Submitted:
01 August 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Osteoarthritis, a Chronic Disease
2. Epigenetics and Osteoarthritis
2.1. DNA Methylation
2.2. Histone Modifications
2.3. Non-Coding RNA (ncRNAs)
3. Inflammation and Diet
4. Bioactive Compounds: Health-Protective Benefits
5. Nutritional Epigenomics: Bioactive Compounds in Dietary Balance and Health
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckwalter, J.A.; Martin, J.A. Osteoarthritis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2006, 58, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, P.M. Impact of osteoarthritis on individuals and society: how much disability? Social consequences and health economic implications. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2002, 14, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, D.; Peleteiro, B.; Araújo, J.; Branco, J.; Santos, R.A.; Ramos, E. The effect of osteoarthritis definition on prevalence and incidence estimates: a systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2011, 19, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malemud, C.J. Biologic basis of osteoarthritis: state of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015, 27, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieppe, P.A.; Lohmander, L.S. Pathogenesis and management of pain in osteoarthritis. Lancet 2005, 365, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Fonseca, J.E.; Gualillo, O.; Henrotin, Y.; Largo, R.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Rocha, F.A.C. Editorial: Inflammation and Biomarkers in Osteoarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 727700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanthawang, T.; Bodden, J.; Joseph, G.B.; Lane, N.E.; Nevitt, M.; McCulloch, C.E.; Link, T.M. Obese and overweight individuals have greater knee synovial inflammation and associated structural and cartilage compositional degeneration: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Skeletal Radiol 2021, 50, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.S.; Valdes, A.M. Cardiovascular disease and osteoarthritis: common pathways and patient outcomes. Eur J Clin Invest 2015, 45, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ouyang, H.; Dass, C.R.; Xu, J. Current research on pharmacologic and regenerative therapies for osteoarthritis. Bone Res 2016, 4, 15040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, P.; Tacconelli, S.; Bruno, A.; Sostres, C.; Lanas, A. Managing the adverse effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2011, 4, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.S.; Visco, C.J. Pharmaceutical therapy for osteoarthritis. PM R 2012, 4, S82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neil, C.K.; Hanlon, J.T.; Marcum, Z.A. Adverse effects of analgesics commonly used by older adults with osteoarthritis: focus on non-opioid and opioid analgesics. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 2012, 10, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, H.I.; Yamada, N.; Cheung, K.S.; Tilley, S.; Clarke, N.M.; Oreffo, R.O.; Kokubun, S.; Bronner, F. Association between the abnormal expression of matrix-degrading enzymes by human osteoarthritic chondrocytes and demethylation of specific CpG sites in the promoter regions. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52, 3110–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, A. Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature 2007, 447, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.M.; Haqqi, T.M. Epigenetics in osteoarthritis: Potential of HDAC inhibitors as therapeutics. Pharmacol Res 2018, 128, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, Y.F.; Meulenbelt, I. The role of epigenetics in osteoarthritis: current perspective. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2017, 29, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.I.; Choi, Y.J. Epigenetics in osteoarthritis and its implication for future therapeutics. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2013, 13, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Abu-Amer, Y.; O'Keefe, R.J.; McAlinden, A. Inflammation and epigenetic regulation in osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res 2017, 58, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, E.L.; Reynard, L.N.; Loughlin, J. The role of inflammation-related genes in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2015, 23, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.C.; Jeffries, M.A. The Epigenomic Landscape in Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2017, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meurs, J.B. Osteoarthritis year in review 2016: genetics, genomics and epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2017, 25, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barter, M.J.; Bui, C.; Young, D.A. Epigenetic mechanisms in cartilage and osteoarthritis: DNA methylation, histone modifications and microRNAs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2012, 20, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Eccles, M.R. DNA methylation and epigenomics: new technologies and emerging concepts. Genome Biol 2015, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Epigenetics and Osteoarthritis. Genes Dis 2015, 2, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Boyle, D.L.; Firestein, G.S. Regulation of DNA methylation in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol 2013, 190, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, K.E.; Reddy, A.B.; Dietzmann, K.; Suriano, A.R.; Kocieda, V.P.; Stewart, M.; Bhatia, M. Epigenetic regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol 2007, 27, 5147–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Otero, M.; Imagawa, K.; de Andrés, M.C.; Coico, J.M.; Roach, H.I.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Marcu, K.B.; Goldring, M.B. Regulated transcription of human matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) and interleukin-1β (IL1B) genes in chondrocytes depends on methylation of specific proximal promoter CpG sites. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 10061–10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Oreffo, R.O.; Gibson, M.B.; Goldring, M.B.; Roach, H.I. DNA demethylation at specific CpG sites in the IL1B promoter in response to inflammatory cytokines in human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60, 3303–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, C.; Barter, M.J.; Scott, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Galler, M.; Reynard, L.N.; Rowan, A.D.; Young, D.A. cAMP response element-binding (CREB) recruitment following a specific CpG demethylation leads to the elevated expression of the matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human articular chondrocytes and osteoarthritis. FASEB J 2012, 26, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Boeuf, S.; Dickhut, A.; Boehmer, S.; Olek, S.; Richter, W. Correlation of COL10A1 induction during chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells with demethylation of two CpG sites in the COL10A1 promoter. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamada, N.; Roach, H.I. Expression of ADAMTS-4 by chondrocytes in the surface zone of human osteoarthritic cartilage is regulated by epigenetic DNA de-methylation. Rheumatol Int 2009, 29, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Kostopoulou, F.; Malizos, K.N.; Tsezou, A. DNA methylation regulates sclerostin (SOST) expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes by bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) induced changes in Smads binding affinity to the CpG region of SOST promoter. Arthritis Res Ther 2015, 17, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.I.; Park, Y.S.; Im, G.I. Changes in the epigenetic status of the SOX-9 promoter in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Bone Miner Res 2013, 28, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imagawa, K.; de Andrés, M.C.; Hashimoto, K.; Itoi, E.; Otero, M.; Roach, H.I.; Goldring, M.B.; Oreffo, R.O. Association of reduced type IX collagen gene expression in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes with epigenetic silencing by DNA hypermethylation. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014, 66, 3040–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; de Andrés, M.C.; Hashimoto, K.; Itoi, E.; Oreffo, R.O. Epigenetic regulation of interleukin-8, an inflammatory chemokine, in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2015, 23, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrés, M.C.; Imagawa, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Roach, H.I.; Goldring, M.B.; Oreffo, R.O. Loss of methylation in CpG sites in the NF-κB enhancer elements of inducible nitric oxide synthase is responsible for gene induction in human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 2013, 65, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, J.; Yan, M. Epigenetic modifications of interleukin-6 in synovial fibroblasts from osteoarthritis patients. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 43592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kang, D.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.H. Epigenetic Regulation of Chondrocyte Catabolism and Anabolism in Osteoarthritis. Mol Cells 2015, 38, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, S.; Cui, Y.; Klaassen, C.D. Molecular targets of epigenetic regulation and effectors of environmental influences. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2010, 245, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruijter, A.J.; van Gennip, A.H.; Caron, H.N.; Kemp, S.; van Kuilenburg, A.B. Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J 2003, 370, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gang, Y.; Bai, L. The Role of HDACs and HDACi in Cartilage and Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 560117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D.A.; Lakey, R.L.; Pennington, C.J.; Jones, D.; Kevorkian, L.; Edwards, D.R.; Cawston, T.E.; Clark, I.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate metalloproteinase gene expression in chondrocytes and block cartilage resorption. Arthritis Res Ther 2005, 7, R503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Derfoul, A.; Pereira-Mouries, L.; Hall, D.J. A novel domain in histone deacetylase 1 and 2 mediates repression of cartilage-specific genes in human chondrocytes. FASEB J 2009, 23, 3539–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, L.C.; Brock, M.; Hemmatazad, H.; Giger, O.T.; Moritz, F.; Trenkmann, M.; Distler, J.H.; Gay, R.E.; Kolling, C.; Moch, H. , et al. Histone deacetylase/acetylase activity in total synovial tissue derived from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 2007, 56, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashiyama, R.; Miyaki, S.; Yamashita, S.; Yoshitaka, T.; Lindman, G.; Ito, Y.; Sasho, T.; Takahashi, K.; Lotz, M.; Asahara, H. Correlation between MMP-13 and HDAC7 expression in human knee osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol 2010, 20, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; Gagarina, V.; Lee, E.J.; Hall, D.J. Regulation of cartilage-specific gene expression in human chondrocytes by SirT1 and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 36300–36310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; Mobasheri, A.; Kumar, A. The Role of Sirtuins in Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2016, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Shen, G. Intra-articular resveratrol injection prevents osteoarthritis progression in a mouse model by activating SIRT1 and thereby silencing HIF-2α. J Orthop Res 2015, 33, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagarina, V.; Gabay, O.; Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; Lee, E.J.; Brady, J.K.; Quon, M.J.; Hall, D.J. SirT1 enhances survival of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes by repressing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and activating the insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, H.; Kumar, A.; Meir, H.; Schwartz, I.; Zini, A.; Haze, A.; Kandel, L.; Mattan, Y.; Liebergall, M.; Dvir-Ginzberg, M. Set7/9 impacts COL2A1 expression through binding and repression of SirT1 histone deacetylation. J Bone Miner Res 2014, 29, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, M.; Peng, H.; Hachem, K.E.; Culley, K.L.; Wondimu, E.B.; Quinn, J.; Asahara, H.; Tsuchimochi, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Goldring, M.B. ELF3 modulates type II collagen gene (COL2A1) transcription in chondrocytes by inhibiting SOX9-CBP/p300-driven histone acetyltransferase activity. Connect Tissue Res 2017, 58, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteagudo, S.; Cornelis, F.M.F.; Aznar-Lopez, C.; Yibmantasiri, P.; Guns, L.A.; Carmeliet, P.; Cailotto, F.; Lories, R.J. DOT1L safeguards cartilage homeostasis and protects against osteoarthritis. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 15889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño Betancourt, M.C.; Cailotto, F.; Kerkhof, H.J.; Cornelis, F.M.; Doherty, S.A.; Hart, D.J.; Hofman, A.; Luyten, F.P.; Maciewicz, R.A.; Mangino, M. , et al. Genome-wide association and functional studies identify the DOT1L gene to be involved in cartilage thickness and hip osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 8218–8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschansky, V.J.; Wahlestedt, C. Non-coding RNAs as direct and indirect modulators of epigenetic regulation. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Dai, L.; Hu, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Ao, Y. Long noncoding RNA related to cartilage injury promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014, 66, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, C.; Zampetaki, A.; Lin, N.Y.; Kleyer, A.; Perricone, C.; Iagnocco, A.; Distler, A.; Langley, S.R.; Gelse, K.; Sesselmann, S. , et al. Signature of circulating microRNAs in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2015, 74, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaki, S.; Asahara, H. Macro view of microRNA function in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2012, 8, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondag, G.R.; Haqqi, T.M. The Role of MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2016, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swingler, T.E.; Niu, L.; Smith, P.; Paddy, P.; Le, L.; Barter, M.J.; Young, D.A.; Clark, I.M. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2019, 37 Suppl 120, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, Z.; Al-Shobaili, H.A.; Rasheed, N.; Mahmood, A.; Khan, M.I. MicroRNA-26a-5p regulates the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase via activation of NF-κB pathway in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 2016, 594, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Rasheed, Z.; Ramamurthy, S.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Voss, F.R.; Haqqi, T.M. MicroRNA-27b regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Cheon, E.J.; Kim, H.A. MicroRNA-558 regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and IL-1β-induced catabolic effects in human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013, 21, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Haqqi, T.M. MicroRNA-199a* regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 2012, 71, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, G.; Meng, F.; Kang, Y. MicroRNA-92a-3p regulates the expression of cartilage-specific genes by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2 in chondrogenesis and degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2017, 25, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Long, D.; Hu, S.; Gu, M.; He, S. , et al. MicroRNA-193b-3p regulates chondrogenesis and chondrocyte metabolism by targeting HDAC3. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2862–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Du, S.; Ding, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Chen, Q. Evidence that miR-146a attenuates aging- and trauma-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting Notch1, IL-6, and IL-1 mediated catabolism. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Shih, K.S.; Wu, Y.W.; Wang, A.W.; Yang, C.R. Histone deacetylase inhibitors increase microRNA-146a expression and enhance negative regulation of interleukin-1β signaling in osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013, 21, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budd, E.; de Andrés, M.C.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; Oreffo, R.O.C. MiR-146b is down-regulated during the chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow derived skeletal stem cells and up-regulated in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 46704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, Z.; Mao, G.; Hu, S.; Zeng, A.; Fu, M. miR-193b-5p regulates chondrocytes metabolism by directly targeting histone deacetylase 7 in interleukin-1β-induced osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem 2019, 120, 12775–12784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukai, T.; Sato, M.; Akutsu, H.; Umezawa, A.; Mochida, J. MicroRNA-199a-3p, microRNA-193b, and microRNA-320c are correlated to aging and regulate human cartilage metabolism. J Orthop Res 2012, 30, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, P.; Politi, L.; Vedova, P.D.; Scandurra, R.; Scotto d'Abusco, A. The inflammatory circuitry of miR-149 as a pathological mechanism in osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int 2014, 34, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, S.; Nakasa, T.; Otsuki, S.; Grogan, S.P.; Higashiyama, R.; Inoue, A.; Kato, Y.; Sato, T.; Lotz, M.K.; Asahara, H. MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araldi, E.; Schipani, E. MicroRNA-140 and the silencing of osteoarthritis. Genes Dev 2010, 24, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.B.; Yang, T.M.; Li, L.; Tian, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.P.; Huang, Q.; Kang, P.D.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.K. , et al. miR-140 Attenuates the Progression of Early-Stage Osteoarthritis by Retarding Chondrocyte Senescence. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, A.C.; Pi, B.; Pan, G.; Pei, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, T. , et al. Melatonin Prevents Osteoarthritis-Induced Cartilage Degradation via Targeting MicroRNA-140. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 9705929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, T.A.; de Souza, G.A.; Ødegaard, B.; Engebretsen, L.; Brinchmann, J.E. microRNA-140 Inhibits Inflammation and Stimulates Chondrogenesis in a Model of Interleukin 1β-induced Osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuddenham, L.; Wheeler, G.; Ntounia-Fousara, S.; Waters, J.; Hajihosseini, M.K.; Clark, I.; Dalmay, T. The cartilage specific microRNA-140 targets histone deacetylase 4 in mouse cells. FEBS Lett 2006, 580, 4214–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, S.; Charlton, S.; Cheung, K.; Hao, Y.; Soul, J.; Reynard, L.N.; Crowe, N.; Swingler, T.E.; Skelton, A.J.; Piróg, K.A. , et al. microRNA-seq of cartilage reveals an overabundance of miR-140-3p which contains functional isomiRs. RNA 2020, 26, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Feng, C.; Wang, C.X.; Xu, D.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Huang, J.F.; Tan, P.L.; Shen, J.M. Circulating microRNA let-7e is decreased in knee osteoarthritis, accompanied by elevated apoptosis and reduced autophagy. Int J Mol Med 2020, 45, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Dudek, K.A.; Murphy, C.L. Regulation of human chondrocyte function through direct inhibition of cartilage master regulator SOX9 by microRNA-145 (miRNA-145). J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.D.; Gilroy, D.W.; Serhan, C.N.; Stockinger, B.; Tak, P.P. The resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2013, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, G.F.; Artis, D. Innate lymphoid cells in the initiation, regulation and resolution of inflammation. Nat Med 2015, 21, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame. Cell 2010, 140, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013, 21, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, W.H.; Lepus, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Raghu, H.; Mao, R.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Sokolove, J. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2016, 12, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, J.P.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Abramson, S.B. Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum 2001, 44, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M.; Tsuchimochi, K.; Ijiri, K.; Li, Y. Defining the roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism. Ann Rheum Dis 2008, 67 Suppl 3, iii75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Zaichenko, L.; Peter, P.; Davis, C.R.; Crowell, J.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Diet quality is associated with circulating C-reactive protein but not irisin levels in humans. Metabolism 2014, 63, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Bibiloni, M.D.M.; Julibert, A.; Bouzas, C.; Argelich, E.; Llompart, I.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Inflammatory Markers. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, D.; Ceriello, A.; Esposito, K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006, 48, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnolo, D.F.; Selmin, O.I. Mediterranean Diet and Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Nutr Today 2017, 52, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Fung, T.T.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Forouhi, N.G. Food based dietary patterns and chronic disease prevention. BMJ 2018, 361, k2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, R.; Sacanella, E.; Estruch, R. The immune protective effect of the Mediterranean diet against chronic low-grade inflammatory diseases. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2014, 14, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Agostoni, C.; Graffigna, G.; Bosio, C.; Donini, L.M.; Marangoni, F. The complex relationship between diet, quality of life and life expectancy: a narrative review of potential determinants based on data from Italy. Eat Weight Disord 2019, 24, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, A.C.; Graves, K.Y.; Sumerau, J.E. Mediation analysis of relationships between chronic inflammation and quality of life in older adults. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, J.A.; Mathers, J.C. Diet induced epigenetic changes and their implications for health. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2011, 202, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milagro, F.I.; Mansego, M.L.; De Miguel, C.; Martínez, J.A. Dietary factors, epigenetic modifications and obesity outcomes: progresses and perspectives. Mol Aspects Med 2013, 34, 782–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.D.; Uthus, E.O. DNA methylation, cancer susceptibility, and nutrient interactions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004, 229, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiker, S.; Karst, S.; Wagener, A.; Brockmann, G.A. High-fat diet leads to a decreased methylation of the Mc4r gene in the obese BFMI and the lean B6 mouse lines. J Appl Genet 2010, 51, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szarc vel Szic, K.; Declerck, K.; Vidaković, M.; Vanden Berghe, W. From inflammaging to healthy aging by dietary lifestyle choices: is epigenetics the key to personalized nutrition? Clin Epigenetics 2015, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toopchizadeh, V.; Dolatkhah, N.; Aghamohammadi, D.; Rasouli, M.; Hashemian, M. Dietary inflammatory index is associated with pain intensity and some components of quality of life in patients with knee osteoarthritis. BMC Res Notes 2020, 13, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Shivappa, N.; Stubbs, B.; Smith, T.; Hébert, J.R.; Cooper, C.; Guglielmi, G.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Maggi, S. The relationship between the dietary inflammatory index and prevalence of radiographic symptomatic osteoarthritis: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Eur J Nutr 2019, 58, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Guo, J.; Tao, K.; Zeng, C.; Lei, G.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of incident knee osteoarthritis: a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2020, 22, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavicchia, P.P.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Hébert, J.R. A new dietary inflammatory index predicts interval changes in serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. J Nutr 2009, 139, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perruccio, A.V.; Chandran, V.; Power, J.D.; Kapoor, M.; Mahomed, N.N.; Gandhi, R. Systemic inflammation and painful joint burden in osteoarthritis: a matter of sex? Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2017, 25, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.; Englund, M.; Struglics, A.; Lohmander, L.S. