1. Introduction
Postoperative ileus (POI) is a common and debilitating complication resulting from delayed gastrointestinal transit following surgery, often leading to increased patient discomfort, prolonged hospital stays, and significant healthcare costs. [
1,
2,
3,
4] Although POI can occur after any type of surgery, it is particularly associated with abdominal procedures, where it remains a major unresolved clinical problem. [
5]
Despite the widespread occurrence of POI, effective therapeutic interventions are lacking, largely due to an incomplete understanding of its pathophysiology. [
6]
Natural anti-inflammatory products are an attractive and safe alternative for modulating inflammatory disorders. The herb Artemisia asiatica Nakai is a traditional oriental medicine that has been used for the treatment of diseases such as inflammation, microbial infection, and cancer. [
7] Eupacidin, an Artemisia herb isopropanol soft extract, is an orally administered drug manufactured by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical. In Korea, it is indicated for the improvement of gastric mucosal lesions (erosion, bleeding, redness, and edema) in acute and chronic gastritis. The drug contains eupatilin as the active ingredient, which corresponds with 30 mg of the active ingredient per 2000 mg.
Eupatilin (5,7-dihydroxy-3′,4′,6-trimethoxyflavone), a pharmacologically active flavonoid mainly found in the genus Artemisia, is known to possess anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, neuroprotective, anti-allergic, and cardioprotective activities. [
8] Several studies on eupatilin reported to possess a variety of biological activities, including protective effect against NSAID-induced enteropathy. [
7]
CKD-495, developed by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical, a component extracted from Cinnamomum cassia, shows an effective protective effect compared to Artemi-siae Argyi Folium extract (eupacidin, eupatilin, etc.) against acute or chronic gastritis in phase III trial. [
9]
Cinnamomum verum and C. cassia Blume are collectively called Cortex Cinnamonmi because of their medicinal cinnamon bark. Cinnamomum verum is more popular elsewhere in the world, whereas C. cassia is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine. [
10] Cinnamic acid is an organic acid that occurs naturally in cinnamon bark and has low toxicity and a broad spectrum of biological activity, including antioxidant effect, free radical scavenging properties, antimicrobial activity, efficacy for diabetes, neurological disorders, and cancer. [
11,
12,
13]
In this study, the prevention and treatment of POI was clinically evaluated by confirming the effect of oral eupacidin, CKD-495, and its indicator components (eupatilin and cinnamic acid) on intestinal permeability in an animal model of POI. Our aim is to provide an experimental basis for and predict the effect of drug repositioning CKD-495.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Animals
Adult male Hartley guinea pigs (Orient Bio Inc.) weighing 300–350 g were used in the present study. They were acclimated to controlled breeding conditions (21 ± 1°C, 50 ± 10% humidity, and 12-hour light/dark cycle commencing at 7 a.m.), and a standard guinea pig diet and water were provided for at least one week prior to surgery. All experimental procedures were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Department of Laboratory Animal Resources, Yonsei Biomedical Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine with Institutional Review Board (IRB) protocol number 2019-0156.
2.2. Group Setting
The guinea pigs were randomly assigned to several groups. Each group was subjected to a surgical procedure; after maintaining a fasting state (except water) from 24 h before the procedure, a mixture of Zoletil (4mL), Rumpun (2mL), and Saline (8mL) was injected into the abdominal cavity to induce unconsciousness. After 15 min, the hair on the abdomen was removed and the abdominal skin was disinfected with an alcohol swab. A minimal peritoneal incision was made after incising the skin and muscle layers of the abdomen. After abdominal incision, the group with sutures without intestinal manipulation was used as a control group. Other groups underwent cecum extraction, gently rubbed with wet gauze for 1 min using fingers, and sutured. The drug test groups were orally administered the following drugs every 12 h from day 0 to day 2 before surgery: eupacidin = 2000 mg/kg; eupatilin = 30 mg/kg; CKD-495 = 1250, 1670, and 2500 mg/kg; and cinnamic acid = 16.3, 21.7, and 32.5 mg/kg. The drug dosages were determined based on previous animal studies. The animal dose of eupatilin was set at 30 mg/kg based on a previous study by another research team using DA-6034, [
14] a similarly active derivative of Artemisia extracts, and eupacidin was set at 2000 mg/kg, which is equivalent to 30 mg/kg of eupatilin. The doses of CKD-495 were set at 1670 mg/kg and 2500 mg/kg to match the 2000 mg/kg dose of eupacidin, based on which the clinical dose trial tried 50 mg and 75 mg of CKD-495 compared to 60 mg of eupacidin, respectively. We added a 1250 mg/kg group, which is half the dose of 2500 mg/kg. Cinnamic acid, which was selected as an indicator component of CKD-495, was administered at 16.3 mg, 21.7 mg, and 32.5 mg/kg, respectively, considering that it contains 13 mg per gram of CKD-495.
