Submitted:
31 July 2024
Posted:
01 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
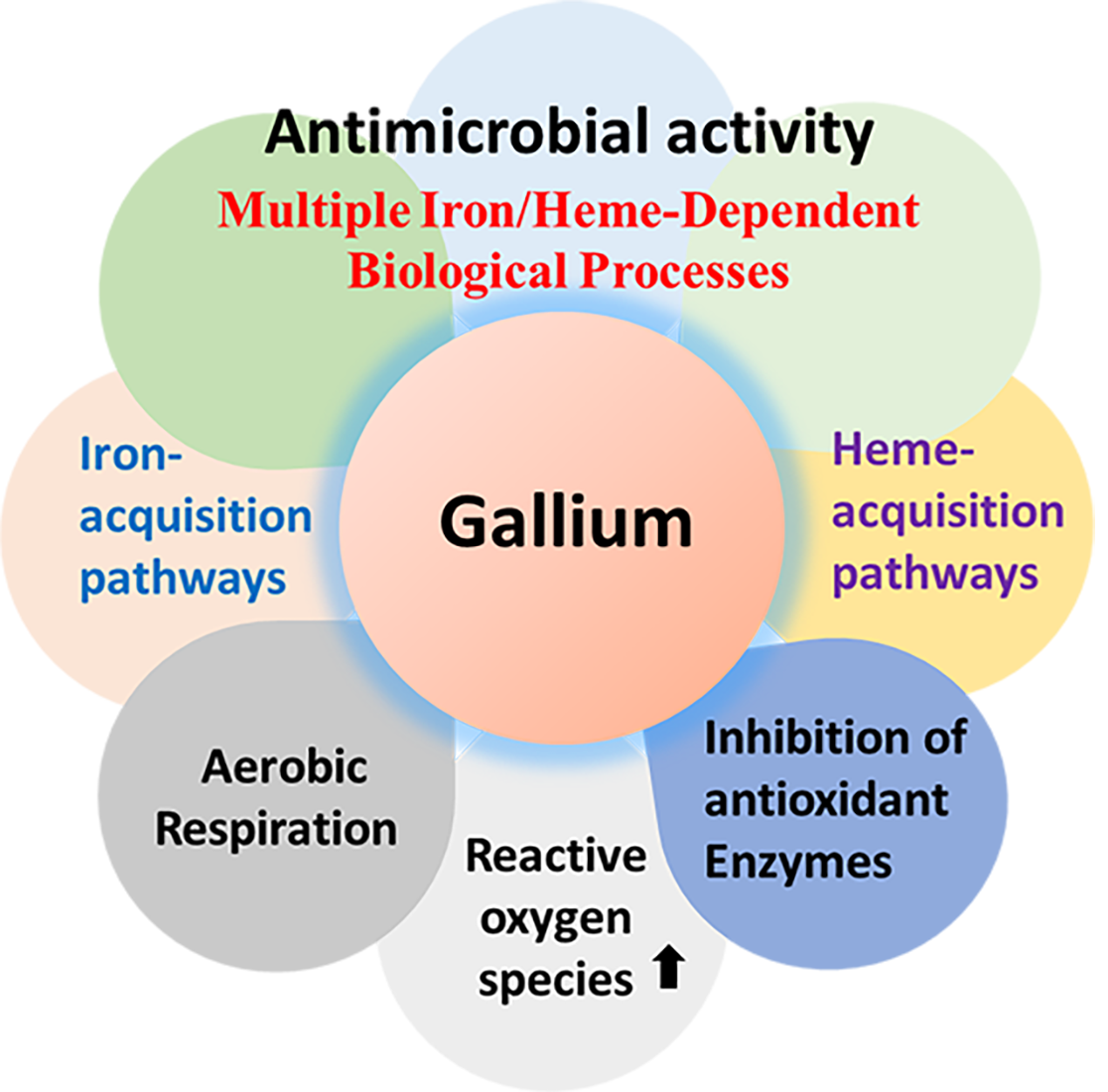
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Action of Ga(III)-Based Compounds
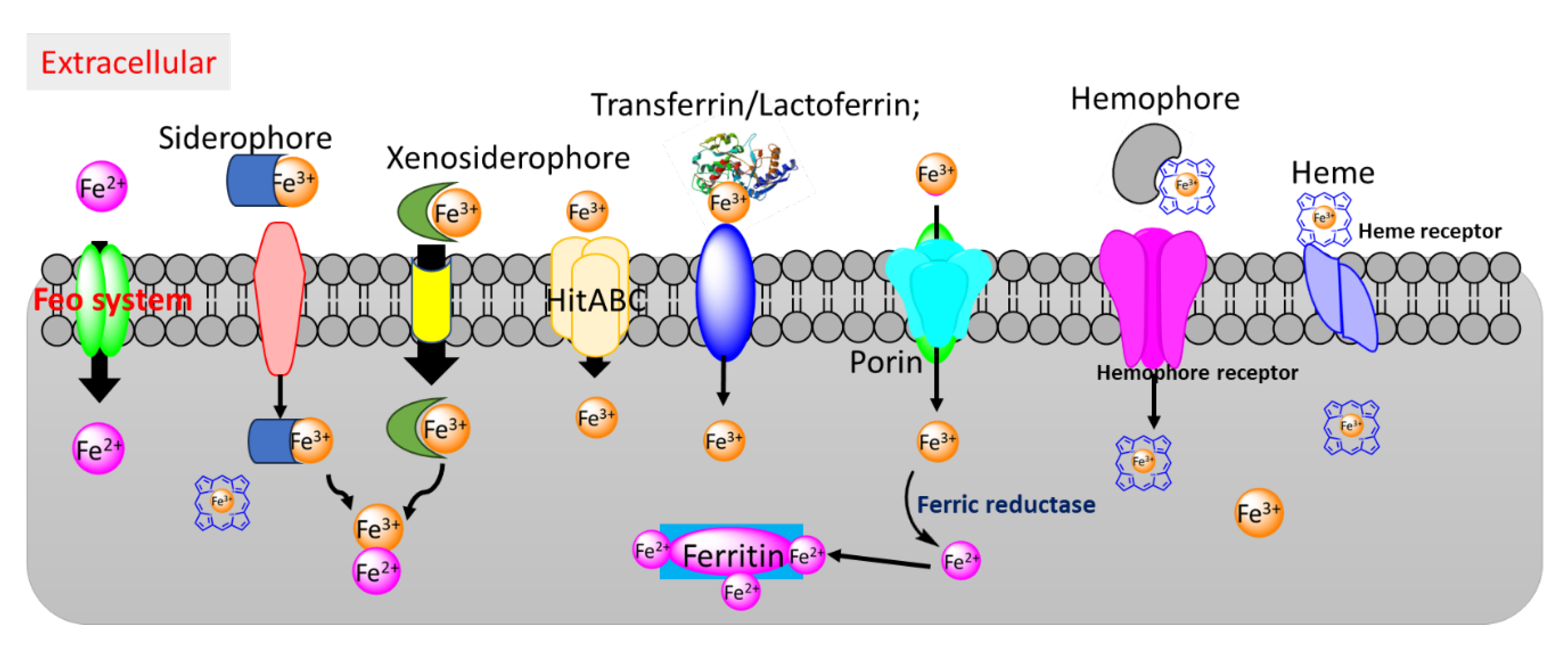
2.1. Iron Acquisition Pathways as a Target for Gallium Antimicrobials
2.2. Heme Acquisition Pathways as a Target for Antimicrobials
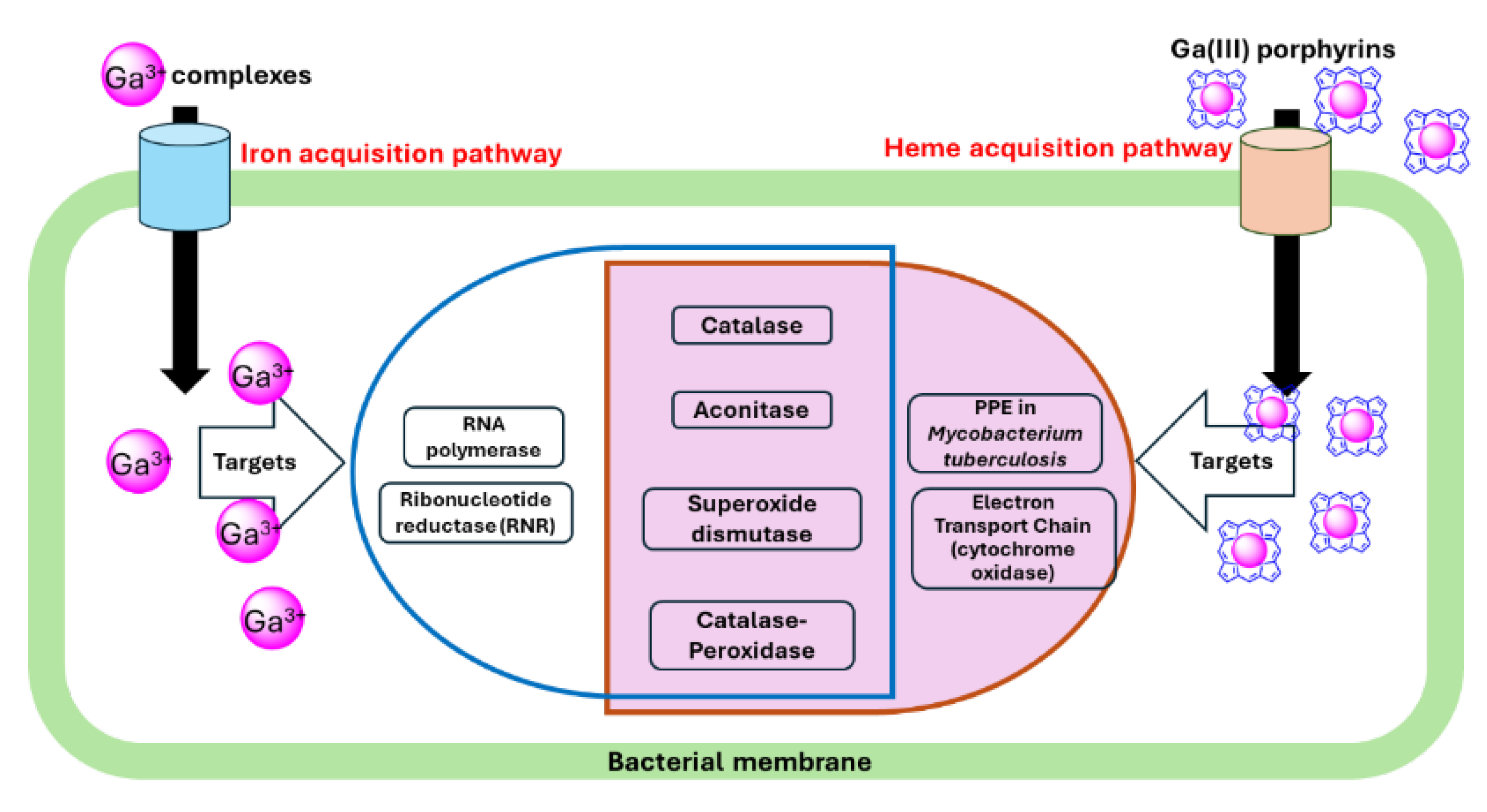
2.3. Potential Targets for Ga(III)-Based Compounds
2.3.1. Ribonucleotide Reductase (RNR)