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial fluid are associated with progression of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in subjects with previous meniscectomy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2015, 23, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Beguerie, J.R.; Zhang, W.; Blizzard, L.; Otahal, P.; Jones, G.; Ding, C. Circulating C reactive protein in osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 2015, 74, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, J.P.; Raynauld, J.P.; Caron, J.; Mineau, F.; Abram, F.; Dorais, M.; Haraoui, B.; Choquette, D.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Decrease in serum level of matrix metalloproteinases is predictive of the disease-modifying effect of osteoarthritis drugs assessed by quantitative MRI in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010, 69, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, J.; Davison, G.; Marcora, S.M.; Mauger, A.R. Effect of a Mediterranean Type Diet on Inflammatory and Cartilage Degradation Biomarkers in Patients with Osteoarthritis. J Nutr Health Aging 2017, 21, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henríquez Sánchez, P.; Ruano, C.; de Irala, J.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Sánchez-Villegas, A. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and quality of life in the SUN Project. Eur J Clin Nutr 2012, 66, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccio, M.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Bonanni, A.; Costanzo, S.; De Lucia, F.; Pounis, G.; Zito, F.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L. , et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with a better health-related quality of life: a possible role of high dietary antioxidant content. BMJ Open 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.M.; Struijk, E.A.; Fransen, H.P.; Onland-Moret, N.C.; de Wit, G.A.; Boer, J.M.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Hoekstra, J.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Peeters, P.H. , et al. The impact of a healthy lifestyle on Disability-Adjusted Life Years: a prospective cohort study. BMC Med 2015, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tasigchana, R.F.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; López-García, E.; Banegas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Guallar-Castillón, P. Mediterranean Diet and Health-Related Quality of Life in Two Cohorts of Community-Dwelling Older Adults. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0151596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Noale, M.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Maggi, S. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with better quality of life: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Am J Clin Nutr 2016, 104, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary patterns: a Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and biological markers of cardiovascular disease risk. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2006, 16, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, G.; Hartman, A.M.; Naughton, D. A reduced dietary questionnaire: development and validation. Epidemiology 1990, 1, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Noale, M.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Smith, T.O.; Cooper, C.; Guglielmi, G.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rizzoli, R. , et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with lower prevalence of osteoarthritis: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Clin Nutr 2017, 36, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsavos, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Tzima, N.; Chrysohoou, C.; Economou, M.; Zampelas, A.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with total antioxidant capacity in healthy adults: the ATTICA study. Am J Clin Nutr 2005, 82, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzianagnostou, K.; Del Turco, S.; Pingitore, A.; Sabatino, L.; Vassalle, C. The Mediterranean Lifestyle as a Non-Pharmacological and Natural Antioxidant for Healthy Aging. Antioxidants (Basel) 2015, 4, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Cano, M.P.; de Ancos, B.; Plaza, L.; Olmedilla, B.; Granado, F.; Martín, A. Mediterranean vegetable soup consumption increases plasma vitamin C and decreases F2-isoprostanes, prostaglandin E2 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in healthy humans. J Nutr Biochem 2006, 17, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Cabrera-Mulero, R.; Rubio-Martín, E.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; Olveira, G.; Valdés, S.; Soriguer, F.; Castaño, L.; Morcillo, S. Methylation levels of the SCD1 gene promoter and LINE-1 repeat region are associated with weight change: an intervention study. Mol Nutr Food Res 2014, 58, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnik, P.; Gabrić, D.; Roohinejad, S.; Barba, F.J.; Granato, D.; Mallikarjunan, K.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Bursać Kovačević, D. An overview of organosulfur compounds from Allium spp.: From processing and preservation to evaluation of their bioavailability, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Food Chem 2019, 276, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Blachier, F.; Tossou, M.C.; Rahu, N. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016, 7432797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, G.; Maisto, M.; Schisano, C.; Ciampaglia, R.; Narciso, V.; Tenore, G.C.; Novellino, E. Resveratrol as a Novel Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus Nutraceutical Agent: An Overview. Viruses 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, G.; Sanduzzi Zamparelli, M.; Santoro, C.; Ciampaglia, R.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Tenore, G.C.; Sanduzzi, A.; Novellino, E. May Polyphenols Have a Role Against Coronavirus Infection? An Overview of. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglio, R.V.; Patti, A.M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Lippi, G.; Rizzo, M.; Toth, P.P.; Banach, M. Polyphenols: Potential Use in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2018, 24, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, L.; Mazzitelli, S.; Arciello, M.; Capo, C.R.; Rotilio, G. Benefits from dietary polyphenols for brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Res 2008, 33, 2390–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surh, Y.J. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer 2003, 3, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Sugioka, Y.; Koike, T. Soybean isoflavone can protect against osteoarthritis in ovariectomized rats. J Food Sci Technol 2020, 57, 3409–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.N.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant Phytochemicals for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhikh, S.; Noskova, S.; Ivanova, S.; Ulrikh, E.; Izgaryshev, A.; Babich, O. Chondroprotection and Molecular Mechanism of Action of Phytonutraceuticals on Osteoarthritis. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, D.J.; Choudhury, M.; Hirsh, D.M.; Hardin, J.A.; Cobelli, N.J.; Sun, H.B. Nutraceuticals: potential for chondroprotection and molecular targeting of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci 2013, 14, 23063–23085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, K.Y.; Pang, K.L. Therapeutic Effects of Olive and Its Derivatives on Osteoarthritis: From Bench to Bedside. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Adamo, S.; Cetrullo, S.; Panichi, V.; Mariani, E.; Flamigni, F.; Borzì, R.M. Nutraceutical Activity in Osteoarthritis Biology: A Focus on the Nutrigenomic Role. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhang, S.N. Recent advance in treatment of osteoarthritis by bioactive components from herbal medicine. Chin Med 2020, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.B.A.R.; Pinheiro-Castro, N.; Novaes, G.M.; Pascoal, G.F.L.; Ong, T.P. Bioactive food compounds, epigenetics and chronic disease prevention: Focus on early-life interventions with polyphenols. Food Res Int 2019, 125, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crascì, L.; Lauro, M.R.; Puglisi, G.; Panico, A. Natural antioxidant polyphenols on inflammation management: Anti-glycation activity vs metalloproteinases inhibition. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2018, 58, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinger, M.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V. Some Important Dietary Polyphenolic Compounds: An Anti-inflammatory and Immunoregulatory Perspective. Mini Rev Med Chem 2018, 18, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Shen, T.; Lou, H. Dietary Polyphenols and Their Biological Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 950–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Cicala, C.; Caiazzo, E.; Izzo, A.A.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Polyphenols: A concise overview on the chemistry, occurrence, and human health. Phytother Res 2019, 33, 2221–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Di Benedetto, R.; Gargiulo, R.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, dietary sources and bioavailability. Ann Ist Super Sanita 2007, 43, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Bo', C.; Bernardi, S.; Marino, M.; Porrini, M.; Tucci, M.; Guglielmetti, S.; Cherubini, A.; Carrieri, B.; Kirkup, B.; Kroon, P. , et al. Systematic Review on Polyphenol Intake and Health Outcomes: Is there Sufficient Evidence to Define a Health-Promoting Polyphenol-Rich Dietary Pattern? Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.J.; Choi, S.I.; Choi, B.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, G.S. Cartilage protective and anti-analgesic effects of ALM16 on monosodium iodoacetate induced osteoarthritis in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019, 19, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, J.; Scofield, R.H.; Barrett, J.R.; Kurien, B.T.; Betts, N.; Lyons, T.J.; Zhao, Y.D.; Basu, A. Strawberries Improve Pain and Inflammation in Obese Adults with Radiographic Evidence of Knee Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Smith, A.; Avalos, M.; South, S.; Crabtree, K.; Wang, W.; Kwon, Y.H.; Vijayagopal, P.; Juma, S. Blueberries Improve Pain, Gait Performance, and Inflammation in Individuals with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Akhtar, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Pomegranate extract inhibits the interleukin-1β-induced activation of MKK-3, p38α-MAPK and transcription factor RUNX-2 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 2010, 12, R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Wang, N.; Hafeez, B.B.; Cheruvu, V.K.; Haqqi, T.M. Punica granatum L. extract inhibits IL-1beta-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases by inhibiting the activation of MAP kinases and NF-kappaB in human chondrocytes in vitro. J Nutr 2005, 135, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Shang, P.; Tang, Q. , et al. Arctigenin prevents the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB axis: In vitro and in vivo studies. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 4183–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Piao, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Astragalin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory mediators production in human osteoarthritis chondrocyte by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation. Int Immunopharmacol 2015, 25, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrotin, Y.E.; Sanchez, C.; Deberg, M.A.; Piccardi, N.; Guillou, G.B.; Msika, P.; Reginster, J.Y. Avocado/soybean unsaponifiables increase aggrecan synthesis and reduce catabolic and proinflammatory mediator production by human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Rheumatol 2003, 30, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henrotin, Y.E.; Deberg, M.A.; Crielaard, J.M.; Piccardi, N.; Msika, P.; Sanchez, C. Avocado/soybean unsaponifiables prevent the inhibitory effect of osteoarthritic subchondral osteoblasts on aggrecan and type II collagen synthesis by chondrocytes. J Rheumatol 2006, 33, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Au, R.Y.; Al-Talib, T.K.; Au, A.Y.; Phan, P.V.; Frondoza, C.G. Avocado soybean unsaponifiables (ASU) suppress TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, COX-2, iNOS gene expression, and prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide production in articular chondrocytes and monocyte/macrophages. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2007, 15, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, R.; Taylor, J.F.; Yazdi, P.G.; Pedersen, B.A. Effects of Arthrocen, an avocado/soy unsaponifiables agent, on inflammatory mediators and gene expression in human chondrocytes. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Cai, L.; Xie, H.; Hu, W.; Wang, T.; Lu, D.; Chen, H. Baicalin suppresses IL-1β-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines via blocking NF-κB in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and shows protective effect in mice osteoarthritis models. Int Immunopharmacol 2017, 52, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.C.; Lee, H.P.; Hung, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Li, T.M.; Tang, C.H. Berberine attenuates CCN2-induced IL-1β expression and prevents cartilage degradation in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2015, 289, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Feng, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y. Butein inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and slows the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2017, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Hao, W.; Li, S. Casticin protects against IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 2019, 842, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.H.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, W.P.; Zhong, H.M.; Wang, X.H. Celastrol, an inhibitor of heat shock protein 90β potently suppresses the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in primary human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 2013, 708, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Hsiao, G.; Lin, K.H.; Hsieh, M.S.; Jayakumar, T.; Wu, T.S.; Sheu, J.R. Cinnamophilin isolated from Cinnamomum philippinense protects against collagen degradation in human chondrocytes. Phytother Res 2013, 27, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Xie, C.; Li, H.; Cheng, L.; Wu, A.; Ni, W. Cryptotanshinone protects against IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2017, 50, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Tanzil, G.; Mobasheri, A.; Sendzik, J.; John, T.; Shakibaei, M. Effects of curcumin (diferuloylmethane) on nuclear factor kappaB signaling in interleukin-1beta-stimulated chondrocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004, 1030, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakibaei, M.; Schulze-Tanzil, G.; John, T.; Mobasheri, A. Curcumin protects human chondrocytes from IL-l1beta-induced inhibition of collagen type II and beta1-integrin expression and activation of caspase-3: an immunomorphological study. Ann Anat 2005, 187, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakibaei, M.; John, T.; Schulze-Tanzil, G.; Lehmann, I.; Mobasheri, A. Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by curcumin leads to inhibition of expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human articular chondrocytes: Implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol 2007, 73, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathy-Hartert, M.; Jacquemond-Collet, I.; Priem, F.; Sanchez, C.; Lambert, C.; Henrotin, Y. Curcumin inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators and metalloproteinase-3 production by chondrocytes. Inflamm Res 2009, 58, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuptniratsaikul, V.; Dajpratham, P.; Taechaarpornkul, W.; Buntragulpoontawee, M.; Lukkanapichonchut, P.; Chootip, C.; Saengsuwan, J.; Tantayakom, K.; Laongpech, S. Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter study. Clin Interv Aging 2014, 9, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuptniratsaikul, V.; Thanakhumtorn, S.; Chinswangwatanakul, P.; Wattanamongkonsil, L.; Thamlikitkul, V. Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Altern Complement Med 2009, 15, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsornsak, P.; Niempoog, S. The efficacy of Curcuma Longa L. extract as an adjuvant therapy in primary knee osteoarthritis: a randomized control trial. J Med Assoc Thai 2012, 95 (Suppl. S1), S51–S58. [Google Scholar]
- Shep, D.; Khanwelkar, C.; Gade, P.; Karad, S. Safety and efficacy of curcumin versus diclofenac in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized open-label parallel-arm study. Trials 2019, 20, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Luo, P.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Nrf2/ARE is a key pathway for curcumin-mediated protection of TMJ chondrocytes from oxidative stress and inflammation. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Leong, D.J.; Xu, L.; He, Z.; Wang, A.; Navati, M.; Kim, S.J.; Hirsh, D.M.; Hardin, J.A.; Cobelli, N.J. , et al. Curcumin slows osteoarthritis progression and relieves osteoarthritis-associated pain symptoms in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Arthritis Res Ther 2016, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakibaei, M.; Mobasheri, A.; Buhrmann, C. Curcumin synergizes with resveratrol to stimulate the MAPK signaling pathway in human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Genes Nutr 2011, 6, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Mukai, S.; Yamada, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Tarumi, E.; Hashimoto, T.; Tamura, C.; Imaizumi, A.; Nishihira, J.; Nakamura, T. Short-term effects of highly-bioavailable curcumin for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled prospective study. J Orthop Sci 2014, 19, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Mukai, S.; Yamada, S.; Murata, S.; Yabumoto, H.; Maeda, T.; Akamatsu, S. The Efficacy and Safety of Highly-Bioavailable Curcumin for Treating Knee Osteoarthritis: A 6-Month Open-Labeled Prospective Study. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord 2020, 13, 1179544120948471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, A.; Lavin, P.; Patwardhan, B.; Chitre, D. A 32-week randomized, placebo-controlled clinical evaluation of RA-11, an Ayurvedic drug, on osteoarthritis of the knees. J Clin Rheumatol 2004, 10, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcaro, G.; Cesarone, M.R.; Dugall, M.; Pellegrini, L.; Ledda, A.; Grossi, M.G.; Togni, S.; Appendino, G. Efficacy and safety of Meriva®, a curcumin-phosphatidylcholine complex, during extended administration in osteoarthritis patients. Altern Med Rev 2010, 15, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, L.; Kim, J.Y. Chondroprotective effect of curcumin and lecithin complex in human chondrocytes stimulated by IL-1β via an anti-inflammatory mechanism. Food Sci Biotechnol 2019, 28, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comblain, F.; Sanchez, C.; Lesponne, I.; Balligand, M.; Serisier, S.; Henrotin, Y. Curcuminoids extract, hydrolyzed collagen and green tea extract synergically inhibit inflammatory and catabolic mediator's synthesis by normal bovine and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes in monolayer. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0121654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Ascola, A.; Irrera, N.; Ettari, R.; Bitto, A.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Atteritano, M.; Campo, G.M.; Minutoli, L.; Arcoraci, V. , et al. Exploiting Curcumin Synergy With Natural Products Using Quantitative Analysis of Dose-Effect Relationships in an Experimental. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari-Beni, M.; Moravejolahkami, A.R.; Gorgian, P.; Askari, G.; Tarrahi, M.J.; Bahreini-Esfahani, N. Herbal formulation "turmeric extract, black pepper, and ginger" versus Naproxen for chronic knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res 2020, 34, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kare, S.K.; Vinay, V.; Maresz, K.; Prisk, V.; Vik, H. Seed Extract-Based Botanical Compositions Alleviate Knee Pain and Improve Joint Function in Mild-to-Moderate Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022, 2022, 2226139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.L.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.R.; Choi, B.K.; Yang, S.H. Anti-osteoarthritic Effects of an Herbal Composition LI73014F2 on Interleukin-1β-induced Primary Human Articular Chondrocytes. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseeb, A.; Chen, D.; Haqqi, T.M. Delphinidin inhibits IL-1β-induced activation of NF-κB by modulating the phosphorylation of IRAK-1(Ser376) in human articular chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013, 52, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Lin, C.; Fu, C.; Lu, H.; Jin, H.; Chen, Q.; Pan, J. The protective effect of Ellagic acid (EA) in osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 125, 109845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Wang, N.; Lalonde, M.; Goldberg, V.M.; Haqqi, T.M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) differentially inhibits interleukin-1 beta-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -13 in human chondrocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004, 308, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.S.; Tseng, C.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Su, S.L.; Lee, H.S. Effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on cyclooxygenase 2, PGE(2), and IL-8 expression induced by IL-1beta in human synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatol Int 2010, 30, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Ahmed, S.; Islam, N.; Goldberg, V.M.; Haqqi, T.M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase and production of nitric oxide in human chondrocytes: suppression of nuclear factor kappaB activation by degradation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB. Arthritis Rheum 2002, 46, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Rahman, A.; Hasnain, A.; Lalonde, M.; Goldberg, V.M.; Haqqi, T.M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the IL-1 beta-induced activity and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide synthase-2 in human chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 2002, 33, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Ahmed, S.; Malemud, C.J.; Goldberg, V.M.; Haqqi, T.M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate selectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced activation of mitogen activated protein kinase subgroup c-Jun N-terminal kinase in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Orthop Res 2003, 21, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Akhtar, N.; Ramamurthy, S.; Voss, F.R.; Haqqi, T.M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits advanced glycation end product-induced expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and matrix metalloproteinase-13 in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 2009, 11, R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses the global interleukin-1beta-induced inflammatory response in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 2011, 13, R93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, S.; Hayashi, S.; Fujishiro, T.; Kawakita, K.; Kanzaki, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Iwasa, K.; Chinzei, N.; Kihara, S.; Haneda, M. , et al. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and matrix loss of chondrocytes is inhibited by eicosapentaenoic acid. J Orthop Res 2015, 33, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshmand, S.; Soung, d.Y.; Lucas, E.A.; Madihally, S.V.; Levenson, C.W.; Arjmandi, B.H. Genistein reduces the production of proinflammatory molecules in human chondrocytes. J Nutr Biochem 2007, 18, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.C.; Wang, C.C.; Lu, J.W.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, S.C.; Ho, Y.J.; Peng, Y.J. Chondroprotective Effects of Genistein against Osteoarthritis Induced Joint Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, P.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Hu, J. Anti-chondrocyte apoptosis effect of genistein in treating inflammation-induced osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep 2020, 22, 2032–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.D.; Marcussen, K.C. Effects of a ginger extract on knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001, 44, 2531–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, Z.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Dehghan, A.; Nadjarzadeh, A.; Huseini, H.F. Effect of ginger powder supplementation on nitric oxide and C-reactive protein in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients: A 12-week double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Tradit Complement Med 2016, 6, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Riva, A.; Morazzoni, P.; Allegrini, P.; Faliva, M.A.; Naso, M.; Miccono, A.; Peroni, G.; Degli Agosti, I.; Perna, S. The effect and safety of highly standardized Ginger (Zingiber officinale) and Echinacea (Echinacea angustifolia) extract supplementation on inflammation and chronic pain in NSAIDs poor responders. A pilot study in subjects with knee arthrosis. Nat Prod Res 2017, 31, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorndoljai, P.; Taneepanichskul, S.; Niempoog, S.; Nimmannit, U. A Comparative of Ginger Extract in Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC) and 1% Diclofenac Gel for Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis (OA). J Med Assoc Thai 2017, 100, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rondanelli, M.; Riva, A.; Allegrini, P.; Faliva, M.A.; Naso, M.; Peroni, G.; Nichetti, M.; Gasparri, C.; Spadaccini, D.; Iannello, G. , et al. The Use of a New Food-Grade Lecithin Formulation of Highly Standardized Ginger (J Pain Res 2020, 13, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariano, A.; Di Sotto, A.; Leopizzi, M.; Garzoli, S.; Di Maio, V.; Gullì, M.; Dalla Vedova, P.; Ammendola, S.; Scotto d'Abusco, A. Antiarthritic Effects of a Root Extract from. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, A.; Ansari, M.Y.; Haqqi, T.M. Harpagoside suppresses IL-6 expression in primary human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Orthop Res 2017, 35, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantre, P.; Cappelaere, A.; Leblan, D.; Guedon, D.; Vandermander, J.; Fournie, B. Efficacy and tolerance of Harpagophytum procumbens versus diacerhein in treatment of osteoarthritis. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblan, D.; Chantre, P.; Fournié, B. Harpagophytum procumbens in the treatment of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Four-month results of a prospective, multicenter, double-blind trial versus diacerhein. Joint Bone Spine 2000, 67, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Tanzil, G.; Hansen, C.; Shakibaei, M. [Effect of a Harpagophytum procumbens DC extract on matrix metalloproteinases in human chondrocytes in vitro]. Arzneimittelforschung 2004, 54, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, R.; Koike, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Tanaka, K. Double-blind placebo-controlled trial of hydroxytyrosol of Olea europaea on pain in gonarthrosis. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmazoglu, Z.; Colakoglu, M.; Banerjee, S.; Bitik, B.; Aktekin, C.N.; Goker, B.; Karasu, C. AB0090 Verbascoside and hydroxytyrosol downregulate stress-related pathways in human osteoarthritic articular chondrocytes. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2018, 77, 1241. [Google Scholar]
