Submitted:
31 July 2024
Posted:
01 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
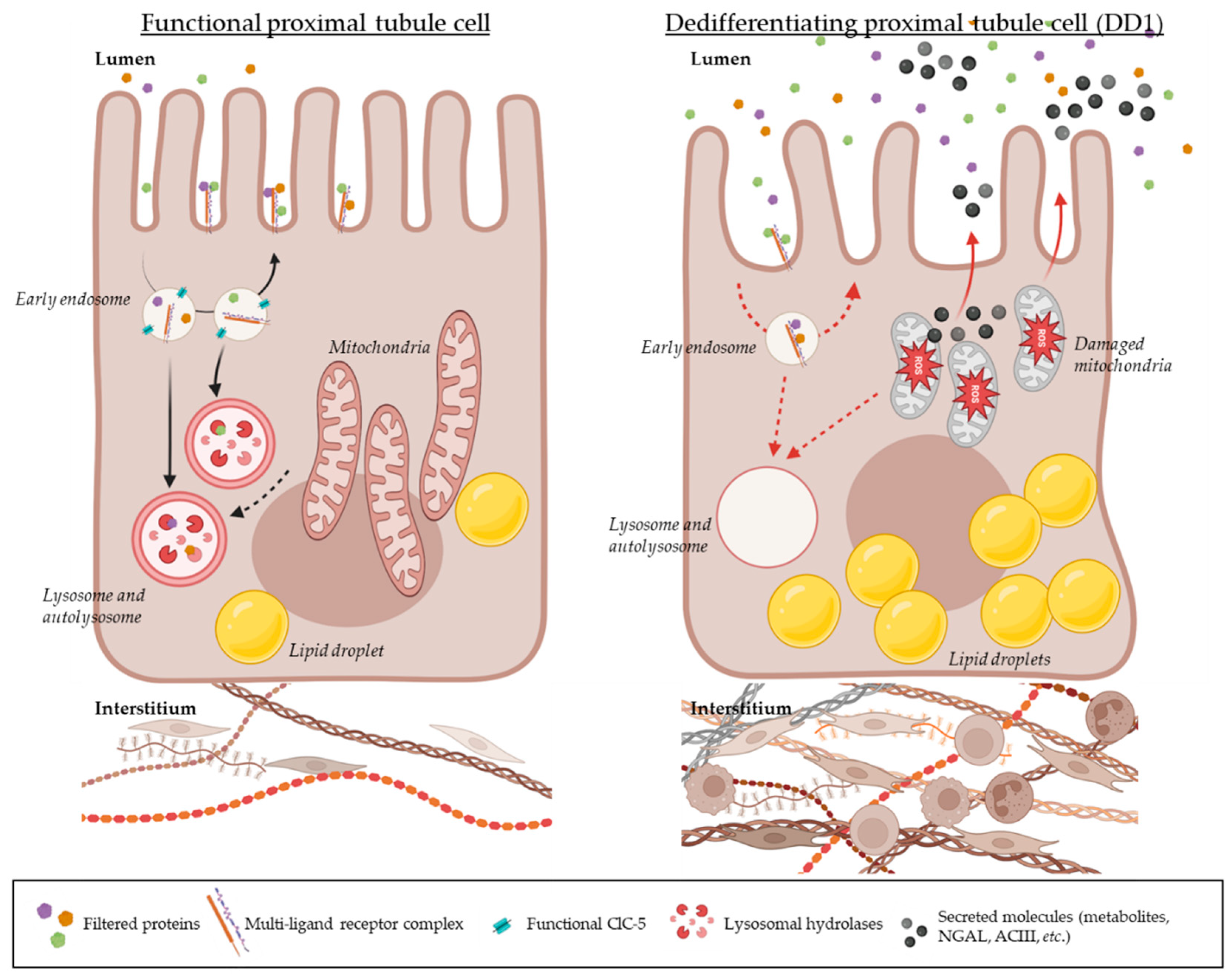
2. A Dysfunctional ClC-5 Leads to Proximal Tubule Dedifferentiation
3. An Alteration of Proximal Tubule Cell Metabolism Is Observed in the Context of Dent Disease Type 1
4. Studies Revealed a Diversity of Potential Biomarkers for the Progression of Dent Disease Type 1
5. Current State of the Art – Hypotheses on Dent Disease Type 1 Progression
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chrysopoulou, M.; Rinschen, M.M. Metabolic Rewiring and Communication: An Integrative View of Kidney Proximal Tubule Function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2024, 86, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, V.; Kramann, R. Metabolic reprogramming heterogeneity in chronic kidney disease. FEBS Open Bio 2023, 13, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour-Hendili, L.; Blanchard, A.; Le Pottier, N.; Roncelin, I.; Lourdel, S.; Treard, C.; González, W.; Vergara-Jaque, A.; Morin, G.; Colin, E.; et al. Mutation Update of theCLCN5Gene Responsible for Dent Disease 1. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Shipman, K.; A Weisz, O. Making a Dent in Dent Disease. Function 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devuyst O, Thakker RV. Dent’s disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010 Oct 14;5:28.
