 mg 2CP in 2 ml EtOH), 2.5 mg/ml 2CP+oral rinse-loaded, ethanol-loaded, and unloaded coupons (n=6). HAp coupons were placed in 1 mL sterile 1X PBS in sterile well plates, and eluates were collected by complete solution change at 3, 6, 9, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 h. The concentration of 2CP in samples was measured with HPLC–UV using the previously mentioned method. The following equation was used to calculate the percent of 2CP released at each time point, where amount of 2CP lost during loading was determined by performing the loading procedure in plastic tubes without coupons (n=3):
3. Results
Loading and Characterization
Based on the ethanol wash study, about 1.5% of 2CP from the loading solution is retained on the coupon surface after the loading procedure, which is about 100 µg for 2.5 mg 2CP in loading solution (
Figure 1). Contact angles also indicate that loading HAp coupon with 2.5 mg/ml of 2CP reduces the wettability of the coupon surface (
Figure 2).
Elution
Elution testing revealed that both 2CP-loaded and 2CP+oral rinse-loaded HAp coupons exhibited a burst release profile of 2CP, with nearly all of the 2CP being released within the initial 9 hours (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
Contact angles for unloaded and 2CP-loaded coupons indicate a hydrophobic surface after loading, suggesting that the majority of 2CP molecules are oriented with the hydrophobic portion exposed while the hydrophilic carboxylic acid portion is closest to the hydroxyapatite. If the majority of the 2CP molecules