- Wauquier, F.; Mevel, E.; Krisa, S.; Richard, T.; Valls, J.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Granel, H.; Boutin-Wittrant, L.; Urban, N.; Berger, J. , et al. Chondroprotective Properties of Human-Enriched Serum Following Polyphenol Extract Absorption: Results from an Exploratory Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Yang, L. Icariin Regulates Cellular Functions and Gene Expression of Osteoarthritis Patient-Derived Human Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Rong, X.F.; Li, R.H.; Wu, X.Y. Icariin inhibits MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 expression through MAPK pathways in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep 2017, 15, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Zou, W.; Wu, R.M.; Yang, J.; Fan, J.N.; Zhao, X.K.; Li, H.Y. Icariin Alleviates IL-1β-Induced Matrix Degradation By Activating The Nrf2/ARE Pathway In Human Chondrocytes. Drug Des Devel Ther 2019, 13, 3949–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscoya, J.; Rodriguez, Z.; Bustamante, S.A.; Okuhama, N.N.; Miller, M.J.; Sandoval, M. Efficacy and safety of freeze-dried cat's claw in osteoarthritis of the knee: mechanisms of action of the species Uncaria guianensis. Inflamm Res 2001, 50, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yu, X.; Hu, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhong, X.; Xu, J.; Shang, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Isofraxidin targets the TLR4/MD-2 axis to prevent osteoarthritis development. Food Funct 2018, 9, 5641–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Li, X.; Qi, W.; Yan, Y.; Chen, K.; Xue, X.; Xu, X.; Feng, Z.; Pan, X. Isofraxidin inhibits interleukin-1β induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol 2018, 64, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Huo, S. Juglanin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in human chondrocytes. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2019, 47, 3614–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Qiao, J.; Guan, D.; Chen, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Licochalcone A on IL-1β-Stimulated Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrés, M.C.; Meiss, M.S.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; González-Benjumea, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Oreffo, R.O. Osteoarthritis treatment with a novel nutraceutical acetylated ligstroside aglycone, a chemically modified extra-virgin olive oil polyphenol. J Tissue Eng 2020, 11, 2041731420922701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, A.T.; Ribeiro, M.; Sousa, C.; Judas, F.; Salgueiro, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; Mendes, A.F. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic and pro-anabolic effects of E-caryophyllene, myrcene and limonene in a cell model of osteoarthritis. Eur J Pharmacol 2015, 750, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Ying, X. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signal with Myricetin for attenuating ECM degradation in human chondrocytes and ameliorating the murine osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 2019, 75, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotece, M.; Conde, J.; Abella, V.; López, V.; Francisco, V.; Ruiz, C.; Campos, V.; Lago, F.; Gomez, R.; Pino, J. , et al. Oleocanthal Inhibits Catabolic and Inflammatory Mediators in LPS-Activated Human Primary Osteoarthritis (OA) Chondrocytes Through MAPKs/NF-κB Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018, 49, 2414–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Zheng, W.; Hu, Z.; Xuan, J.; Ni, W.; Pan, X. Oleuropein inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Food Funct 2017, 8, 3737–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Eirín, M.; Carpintero-Fernández, P.; Sánchez-Temprano, A.; Varela-Vázquez, A.; Paíno, C.L.; Casado-Díaz, A.; Continente, A.C.; Mato, V.; Fonseca, E.; Kandouz, M. , et al. Senolytic activity of small molecular polyphenols from olive restores chondrocyte redifferentiation and promotes a pro-regenerative environment in osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 15882–15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmazoglu, Z.; Bek, Z.A.; Sarıbaş, G.S.; Özoğul, C.; Goker, B.; Bitik, B.; Aktekin, C.N.; Karasu, Ç. TLR4, RAGE, and p-JNK/JNK mediated inflammatory aggression in osteoathritic human chondrocytes are counteracted by redox-sensitive phenolic olive compounds: Comparison with ibuprofen. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2020, 14, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Xie, Z.; Pei, J.; Wang, B.; Gao, Y.; Qu, Y. Puerarin alters the function of monocytes/macrophages and exhibits chondroprotection in mice. Mol Med Rep 2019, 19, 2876–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Yu, T.; Peng, L.; Wang, L.; Liao, Z.; Xu, W. PIM1, CYP1B1, and HSPA2 Targeted by Quercetin Play Important Roles in Osteoarthritis Treatment by. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019, 2019, 1205942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; He, J.; Gu, H.; Jiang, M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L. Resveratrol inhibits the development of obesity-related osteoarthritis via the TLR4 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Connect Tissue Res 2019, 60, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouf, B.H.; Hussain, S.A.; Ali, Z.S.; Ahmmad, R.S. Resveratrol Supplementation Reduces Pain and Inflammation in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients Treated with Meloxicam: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. J Med Food 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaei, M.; John, T.; Seifarth, C.; Mobasheri, A. Resveratrol inhibits IL-1 beta-induced stimulation of caspase-3 and cleavage of PARP in human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007, 1095, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaki, C.; Keshishzadeh, N.; Fischer, K.; Shakibaei, M. Regulation of inflammation signalling by resveratrol in human chondrocytes in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 2008, 75, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, M.; Attur, M.; Palmer, G.; Al-Mussawir, H.E.; Kennish, L.; Patel, J.; Abramson, S.B. The antioxidant resveratrol protects against chondrocyte apoptosis via effects on mitochondrial polarization and ATP production. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; He, J.; Jiang, M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Gu, H. Resveratrol Exerts Anti-Osteoarthritic Effect by Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway via the TLR4/Akt/FoxO1 Axis in IL-1β-Stimulated SW1353 Cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 2020, 14, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csaki, C.; Mobasheri, A.; Shakibaei, M. Synergistic chondroprotective effects of curcumin and resveratrol in human articular chondrocytes: inhibition of IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Arthritis Res Ther 2009, 11, R165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, K.; Shen, S.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, S.; Ma, J.; Zhao, X. Sanguinarine protects against osteoarthritis by suppressing the expression of catabolic proteases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62900–62913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Zhou, K.; Li, D.; Xie, X.; Jun, F.; Wang, J. Schisantherin A suppresses interleukin-1β-induced inflammation in human chondrocytes via inhibition of NF-κB and MAPKs activation. Eur J Pharmacol 2016, 780, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phitak, T.; Pothacharoen, P.; Settakorn, J.; Poompimol, W.; Caterson, B.; Kongtawelert, P. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of sesamin. Phytochemistry 2012, 80, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.A.; Yeo, Y.; Jung, H.A.; Jung, Y.O.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.J. Phase 2 enzyme inducer sulphoraphane blocks prostaglandin and nitric oxide synthesis in human articular chondrocytes and inhibits cartilage matrix degradation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012, 51, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.A.; Yeo, Y.; Kim, W.U.; Kim, S. Phase 2 enzyme inducer sulphoraphane blocks matrix metalloproteinase production in articular chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009, 48, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, A.; Stanic, I.; Cetrullo, S.; Borzì, R.M.; Filardo, G.; Flamigni, F. Sulforaphane protects human chondrocytes against cell death induced by various stimuli. J Cell Physiol 2011, 226, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.K.; Jupp, O.; de Ferrars, R.; Kay, C.D.; Culley, K.L.; Norton, R.; Driscoll, C.; Vincent, T.L.; Donell, S.T.; Bao, Y. , et al. Sulforaphane represses matrix-degrading proteases and protects cartilage from destruction in vitro and in vivo. Arthritis Rheum 2013, 65, 3130–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.; Gardner, S.; Jupp, O.; Bullough, A.; Butters, S.; Watts, L.; Donell, S.; Traka, M.; Saha, S.; Mithen, R. , et al. Isothiocyanates are detected in human synovial fluid following broccoli consumption and can affect the tissues of the knee joint. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Jeong, G.J.; Im, G.I. Sulforaphane-PLGA microspheres for the intra-articular treatment of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5359–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, T.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Taraxasterol inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 2015, 756, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Jeong, J.W.; Lee, D.S.; Yim, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Han, M.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, G.Y.; Park, E.K. , et al. Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, T.; Guan, D. Thymoquinone Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Inflammation in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes by Suppressing NF-κB and MAPKs Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 2015, 38, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.M.; Haseeb, A.; Ansari, M.Y.; Haqqi, T.M. A wogonin-rich-fraction of Scutellaria baicalensis root extract exerts chondroprotective effects by suppressing IL-1β-induced activation of AP-1 in human OA chondrocytes. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 43789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.M.; Haseeb, A.; Ansari, M.Y.; Devarapalli, P.; Haynie, S.; Haqqi, T.M. Wogonin, a plant derived small molecule, exerts potent anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects through the activation of ROS/ERK/Nrf2 signaling pathways in human Osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 106, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Ahmad, I.; Ansari, M.Y.; Haqqi, T.M. Wogonin, a natural flavonoid, intercalates with genomic DNA and exhibits protective effects in IL-1β stimulated osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Chem Biol Interact 2017, 274, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yue, L.; Yang, H.; Fan, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, C.; Lin, M. , et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of amurensin H by regulating TLR4/Syk/NF-κB signals. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K. Artesunate attenuates ACLT-induced osteoarthritis by suppressing osteoclastogenesis and aberrant angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother 2017, 96, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Guo, X.H.; Tang, C.; Yue, S.T.; Shi, L.; Qiang, B. Effects of Artesunate on the Expressions of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1, Osteopontin and C-Telopeptides of Type II Collagen in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Pharmacology 2018, 101, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumediene, K.; Felisaz, N.; Bogdanowicz, P.; Galera, P.; Guillou, G.B.; Pujol, J.P. Avocado/soya unsaponifiables enhance the expression of transforming growth factor beta1 and beta2 in cultured articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 1999, 42, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Afify, A.S.A.; El-Akabawy, G.; El-Sherif, N.M.; El-Safty, F.E.A.; El-Habiby, M.M. Avocado soybean unsaponifiables ameliorates cartilage and subchondral bone degeneration in mono-iodoacetate-induced knee osteoarthritis in rats. Tissue Cell 2018, 52, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinecke, L.F.; Grzanna, M.W.; Au, A.Y.; Mochal, C.A.; Rashmir-Raven, A.; Frondoza, C.G. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 production in chondrocytes by avocado soybean unsaponifiables and epigallocatechin gallate. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2010, 18, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ownby, S.L.; Fortuno, L.V.; Au, A.Y.; Grzanna, M.W.; Rashmir-Raven, A.M.; Frondoza, C.G. Expression of pro-inflammatory mediators is inhibited by an avocado/soybean unsaponifiables and epigallocatechin gallate combination. J Inflamm (Lond) 2014, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frondoza, C.G.; Fortuno, L.V.; Grzanna, M.W.; Ownby, S.L.; Au, A.Y.; Rashmir-Raven, A.M. α-Lipoic Acid Potentiates the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables in Chondrocyte Cultures. Cartilage 2018, 9, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzanna, M.W.; Secor, E.J.; Fortuno, L.V.; Au, A.Y.; Frondoza, C.G. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Carprofen Is Enhanced by Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables, Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate Combination in Chondrocyte Microcarrier Spinner Culture. Cartilage 2020, 11, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, P.; Liu, R.; Meng, Q.; Li, S. Baicalin promotes extracellular matrix synthesis in chondrocytes via the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Exp Ther Med 2020, 20, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Lu, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Li, Z. Baicalin prevents the apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes by inhibiting the oxidative stress induced by H2O2. Mol Med Rep 2017, 16, 2985–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, P.D.; Jeong, H.S.; Chun, C.S.; Kim, H.M. Baekjeolyusin-tang and its active component berberine block the release of collagen and proteoglycan from IL-1β-stimulated rabbit cartilage and down-regulate matrix metalloproteinases in rabbit chondrocytes. Phytother Res 2011, 25, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.F.; Chen, W.P.; Tang, J.L.; Bao, J.P.; Wu, L.D. Protective effects of berberine in an experimental rat osteoarthritis model. Phytother Res 2011, 25, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Xia, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Zheng, X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, B. Berberine ameliorates cartilage degeneration in interleukin-1β-stimulated rat chondrocytes and in a rat model of osteoarthritis via Akt signalling. J Cell Mol Med 2014, 18, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Yu, L.; He, B.; Wu, S.H.; Zhao, Q.; Xia, S.Q.; Mei, H.J. Berberine prevents nitric oxide-induced rat chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degeneration in a rat osteoarthritis model via AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, H.; Li, Y.; Deng, M.; He, B.; Xia, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S. Berberine promotes proliferation of sodium nitroprusside-stimulated rat chondrocytes and osteoarthritic rat cartilage via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2016, 789, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, P.; Hou, Y.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.; Zhan, J.; Luo, D.; Gu, M.; Lin, D. Berberine inhibits the interleukin-1 beta-induced inflammatory response via MAPK downregulation in rat articular chondrocytes. Drug Dev Res 2019, 80, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Chen, H.; Xu, C. Chondro-protective effects of celastrol on osteoarthritis through autophagy activation and NF-κB signaling pathway inhibition. Inflamm Res 2020, 69, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ha, C.; Lin, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Gong, M. Celastrol attenuates pain and cartilage damage via SDF-1/CXCR4 signalling pathway in osteoarthritis rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 2018, 70, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.D.; Zhang, B.L.; Yang, J.B.; Zhou, K. Celastrol ameliorates endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis of osteoarthritis via regulating ATF-6/CHOP signalling pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol 2020, 72, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, J.T.; Ma, B.J.; Ji, Y.; Jin, Y.Y.; Wu, S.Y.; Wu, T.; Ma, K. Intra-articular delivery of celastrol by hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-sensitive anti-inflammatory therapy against knee osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Ahn, S.; Noh, H.Y.; Kumar, N.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Therapeutic potential of compound K as an IKK inhibitor with implications for osteoarthritis prevention: an in silico and in vitro study. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2016, 52, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Guo, C.; Hua, L.; Xue, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D. Crocin Attenuates Joint Pain and Muscle Dysfunction in Osteoarthritis Rat. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Zhong, H.; Qi, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, S.; Wang, X. Anti-arthritic effects of crocin in interleukin-1β-treated articular chondrocytes and cartilage in a rabbit osteoarthritic model. Inflamm Res 2013, 62, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clutterbuck, A.L.; Mobasheri, A.; Shakibaei, M.; Allaway, D.; Harris, P. Interleukin-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2009, 1171, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clutterbuck, A.L.; Allaway, D.; Harris, P.; Mobasheri, A. Curcumin reduces prostaglandin E2, matrix metalloproteinase-3 and proteoglycan release in the secretome of interleukin 1β-treated articular cartilage. F1000Res 2013, 2, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Gu, J.H.; Wang, F.Y.; Shang, X.S.; Tao, H.R.; Wang, X. Regulation of type II collagen, matrix metalloproteinase-13 and cell proliferation by interleukin-1β is mediated by curcumin via inhibition of NF-κB signaling in rat chondrocytes. Mol Med Rep 2017, 16, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Feng, K.; Li, J.; Yu, D.; Fan, Q.; Tang, T.; Yao, X.; Wang, X. Curcumin Inhibits Apoptosis of Chondrocytes through Activation ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways Induced Autophagy. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; He, B.; Guo, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Involvement of TLR4 in the protective effect of intra-articular administration of curcumin on rat experimental osteoarthritis. Acta Cir Bras 2019, 34, e201900604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.L.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.R.; Choi, B.K.; Yang, S.H. Herbal Composition LI73014F2 Alleviates Articular Cartilage Damage and Inflammatory Response in Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis in Rats. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.H.; Ye, C.Y.; Chen, E.M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.H. Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo. Int Immunopharmacol 2018, 61, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lang, Y.; Li, L.; Liang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Fang, R.; Meng, Q. Effect of emodin on chondrocyte viability in an. Exp Ther Med 2018, 16, 5384–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Bai, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Gao, L. Emodin protects knee joint cartilage in rats through anti-matrix degradation pathway: An in vitro and in vivo study. Life Sci 2021, 269, 119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, J.P.; Gandy, J.C.; Brown, J.L.; Sordillo, L.M. Omega-3 fatty acids and docosahexaenoic acid oxymetabolites modulate the inflammatory response of equine recombinant interleukin1β-stimulated equine synoviocytes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 2019, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wann, A.K.; Mistry, J.; Blain, E.J.; Michael-Titus, A.T.; Knight, M.M. Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid reduce interleukin-1β-mediated cartilage degradation. Arthritis Res Ther 2010, 12, R207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal, Z.; Longman, A.J.; Hurst, S.; Duggan, K.; Caterson, B.; Hughes, C.E.; Harwood, J.L. Relative efficacies of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in reducing expression of key proteins in a model system for studying osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2009, 17, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shou, K.; Gong, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Bao, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Osteoarthritis by Suppressing the Activation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int 2018, 2018, 8384576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Shi, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, R.; Wu, D.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J. Geniposide Suppresses Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Rat Chondrocytes via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 2018, 41, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Bao, T.Z.; Chen, K.; Zhu, C.M.; Wan, F.; Tan, Y.L.; Yan, F. [Effects of geniposide on SNP-induced apoptosis of chondrocyte and cell cycle]. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2013, 26, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Ding, W.; Wu, N.; Jiang, S.; Li, W. Protective Effect of Genistein on Condylar Cartilage through Downregulating NF-. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019, 2629791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Crane, J.; Xie, H.; Jin, X.; Zhen, G.; Li, C.; Xie, L.; Wang, L.; Bian, Q.; Qiu, T. , et al. Halofuginone attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibition of TGF-β activity and H-type vessel formation in subchondral bone. Ann Rheum Dis 2016, 75, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Xu, B.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Ji, B.; Zhang, Z.; Amat, A.; Cao, L. Halofuginone Attenuates Osteoarthritis by Rescuing Bone Remodeling in Subchondral Bone Through Oral Gavage. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Xu, B.; Ma, H.; Ji, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Amat, A.; Cao, L. Halofuginone attenuates articular cartilage degeneration by inhibition of elevated TGF-β1 signaling in articular cartilage in a rodent osteoarthritis model. Mol Med Rep 2017, 16, 7679–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrubasik, J.E.; Lindhorst, E.; Neumann, E.; Gerlach, U.; Faller-Marquardt, M.; Torda, T.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Chrubasik, S. Potential molecular basis of the chondroprotective effect of Harpagophytum procumbens. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, D.; Geng, C.; Jiang, L.; Cao, J.; Yoshimura, H.; Zhong, L. Effects of hydroxytyrosol-20 on carrageenan-induced acute inflammation and hyperalgesia in rats. Phytother Res 2009, 23, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuma, M.; Haruka, K.; Mutsuto, W.; Toshiki, M.; Kenshiro, M.; Akane, T.; Hiroshi, M.; Yoshihiro, N. Olive leaf extract prevents cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis of STR/ort mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2018, 82, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mével, E.; Merceron, C.; Vinatier, C.; Krisa, S.; Richard, T.; Masson, M.; Lesoeur, J.; Hivernaud, V.; Gauthier, O.; Abadie, J. , et al. Olive and grape seed extract prevents post-traumatic osteoarthritis damages and exhibits in vitro anti IL-1β activities before and after oral consumption. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 33527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Luo, J.; Jing, X.; Xiang, W.; Guo, J.; Yao, X.; Liang, S.; Guo, F.; Xu, T. Hyperoside ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Jiao, F. Icariin accelerates cartilage defect repair by promoting chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs under conditions of oxygen-glucose deprivation. J Cell Mol Med 2022, 26, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Guo, F.; Xu, T. Role of IFT88 in icariin-regulated maintenance of the chondrocyte phenotype. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Qin, F.W.; Tang, W.; Liu, D.H.; Wu, P.Y.; Jiao, F. Icariin inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and angiogenesis by regulating the TDP-43 signaling pathway. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2019, 7, e00586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mi, B.; Lv, H.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, L.; Xue, H.; Panayi, A.C.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W. Shared KEGG pathways of icariin-targeted genes and osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, D.; Jiao, F. Icariin protects rabbit BMSCs against OGD-induced apoptosis by inhibiting ERs-mediated autophagy via MAPK signaling pathway. Life Sci 2020, 253, 117730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.P.; Hu, Z.N.; Jin, L.B.; Wu, L.D. Licochalcone A Inhibits MMPs and ADAMTSs via the NF-κB and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways in Rat Chondrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017, 43, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Qi, W.; Zhan, J.; Lin, Z.; Lin, J.; Xue, X.; Pan, X.; Zhou, Y. Activating Nrf2 signalling alleviates osteoarthritis development by inhibiting inflammasome activation. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 13046–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wang, S.; He, J.; Bian, Y. Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-activated apoptosis and related inflammation in chondrocytes. Mol Med Rep 2022, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Huang, G. Intra-articular delivery of tetramethylpyrazine microspheres with enhanced articular cavity retention for treating osteoarthritis. Asian J Pharm Sci 2018, 13, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Feng, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, K.; Sun, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, C.H.; Lu, W.W.; Chiu, K.Y. Magnoflorine with hyaluronic acid gel promotes subchondral bone regeneration and attenuates cartilage degeneration in early osteoarthritis. Bone 2018, 116, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Hong, M.; Xu, L.; Yang, K.; Li, C.; Sun, T.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, H.; Lu, W.W.; Chiu, K.Y. Prevent action of magnoflorine with hyaluronic acid gel from cartilage degeneration in anterior cruciate ligament transection induced osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 126, 109733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, A.; Gómez, R.; Sperry, J.; Conde, J.; Bianco, G.; Meli, R.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Smith, A.B.; Gualillo, O. Effect of oleocanthal and its derivatives on inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide in a murine chondrocyte cell line. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotece, M.; Gómez, R.; Conde, J.; Lopez, V.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Lago, F.; Smith, A.B.; Gualillo, O. Further evidence for the anti-inflammatory activity of oleocanthal: inhibition of MIP-1α and IL-6 in J774 macrophages and in ATDC5 chondrocytes. Life Sci 2012, 91, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aini, H.; Ochi, H.; Iwata, M.; Okawa, A.; Koga, D.; Okazaki, M.; Sano, A.; Asou, Y. Procyanidin B3 prevents articular cartilage degeneration and heterotopic cartilage formation in a mouse surgical osteoarthritis model. PLoS One 2012, 7, e37728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, I.; Koike, M.; Nakashima, S.; Mizutani, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Sawada, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Sugimoto, A.; Nojiri, H. , et al. Apple procyanidins promote mitochondrial biogenesis and proteoglycan biosynthesis in chondrocytes. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.W.; Wen, Y.J.; Song, X.P.; Hu, H.L.; Li, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhao, M.C.; Gao, L. Puerarin inhibits the development of osteoarthritis through antiinflammatory and antimatrix-degrading pathways in osteoarthritis-induced rat model. Phytother Res 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Sun, H.; Hong, H.; Jin, J.; Bei, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X. Puerarin suppresses inflammation and ECM degradation through Nrf2/HO-1 axis in chondrocytes and alleviates pain symptom in osteoarthritic mice. Food Funct 2021, 12, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shan, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, N.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, C.; Wang, F. Puerarin Attenuates Osteoarthritis via Upregulating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase/Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator-1 Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis Rats. Pharmacology 2018, 102, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ji, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Protective effects of quercetin against inflammation and oxidative stress in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Drug Dev Res 2019, 80, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gui, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, L.; Lin, K.; Xu, Y. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 145, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, T. Therapeutic effect and mechanism of action of quercetin in a rat model of osteoarthritis. J Int Med Res 2020, 48, 300060519873461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permatasari, D.A.; Karliana, D.; Iskandarsyah, I.; Arsianti, A.; Bahtiar, A. Quercetin prevent proteoglycan destruction by inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9, matrix metalloproteinase-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-5 expressions on osteoarthritis model rats. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2019, 10, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britti, D.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Gugliandolo, E.; Fusco, R.; Schievano, C.; Morittu, V.M.; Evangelista, M.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. A novel composite formulation of palmitoylethanolamide and quercetin decreases inflammation and relieves pain in inflammatory and osteoarthritic pain models. BMC Vet Res 2017, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, J.S.; Chen, J.W.; Li, F.; Tian, J. Effect of resveratrol on cartilage protection and apoptosis inhibition in experimental osteoarthritis of rabbit. Rheumatol Int 2012, 32, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmali, N.; Esenkaya, I.; Harma, A.; Ertem, K.; Turkoz, Y.; Mizrak, B. Effect of resveratrol in experimental osteoarthritis in rabbits. Inflamm Res 2005, 54, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Jia, J.; Jin, X.; Tong, W.; Tian, H. Resveratrol ameliorates inflammatory damage and protects against osteoarthritis in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, L. Oral Resveratrol Prevents Osteoarthritis Progression in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2016, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, M.N.; Sanchez, C.; Membrez Scalfo, F.; Drion, P.; Comblain, F.; Taralla, S.; Donneau, A.F.; Offord, E.A.; Henrotin, Y. Oleuropein or rutin consumption decreases the spontaneous development of osteoarthritis in the Hartley guinea pig. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2015, 23, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Santoso, M.B.; Wu, L.D. Sclareol exerts anti-osteoarthritic activities in interleukin-1β-induced rabbit chondrocytes and a rabbit osteoarthritis model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015, 8, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Shang, X.; Ni, Z.; Shi, G. Shikonin inhibits inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis by regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med 2016, 12, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, B.; Xue, F.; Yang, W.; Chang, R.; Ma, K.; Qiu, Y. Shikonin inhibits inflammatory responses in rabbit chondrocytes and shows chondroprotection in osteoarthritic rabbit knee. Int Immunopharmacol 2015, 29, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gai, P.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Shikonin protects chondrocytes from interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis by regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015, 8, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.D.; Deng, M.; Ao, Y.F.; Yu, C.L.; Wang, J.Q.; Yu, J.K.; Cui, G.Q.; Hu, Y.L. Protective effect of sinomenine on cartilage degradation and chondrocytes apoptosis. Yakugaku Zasshi 2010, 130, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Yu, K. Sinomenine contributes to the inhibition of the inflammatory response and the improvement of osteoarthritis in mouse-cartilage cells by acting on the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 2019, 75, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, B.; Poulet, B.; Aljazzar, A.; de Souza, R.; Piles, M.; Hopkinson, M.; Shervill, E.; Pollard, A.; Chan, B.; Chang, Y.M. , et al. Stable sulforaphane protects against gait anomalies and modifies bone microarchitecture in the spontaneous STR/Ort model of osteoarthritis. Bone 2017, 103, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudirman, S.; Chen, C.K.; Long, B.T.; Chang, H.W.; Tsou, D.; Kong, Z.L. Nut Triterpene-Rich Extract Ameliorates Symptoms of Inflammation on Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis in Obese Rats. J Pain Res 2020, 13, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Jo, H.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Nam, D.C.; Lee, C.J.; Hwang, S.C. Chondroprotective Effects of Wogonin in Experimental Models of Osteoarthritis in vitro and in vivo. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2015, 23, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.F.; Starr, E.G.; Goodman, M.A.; Hanson, R.B.; Palmer, T.A.; Woolstenhulme, J.B.; Weyand, J.A.; Marchant, A.D.; Bueckers, S.L.; Nelson, T.K. , et al. Topical Application of Wogonin Provides a Novel Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, O.S.; Sant, K.E.; Dolinoy, D.C. Nutrition and epigenetics: an interplay of dietary methyl donors, one-carbon metabolism and DNA methylation. J Nutr Biochem 2012, 23, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Friso, S. Epigenetics: A New Bridge between Nutrition and Health. Adv Nutr 2010, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Bhawal, S.; Kapila, S.; Yadav, H.; Kapila, R. Health-promoting role of dietary bioactive compounds through epigenetic modulations: a novel prophylactic and therapeutic approach. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 619–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahid, F.; Zand, H.; Nosrat-Mirshekarlou, E.; Najafi, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. The role dietary of bioactive compounds on the regulation of histone acetylases and deacetylases: a review. Gene 2015, 562, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley-Evans, S.C. Developmental programming of health and disease. Proc Nutr Soc 2006, 65, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmurzynska, A. Fetal programming: link between early nutrition, DNA methylation, and complex diseases. Nutr Rev 2010, 68, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirtle, R.L.; Skinner, M.K. Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Genet 2007, 8, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharski, R.; Maleszka, J.; Foret, S.; Maleszka, R. Nutritional control of reproductive status in honeybees via DNA methylation. Science 2008, 319, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, G.L.; Kodell, R.L.; Moore, S.R.; Cooney, C.A. Maternal epigenetics and methyl supplements affect agouti gene expression in Avy/a mice. FASEB J 1998, 12, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aagaard-Tillery, K.M.; Grove, K.; Bishop, J.; Ke, X.; Fu, Q.; McKnight, R.; Lane, R.H. Developmental origins of disease and determinants of chromatin structure: maternal diet modifies the primate fetal epigenome. J Mol Endocrinol 2008, 41, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinoy, D.C.; Weidman, J.R.; Waterland, R.A.; Jirtle, R.L. Maternal genistein alters coat color and protects Avy mouse offspring from obesity by modifying the fetal epigenome. Environ Health Perspect 2006, 114, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, W.C.; Wu, K.L.H.; Leu, S.; Chan, J.Y.H. Resveratrol Prevents the Development of Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Plus Post-Weaning High-Fructose Consumption through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Nutrient-Sensing Signals, and Gut Microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res 2018, e1800066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remely, M.; Lovrecic, L.; de la Garza, A.L.; Migliore, L.; Peterlin, B.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, A.J.; Haslberger, A.G. Therapeutic perspectives of epigenetically active nutrients. Br J Pharmacol 2015, 172, 2756–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, M.; Srinivasan, A. Epigenetic Gene Regulation by Dietary Compounds in Cancer Prevention. Adv Nutr 2019, 10, 1012–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Shim, J.Y.; Zhu, B.T. Mechanisms for the inhibition of DNA methyltransferases by tea catechins and bioflavonoids. Mol Pharmacol 2005, 68, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, K.D. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 2005, 6, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet 2008, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, C.S. Dietary polyphenols may affect DNA methylation. J Nutr 2007, 137, 223S–228S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, E.E.; Bachman, K.E.; Myöhänen, S.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B. Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat Genet 1999, 21, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Kumar, D.; Srivastava, R.K. Epigenetic modifications by dietary phytochemicals: implications for personalized nutrition. Pharmacol Ther 2013, 138, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, A.; Balaguer, F.; Goel, A. Cancer chemoprevention by dietary polyphenols: promising role for epigenetics. Biochem Pharmacol 2010, 80, 1771–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, X. Correlation analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNA HOTAIR with PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway and inflammation in patients with osteoarthritis and the effect of baicalin intervention. J Orthop Surg Res 2023, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. Baicalin Protects Human OA Chondrocytes Against IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and ECM Degradation by Activating Autophagy via MiR-766-3p/AIFM1 Axis. Drug Des Devel Ther 2020, 14, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L. Baicalin alleviates IL-1β-induced inflammatory injury via down-regulating miR-126 in chondrocytes. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 99, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Qi, D.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Goodman, S.B.; Kang, L.; Song, Q.; Fan, Z.; Maloney, W.J.; Wang, Y. Cryptotanshinone Protects Cartilage against Developing Osteoarthritis through the miR-106a-5p/GLIS3 Axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Cao, G.; Ba, X.; Jiang, H. Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate promotes extracellular matrix and inhibits inflammation in IL-1B stimulated chondrocytes by the PTEN/miRNA-29b pathway. Pharm Biol 2022, 60, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Rasheed, N.; Al-Shaya, O. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate modulates global microRNA expression in interleukin-1β-stimulated human osteoarthritis chondrocytes: potential role of EGCG on negative co-regulation of microRNA-140-3p and ADAMTS5. Eur J Nutr 2018, 57, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Rasheed, N.; Al-Shobaili, H.A. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate up-regulates microRNA-199a-3p expression by down-regulating the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in stimulated human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Cell Mol Med 2016, 20, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Feng, Z.; You, S.; Zhang, H.; Tao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y. Fisetin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through activating SIRT1 and attenuates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2017, 45, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetrullo, S.; D'Adamo, S.; Guidotti, S.; Borzì, R.M.; Flamigni, F. Hydroxytyrosol prevents chondrocyte death under oxidative stress by inducing autophagy through sirtuin 1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1860, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchini, A.; Cetrullo, S.; D'Adamo, S.; Guidotti, S.; Minguzzi, M.; Borzì, R.M.; Flamigni, F. Hydroxytyrosol prevents increase of osteoarthritis markers in human chondrocytes treated with hydrogen peroxide or growth-related oncogene α. PLoS One 2014, 9, e109724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Adamo, S.; Cetrullo, S.; Guidotti, S.; Borzì, R.M.; Flamigni, F. Hydroxytyrosol modulates the levels of microRNA-9 and its target sirtuin-1 thereby counteracting oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte death. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2017, 25, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Adamo, S.; Cetrullo, S.; Borzì, R.M.; Flamigni, F. Effect of oxidative stress and 3-hydroxytyrosol on DNA methylation levels of miR-9 promoters. J Cell Mol Med 2019, 23, 7885–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Yan, W.; Xu, K.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Ran, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, L. Oleanolic Acid Decreases IL-1. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 7517219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Jiang, P. Oleanolic acid mitigates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte dysfunction by regulating miR-148-3p-modulated FGF2 expression. J Gene Med 2020, 22, e3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xu, G.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L. Exosomes Derived from Quercetin-Treated Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Progression of Osteoarthritis Through Delivering miR-124-3p to Chondrocytes. DNA Cell Biol 2024, 43, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Xing, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Hao, Y.; Qiu, B. Resveratrol Improves the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating the SIRT1-FoxO1 Pathway-Mediated Cholesterol Metabolism. Mediators Inflamm 2023, 2023, 2936236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Zhang, W.; Cui, S.Y.; Fan, J.B.; Zhu, X.H.; Liu, W. Identification and validation of key long non-coding RNAs in resveratrol protect against IL-1β-treated chondrocytes via integrated bioinformatic analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 2021, 16, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Hu, B.; Zhang, M. Sirt1 regulates apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in resveratrol-treated osteoarthritis chondrocytes via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med 2017, 14, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, É.; Delalandre, A.; Lajeunesse, D. Beneficial effect of resveratrol on phenotypic features and activity of osteoarthritic osteoblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 2017, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.; Su, X.; Teng, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, M. Cryptotanshinone interferes with chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the expression of miR-574-5p. Mol Med Rep 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Long, Y.; Yang, J.M.; Wu, Y.L.; Dong, L.Y.; Zhong, Y.B.; Luo, Y.; Wang, M.Y. Curcumin regulates autophagy through SIRT3-SOD2-ROS signaling pathway to improve quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy in KOA rat model. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Ge, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Tang, T.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. Curcumin Inhibits the PERK-eIF2. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 8574386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Xu, X.; Yi, P.; Hao, Y. Curcumin reinforces MSC-derived exosomes in attenuating osteoarthritis via modulating the miR-124/NF-kB and miR-143/ROCK1/TLR9 signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 10855–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Lei, Z.; Yang, X. Fisetin suppresses chondrocyte senescence and attenuates osteoarthritis progression by targeting sirtuin 6. Chem Biol Interact 2024, 390, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, L.Q.; Yao, S.X.; Liu, H.L.; Li, M.; Duan, N.; Ma, J.B. Hydroxytyrosol inhibits the inflammatory response of osteoarthritis chondrocytes via SIRT6-mediated autophagy. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 4035–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.; Zhu, T.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J. Quercetin Modulates Ferroptosis via the SIRT1/Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathway and Attenuates Cartilage Destruction in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Chen, Z.; Pengcheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 18192–18205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X. Quercetin attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and biogenesis via upregulated AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway in OA rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 103, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Xing, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Hao, Y.; Qiu, B. Resveratrol protection against IL-1β-induced chondrocyte damage via the SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res 2022, 17, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; You, W.; Tang, X.; Li, X.; Gong, Z. Therapeutic effect of Resveratrol in the treatment of osteoarthritis via the MALAT1/miR-9/NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 2020, 19, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Wang, J.G.; Xiao, D.M.; Fan, M.; Wang, D.P.; Xiong, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S.L. Resveratrol inhibits interleukin 1β-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in articular chondrocytes by activating SIRT1 and thereby suppressing nuclear factor-κB activity. Eur J Pharmacol 2012, 674, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M. Saikosaponin D alleviates inflammatory response of osteoarthritis and mediates autophagy via elevating microRNA-199-3p to target transcription Factor-4. J Orthop Surg Res 2024, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.C.; Li, P.N.; Chen, C.J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Zheng, L.J.; Li, P. Sinomenine Attenuates Cartilage Degeneration by Regulating miR-223-3p/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling. Inflammation 2019, 42, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, W.; Zeng, J.; Shao, X.; Xu, L.; Jia, L.; He, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, C. , et al. Tougu Xiaotong capsules may inhibit p38 MAPK pathway-mediated inflammation: In vivo and in vitro verification. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 249, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
