Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
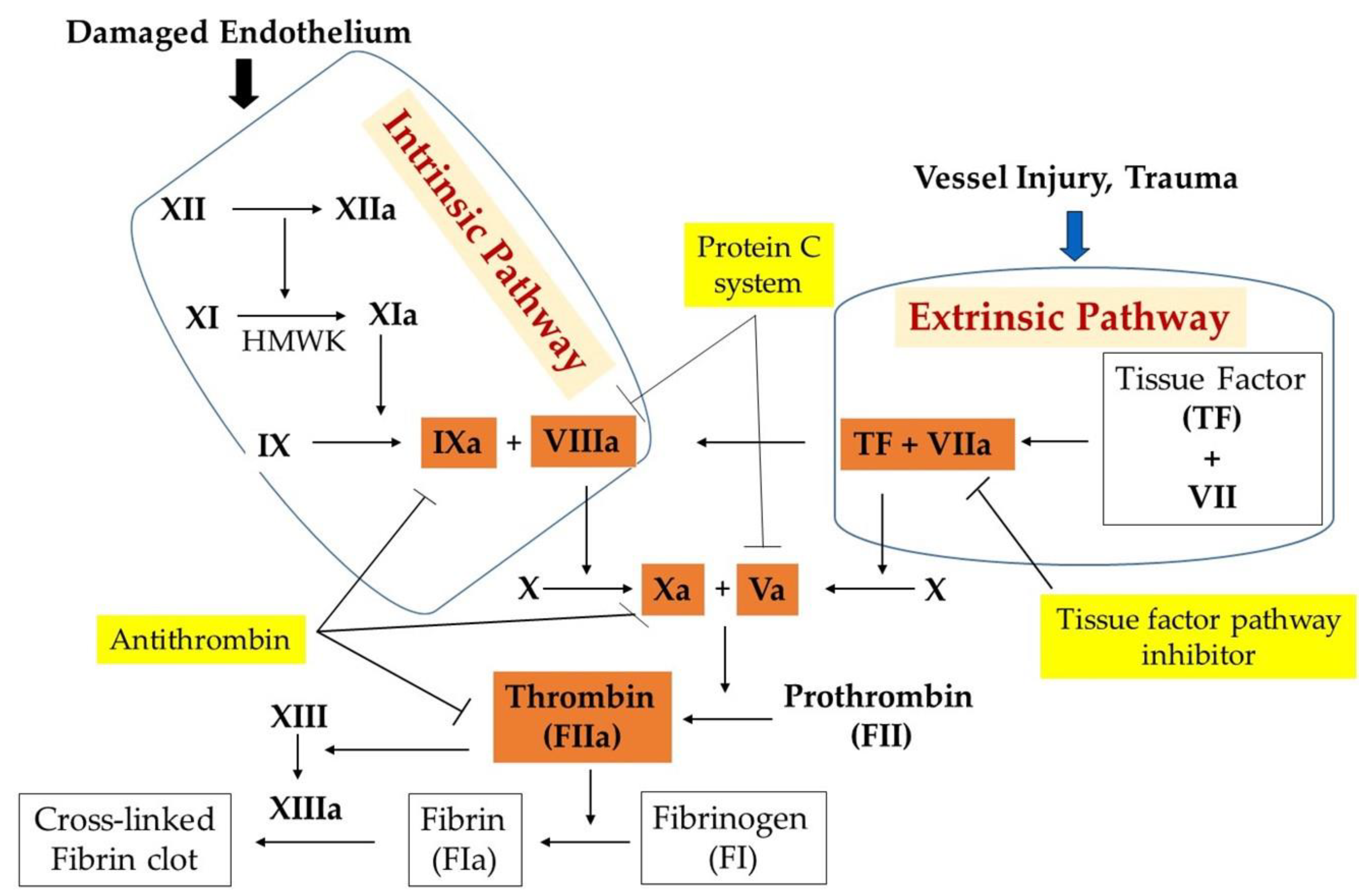
2. Blood Coagulation System
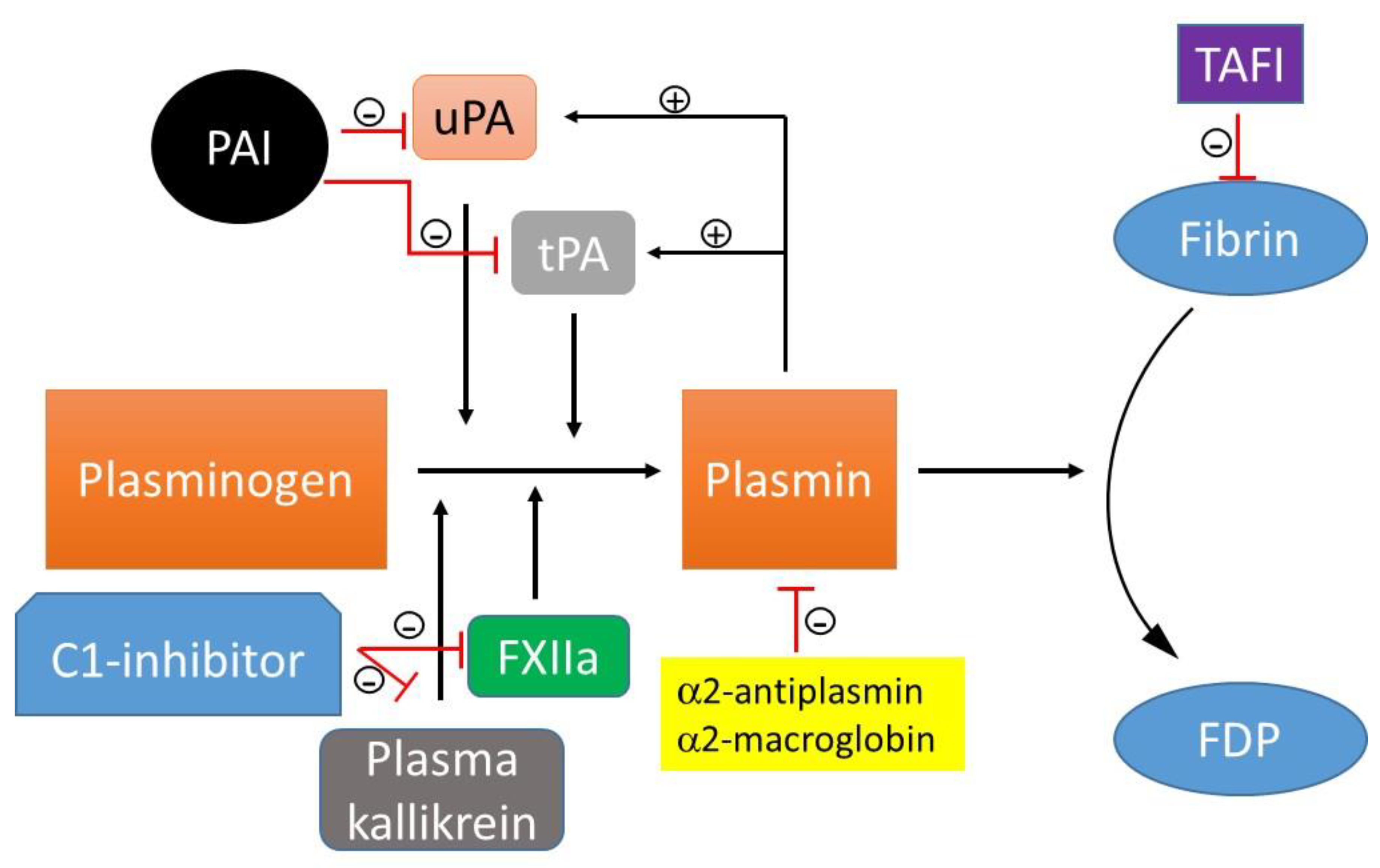
3. Fibrinolysis
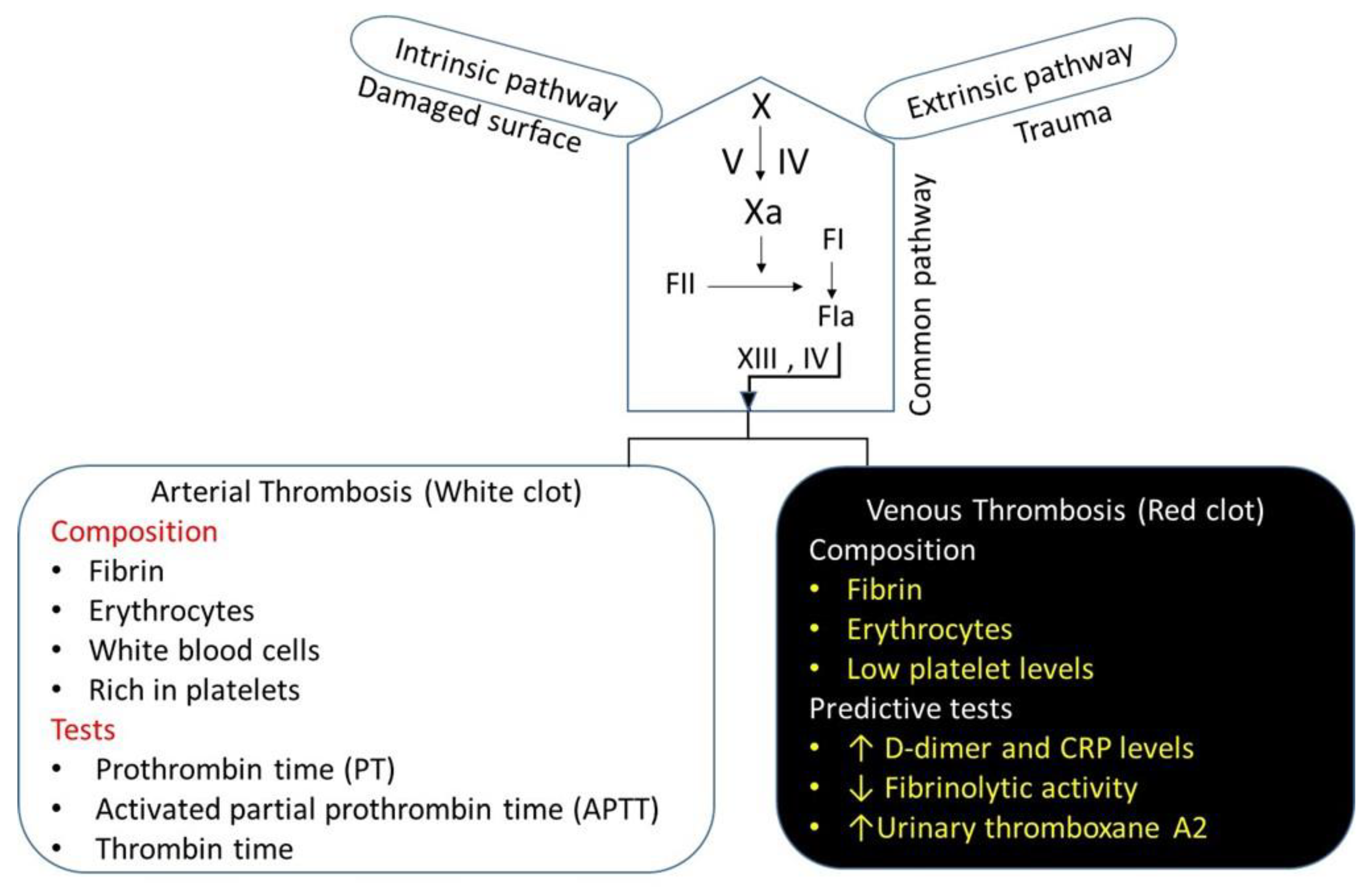
4. The Physiology of Thrombosis
5. Pharmacotherapy of VTE: An Update
6. Drugs in Development for VTE
6.1. FXI as a Novel Drug Target
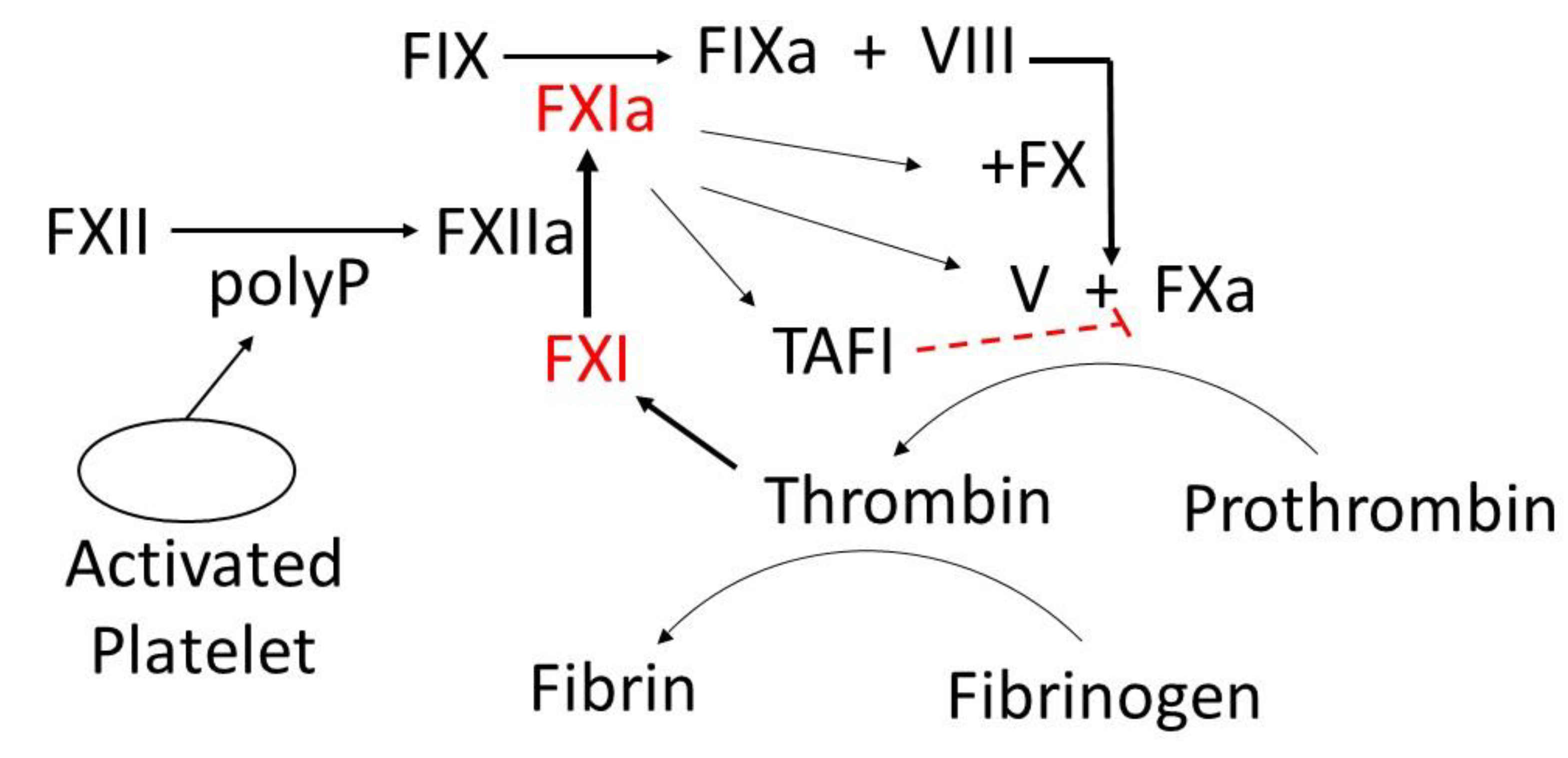
6.2. P-Selectin/PSGL-1 Pathway
|
Conditions |
Compounds |
Mechanism of Action |
Phase |
Sponsor |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary embolism; thrombotic disease VTE prophylaxis with anticoagulation after total knee replacement surgery VTE Thromboembolism of vein VTE in colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, non-small cell lung cancer |
DS-1040b JNJ-64179375 SelK2 Isoquercetin |
Inhibits the activated form of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFIa). Specific exosite 1 thrombin inhibitor Targets PSGL-1 and blocks its interactions Decreases D-dimer, P-selectin, and platelet-dependent fibrin generation |
Phase1|Phase2 Phase2 Phase2 Phase2|Phase3 |
Daiichi Sankyo Janssen Research & Development, LLC Tetherex Pharmaceuticals Corporation Quercegen Pharmaceutical; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) |
[118,119] [120,121] [122] [123] |
6.3. New Modes of Delivery for Anti-Thrombotic Drugs
6.3.1. Polymers
6.3.2. PEGylation
6.3.3. Liposomes
6.3.4. Echogenic Liposome
6.3.5. Polymeric Nanoparticles
6.3.6. Dendrimers
6.3.7. Mechanically Activated Nanotherapeutics
6.3.8. Platelet-Based Drug Delivery System
7. Future Implications and Research Opportunities
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACCP | American College of Chest Physicians |
| ADP | Adenosine Diphosphate |
| AIDS | Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome |
| APTT | Activated Partial Prothrombin Time |
| ASOIs | Antisense Oligonucleotide Inhibitors |
| AuIONP+ | Gold-Iron Oxide Nanoparticles |
| C1-Inhibitor | C1-Esterase Inhibitor |
| CAD | Chronic Artery Disease |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| COX | Cyclooxygenase |
| CREKA | Cys-Arg-Glu-Lys-Ala |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| DIC | Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation |
| DOACs | Direct Oral Anticoagulants |
| DSPE | 1,2-Distearoyl-Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphoethanolamine |
| DVT | Deep Vein Thrombosis |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| ELIP | Echogenic Liposomes |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| FDP | Fibrin Degradation Products |
| Fibrinogen | Factor I |
| FIX | Factor IX |
| FIXa | Activated Factor IX |
| Fuc | Fucoidan |
| FVII | Factor VII |
| FVIIa | Activated Factor VII |
| FVIII | Factor VIII |
| FVIIIa | Activated Factor VIII |
| FX | Factor X |
| FXa | Activated Factor X |
| FXI | Factor XI |
| FXIa | Activated Factor XI |
| FXII | Factor XII |
| FXII | Factor XIII |
| FXIIa Hageman Factor | Activated Factor XII |