The number of guinea pigs in each group was 5–8. While tissue samples were obtained from the ileum of each guinea pig used in this study, POI and drug group tissue samples were specifically harvested 3 h after surgery. We used CO2 gas to euthanize the guinea pigs before harvesting their intestinal tissues.
Various markers were measured in the harvested ileum. An Ussing chamber (EM-CSYS-2; Physiologic Instruments, San Diego, CA, USA) was used to analyze intestinal permeability, while leukocyte count and calprotectin expression were measured to evaluate intestinal inflammation. We measured the expression of claudin-1 and -2 to evaluate the alterations in the tight junction proteins. We compared the measurements between the control and POI groups and between the POI and drug groups.
2.3. Intestinal Permeability
To evaluate intestinal permeability, the harvested tissues were placed in a modified Ussing chamber. Krebs–Ringer bicarbonate solution (2 mL) was added to each half chamber, and the mucosal and serosal sides of the specimens were bathed. At a temperature of 37°C, both sides were maintained in a gas mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2. After an equilibration period of 30 minutes, the KRB containing horseradish peroxidase (HRP) at a final concentration of 0.4 mg/mL was substituted for the KRB in the chamber of the mucosal side. The KRB on the serosal side was replaced with fresh KRB: a 0.3 mL sample was collected and replaced with 0.3 mL KRB. Samples from the chamber on the serosal side were enzymatically analyzed using the modified Worthington method. o-Dianisidine dihydrochloride (OPD; Sigma Chemical Co., St Louis, MO, USA) was used as the substrate. Samples (50 μL) were transferred to a microtiter, and 100 μL of an OPD working solution (stable peroxide buffer diluted 1:10 in OPD) was added to each well. Subsequently, the plates were incubated at room temperature while shaking at 300 rpm. After 30 min, 2.5 M sulfuric acid (100 μL) was added. After 10 min, the absorbance of the decolorized reaction product was measured at 492 nm using a microplate reader (Model 680; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). All samples were analyzed in duplicate and measured using a standard curve. The HRP flux is represented as ng/2hr/mm2 during steady-state permeation. Intestinal permeability via the Ussing chamber was expressed as a percent-change compared to the mean value of the control group.
2.4. Intestinal Inflammation
Histological sections were obtained from the muscle layers of the harvested ileum and proximal colon. The sections were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin. Embedded sections were sliced into 4 μm thickness and then subjected to hematoxylin and eosin staining. We compared the number of leukocytes per high-power field between the control and POI groups and between the vehicle and probiotic groups.
2.5. Tight Junction Proteins
The expression of claudin-1 and -2 was determined using immunofluorescence analysis. At 3 hours after the operation, the histological sections from the ileum were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded with paraffin, and sliced into 4 μm thick sections. Tissues were then deparaffinized, rehydrated, and rinsed using standard methods. The slide sections were incubated overnight with the primary antibody for claudin-1 (1:50; Invitrogen) or claudin-2 (1:200; Invitrogen) at 4°C, followed by washing and incubation with the secondary antibody goat anti-rabbit IgG-fluorescein isothiocyanate (1:200; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 30 minutes at 37°C. The stained samples were evaluated under a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss Axio Imager Z1; Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) and the images were analyzed using MetaMorph microscopy automation (MDS Analytical Technologies, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) and ImageJ (NIH and LOCI, University of Wisconsin, USA).