- Ehlayel, A.M.; Copelovitch, L. Update on Dent Disease. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2018, 66, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnous, M.G.; Arroyo, J.; Cogal, A.G.; Anglani, F.; Kang, H.G.; Sas, D.; Harris, P.C.; Lieske, J.C. The Site and Type of CLCN5 Genetic Variation Impact the Resulting Dent Disease-1 Phenotype. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwon, N.; Günther, W.; Schwake, M.; Bösl, M.R.; Jentsch, T.J. ClC-5 Cl--channel disruption impairs endocytosis in a mouse model for Dent's disease. Nature 2000, 408, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Devuyst, O.; Courtoy, P.J.; Wang, X.-T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Thakker, R.V.; Guggino, S.; Guggino, W.B. Mice lacking renal chloride channel, CLC-5, are a model for Dent's disease, a nephrolithiasis disorder associated with defective receptor-mediated endocytosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.K.; Yoo, K.W.; Atala, A.; Lu, B. Lentiviral vector mediated gene therapy for type I Dent disease ameliorates Dent disease-like phenotypes for three months in ClC-5 null mice. Mol. Ther. - Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 27, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipman, K.E.; Baty, C.J.; Long, K.R.; Rbaibi, Y.; Cowan, I.A.; Gerges, M.; Marciszyn, A.L.; Kashlan, O.B.; Tan, R.J.; Edwards, A.; et al. Impaired Endosome Maturation Mediates Tubular Proteinuria in Dent Disease Cell Culture and Mouse Models. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 34, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novarino, G.; Weinert, S.; Rickheit, G.; Jentsch, T.J. Endosomal Chloride-Proton Exchange Rather Than Chloride Conductance Is Crucial for Renal Endocytosis. Science 2010, 328, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakhi IB, De Combiens E, Frachon N, Durussel F, Brideau G, Nemazanyy I, Frère P, Thévenod F, Lee WK, Zeng Q, Klein C, Lourdel S, Bignon Y. A novel transgenic mouse model highlights molecular disruptions involved in the pathogenesis of Dent disease 1. Gene. 2024 Nov 30;928:148766.