| Ga(III) | Target | Bacteria | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ga(NO3)3 | Aconitase | M. tuberculosis, M. abscessus | [60,63] |
| Ribonucleotide reductase | M. tuberculosis, P. aeruginosa PAO1 | [8,60] | |
| Catalase | M. abscessus, P. aeruginosa PAO1, K.pneumoniae, F. novicida | [8,64,65,66] | |
| Superoxide dismutases | P. aeruginosa 103 | [64] | |
| GaPP | Catalase | MRSA, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa 103, M. abscessus. | [63,64,65,67] |
| Superoxide dismutases | P. aeruginosa 103 | [64] | |
| Aconitase | M. abscessus | [63] |
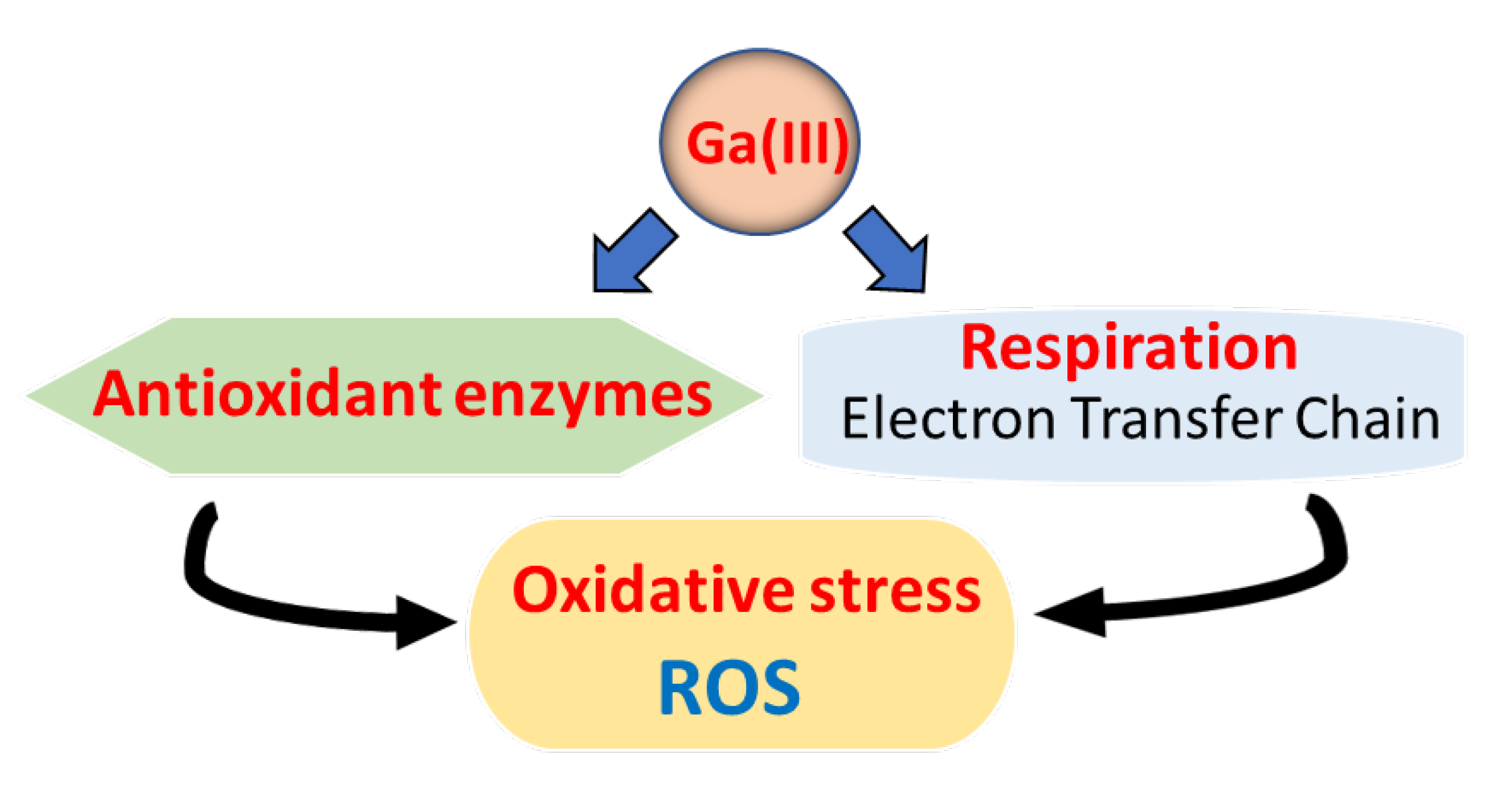
2.3.2. Oxidative Phosphorylation and Cytochrome Oxidases
2.3.3. RNA Polymerase
2.3.4. Aconitase
2.3.5. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Enzymes
2.3.6. Catalase
2.3.7. Superoxide Dismutase
2.3.8. Peroxidases
3. Conclusion and Prospective Views
References
- Turner, RJ. Metal-based antimicrobial strategies. Microb Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, RJ. The good, the bad, and the ugly of metals as antimicrobials. Biometals. 2024, 37, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, A; Verderosa, AD; Elliott, AG; Zuegg, J; Blaskovich, MAT. Metals to combat antimicrobial resistance. Nat Rev Chem. 2023, 7, 202–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtuldu F, Mutlu N, Boccaccini AR, Galusek D. Gallium containing bioactive materials: A review of anticancer, antibacterial, and osteogenic properties. Bioact Mater. 2022, 17: 125-146.