2.6. Statistical Method
The data are expressed as the mean ± SE, and statistical analysis was performed by a non-parametric test using the Mann-Whitney U test between the two groups and a Kruskal-Wallis H test for multiple comparisons. SPSS version 26.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analysis. A two-tailed P-value of < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Intestinal Permeability
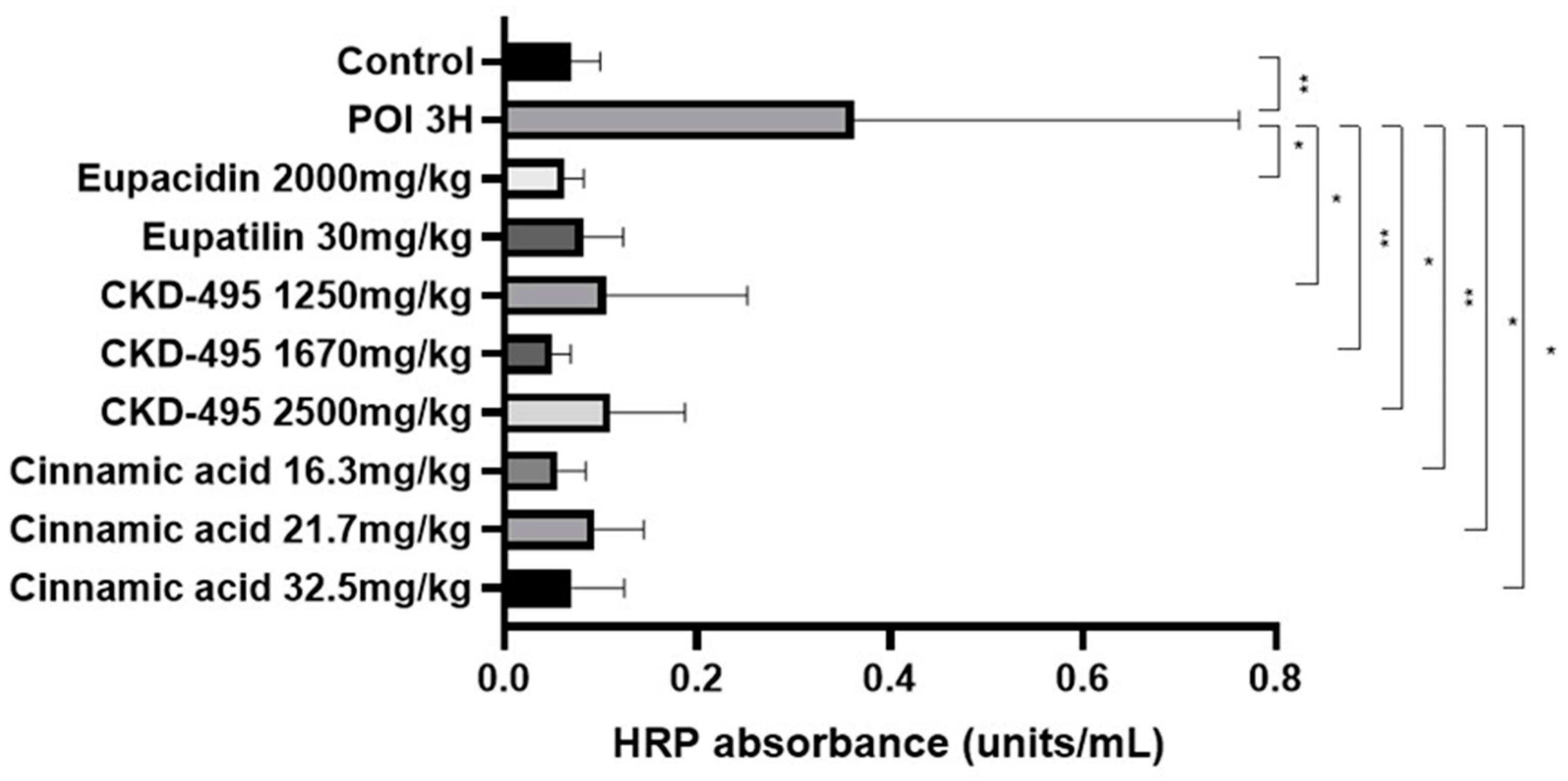
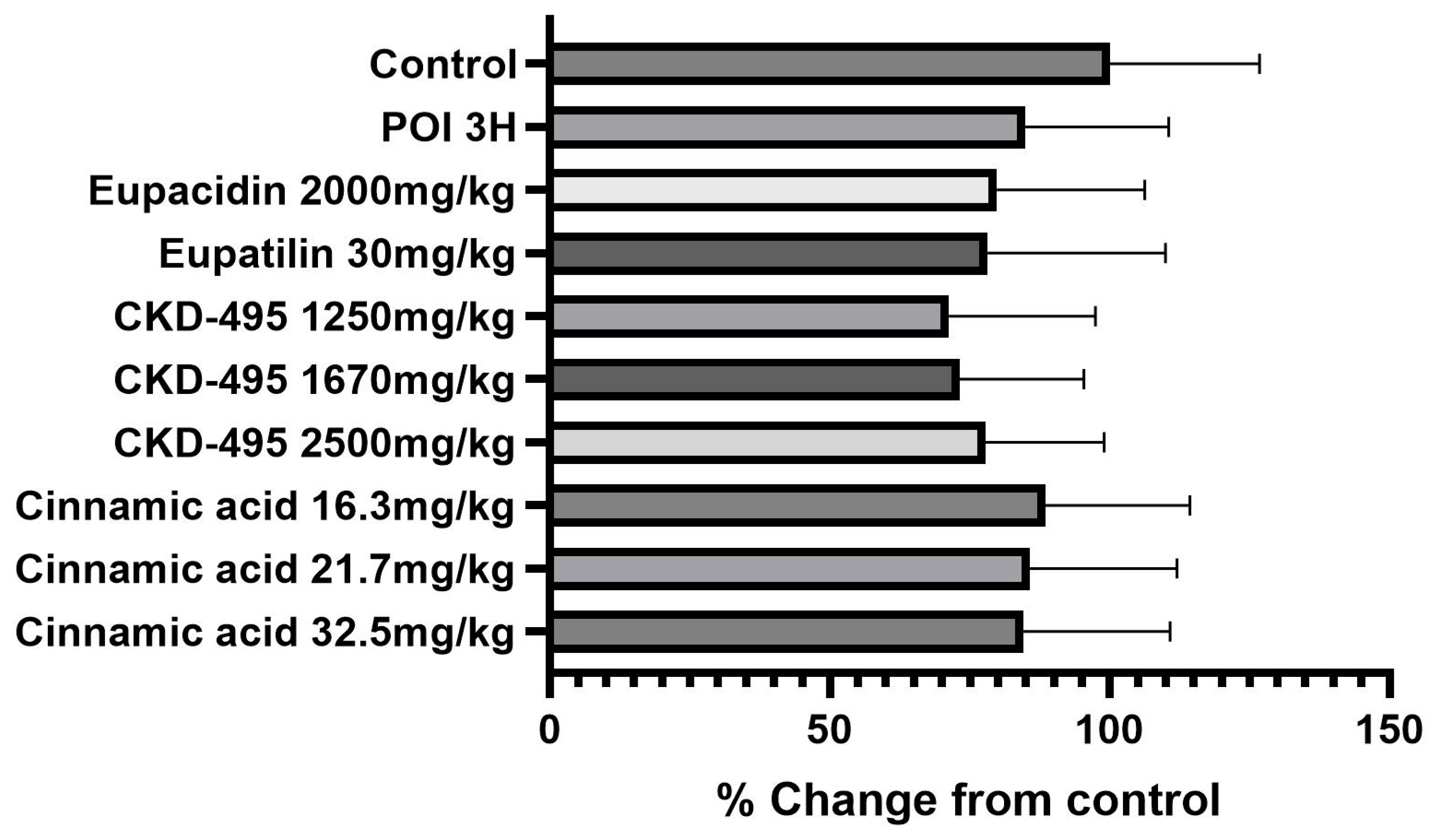
Intestinal permeability was indirectly confirmed through horseradish peroxidase (HRP) absorbance measurement in 6 subjects in the normal control group, 8 in the POI group, 6 in the eupacidin 2000 mg/kg administration group, 7 in the eupatilin 30 mg/kg administration group, 6 in the CKD-495 doses (1250, 1670, 2500 mg/kg) administration groups, 5 in the cinnamic acid 16.3 mg/kg administration group, 6 in the cinnamic acid 21.7 mg/kg administration group, and 5 subjects in the cinnamic acid 32.5 mg/kg ad-ministration group. HRP absorbance was significantly increased in the POI group compared with the control group (0.07±0.03 vs 0.36±0.4, p=0.01), and decreased in all drug groups compared with the POI group (
Figure 1).