- Reynolds, C.J.; Gillen, C.M.; Burke, R.; Tsering, Y.; Loucks, E.; Judd-Mole, S.; Dow, J.A.; Romero, M.F. Drosophila ClC-c Is a Homolog of Human CLC-5 and a New Model for Dent Disease Type 1. Kidney360 2024, 5, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorvin, C.M.; Wilmer, M.J.; Piret, S.E.; Harding, B.; Heuvel, L.P.v.D.; Wrong, O.; Jat, P.S.; Lippiat, J.D.; Levtchenko, E.N.; Thakker, R.V. Receptor-mediated endocytosis and endosomal acidification is impaired in proximal tubule epithelial cells of Dent disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 7014–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, M.; Burballa, C.; Cantero-Recasens, G.; Butnaru, C.M.; Malhotra, V.; Ariceta, G.; Sarró, E.; Meseguer, A. Novel Dent disease 1 cellular models reveal biological processes underlying ClC-5 loss-of-function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1413–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, H.; Cebotaru, L.; Hryciw, D.H.; Weinman, E.J.; Donowitz, M.; Guggino, S.E.; Guggino, W.B. ClC-5: role in endocytosis in the proximal tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2005, 289, F850–F862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Gao, L.; Guan, Y.; Gu, W.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, F.; et al. Dent disease 1-linked novel CLCN5 mutations result in aberrant location and reduced ion currents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grand, T.; Mordasini, D.; L'Hoste, S.; Pennaforte, T.; Genete, M.; Biyeyeme, M.-J.; Vargas-Poussou, R.; Blanchard, A.; Teulon, J.; Lourdel, S. Novel CLCN5 mutations in patients with Dent’s disease result in altered ion currents or impaired exchanger processing. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grand, T.; L'Hoste, S.; Mordasini, D.; Defontaine, N.; Keck, M.; Pennaforte, T.; Genete, M.; Laghmani, K.; Teulon, J.; Lourdel, S. Heterogeneity in the processing of CLCN5 mutants related to Dent disease. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignon, Y.; Alekov, A.; Frachon, N.; Lahuna, O.; Doh-Egueli, C.J.-B.; Deschênes, G.; Vargas-Poussou, R.; Lourdel, S. A novel CLCN5 pathogenic mutation supports Dent disease with normal endosomal acidification. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhi, I.; Bignon, Y.; Frachon, N.; Hureaux, M.; Arévalo, B.; González, W.; Vargas-Poussou, R.; Lourdel, S. Diversity of functional alterations of the ClC-5 exchanger in the region of the proton glutamate in patients with Dent disease 1. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, N.; Yamada, H.; Yamazaki, O.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, A.; Ashida, A.; Yamamoto, D.; Kaku, Y.; Sekine, T.; et al. A pure chloride channel mutant of CLC-5 causes Dent’s disease via insufficient V-ATPase activation. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2016, 468, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang MH, Brown MR, Liu Y, Gainullin VG, Harris PC, Romero MF, Lieske JC. Cl- and H+ coupling properties and subcellular localizations of wildtype and disease-associated variants of the voltage-gated Cl-/H+ exchanger ClC-5. J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 7;295(6):1464–73.
- Jentsch, T.J.; Pusch, M. CLC Chloride Channels and Transporters: Structure, Function, Physiology, and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1493–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, W.; Lüchow, A.; Cluzeaud, F.; Vandewalle, A.; Jentsch, T.J. ClC-5, the chloride channel mutated in Dent’s disease, colocalizes with the proton pump in endocytotically active kidney cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1998, 95, 8075–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshbach, M.L.; Weisz, O.A. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis in the Proximal Tubule. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenken, A.; Cerutti, G.; Brasch, J.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Aziz, Z.; Robbins-Juarez, S.Y.; Chavez, E.Y.; Ahlsen, G.; et al. Structures of LRP2 reveal a molecular machine for endocytosis. Cell 2023, 186, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Homaei, A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Akhtar, N. Cathepsins: Proteases that are vital for survival but can also be fatal. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hryciw, D.H.; Wang, Y.; Devuyst, O.; Pollock, C.A.; Poronnik, P.; Guggino, W.B. Cofilin Interacts with ClC-5 and Regulates Albumin Uptake in Proximal Tubule Cell Lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40169–40176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed AA, Loh NY, Terryn S, Lippiat JD, Partridge C, Galvanovskis J, Williams SE, Jouret F, Wu FT, Courtoy PJ, Nesbit MA, Rorsman P, Devuyst O, Ashcroft FM, Thakker RV. CLC-5 and KIF3B interact to facilitate CLC-5 plasma membrane expression, endocytosis, and microtubular transport: relevance to pathophysiology of Dent’s disease. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):F365-80.
