1. Introduction
The skin of a human has a surface area of about 1.5–2.0 m2, making it the largest organ in the body. It acts as a powerful barrier protecting against harmful effects from foreign substances and environmental pollutants [
1]. Sun exposure is a major cause of skin damage. Around half of the Saudi population devotes 10 hours or more to sun exposure each week, exposing themselves to significant ultraviolet (UV) radiation [
2]. This excessive sun exposure is linked to various short-term and long-term detrimental effects on the skin [
3]. UV exposure is identified as a modifiable risk element for squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and other forms of skin malignancies [
3,
4,
5,
6]. Over the last forty years, there has been a consistent rise in the incidence of skin cancer globally, representing one-third of all cancer cases worldwide [
7]. Notably, a substantial portion of an individual's lifetime sun exposure occurs during childhood and adolescence [
8].
To protect yourself from the sun, avoid exposure between 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m., seek shade, and use broad-spectrum sunscreen, along with wide-brimmed hats, protective clothing, and sunglasses [
9,
10]. Many sun protection programs have been implemented in numerous Western nations to increase public awareness of sun exposure risk and encourage the use of sun protection measures. An increase in awareness among populations has been observed. Nevertheless, compliance with sun protection remains insufficient [
11]. In Saudi Arabia, there were few studies on this matter. Not much is known about the awareness of the Saudi population about the use of sun protection measures. Information from this study may help design effective interventions [
12].
In 2010, Ahmad A. Al Robaee's study in Qassim Province found that although 56% were aware of the link between sun exposure and skin cancer, sunscreen use was only 8.3%. Factors associated with sunscreen use included gender, education, and skin type [
2]. A 2022 study in Riyadh by Amal Al-Balbeesi et al. showed that while most participants had heard of sunscreen and used it before, knowledge gaps existed regarding its proper application and SPF recommendations [
10]. More recently, in 2024, Emad Bahashwan's study in the Aseer region revealed that 16.0% of participants used sunscreen regularly, with a total of 74.0% reporting sunscreen use. Increased sun exposure correlated with higher awareness levels of sun damage, influencing sunscreen use [
13].
These findings underscore the need for targeted educational efforts to enhance sunscreen knowledge and encourage its consistent use among the Saudi population. Raising public awareness is crucial, especially in a country like Saudi Arabia, where the climate predisposes its residents to significant sun exposure.
2. Materials and Methods
The study was conducted as a descriptive cross-sectional survey utilizing an online-administered questionnaire. The estimated study period ranged between 4 to 6 months. The cross-sectional design allowed for the collection of data from a specific population at a single point in time.
Participant Selection and Withdrawal
Inclusion Criteria:
All individuals who were older than 18 years, college students residing in Saudi Arabia, and willing to participate were included in the study.
Exclusion Criteria:
Individuals were excluded if they refused to consent, were non-communicative, or were non-college students younger than 18 years.
Study Procedures
A straightforward and clear online questionnaire was distributed among college students in Saudi Arabia. The questionnaire was designed in Arabic, based on a previously validated survey, with items and questions selected from a comprehensive literature review to ensure public comprehension. Participants received an online link that included detailed information about the survey’s objectives, the target population, and a consent form for participation. Upon receiving approval from the Institutional Research Board, the survey was disseminated online. A sample of the questionnaire was provided in the appendix.
Data Collection and Management
Data was collected through an online survey designed using Google Forms and distributed to the target population in Arabic. The survey comprised several sections:
Consent for participation
Sociodemographic information
Awareness and Knowledge of Sun Exposure
Sunscreen Usage
The online format facilitated easy access and completion for participants, while the structured sections ensured comprehensive data collection relevant to the study objectives.
Data analysis:
The data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 26 and involved the use of descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, and multivariate logistic regression analysis. Descriptive statistics summarized the demographic characteristics and responses of participants through means, standard deviations, frequencies, and percentages. Chi-square tests were employed to examine the relationships between categorical variables, such as gender, age, educational level, and region, and participants' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding sun exposure and sunscreen use. A p-value of less than 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3. Results
The study included 388 college students, with a slightly higher representation of females (53.9%) compared to males (46.1%). The majority of participants were aged between 18-23 years, comprising 68% of the sample. The most prevalent educational levels among participants were the 1st year (27.1%) and the 3rd and 5th years (both 15.2%) college students. The College of Health Sciences had the highest representation, with 36.3% of participants. Geographically, the participants were most commonly from the Eastern region (25.8%) and the Central region (21.1%) of Saudi Arabia. Regarding formal education about the dangers of sun exposure, 43.0% of participants reported not having received any, while 40.7% had received such education (
Table 1).