were oriented with their carboxylic acid functional group exposed, the wettability of the coupon would be greater, and the contact angle would be less than the reported contact angles in these studies. This finding is important as less bacterial adhesion occurs on hydrophobic surfaces compared to hydrophilic oral surfaces [
5]. As these studies were limited in characterization of the 2CP-loaded HAp surface, other coating characterizations, including attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Raman spectroscopy would be useful for understanding how 2CP is adsorbing and orienting on the HAp surface. ATR-FTIR was attempted with unloaded and 2CP-loaded HAp coupons; however, surface roughness of coupons caused signal noise.
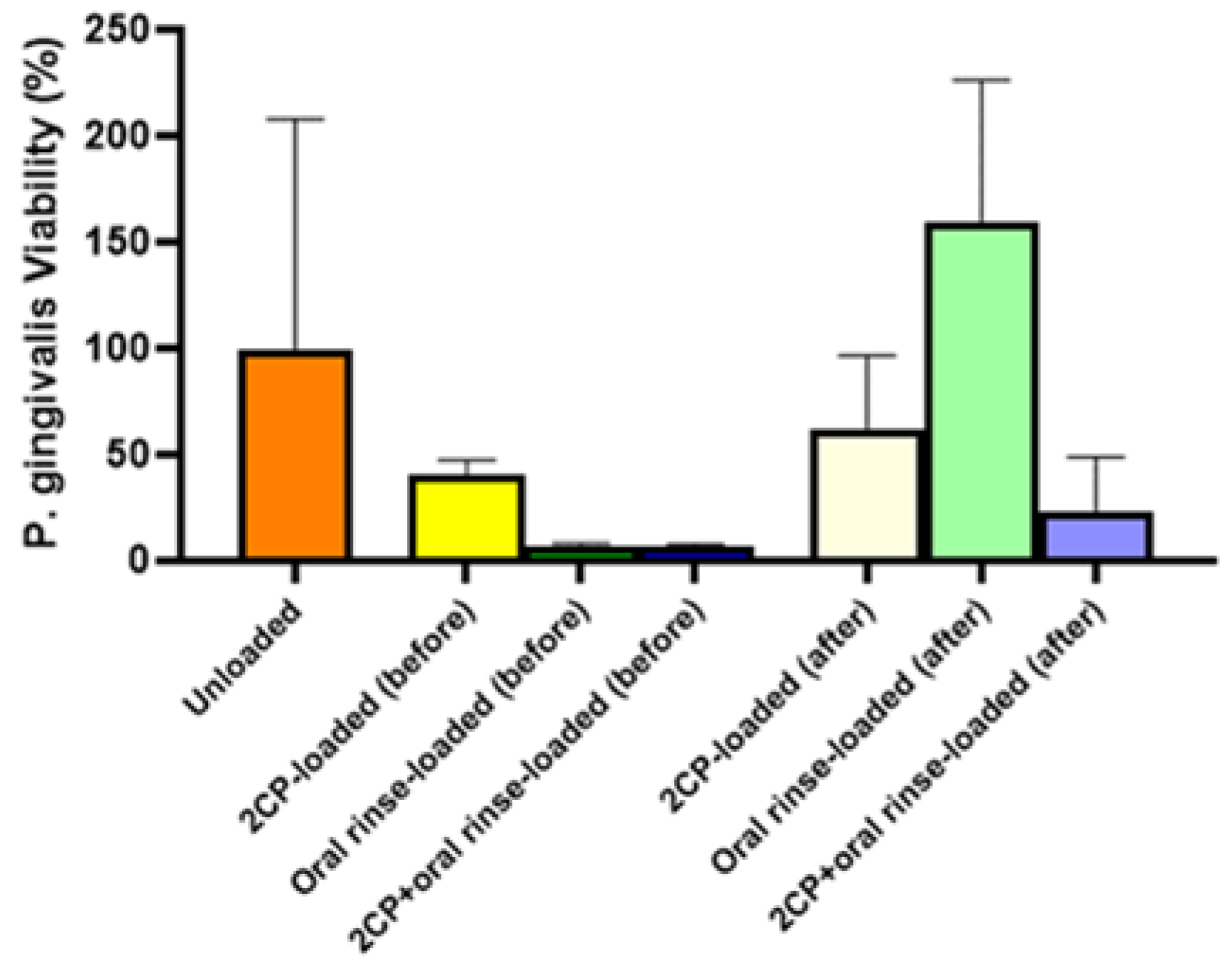
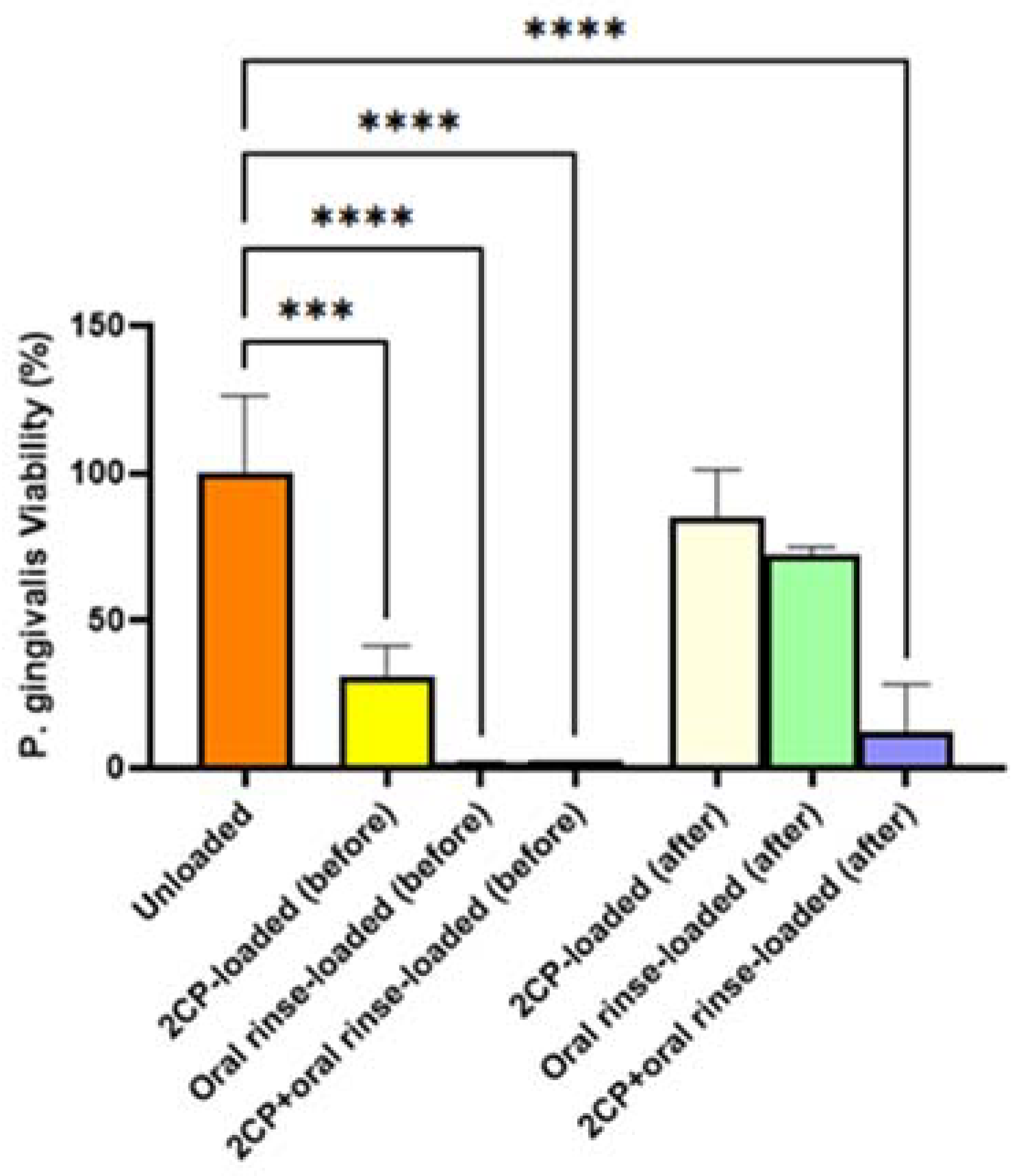
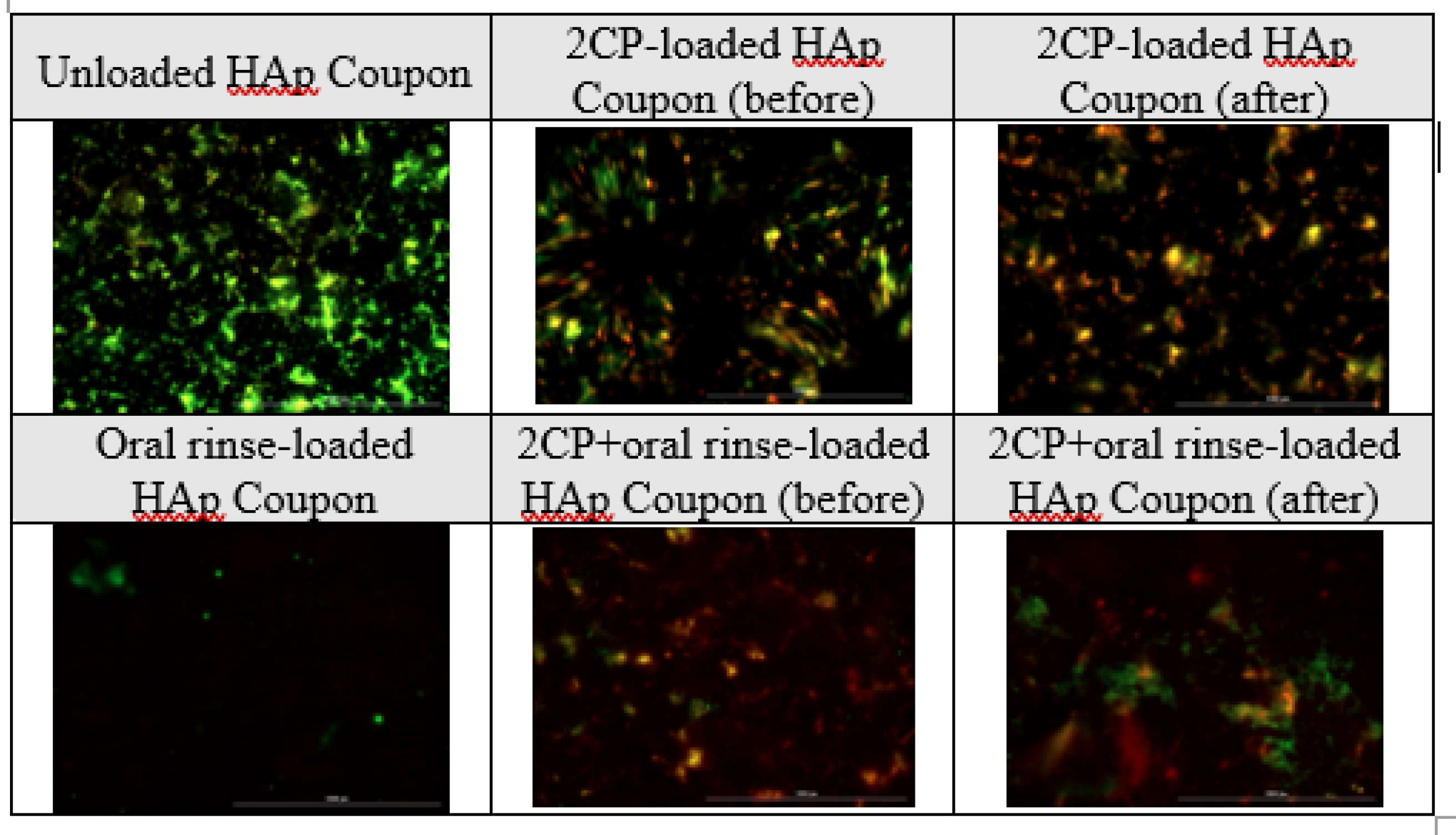
Although elution testing suggests complete release of 2CP from the coupon surface in 12 hours, this release profile would be acceptable for applying 2CP to teeth and dental implants, as mouthwashes are often prescribed for use twice daily. The elution results that the majority of the loaded 2CP is released by 12 hours when sampling every 3 hours support the bacterial result that previously eluted coupons were not able to significantly reduce
P. gingivalis viability. Although biofilm growth on 2CP-loaded HAp coupons after 3-day elution was not significantly different than on unloaded HAp coupons, fully loaded 2CP-HAp coupons significantly reduced biofilm viability, compared to the unloaded control (p<0.01). Oral rinse-loaded and 2CP+oral rinse-loaded HAp coupons had the greatest reduction in