- Lourdel, S.; Grand, T.; Burgos, J.; González, W.; Sepúlveda, F.V.; Teulon, J. ClC-5 mutations associated with Dent’s disease: a major role of the dimer interface. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2011, 463, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekov, A.K. Mutations associated with Dent's disease affect gating and voltage dependence of the human anion/proton exchanger ClC-5. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polesel, M.; Kaminska, M.; Haenni, D.; Bugarski, M.; Schuh, C.; Jankovic, N.; Kaech, A.; Mateos, J.M.; Berquez, M.; Hall, A.M. Spatiotemporal organisation of protein processing in the kidney. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devuyst, O.; Jouret, F.; Auzanneau, C.; Courtoy, P.J. Chloride Channels and Endocytosis: New Insights from Dent’s Disease and ClC-5 Knockout Mice. Nephron Physiol. 2005, 99, p69–p73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.R.; Rbaibi, Y.; Kashlan, O.B.; Weisz, O.A. Receptor-associated protein impairs ligand binding to megalin and megalin-dependent endocytic flux in proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2023, 325, F457–F464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, E.I.; Devuyst, O.; Dom, G.; Nielsen, R.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Verroust, P.; Leruth, M.; Guggino, W.B.; Courtoy, P.J. Loss of chloride channel ClC-5 impairs endocytosis by defective trafficking of megalin and cubilin in kidney proximal tubules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 8472–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braulke, T.; Geuze, H.; Slot, J.; Hasilik, A.; Vonfigura, K. On The Effects of Weak Bases and Monensin on Sorting and Processing of Lysosomal-Enzymes in Human-Cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987, 43, 316–321.
- Nielsen, R.; Courtoy, P.J.; Jacobsen, C.; Dom, G.; Lima, W.R.; Jadot, M.; Willnow, T.E.; Devuyst, O.; Christensen, E.I. Endocytosis provides a major alternative pathway for lysosomal biogenesis in kidney proximal tubular cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 5407–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchiaro, P.; De Pasquale, V.; Della Morte, R.; Tafuri, S.; Avallone, L.; Pizard, A.; Moles, A.; Pavone, L.M. The Multifaceted Role of the Lysosomal Protease Cathepsins in Kidney Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo-Medved D, Moin K, Sloane B. Cathepsin B. AFCS-Nat Mol Pages [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2020 Nov 23];2011. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5541861/.
- Gailly, P.; Jouret, F.; Martin, D.; Debaix, H.; Parreira, K.; Nishita, T.; Blanchard, A.; Antignac, C.; Willnow, T.; Courtoy, P.; et al. A novel renal carbonic anhydrase type III plays a role in proximal tubule dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, A.; Curis, E.; Guyon-Roger, T.; Kahila, D.; Treard, C.; Baudouin, V.; Bérard, E.; Champion, G.; Cochat, P.; Dubourg, J.; et al. Observations of a large Dent disease cohort. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, P.; Schnellmann, R.G. Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protasoni, M.; Zeviani, M. Mitochondrial Structure and Bioenergetics in Normal and Disease Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herst, P.M.; Rowe, M.R.; Carson, G.M.; Berridge, M.V. Functional Mitochondria in Health and Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 296–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devin, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; et al. Mitochondria: Ultrastructure, Dynamics, Biogenesis and Main Functions. In: Mitochondria in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes [Internet]. Elsevier Inc 2019. Academic Press; 2019 [cited 2024 Jul 14]. p. 3–32. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128117521000018.