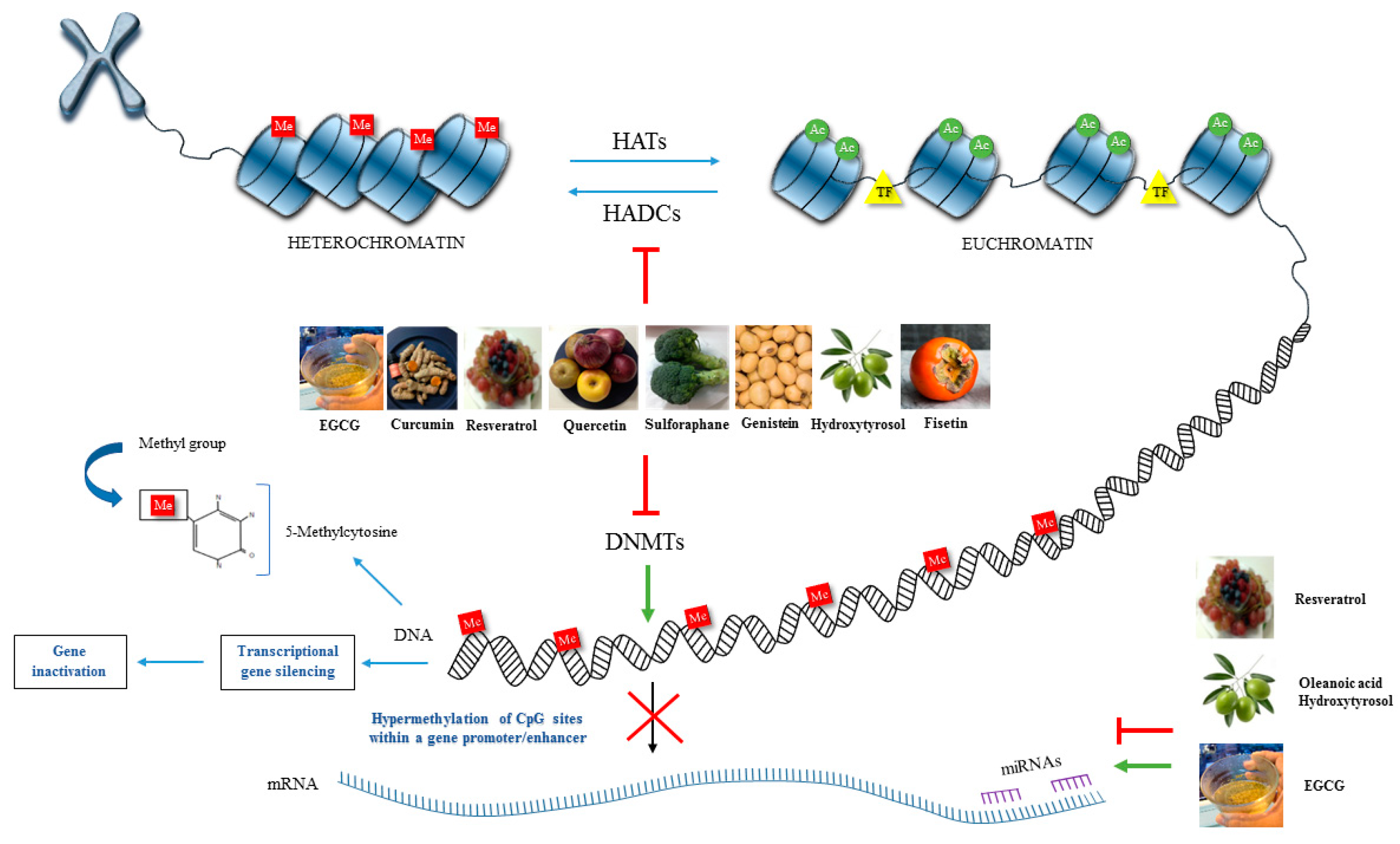
| Bioactive compounds | Sources/classes | Effects of bioactive compounds | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ALM16 Herbal mixture Major active compounds: (calycosin, calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside) lithospermic acid |
Dried roots of: (Astragalus membranaceus) Isoflavonoids (Lithospermum erythrorhizon) Phenolic acid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced SW1353 chondrocytes: Prevented glycosaminoglycan degradation Inhibited MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 levels |
[146] |
|
Anthocyanidins: (Cyanidin-3-glucoside, pelargoni din3-glucoside) Flavonols: (Quercetin, kaempferol, mirycetin) Flavanols: (Epigallocatechin 3-gallate, catechin) Ellagitannins |
(Fragaria ananassa) Strawberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) Blueberry (Punica granatum L) pomegranate Approx. 40 Phenolic compounds identified: Flavonoids Tannins |
Effects in obese patients with knee OA: Alleviated pain and enhanced quality of life Decreased markers of inflammation and cartilage degradation Decreased IL-6, IL-1β, and MMP-3 levels in blood samples Effects in knee OA patients: Decreased pain and stiffness and improved gait performance and quality of life Improvement in daily physical activities Effects in OA chondrocytes: Suppressed the IL-1β-induced activation of RUNX-2, MKK3/6 and p38-MAPK isoforms in chondrocytes derived from OA cartilage Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Downregulated MMP1, MMP3, and MMP13 mRNA expression Inhibited activation of APKs and the DNA binding activity of NF-κB |
[147] [148] [149] [150] |
|
Arctigenin (Phenylpropanoid dibenzylbutyrolactone) |
Arctium lappa Greater burdock Lignan |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Decreased ECM degradation Enhanced ECM synthesis and upregulated COL2A1 and ACAN Downregulated MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 Decreased IL6, NOS2, TNFA and COX2 in mRNA and protein expression Inhibition of NF-κB/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway |
[151] |
|
Astragalin (kaempferol 3-glu-coside) |
Leaf extract of: Rosa agrestis Flavonoids |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammatory responses Inhibited NO, PGE2, NF-κB, ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK production by PPAR-γ activation in a dose-dependent manner |
[152] |
|
Avocado/Soybean Unsaponificables ASU (β-sitosterol, campesterol, and stigmasterol) Triterpenes |
Persea gratissima and Glycine max mixture of avocado and soybean unsaponifiables (Phytosterols) Triterpene alcohols |
Effects in IL-1β induced OA chondrocytes: Promoted cartilage repair Inhibited IL-6, IL-8, MIP-1β, MMP-3, NO, and PGE2 production Stimulated TIMP-1, TGF-β1, and ACAN production Effects in OA subchondral osteoblasts/OA chondrocytes: Promoted regulation of anabolic and catabolic processes Downregulated ALP, OC, and TGF-β1 levels Prevented inhibition of ECM components (COL2A1 and ACAN mRNA expression) Effects in LPS-stimulated monocyte/macrophage-like cell associated with the synovial membrane: Showed anti-inflammatory effects Supressed TNFA, IL1B, COX2, NOS2 gene expression Downregulated PGE2 and nitrite production Effects in chondrocytes: Attenuate inflammatory response both at gene transcription and protein level Reduced G-CSF, RANTES and PGE2 levels induced by LPS Increased 12,13-DiHOME |
[153] [154] [155] [156] |
| Baicalin |
(Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi) Mainly extracted from dry root Flavone glycoside (flavonoid) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Reduced COX2, NOS2, MMP3, MMP13 and ADAMTS5 gene expression via inhibition of NF-κB activation Inhibited NO and PGE2 production Inhibited the downregulation of ACAN and COL2A1 mRNA |
[157] |
| Berberine | Medicinal herbs: Hydrastis canadensis Berberis aristate Cortex phellodendri Coptis chinensis Isoquinoline-derivative alkaloid |
Effects in OA synovial fibroblast: Attenuated CCN2-induced IL-1β expression, via inhibition of ROS-related ASK1, p38/JNK, NF-κB signalling pathways |
[158] |
|
Butein |
Rhus verniciflua stem bark of cashews and the genera Dahlia, Butea, Searsia (Rhus) and Coreopsis are common sources Chalcones (flavonoids) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Inhibited IκB-α degradation and NF-κB p65 activation Downregulated COX2, NOS2, IL6, TNFA, MMP13 gene and protein expression Inhibited MMP1, MMP3, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 mRNA expression Reduced the degradation of COL2A1 and SOX9 mRNA and protein expression Downregulated NO and PGE2 production |
[159] |
|
Casticin (Vitexicarpin) |
Vitex rotundifolia L Polymethoxyflavonoid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Prevented inflammation by inhibition of NF-κB signalling pathway Decreased NO, PGE2, TNF-α, IL-6, MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 production Inhibited NOS2 and COX2 mRNA and protein expression Increased ACAN and COL2A1 mRNA expression |
[160] |
| Celastrol |
(Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F.) root bark "Thunder of God Vine" Pentaciclic Triterpenes |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Suppressed the activation NF-κB in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes Inhibited HSP90B, COX2, NOS2, MMP1, MMP3, MMP13 mRNA and protein expression Decreased NO and PGE2 levels |
[161] |
| Cinnamophilin |
(Cinnamomum philippinense) Extracted from the root Lignan |
Effects in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 chondrocytic cell line: Showed chondroprotective properties against collagen matrix breakdown Inhibited MMP-1, and MMP-13 activity via inhibition of NF-κB, JNK, ERK, and p38 MAPK Inhibited IκB-α degradation, and phosphorylation of IKK-α/β and p65 Blocked the activity of c-Jun by inhibition of JNK |
[162] |
|
Cryptotanshinone |
(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) Extracted from the root of the plant Diterpene quinones |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammation by suppression of nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and MAPK activation Inhibited phosphorylation of IκB, IKKα/β and IκBα degradation Suppressed NO, PGE2, IL-6, TNF-α, NOS2, COX-2, MMP-3, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-5 levels |
[163] |
|
Curcuminoids: Curcumin Demethoxycurcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin |
(Curcuma longa) (Curcuma domestica) Turmeric rhizome Diarylheptanoids (Phenolic compounds) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Protected against catabolic effects Inhibited suppression of COL2A1 synthesis Inhibited NF-κB signalling pathway and prevented its translocation to the nucleus Inhibited MMP-3 synthesis Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Demonstrated chondroprotective, anti-apoptotic and anti-catabolic properties Inhibited cell degradation Inhibited suppression of COL2A1 Increased β1-integrin receptors synthesis Decreased caspase-3 activation (antiapoptotic effect) Effects in chondrocytes: Demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects stimulated by IL-1 and TNF-α Suppressed NF-κB activation and inhibited p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation Blocked the IκBα phosphorylation and degradation Inhibited IL-1β-induced Akt phosphorylation Inhibited COX-2 and MMP-9 synthesis Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes/OA cartilage explants: Demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity Suppressed ECM degradation Inhibited MMP-3, PGE2, NO, IL-6, and IL-8 production Effects in knee OA patients: Showed that C. domestica extracts were as efficacious as ibuprofen Demonstrated pain reduction and functional improvement Showed fewer gastrointestinal adverse effects than ibuprofen Effects in knee OA patients: Enhanced knee functions and reduced knee pain Demonstrated the efficacy and safety of curcumin extract 2,000 mg/day equivalent to ibuprofen 800 mg/day for 6 weeks therapy Effects in knee OA patients: Showed potential beneficial effects as adjuvant therapy with diclofenac in knee OA Showed additive improvement in decreasing pain Reduced inflammation without increasing the side effects in comparison with diclofenac alone Effects in knee OA patients: Proved to be an alternative treatment option in patients with knee OA who are intolerant to the side effects of diclofenac Demonstrated gastroprotective and antiulcer effects, compared with the adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Effects in IL-1β-induced temporomandibular joint chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cartilage protective effects by activating the NRF2/ARE (HO-1, SOD2, NQO-1, and GCLC) pathway Inhibited NOS2, COX2, IL6, MMP1, MMP3, MMP9, MMP13, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 mRNA and protein levels Increased COL2A1 and ACAN mRNA expression |
[164] [165] [166] [167] [168] [169] [170] [171] [172] |
|
Curcumin nanoparticles |
Topical treatment |
Effects in IL1β-induced chondrocytes: Enhanced chondroprotective properties against the production of inflammatory and catabolic mediators Reduced IL1B, TNFA, ADAMTS5, MMP1, MMP3, and MMP13 mRNA expression Increased levels of the chondroprotective transcriptional regulator CITED2 gene |
[173] |
|
Combination: Curcumin with resveratrol |
Resveratrol (trans-3, 4′- trihydroxystilbene) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammatory and catabolic effects and activated β1-integrin and Erk1/2 Demonstrated synergistic effects in suppressing apoptosis |
[174] |
| Theracurmin | Highly bioavailable form of curcumin (A surface-controlled water-dispersible form of curcumin) |
Effects in knee OA patients: Showed high bioavailability and it was 27-fold higher than that of curcumin powdery without adverse effects Effects in knee OA patients: Showed high absorption and enhanced chondroprotective effects Reduce pain and decreased NSAID necessity Demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects Showed efficacy and safety therapeutic (180 mg/day orally for six months) |
[175] [176] |
|
RA-11 (Nutraceutical mixture) |
Curcuma longa (Withania somnifera), Ashwagandha Terpenoids, flavonoids, tannins, alkaloids (Boswellia serrata) Olibano Boswellic acids (terpenoid) (Zingiber officinale), Ginger Phenolic and terpene compounds |
Effects in knee OA patients: Demonstrated greater potency, efficacy, and excellent safety in the treatment of OA knees over 32 weeks-therapy Showed significant reduction in the pain VAS and the modified WOMAC index scores (pain, stiffness, and physical function difficulty) Safety assessments were based on results of the physical examinations, clinical and laboratory tests, and adverse events |
[177] |
|
Phytosome complex (Meriva) |
Curcuminoid mixture- phosphatidylcholine (soy lecithin, a phospholipid) |
Effects in OA patients: Improved oral absorption and bioavailability Reduced all WOMAC scores (pain sensation, joint stiffness, and physical function) after eight months treatment with 200 mg curcumin/d Decreased inflammatory markers sCD40L, IL-1β, IL-6, sVCAM-1, and ESR Decreased use of NSAIDs/painkillers and gastrointestinal complications Improved emotional functions and quality of life Effects in IL-1β-induced HCH-c chondrocytes: improved the solubility of curcumin and enhanced chondroprotective effect via anti-inflammatory mechanism in chondrocytes Suppressed MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP9, MMP13, NOS2 and COX2 mRNA expressions Inhibited TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and PGE2 levels |
[178] [179] |
|
Mixture: Curcuminoids Hydrolyzed collagen and Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
(Curcuma longa L) Turmeric rhizome Polyphenols Hydrolyzed collagen (High levels of glycine and proline, amino acids for the stability and regeneration of cartilage) (Camellia sinensis) Green tea Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (flavanol) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Showed additive and synergistic effects Demonstrated significantly more efficient to inhibit inflammation and catabolic processes Suppressed NF-κB activation and its translocation to nucleus via inhibition of phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα and p65 phosphorylation Inhibited MMP-3, IL-6, NO production |
[180] |
|
Combination: Curcumin, Flavocoxid: baicalin and catechin β-caryophyllene |
(Curcuma longa) Phenolic compounds (Scutellaria baicalensis, Baikal skullcap) and (Acacia catechu, catechu) Baicalin and catechin Flavonoids (Copaifera spp, copaiba) and (Cannabis spp, marijuana/hemp) β-caryophyllene, a (bicyclic sesquiterpene) |
Effects in LPS and IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes: Demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity, safety and did not affect cell viability in chondrocytes Reduced IL1B mRNA in a dose-dependent manner Showed strong synergy potential for OA treatment Reduced the transcription factors NFKB and STAT3 mRNA expression Increased COL2A1 mRNA expression |
[181] |
|
Botanical formulation (Mixodin): Curcumin, Gingerols, and Pyrene |
(Curcuma longa) Turmeric Phenolic compounds (Zingiber officinale) Ginger Gingerols Phenolic compounds (Piper nigrum) Black pepper Pyrene (Alkaloid) |
Effects in knee OA patients: Showed synergic, anti-inflammatory and hypoalgesic effects in chronic knee OA (twice a day for 4 weeks) Observed as a safe alternative to chemical drugs, with lower adverse effects than Naproxen Decreased PGE2 levels in blood samples (curcumin 300 mg, gingerols 7.5 mg, and piperine 3.75 mg) similar to Naproxen drug (250 mg twice a day) |
[182] |
|
Botanical composition NXT15906F6: ethanol/aqueous extract of tamarind seed (proantocyanidins) and aqueous ethanol extract of turmeric (curcuminoids) NXT19185: (combination of NXT15906F6 plus an aqueous ethanol extract of mangosteen (α-mangostin, β-mangostin, and γ-mangostin) and (epicatechin and quercetin) |
Tamarindus indica Tamarind seeds Polyphenols Curcuma longa Garcinia mangostana fruit rind Polyphenolic xanthones Flavonoids |
Effects in knee OA patients/serum/urine: NXT15906F6 (250 mg) or NXT19185 (300 mg) daily for 50-6 days Decreased inflammatory processes, joint pain and stiffness Improved musculoskeletal function Inhibited TNF-α, IL-6, MMP-3 and CRP levels in serum Protected against cartilage erosion Reduced CTX-II (a cartilage degradation marker) in urine sample Reduced WOMAC, VAS, stair climb test scores Improved lequesne's functional index, the 6-minute walk test and knee flexion range of motion scores |
[183] |
|
Botanical composition (LI73014F2 2:1:2 ratio): Gallic acid, chebulagic acid, chebulic acid, chebulinic acid, gallotannins, ellagitannins (punicalagin), ellagic acid Diferuloylmethane Demethoxycurcumin Bisdemethoxycurcumin, and turmeric acid Boswellic acids: 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid, 11-keto-β-boswellic acid, and β-boswellic acid |
(Terminalia chebula) fruit myrobalan Tannins (polyphenols) (Curcuma longa) Polyphenols (Boswellia serrata) Olibanum Pentacyclic triterpenes |
Effects in IL-1β-induced HCHs chondrocytes: Reduced inflammation and apoptosis, via inhibition of the NF-κB/MAPK signalling pathway Inhibited pro-inflammatory mediators (COX-2, 5-LOX, and metabolic pathways products mPGES-1, PGE2, and LTB-4 Decreased IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9 and MMP-13 protein levels Provided therapeutic efficacy in OA management by reducing cartilage damage |
[184] |
| Delphinidin | Pomegranate, berries, dark grapes, aubergine, tomato, carrot, purple sweet potatoes, red cabbage, and red onion Anthocyanidin (Flavonoid) Delphinidin the most abundant anthocyanidin present in pomegranate fruit extract (Punica granatum) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Inhibited phosphorylation of IκB, IKKα/β, NIK, IRAK1 Inhibited COX2 mRNA and protein expression and PGE2 production via suppression of NF-κB activation Downregulated IKKB mRNA and protein expression |
[185] |
| Ellagic acid | Fruit peel of raspberries, strawberries, cranberries, pomegranate, walnuts, pecans, grapes Dimeric derivative of gallic acid Phenolic compound |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammation, and ECM loss Upregulated COL2A1 and ACAN Suppressed NF-κB p65 activation Decreased NO, PGE2, IL-6, TNF-α, ADAMTS-5 and MMP-13 in a dose-dependent manner Inhibited NOS2, and COX2 mRNA and protein expression |
[186] |
|
Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate |
Camellia sinensis Green tea Flavan-3-ols or flavanols (Flavonoids) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Showed anti- inflammatory and anti-catabolic effects in a dose-dependent manner Inhibited MMP1 and MMP13 mRNA and protein expression Inhibited NF-κB and AP1 levels Effects in cartilage explants: Inhibited cartilage matrix degradation Downregulated glycosaminoglycans release Effects in IL-1β-induced OA synovial fibroblasts: Showed efficacy in the control of inflammation Inhibited COX2 mRNA and protein expression Supressed PGE2 and IL-8 production Effects in IL-1β–induced OA chondrocytes: Decreased NOS2 mRNA and protein expression and NO production Inhibited NF-κB p65 activation and translocation to the nucleus by suppressing the degradation of its inhibitory protein IκBα in the cytoplasm Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Antioxidant properties against cytotoxicity Inhibited ROS release and accumulation from both intracellular and extracellular environments Inhibited PGE-2, NO, COX-2 and NOS2 production Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Inhibited catabolic mediators of cartilage degradation Inhibited JNK isoforms phosphorylation and activation Blocked c-Jun phosphorylation in the cytoplasm and reduced the DNA binding activity of AP-1 in the nuclei Effects in OA chondrocytes: Suppressed the AGE-induced TNFA and MMP13 mRNA and protein expression Inhibited AGE-BSA-induced degradation of IκBα and nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 Inhibited MAPK and NF-κB activation Effects in IL-1β-stimulated OA chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory activity Inhibited NF-κB and MAPKs pathway Inhibited TRAF6 mRNA and protein expression Downregulated IL6, IL8, TNFA, IL1B, IL7, GMCSF mRNA and protein expression Blocked ENA78, GRO, GROA, MCP1, MIP1B, MIP3A, GCP2, IP10 and NAP2 chemokines expression |
[187] [188] [189] [190] [191] [192] [193] |
|
Fatty acids n-3 PUFAs omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids |
Soybean, canola, olive oils, flaxseed, walnuts, marine phytoplankton and fish oil ALA: α-linolenic acid EPA: eicosapentaenoic DHA: docosahexaenoic |
EPA decreased MMP3 and MMP13 mRNA EPA reduced chondrocyte apoptosis by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and p53 |
[194] |
| Genistein | (Gycine max) soybean Isoflavone (flavonoids) |
Effects in LPS-induced chondrocytes: Suppressed COX-2 and NO protein levels in a dose-dependent manner Reduced IL-1β and YKL-40 (a marker of cartilage degradation) levels Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Reduced inflammation and oxidative stress Decreased MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, MMP-9, NO, COX-2, NOS2 Stimulated HO-1 associated with NRF-2 pathway activation Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Upregulated COL2A1, ACAN and ERα protein expression in a dose-dependent manner Inhibited apoptosis Reduced caspase 3 and TNF-α levels |
[195] [196] [197] |
|
Gingerols Shogaols |
Zingiber officinale and Alpinia galanga Phenolic compounds |
Effects in knee OA patients: Demonstrated improvement in WOMAC index and VAS pain profiles (6 weeks treatment 225 mg/twice day) Showed a good safety profile with mostly mild gastrointestinal side effects Effects in knee OA patients: Reduced inflammatory markers (1 g/d for 3 months) Decreased CRP and NO in serum and improve pain and mobility |
[198] [199] |
|
Gingerols and shogaols + isobutylamides and 2- methylbutylamimide |
Highly standardised ginger and echinacea extract Zingiber officinale Echinacea angustifolia Roots (Alkylamides: fatty acid amides) |
Effects in knee OA patients: Showed anti-inflammatory, synergistic properties during four-week supplementation Reduced chronic pain and improved knee function Showed to be safe without relevant side effects Could be an alternative in subjects of NSAIDs non-responders |
[200] |
|
Gingerols Shogaols Nanoparticles |
Zingiber officinale ginger extract in nanostructure lipid carrier |
Effects in knee OA patients: Decreased stiffness and the reduction of pain was significantly greater than compared to topical diclofenac (12 weeks treatment) Improved physical function |
[201] |
|
Gingerols, shogaols and Spilanthol (MITIDOL) |
Zingiber officinale Acmella oleracea Sphilantol (alkamide) food-grade lecithin formulation of standardized extracts |
Effects in knee OA patients: Showed reduction of markers of inflammation (CRP and erythrocyte sedimentation rate) Antioxidant and analgesic properties Improved knee function and free of side effects |
[202] |
|
Harpargoside, Harpagide y Procumbide β-cariofileno, α-humuleno y α-copaeno Oleanolic acid, Ursolic acid and 3β-acetyloleanolic acid Eugenol Acteoside and Isoacteoside |
Harpagophytum procumbens (HP) devil’s claw root HP extract Iridoid glucosides Sesquiterpenes Triterpenes Monoterpene Phenolic glycosides |
Effects in fibroblast-like synoviocytes/synovial membrane/OA patients: Showed anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive HPEH2O, HPEDMSO increased CB2 mRNA expression and inhibited PI-PLC β2 isoform expression All the HPE extracts inhibited FAAH mRNA expression and enzymatic activity (HPEEtOH100 was the most effective) Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Suppressed inflammatory cytokines/chemokines Inhibited IL6, and MMP13 mRNA expression Suppressed c-FOS/AP-1 transcription factor Effects in knee and hip OA patients: Showed efficacy and superior safety as therapeutic agent (2610 mg of powdered cryoground powder) compared to diacerhein (100 mg/day) for 4 months Showed lower adverse effects than diacerhein Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Suppressed MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9 production via inhibition of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β synthesis |
[203] [204] [205,206] [207] |
|
Hydroxytyrosol (HT) |
Olea europea L Olive leaf extract Fruits extra virgin oil HT is more abundant in the processed fruit and olive oil Secoiridoid derivative |
Effects in knee OA patients: Demonstrated pain inhibition over a 4 weeks/period Decreased pain measurement index (Japanese Orthopaedic Association score) and VAS scores HT was considered effective when reaches the knee joint in an unmetabolised form Showed antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties |
[208] |
|
HT and Verbascoside |
Verbascoside: Hydroxycinnamic acid derivative (phenolic compound) |
Effects in OA chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective effects and reduced intracellular ROS generation Suppressed oxidative stress via p38 and JNK signalling pathways HT downregulated ICE /caspase-1 indicating a potential anti-inflammatory effect |
[209] |
|
Hydroxytyrosol / Procyanidins (Oleogrape®SEED) |
(Extract from olive and grape seed): (Olea europea L) mainly found in olive leaf and oil Phenolic compound (Vitis vinifera, grape) Flavonoids Other sources: pine bark, cocoa, raspberry, vegetables, legumes, nuts |
Effects in IL-1β-Induced chondrocytes: Demonstrated chondroprotective properties Decreased NO, PGE2, and MMP-13 production Reduced NF-κB p65 signalling pathway Effects of serum enriched with HT/procyanidins metabolites on primary articular chondrocytes stimulated with IL-1β (ex vivo methodology): Reduced NO, PGE2, and MMP-13 levels |
[210] |
| Icariin |
Epimedium sagittatum flavonol glycoside |
Effects in OA fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Inhibited inflammatory response, apoptosis, ER stress and ECM degradation Decreased IL1β, MMP14, and GRP78 gene and protein expression Effects in IL-1β-induced SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells: Showed chondroprotective properties and inhibited MMP1, MMP3 and MMP13 gene and protein expression via MAPK pathways Inhibited the phosphorylation of p38, ERK and JNK Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Demonstrated chondroprotective and antioxidants functions without cytotoxic effects by activation of NRF2 mRNA Inhibited ECM degradation and ROS production Promoted SOD1, SOD2 mRNA and GPX activity Decreased MMP3, MMP9, MMP13 and ADAMTS4 mRNA expression |
[211] [212] [213] |
|
Indole tetracyclic alkaloids Oxindole alkaloids Indole pentacyclic alkaloid Glycoindole alkaloids Quinovic acids Tannins |
Uncaria guianensis Uncaria tomentosa cat's claw alkaloids triterpenes heterosides polyphenols |
Effects in knee OA patients: Showed antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties Alleviated knee pain and promoted benefit to the joints, tolerability and safety at high concentrations Reduced the toxic side effects of NSAIDs and had no deleterious effects on blood or liver function or other significant side-effect Improved OA management and treatment |