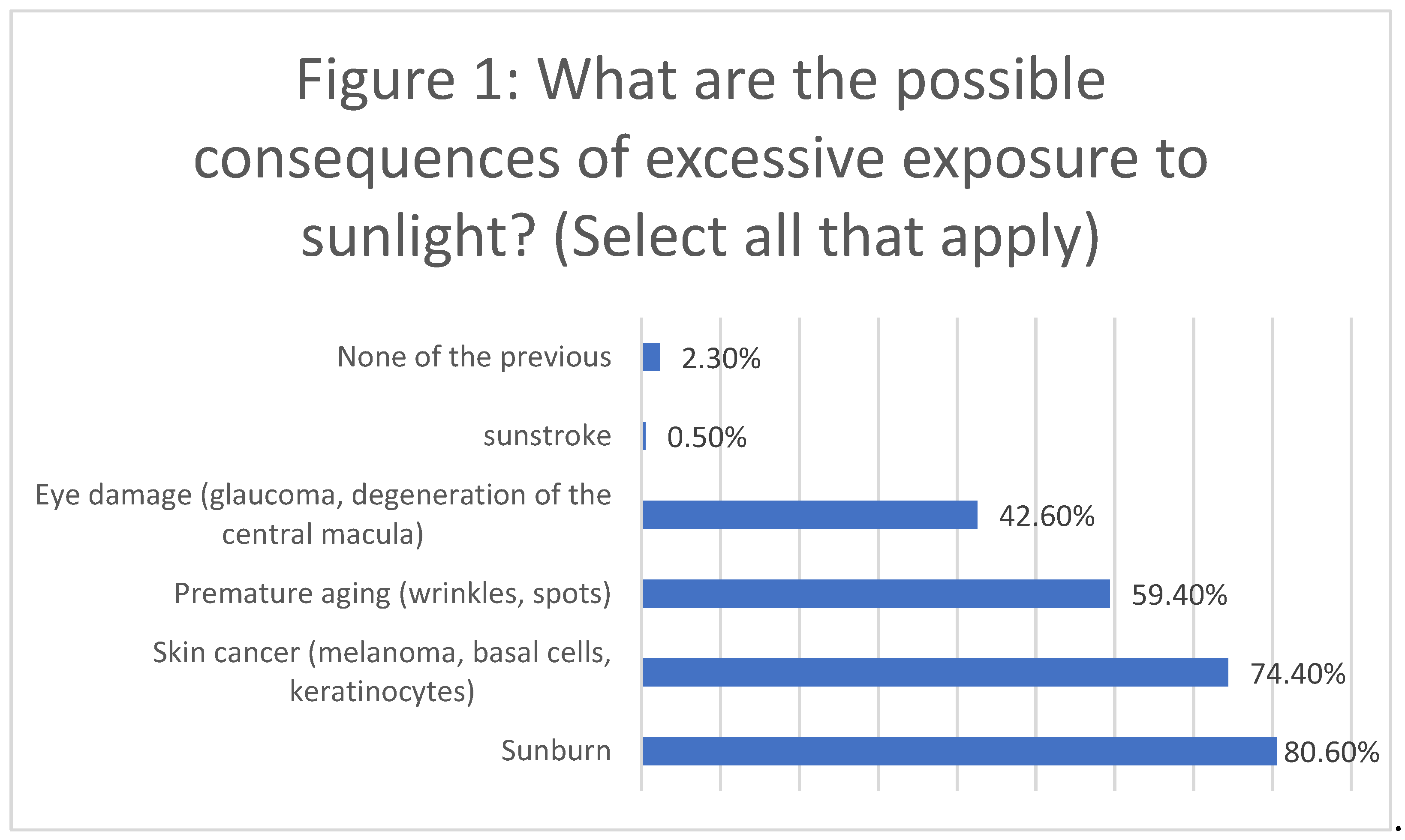
The study assessed the consequences of excessive sunlight exposure and participants' awareness and use of sunscreen. Among the 388 respondents, the most commonly identified consequences of excessive sunlight exposure were sunburn, cited by 80.6% of participants, and skin cancer (melanoma, basal cells, keratinocytes), mentioned by 74.4%. Premature aging (wrinkles, spots) was recognized by 59.4%, while 42.6% were aware of the risk of eye damage (glaucoma, degeneration of the central macula) (Figure 1).
Regarding knowledge about the effects of varying sun exposure on different skin types and colors, 31.4% of participants reported knowing to some extent, followed by 26.8% with intermediate knowledge and 21.1% with good knowledge. Only 5.7% claimed excellent knowledge, while 14.9% admitted they did not know at all. When rating their knowledge of the harmful effects of skin exposure to sunlight, the most common response was intermediate knowledge (40.7%), followed by low knowledge (27.8%) and high knowledge (18.8%). Very low and very high knowledge were less common, at 8.8% and 3.9%, respectively. In terms of sunscreen usage during peak sunlight hours (10 am to 4 pm), 29.9% of participants reported using sunscreen sometimes, 27.3% never used it, and 22.9% used it rarely. Only 19.8% stated they always used sunscreen during these hours (
Table 2).