P. gingivalis planktonic and biofilm growth compared to the control; however, this result is expected since the target of chlorhexidine is to kill bacteria. Other medium-chain fatty acids, and in particular linoleic acid, have been found to inhibit oral bacteria [
21]. Because of the need for healthy oral flora, removing opportunistic and disease-causing bacteria, or preventing their attachment, is of more importance than removing all oral bacteria.
Moreover, findings from these studies suggest the potential of incorporating 2CP into chlorhexidine mouthwash to reduce plaque formation. In a 2015 study on the combination of low concentrations of C2DA and chlorhexidine to remove dental plaque formed by
Streptococcus mutans and
Candida albicans, biofilms were grown on saliva-coated hydroxyapatite discs for 48 h and then treated for one minute with chlorhexidine (0.08%, 0.06% and 0.04%) or combined chlorhexidine and C2DA two times a day for 3 days [
22]. This study resulted in significant dispersal of biofilm by 310 nM C2DA with 0.04% chlorhexidine, suggesting synergy between C2DA and chlorhexidine, even at low concentrations [
22]. These results, coupled with the current study's findings on 2CP, support the possible inclusion of 2CP into chlorhexidine mouthwash for effective delivery to natural teeth and HAp-coated dental implants.
Natural tooth enamel and dentin have trace amounts of ions such as sodium, magnesium, iron, and fluoride. A study investigating the combination of fluoride with HAp concluded that there is synergy between the two materials for preventing erosion and demineralization [
23]. Studies have also reported that zinc-doped HAp specifically reduces the viability of
S. mutans and prevents halitosis, or bad breath [
24,
25,
26]. Other studies have suggested that silver ions released from HAp can inhibit
E. coli and
S. aureus growth [
27]. Future work is needed to assess the combined effects of 2CP-loaded hydroxyapatite that is doped with ions. Another calcium phosphate, beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), appears as a transitional phase of HAp and is the most clinically used non-HAp calcium phosphate. In studies investigating the changes in β-TCP structure with the addition of carboxylic acids to produce functionalized β-TCP (fTCP), fTCP-containing toothpaste increased remineralization of enamel lesions compared to natural pH cycling and reduced white spot lesions compared to fluoride toothpaste [
28,
29,
30]. A potential future study could assess 2CP-loaded TCP for antimicrobial and remineralization potential. Some studies have also developed Hap sheets that are ultra-thin to improve fusion with tooth surfaces as well as dental implant surfaces [
28]. These sheets are advantageous because the structure mimics that of the natural teeth while having flexibility and strong adhesion with the tooth surface without bonding agents [
31]. A future study could incorporate 2CP loading onto HAp sheets, instead of the Hap coupons used in this work.