[214] |
| Isofraxidin |
Siberian ginseng and Apium graveolens Coumarin (phenolic compound) |
Effects in LPS-induced OA chondrocytes: Decreased iNOS, COX-2, NO, PGE2, TNF-α and IL-6 levels Suppressed ECM degradation Inhibited TLR4/MD-2 complex formation, and NF-κB signalling pathway Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Suppressed inflammatory mediators and ECM degradation through inhibiting NF-κB pathway Inhibited IκB-α degradation Blocked NO and PGE2 production Inhibited COX2, NOS2, MMP1, MMP3, MMP13, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 mRNA expression and protein levels Increased ACAN and COL2A1 levels |
[215] [216] |
|
Juglanin |
Polygonum aviculare Juglans regia L Diarylheptanoid derivative Flavonoids |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammatory responses through suppressing phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 Suppressed IκBα degradation Inhibited NO, PGE2, IL-6, TNF-α, MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 levels Decreased NOS2, COX2, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 mRNA and protein expression |
[217] |
| Licochalcone A |
Glycyrrhiza glabra, liquorice root Glycyrrhiza inflate Flavonoids |
Effects in IL-1β or TNF-α-induced OA chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory properties Inhibited PGE2 and NO production Inhibited MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 levels Inhibited NOS2 and COX2 mRNA expression Inhibited NF-κB activation and IκBα degradation Increased NRF2 and HO1 mRNA and protein expression |
[218] |
|
Acetylated ligstroside aglycone: (Chemically acetylated version of ligstroside aglycone) |
(Olea europea L) Extra virgin olive oil Ligstroside aglycone (p-HPEA-Elenolic acid) Secoiridoids |
Effects in IL-1β/Oncostantin M-induced OA chondrocytes/OA cartilage: Reduced NOS2, MMP13 gene and protein expression Enhanced anti-inflammatory activity compared to the natural compound ligstroside Inhibited NO levels, proteoglycan loss and cartilage degradation |
[219] |
|
Myrcene |
Eryngium duriaei monoterpene |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory and anti-catabolic properties in human chondrocytes Inhibited NOS2 mRNA expression and activity, and NF-κB pathway Reduced MMP1, and MMP13 gene expression Decreased phosphorylation of JNK, p38, and ERK1/2 Increased TIMP1 and TIMP3 mRNA Decreased COL1 mRNA and promoted the maintenance of the differentiated chondrocyte phenotype |
[220] |
| Myricetin |
Labisia pumila Trigonella foenum graecum L Anacardium and Mangifera species (Anacardiaceae) Grapes, berries, chard spinach, broadbeans, garlic, peppers Flavonol |
Effects in IL-1β stimulated chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammatory mediators and cytokines and exerted no significant cytotoxic effect in a dose dependent manner Inhibited NOS2 and COX2 mRNA and protein Decreased NO and PGE2 production Suppressed TNF-α and IL-6 levels Inhibited ECM degradation and inhibited ADAMTS5 and MMP13 gene expression Promoted ACAN and COL2A1 gene Inhibited NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation and activation and inhibited IκBα degradation Increased NRF2 translocate into nuclear and activation and HO-1 expression in cytoplasm against inflammation response via PI3K/Akt |
[221] |
|
Oleocanthal (decarboxymethyl ligstroside aglycone) |
(Olea europea L) Fruits, leaves, extra virgin oil Secoiridoid derivative (Phenolic compounds) |
Effects in LPS-activated OA chondrocytes: Suppressed inflammation and OA progression Blocked MAPKs/NF-κB pathways Inhibition of NOS2 and NO protein synthesis Inhibited IL6, IL8, COX2, NOS2, MIP1α, TNFA, LCN2, MMP13 and ADAMTS5 mRNA expression |
[222] |
|
Leuropein |
(Olea europea L) olive leaves and seeds, pulp and peel of unripe olives, extra virgin oil Oleuropein is present in high amounts in unprocessed olive fruit Secoiridoid (Phenolic compounds) |
Effects in IL-1β-stimulated OA chondrocytes: Suppressed phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and nuclear translocation, IκB-α degradation, and MAPK activation Inhibited COX2, NOS2, MMP1, MMP13, and ADAMTS5 mRNA expression Inhibited degradation of ACAN and COL2A1 Inhibited NO and PGE2 production Effects in primary OA chondrocytes (OACs)/ human mesenchymal stem cells /synoviocytes/bone cells: Reduced conexin 43 protein expression, gap junction intercellular communication and TWIST1 mRNA and increased COL2A1 and ACAN mRNA in OACs Reduced inflammatory and catabolic factors IL1B, IL6, COX2 and MMP3 mRNA expression and protein levels in OACs Restored chondrocyte phenotype Enhanced osteogenesis and chondrogenesis in hMSCs Improved cartilage and joint regeneration Showed a significant reduction of senescent cells in OACs, synoviocytes and bone cells |
[223] [224] |
|
Oleuropein Hydroxytyrosol, Verbascoside, Luteolin, (ZeyEX) |
(Olea europaea L, olive leaves) Olive leaf extract Polyphenolic compounds |
Effects in OA chondrocytes: Inhibited IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α and improved COL2A1 levels Inhibited p-JNK/JNK ratio whereas it was unaffected by ibuprofen Inhibited Casp-1/ICE, ROS, lipid hydroperoxide, 4-Hydroxynonenal-protein adduct, advanced glycation (glycoxidation)-end product-protein adduct AGE, 3-Nitrotyrosine 3-NT, GM-CSF, COMP, receptor for advanced glycation end products RAGE and TLR4 levels |
[225] |
|
Puerarin |
(Radix puerariae) Root of Pueraria Phytoestrogen (Isoflavone) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Showed antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects and increased cell proliferation Decreased PGE-2, IL-6 and TNF-α levels Effects in IL-1β-treated monocytes/macrophage: Reduced IL-6, IL-12 and TNF-α expression Increased TGF-β1 and IL-10 levels |
[226] |
|
Quercetin |
(Achyranthes bidentata) Flavonol (flavonoid) |
The docking of PIM1-quercetin, CYP1B1-quercetin, and HSPA2-quercetin by Achyranthes bidentata: PIM1, CYP1B1, and HSPA2 were the key targeted proteins of quercetin in the treatment of OA | [227] |
| Resveratrol | Root extracts of the weed Polylygonum cuspidatum Vitis vinifera red grapes, blueberries cranberries, peanuts, Stilbenes (polyphenols) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced SW1353 cell line: Inhibition of TLR4 was related to PI3K/Akt activation PI3K/Akt activation was attenuated after TLR-4 pathway was blocked by TLR-4 inhibitor CLI-095 Resveratrol failed to reduce TLR4 protein expression after PI3K inhibitor LY294002 blocked PI3K/ Akt signalling Effects in knee OA patients: Demonstrated efficacy and safety as an adjuvant with meloxican during a 90-day period Decreased knee joint pain (dose 500 mg/day) without adverse effects Effects in serum: Decreased biomarkers of inflammation IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, CRP Effects in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective effects Suppressed the activation of IL-1β-induced catabolism and apoptosis in human chondrocytes in vitro Blocked the downregulation of cartilage matrix marker COL2A1 and the cell matrix receptor β1-integrin protein expression Inhibited caspase-3 activation and cleavage of PARP in a time-dependent manner Effects in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes: Protected against catabolic effects Inhibited membrane-bound IL-1β and mature IL-1β protein production Inhibited p53 accumulation in a dose-dependent manner and induced degradation of p53 by ubiquitin-independent pathway Inhibited p53-dependent apoptosis Suppressed ROS, caspase 3 activation, and PARP cleavage Effects in IL-1β-stimulated OA chondrocytes: Blocked mitochondrial membrane depolarization, maintained mitochondrial function and restored ATP levels Inhibited apoptosis via inhibition of PGE2 through suppression of COX2 mRNA and protein expression Reduced (apoptotic markers) cytochrome c release from mitochondria and annexin V Inhibited DNA fragmentation Effects IL-1β-stimulated OA cartilage explants: Increased proteoglycan synthesis Decreased MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13 Inhibited PGE2 and leukotriene B4 levels Effects in IL-1β-induced SW1353 cells: Demonstrated anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoarthritic properties Inhibited TLR4/NF-кB and inflammatory responses via inhibition of MyD88-dependent and-independent signalling pathways Decreased IL-6 levels Activated PI3K/Akt pathway and inactivated FoxO1 in a time-dependent manner Inactivated FoxO1 reduced TLR4 expression and inflammation PI3K/Akt and FoxO1 are regulated by TLR4 Established a self-limiting mechanism of inflammation |
[228] [229] [230] [231] [232] [233] |
|
Mixture Resveratrol and Curcumin |
(Phenolic compounds) | Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and anti-cytotoxic synergistic effects Increased anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Traf1 in a time-dependent manner Supressed NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation in a time-and concentration-dependent mannerInhibited COX-2, MMP-3, MMP-9, VEGF, caspase-3, and PARP cleavage levels Increased COL2A1 and SOX-9 production Resveratrol blocked IκBα degradation and curcumin inhibited IKK Effects in IL-1β or U0126-stimulated chondrocytes: Showed synergistic chondroprotective efficacy and ameliorated inflammatory effects Decreased apoptotic cells and resveratrol potentiated anti-apoptotic effects of curcumin Inhibited caspase-3 activation and degradation of β-1integrins Blocked the downregulation of Erk1/2 in a dose- and time-dependent manner |
[234] [174] |
| Sanguinarine | The roots of: Sanguinaria canadensis Benzophenanthridine alkaloid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Inhibited OA progression Inhibited MMP1a, MMP3, MMP13, and ADAMTS5 mRNA and protein expression Inhibited NF-κB and JNK signalling pathways |
[235] |
| Schisantherin A | The fruits of: Schisandra sphenathera Dibenzocyclooctadiene Lignan |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective Inhibited NOS2, COX-2, NO, PGE2, and TNF-α, MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 production Inhibited NF-κB p65 translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus, and inhibited MAPKs activation and IκBα degradation in a dose-dependent manner |
[236] |
| Sesamin |
Sesamun indicum sesame seed oil lignan |
Effects in IL-1β induced chondrocytes: Inhibited p38 and JNK phosphorylation Decreased MMP1, MMP3 and MMP13 mRNA and protein expression |
[237] |
|
Sulforaphane |
Brassica oleracea italica cruciferous vegetables (abundant in broccoli) Isothiocyanate |
Effects in IL-1β- or TNF-α-treated OA chondrocytes/ cartilage explant: Showed anti-inflammatory and immune modulatory effects Induced the phase 2 enzymes activity NQO1 (one of the most potent inducers) Inhibited NF-κB p65 pathway by down-regulating IκB-α degradation and IKK-αβ and IκB-α phosphorylation Inhibited COX2, PTGES and NOS2 mRNA and protein expression even at low concentrations Inhibited PGE2 an NO production in chondrocytes and explant culture Suppressed proteoglycan and COL2A1 degradation in cartilage explant culture Effects in IL-1 or TNF-α-treated OA chondrocytes: Sulforaphane was not cytotoxic at up to 20 μM Demonstrated anti-inflammatory mechanism mediated by NQO1 activity Inhibited NF-κB and JNK activation Inhibited MMP1, MMP3 and MMP13 mRNA and protein expression Effects in C-28/I2 cell line/OA chondrocytes induced by TNF/CHX, DENSPM/CHX, H2O2 GROα: showed cytoprotective effects Inhibited apoptosis, hypertrophic differentiation and ECM degradation Reduced the active/phosphorylated JNK Inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation and suppressed caspase 3, caspase 8 and caspase 9 activation Increased active/phosphorylated Akt protein Effects in IL-1/OSM–induced OA chondrocytes/ SW-1353 cell line/ synovial cells: Inhibited ADAMTS4, ADAMTS5, MMP1, MMP13, mRNA expression (sulforaphane acted independently of NRF2) in chondrocytes and synovial cells Induced HMOX1 (an NRF2-regulated gene) mRNA expression Inhibited NOS2, IL6, IL8 genes Blocked inflammation and inhibited cartilage destruction by attenuating NF-κB signalling Inhibited of p38 MAPK isoform Accumulated sulforaphane-GSH metabolites Effects in knee OA patients: Isothiocyanates were detected in the synovial fluid and in blood plasma of the high glucosinolate group, but not the low glucosinolate group Demonstrated biological impact on the joint tissues Synovial fluid protein profile and common plasma proteins showed significantly different levels of expression in low and high glucosinolate groups Decreased CXCL10 and increased IRX3 in fat tissue in the high glucosinolate group |
[238] [239] [240] [241] [242] |
|
Sulforaphane– microsphere system |
Sulforaphane-Poly (D, L-lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) microspheres | Effects in LPS-induced OA chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective properties Inhibited anti-inflammatory markers Inhibited COX2, ADAMTS5 and MMP2 mRNA and protein expression |
[243] |
|
Taraxasterol |
Taraxacum officinale Pentacyclic-triterpene |
Effects in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes: Suppressed inflammatory mediators via inhibition of NF-κB p65 translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus and IκBα degradation Inhibited NO, NOS2, PGE2, COX-2, MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 production in a dose-dependent manner |
[244] |
|
Terpenoid compounds (tuberatoide B, loliolide, sargachromenol, sargachromanol D, sargachromanol G, sargaquinoic acid, sargahydroquinoic acid, isoketocharolic acid/IKCA, isonahocol E3, and fucosterol) Phlorotannins Eicosapentaenoic acid EPA |
Sargassum seaweed (Terpenoids) Polyphenols Fatty acid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced SW1353 cell line: Inhibited oxidative stress and inflammatory responses Suppressed NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt signalling pathways Inhibited IL-1β-Induced NOS2 and COX2 mRNA and protein expression Decreased NO, PGE2 production Inhibited IL-1β-induced MMP1, MMP3, and MMP13 mRNA and protein expression |
[245] |
|
Thymoquinone (active metabolite) |
Nigella sativa Black cumin oil Monoterpene |
Effects in IL-1β-stimulated OA chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects via inhibition of NF-κB p65 and MAPKs activation Inhibited IκBα degradation Suppressed COX-2, NOS2, NO, PGE2, MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 production |
[246] |
|
Wogonin |
The root extract of: Scutellaria baicalensis Flavone |
Effects in IL-1β induced OA chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective effects Inhibited IL6 and MMP13 mRNA and protein expression in a dose dependent manner Suppressed MMP3, MMP9 and ADAMTS4 mRNA expression Suppressed oxidative and nitrosative stress by suppressing NOS2 gene and protein expression and ROS and reactive nitrogen species Supressed COX2 mRNA and protein expression and PGE2 production Inhibited c-Fos/AP-1 activity Enhanced COL2A1 and ACAN gene expression Effects in IL-1β induced OA cartilage explant: Suppressed glycosaminoglycan release Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Suppressed oxidative stress, inflammation and matrix degradation Increased NRF2 activation and activated transcription of NRF2-dependent genes HO1, GCLC, SOD2 and NQO1 and the upstream kinase ERK1/2 Inhibited MMP13, MMP3, MMP9, ADAMTS4 mRNA expression and protein expression Inhibited IL6, COX2 and NOS2 mRNA and protein expression Inhibited NO and PGE2 production Upregulated COL2A1, and ACAN mRNA and protein expression Effects in IL-1β-induced cartilage explants: Restored COL2A1 and glycosaminoglycan contents in a dose dependent manner Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Demonstrated cytoprotective properties Showed genomic DNA binding ability through intercalation mechanism and the intercalation was found between DNA base pairs guanine and cytosine Inhibited genomic DNA fragmentation and ROS generation Provided stability of DNA against chemical denaturation Inhibited DNA denaturation mediated by DMSO Inhibited apoptosis and apoptotic pathways and upregulated anti-apoptotic proteins |
[247] [248] [249] |
| Bioactive compounds | Sources/classes | Effects of bioactive compounds | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ALM16 Herbal mixture Major active compounds: (calycosin, calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside) lithospermic acid |
Dried roots of (Astragalus membranaceus) Isoflavonoids (Lithospermum erythrorhizon) phenolic acid |
Effects in OA cartilage/ OA-induced rats: Showed synergistic or additive chondroprotective properties of each extract Demonstrated a potent protective effect on articular cartilage, anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions (dose 200 mg/Kg) Attenuated histopathological lesions in cartilage, pain symptoms, mechanical allodynia, and thickness of the paw edema |
[146] |
|
Amurensin H (Vam3) |
Vitis amurensis Dihydroxy-stilbene Oligostilbenoid (resveratrol dimer) |
Effects in IL-1β-stimulated rat chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects Inhibited oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and ECM degradation (increased glycosaminoglycan and Col2a1 levels) Inhibited Nos2, nitric oxide, Pge2, Cox-2, Il-6, Il-17, Tnf-α, Mmp-9, Mmp-13 levels, Tlr4, Traf-6, Syk and Nf-κb protein expression in a dose dependent manner Effects in OA cartilage/subchondral bone: decreased OA progression, cartilage fibrillation, cartilage loss, subchondral bone erosion and inflammation |
[250] |
|
Arctigenin (Phenylpropanoid dibenzylbutyrolactone) |
Arctium lappa Greater burdock Lignan |
Effects in OA cartilage Inhibited OA development, attenuated histological damage and showed lower OARSI score Mitigated cartilage erosion, hypocellularity and proteoglycan loss |
[152] |
|
Artesunate (Artemisinin) |
Artemissia annua Sesquiterpene lactone |
Effects in osteoclast/synovium/OA-induced rat: Showed anti-inflammatory activity Inhibited osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis Downregulated Vegf, Hgf and Angp1 Inhibited Il-6, Il-1β, Tnf-α, Pge2 activity and JAK/STAT pathway Increased Col2a1, Il-4, Igf-1 and Tgf-β Effects in rat OA cartilage: Inhibited OA development Upregulated Igf-1 and reduced Opn, and c-telopeptides of type II collagen levels |
[251] [252] |
|
Avocado/Soybean Unsaponificables ASU (β-sitosterol, campesterol, and stigmasterol) Triterpenes |
Persea gratissima and Glycine max mixture of avocado and soybean unsaponifiables (Phytosterols) Triterpene alcohols |
Effects in bovine articular chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective properties Enhanced Tgfb1, Tgfb2 mRNA expression Increased Pai-1 production Induced ECM repair mechanisms Effects in bovine chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory effects Reduced the progression of cartilage damage Inhibited Tnfa, Il1b, Cox2, and Nos2 gene expression and downregulated Pge2 and nitrite production in LPS-activated chondrocytes Effects in OA cartilage/ synovial membrane/ subchondral bone/OA-induced rat: Showed anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties in MIA-induced OA rat Reduced histopathological damage of synovial membrane, articular cartilage, and subchondral bone with a significant decrease in the Mankin score Decreased Tnf-α and Mmp-13 and increased Col2a1 and Acan synthesis Reduced Nos2 in both OA cartilage and subchondral bone |
[253] [159] [254] |
|
Mixture: ASU and Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate |
Effects in IL-1β and TNF-α -activated equine chondrocytes: This combination potentiated the anti-inflammatory activity Suppressed Cox2 gene expression and Pge2 production, associated with inhibition of Nf-κb translocation from cytoplasm to the nucleus Effects in equine chondrocytes: Demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity in cytokine-activated articular chondrocytes Decreased Tnfa, Il6, Cox2, Il8 gene expression and Pge-2 synthesis through Nf-κb nuclear translocation inhibition |
[255] [256] |
|
|
ASU + α-lipoic acid combination |
Effects in LPS, IL-1β or H2O2-activated equine chondrocytes: Showed a potential combination anti-inflammatory and antioxidant in OA management Inhibited Pge-2 production significantly more than ASU alone or α-lipoic acid alone Reduced nuclear translocation/activation of Nf-κb |
[257] |
|
|
Combination (ASU +glucosamine +chondroitin) |
Effects in canine chondrocytes: The combination potentiated the anti-inflammatory effect of a low concentration of NSAID in the management of OA The inhibitory effect on Il-6, Il-8, and Mcp-1 production was significantly more than carprofen in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocyte microcarrier spinner cultures The combination together with a lower dose of carprofen reduced Pge2 production significantly more than either treatment alone |
[258] |
|
| Baicalin |
(Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi) Mainly extracted from dry root Flavone glycoside (flavonoid) |
Effects in mice OA cartilage/synovium/OA-induced mice: Attenuated OA progression Decreased proteoglycan loss and cartilage degradation and the OARSI scores Ameliorated synovitis Effects in mouse chondrocytes: Enhanced ECM synthesis by activating the Hif-1α/Sox-9 pathway and chondrogenic marker expression Increased Col2a and Acan gene expression Inhibited catabolic genes: Adamts5, Mmp9, Mmp13 and prolyl hydroxylases Effects in rat chondrocytes: Inhibited oxidative activity, ROS production and apoptotic cell death of endplate chondrocytes induced by H2O2 Upregulated Enos mRNA Reduced malondialdehyde levels, and increased sod Downregulated apoptotic signalling indicators: Parp cleavage, Bax and pro-Casp-3 protein expression |
[157] [259] [260] |
| Berberine | Medicinal herbs: Hydrastis canadensis Berberis aristate Cortex phellodendri Coptis chinensis isoquinoline-derivative alkaloid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced rabbit chondrocytes: Inhibited Mmp3 and Adamts5 gene expression in chondrocytes Increased Timp1, Acan and Col2a1 gene expression Effects in rabbit cartilage explants: Inhibited cartilage degradation Inhibited release of collagen and GAG fragment Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes/ cartilage explants: Showed chondroprotective properties and reduced articular cartilage destruction Inhibited glycosaminoglycan release and no production by high-dose berberine Suppressed Mmp1, Mmp3 and Mmp13 mRNA and protein expression in a dose-dependent manner and upregulated Timp1 mRNA and protein expression in chondrocytes /cartilage explant (100 µm optimum concentration) Effects in IL-1β-stimulated rat chondrocytes: Showed the maintenance of chondrocyte survival and promoted matrix production in IL-1β-stimulated articular chondrocytes Activated Akt/p70S6K/S6 signalling pathway Effects in rat OA cartilage: Protected articular cartilage and reduced matrix degradation Enhanced Col2a1, p-Akt and p-S6 levels Effects in rat chondrocytes: Attenuated SNP-stimulated chondrocyte apoptosis via activating AMPK signalling and inhibition of p38 MAPK activity Suppressed SNP-induced Nos2 protein expression Effects in OA cartilage: Showed chondroprotective effect Decreased cartilage degradation, Casp-3, and Bax protein expression Increased Bcl-2 expression, and enhanced Col2a1 synthesis Effects in rat chondrocytes: Promoted SNP-stimulated chondrocyte proliferation via activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway Upregulated Ccnd1, Ctnnb1 and Myc gene expression Reduced Gsk3b and Mmp7 mRNA expression Effects in OA cartilage: Decreased OA progression and cartilage degradation Reduced Mankin scores Enhanced Ctnnb1 and Pcna expression Effects in IL-1β -induced rat OA cartilage: Prevented cartilage degradation Inhibited proteoglycan loss Decreased immunostaining of IL-1β in the superficial and middle zones of cartilage Effects in rat chondrocytes: Demonstrated anti-catabolic and anti-inflammatory properties Inhibited Nos2, Cox2, Mmp3, Mmp13, Tnfa, and Il6 mRNA and protein expression Decreased the phosphorylation of MAPK (ERK, JNK, and p38) signalling pathway Increased Col2a1 protein expression |
[261] [262] [263] [264] [265] [158] [266] |
|
Butein |
Rhus verniciflua stem bark of cashews and the genera Dahlia, Butea, Searsia (Rhus) and Coreopsis are common sources Chalcones (flavonoids) |
Effects in rat OA cartilage/synovium/ subchondral bone: Inhibited proteoglycan loss and cartilage fibrillation and degradation Decreased OARSI score Alleviated synovitis Reduced subchondral bone plate thickness |
[159] |
| Celastrol |
(Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F.) root bark "Thunder of God Vine" Pentaciclic Triterpenes |
Effects in rat chondrocytes/OA articular cartilage (dose-dependent manner): Inhibited inflammatory response and Nf-κb signalling pathway Ameliorated apoptosis by enhancing autophagy Decreased cleaved Casp-3, p-IκBα, p-p65 protein expression and Bax, Sqstm1, Il6, Tnfa mRNA and protein expression Increased Bcl2, Ccnd1 mRNA and protein expression and Lc3-II levels Attenuated articular cartilage degradation Ameliorated cartilage loss and osteophyte formation Effects in OA cartilage: Attenuated cartilage damage and joint pain Suppressed Sdf1/Cxcr4 mRNA pathway Decreased Mmp13 and Adamts5 mRNA and protein expression Increased Col2a1 and Acan mRNA expression Effects in rabbit chondrocytes: Decreased apoptosis via Atf6/Chop pathway Inhibited Bip, Aft6, Chop and Xbp1(endoplasmic reticulum stress, ERs markers) mRNA and protein expression Decreased Casp3 and Casp9 mRNA and protein expression Effects in rat OA articular cartilage/synovium: Reduced articular cartilage injury, synovial hyperplasia and articular wear in the knee joints |