- Bernstein, LR. Mechanisms of therapeutic activity for gallium. Pharmacol Rev. 1998, 50, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chitambar, CR. Gallium and its competing roles with iron in biological systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016, 1863, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F; Liu, F; Huang, K; Yang, S. Advancement of Gallium and Gallium-Based Compounds as Antimicrobial Agents. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 827960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss CH, Kaneko Y, Khuu L, et al. Gallium disrupts bacterial iron metabolism and has therapeutic effects in mice and humans with lung infections. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(460).
- Hacht, B. Gallium(III) Ion Hydrolysis under Physiological Conditions. Bulletin of The Korean Chemical Society. 2008, 29, 372–376. [Google Scholar]
- Chitambar, CR. The therapeutic potential of iron-targeting gallium compounds in human disease: From basic research to clinical application. Pharmacol Res. 2017, 115, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelson, AB; Carnevali, M; Truong-Le, V. Gallium-based anti-infectives: targeting microbial iron-uptake mechanisms. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, LR; Tanner, T; Godfrey, C; Noll, B. Chemistry and pharmacokinetics of gallium maltolate, a compound with high oral gallium bioavailability. Met Based Drugs. 2000, 7, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collery, P; Domingo, JL; Keppler, BK. Preclinical toxicology and tissue gallium distribution of a novel antitumour gallium compound: tris (8-quinolinolato) gallium (III). Anticancer Res. 1996, 16, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darwesh AMF, Imberti C, Bartnicka JJ, et al. In Vivo Trafficking of the Anticancer Drug Tris(8-Quinolinolato) Gallium (III) (KP46) by Gallium-68/67 PET/SPECT Imaging. Molecules. 2023, 28.
- Valiahdi, SM; Heffeter, P; Jakupec, MA; et al. The gallium complex KP46 exerts strong activity against primary explanted melanoma cells and induces apoptosis in melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res. 2009, 19, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffin, RN; Blair, VL; Kedzierski, L; Andrews, PC. Alkyl gallium(III) quinolinolates: A new class of highly selective anti-leishmanial agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2020, 186, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F; Ma, S; Liu, S; et al. A novel antimicrobial strategy for bacterial infections: Gallium-based materials. Colloid and Interface Science Communications. 2023, 56, 100735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M; Parker, CJ; Shaw, ZL; et al. Metallic Gallium Droplets Exhibit Poor Antibacterial Properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024, 16, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour, N; Hurrell, R; Kelishadi, R. Review on iron and its importance for human health. J Res Med Sci. 2014, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cassat, JE; Skaar, EP. Iron in infection and immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2013, 13, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandersman C, Delepelaire P. Bacterial iron sources: from siderophores to hemophores. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004, 58: 611-647.