| FXIIIa | Activated Factor XIII |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GP IIb/IIIa | Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa |
| HMWH | High-Molecular-Weight Heparin |
| INR | Target International Normalized Ratio |
| LBK | Lumbrokinase |
| LIFU | Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound |
| LMWH | Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin |
| MOF | Metal-Organic-Framework |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| NHLBI | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute |
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| P2Y12 | Purinergic Receptor Type Y, Subtype 12 |
| PA | Plasminogen Activator |
| PAI | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor |
| PE | Pulmonary Embolism |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| PFH | Perfluorohexane |
| PLGA | Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) |
| PNP | P-camouflaged Polymeric Nanoparticles |
| polyP | Platelet-Derived Polyphosphate |
| PPACK | D-phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-chloromethyl Ketone |
| PPCD | Doxorubicin-Polymer Conjugates |
| Prothrombin | Factor II |
| PSGL-1 | P-selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1 |
| PT | Prothrombin Time |
| RGD | (Arg-Gly-Asp) Peptide |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| rtPA | Recombinant tPA |
| SAK | Staphylokinase |
| SCAD | Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection |
| SK | Streptokinase |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| TAFI | Thrombin-Activated Fibrinolysis Inhibitor |
| TF | Tissue Factor |
| TFPI | Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitors |
| Thrombin | Activated Factor II |
| tPA | Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator |
| TT | Thrombin Time |
| U.S. | United States |
| UK | Urokinase |
| UK@Fuc-TI/PPCD | Urokinase (UK) in Fucoidan-Based Core-Shell Nanoparticles |
| uPA | Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator |
| uPA@CFs | Urokinase Plasminogen Activators (uPA)-Loaded Metal-Organic-Framework (MOF) Derived Carbon-Based Materials |
| VTE | Venous Thromboembolism |
| vWF | Von Willebrand factor |
References
- Beckman, M. G.; Hulihan, M. M.; Byams, V. R.; Oakley, M. A.; Reyes, N.; Trimble, S.; Grant, A. M. , Public health surveillance of nonmalignant blood disorders. Am J Prev Med 2014, 47, (5). 664–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendelboe, A. M.; Raskob, G. E. , Global Burden of Thrombosis: Epidemiologic Aspects. Circ Res 2016, 118, (9). 1340–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, M. G.; Hooper, W. C.; Critchley, S. E.; Ortel, T. L. , Venous thromboembolism: a public health concern. Am J Prev Med 2010, 38, (4 Suppl). S495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Goldberg, R. J.; Anderson, F. A.; Kiefe, C. I.; Spencer, F. A., Secular trends in occurrence of acute venous thromboembolism: the Worcester VTE study (1985-2009). Am J Med 2014, 127, (9), 829-39.e5.