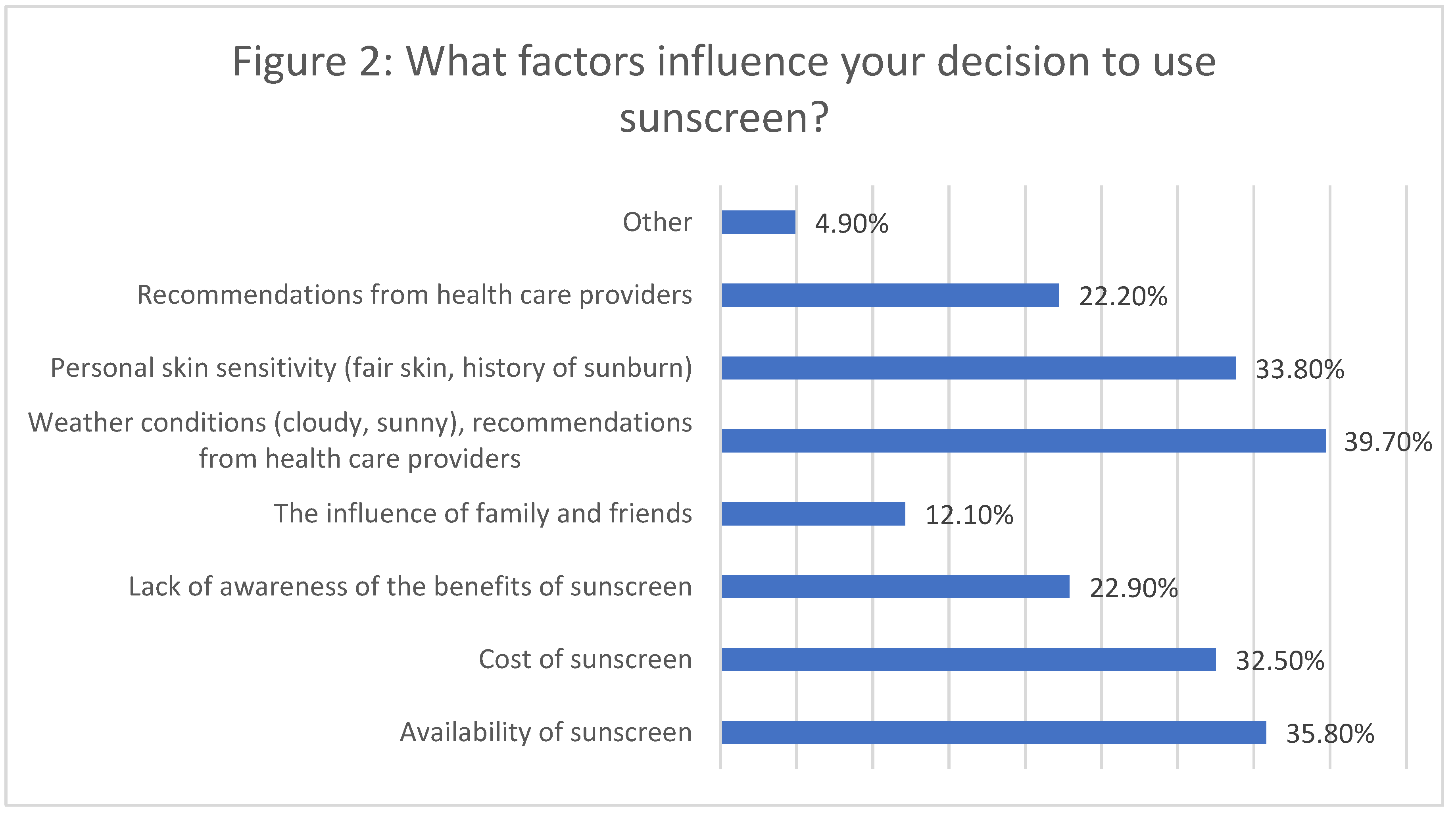
The factors influencing sunscreen use were weather conditions and recommendations from healthcare providers, which influenced 39.7% of participants. Other common factors included the availability of sunscreen (35.8%), personal skin sensitivity (33.8%), and the cost of sunscreen (32.5%) (Figure 2).
In terms of sunscreen use practices, 25.8% of participants reported never using sunscreen when outdoors, while 21.9% used it sometimes, and 21.4% used it rarely. Only 11.6% reported using sunscreen every time they were outdoors. Additionally, when asked if wearing a face covering such as a niqab provides adequate sun protection and eliminates the need for sunscreen, 31.4% agreed, while 25.0% remained neutral, and 17.0% disagreed. Regarding self-examination for unusual skin changes, 57.2% of participants reported never conducting self-examinations, while 26.8% did so rarely. Only 8.2% performed self-examinations every couple of months. Notably, 78.6% of participants had not been diagnosed with any sun-related skin conditions, while 21.4% were unsure. Knowledge of the sun protection factor (SPF) on sunscreen products was lacking, with 50.8% of participants unaware of its meaning. Conversely, 70.6% believed that regular sunscreen use could reduce the risk of skin cancer. Furthermore, 40.7% considered skin protection from the sun to be extremely important, and 26.8% deemed it very important (
Table 3).