- Wilson, BR; Bogdan, AR; Miyazawa, M; Hashimoto, K; Tsuji, Y. Siderophores in Iron Metabolism: From Mechanism to Therapy Potential. Trends Mol Med. 2016, 22, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, VI; Bachman, MA. Diverging roles of bacterial siderophores during infection. Metallomics. 2015, 7, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrow, NL; Fleming, RE; Minnick, MF. Sequestration and scavenging of iron in infection. Infect Immun. 2013, 81, 3503–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbane, F; Jarrett, C; Gardner, D; Long, D; Hinnebusch, BJ. Role of the Yersinia pestis yersiniabactin iron acquisition system in the incidence of flea-borne plague. PLoS One. 2010, 5, e14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banin, E; Lozinski, A; Brady, KM; et al. The potential of desferrioxamine-gallium as an anti-Pseudomonas therapeutic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105, 16761–16766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangipani, E; Bonchi, C; Minandri, F; Imperi, F; Visca, P. Pyochelin potentiates the inhibitory activity of gallium on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5572–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A; Savino, C; Ahn, SH; Yang, Z; Van Lanen, SG; Boros, E. Theranostic Gallium Siderophore Ciprofloxacin Conjugate with Broad Spectrum Antibiotic Potency. J Med Chem. 2019, 62, 9947–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratledge, C. Iron, mycobacteria and tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2004, 84, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobin, J; Horwitz, MA. Exochelins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis remove iron from human iron-binding proteins and donate iron to mycobactins in the M. tuberculosis cell wall. J Exp Med. 1996, 183, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobin, J; Moore, CH; Reeve JR, Jr; Wong, DK; Gibson, BW; Horwitz, MA. Iron acquisition by Mycobacterium tuberculosis: isolation and characterization of a family of iron-binding exochelins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995, 92, 5189–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneghetti, F; Villa, S; Gelain, A; et al. Iron Acquisition Pathways as Targets for Antitubercular Drugs. Curr Med Chem. 2016, 23, 4009–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyam, M; Shilkar, D; Verma, H; et al. The Mycobactin Biosynthesis Pathway: A Prospective Therapeutic Target in the Battle against Tuberculosis. J Med Chem. 2021, 64, 71–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam, M; Shilkar, D; Rakshit, G; Jayaprakash, V. Approaches for targeting the mycobactin biosynthesis pathway for novel anti-tubercular drug discovery: where we stand. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022, 17, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, MJ; Walz, AJ; Zhu, H; et al. Design, synthesis, and study of a mycobactin-artemisinin conjugate that has selective and potent activity against tuberculosis and malaria. J Am Chem Soc. 2011, 133, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olakanmi, O; Britigan, BE; Schlesinger, LS. Gallium disrupts iron metabolism of mycobacteria residing within human macrophages. Infect Immun. 2000, 68, 5619–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandara, L; Salamunic, I. Iron metabolism: current facts and future directions. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012, 22, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, H; Chim, N; Credali, A; Goulding, CW. Heme uptake in bacterial pathogens. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 2014, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y; Guo, M. Bacterial heme-transport proteins and their heme-coordination modes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009, 481, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard KL, Kelley BR, Johnson JG. Heme Uptake and Utilization by Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019, 9: 81.
- Chao, A; Sieminski, PJ; Owens, CP; Goulding, CW. Iron Acquisition in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem Rev. 2019, 119, 1193–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, CP; Du, J; Dawson, JH; Goulding, CW. Characterization of heme ligation properties of Rv0203, a secreted heme binding protein involved in Mycobacterium tuberculosis heme uptake. Biochemistry. 2012, 51, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, CP; Chim, N; Graves, AB; et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis secreted protein Rv0203 transfers heme to membrane proteins MmpL3 and MmpL11. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288, 21714–21728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullius MV, Nava S, Horwitz MA. PPE37 Is Essential for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Heme-Iron Acquisition (HIA), and a Defective PPE37 in Mycobacterium bovis BCG Prevents HIA. Infect Immun. 2019, 87.