- Naess, I. A.; Christiansen, S. C.; Romundstad, P.; Cannegieter, S. C.; Rosendaal, F. R.; Hammerstrøm, J. , Incidence and mortality of venous thrombosis: a population-based study. J Thromb Haemost 2007, 5, (4). 692–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutsey, P. L.; Zakai, N. A. , Epidemiology and prevention of venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Cardiol 2023, 20, (4). 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søgaard, K. K.; Schmidt, M.; Pedersen, L.; Horváth–Puhó, E.; Sørensen, H. T. , 30-Year Mortality After Venous Thromboembolism. Circulation 2014, 130, (10). 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagot, C. N.; Arya, R. , Virchow and his triad: a question of attribution. Br J Haematol 2008, 143, (2). 180–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H. K. , Pathophysiology of venous thromboembolism. Semin Thromb Hemost 1991, 17 Suppl 3, 250–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ortel, T. L.; Neumann, I.; Ageno, W.; Beyth, R.; Clark, N. P.; Cuker, A.; Hutten, B. A.; Jaff, M. R.; Manja, V.; Schulman, S.; Thurston, C.; Vedantham, S.; Verhamme, P.; Witt, D. M.; D. Florez, I.; Izcovich, A.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Ross, S.; J. Schünemann, H.; Wiercioch, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. American Society of Hematology 2020 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism: Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. Blood Advances 2020, 4, (19). 4693–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, L. K.; Kline, J. A. , Metabolic syndrome increases risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence after acute deep vein thrombosis. Blood advances 2020, 4, (1). 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ge, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. , Association Between Blood Lipid Levels and Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2022, 28, 10760296221121282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Feng, R.; Jiang, S.; Chang, G.; Hu, Z.; Yao, C.; Jia, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. , Stent patency rates and prognostic factors of endovascular intervention for iliofemoral vein occlusion in post-thrombotic syndrome. BMC Surg 2022, 22, (1). 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogo, A.; Bernardi, E.; Prandoni, P.; Girolami, B.; Noventa, F.; Simioni, P.; Girolami, A. , Acquired risk factors for deep-vein thrombosis in symptomatic outpatients. Arch Intern Med 1994, 154, (2). 164–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Kalantar, E.; Hosseini, M. S.; Tabibian, S.; Shamsizadeh, M.; Dorgalaleh, A. , Genetic risk factors in patients with deep venous thrombosis, a retrospective case control study on Iranian population. Thromb J 2015, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, K. , What Is Pulmonary Embolism? JAMA 2023, 329, (1). 104–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbicki, A.; Perrier, A.; Konstantinides, S.; Agnelli, G.; Galiè, N.; Pruszczyk, P.; Bengel, F.; Brady, A. J.; Ferreira, D.; Janssens, U.; Klepetko, W.; Mayer, E.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Bassand, J. P. , Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2008, 29, (18). 2276–315. [Google Scholar]
- Bĕlohlávek, J.; Dytrych, V.; Linhart, A. , Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism. Exp Clin Cardiol 2013, 18, (2). 129–38. [Google Scholar]
- Meignan, M.; Rosso, J.; Gauthier, H.; Brunengo, F.; Claudel, S.; Sagnard, L.; d'Azemar, P.; Simonneau, G.; Charbonnier, B. , Systematic lung scans reveal a high frequency of silent pulmonary embolism in patients with proximal deep venous thrombosis. Arch Intern Med 2000, 160, (2). 159–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heit, J. A.; Spencer, F. A.; White, R. H. , The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2016, 41, (1). 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, M. D.; Heit, J. A.; Mohr, D. N.; Petterson, T. M.; O'Fallon, W. M.; Melton, L. J. , 3rd, Trends in the incidence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a 25-year population-based study. Arch Intern Med 1998, 158, (6). 585–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapson, V. F. , Acute Pulmonary Embolism. New England Journal of Medicine 2008, 358, (10). 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S. Z.; Kroll, A.; Goldberg, R. J.; Emery, C.; Spencer, F. A. , Venous thromboembolism in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 2012, 125, (7). 709–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, R. E.; Ligon, B. L. , Thromboembolic complications associated with brain tumors. J Neurooncol 1994, 22, (2). 173–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedovati, M. C.; Giustozzi, M.; Becattini, C. , Venous thromboembolism and cancer: Current and future role of direct-acting oral anticoagulants. Thromb Res 2019, 177, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riess, H.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Pelzer, U.; Klamroth, R.; Linnemann, B. , Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Considerations: An Update Based on the Revised AWMF S2k Guideline. Hamostaseologie 2024, 44, (2). 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, K. L.; Badowski, M. E. , Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pharmacotherapy 2010, 30, (12). 1292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaff, M. R. , Medical aspects of pregnancy. Cleve Clin J Med 1994, 61, (4). 263–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raia-Barjat, T.; Edebiri, O.; Chauleur, C. , Venous Thromboembolism Risk Score and Pregnancy. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 863612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrauskiene, V.; Falk, M.; Waernbaum, I.; Norberg, M.; Eriksson, J. W. , The risk of venous thromboembolism is markedly elevated in patients with diabetes. Diabetologia 2005, 48, (5). 1017–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. , Global Prevalence of Diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, (5). 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y. H.; Lin, Y. S.; Chen, C. H.; Tsai, K. Y.; Hung, Y. C.; Chen, H. J.; Liao, W. C.; Ho, W. C. , Type 1 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism: A retrospective population-based cohort study. PLoS One 2020, 15, (1). e0226997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, W.; Nemeth, B.; de Lusignan, S.; Field, B.; Feher, M. D.; Munro, N.; Roberts, L. N.; Arya, R.; Whyte, M. B. , Effect of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes on the risk of venous thromboembolism. Diabetic Medicine 2021, 38, (5). e14452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariani, K.; Mavrakanas, T.; Combescure, C.; Perrier, A.; Marti, C. , Is diabetes mellitus a risk factor for venous thromboembolism? A systematic review and meta-analysis of case–control and cohort studies. European Journal of Internal Medicine 2016, 28, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczynska, M.; Fil, K.; Bazanek, M.; Undas, A. , Prolonged duration of type 2 diabetes is associated with increased thrombin generation, prothrombotic fibrin clot phenotype and impaired fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 2014, 111, (04). 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatier, F.; Darmon, P.; Hugel, B.; Combes, V.; Sanmarco, M.; Velut, J.-G.; Arnoux, D.; Charpiot, P.; Freyssinet, J.-M.; Oliver, C.; Sampol, J.; Dignat-George, F. , Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetic Patients Display Different Patterns of Cellular Microparticles. Diabetes 2002, 51, (9). 2840–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C. P. , Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int Suppl (2011) 2022, 12, (1). 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffmann, R. H.; Veltkamp, J. J.; Van Tilburg, N. H.; Van Es, L. A. , Acquired antithrombin III deficiency and thrombosis in the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Med 1978, 65, (4). 607–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J. A.; Leibson, C. L.; Ashrani, A. A.; Petterson, T. M.; Bailey, K. R.; Melton, L. J., Is Diabetes Mellitus an Independent Risk Factor for Venous Thromboembolism? Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2009, 29, (9), 1399-1405.
- Deischinger, C.; Dervic, E.; Nopp, S.; Kaleta, M.; Klimek, P.; Kautzky-Willer, A. , Diabetes mellitus is associated with a higher relative risk for venous thromboembolism in females than in males. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 194, 110190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallon, E. M.; Ebekozien, O.; Sanchez, J.; Staggs, V. S.; Ferro, D.; McDonough, R.; Demeterco-Berggren, C.; Polsky, S.; Gomez, P.; Patel, N.; Prahalad, P.; Odugbesan, O.; Mathias, P.; Lee, J. M.; Smith, C.; Shyu, C. R.; Clements, M. A. , Impact of diabetes status and related factors on COVID-19-associated hospitalization: A nationwide retrospective cohort study of 116,370 adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 194, 110156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roopkumar, J.; Swaidani, S.; Kim, A. S.; Thapa, B.; Gervaso, L.; Hobbs, B. P.; Wei, W.; Alban, T. J.; Funchain, P.; Kundu, S.; Sangwan, N.; Rayman, P.; Pavicic, P. G., Jr.; Diaz-Montero, C. M.; Barnard, J.; McCrae, K. R.; Khorana, A. A. , Increased Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism with Cancer Immunotherapy. Med 2021, 2, (4). 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elice, F.; Rodeghiero, F.; Falanga, A.; Rickles, F. R. , Thrombosis associated with angiogenesis inhibitors. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2009, 22, (1). 115–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C. E.; Grover, S. P.; Humphries, J.; Saha, P.; Patel, A. P.; Patel, A. S.; Lyons, O. T.; Waltham, M.; Modarai, B.; Smith, A., Antiangiogenic Therapy Inhibits Venous Thrombus Resolution. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2014, 34, (3), 565-570.
- Zangari, M.; Fink, L. M.; Elice, F.; Zhan, F.; Adcock, D. M.; Tricot, G. J. , Thrombotic events in patients with cancer receiving antiangiogenesis agents. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27, (29). 4865–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackman, N.; Tilley, R. E.; Key, N. S., Role of the Extrinsic Pathway of Blood Coagulation in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2007, 27, (8), 1687-1693.
- Sorensen, A. B.; Madsen, J. J.; Svensson, L. A.; Pedersen, A. A.; Østergaard, H.; Overgaard, M. T.; Olsen, O. H.; Gandhi, P. S. , Molecular Basis of Enhanced Activity in Factor VIIa-Trypsin Variants Conveys Insights into Tissue Factor-mediated Allosteric Regulation of Factor VIIa Activity. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, (9). 4671–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvas, C. L.; Larsen, J. B., The Fibrinolytic System and Its Measurement: History, Current Uses and Future Directions for Diagnosis and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, (18).
- Lin, H.; Xu, L.; Yu, S.; Hong, W.; Huang, M.; Xu, P., Therapeutics targeting the fibrinolytic system. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 2020, 52, (3), 367-379.
- Sillen, M.; Declerck, P. J., A Narrative Review on Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Its (Patho)Physiological Role: To Target or Not to Target? Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, (5).
- PANNELL, R.; KUNG, W.; GUREWICH, V. , C1-inhibitor prevents non-specific plasminogen activation by a prourokinase mutant without impeding fibrin-specific fibrinolysis. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2007, 5, (5). 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnoff, O. D.; Pensky, J.; Ogston, D.; Naff, G. B. , The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med 1969, 129, (2). 315–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosnier, L. O.; Bouma, B. N., Regulation of Fibrinolysis by Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor, an Unstable Carboxypeptidase B That Unites the Pathways of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2006, 26, (11), 2445-2453.
- Sillen, M.; Declerck, P. J., Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFI): An Updated Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, (7).
- Mast, A. E., Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2016, 36, (1), 9-14.
- Dahlbäck, B.; Villoutreix, B. O., Regulation of Blood Coagulation by the Protein C Anticoagulant Pathway. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2005, 25, (7), 1311-1320.
- Ji, Y.; Temprano-Sagrera, G.; Holle, L. A.; Bebo, A.; Brody, J. A.; Le, N.-Q.; Kangro, K.; Brown, M. R.; Martinez-Perez, A.; Sitlani, C. M.; Suchon, P.; Kleber, M. E.; Emmert, D. B.; Bilge Ozel, A.; Dobson, D. V. A.; Tang, W.; Llobet, D.; Tracy, R. P.; Deleuze, J.-F.; Delgado, G. E.; Gögele, M.; Wiggins, K. L.; Souto, J. C.; Pankow, J. S.; Taylor, K. D.; Trégouët, D.-A.; Moissl, A. P.; Fuchsberger, C.; Rosendaal, F. R.; Morrison, A. C.; Soria, J. M.; Cushman, M.; Morange, P.-E.; März, W.; Hicks, A. A.; Desch, K. C.; Johnson, A. D.; de Vries, P. S.; CHARGE Consortium Hemostasis Working Group, I. C.; Wolberg, A. S.; Smith, N. L.; Sabater-Lleal, M., Antithrombin, Protein C, and Protein S: Genome and Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies Identify 7 Novel Loci Regulating Plasma Levels. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2023, 43, (7), e254-e269.