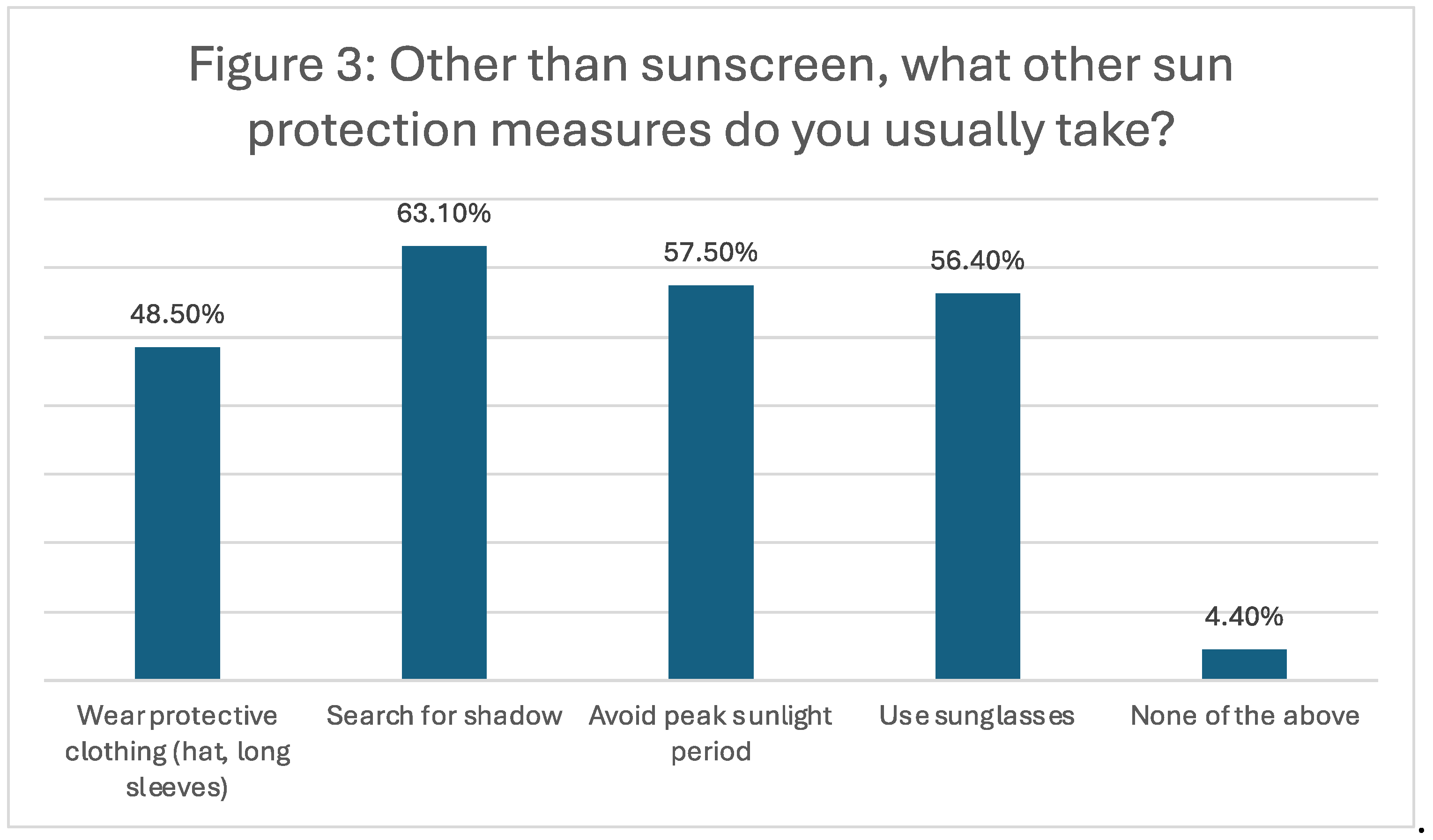
Apart from sunscreen, the most common sun protection measures included seeking shade (63.1%), avoiding peak sunlight periods (57.5%), and wearing sunglasses (56.4%). Protective clothing was also popular, with 48.5% of participants using it (Figure 3).
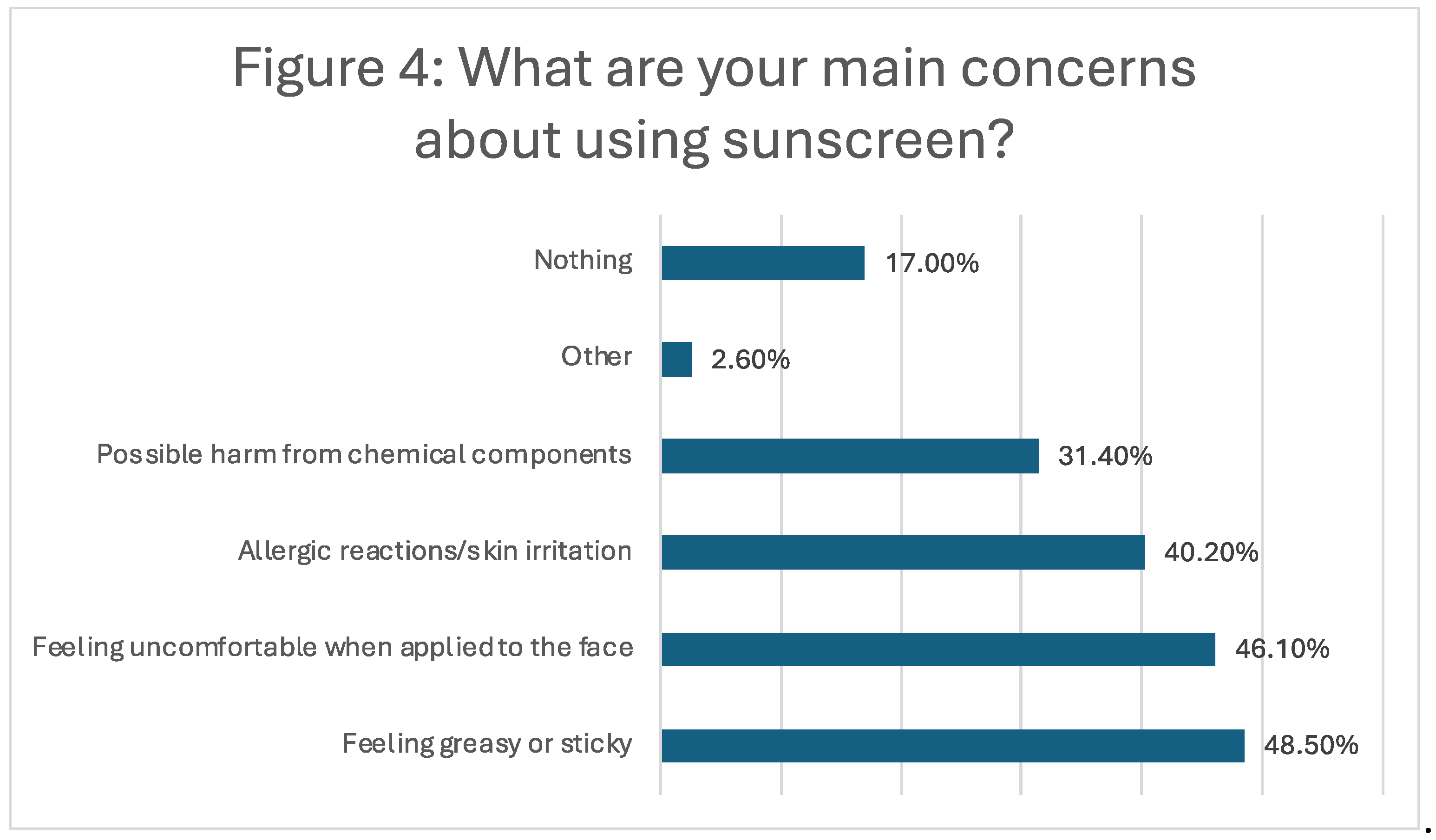
Concerns about using sunscreen were prevalent, with 48.5% of participants feeling it was greasy or sticky, 46.1% feeling uncomfortable when applied to the face, and 40.2% worried about allergic reactions or skin irritation. Concerns about possible harm from chemical components were noted by 31.4% of participants (Figure 4).
The study investigated the frequency of sunscreen use among participants outdoors, analyzing various demographic factors. Males were significantly less likely to use sunscreen regularly compared to females. Among males, 44.7% never used sunscreen, while only 9.6% of females reported the same. Conversely, 17.7% of females used sunscreen every time they were outdoors, compared to just 4.5% of males. Sunscreen use varied by age group, with those aged 18-20 years and 21-23 years being more likely to use sunscreen sometimes or most of the time. Specifically, 29.5% of participants aged 21-23 used sunscreen sometimes. Participants aged 30 or older were the least likely to use sunscreen regularly, with 50.0% never using it and none using it every time they were outdoors. Sunscreen use also differed by educational level. First-year students were the most likely to never use sunscreen (43.8%), while second-year students showed more balanced responses, with 35.7% using sunscreen sometimes. Interns and 3rd-year students exhibited varied use patterns, with around 34.2% of interns and 28.8% of 3rd-year students rarely using sunscreen. Participants who had received formal education or information about the dangers of sun exposure were more likely to use sunscreen regularly. Among those with formal education, 17.7% used sunscreen every time they were outdoors, compared to 7.2% of those without formal education and 7.9% of those unsure about receiving such education; however, slight significance was reported (P=0.067) (
Table 4).
4. Discussion