[267] [268] [269] |
|
Celastrol Nanocomplex |
Celastrol+ Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles+Chitosan |
Effects in rat chondrocytes Inhibited Mmp-3, Mmp-13, Il-1β, Tnf-α levels and Nf-kb signalling pathway Reduced inflammation Effects in OA cartilage/synovium/subchondral bone/OA-induced rat: Demonstrated high biosolubility and decreased cartilage damage Showed protective effect on cartilage and subchondral bone Reduced knee swelling and synovial inflammation |
[270] |
| Compound K |
Panax ginseng roots, fruits, leaves, flower buds Gingenoside (tetracyclic triterpenoid) |
Effects in mouse pre-osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells: Protected against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity Alleviated inflammatory response Stimulated osteoblastic cell differentiation and mineralization Inhibited ROS and NO levels Increased Alp, Col2a, and Ocn mRNA Decreased Ikk and Il1b mRNA expression |
[271] |
|
Criptotanshinon |
(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) Extracted from the root of the plant Diterpene quinones |
Effects in OA cartilage/suchondral bone/OA-induced mice: Decreased cartilage destruction and protected against OA progression Reduced the OARSI scores and subchondral bone plate thickness |
[163] |
| Crocin | Effects in mouse skeletal muscle cell line C2C12: Suppressed Il-6 by downregulation of Jnk level Effects in muscle tissue/OA-induced rats: Reduced joint pain, inflammation, muscular lipid peroxidation and Nrf2 mRNA expression Attenuated muscular oxidative stress through inhibiting muscular ROS generation Attenuated muscle dysfunction and decreased muscular Il-6 production Increased citrate synthase activity and Myh9 mRNA expression Increased glutathione production and Gpx1 mRNA and activity Effects in IL-1β-induced rabbit chondrocytes: Inhibited Mmp1, Mmp3 and Mmp13 gene and protein expression Inhibited Nf-κb pathway and suppressing degradation of IκBα Effects in rabbit OA cartilage: Suppressed cartilage degradation Reduced Mmp1, Mmp3 and Mmp13 genes |
[272] [273] |
|
|
Curcuminoids: Curcumin Demethoxycurcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin |
(Curcuma longa) (Curcuma domestica) Turmeric rhizome Diarylheptanoids (Phenolic compounds) |
Effects in IL-1β-stimulated equine articular cartilage explant: Inhibited cartilage degradation Decreased GAG release at high concentrations Effects in IL-1β-stimulated equine cartilage explants: Showed anti-catabolic and anti-inflammatory properties at low concentrations (non-cytotoxic concentrations) Reduced proteoglycans loss Decreased Pge2 and Mmp-3 release Effects in rat temporomandibular joint OA cartilage: Showed anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective properties Reduced cartilage erosion and proteoglycan loss Decreased Nos2, Cox2, Il1b, Mmp9, Mmp13 protein levels and increased Nrf2 protein level Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Blocked Nf-κb signalling pathway by suppressing Ikba mRNA phosphorylation and subunit Rela mRNA nuclear translocation Decreased Mmp13 mRNA and protein expression and upregulated Col2a1 mRNA and protein expression in a time-dependent manner Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Suppressed apoptosis marker (Casp-3) through autophagy via Mapk/Erk1/2 activation pathway and increased autophagy markers (Lc3-II, and Beclin-1) Effects in rats OA cartilage/ synovial tissues/rat OA-induced knee: Improved inflammatory lesions by intra-articular injection Inhibited LPS-induced overexpression of Tlr4 and its downstream Nfkb pathway mRNA and protein expression Decreased inflammatory cytokines LPS-induced Il-1β and Tnf-α production in synovial membrane |
[274] [275] [172] [276] [277] [278] |
|
Curcumin nanoparticles |
Topical treatment | Effects in cartilage/OA mice: Slowed OA progression and decreased ECM degradation, cartilage erosion, and aggrecan loss Reduced Mmp-13 and Adamts-5 levels Reduced pain and improved locomotor behaviour Effects in infrapatellar fat pad: Suppressed Cfd, Lep, Adipoq, adipo-regulatory transcription factors /enhancer binding protein alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, and Mmp13 and Adamts5 mRNA Effects in synovium/subchondral bone: Reduced synovitis and subchondral plate thickness |
[173] |
|
Mixture: Curcuminoids Hydrolyzed collagen and Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
(Curcuma longa L) Turmeric Polyphenols Hydrolyzed collagen (High levels of glycine and proline, amino acids essential for the stability and regeneration of cartilage) (Camellia sinensis) Green tea Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (Flavanol) |
Efects in IL-1β stimulated bovine chondrocytes: Demonstrated anticatabolic, anti-inflammatory, additive and synergistic properties Decreased Il6, Nos2, Cox2, Mmp3, Adamts5 and Adamts4 gene expression Inhibited NO, Pge2 production |
[180] |
|
Herbal composition LI73014F2 (2:1:2 ratio): Gallic acid, chebulagic acid, chebulic acid, chebulinic acid, gallotannins, ellagitannins (punicalagin), ellagic acid Diferuloylmethane Demethoxycurcumin Bisdemethoxycurcumin, and turmeric acid Boswellic acids: 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid, 11-keto-β-boswellic acid, and β-boswellic acid |
(Terminalia chebula) fruit myrobalan Tannins (polyphenols) (Curcuma longa) Polyphenols (Boswellia serrata) Olibanum Pentacyclic triterpenes |
Effects in cartilage/ synovium/OA-induced rats: Decreased pro-inflammatory mediators such as Cox-2, Pge2, Lox5, and Ltb-4 Decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines: Il-1β, Il-6, and Tnf-α, 89%, 84%, and 38%, respectively Reduced Mmp-2, Mmp-3, Mmp-13 levels Alleviated joint pain by suppressing synovial membrane and cartilage degradation (dose 50 mg/Kg/day for three weeks) |
[279] |
|
Ellagic acid |
Fruit peel of raspberries, strawberries, cranberries, pomegranate, walnuts, pecans, grapes Dimeric derivative of gallic acid Phenolic compound |
Effects in cartilage/ synovium/OA-induced mouse Protected against cartilage degradation Inhibited proteoglycan loss Decreased OARSI score Alleviated synovitis Delayed OA progression |
[186] |
| Emodin | The root and rhizome of Rheum palmatum Anthraquinone derivative (Phenols) |
Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Decreased Mmp3, Mmp13, Adamts4 and Adamts5 mRNA and protein expression by suppression of NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathway Increased Acan and Col2a1 mRNA and protein expression Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rats Protected against the development and OA progression Reduced cartilage degradation Decreased Mmp3, Mmp13 and Ctnnb1 mRNA Effects in IL-1β-induced by rat chondrocytes: Reduced cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner Inhibited nitric oxide and pge-2 levels and Mmp1 and Mmp13 mRNA expression Inhibited ERK activation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway Effects in IL-1β- induced rat chondrocytes/ cartilage: Alleviated inflammation and reduced Mmp3, Mmp13 and Adamts4 mRNA and protein expression Reduced cartilage matrix degradation Protected knee joint cartilage Effects in serum/OA-induced rat: Inhibited Nos2, no, Cox-2 and Pge2 levels Emodin at 80 mg/Kg is comparable to celecoxib at 2.86 mg/Kg |
[280] [281] [282] |
|
Fatty acids n-3 PUFAs omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids |
Soybean, canola, olive oils, flaxseed, walnuts, marine phytoplankton and fish oil ALA: α-linolenic acid EPA: eicosapentaenoic DHA: docosahexaenoic |
Effects in equine synoviocyte culture: n-3 PUFAs EPA and DHA modulated inflammatory response and reduced Adamts4, Mmp1, Mmp13, Il1b, Il6, and Cox2 genes, stimulated by recombinant equine (re)IL-1β DHA-derived docosanoids such as resolvin D1 and D2, maresin 1 and protectin DX reduced Adamts4, Mmp1, Mmp13, Il6, and Cox2 genes Effects in IL-1β-mediated bovine cartilage explants: EPA and DHA reduced ECM degradation Demonstrated that EPA maintained a reduced expression of Adamt4, Adamts5, Mmp3 and Mmp13, and Cox2 gene until the end of the 5-day treatment Effects in IL-1α-induced bovine chondrocytes: n-3 PUFAs showed beneficial effect against the inflammation and cartilage degradation EPA was the most effective, followed by DHA and ALA acid. The n-6 PUFA (omega 6), arachidonic acid (AA) had no effect n-3 PUFAs reduced Cox2, Adamts4, Adamts5, Mmp3, Mmp13, Il1a, Il1b and Tnfa mRNA Effects in OA cartilage/OA-induced mouse EPA Intra-articular injection treatment decreased matrix degradation and mankin scores Reduced Mmp-13 protein expression Inhibited OA progression |
[283] [284] [285] [194] |
|
Geniposide |
Extract of the fruit Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, zhizi Iridoid glycoside (monoterpenoids) |
Effects in rabbit OA chondrocytes/ synovial fluid /OA-induced rabbit: Showed anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing p38 MAPK signalling pathway Inhibited Il1b, Tnfa, and Mmp13 gene expression and protein expression Inhibited oxidative stress Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammation and apoptosis Inhibited Bax, Cyto-c, cleaved-Casp3, no, Pge2, Nos2, Cox-2, and Mmp-13 protein expression Increased Bcl-2 and Col2a1 protein expression Inhibited Pi3k/Akt/Nf-κb phosphorylation signalling pathway Effects in OA cartilage/OA-induced rat: Reduced cartilage damage and OARSI scores Inhibited OA progression Effects in rat chondrocytes: Promoted chondrocytes proliferation Inhibited sodium nitroprusside-induced apoptosis by reduction of NO levels |
[286] [287] [288] |
| Genistein | (Gycine max) soybean Isoflavone (flavonoids) |
Effects in OA condyle cartilage/ temporomandibular joint OA-induced rat: Observed more therapeutic effects on cartilage repairmen in high dose Decreased NF-κB phospho-p65 signalling Inhibited Il1b and Tnfa mRNA expression Effects in IL-1β-induced OA cartilage/OA-induced rat Reduced Inflammation and prevented ECM degradation Decreased OARSI score Attenuated OA progression Effects in IL-1β-induced OA cartilage/OA-induced rat Reduced cartilage degradation induced Increased collagen II, Acan, and ERα levels Downregulated caspase 3 levels Effects in synovial fluid: Reduced Tnf-α, and Il-1β levels |
[289] [196] [197] |
| Halofuginone |
Dichroa febrifuga Alkaloid |
Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rodents: Decreased proteoglycan loss and calcification of articular cartilage Reduced Col10, Mmp-13 and Adamts-5 Increased lubricin, Col2a1, and Acan levels Effects in subchondral bone: Inhibited osteoclastogenesis by decreasing Th17 cells and RANKL expression Inhibited the formation of osteoid islets by suppressing elevated Tgf-β activity Attenuated aberrant angiogenesis Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mice Attenuated cartilage degradation and OA progression Reduced Col10 and Mmp-13 levels Effects in subchondral bone: Improved subchondral bone microarchitecture Reduced abnormal bone resorption Decreased abnormally elevated Tgf-β activity and release from bone mineral matrix and inhibited osteoid islets formation Inhibited aberrant angiogenesisin in early-stage OA administered by oral gavage Effects in ATDC5 murine chondrogenic cell line 6.25, 12.5 and 25 ng/ml did not affect chondrocytic viability Inhibited Tgf-β1 signalling and downregulated p-Smad2 protein in a dose and time-dependent manner Effects in cartilage/OA-induced murine: Prevented cartilage damage by inhibition of elevated levels of Tgf-β1 signalling Reduced p-Smad2/3 levels Downregulated proteoglycan loss Decreased Col10 expression and Mmp-13 levels |
[290] [291] [292] |
|
Harpargoside, Harpagide y Procumbide β-cariofileno, α-humuleno y α-copaeno Oleanolic acid, ursolic acid and 3β-acetyloleanolic acid Eugenol Acteoside and Isoacteoside |
Harpagophytum procumbens (HP) devil’s claw root extract Iridoid glucosides Sesquiterpenes Triterpenes Monoterpene Phenolic glycosides |
Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rabbit: Showed chondroid regeneration Increased elastic and collagen fibres Increased Timp2 mRNA expression |
[293] |
|
Hydroxytyrosol (HT) |
Olea europea L Olive leaf extract Fruits Extra virgin olive oil HT is more abundant in the processed fruit and olive oil Secoiridoid derivative |
Effects in cartilage/synovial membrane/OA-induced rat Showed anti-inflammatory activity and prevented articular cartilage and bone destruction induced by kaolin and carrageenan Attenuated synovial membrane and periarticular soft tissue edema and decreased inflammatory infiltration including macrophages and lymphocytes Ameliorated paw swelling Effects in cartilage/synovial cells/STR/ort mice: Inhibited cartilage destruction and suppressed OA progression on knee joint Enhanced Has2 mRNA expression and improved high molecular hyaluronan production by synovial cells |
[294] [295] |
|
Hydroxytyrosol /Procyanidins (Oleogrape®SEED) |
(Extract from olive and grape seed): (Olea europea L) mainly found in olive leaf and oil Phenolic compound (Vitis vinifera, grape) Flavonoids Other sources: pine bark, cocoa, raspberry, vegetables, legumes, nuts |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes/OA-induced rabbit: Showed anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective properties Inhibited Nos2, Cox2, Mmp13 genes and NO, Pge2 and Mmp-13 production Effects in cartilage: Reduced OARSI score and cartilage degradation Effects in serum: Downregulated NO, Pge2 and Mmp-13 levels Conserved their bioactivity and bioavailable in serum after undergoing digestive process |
[296] |
| Hyperoside |
(Hypericum perforatum) fruits and herbs of different plant families (Hypericaceae, Rosaceae, Ericaceae, Campanulaceae, and Labiatae) Flavonoid glycoside |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes/OA-induced mice: Inhibited inflammation and attenuated ECM degradation Decreased Nos2, Cox-2, Adamts-5, Mmp-3, and Mmp-13 Upregulated collagen II, Acan, and Sox-9 Suppressed Pi3k/Akt/Nf-κb and Mapk pathways Attenuated oxidative stress and apoptosis via Nrf2/Bax/Bcl-xl axis Decreased ROS level Enhancing Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway to counteract Nf-κb activation Effects in cartilage: Inhibited GAG loss and cartilage destruction, and decreased the OARSI scores Increased Nrf2 levels |
[297] |
|
Icariin |
Epimedium sagittatum flavonol glycoside |
Effects in bone mesenchymal stem cells: Icarin promoted chondrogenic differentiation and Acan, Bmp2 and Col2a1 protein expression Effects in rabbit cartilage tissue: Repaired knee cartilage damage and enhanced Col2a1 expression (treatment with icarin plus bone mesenchymal stem cells was even more effective than the effect produced by either treatment alone in a time-dependent manner) Effects in ATDC5 cell line/ rat chondrocyte: Promoted ECM secretion and enhanced Col2a1 and Sox9 gene expression in a concentration-dependent manner Enhanced Ift88 gene and protein expression and ciliary assembly and promoted Erk phosphorylation Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rat: Improved histological cartilage phenotype and attenuated cartilage degradation Effects in TDP-43 chondrocyte lines/synovial tissue/serum/OA induced rat Inhibited Tdp43 overexpression induced apoptosis Attenuated the formation of neovascularization in the synovial tissue in rat OA model Decreased Vegf and Hif-1α in synovial tissue and serum Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Inhibited chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammatory cytokines production through the suppression of Nf-κb p65 phosphorylation and Mapk signalling Upregulated Akt activation Increased Ikbα protein Induced chondrocyte autophagy Decreased Il6 and Tnfa gene and protein expression Effects in (oxygen, glucose and serum deprivation)-induced rabbit bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Inhibited inhibited ERs markers levels and autophagy Protected against cytotoxicity and apoptosis by inactivation of mapk signalling by three specific siRNAs (Erk, p38 and Jnk) pathway |
[298] [299] [300] [301] [302] |
|
Indole tetracyclic alkaloids Oxindole alkaloids Indole pentacyclic alkaloid Glycoindole alkaloids Quinovic acids Tannins |
Uncaria guianensis Uncaria tomentosa cat's claw alkaloids triterpenes heterosides polyphenols |
Effects in LPS-induced murine macrophages (RAW 264.7 cells): Showed antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties and showed to be an effective treatment for OA Inhibited Tnf-α and Pge2 production |
[214] |
| Isofraxidin |
Siberian ginseng and Apium graveolens Coumarin (phenolic compound) |
Effects in OA cartilage/serum/OA-induced mouse: Reduced subchondral bone plate thickness and prevented calcification and erosion of cartilage Inhibited inflammatory cytokines in serum |
[215] |
| Licochalcone A |
Glycyrrhiza glabra, licorice root Glycyrrhiza inflate Flavonoids |
Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Reduced Adamts5, Adamts4, Mmp13 and Mmp1 mRNA expression Suppressed the phosphorylation of Ikkα/β and p65 and increased Iκbα expression Inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway Upregulated Col2a1 expression Effects in LPS-induced mouse chondrocyte: Mitigated ECM degradation by enhancing Acan and Col2a1production Decreased chondrocytes pyroptosis through Nrf2/Ho-1/Nf-κb pathway Inhibited Nlrp3, Asc, Gsdmd, Casp1, Il18, Il1b mRNA and protein expression Reduced Iκb-α degradation and the translocation of p65 to the nucleus Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mouse: Inhibited cartilage erosion, proteoglycan loss and reduced OARSI score Enhanced Nrf2 and mitigated OA progression Decreased Il-1β and Il-18 protein expression in air pouch mouse model |
[303] [304] |
|
Ligustrazine (Tetramethylpyrazine) |
Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort Rhizoma Alkaloids |
Effects in IL-1β-exposed rat chondrocytes: Suppressed apoptosis and ER stress-related factors (Grp78 and Chop) Suppressed Il6, Il1b, Nos2, Cox2, Tnfa, Mmp3, Mmp13, Adamts4 and Adamts5 mRNA expression Prevented ECM destruction Increased Acan and Col2a1 mRNA |
[305] |
|
Tetramethylpyrazine-Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid microspheres |
Effects in cartilage/synovium/OA-induced rats: Improved efficacy and therapeutic effect by intra-articular injection of microspheres Demonstrated to be histologically safe Protected against cartilage damage Inhibited proteoglycan loss Decreased articular inflammation and reduced joint swelling |
[306] | |
|
Magnoflorine |
Sinomenium acutum alkaloid |
Effects in subchondral trabecular bone/ osteoblastic cell line/cartilage/OA-induced guinea pig: Promoted subchondral bone regeneration and prevented OA progression Stimulated osteoblasts proliferation and mineralization Upregulated Lrp5, Ctnnb1, Runx2, Ocn and Erk2 mRNA expression and downregulated Nfκb (p105) gene in osteoblasts Attenuated cartilage degradation and increased Acan, Bmp7, Sox5, Tgf-β1 and chondrogenic cells Effects in cartilage/primary chondroprogenitor cells /synovial fluid/subchondral bone/OA-induced rats: Promoted cartilage regeneration and enhanced Acan, Bmp7, Sox5, Tgf-β1 and chondrogenic cells Increased chondrogenesis and chondrogenic signals such as Col2a, Comp, Tnc and Sox9 mRNA expression and downregulated Nf-κb (p105) and Erk2 gene in chondrogenic cells Decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines Il-17a, Il-12, Tnf-α, Inf-γ and Il-6 and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine Il-10 in synovial fluid Maintained the stabilization of trabecular bone microstructure |
[307] [308] |
| Myricetin |
Labisia pumila Trigonella foenum-graecum L Species of Anacardium and Mangifera (Anacardiaceae) Grapes, berries, chard spinach, broadbeans, garlic, peppers Flavonol |
Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mice: Inhibited articular cartilage matrix degradation and reduced OARSI score by intragastric administration Inhibited inflammation response and ameliorated OA progression through Pi3k/Akt mediated the increased Nrf2/Ho-1 signalling pathway Inhibition of Pi3k/Akt signalling abolished Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway activation and the suppression of Nf-κb |
[221] |
|
Oleocanthal (decarboxymethyl ligstroside aglycone) |
(Olea europea L) Fruits, leaves, extra virgin oil Secoiridoid derivative (Phenolic compounds) |
Effects LPS-induced ATDC-5 murine chondrogenic cell line: Oleocanthal and its derivative 231 reduced Nos2 protein expression and NO production in a dose-dependent manner Decreased p38 protein expression at the highest dose (25µM was linked to a cytotoxic effect) Synthetic derivative 231 showed no cytotoxicity even at higher concentrations Effects in LPS-induced murine chondrogenic cell line/murine macrophages: Demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects Inhibited Mip1a and Il6 mRNA and protein expression in chondrocytes and macrophage Inhibited nitric oxide production via Nos2 downregulation and decreased Il-1β, Tnf-α and Gm-csf levels in macrophages |
[309] [310] |
| Procyanidin | (Vitis vinifera) grape seed extracts (Malus pumila, Malus domestica Borkh. cv. Fuji) Apple Procyanidins (flavonoid) |
Effects in H2O2 or IL-1β-treated chondrocytes /cartilage/ synovial tissue/OA-induced mice: Demonstrated antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory effects Enhanced Acan and Col2a1 mRNA Suppression of Nos2 mRNA expression Prevented heterotopic cartilage formation Reduced inos protein levels in synovial tissues Effects in chondrocytes/OA-induced mice: Inhibited cartilage damage induced by mitochondrial dysfunction of chondrocytes Enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis with upregulation of Pgc1a gene expression Promoted mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity Upregulated Acan gene synthesis and regulated proteoglycan homeostasis Downregulated Mmp3 and Mmp13 catabolic genes |
[311] [312] |
|
Puerarin |
(Radix puerariae) Root of Pueraria Phytoestrogen (Isoflavone) |
Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mice: Attenuated inflammatory responses Ameliorated cartilage damage and sinovitis Effects in blood monocytes/macrophages: Decreased myeloid-derived C-C chemokine receptor 2+/lymphocyte Ag 6C+ monocytes Reduced Ccl2 mRNA Suppressed proinflammatory monocyte recruitment Effects cartilage/OA-induced rats Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective Ameliorated cartilage loss and upregulated Col2a1 levels Inhibited Mmp-3, Mmp-13, Adamts-5, Cox-2 Effects in serum: Inhibited Il-1β, Il-6, and Tnf-α levels Inhibited OA biomarkers: Ctx-II, Ctx-I and Comp, and stimulated the N-terminal propeptide of type II collagen expression and inhibited bone resorption and promoted bone formation Effects on IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Suppressed inflammatory mediators, apoptosis, and ECM degradation by inhibiting Nf-κb through Nrf2 nucleus expression and activation and Ho-1 cytoplasm expression in a dose-dependent manner Decreased Bax and Casp-3 Reduced Nos2, Cox2, Tnfa and Il6 mRNA and protein expression Decreased NO and Pge2 production Decreased Mmp-13 and Adamts-5 levels Upregulated Acan and Col2a1 Effects on cartilage /OA-induced mice: Decreased cartilage damage and OARSI score Alleviated OA progression and pain symptoms Effects on OA and OA-associated mitochondrial dysfunctions in rats: Alleviated mechanical hyperalgesia and cartilage damage Increased mitochondrial biogenesis Attenuated mitochondrial dysfunctions in OA rats AMPK inhibitor Compound C abolished puerarin’s effects |
[226] [313] [314] [315] |
|
Quercetin |
Achyranthes bidentata Ageratum conyzoides Chrysanthemum psyllium, Eleutherococcus senticosus Juglans regia L flowers, leaves, and fruits broccoli, onions, apples, berry crops, grapes, dark cherries, and green vegetables Flavonol (flavonoid) |
Effects in cartilage/serum/synovial tissue/ synovial fluid/OA-induced rabbit: Showed comparable effects as celecoxib Reduced cartilage damage and OARSI score Inhibited Mmp-13, oxidative stress and increased Sod (major active molecule to scavenge free radical) and Timp-1 levels Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and immunomodulatory effects Inhibited the degradation of cartilage matrix, Col2a1 and Acan mRNA and protein expression Inhibited Akt activation and Iκbα degradation Inhibited Nf-κb p65 phosphorylation and translocation into the nucleus Decreased Pge2, NO, and Mmp13, Nos2 and Cox2 mRNA expression and protein levels Decreased Adamts4 mRNA expression Decreased apoptosis by inhibiting Casp-3 Restored mitochondrial membrane potential Effects in synovial macrophage/OA-induced rat: Induced M2 polarization of macrophages and promoted pro-chondrogenic cytokines for cartilage repair and attenuated OA progression Effects in OA-induced rats: Showed anti-inflammatory effects and reduced toe volume and joint diameter Alleviated OA symptoms in a dose-dependent manner Effects in serum: Inhibited Il-1β and Tnf-α production Effects in joint tissues: Improved cartilage structure Suppressed Tlr4 and Nf-κb pathway |
[316] [317] [318] |
|
Quercetin Nanoparticle gel |
Flavonol | Effects in blood serum/OA-induced rat Quercetin-loaded nanoparticle gel and A. conyzoides L. extract gel reduced Il-1β, Mmp-9, Mmp-13 and, Adamts-5 levels Effects in knee joint: Prevented OA progression, and proteoglycan degradation |
[319] |
|
Compound: Quercetin with palmitoylethanolamide (PEA- Q) |