- Kubier, A.; O'Brien, M. , Endogenous anticoagulants. Top Companion Anim Med 2012, 27, (2). 81–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S. P.; Mackman, N. , Anticoagulant SERPINs: Endogenous Regulators of Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 878199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arble, E.; Arnetz, B. B. , Anticoagulants and the Hemostatic System: A Primer for Occupational Stress Researchers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, (20). 10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahnström, J. , The potential of serpins for future treatment for haemophilia. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2019, 17, (10). 1629–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Bresette, C.; Liu, Z.; Ku, D. N. , Occlusive thrombosis in arteries. APL Bioeng 2019, 3, (4). 041502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkarithi, G.; Duval, C.; Shi, Y.; Macrae, F. L.; Ariëns, R. A. S. , Thrombus Structural Composition in Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2021, 41, (9). 2370–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackman, N. , New insights into the mechanisms of venous thrombosis. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, (7). 2331–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockett, F. B.; Thomas, M. L. , The iliac compression syndrome. Br J Surg 1965, 52, (10). 816–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moudgill, N.; Hager, E.; Gonsalves, C.; Larson, R.; Lombardi, J.; DiMuzio, P. , May-Thurner syndrome: case report and review of the literature involving modern endovascular therapy. Vascular 2009, 17, (6). 330–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heestermans, M.; Poenou, G.; Duchez, A. C.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Bertoletti, L.; Cognasse, F., Immunothrombosis and the Role of Platelets in Venous Thromboembolic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, (21).
- Mereweather, L. J.; Constantinescu-Bercu, A.; Crawley, J. T. B.; Salles-Crawley, I. I. , Platelet–Neutrophil Crosstalk in Thrombosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, (2). 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigle, P. Anticoagulation: Updated Guidelines for Outpatient Management; 2019; pp 426-434.
- Marcucci, M.; Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta, I.; Yang, S.; Germini, F.; Gupta, S.; Agarwal, A.; Ventresca, M.; Tang, S.; Morgano, G. P.; Wang, M.; Ahmed, M. M.; Neumann, I.; Izcovich, A.; Criniti, J.; Popoff, F.; Devereaux, P. J.; Dahm, P.; Anderson, D.; Lavikainen, L. I.; Tikkinen, K. A. O.; Guyatt, G. H.; Schünemann, H. J.; Violette, P. D. , Benefits and harms of direct oral anticoagulation and low molecular weight heparin for thromboprophylaxis in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised trials. Bmj 2022, 376, e066785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczynska, M.; Kupis, R. W.; Bijak, P.; Malinowski, K. P.; Undas, A. , Acceptance of a potential major bleeding among patients with venous thromboembolism on long-term oral anticoagulation: the knowledge of the disease and therapy matters. Thrombosis research 2020, 193, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achebe, I.; Mbachi, C.; Palacios, P.; Wang, Y.; Asotibe, J.; Ofori-Kuragu, A.; Gandhi, S. , Predictors of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Thrombosis research 2020, 199, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S. Z. , Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Circulation 2006, 114, (3). e42–e47. [Google Scholar]
- Flumignan, C. D.; Nakano, L. C.; Baptista-Silva, J. C.; Flumignan, R. L. , Antiplatelet agents for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2022, 7, (7). CD012369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, R.; Garcia, D. , Does aspirin prevent venous thromboembolism? Hematology 2020, 2020, (1). 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborative overview of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy--III: Reduction in venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism by antiplatelet prophylaxis among surgical and medical patients. Antiplatelet Trialists' Collaboration. BMJ 1994, 308, (6923), 235-46.
- Landel, J. B.; Bauters, A.; Delhaye, C.; Bonello, L.; Sudre, A.; Susen, S.; Bauters, C.; Lablanche, J. M.; Lemesle, G. , Impact of initial clinical presentation on clopidogrel low response. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 2013, 106, (11). 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, R. D. , Ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis in arterial and venous peripheral occlusions: fibrinogen level effects. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2010, 21, (8). 1165–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y. H.; Zhu, X. Y.; Fan, L. H.; Xu, H. F. , Pulmonary embolism in patients with chronic coronary syndrome masquerading as acute coronary syndrome: a case report and literature review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2024, 24, (1). 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casula, M.; Casu, G.; Talanas, G.; Spano, A.; Tantry, U.; Bilotta, F.; Micheluzzi, V.; Merella, P.; Porcheddu, T.; Gorog, D. A.; Bonaca, M.; Jeong, Y. H.; Farkouh, M. E.; Kubica, J.; Isgender, M.; Gurbel, P. A.; Navarese, E. P. , Efficacy and Safety of P2Y(12) monotherapy vs standard DAPT in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: meta-analysis of randomized trials. Curr Probl Cardiol 2024, 49. (8), 102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetes-Related Complications and Mortality in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Different Oral Anticoagulants. Annals of Internal Medicine 2022, 175, (4). 490–498.
- Lip, G. Y. H.; Keshishian, A. V.; Kang, A. L.; Li, X.; Dhamane, A. D.; Luo, X.; Balachander, N.; Rosenblatt, L.; Mardekian, J.; Nadkarni, A.; Pan, X.; Di Fusco, M.; Garcia Reeves, A. B.; Yuce, H.; Deitelzweig, S. B. , Effectiveness and Safety of Oral Anticoagulants in Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2020, 95, (5). 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aursulesei, V. ; Costache, II, Anticoagulation in chronic kidney disease: from guidelines to clinical practice. Clin Cardiol 2019, 42, (8). 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenjickal, E. J.; Travlos, C. K.; Marques, P.; Mavrakanas, T. A. , Anticoagulation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. American Journal of Nephrology 2023, 55, (2). 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Lim, E.; Covic, A.; Verhamme, P.; Gale, C. P.; Camm, A. J.; Goldsmith, D. , Anticoagulation in Concomitant Chronic Kidney Disease and Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2019, 74, (17). 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camm, A. J.; Sabbour, H.; Schnell, O.; Summaria, F.; Verma, A. , Managing thrombotic risk in patients with diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022, 21, (1). 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corken, A. L.; Ong, V.; Kore, R.; Ghanta, S. N.; Karaduta, O.; Pathak, R.; Rose, S.; Porter, C.; Jain, N. , Platelets, inflammation, and purinergic receptors in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delluc, A.; Lacut, K.; Rodger, M. A. , Arterial and venous thrombosis: What's the link? A narrative review. Thromb Res 2020, 191, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogeng'o, J. A.; Obimbo, M. M.; Olabu, B. O.; Gatonga, P. M.; Ong'era, D. , Pulmonary thromboembolism in an East African tertiary referral hospital. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2011, 32, (3). 386–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S. J.; Patell, R.; Zwicker, J. I.; Kazi, D. S.; Hollenbeck, B. L. , Venous Thromboembolism in Total Hip and Total Knee Arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, (12). e2345883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.; Al-Horani, R. A., Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Major Orthopedic Surgeries and Factor XIa Inhibitors. Med Sci (Basel) 2023, 11, (3).
- Guan, Y.; Zeng, Z. , Delayed pulmonary embolism after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, (1). e24230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, N.; Sun, G. , Fondaparinux sodium and low molecular weight heparin for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in Chinese patients with major orthopedic surgery or trauma: a real-world study. BMC Surg 2022, 22. (1), 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Subedi, A. , Antithrombotic Therapy for Heart Failure in Sinus Rhythm - A Concise Review. S D Med 2024, 77, (5). 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Lip, G. Y. H.; Banerjee, A.; Boriani, G.; Chiang, C. E.; Fargo, R.; Freedman, B.; Lane, D. A.; Ruff, C. T.; Turakhia, M.; Werring, D.; Patel, S.; Moores, L. , Antithrombotic Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2018, 154, (5). 1121–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, I.; Radunovic, A.; Timcic, S.; Odanovic, N.; Radoicic, D.; Dukuljev, N.; Krljanac, G.; Otasevic, P.; Apostolovic, S. , Drugs for spontaneous coronary dissection: a few untrusted options. Front Cardiovasc Med 2023, 10, 1275725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafi, A.; Friedman, O.; Kim, I. , Use of low-dose thrombolytics for treatment of intracardiac thrombus and massive pulmonary embolus after aborted liver transplant leads to recovery of right ventricular function and redo liver transplantation. BMJ Case Rep 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, L.; Girard, P.; Elias, A.; Espitia, O.; Schmidt, J.; Couturaud, F.; Mahe, I.; Sanchez, O.; Group, I. C. W. , Recurrent venous thromboembolism in anticoagulated cancer patients: Diagnosis and treatment. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 2024, 117, (1). 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M. L.; Nachman, P. H.; Mooberry, M. J.; Crona, D. J.; Derebail, V. K. , Recurrent venous thromboembolism in primary membranous nephropathy despite direct Xa inhibitor therapy. J Nephrol 2019, 32, (4). 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, L., Factor XIa Inhibitors as a Novel Anticoagulation Target: Recent Clinical Research Advances. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16, (6).
- Plautz, W. E.; Sekhar Pilli, V. S.; Cooley, B. C.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Westmark, P. R.; Getz, T.; Paul, D.; Bergmeier, W.; Sheehan, J. P.; Majumder, R., Anticoagulant Protein S Targets the Factor IXa Heparin-Binding Exosite to Prevent Thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2018, 38, (4), 816-828.
- Srivastava, P.; Gailani, D. , The rebirth of the contact pathway: a new therapeutic target. Curr Opin Hematol 2020, 27, (5). 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puy, C.; Rigg, R. A.; McCarty, O. J. , The hemostatic role of factor XI. Thromb Res 2016, 141, (Suppl 2). (Suppl 2), S8–s11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühl, H.; Friemann, A. M.; Reda, S.; Schwarz, N.; Winterhagen, F. I.; Berens, C.; Müller, J.; Oldenburg, J.; Pötzsch, B. , Activated Factor XI is Increased in Plasma in Response to Surgical Trauma but not to Recombinant Activated FVII-Induced Thrombin Formation. J Atheroscler Thromb 2022, 29, (1). 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puy, C.; Tucker, E. I.; Matafonov, A.; Cheng, Q.; Zientek, K. D.; Gailani, D.; Gruber, A.; McCarty, O. J. , Activated factor XI increases the procoagulant activity of the extrinsic pathway by inactivating tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood 2015, 125, (9). 1488–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S. J.; Herzog, R. W.; Margaritis, P.; Arruda, V. R.; Chu, K.; Golden, J. A.; Labosky, P. A.; High, K. A. , A viable mouse model of factor X deficiency provides evidence for maternal transfer of factor X. J Thromb Haemost 2008, 6, (2). 339–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskob, G. E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A. N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B. J.; Hylek, E. M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S. V.; McCumber, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Wendelboe, A.; Weitz, J. I.; Day, I. S. C. f. W. T. , Thrombosis: a major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2014, 34, (11). 2363–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, A.; Laudani, C.; Spagnolo, M.; Agnello, F.; Faro, D. C.; Finocchiaro, S.; Legnazzi, M.; Mauro, M. S.; Mazzone, P. M.; Occhipinti, G.; Rochira, C.; Scalia, L.; Capodanno, D. , Pharmacology and Clinical Development of Factor XI Inhibitors. Circulation 2023, 147, (11). 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut, M. A. E. , Nadir; Storey, Robert F, Factor XI and XIa inhibition: a new approach to anticoagulant therapy. The British Journal of Cardiology 2024, 31, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, N. C.; Weitz, J. I. , New Therapeutic Targets for the Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism With a Focus on Factor XI Inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2023, 43, (10). 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, J. I.; Eikelboom, J. W. , What Is the Future of Factor XI Inhibitors? Circulation 2022, 146, (25). 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occhipinti, G.; Laudani, C.; Spagnolo, M.; Finocchiaro, S.; Mazzone, P. M.; Faro, D. C.; Mauro, M. S.; Rochira, C.; Agnello, F.; Giacoppo, D.; Ammirabile, N.; Landolina, D.; Imbesi, A.; Sangiorgio, G.; Greco, A.; Capodanno, D. , Pharmacological and clinical appraisal of factor XI inhibitor drugs. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2024, 10, (3). 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presume, J.; Ferreira, J.; Ribeiras, R. , Factor XI Inhibitors: A New Horizon in Anticoagulation Therapy. Cardiol Ther 2024, 13, (1). 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campello, E.; Simioni, P.; Prandoni, P.; Ferri, N., Clinical Pharmacology of Factor XI Inhibitors: New Therapeutic Approaches for Prevention of Venous and Arterial Thrombotic Disorders. J Clin Med 2022, 11, (21).