The current study provides valuable insights into sunscreen usage behaviors and the level of awareness regarding the risks of sun exposure among college students. These findings are critical as they highlight gaps in knowledge and practice, informing future educational interventions aimed at reducing the incidence of sun-related health issues, particularly skin cancer.
The data reveals significant gender differences in sunscreen use, with males significantly less likely to use sunscreen compared to females. This finding aligns with previous research indicating that females are generally more aware of and proactive about skin protection measures compared to males [
14,
15,
16,
17]. The higher usage of sunscreen among females could be attributed to greater awareness and societal norms that emphasize skin care for women [
2,
13]. Interventions targeting male students could help in bridging this gap by increasing their awareness and promoting sunscreen use.
Age also played a significant role in sunscreen usage patterns. Participants aged 18-20 and 21-23 years were more likely to use sunscreen sometimes or most of the time. This trend could be explained by increased health awareness and access to information among younger students, who are often more exposed to educational campaigns and social media messages regarding sun safety [
13,
14]. In contrast, participants aged 30 or older were the least likely to use sunscreen regularly, with 50.0% never using it. This lower rate of usage among older participants may be due to a lack of targeted educational efforts toward this age group or ingrained habits formed over the years [
18,
19].
Education about the dangers of sun exposure appears to positively influence sunscreen use. Among participants who had received formal education, 17.7% used sunscreen every time they were outdoors, compared to 7.2% of those without formal education. This underscores the importance of formal educational programs in promoting healthy behaviors [
20,
21]. However, the insignificance level indicates that while there is a positive trend, it is not strong enough to conclusively affirm the impact without further investigation. Enhancing the quality and reach of educational interventions could potentially improve these outcomes.