- Mitra, A; Speer, A; Lin, K; Ehrt, S; Niederweis, M. PPE Surface Proteins Are Required for Heme Utilization by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PPE Surface Proteins Are Required for Heme Utilization by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. MBio. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M; Tanaka, WN; Zhu, H; Xie, G; Dooley, DM; Lei, B. Direct hemin transfer from IsdA to IsdC in the iron-regulated surface determinant (Isd) heme acquisition system of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283, 6668–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniau, C; Gilli, R; Izadi-Pruneyre, N; et al. Thermodynamics of heme binding to the HasA(SM) hemophore: effect of mutations at three key residues for heme uptake. Biochemistry. 2003, 42, 10627–10633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojiljkovic, I; Kumar, V; Srinivasan, N. Non-iron metalloporphyrins: potent antibacterial compounds that exploit haem/Hb uptake systems of pathogenic bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1999, 31, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozja, J; Yi, K; Shafer, WM; Stojiljkovic, I. Porphyrin-based compounds exert antibacterial action against the sexually transmitted pathogens Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Haemophilus ducreyi. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2004, 24, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi S, Visca P, Frangipani E. Gallium-Protoporphyrin IX Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa Growth by Targeting Cytochromes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017, 7.
- Zhang, H; Li, Q; Qi, X; et al. Iron-blocking antibacterial therapy with cationic heme-mimetic gallium porphyrin photosensitizer for combating antibiotic resistance and enhancing photodynamic antibacterial activity. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2023, 451, 138261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai L, Yang K-W. Porphyrin-vancomycin: A highly promising conjugate for the identification and photodynamic inactivation of antibiotic resistant Gram-positive pathogens. Dyes and Pigments. 2015, 120: 228-238.
- Dosselli, R; Gobbo, M; Bolognini, E; Campestrini, S; Reddi, E. Porphyrin−Apidaecin Conjugate as a New Broad Spectrum Antibacterial Agent. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2010, 1, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlund, P; Reichard, P. Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006, 75, 681–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintchak, MD; Arjara, G; Kellogg, BA; Stubbe, J; Drennan, CL. The crystal structure of class II ribonucleotide reductase reveals how an allosterically regulated monomer mimics a dimer. Nat Struct Biol. 2002, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, V; Angelova, S; Markova, N; Dudev, T. Gallium as a Therapeutic Agent: A Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Competition between Ga(3+) and Fe(3+) Ions in Metalloproteins. J Phys Chem B. 2016, 120, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitambar, CR; Antholine, WE. Iron-targeting antitumor activity of gallium compounds and novel insights into triapine(®)-metal complexes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircheva, N; Dudev, T. Novel Insights into Gallium’s Mechanism of Therapeutic Action: A DFT/PCM Study of the Interaction between Ga(3+) and Ribonucleotide Reductase Substrates. J Phys Chem B. 2019, 123, 5444–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzilli, LG; De Castro, B; Caradonna, JP; Stewart, RC; Van Vuuren, CP. Nucleoside complexing. A Raman and carbon-13 NMR spectroscopic study of the binding of hard and soft metal species. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1980, 102, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olakanmi, O; Kesavalu, B; Pasula, R; Abdalla, MY; Schlesinger, LS; Britigan, BE. Gallium nitrate is efficacious in murine models of tuberculosis and inhibits key bacterial Fe-dependent enzymes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 6074–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith BD, Karp JE. Ribonucleotide reductase: an old target with new potential. Leuk Res. Vol 27. England; 2003:1075-1076.
- Jordan, A; Torrents, E; Sala, I; Hellman, U; Gibert, I; Reichard, P. Ribonucleotide reduction in Pseudomonas species: simultaneous presence of active enzymes from different classes. J Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi S-r, Switzer B, Britigan BE, Narayanasamy P. Gallium Porphyrin and Gallium Nitrate Synergistically Inhibit Mycobacterial Species by Targeting Different Aspects of Iron/Heme Metabolism. ACS Infectious Diseases 2020.