- Ludwig, R. J.; Schön, M. P.; Boehncke, W. H. , P-selectin: a common therapeutic target for cardiovascular disorders, inflammation and tumour metastasis. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2007, 11, (8). 1103–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ed Rainger, G.; Chimen, M.; Harrison, M. J.; Yates, C. M.; Harrison, P.; Watson, S. P.; Lordkipanidzé, M.; Nash, G. B. , The role of platelets in the recruitment of leukocytes during vascular disease. Platelets 2015, 26, (6). 507–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I. I.; Apta, B. H. R.; Bonna, A. M.; Harper, M. T. , Platelet P-selectin triggers rapid surface exposure of tissue factor in monocytes. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, (1). 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankyo, D., Study to Assess the Safety, Pharmacokinetics/Dynamics of DS-1040b in Subjects With Acute Submassive Pulmonary Embolism. ClinicalTrials.Gov, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02923115: 2024.
- Zhou, J.; Kochan, J.; Yin, O.; Warren, V.; Zamora, C.; Atiee, G.; Pav, J.; Orihashi, Y.; Vashi, V.; Dishy, V. , A first-in-human study of DS-1040, an inhibitor of the activated form of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor, in healthy subjects. J Thromb Haemost 2017, 15, (5). 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen Research & Development, L., A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous JNJ-64179375 Versus Oral Apixaban in Participants Undergoing Elective Total Knee Replacement Surgery (TEXT-TKR). Janssen Research & Development, LLC, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03251482, 2019.
- Wilson, S. J.; Connolly, T. M.; Peters, G.; Ghosh, A.; Johnson, M.; Newby, D. E. , Exosite 1 thrombin inhibition with JNJ-64179375 inhibits thrombus formation in a human translational model of thrombosis. Cardiovasc Res 2019, 115, (3). 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporation, T. P., Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of SelK2 to Prevent Blood Clots in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Replacement. ClinicalTrials.Gov, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03812328: 2024.
- Zwicker, J., Cancer Associated Thrombosis and Isoquercetin (CATIQ). ClinicalTrials.Gov, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02195232: 2021.
- FDA, Considering whether an FDA-regulated product involves the application of nanotechnology. 2014, https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/considering-whether-fda-regulated-product-involves-application-nanotechnology.
- De Jong, W. H.; Hagens, W. I.; Krystek, P.; Burger, M. C.; Sips, A. J. A. M.; Geertsma, R. E. , Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 2008, 29, (12). 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. , Nanomedicine: Principles, Properties, and Regulatory Issues. Front Chem 2018, 6, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Sun, K.; Baker Jr, J. R. , Spontaneous formation of functionalized dendrimer-stabilized gold nanoparticles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2008, 112, (22). 8251–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J. K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L. F.; Campos, E. V. R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M. d. P.; Acosta-Torres, L. S.; Diaz-Torres, L. A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M. K.; Sharma, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Shin, H.-S. , Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, (1). 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiners, K.; Hamm, P.; Gutmann, M.; Niedens, J.; Nowak-Król, A.; Pané, S.; Lühmann, T. , Site-specific PEGylation of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2023, 192, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuragawa, N.; Shimizu, K.; Kondo, K.; Kondo, S.; Niwa, M. , Studies on the effect of PEG-modified urokinase on coagulation-fibrinolysis using beagles. Thromb Res 1986, 41, (5). 627–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Gonias, S. L.; Pizzo, S. V. , A nonantigenic covalent streptokinase-polyethylene glycol complex with plasminogen activator function. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 1985, 75, (2). 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmawati, H.; Damanhuri, F.; Agustian Darfiansyah, I.; Retnoningrum, D. , Pegylation of recombinant mutein streptokinase from overproduction in escherchia coli BL21 and study on the fibrinolityc activity in vitro. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014, 6, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, B. , Effect of site-specific PEGylation on the fibrinolytic activity, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetics of staphylokinase. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica 2014, 46, (9). 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Hu, C.; Yu, W.; Hu, T. , Conjugation with Eight-Arm PEG Markedly Improves the In Vitro Activity and Prolongs the Blood Circulation of Staphylokinase. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2018, 29, (2). 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Ahsan, F. , Inhalable liposomes of low molecular weight heparin for the treatment of venous thromboembolism. J Pharm Sci 2010, 99, (11). 4554–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeremans, J. L. M.; Prevost, R.; Bekkers, M. E. A.; Los, P.; Emeis, J. J.; Kluft, C.; Crommelin, D. J. A. , Thrombolytic Treatment with Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator (t-PA) Containing Liposomes in Rabbits: a Comparison with Free t-PA. Thromb Haemost 1995, 73, (03). 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palekar, R. U.; Myerson, J. W.; Schlesinger, P. H.; Wickline, S. A.; Pan, H., Abstract 12047: Thrombin-inhibiting Liposomes for Safe, Site-specific Inhibition of Acute Thrombosis. Circulation 2012, 126, (suppl_21), A12047-A12047.
- Palekar, R. U.; Myerson, J. W.; Schlesinger, P. H.; Sadler, J. E.; Pan, H.; Wickline, S. A. , Thrombin-Targeted Liposomes Establish a Sustained Localized Anticlotting Barrier against Acute Thrombosis. Molecular Pharmaceutics 2013, 10, (11). 4168–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z. N. , Targeted nano-delivery strategies for facilitating thrombolysis treatment in ischemic stroke. Drug Deliv 2021, 28, (1). 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Feng, X.; Jin, R.; Li, G. , Tissue plasminogen activator-based nanothrombolysis for ischemic stroke. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2018, 15, (2). 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, P.; Hagemeyer, C. E.; Esser, L.; Voelcker, N. H. , Theranostic nanoparticles for the management of thrombosis. Theranostics 2022, 12, (6). 2773–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Jin, H.; Nan, D.; Li, M.; Fan, C.; Liu, Y.; Lv, P.; Cui, W.; Sun, Y.; Hao, H.; Qu, X.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y. , In vivo evaluation of urokinase-loaded hollow nanogels for sonothrombolysis on suture embolization-induced acute ischemic stroke rat model. Bioact Mater 2018, 3, (1). 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, M.; Yang, T.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Hong, K.; Wang, S.; Xin, H.; Ding, X. , Near-Infrared Triggered Release of uPA from Nanospheres for Localized Hyperthermia-Enhanced Thrombolysis. Advanced Functional Materials 2017, 27, (40). 1701824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, S. T.; Moody, M. R.; Kim, H.; Smulevitz, B.; Huang, S. L.; Holland, C. K.; McPherson, D. D.; Klegerman, M. E. , Thrombolytic efficacy of tissue plasminogen activator-loaded echogenic liposomes in a rabbit thrombus model. Thromb Res 2012, 130, (4). 629–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandadai, M. A.; Mukherjee, P.; Shekhar, H.; Shaw, G. J.; Papautsky, I.; Holland, C. K. , Microfluidic manufacture of rt-PA -loaded echogenic liposomes. Biomed Microdevices 2016, 18, (3). 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. P.; Liu, C. H.; Hsu, H. L.; Wu, T.; Lu, Y. J.; Ma, Y. H. , Magnetically controlled release of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator from chitosan nanocomposites for targeted thrombolysis. J Mater Chem B 2016, 4, (15). 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fithri, N. A.; Wu, Y.; Cowin, G.; Akther, F.; Tran, H. D. N.; Tse, B.; van Holthe, N. W.; Moonshi, S. S.; Peter, K.; Wang, X.; Truong, N. P.; Ta, H. T. , Gold-iron oxide nanoparticle: A unique multimodal theranostic approach for thrombosis. Applied Materials Today 2023, 31, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayon, A.; Jamshidi, R.; Esmaeili, A., Targeted thrombolysis of tissue plasminogen activator and streptokinase with extracellular biosynthesis nanoparticles using optimized Streptococcus equi supernatant. Int J Pharm 2016, 501, (1-2), 300-10.
- Shaw, G. J.; Meunier, J. M.; Huang, S. L.; Lindsell, C. J.; McPherson, D. D.; Holland, C. K. , Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis with tPA-loaded echogenic liposomes. Thromb Res 2009, 124, (3). 306–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagisawa, K.; Nishioka, T.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Takase, B.; Ishihara, M.; Kurita, A.; Yoshimoto, N.; Nishida, Y.; Iida, K.; Luo, H.; Siegel, R. J. , Thrombus-targeted perfluorocarbon-containing liposomal bubbles for enhancement of ultrasonic thrombolysis: in vitro and in vivo study. J Thromb Haemost 2013, 11, (8). 1565–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanpour, S.; Kim, H. J.; Saadati, A.; Tebon, P.; Xue, C.; van den Dolder, F. W.; Thakor, J.; Baradaran, B.; Mosafer, J.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; de Barros, N. R.; Hashemzaei, M.; Lee, K. J.; Lee, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Cho, H. J.; Ahadian, S.; Ashammakhi, N.; Dokmeci, M. R.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Khademhosseini, A. , Thrombolytic Agents: Nanocarriers in Controlled Release. Small 2020, 16, (40). e2001647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, V., Creation of tPA conjugated dendrimer nanoparticles (780.4). The FASEB Journal 2014, 28, (S1), 780.4.