The study also assessed participants' knowledge about the effects of sun exposure and their awareness of the importance of sunscreen. While almost one third of participants reported knowing to some extent about the effects of varying sun exposure on different skin types and colors, only 5.7% claimed excellent knowledge. Additionally, 40.7% rated their knowledge of the harmful effects of skin exposure to sunlight as intermediate, indicating a moderate level of awareness. This gap in knowledge suggests that there is room for improvement in educational efforts to enhance understanding of sun-related risks and the importance of preventive measures like sunscreen use.
The study identified several barriers to regular sunscreen use, including the perception that it is greasy or sticky, discomfort when applied to the face, and concerns about allergic reactions or skin irritation. These concerns are consistent with previous research highlighting common deterrents to sunscreen use [
2,
17,
22,
23]. Addressing these barriers through the development of more user-friendly sunscreen formulations and better education about the importance of sunscreen can help increase its usage. For example, promoting sunscreens that are non-greasy, hypoallergenic, and suitable for sensitive skin could alleviate some of these concerns
Apart from sunscreen, other sun protection measures such as seeking shade, avoiding peak sunlight periods, and wearing sunglasses were also commonly practiced by participants. This holistic approach to sun protection is crucial as it reduces overall exposure to harmful UV rays. Encouraging a combination of protective behaviors, rather than relying solely on sunscreen, can enhance the effectiveness of sun safety strategies.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study highlights the insufficient usage of sunscreen among university students in Saudi Arabia. Significant gender, age, educational level, and geographical differences were found in sunscreen use among college students. While females, younger participants, and those with formal education about sun exposure are more likely to use sunscreen regularly, significant gaps remain, particularly among males and older students. Addressing these disparities through targeted educational interventions and addressing barriers to sunscreen use can improve sun protection behaviors. Future research should explore the effectiveness of different educational strategies and the development of user-friendly sunscreen products to enhance compliance and reduce the risk of sun-related health issues.
References
- Manikrao Donglikar, M.; Laxman Deore, S. Sunscreens: A review. Pharmacogn J. 2016, 8, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Robaee, A.A. Awareness to sun exposure and use of sunscreen by the general population. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2010, 10, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.; Wang, S.Q.; Burnett, M.; Osterwalder, U.; Lim, H.W. Photoprotection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013, 69, e1–e853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Program, NT. 15th Report on Carcinogens. Natl Toxicol Progr. Published online 2021. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.K. Prevention and Early Detection Strategies for Melanoma and Skin Cancer. Arch Dermatol. 1996, 132, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coups, E.J.; Manne, S.L.; Heckman, C.J. Multiple Skin Cancer Risk Behaviors in the U.S. Population. Am J Prev Med. 2008, 34, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DSR; RJF; LMD; DSR; JCB; RM Cancer of the Skin. WB Saunders Co; 2004.
- Kennedy, C.; Willemze, R.; de Gruijl, F.R.; Bouwes Bavinck, J.N.; Bajdik, C.D. The Influence of Painful Sunburns and Lifetime Sun Exposure on the Risk of Actinic Keratoses, Seborrheic Warts, Melanocytic Nevi, Atypical Nevi, and Skin Cancer. J Invest Dermatol. 2003, 120, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsner, R.S.; Parker, D.F.; Brathwaite, N.; Thomas, A.; Tejada, F.; Trapido, E.J. Sun Protection Policies in Miami-Dade County Public Schools: Opportunities for Skin Cancer Prevention. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005, 22, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Balbeesi, A.; AlMukhadeb, E.; BinMayouf, M.; et al. Dermatology Patients’ Knowledge of Sunscreen Guidelines at a University Hospital in Saudi Arabia. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022, 15, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuqati, R.R.; Alamri, A.S.; Almuqati, N.R. Knowledge, attitude, and practices toward sun exposure and use of sun protection among non-medical, female, university students in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study. Int J Women’s Dermatology. 2019, 5, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaalan, Z.M.; Ghazy, A.A.; Altaymani, A.M.; Alruwaili, A.J. Awareness & attitude toward sunscreen use and sun protection in Al-Jouf region, Saudi Arabia. Med Sci. 2022, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahashwan, E. Awareness and knowledge of sun exposure and use of sunscreen among adults in Aseer region, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm J. 2024, 32, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, S.Y.; Alraddadi, E.A.; Ramadan, M.; Alsalamah, F.; Alghumuy, R.; Aljuhani, F.F. Assessment of prevalence of sunscreen use and related practices among people living in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey-based study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024, 23, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abroms, L.; Jorgensen, C.M.; Southwell, B.G.; Geller, A.C.; Emmons, K.M. Gender Differences in Young Adults’ Beliefs About Sunscreen Use. Heal Educ Behav. 2003, 30, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shih, J.; Tran, A.; et al. Gender-Based Differences and Barriers in Skin Protection Behaviors in Melanoma Survivors. J Skin Cancer. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Godse, K.; Patil, S.; Nadkarni, N. Knowledge and attitude of general population toward effects of sun exposure and use of sunscreens. Indian J Dermatol. 2018, 63, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond-Lezman, J.R.; Riskin, S. Attitudes, Behaviors, and Risks of Sun Protection to Prevent Skin Cancer Amongst Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Cureus. Published online February 13, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gambetta, P.; Moscoso-Porras, M.G.; Taype-Rondan, A. Factors associated with regular sunscreen use by medical students of a Peruvian university. J Prev Med Hyg. 2016, 57, E172–E177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pulimeno, M.; Piscitelli, P.; Colazzo, S.; Colao, A.; Miani, A. School as ideal setting to promote health and wellbeing among young people. Heal Promot Perspect. 2020, 10, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jorge, D.; González-Luis, M.A.; Rodríguez-Jiménez M del, C.; Ariño-Mateo, E. Educational Programs for the Promotion of Health at School: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021, 18, 10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, M.; Sander, M.; Burbidge, T.; Beecker, J. The efficacy and safety of sunscreen use for the prevention of skin cancer. Can Med Assoc J. 2020, 192, E1802–E1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.; Beazer, I.R.; Su, S.; Bounsanga, J.; Hon, E.S.; Lipsky, M.S. An Exploration of the Use and Impact of Preventive Measures on Skin Cancer. Healthcare. 2022, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Table 1.