- Cassina, L.; Chiaravalli, M.; Boletta, A. Increased mitochondrial fragmentation in polycystic kidney disease acts as a modifier of disease progression. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 6493–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, B.P.; Chen, Z.; Berquez, M.; Debaix, H.; Tokonami, N.; Prange, J.A.; van de Hoek, G.; Alessio, C.; Raimondi, A.; Nevo, N.; et al. Impaired autophagy bridges lysosomal storage disease and epithelial dysfunction in the kidney. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanriover, C.; Copur, S.; Ucku, D.; Cakir, A.B.; Hasbal, N.B.; Soler, M.J.; Kanbay, M. The Mitochondrion: A Promising Target for Kidney Disease. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.; Morales, M.M.; Sousa-Menzes, J.; Ornellas, D.; Sipes, J.; Cui, Y.; Cui, I.; Hulamm, P.; Cebotaru, V.; Cebotaru, L.; et al. Transcriptional adaptation to Clcn5 knockout in proximal tubules of mouse kidney. Physiol. Genom. 2008, 33, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faivre, A.; Verissimo, T.; Auwerx, H.; Legouis, D.; de Seigneux, S. Tubular Cell Glucose Metabolism Shift During Acute and Chronic Injuries. Front. Med. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, O.E.; Kalhan, S.C.; Hanson, R.W. The Key Role of Anaplerosis and Cataplerosis for Citric Acid Cycle Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30409–30412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrens, JF. Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J Physiol. 2003 Oct 15;552(Pt 2):335–44.
- Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis. 2007 May 1;12(5):913–22.
- Guggino, SE. Can we generate new hypotheses about Dent’s disease from gene analysis of a mouse model? Exp Physiol. 2009 Feb;94(2):191–6.
- Iglesias, J.; Abernethy, V.E.; Wang, Z.; Lieberthal, W.; Koh, J.S.; Levine, J.S. Albumin is a major serum survival factor for renal tubular cells and macrophages through scavenging of ROS. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1999, 277, F711–F722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devuyst O, Luciani A. Chloride transporters and receptor-mediated endocytosis in the renal proximal tubule. J Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;593(18):4151–64.
- Kang, H.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Choi, P.; Ko, Y.-A.; Han, S.H.; Chinga, F.; Park, A.S.D.; Tao, J.; Sharma, K.; Pullman, J.; et al. Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Tan, E.; Shi, H.; Ren, X.; Wan, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, J.; et al. Mitochondrial oxidative damage reprograms lipid metabolism of renal tubular epithelial cells in the diabetic kidney. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levental I, Lyman E. Regulation of membrane protein structure and function by their paralipidomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Feb;24(2):107–22.
- Cornelius, F. Modulation of Na,K-ATPase and Na-ATPase Activity by Phospholipids and Cholesterol. I. Steady-State Kinetics. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 8842–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.J.; Krueger, E.W.; Weller, S.G.; Johnson, K.M.; Casey, C.A.; Schott, M.B.; McNiven, M.A. Direct lysosome-based autophagy of lipid droplets in hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 117, 32443–32452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, CT. Carbonic anhydrases--an overview. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(7):603–14.
- Silagi, E.S.; Batista, P.; Shapiro, I.M.; Risbud, M.V. Expression of Carbonic Anhydrase III, a Nucleus Pulposus Phenotypic Marker, is Hypoxia-responsive and Confers Protection from Oxidative Stress-induced Cell Death. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Räisänen SR, Lehenkari P, Tasanen M, Rahkila P, Härkönen PL, Väänänen HK. Carbonic anhydrase III protects cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 1999 Mar;13(3):513–22.
- Krebs, H.; Johnson, W. The role of citric acid in intermediate metabolism in animal tissues. FEBS Lett. 1980, 117, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux RJ, Singh R, Brewer G, Auger C, Lemire J, Appanna VD. Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase work in tandem to modulate the antioxidant alpha-ketoglutarate during oxidative stress in Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(12):3804–10.
- A McDonough, M.; Loenarz, C.; Chowdhury, R.; Clifton, I.J.; Schofield, C.J. Structural studies on human 2-oxoglutarate dependent oxygenases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, L.; Yao, K. The Antioxidative Function of Alpha-Ketoglutarate and Its Applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sole, M.J.; Madapallimattam, A.; Baines, A.D. An active pathway for serotonin synthesis by renal proximal tubules. Kidney Int. 1986, 29, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erikci, A.; Ucar, G.; Yabanoglu-Ciftci, S. Role of serotonin in the regulation of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, K.; Scholpa, N.E.; Schnellmann, J.G.; Schnellmann, R.G. Serotonin regulation of mitochondria in kidney diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, G.H.; Schrader, J.; Deussen, A. Turnover of adenosine in plasma of human and dog blood. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1989, 256, C799–C806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, T.X.; Omura, G.A.; Stoltz, R.R.; Kisicki, J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Peldesine (BCX-34), a Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Inhibitor, following Single and Multiple Oral Doses in Healthy Volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, J.W.; Walter, G.A.; O'Regan, M.H.; Stair, R.E. Increases in Cerebral Cortical Perfusate Adenosine and Inosine Concentrations during Hypoxia and Ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1987, 7, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L F, F H, V K, E H, E B, R F, T S, A JN, A N. Enhanced accumulation of pericardial fluid adenosine and inosine in patients with coronary artery disease. Life Sci. 1999 Jan 1;65(10):1005–12.