- Huang, M.; Lü, S.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.-F.; Qi, T.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M. , A nattokinase carrier bonding with polyglutamic acid peptide dendrimer for improved thrombolysis. Polymers for Advanced Technologies 2019, 30, (9). 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gao, C.; Lü, S.; Xu, X.; Wen, N.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M. , Construction of polylysine dendrimer nanocomposites carrying nattokinase and their application in thrombolysis. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2018, 106, (2). 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Thomas, C.; Ahsan, F. , Dendrimers as a carrier for pulmonary delivery of enoxaparin, a low-molecular weight heparin. J Pharm Sci 2007, 96, (8). 2090–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C. F.; Campbell, R. A.; Brooks, A. E.; Assemi, S.; Tadjiki, S.; Thiagarajan, G.; Mulcock, C.; Weyrich, A. S.; Brooks, B. D.; Ghandehari, H.; Grainger, D. W. , Cationic PAMAM dendrimers aggressively initiate blood clot formation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, (11). 9900–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeibi Shirejini, S.; Carberry, J.; Alt, K.; Gregory, S. D.; Hagemeyer, C. E. , Shear-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems in Medical Devices: Focus on Thrombosis and Bleeding. Advanced Functional Materials 2023, 33, (37). 2303717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greineder, C. F.; Howard, M. D.; Carnemolla, R.; Cines, D. B.; Muzykantov, V. R. , Advanced drug delivery systems for antithrombotic agents. Blood 2013, 122, (9). 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korin, N.; Kanapathipillai, M.; Matthews, B. D.; Crescente, M.; Brill, A.; Mammoto, T.; Ghosh, K.; Jurek, S.; Bencherif, S. A.; Bhatta, D.; Coskun, A. U.; Feldman, C. L.; Wagner, D. D.; Ingber, D. E. , Shear-activated nanotherapeutics for drug targeting to obstructed blood vessels. Science 2012, 337, (6095). 738–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korin, N.; Gounis, M. J.; Wakhloo, A. K.; Ingber, D. E. , Targeted Drug Delivery to Flow-Obstructed Blood Vessels Using Mechanically Activated Nanotherapeutics. JAMA Neurology 2015, 72, (1). 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marosfoi, M. G.; Korin, N.; Gounis, M. J.; Uzun, O.; Vedantham, S.; Langan, E. T.; Papa, A.-L.; Brooks, O. W.; Johnson, C.; Puri, A. S.; Bhatta, D.; Kanapathipillai, M.; Bronstein, B. R.; Chueh, J.-Y.; Ingber, D. E.; Wakhloo, A. K. , Shear-Activated Nanoparticle Aggregates Combined With Temporary Endovascular Bypass to Treat Large Vessel Occlusion. Stroke 2015, 46, (12). 3507–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Di, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Pang, N.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, Z.; Wang, M.; Dai, K.; Yan, R.; Li, S.; Nie, G. , Engineered Nanoplatelets for Targeted Delivery of Plasminogen Activators to Reverse Thrombus in Multiple Mouse Thrombosis Models. Adv Mater 2020, 32, (4). e1905145. [Google Scholar]
- Veronese, F. M.; Pasut, G. , PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov Today 2005, 10, (21). 1451–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Beasock, D.; Fessler, A.; Szebeni, J.; Ljubimova, J. Y.; Afonin, K. A.; Dobrovolskaia, M. A. , To PEGylate or not to PEGylate: Immunological properties of nanomedicine's most popular component, polyethylene glycol and its alternatives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2022, 180, 114079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M. L. A.; Bindini, E.; Moretti, P.; Soler Illia, G.; Amenitsch, H.; Andreozzi, P.; Ortore, M. G.; Moya, S. E. , Impact of PEGylation on the degradation and pore organization in mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A study of the inner mesoporous structure in physiologically relevant ionic conditions. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2022, 219, 112797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Devedec, F.; Strandman, S.; Hildgen, P.; Leclair, G.; Zhu, X. X. , PEGylated bile acids for use in drug delivery systems: enhanced solubility and bioavailability of itraconazole. Mol Pharm 2013, 10, (8). 3057–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gajbhiye, K. R.; Pawar, A.; Mahadik, K. R.; Gajbhiye, V. , PEGylated nanocarriers: A promising tool for targeted delivery to the brain. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2020, 187, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, T. C. R.; Willis, R.; Pericleous, C.; Ripoll, V. M.; Giles, I. P.; Isenberg, D. A.; Brasier, A. R.; Gonzalez, E. B.; Papalardo, E.; Romay-Penabad, Z.; Jamaluddin, M.; Ioannou, Y.; Rahman, A. , PEGylated Domain I of Beta-2-Glycoprotein I Inhibits the Binding, Coagulopathic, and Thrombogenic Properties of IgG From Patients With the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, M. R.; Wan, H. T. , Discussion about several potential drawbacks of PEGylated therapeutic proteins. Biol Pharm Bull 2014, 37, (3). 335–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, M.-r.; Wan, H.-t. , Discussion about Several Potential Drawbacks of PEGylated Therapeutic Proteins. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2014, 37, (3). 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddu, S. H. S.; Acharya, D.; Hala, V.; Jani, H.; Pande, S.; Patel, C.; Shahwan, M.; Jwala, R.; Ranch, K. M. , An Update on Strategies to Deliver Protein and Peptide Drugs to the Eye. ACS Omega 2023, 8, (39). 35470–35498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanlu, M.; Eskandani, M.; Barar, J.; Jaymand, M.; Pakchin, P. S.; Farhoudi, M. , Enhanced thrombolysis using tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)-loaded PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles for ischemic stroke. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2019, 53, 101165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Hu, C.; Yu, W.; Hu, T. , Conjugation with Eight-Arm PEG Markedly Improves the In Vitro Activity and Prolongs the Blood Circulation of Staphylokinase. Bioconjug Chem 2018, 29, (2). 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, D.; Jin, H.; Yang, D.; Yu, W.; Jia, J.; Yu, Z.; Tan, H.; Sun, Y.; Hao, H.; Qu, X.; Huang, Y. , Combination of Polyethylene Glycol-Conjugated Urokinase Nanogels and Urokinase for Acute Ischemic Stroke Therapeutic Implications. Transl Stroke Res 2021, 12, (5). 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H. X.; O'Rear, E. A. , An In Vitro Thrombolysis Study Using a Mixture of Fast-Acting and Slower Release Microspheres. Pharm Res 2016, 33, (7). 1552–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. , Liposomes: structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, (5). e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddah, S.; Khreich, N.; Kaddah, F.; Charcosset, C.; Greige-Gerges, H. , Cholesterol modulates the liposome membrane fluidity and permeability for a hydrophilic molecule. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2018, 113, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriwidodo; Umar, A. K.; Wathoni, N.; Zothantluanga, J. H.; Das, S.; Luckanagul, J. A., Liposome-polymer complex for drug delivery system and vaccine stabilization. Heliyon 2022, 8, (2), e08934.
- Yao, X.; Fan, X.; Yan, N. , Cryo-EM analysis of a membrane protein embedded in the liposome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2020, 117, (31). 18497–18503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, N.; Udayakumar, T. S.; D'Souza, W. D.; Simone, C. B., 2nd; Raghavan, S. R.; Polf, J.; Mahmood, J., Liposomes: Clinical Applications and Potential for Image-Guided Drug Delivery. Molecules 2018, 23, (2).
- Edwards, K.; Johnsson, M.; Karlsson, G.; Silvander, M. , Effect of polyethyleneglycol-phospholipids on aggregate structure in preparations of small unilamellar liposomes. Biophys J 1997, 73, (1). 258–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A. L.; Groom, C. R. , The druggable genome. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2002, 1, (9). 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, C. , Strategies to Obtain Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Small Hydrophilic Molecules. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J. , Lipid-Based Nanotechnology: Liposome. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, (1). 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbayoumi, T. A.; Torchilin, V. P. , Liposomes for targeted delivery of antithrombotic drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2008, 5, (11). 1185–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiecinski, J.; Peetermans, M.; Liesenborghs, L.; Na, M.; Björnsdottir, H.; Zhu, X.; Jacobsson, G.; Johansson, B. R.; Geoghegan, J. A.; Foster, T. J. , Staphylokinase control of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and detachment through host plasminogen activation. The Journal of infectious diseases 2016, 213, (1). 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L. T.; Vogel, H. J. , Staphylokinase has distinct modes of interaction with antimicrobial peptides, modulating its plasminogen-activation properties. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, (1). 31817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, V.; Gacchina Johnson, C.; Negussie, A. H.; Sharma, K. V.; Dreher, M. R.; Wood, B. J. , Temperature-sensitive liposome-mediated delivery of thrombolytic agents. Int J Hyperthermia 2015, 31, (1). 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eck, R. J.; Elling, T.; Sutton, A. J.; Wetterslev, J.; Gluud, C.; van der Horst, I. C. C.; Gans, R. O. B.; Meijer, K.; Keus, F. , Anticoagulants for thrombosis prophylaxis in acutely ill patients admitted to hospital: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 378, e070022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, G. T.; Arica, M. Y.; Hasirci, V. , Low-molecular-weight heparin-conjugated liposomes with improved stability and hemocompatibility. Drug Deliv 1998, 5, (4). 257–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-K.; Kim, C.-K. , Topical delivery of low-molecular-weight heparin with surface-charged flexible liposomes. Biomaterials 2006, 27, (2). 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjoub, H.; Roméo, P.; Leung, T. K.; Burelle, D.; Cartier, R.; Basmadjian, A. J., Sudden death after intravenous administration of a perflutren contrast agent: a case of pseudocomplication? J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2009, 22, (6), 753.e5-8.
- Muskula, P. R.; Main, M. L., Safety With Echocardiographic Contrast Agents. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging 2017, 10, (4), e005459.
- Szijjarto, C.; Rossi, S.; Waton, G.; Krafft, M. P. , Effects of perfluorocarbon gases on the size and stability characteristics of phospholipid-coated microbubbles: Osmotic effect versus interfacial film stabilization. Langmuir 2012, 28, (2). 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, C. , Gas vesicles enable ultrasound imaging. Nature Methods 2018, 15, (3). 159–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S. R.; Lafond, M.; Haworth, K. J.; Escudero, D. S.; Ionascu, D.; Frierson, B.; Huang, S.; Klegerman, M. E.; Peng, T.; McPherson, D. D.; Genstler, C.; Holland, C. K. , Initiating and imaging cavitation from infused echo contrast agents through the EkoSonic catheter. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, (1). 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D. A.; Vaidya, S. S.; Kopechek, J. A.; Huang, S. L.; Klegerman, M. E.; McPherson, D. D.; Holland, C. K. , Ultrasound-triggered release of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator from echogenic liposomes. Ultrasound Med Biol 2010, 36, (1). 145–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-L. , Liposomes in ultrasonic drug and gene delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2008, 60, (10). 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiukinhoy-Laing, S. D.; Buchanan, K.; Parikh, D.; Huang, S.; Macdonald, R. C.; McPherson, D. D.; Klegerman, M. E. , Fibrin targeting of tissue plasminogen activator-loaded echogenic liposomes. Journal of Drug Targeting 2007, 15, (2). 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G. J.; Meunier, J. M.; Huang, S.-L.; Lindsell, C. J.; McPherson, D. D.; Holland, C. K. , Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis with tPA-loaded echogenic liposomes. Thrombosis research 2009, 124, (3). 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D. A.; Vaidya, S.; Kopechek, J. A.; Hitchcock, K. E.; Huang, S. L.; McPherson, D. D.; Holland, C. K., Echogenic liposomes loaded with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) for image-guided, ultrasound-triggered drug release. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2007, 122, (5_Supplement), 3007-3007.