Demographic factors of the participants.
Table 1.
Demographic factors of the participants.
| |
Count |
Column N % |
| Gender |
Male |
179 |
46.1% |
| Female |
209 |
53.9% |
| Age |
18-20 |
132 |
34.0% |
| 21-23 |
132 |
34.0% |
| 24-26 |
111 |
28.6% |
| 27-29 |
9 |
2.3% |
| 30 or older |
4 |
1.0% |
| Educational level |
1st year |
105 |
27.1% |
| 2nd year |
42 |
10.8% |
| 3rd year |
59 |
15.2% |
| 4th year |
56 |
14.4% |
| 5th year |
59 |
15.2% |
| 6th year |
29 |
7.5% |
| Intern |
38 |
9.8% |
| College |
College of Health Sciences (Medicine, Dentistry, Pharmacy, Laboratories, Health Informatics) |
141 |
36.3% |
| College of Human Sciences (Arabic/English, History, Geography) |
37 |
9.5% |
| College of Science (mathematics, physics, chemistry, statistics, biology) |
41 |
10.6% |
| Faculty of Sharia (Sharia, Islamic Studies, Regulations and Law) |
45 |
11.6% |
| College of Computer Engineering and Science |
69 |
17.8% |
| College of Business Administration |
51 |
13.1% |
| Other |
4 |
1.0% |
| Region |
Central region |
82 |
21.1% |
| Northern region |
74 |
19.1% |
| Southern region |
63 |
16.2% |
| Eastern region |
100 |
25.8% |
| Western region |
69 |
17.8% |
| Have you received formal education (formal education means: education by schools, universities, or official awareness bodies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) or information about the dangers of exposure to sunlight? |
No |
167 |
43.0% |
| Yes |
158 |
40.7% |
| Not sure |
63 |
16.2% |
Table 2.
Level of awareness of the participants considering sun exposure and the importance of sunscreen.
Table 2.
Level of awareness of the participants considering sun exposure and the importance of sunscreen.
| |
Count |
Column N % |
| How much do you know about the effects of varying sun exposure on people with different skin types and colors? |
I do not know at all |
58 |
14.9% |
| I know to some extent |
122 |
31.4% |
| Intermediate knowledge |
104 |
26.8% |
| Good knowledge |
82 |
21.1% |
| Excellent knowledge |
22 |
5.7% |
| How would you rate your knowledge of the harmful effects of skin exposure to sunlight (e.g., sunburn, skin cancer, premature aging)? |
Very low |
34 |
8.8% |
| Low |
108 |
27.8% |
| Intermediate |
158 |
40.7% |
| High |
73 |
18.8% |
| Very high |
15 |
3.9% |
| Do you use sunscreen when you go out during peak sunlight period (10 am to 4 pm)? |
Never |
106 |
27.3% |
| Rarely |
89 |
22.9% |
| Sometime |
116 |
29.9% |
| Always |
77 |
19.8% |
Table 3.
Practice considering using of sunscreens.
Table 3.
Practice considering using of sunscreens.
| |
Count |
Column N % |
| How often do you use sunscreen when outdoors? |
Never |
100 |
25.8% |
| Rarely |
83 |
21.4% |
| Sometime |
85 |
21.9% |
| Most time |
75 |
19.3% |
| Every time |
45 |
11.6% |
| Do you think that wearing a covering over the face such as a niqab provides adequate protection against exposure to the sun's rays and eliminates the need for sunscreen? |
Strongly disagree |
39 |
10.1% |
| Disagree |
66 |
17.0% |
| Neutral |
97 |
25.0% |
| Agree |
122 |
31.4%) |
| Strongly agree |
64 |
16.5% |
| How often do you self-examine for unusual signs or changes in the skin? |
Never |
222 |
57.2% |
| Rarely |
104 |
26.8% |
| Once a year |
15 |
3.9% |
| Every couple of months |
32 |
8.2% |
| Every month |
15 |
3.9% |
| Have you been diagnosed with any skin condition related to sun exposure (such as sunburn, skin cancer)? |
No |
304 |
78.6% |
| Yes |
0 |
0.0% |
| Not sure |
83 |
21.4% |
| Do you know what the sun protection factor (SPF) on sunscreen products means? |
No |
197 |
50.8% |
| Yes |
85 |
21.9% |
| To some extent, I have a general idea that I am not entirely sure |
106 |
27.3% |
| Do you think it is important to protect your skin from the sun's rays? |
Not completely important |
14 |
3.6% |
| Not important |
31 |
8.0% |
| Important |
81 |
20.9% |
| Very important |
104 |
26.8% |
| Extremely very important |
158 |
40.7% |
| Do you think that using sunscreen regularly can reduce the risk of skin cancer? |
No |
42 |
10.8% |
| Yes |
274 |
70.6% |
| Not sure |
72 |
18.6% |
Table 4.