Flavonol with fatty acid amide |
Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rat Reduced histological cartilage damage induced by sodium monoiodoacetate injection Decreased hyperalgesia, infiltration of inflammatory cells and reduced myeloperoxidase induced by carrageenan Improved locomotor function Effects in serum: Reduced Il-1β, Tnf-α, Mmp-1, Mmp-3 and Mmp-9, and nerve growth factor levels associated with nociceptive and neuropathic pain Showed similar or even greater effects than compared to oral meloxicam |
[320] |
| Resveratrol | Root extracts of the weed Polylygonum cuspidatum Vitis vinifera red grapes, blueberries cranberries, peanuts, Stilbenes (polyphenols) |
Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mice Reduced articular cartilage damage and Mankin and OARSI scores Decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines levels by inhibiting Tlr4/Nf-κb signalling via downregulation of Myd88-dependent and -independent signalling pathway Activation of Pi3k/Akt pathway Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rabbit Exhibited cartilage protective effect in a dose-dependent manner of 10–50 μMol/Kg Reduced matrix proteoglycan content loss Inhibited chondrocyte apoptosis in vivo Effects in synovial fluid: Reduced NO production Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rabbits: Protected against cartilage destruction by intra-articular injection (10 µMol/Kg resveratrol once a day for two weeks) Decreased cartilage lesions such as fibrillation, fissures and reduced matrix proteoglycan content loss Effects in synovium: Statistically scores of synovial inflammation did not show difference between control rabbits receiving dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO) only and resveratrol in DMSO groups Effects in joint tissues/OA-induced rats Inhibited Tnf-α, Il-1β, Il-6, Il-18, Casp-3 and Casp-9 activity Suppressed Nf-κb and Nos2 protein expression Activated Ho-1/Nrf-2 signalling Effects in cartilage/OA-induced C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet: Inhibited cartilage lesion and suppressed chondrocyte apoptosis on obesity-related OA Decreased body weight in obese mice and inhibited OA development by reducing biomechanical overloading and inflammatory factors (doses of 22.5 mg/Kg and 45 mg/Kg) by oral gavage Reduced the degradation of Col2a1 Effects in serum: Reduced triglyceride and cholesterol levels in serum but none these reductions were statistically significant Decreased levels of Ctx-II (45 mg/Kg doses) |
[228] [321] [322] [323] [324] |
|
Rutin (quercetin-3-O-rutinoside) Oleuropein Rutin/Curcumin |
Abundantly found in: Ruta graveolens, rue Passionflower Buckwheat Apple Flavonol |
Effects in cartilage/blood samples/synovium/ OA-induced guinea pig: Decreased OA progression, reduced cartilage degradation and protected against inflammatory and catabolic processes Rutin decreased OA biomarkers: Coll2-1, Coll2-1NO2, and args neoepitope aggrecan fragments levels in serum Oleuropein decreased osteophyte formation in cartilage, decreased synovial histological score and decreased Pge2 and Coll2-1NO2 levels in serum Rutin/curcumin mixture decreased Coll2-1, Fib3-1 and Fib3-2 in serum |
[325] |
| Sanguinarine | The roots of: Sanguinaria canadensis Benzophenanthridine alkaloid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced cartilage explants: Inhibited OA progression and protected against cartilage degradation Inhibited Mmp-1a, Mmp-3, Mmp-13, and Adamts-5 positive cells Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mice: Improved cartilage surface in a dose-dependent manner and decreased OARSI score Inhibited Mmp1a, Mmp3, Mmp13, and Adamts5 mRNA expression and positive cells |
[235] |
|
Sclareol |
Salvia sclarea Diterpene |
Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Chondroprotective properties and showed no adverse effects on cell viability with concentrations of 1, 5, and 10 μg/mL Inhibited Mmp1, Mmp3, Mmp13, Cox2 and Nos2 gene and protein expression Suppressed Mmp1, Cox2 and Nos2 protein level Inhibited NO and Pge2 production Upregulated Timp1 gene and protein expression Effects in cartilage/ OA-induced rabbit: Decreased Mmp1, Mmp3, Mmp13, Cox2 and Nos2 and increased Timp1 gene expression Ameliorated cartilage degradation by intra-articular injection and reduced Mankin score |
[326] |
| Sesamin |
Sesamun indicum sesame seed oil lignan |
Effects in porcine cartilage explants: Inhibited degradation of proteoglycan cultures treated with IL-1β Inhibition of IL-1β/OSM-induced collagen degradation and hydroxyproline release Effects in cartilage/papain-induced OA rat Inhibited cartilage degradation and OA progression Increased proteoglycans and Col2a1 deposition in a dose-dependent manner |
[237] |
| Shikonin | Dried roots of: Lithospermum erythronrhizon Naphthoquinone (phenols) |
Effects in blood samples/OA tissue /OA-induced rat Inhibited inflammation and inhibited Il-1β, Tnf-α and Nos2 in blood Suppressed Nf-κb pathway protein expression Decreased Cox-2 protein expression and Casp-3 activity Upregulated phosphorylated Akt protein level Effects in IL-1β-induced rabbit chondrocytes: Anti-inflammatory and chondro-protective properties Inhibited Mmp1, Mmp3 and Mmp13 gene and protein expression Increased timp1 gene and protein expression Suppressed Nf-κb p65 activation Suppressed Iκbα degradation Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rabbit: Decreased cartilage damage by intraarticular injection treatment Suppressed Mmp1, Mmp3 and Mmp13 gene Enhanced Timp1 gene expression Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Reduced the cytotoxicity induced by IL-1β Inhibited chondrocyte apoptosis by enhancing Pi3k/Akt signalling pathway Suppressed Casp-3 activation and reduced cytochrome c release Increased Bcl-2 and decreased Bax expression Inhibited Mmp13 mRNA and protein expression Increased Timp1 mRNA and protein expression |
[327] [328] [329] |
| Sinomenine |
Sinomenium acutum Alkaloids |
Effects in IL-1β-treated rabbit cartilage explants: Showed chondroprotective effects Inhibited proteoglycan degradation Suppressed Mmp3 gene and protein expression Upregulated Timp1 mRNA and protein expression in a dose-dependent manner Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Decreased DNA fragmentation Inhibited Casp-3 activity and apoptotic chondrocytes in a dose-dependent manner Effects in IL-1β-induced mice chondrocytes: Inhibited inflammatory response and ECM degradation in a dose-dependent manner Decreased Mmp-3, Mmp-13 and Adamts-5 levels Upregulated Col2a1 and Acan synthesis Inhibited NO, Pge2, Nos2, Cox-2, Il-6 and Tnf-α protein level Protected against OA progression by activation of Nrf2/Ho-1 signalling pathway and inhibition of p-Nf-κb p65 nuclear translocation and activation and inhibited Iκbα degradation Effects in cartilage/OA-induced mouse: Reduced OARSI scores and inhibited cartilage degradation |
[330] [331] |
|
Sulforaphane |
Brassica oleracea italica cruciferous vegetables (abundant in broccoli) Isothiocyanate |
Effects in IL-1/OSM–induced bovine nasal cartilage explant/OA induced murine Showed chondroprotective effects Inhibited GAG and hydroxyproline release Inhibited cartilage destruction |
[241] |
|
SFX-01®, a stable synthetic form of sulforaphane |
Synthetic sulforaphane- alpha-cyclodextrin inclusion complex |
Effects in STR/Ort OA mice: Lead to greater symmetry in gait Improved bone microarchitecture Reduced osteoclast number and bone resorption Enhanced trabecular bone mass in the metaphyseal compartment Enhanced cortical bone mass Decreased Ctx-I protein levels in serum Increased procollagen type I NH2-terminal propeptide protein level in serum |
[332] |
|
Sulforaphane– microsphere system |
Sulforaphane-Poly (D, L-lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) microspheres | Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rat: Decreased cartilage degradation and OA progression by intra-articular injection system Decreased fibrillation, proteoglycans loss and OARSI score Reduced synovial inflammation |
[243] |
|
Terpenoid compounds (tuberatolide B, loliolide, sargachromenol, sargachromanol D, sargachromanol G, sargaquinoic acid, sargahydroquinoic acid, isoketochabrolic acid/IKCA, isonahocol E3 and fucosterol) Phlorotannins Eicosapentaenoic acid EPA |
Sargassum seaweed (Terpenoids) Polyphenols Fatty acid |
Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes Demonstrated antioxidant activity Inhibited Nos2 and Cox2 mRNA and protein expression Decreased NO, Pge2 production |
[245] |
|
Triterperne concentrates (lupeol, α-amyrin, β-amyrin, butyrospermol) |
Vitellaria paradoxa nut triterpenoids |
Effects in plasma/knee cartilage/OA-induced obese rat: Reduced oxidative stress and suppressed proinflammatory cytokines Enhanced enzymatic antioxidant activities Reduced total colesterol and increased high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol in blood plasma sample Decreased Tnf-α, Il-1β, and Il-6 levels Reduced malondialdehyde (lipid peroxidation) level and NO release in plasma Attenuated cartilage damage and suppressed OA development Reduced knee swelling, weight-bearing and pain |
[333] |
|
Wogonin |
The root extract of: Scutellaria baicalensis Flavone |
Effects in IL-1β-induced rabbit chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective effects Inhibited Mmp3, Mmp1, Mmp13, and Adamts4 and restored Col2a1 gene expression Inhibited Mmp3 protein synthesis and its caseinolytic activity Effects in IL-1β-induced cartilage/OA-induced rats: Inhibited Mmp3 production via intraarticular injection into the knee joint (dose 50 or 100 μM) Effects in cartilage/ OA-induced mice Demonstrated efficacy and safety as a transdermal cream treatment Inhibited OA progression Reduced OARSI and Mankin scores Increased running wheel activity and decreased pain perception Decreased biomarkers associated with cartilage degradation Inhibited Tgf-β1, Htra1, Mmp-13 and Nf-κb protein expression |
[334] [335] |
| Bioactive compounds | Sources/classes | Effects of bioactive compounds | Ref. |
| Baicalin |
(Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi) Mainly extracted from dry root Flavone glycoside (Flavonoid) |
lncRNA HOTAIR was highly expressed in OA chondrocytes. Baicalin exerted therapeutic effects by inhibiting the expression of lncRNA HOTAIR, decreasing the protein levels of p-PI3K and p-AKT, and increasing the protein levels of PTEN, APN, and ADIPOR1. Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Protected against ECM degradation and apoptosis Restored autophagy activity by the upregulation of miR-766-3p Suppressed the expressions of BAX and cleaved-caspase-3 Promoted BCL-2 protein expression and increased GAG content Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Protected against inflammatory injury Deactivated NF-κB signalling pathway by down-regulation of miR-126 on IL-1β-stimulated cells Downregulated IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α (pro-inflammatory factors) and decreased cell apoptosis |
[357] [358] [359] |
|
Cryptotanshinone |
(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) Extracted from the root of the plant Diterpene quinones |
Effects in chondrocytes: Regulated miRNAs expression Increased miR-106a-5p and PAX5 expression miR-106a-5p was positively associated with PAX5 and negatively correlated with GLIS3 expression Effects on tissues: Protected cartilage against developing OA through regulation of PAX5/miR-106a-5p/GLIS3 |
[360] |
|
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
Camellia sinensis Green tea Flavan-3-ols (flavanols) |
Effects in OA patients’ cartilage tissues and IL-1β stimulated chondrocytes: Increases viability (20 and 50 µM) and decreases miR-29b-3p, MMP-12 and IL-6 levels in in IL-1β stimulated chondrocytes MiR-29b-3p mimics reversed the effects above 50 μM EGCG PTEN overexpression abrogated the effects of miR-29b-3p mimics Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes:Inhibited inflammatory response via modulation of miRNAs expressions Inhibited ADAMTS5 gene expression via up-regulation of miR-140-3p Decreased let-7e-5p, miR-103a-3p, miR-151a-5p, miR-195-5p, miR-222-3p, miR-23a-3p, miR-23b-3p, miR-26a-5p, miR-27a-3p, miR-29b-3p, miR-3195, miR-3651, miR-4281, miR-4459, miR-4516, miR-762, and miR-125b-5p Upregulated let-7 family (let-7a-5p, let-7b-5p, let-7c, let-7d-5p, let-7f-5p, let-7i-5p), miR-140-3p, miR-193a-3p, miR-199a-3p, miR-27b-3p, miR-29a-3p, miR-320b, miR-34a-5p, miR-3960, miR-4284, miR-4454, miR-497-5p, miR-5100, and miR-100-5p Effects in OA chondrocytes: Showed ability to inhibit inflammatory response via modulation of miRNAs expressions Inhibited COX2 gene expression and PGE2 production via up-regulation of miR-199a-3p expression |
[361] [362] [363] |
|
Fisetin |
Persimmons, mangoes, grapes, apples, peaches, strawberries, peaches, onions, tomatoes, and cucumbers Flavonol |
Effects in IL-1β-induced OA chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory effects through activating SIRT-1 Inhibited the degradation of SOX9, ACAN and COL2A1 mRNA and protein expression Decreased NO, PGE2, IL-6, TNF-α production Inhibited NOS2, COX2, MMP3, MMP13 and ADAMTS5 expression at the mRNA and protein levels |
[364] |
|
Hydroxytyrosol (HT) |
Olea europea L fruits and leaves extra virgin olive oil Secoiridoid derivative |
Effects in C-28/I2 and primary OA chondrocytes: Showed chondroprotective and antioxidant effects Protected from DNA damage and cell death induced by oxidative stress Increased P62 mRNA transcription and autophagy activation by SIRT1 pathways Effects in OA chondrocytes: Reduced oxidative stress and DNA damage Prevented the increase in cell death and caspases activation Decreased expression of pro-inflammatory genes (COX2, NOS2) and of genes driving chondrocyte terminal differentiation (RUNX2, MMP13 and VEGF) Increased SIRT1 mRNA expression in GROa-stimulated micromasses Effects in C-28/I2 and OA chondrocytes: Protected against oxidative stress and modulated through epigenetic mechanism Reduced miR-9 levels (involved in oxidative stress and influence OA-related gene expression) by enhancing SIRT-1 Reduced MMP13, VEGF and RUNX2 genes Effects in C-28/I2 chondrocytes: miR-9 promoters were demethylated by SIRT1 silencing miR-9 promoters 1q22 (MIR9-1), 5q14.3 (MIR9-2), and 15q26.1 (MIR9-3) were hypomethylated in cells treated with H2O2 and hypermethylated in cells treated with HT alone or together with H2O2 in oxidative stress conditions |
[365] [366] [367] [368] |
| Oleanolic acid |
Ligustri lucidi extracted from fructus pentacyclic triterpenoid |
SIRT3 anti-inflammatory effect underlying in oleanolic acid- (OLA-) prevented interleukin-1β- (IL-1β-) induced FLS dysfunction was evaluated in vitro SIRT3 activation by OLA inhibited synovial inflammation by suppressing the NF-κB signal pathway in FLS Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes: Alleviated chondrocytes growth inhibition and the cell membrane and DNA damage Protective effects by activating miR-148-3p-mediated FGF2 Showed antiapoptotic effect by inhibition of FGF2 |
[369] [370] |
| Quercetin |
(Achyranthes bidentata) (Ageratum conyzoides) flowers, leaves, and fruits of plants such as Chrysanthemum psyllium, Eleutherococcus senticosus, Juglans regia L onions, apples, broccoli, berry crops, grapes, dark cherries, and green vegetables Flavonol (Flavonoid) |
Role of BMSC-derived exosomes in quercetin-mediated progression of OA both in vitro and in vivo (OA patients) IL-1β notably upregulated MMP13 and ADAMT5 and reduced the expression of COL2A1 in chondrocytes, which were rescued by conditioned medium of Quercetin-treated BMSCs Exosomes derived from Quercetin-treated BMSCs inhibited OA progression through the upregulation of miR-124-3p |
[371] |
| Resveratrol | Root extracts of the weed: Polylygonum cuspidatum Vitis vinifera red grapes, blueberries cranberries, peanuts Stilbenes (polyphenols) |
For the in vitro studies, RES increased the expression of SIRT1 and phosphorylation of FoxO1 in IL-1β-treated chondrocytes, promoted the expression of cholesterol efflux factor liver X receptor alpha (LXRα), and inhibited the expression of cholesterol synthesis-associated factor sterol-regulatory element binding proteins 2 (SREBP2). This reduced IL-1β-induced chondrocytes cholesterol accumulation In vivo experiments showed that RES can alleviate cholesterol build-up and pathological changes in OA cartilage RES regulates cholesterol build-up in osteoarthritic articular cartilage via the SIRT1/FoxO1 pathway, thereby improving the progression of OA Totally, 1016 differentially expressed lncRNAs were identified (493 downregulated) between control and resveratrol-treated chondrocytes This study for the first time detected the differential expressed lncRNAs involved in resveratrol-treated chondrocytes via employing bioinformatics methods Effects in OA chondrocytes: Increased SIRT1 mRNA and protein expression SIRT-1 regulated apoptosis and ECM degradation via the WNT/β-catenin signalling pathway Decreased BAX, proCASP-3 and proCASP-9, MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, WNT3A, WNT5A, WNT7A, and CTNNB1 protein expression Effects in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes Prevented OA progression by increased of SIRT1 and silencing NF-κB p65 and HIF-2α Decreased NOS2, MMP13 and restored COL2A1 and ACAN gene expression Effects in OA osteoblasts/subchondral bone tissue: Reduced ALP activity at a high dose Upregulated SIRT-1 activity and reduced the expression of leptin Increased the mineralization Increased the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and WNT/β-catenin signalling |
[372] [373] [374] [49] [375] |
| Bioactive compounds | Sources/classes | Effects of bioactive compounds | Ref. |
| Cryptotanshinone |
(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) Extracted from the root of the plant Diterpene quinones |
Effects in OA mouse model: Affects chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating miR-574-5p expression and, then interfering with YAF2 Regulates miR-574-5p promoter methylation |
[376] |
|
Curcuminoids: Curcumin Demethoxycurcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin |
(Curcuma longa) (Curcuma domestica) Turmeric rhizome Diarylheptanoids (Phenolic compounds) |
Effects in KOA rat model: Protective effect against quadriceps femoris atrophy and improves KOA Reduction of ROS-induced autophagy via the SIRT3-SOD2 pathway Effects in TBHP-treated rat chondrocytes: Protected from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis Suppressed ER stress biomarkers (Perk-Eif2a-Atf4-Chop) pathway via activation of the mRNA and Sirt1 protein expression Increased Col2a1 and Bcl2 gene expression and downregulated cleaved-Casp-3 and cleaved-Parp (proapoptotic proteins) levels Effects in cartilage/OA-induced rat: Demonstrated therapeutic efficacy (treatment: 50 mg/Kg and 150 mg/Kg once daily for 8 weeks by intraperitoneal injection) Attenuated knee joint degradation and inhibited OA progression Reduced cleaved-Casp-3 and Chop levels Activated Sirt1 expression and decreased chondrocyte apoptosis and ER stress Ameliorated chondrocytes and proteoglycans loss Decreased OARSI score in a dose-dependent manner Effects in IL-1β-induced primary chondrocytes/ OA-induced mice: Attenuated OA progression and decreased apoptosis by exosomes derived from curcumin-treated mesenchymal stem cells Upregulated miR-143 and miR-124 expression by reducing the DNA methylation of their promoters Inhibited Nfkb, Rock1 and Tlr9 mRNA and protein expression |
[377] [378] [379] |
|
Fisetin |
Persimmons, mangoes, grapes, apples, peaches, strawberries, peaches, onions, tomatoes, and cucumbers Flavonol |
Effects on DMM rats and IL-1β-treated chondrocytes: FST can activate SIRT6 The alleviative effects of FST against inflammation, ECM degradation, apoptosis, and senescence in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes were also confirmed FST attenuates injury-induced aging-related phenotype changes in chondrocytes through the targeting of SIRT6 Effects in cartilage/subchondral bone/synovium/ OA-induced mice models Exhibited less cartilage destruction and attenuated OA progression Decreased OARSI score Reduced subchondral bone plate thickness Alleviated synovitis |
[380] [364] |
|
Hydroxytyrosol (HT) |
Olea europea L fruits and leaves extra virgin oil Secoiridoid derivative |
Effects in TNF-α-induced rat chondrocytes: Showed anti-inflammatory activity Inhibited Il-1β, Il-6 and Mcp-1 proteins by upregulating Sirt6 mRNA and protein levels Promoted autophagy process through Sirt6 |
[381] |
|
Quercetin |
(Achyranthes bidentata) (Ageratum conyzoides) flowers, leaves, and fruits of plants such as Chrysanthemum psyllium, Eleutherococcus senticosus, Juglans regia L onions, apples, broccoli, berry crops, grapes, dark cherries, and green vegetables Flavonol (Flavonoid) |
Inhibited the expression of IL-1β-induced MMP-3, MMP13, iNOS and COX-2, and promoted COL type II expression in vitro In an OA rat model induced by ACLT, QUE treatment improved articular cartilage damage, reduced joint pain, and normalized abnormal subchondral bone remodelling. QUE also reduced serum IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP3, CTX-II, and COMP, thereby slowing the progression of OA Exerts its protective effect on chondrocytes by activating the SIRT1/Nrf-2/HO-1 and inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis Effects in chondrocytes/ OA-induced rat: chondroprotective and antioxidant properties Inhibited oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress, and chondrocyte apoptosis by activating Sirt-1 and Ampk signalling pathway Downregulated Chop, Grp78, P-perk, P-ire1α, Atf6 (ERstress biomarkers) and, cleaved-Casp-3 and cleaved-Parp (apoptosis biomarkers) levels Upregulated Bcl-2 protein expression levels Attenuated cartilage degradation of knee joint (dose: intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg/Kg - 100 mg/Kg once daily for 12 weeks) Effects in rat OA chondrocytes: Upregulated Ampk/Sirt-1 signalling pathway Effects on cartilage/blood/OA-induced rat: Inhibited inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS (100 mg/Kg oral treatment/daily, 7 days) Increased ATP, GSH and GPx levels Inhibited nitrite, Mmp-3 and Mmp-13 levels in blood samples |
[382] [383] [384] |
| Resveratrol | Root extracts of the weed: Polylygonum cuspidatum Vitis vinifera red grapes, blueberries cranberries, peanuts Stilbenes (polyphenols) |
Results showed that RES regulates the ECM metabolism, autophagy, and apoptosis of OA chondrocytes through the SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway to ameliorate IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury Effects in OA cartilage/ OA-induced mice: Prevented OA cartilage destruction and improved cartilage structure (dose: 100 µg) by intraarticular injection Increased Sirt-1 expression and reduced Nf-κb p65 and Hif-2α Reduced subchondral bone plate thickness and prevented calcified cartilage damage Decreased Nos2 and Mmp-13 and inhibited Col2a1 degradation and proteoglycans loss Effects in chondrocytes/cartilage/OA-induced mice: Promoted chondroprotective effects by intra-articular injection chondrocyte and increased the growth rate of chondrocyte Decreased Il-6, Mmp-13 and Casp-3 protein expression levels Increased miR-9 expression levels Decreased Malat1 and Nfkb1 gene and protein expression Malat1 and Nfκb1 were identified as potential target genes of miR-9 Effects in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes: Exerted anti-inflammatory properties and inhibited Nf-κb pathway by activating Sirt-1 Suppressed Nos2 expression and NO production Decreased DNA-binding activity of p65 by upregulation of Sirt-1 Inhibited Lys310-acetylated p65 accumulation in the nucleus |
[385] [49] [386] [387] |
| Saikosaponin D |
Radix bupleri Triterpene saponin |
In in vivo experiments, SSD ameliorated cartilage histopathological damage, decreased inflammatory factor content and promoted autophagy in OA mice Also, miR-199-3p expression was downregulated and TCF4 expression was upregulated in cartilage tissues of OA mice In in vitro experiments, SSD inhibited the inflammatory response and promoted autophagy in OA chondrocytes. Downregulation of miR-199-3p attenuated the effect of SSD on OA chondrocytes. |
[388] |
| Sinomenine |
Sinomenium acutum Alkaloids |
Effects on cartilage/ OA mice: Inhibited articular cartilage damage by increase of miR-223-3p expression via inactivation of the Nlrp3 inflammasome signalling. Nlrp3 was a direct target of miR-223-3p Blocked inflammatory response (Tnf-α, Il-1β, Il-6, and Il-18) Effects in chondrocytes: Overexpression of miR-223-3p inhibited IL-1β-induced apoptosis and inhibited Il-1β and Il-18 levels |
[389] |
|
TXC compound: Paeoniflorin Ferulic acid Isofraxidin Rosmarinic acid |
Dried roots of: (Paeonia lactiflora Pall, Morindae officinalis Ligusticum wallichii Sarcandra glabra) Monoterpene glycosides Hydroxycinnamic acid Coumarin Hydroxycinnamic acid |
Effects in knee OA cartilage/subchondral bone/OA-induced rats: Showed therapeutic effects in cartilage protection and subchondral bone remodelling Downregulated Mmp9, Adamts5, Col5a1, Col1a1, Mmp3, Mmp13, and Postn gene and protein expression Effects in LPS-exposed rat chondrocytes: Decreased Il-1β, Il-6, Tnf-α, Mmp-9 and p38 MAPK pathway in LPS-exposed chondrocytes Increased miR-27b, miR-140, and miR-92a-3p and decreased miR-34a expression Suppressed Adamts4, Adamts5, Mmp3, and Mmp13 mRNA and protein expression |
[390] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