- Holland, C. K.; McPherson, D. D. , ECHOGENIC LIPSOMES FOR TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging 2009, 2009, 755–758. [Google Scholar]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J. D. , Complement: a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat Immunol 2010, 11, (9). 785–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassa, C.; Shaw, S. Y.; Weissleder, R. , Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: a versatile platform for targeted molecular imaging, molecular diagnostics, and therapy. Acc Chem Res 2011, 44, (10). 842–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A. K.; Luciani, N.; Gazeau, F.; Aubertin, K.; Bonneau, S.; Chauvierre, C.; Letourneur, D.; Wilhelm, C. , Combining magnetic nanoparticles with cell derived microvesicles for drug loading and targeting. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, (3). 645–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Saint Victor, M.; Crake, C.; Coussios, C. C.; Stride, E. , Properties, characteristics and applications of microbubbles for sonothrombolysis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2014, 11, (2). 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Li, T. S.; Malliaras, K.; Davis, D. R.; Zhang, Y.; Marban, E. , Magnetic targeting enhances engraftment and functional benefit of iron-labeled cardiosphere-derived cells in myocardial infarction. Circ Res 2010, 106, (10). 1570–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagg, W. S.; Liu, N.; Yang, M. J.; Cheng, K.; Chung, E.; Kim, J. S.; Wu, G.; Fair, J. , Magnetic Targeting of Stem Cell Derivatives Enhances Hepatic Engraftment into Structurally Normal Liver. Cell Transplant 2017, 26, (12). 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Lin, J.; Hu, K.; Xin, H.; Wang, X. , Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy with Metal-Organic-Framework-Derived Carbon Based Platforms with Multimodal Capabilities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, (21). 24453–24462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, M.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, B.; Wang, Z. G.; Ran, H. T.; Guo, D. , Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound-Responsive Phase-Transitional Nanoparticles for Thrombolysis without Vascular Damage: A Synergistic Nonpharmaceutical Strategy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, (3). 3387–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Pang, Z. , Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Targeting. Biomolecules 2019, 9, (12). 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Deng, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, P.; Wang, N. , Dendrimers as Nanocarriers for the Delivery of Drugs Obtained from Natural Products. Polymers 2023, 15, (10). 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadrack, D. M.; Swai, H. S.; Munissi, J. J. E.; Mubofu, E. B.; Nyandoro, S. S. , Polyamidoamine Dendrimers for Enhanced Solubility of Small Molecules and Other Desirable Properties for Site Specific Delivery: Insights from Experimental and Computational Studies. Molecules 2018, 23, (6). 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhleier, E.; Wehner, W., F., & Vogtle, F.,(1978).“Cascade”-and “nonskid-chain-like” syntheses of molecular cavity topologies. Synthesis, 155-158.
- Tomalia, D. A.; Baker, H.; Dewald, J.; Hall, M.; Kallos, G.; Martin, S.; Roeck, J.; Ryder, J.; Smith, P. , A New Class of Polymers: Starburst-Dendritic Macromolecules. Polymer Journal 1985, 17, (1). 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K. , Dendrimer-based bionanomaterials produced by surface modification, assembly and hybrid formation. Polymer Journal 2012, 44, (6). 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenson, S.; Tomalia, D. A. , Dendrimers in biomedical applications--reflections on the field. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2005, 57, (15). 2106–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Kittrell, S.; Yeudall, W. A.; Yang, H. , Folic acid-decorated polyamidoamine dendrimer mediates selective uptake and high expression of genes in head and neck cancer cells. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2016, 11, (22). 2959–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daralnakhla, H.; Saher, O.; Zamolo, S.; Bazaz, S.; P. Bost, J.; Heitz, M.; Lundin, K. E.; EL Andaloussi, S.; Darbre, T.; Reymond, J.-L.; Zain, R.; Smith, C. I. E., Lipophilic Peptide Dendrimers for Delivery of Splice-Switching Oligonucleotides. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, (1), 116.
- Marcinkowska, M.; Sobierajska, E.; Stanczyk, M.; Janaszewska, A.; Chworos, A.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B., Conjugate of PAMAM Dendrimer, Doxorubicin and Monoclonal Antibody-Trastuzumab: The New Approach of a Well-Known Strategy. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, (2).
- Sharma, R.; Liaw, K.; Sharma, A.; Jimenez, A.; Chang, M.; Salazar, S.; Amlani, I.; Kannan, S.; Kannan, R. M. , Glycosylation of PAMAM dendrimers significantly improves tumor macrophage targeting and specificity in glioblastoma. J Control Release 2021, 337, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C. F.; Campbell, R. A.; Franks, Z.; Gibson, C. C.; Thiagarajan, G.; Vieira-de-Abreu, A.; Sukavaneshvar, S.; Mohammad, S. F.; Li, D. Y.; Ghandehari, H.; Weyrich, A. S.; Brooks, B. D.; Grainger, D. W. , Cationic PAMAM dendrimers disrupt key platelet functions. Mol Pharm 2012, 9, (6). 1599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisina, R.; Mukhametova, L.; Ivanova, E. , Influence cationic and anionic PAMAM dendrimers of low generation on selected hemostatic parameters in vitro. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2020, 109, 110605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S. T.; Stern, S.; Clogston, J. D.; Zheng, J.; Adiseshaiah, P. P.; Dobrovolskaia, M.; Lim, J.; Patri, A. K.; Sun, X.; Simanek, E. E. , Biological assessment of triazine dendrimer: toxicological profiles, solution behavior, biodistribution, drug release and efficacy in a PEGylated, paclitaxel construct. Mol Pharm 2010, 7, (4). 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrizi, T. Z.; Kafiabad, S. A.; Eshghi, P. , Effects and treatment applications of polymeric nanoparticles on improving platelets' storage time: a review of the literature from 2010 to 2020. Blood Res 2021, 56, (4). 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Lü, S.; Gao, C.; Yang, J.; Yan, X.; Li, T.; Wen, N.; Huang, M.; Liu, M. , Multiarm-polyethylene glycol-polyglutamic acid peptide dendrimer: Design, synthesis, and dissolving thrombus. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2018, 106, (6). 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buwalda, S. J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W. E. , Hydrogels for Therapeutic Delivery: Current Developments and Future Directions. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, (2). 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Li, K.; Jia, X.; Wei, Q.; Qi, H.; Zhang, J. , Functionally integrating nanoparticles alleviate deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy and rescue intrauterine growth restriction. Nature Communications 2022, 13, (1). 7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, H. R.; Sakariassen, K. S. , Factors controlling thrombus formation on arterial lesions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1985, 454, 162–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakariassen, K. S.; Joss, R.; Muggli, R.; Kuhn, H.; Tschopp, T. B.; Sage, H.; Baumgartner, H. R. , Collagen type III induced ex vivo thrombogenesis in humans. Role of platelets and leukocytes in deposition of fibrin. Arteriosclerosis 1990, 10, (2). 276–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakariassen, K. S.; Orning, L.; Turitto, V. T. , The impact of blood shear rate on arterial thrombus formation. Future Sci OA 2015, 1, (4). Fso30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooij, B. J. M.; Závodszky, G.; Hoekstra, A. G.; Ku, D. N. , Biorheology of occlusive thrombi formation under high shear: in vitro growth and shrinkage. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, (1). 18604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pei, Y.; Gao, L.; He, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, L. , Shear force responsive and fixed-point separated system for targeted treatment of arterial thrombus. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M. R.; Storey, R. F. , The role of platelets in inflammation. Thromb Haemost 2015, 114, (3). 449–58. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, L. A.; Anderson, C. J.; Novelli, E. M. , Targeting P-Selectin Adhesion Molecule in Molecular Imaging: P-Selectin Expression as a Valuable Imaging Biomarker of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. J Nucl Med 2019, 60, (12). 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappelmayer, J.; Nagy, B., Jr. , The Interaction of Selectins and PSGL-1 as a Key Component in Thrombus Formation and Cancer Progression. Biomed Res Int 2017, 2017, 6138145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabshomali, A.; Bazzazzadehgan, S.; Mahdi, F.; Shariat-Madar, Z. , Potential Benefits of Antioxidant Phytochemicals in Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2023, 28, (20). 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, K.; Massberg, S. , Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021, 18, (9). 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichterle, O.; Lim, D. , Hydrophilic gels for biological use. Nature 1960, 185, (4706). 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinawang, G.; Osaki, M.; Takashima, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. , Biofunctional hydrogels based on host–guest interactions. Polymer Journal 2020, 52, (8). 839–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzSimons, T. M.; Oentoro, F.; Shanbhag, T. V.; Anslyn, E. V.; Rosales, A. M. , Preferential control of forward reaction kinetics in hydrogels crosslinked with reversible conjugate additions. Macromolecules 2020, 53, (10). 3738–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereroudakis, E.; Bantawa, M.; Lafleur, R. P. M.; Parisi, D.; Matsumoto, N. M.; Peeters, J. W.; Del Gado, E.; Meijer, E. W.; Vlassopoulos, D. , Competitive Supramolecular Associations Mediate the Viscoelasticity of Binary Hydrogels. ACS Cent Sci 2020, 6, (8). 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A. C.; Stabenfeldt, S. E.; Ahn, B.; Hannan, R. T.; Dhada, K. S.; Herman, E. S.; Stefanelli, V.; Guzzetta, N.; Alexeev, A.; Lam, W. A.; Lyon, L. A.; Barker, T. H. , Ultrasoft microgels displaying emergent platelet-like behaviours. Nat Mater 2014, 13, (12). 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sands, M.; Han, X.; Tsipursky, M.; Irudayaraj, J. , Hydrogel-Based Oxygen and Drug Delivery Dressing for Improved Wound Healing. ACS Omega 2024, 9, (22). 24095–24104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, J. R.; Adebowale, K.; Zhao, Z.; Mitragotri, S., Hydrogels in the clinic: An update. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine n/a, (n/a), e10680.
- Andrgie, A. T.; Darge, H. F.; Mekonnen, T. W.; Birhan, Y. S.; Hanurry, E. Y.; Chou, H. Y.; Wang, C. F.; Tsai, H. C.; Yang, J. M.; Chang, Y. H., Ibuprofen-Loaded Heparin Modified Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Inhibiting Excessive Inflammation and Promoting Wound Healing. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, (11).
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Long, L.; Yang, L.; Fu, D.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y., Inflammation-Responsive Drug-Loaded Hydrogels with Sequential Hemostasis, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Behavior for Chronically Infected Diabetic Wound Treatment. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2021, 13, (28), 33584-33599.