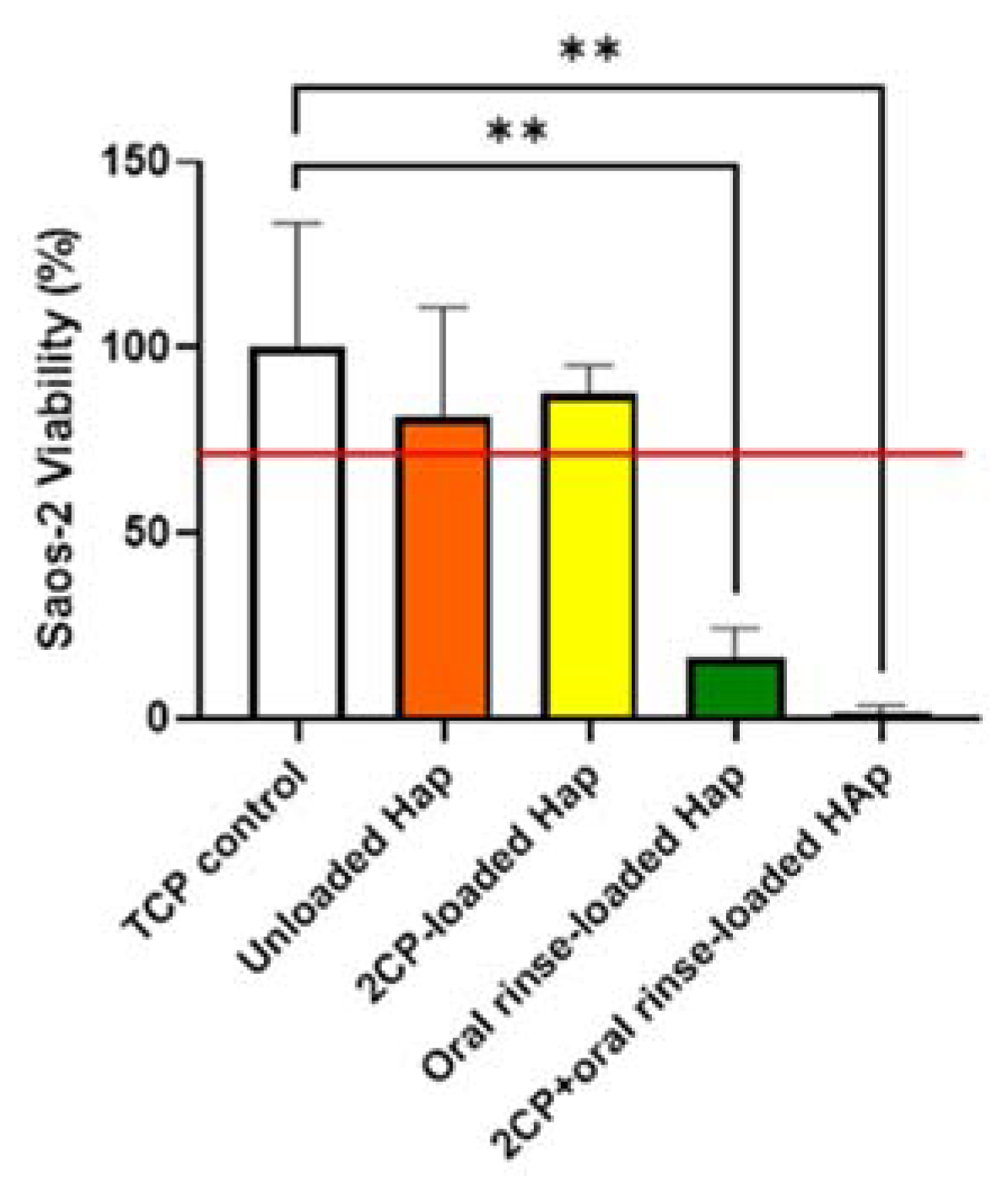
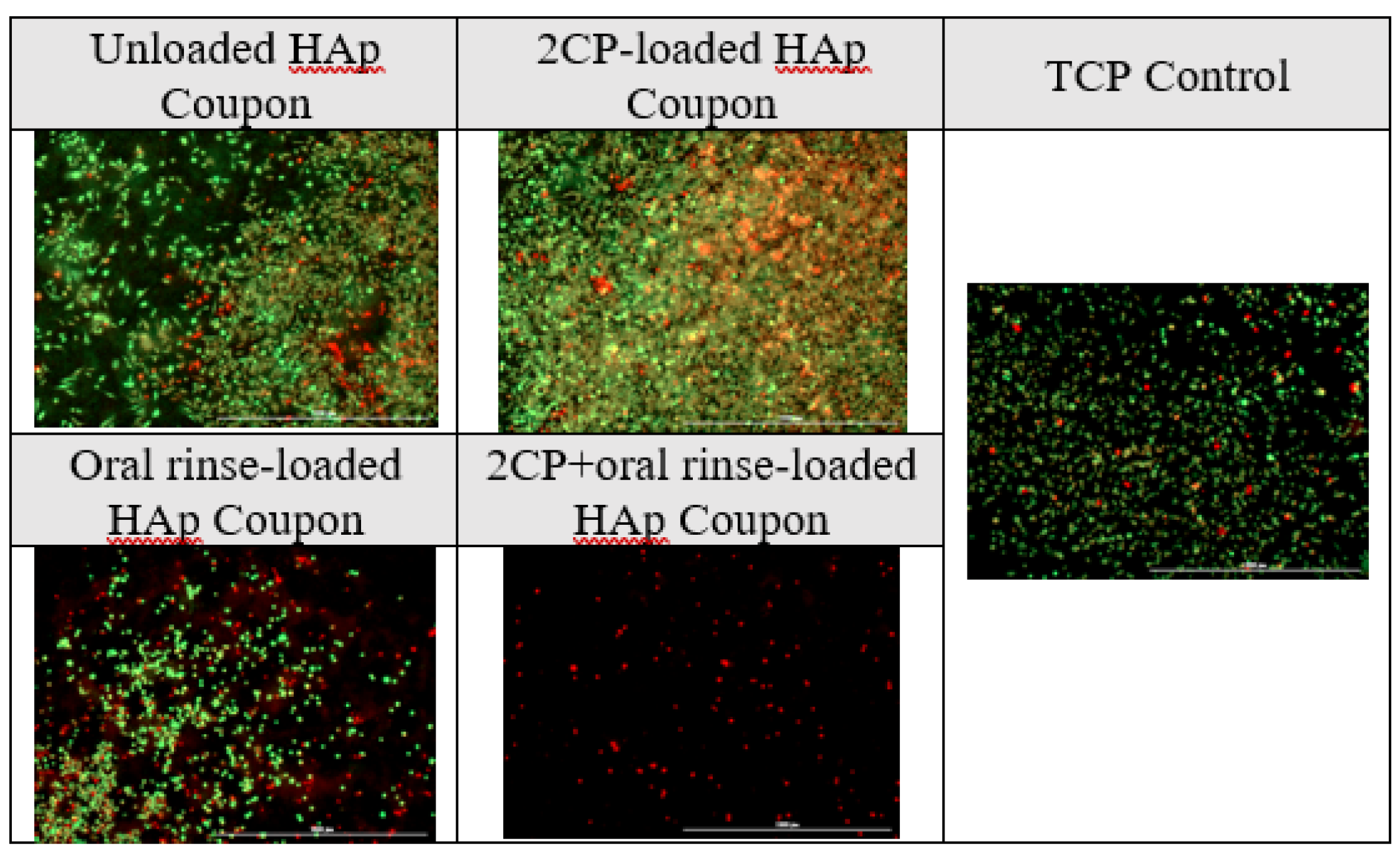
The cytotoxicity results support literature review, as oral rinse groups significantly reduced viability of Saos-2 cells. Opposingly, 2CP-loaded HAp, when fully loaded, reduces the viability of
P. gingivalis biofilm while also not disrupting the viability of Saos-2 cells when using a loading concentration of 2.5 mg/mL, which deposits approximately 100 µg/mL of 2CP on the HAp surface. This is consistent with previous research showing that 125 μg/mL of 2CP disperses approximately 100% of
S. aureus cells, and 2CP concentrations below 1 mg/mL support fibroblast viability above 80% [
20]. 2CP-loaded HAp coupon groups had a relative cell viability ≥70% of the control group, and therefore met the qualifications to be considered non-cytotoxic, as defined by the ISO 10993-5 Biological Evaluations of Medical Devices standard when evaluating medical devices for in vitro cytotoxicity [
32]. Connecting the antimicrobial studies with the cytocompatibility studies, chlorhexidine-containing oral rinse is effective at reducing bacterial viability, but also reduces the viability of bone cells. The comparable qualities of 2CP to chlorhexidine may still be enough for the replacement of this “gold standard” with 2CP in oral products due to the risk of toxicity with chlorhexidine, while 2CP is considered biocompatible. This cytocompatibility direct contact assay could be improved by including coupon groups after elution, similar to bacterial assays.