- Welihinda, A.A.; Kaur, M.; Greene, K.; Zhai, Y.; Amento, E.P. The adenosine metabolite inosine is a functional agonist of the adenosine A2A receptor with a unique signaling bias. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, S.; Mirandola, P.; Milani, D.; Varani, K.; Gessi, S.; Klotz, K.-N.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine Receptors as Mediators of Both Cell Proliferation and Cell Death of Cultured Human Melanoma Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabley, J.G.; Pacher, P.; Liaudet, L.; Soriano, F.G.; Haskó, G.; Marton, A.; Szabó, C.; Salzman, A.L. Inosine reduces inflammation and improves survival in a murine model of colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2003, 284, G138–G144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garay-Rojas, E.; Harper, M.; Hraba-Renevey, S.; Kress, M. An apparent autocrine mechanism amplifies the dexamethasone- and retinoic acid-induced expression of mouse lipocalin-encoding gene 24p3. Gene 1996, 170, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maritzen, T.; Rickheit, G.; Schmitt, A.; Jentsch, T. Kidney-specific upregulation of vitamin D3 target genes in ClC-5 KO mice. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonafine, M.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; Jaisser, F. More than a simple biomarker: the role of NGAL in cardiovascular and renal diseases. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.J.; Platt, F.M.; Lloyd-Evans, E.; Galione, A. Molecular mechanisms of endolysosomal Ca2+ signalling in health and disease. Biochem. J. 2011, 439, 349–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott CC, Gruenberg J. Ion flux and the function of endosomes and lysosomes: pH is just the start: the flux of ions across endosomal membranes influences endosome function not only through regulation of the luminal pH. BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Feb;33(2):103–10.
- Yu W, Beaudry S, Negoro H, Boucher I, Tran M, Kong T, Denker BM. H2O2 activates G protein, alpha 12 to disrupt the junctional complex and enhance ischemia reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U A. 2012 Apr 24;109(17):6680–5.
- Lima, W.R.; Parreira, K.S.; Devuyst, O.; Caplanusi, A.; N′Kuli, F.; Marien, B.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Alves, P.M.; Verroust, P.; Christensen, E.I.; et al. ZONAB Promotes Proliferation and Represses Differentiation of Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi C, Luciani A, Nevo N, Antignac C, Terryn S, Devuyst O. Dedifferentiation and aberrations of the endolysosomal compartment characterize the early stage of nephropathic cystinosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2014 May 1;23(9):2266–78.
- Wright, J.; Morales, M.M.; Sousa-Menzes, J.; Ornellas, D.; Sipes, J.; Cui, Y.; Cui, I.; Hulamm, P.; Cebotaru, V.; Cebotaru, L.; et al. Transcriptional adaptation to Clcn5 knockout in proximal tubules of mouse kidney. Physiol. Genom. 2008, 33, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallan, S.; Afkarian, M.; Zelnick, L.R.; Kestenbaum, B.; Sharma, S.; Saito, R.; Darshi, M.; Barding, G.; Raftery, D.; Ju, W.; et al. Metabolomics and Gene Expression Analysis Reveal Down-regulation of the Citric Acid (TCA) Cycle in Non-diabetic CKD Patients. EBioMedicine 2017, 26, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.-M.; Lee, C.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Sun, C.-Y. Clinical Value of NGAL, L-FABP and Albuminuria in Predicting GFR Decline in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e54863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