The relation between using of sunscreen and demographic factors.
Table 4.
The relation between using of sunscreen and demographic factors.
| |
How often do you use sunscreen when outdoors? |
| Never |
Rarely |
Sometime |
Most time |
Every time |
P-value |
| Count |
Row N % |
Count |
Row N % |
Count |
Row N % |
Count |
Row N % |
Count |
Row N % |
| Gender |
Male |
80 |
44.7% |
41 |
22.9% |
23 |
12.8% |
27 |
15.1% |
8 |
4.5% |
0.000* |
| Female |
20 |
9.6% |
42 |
20.1% |
62 |
29.7% |
48 |
23.0% |
37 |
17.7% |
| Age |
18-20 |
47 |
35.6% |
23 |
17.4% |
21 |
15.9% |
24 |
18.2% |
17 |
12.9% |
0.035* |
| 21-23 |
23 |
17.4% |
32 |
24.2% |
39 |
29.5% |
19 |
14.4% |
19 |
14.4% |
| 24-26 |
25 |
22.5% |
27 |
24.3% |
23 |
20.7% |
28 |
25.2% |
8 |
7.2% |
| 27-29 |
3 |
33.3% |
1 |
11.1% |
1 |
11.1% |
3 |
33.3% |
1 |
11.1% |
| 30 or older |
2 |
50.0% |
0 |
0.0% |
1 |
25.0% |
1 |
25.0% |
0 |
0.0% |
| Educational level |
1st year |
46 |
43.8% |
16 |
15.2% |
16 |
15.2% |
16 |
15.2% |
11 |
10.5% |
0.000* |
| 2nd year |
8 |
19.0% |
8 |
19.0% |
15 |
35.7% |
4 |
9.5% |
7 |
16.7% |
| 3rd year |
8 |
13.6% |
17 |
28.8% |
13 |
22.0% |
13 |
22.0% |
8 |
13.6% |
| 4th year |
4 |
7.1% |
16 |
28.6% |
15 |
26.8% |
12 |
21.4% |
9 |
16.1% |
| 5th year |
15 |
25.4% |
11 |
18.6% |
16 |
27.1% |
16 |
27.1% |
1 |
1.7% |
| 6th year |
6 |
20.7% |
7 |
24.1% |
6 |
20.7% |
5 |
17.2% |
5 |
17.2% |
| Intern |
13 |
34.2% |
8 |
21.1% |
4 |
10.5% |
9 |
23.7% |
4 |
10.5% |
| College |
College of Health Sciences (Medicine, Dentistry, Pharmacy, Laboratories, Health Informatics) |
34 |
24.1% |
34 |
24.1% |
29 |
20.6% |
28 |
19.9% |
16 |
11.3% |
0.156 |
| College of Human Sciences (Arabic/English, History, Geography) |
5 |
13.5% |
6 |
16.2% |
14 |
37.8% |
8 |
21.6% |
4 |
10.8% |
| College of Science (mathematics, physics, chemistry, statistics, biology) |
11 |
26.8% |
8 |
19.5% |
4 |
9.8% |
10 |
24.4% |
8 |
19.5% |
| Faculty of Sharia (Sharia, Islamic Studies, Regulations and Law) |
21 |
46.7% |
7 |
15.6% |
8 |
17.8% |
6 |
13.3% |
3 |
6.7% |
| College of Computer Engineering and Science |
19 |
27.5% |
17 |
24.6% |
16 |
23.2% |
13 |
18.8% |
4 |
5.8% |
| College of Business Administration |
10 |
19.6% |
10 |
19.6% |
13 |
25.5% |
9 |
17.6% |
9 |
17.6% |
| Other |
0 |
0.0% |
1 |
25.0% |
1 |
25.0% |
1 |
25.0% |
1 |
25.0% |
| Region |
Central region |
13 |
15.9% |
15 |
18.3% |
21 |
25.6% |
20 |
24.4% |
13 |
15.9% |
0.037 |
| Northern region |
11 |
14.9% |
18 |
24.3% |
18 |
24.3% |
15 |
20.3% |
12 |
16.2% |
| Southern region |
14 |
22.2% |
17 |
27.0% |
14 |
22.2% |
12 |
19.0% |
6 |
9.5% |
| Eastern region |
39 |
39.0% |
18 |
18.0% |
22 |
22.0% |
15 |
15.0% |
6 |
6.0% |
| Western region |
23 |
33.3% |
15 |
21.7% |
10 |
14.5% |
13 |
18.8% |
8 |
11.6% |
| Have you received formal education or information about the dangers of exposure to sunlight? |
No |
47 |
28.1% |
31 |
18.6% |
38 |
22.8% |
39 |
23.4% |
12 |
7.2% |
0.067 |
| Yes |
34 |
21.5% |
36 |
22.8% |
35 |
22.2% |
25 |
15.8% |
28 |
17.7% |
| Not sure |
19 |
30.2% |
16 |
25.4% |
12 |
19.0% |
11 |
17.5% |
5 |
7.9% |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