Other further studies should involve recharging of coated surface with 2CP as well as rechallenging coupons with bacteria. Additionally, future studies could be used to determine if lower concentrations of mouthwash would support the action of 2CP while supporting osteoblast growth. The methods used in these studies for loading HAp with 2CP were performed for 3 hours at 40°C and 50 rpm; however, to meet more expected loading conditions when applying the 2CP loading strategy as an oral rinse, the time length should decrease to closer to 1 minute and the rotational speed should increase to mimic the action of a mouthwash. Lastly, future studies should evaluate the long-term cytotoxicity and biofilm inhibition properties of 2CP-loaded HAp coupons, as the studies in this
5. Conclusions
The purpose of this work was to determine if 2CP immersion loading could be applied to natural teeth and dental implants to help prevent and reduce dental plaque and development of caries, gingivitis, and peri-implantitis. The studies presented in this thesis demonstrate successful loading of hydroxyapatite coupons with 2CP, elution of 2CP from the hydroxyapatite surface, and dual behavior of significantly reducing P. gingivalis biofilm viability while supporting Soas-2 cell viability. The developed 2CP loading strategy could potentially be applied to HAp-coated implants and natural teeth. In conclusion, the results of these studies support the hypothesis that 2CP-loaded hydroxyapatite coupons coated through immersion loading at a concentration of 2.5 mg/ml will release 2CP at levels sufficient for biofilm inhibition while supporting osteoblast growth and proliferation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, JAJ and ECM.; methodology, JAJ. ECM, TF, and JDB; formal analysis, ECM and MW.; investigation, ECM, MW, and TY; writing—original draft preparation, ECM.; writing—review and editing, MW and TY.; data curation--EMB; supervision, JAJ.; project administration, JAJ; funding acquisition, JAJ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Study supported by the National Science Foundation, Award No. 1945094.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jermiah Tate, Yogita Dintakurthi, and Hanna Jones for help with elution sample collection, Felio Perez and Rabeta Yeasmin for help with SEM, Dr. Jay Tippabattini for HPLC preparation, Elizabeth Matlock-Buchanan for document editing, and Dr. Daniel Baker, Rachel Wiley, and Brian Hoffman for 2CP preparation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Albino, J.; Dye, B.; Ricks, T. Surgeon General’s Report: Oral Health in America: Advances and Challenges. National Institutes of Health. 2020.
- Klinge, B.; Hultin, M.; Berglundh, T. Peri-implantitis. Dental Clinics 2005, 49, 661-676.
- Armellini, D.; Reynolds, M.A.; Harro, J.M.; Molly, L. Biofilm Formation on Natural Teeth and Dental Implants: What is the Difference? The role of biofilms in device-related infections 2009, 109-122.
- Padovani, G.C.; Fùcio, S.B.P.; Ambrosano, G.M.B.; Correr-Sobrinho, L.; Puppin-Rontani, R.M. In situ bacterial accumulation on dental restorative materials. CLSM/COMSTAT analysis. Am J Dent. 2015, 28, 3–8.
- Busscher, H.; Rinastiti, M.; Siswomihardjo, W.; van der Mei, H. Biofilm Formation on Dental Restorative and Implant Materials. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 657–665. [CrossRef]
- Kurtzman, G.M.D.; Horowitz, R.A.D.; Johnson, R.; Prestiano, R.A.; Klein, B.I. The systemic oral health connection: Biofilms. Medicine 2022, 101, e30517. [CrossRef]
- Schaudinn, C.; Gorur, A.; Keller, D.; Sedghizadeh, P.P.; Costerton, J.W. Periodontitis: an archetypical biofilm disease. J Am Dent Assoc 2009, 140, 978-986.
- Bose, S.; Tarafder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Hydroxyapatite coatings for metallic implants. In Hydroxyapatite (Hap) for biomedical applications; Elsevier: 2015; pp. 143-157.
- Berglundh, T.; Persson, L.; Klinge, B. A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002, 29 (Suppl. 3), 197–212. [CrossRef]
- Snauwaert, K.; Duyck, J.; van Steenberghe, D.; Quirynen, M.; Naert, I. Time dependent failure rate and marginal bone loss of implant supported prostheses: a 15-year follow-up study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2000, 4, 0013–0020. [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S. Determination of the success and failure of root-form osseointegrated dental implants.. Adv. Dent. Res. 1999, 13, 173–180. [CrossRef]
- Solderer, A.; Al-Jazrawi, A.; Sahrmann, P.; Jung, R.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R. Removal of failed dental implants revisited: Questions and answers. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2019, 5, 712–724. [CrossRef]
- Gamagedara, T.; Rathnayake, U.; Rajapakse, R. Facile synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by a polymer-assisted method: morphology, mechanical properties and formation mechanism. J Clin Invest 2018, 1, 1-5.