- Zhang, D.; Ren, Y.; He, Y.; Chang, R.; Guo, S.; Ma, S.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. , In situ forming and biocompatible hyaluronic acid hydrogel with reactive oxygen species-scavenging activity to improve traumatic brain injury repair by suppressing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Materials Today Bio 2022, 15, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K. H.; Wang, L.-S.; Kurisawa, M. , Injectable biodegradable hydrogels: progress and challenges. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2013, 1, (40). 5371–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermonden, T.; Censi, R.; Hennink, W. E. , Hydrogels for Protein Delivery. Chemical Reviews 2012, 112, (5). 2853–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J. M.; Peer, D. , Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nature Communications 2018, 9, (1). 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Lai, R.; Qiu, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Mi, B.; Wu, M.; Wang, J. , Translational Challenges and Prospective Solutions in the Implementation of Biomimetic Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, (11). 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Dou, H. , Thrombus-Targeting Polymeric Nanocarriers and Their Biomedical Applications in Thrombolytic Therapy. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 763085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ts'ao, C. H.; Spaet, T. H. , Ultramicroscopic changes in the rabbit inferior vena cava following partial constriction. Am J Pathol 1967, 51, (5). 789–813. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, S.; Ranjan, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Kashif, M.; Daniel, E. A.; Al-Dabet, M. d. M.; Bock, F.; Nazir, S.; Huebner, H.; Mertens, P. R.; Fischer, K.-D.; Zenclussen, A. C.; Offermanns, S.; Aharon, A.; Brenner, B.; Shahzad, K.; Ruebner, M.; Isermann, B. , Maternal extracellular vesicles and platelets promote preeclampsia via inflammasome activation in trophoblasts. Blood 2016, 128, (17). 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, S.; Isermann, B. , Crosstalk between inflammation and coagulation: Focus on pregnancy related complications. Thrombosis Update 2021, 5, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, I.; Nielsen, S. F.; Nordestgaard, B. G. , Complement C3 and High Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: 80517 Individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study. Clinical Chemistry 2016, 62, (3). 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budnik, I.; Brill, A. , Immune Factors in Deep Vein Thrombosis Initiation. Trends Immunol 2018, 39, (8). 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, M.; Puteri, M. U.; Saputri, F. C.; Sauriasari, R.; Widyantoro, B., Platelet Glycoprotein-Ib (GPIb) May Serve as a Bridge between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and Atherosclerosis, Making It a Potential Target for Antiplatelet Agents in T2DM Patients. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, (7).
- van der Meijden, P. E. J.; Heemskerk, J. W. M. , Platelet biology and functions: new concepts and clinical perspectives. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019, 16, (3). 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, S. S.; Baker, P. N.; Deehan, D. J.; Port, A.; Reed, M. R. , Evidence-base for aspirin as venous thromboembolic prophylaxis following joint replacement. Bone Joint Res 2014, 3, (5). 146–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denorme, F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; De Meyer, S. F. , von Willebrand Factor and Platelet Glycoprotein Ib: A Thromboinflammatory Axis in Stroke. Frontiers in Immunology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Handa, M.; Kawano, K.; Kamata, T.; Murata, M.; Araki, Y.; Anbo, H.; Kawai, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Itagaki, I.; et al. , The role of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen in platelet aggregation under varying shear stress. J Clin Invest 1991, 87, (4). 1234–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Murata, M.; Handa, M.; Takahashi, E.; Yoshioka, A.; Fujimura, Y.; Fukuyama, M.; Handa, S.; Ogawa, S. , Epinephrine augments von Willebrand factor-dependent shear-induced platelet aggregation. Circulation 1992, 86, (6). 1859–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayal, S.; Wilson, K. M.; Motto, D. G.; Miller, F. J., Jr.; Chauhan, A. K.; Lentz, S. R. , Hydrogen peroxide promotes aging-related platelet hyperactivation and thrombosis. Circulation 2013, 127, (12). 1308–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S. A.; Bozarth, J. M.; Naik, U. P.; Slee, A. , Platelet GPIIb/IIIa binding characteristics of small molecule RGD mimetic: distinct binding profile for Roxifiban. Br J Pharmacol 2001, 133, (3). 331–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga-Szabo, D.; Pleines, I.; Nieswandt, B., Cell Adhesion Mechanisms in Platelets. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2008, 28, (3), 403-412.
- Goto, S.; Tamura, N.; Li, M.; Handa, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Handa, S.; Ruggeri, Z. M. , Different effects of various anti-GPIIb-IIIa agents on shear-induced platelet activation and expression of procoagulant activity. J Thromb Haemost 2003, 1, (9). 2022–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y. T.; Noh, Y. W.; Han, J. H.; Cai, Q. Y.; Yoon, K. H.; Chung, B. H. , Biocompatible polymer-nanoparticle-based bimodal imaging contrast agents for the labeling and tracking of dendritic cells. Small 2008, 4, (10). 1640–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Meng, N.; Guo, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, K.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. , Platelet membrane-functionalized nanoparticles with improved targeting ability and lower hemorrhagic risk for thrombolysis therapy. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 328, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | Elimination | Risk | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Anticoagulants
Vitamin K antagonists
Antiplatelets
Thrombolytics
|
|
|
Approved
Approved
Approved
|
| Recommended Antithrombotic Drugs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compelling Indications | Anticoagulants | Antiplatelets | Thrombolytics | Ref. |
|
Coronary artery disease (CAD) CAD undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention Chronic kidney disease
Diabetes Knee replacement, orthopedic surgery Heart failure
Liver disease Recurrent VTE
|
Anticoagulants
Non–vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants Warfarin Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, LMWH, Fondaparinux Warfarin, oral anticoagulants Alteplase Heparins, apixaban, fondaparinux |
Antiplatelet Clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor Purinergic receptor antagonists Aspirin Aspirin Aspirin and clopidogrel, |
Thrombolytics Thrombolytic Urokinase thrombolysis |
[77,78,79] [80] [81,82] [83] [83] [84,85] [86,87,88,89] [90,91,92,93] [94,95] [96] [97] [98,99] |
| Nano-Drugs | Characteristics | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
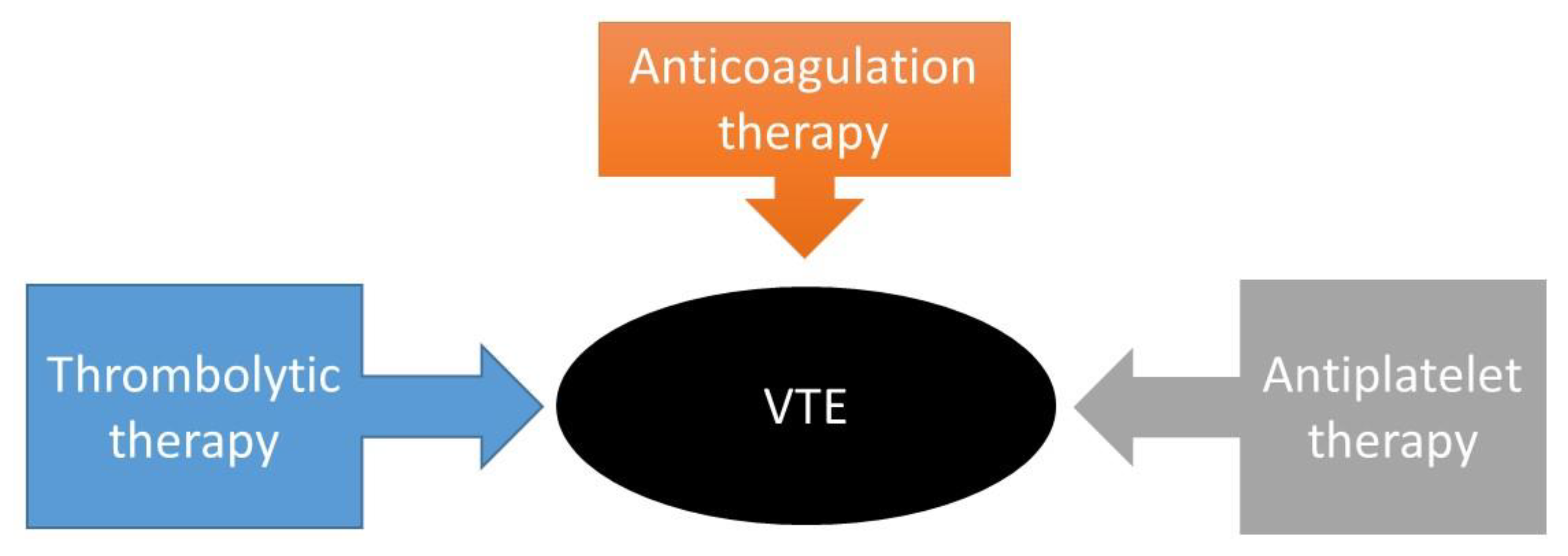
PEGylation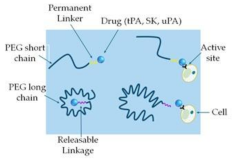
|
PEG-tPA PEG-UK PEG-SK PEG-SAK PEG-maleimide-(poly-SAK) |
Reduced proteolytic activity Slower inhibition kinetics by PAI-1 Increased fibrinolysis Resistant to plasmin cleavage Increased fibrinolysis Slightly increased fibrinolysis Increased bioactivity |
[129] [130] [131,132] [133] [134] |
Liposome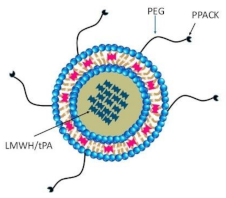
|
A circular-shaped diacyl-chain phospholipids/ phospholipid-attached PEG with cholesterol
|
Reduce thrombus weight Improve thrombolytic efficacy, reduce tPA-induced hemorrhage Prolong inhibition of thrombosis, reduced systemic side effects |
[135] [136] [137,138] |
Echogenic liposome & Polymeric nanoparticles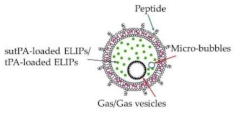 |
tPA-loaded ELIPs NIR-stimulated uPA release Magnetic nanoparticles Ultrasound-guided RDG-modified ELIPs |
Enhance thrombolytic efficiency Significant thrombolysis Prolong circulating tPA Improve thrombolytic efficacy Minimize off-target effects Similar thrombolysis, reduce the dose of tPA Complete thrombus elimination Effective thrombolysis in a rat embolism model Enhanced thrombolytic efficacy of tPA Improve recanalization rate |
[139,140,141] [142] [143] [139,144,145] [146] [146] [147] [148] [149] [150] |
Dendrimer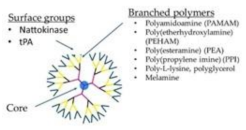
|
tPA-dendrimer complex Nattokinase-dendrimer complex LMWH-dendrimer complex Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers Poly(lysine) dendrimers |
High clot-dissolving activity Effective thrombolytic effect Prevents DVT Induce fibrinogen aggregation, contribute to the in vivo DIC, produce rapid coagulation Ideal carriers of protein drugs |
[151] [152] [153,154] [155] [156] [154] |
Mechanically activated nanotherapeutics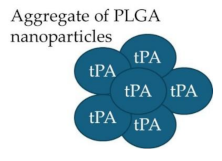
|
tPA- PLGA Shear-activated nanoparticle (tPA-SA-NP) complex tPA-loaded SA-NP and temporary endovascular bypass (TEB) |
Rapid clot dissolution Increase recanalization, reduce distal embolization |
[157,158] [159,160] [161] |
Platelet-based drug delivery system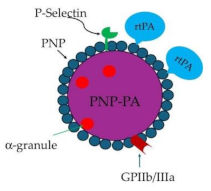
|
rtPA-PNP-PA | Thrombolysis | [162] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