- Scott, ZW; Choi, SR; Talmon, GA; Britigan, BE; Narayanasamy, P. Combining Gallium Protoporphyrin and Gallium Nitrate Enhances In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Role of Inhibition of Bacterial Antioxidant Enzymes and Resultant Increase in Cytotoxic Reactive Oxygen Species. ACS Infect Dis. 2022, 8, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott Z, Choi S-r, Britigan BE, Narayanasamy P. Dual Gallium Drug Treatment Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Efficacy and Potential Mechanism(s) of Action and Resistance. Advanced Therapeutics. 2024, n/a(n/a), 2400147.
- Olakanmi, O; Gunn, JS; Su, S; Soni, S; Hassett, DJ; Britigan, BE. Gallium disrupts iron uptake by intracellular and extracellular Francisella strains and exhibits therapeutic efficacy in a murine pulmonary infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, SR; Talmon, GA; Hearne, K; et al. Combination Therapy with Gallium Protoporphyrin and Gallium Nitrate Exhibits Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity In Vitro and In Vivo against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Pharm. 2023, 20, 4058–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, S; Visaggio, D; Pirolo, M; Frangipani, E; Bernstein, L; Visca, P. Antimicrobial Activity of Gallium Compounds on ESKAPE Pathogens. Antimicrobial Activity of Gallium Compounds on ESKAPE Pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y; Han, B; Xie, Y; et al. Combination of gallium(iii) with acetate for combating antibiotic resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem Sci. 2019, 10, 6099–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemke AC, Madison CJ, Kasturiarachi N, Pearce LL, Peterson J. Antimicrobial Synergism Toward Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Gallium(III) and Inorganic Nitrite. Front Microbiol. 2020, 11: 2113.
- Bériault, R; Hamel, R; Chenier, D; Mailloux, RJ; Joly, H; Appanna, VD. The overexpression of NADPH-producing enzymes counters the oxidative stress evoked by gallium, an iron mimetic. Biometals. 2007, 20, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang Y, Yang X, Zhang S, et al. Comparative proteomics unveils the bacteriostatic mechanisms of Ga(III) on the regulation of metabolic pathways in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Proteomics. 2023, 289: 105011.
- Deisseroth, A; Dounce, AL. Catalase: Physical and chemical properties, mechanism of catalysis, and physiological role. Physiol Rev. 1970, 50, 319–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A; Yan, LJ; Jana, CK; Das, N. Role of Catalase in Oxidative Stress- and Age-Associated Degenerative Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 9613090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugna, M; Tasse, L; Hederstedt, L. In vivo production of catalase containing haem analogues. Febs j. 2010, 277, 2663–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M; Tian, P; Li, Q; et al. Gallium Nitrate Enhances Antimicrobial Activity of Colistin against Klebsiella pneumoniae by Inducing Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation. Microbiol Spectr. 2023, 11, e0033423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasnacht, M; Polacek, N. Oxidative Stress in Bacteria and the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. Front Mol Biosci. 2021, 8, 671037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broxton, CN; Culotta, VC. SOD Enzymes and Microbial Pathogens: Surviving the Oxidative Storm of Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y; Abreu, IA; Cabelli, DE; et al. Superoxide dismutases and superoxide reductases. Chem Rev. 2014, 114, 3854–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmuldeen, H; Alghamdi, R; Alghofaili, F; Yesilkaya, H. Functional assessment of microbial superoxide dismutase isozymes suggests a differential role for each isozyme. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019, 134, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wengenack, NL; Jensen, MP; Rusnak, F; Stern, MK. Mycobacterium tuberculosis KatG is a peroxynitritase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999, 256, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L; Kiss, F; Bakó, A; et al. Effect of gallium on photosynthetic pigments and peroxidase activity of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Journal of Plant Nutrition. 1989, 12, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangoshaei, P; Hassani, L; Mohammadi, F; Hamidi, A; Mohammadi, K. Investigating the effect of gallium curcumin and gallium diacetylcurcumin complexes on the structure, function and oxidative stability of the peroxidase enzyme and their anticancer and antibacterial activities. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015, 20, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