- Adamopoulos, O.; Papadopoulos, T. Nanostructured bioceramics for maxillofacial applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1587–1597. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Nissan, B.; Choi, A.; Roest, R.; Latella, B.; Bendavid, A. Adhesion of hydroxyapatite on titanium medical implants. In Hydroxyapatite (HAp) for biomedical applications; Elsevier: 2015; pp. 21-51.
- Zablotsky, M.H. HYDROXYAPATITE COATINGS IN IMPLANT DENTISTRY. Implant. Dent. 1992, 1, 253–257. [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G.; Marques, C.N.H. A Fatty Acid Messenger Is Responsible for Inducing Dispersion in Microbial Biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1393–1403. [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.A.; Courtney, H.S.; Haggard, W.O. Cis-2-decenoic Acid Inhibits S. aureus Growth and Biofilm In Vitro: A Pilot Study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 2663–2670. [CrossRef]
- Regeimbal, J.M.; Jacobs, A.C.; Corey, B.W.; Henry, M.S.; Thompson, M.G.; Pavlicek, R.L.; Quinones, J.; Hannah, R.M.; Ghebremedhin, M.; Crane, N.J.; et al. Personalized Therapeutic Cocktail of Wild Environmental Phages Rescues Mice from Acinetobacter baumannii Wound Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5806–5816. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, Z.L.; Awais, R.; Harris, M.; Raji, B.; Hoffman, B.C.; Baker, D.L.; Jennings, J.A. 2-Heptylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid Disperses and Inhibits Bacterial Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 645180. [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Era, M.; Kawahara, T.; Kanyama, T.; Morita, H. Antibacterial Effect of Fatty Acid Salts on Oral Bacteria. Biocontrol Sci. 2015, 20, 209–213. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Badi, A.; Sepehr, S.; Babaie-Naiej, H. A combination of cis-2-decenoic acid and chlorhexidine removes dental plaque. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 1655–1661. [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.M.; Comar, L.P.; Vertuan, M.; Neto, C.F.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Magalhães, A.C. Effect of an Experimental Paste with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Fluoride on Dental Demineralisation and Remineralisation in situ. Caries Res. 2015, 49, 499–507. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Al-Bayatee, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shavandi, A.; Brunton, P.; Ratnayake, J. Hydroxyapatite in Oral Care Products—A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 4865. [CrossRef]
- Hannig, M.; Hannig, C. Nanomaterials in preventive dentistry. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 565–569. [CrossRef]
- Harks, I.; Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Schlagenhauf, U.; May, T.W.; Gravemeier, M.; Prior, K.; Petersilka, G.; Ehmke, B. Impact of the Daily Use of a Microcrystal Hydroxyapatite Dentifrice on De Novo Plaque Formation and Clinical/Microbiological Parameters of Periodontal Health. A Randomized Trial. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0160142. [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Barba, F.; Miranda, M.; Guitián, F.; Torrecillas, R.; Moya, J.S. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of a Silver-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite. J. Nanomater. 2009, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Hamba, H.; Nakamura, K.; Nikaido, T.; Tagami, J.; Muramatsu, T. Remineralization of enamel subsurface lesions using toothpaste containing tricalcium phosphate and fluoride: an in vitro µCT analysis. BMC Oral Heal. 2020, 20, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, A.C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Ottobelli, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Brambilla, E. Substituted Nano-Hydroxyapatite Toothpastes Reduce Biofilm Formation on Enamel and Resin-Based Composite Surfaces. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 36. [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-Y.; Chong, H.-J.; Lee, E.-H.; Chang, N.-Y.; Chae, J.-M.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, S.-C.; Kang, K.-H. Effects of various toothpastes on remineralization of white spot lesions. Korean J. Orthod. 2014, 44, 113–8. [CrossRef]
- Hontsu, S.; Yoshikawa, K. Ultra-thin hydroxyapatite sheets for dental applications. In Hydroxyapatite (hap) for biomedical applications; Elsevier: 2015; pp. 129-142.
- ISO, E. 10993-5. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland 2009.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).