3.2. Intestinal Inflammation
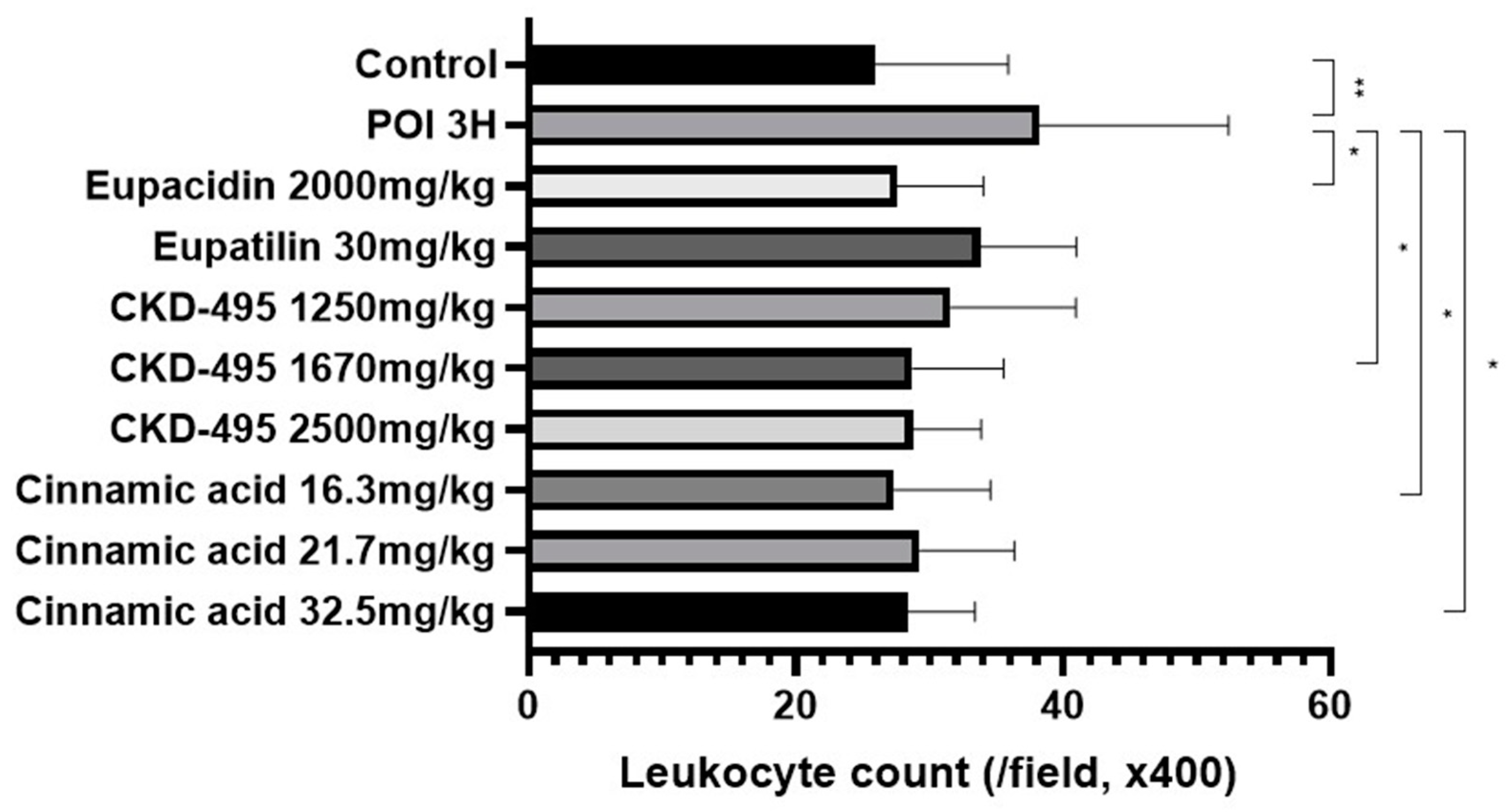
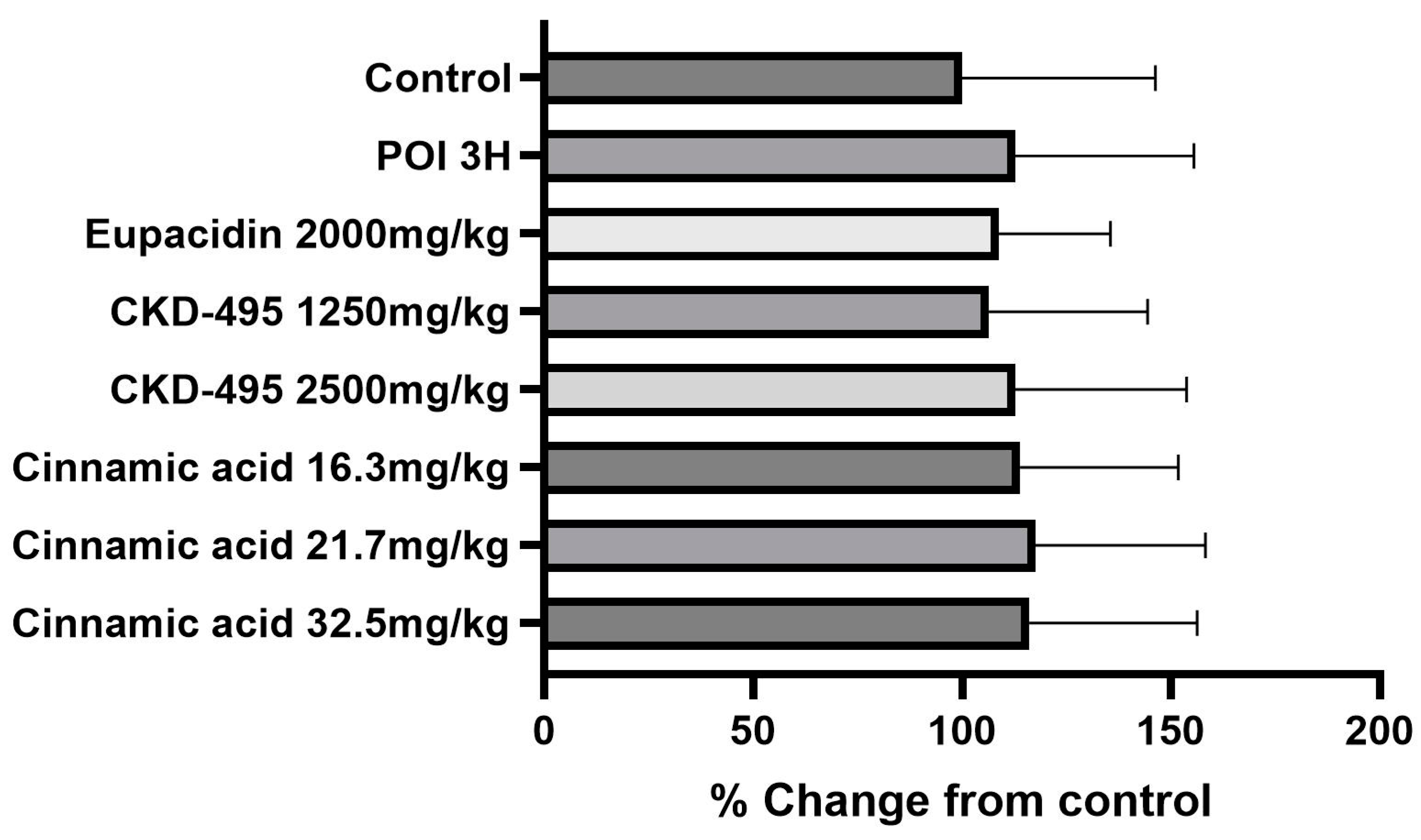
The intestinal inflammatory grade was measured using the leukocyte count of the same number of subjects in the permeability study, 6 subjects in the normal control group, 8 in the POI group, 6 in the eupacidin group, 7 in the eupatilin group, 6 in the CKD-495 doses (1250, 1670, 2500 mg/kg) groups, 5/6/5 in the cinnamic acid groups (16.3 mg/kg, 21.7 mg/kg 32.5 mg/kg). Leukocyte counts were significantly increased in the POI group compared with the control group (25.95±9.92 vs 38.23±14.15, p=0.004), and decreased in all drug groups compared with the POI group (
Figure 2).
3.3. Tight Junction Proteins
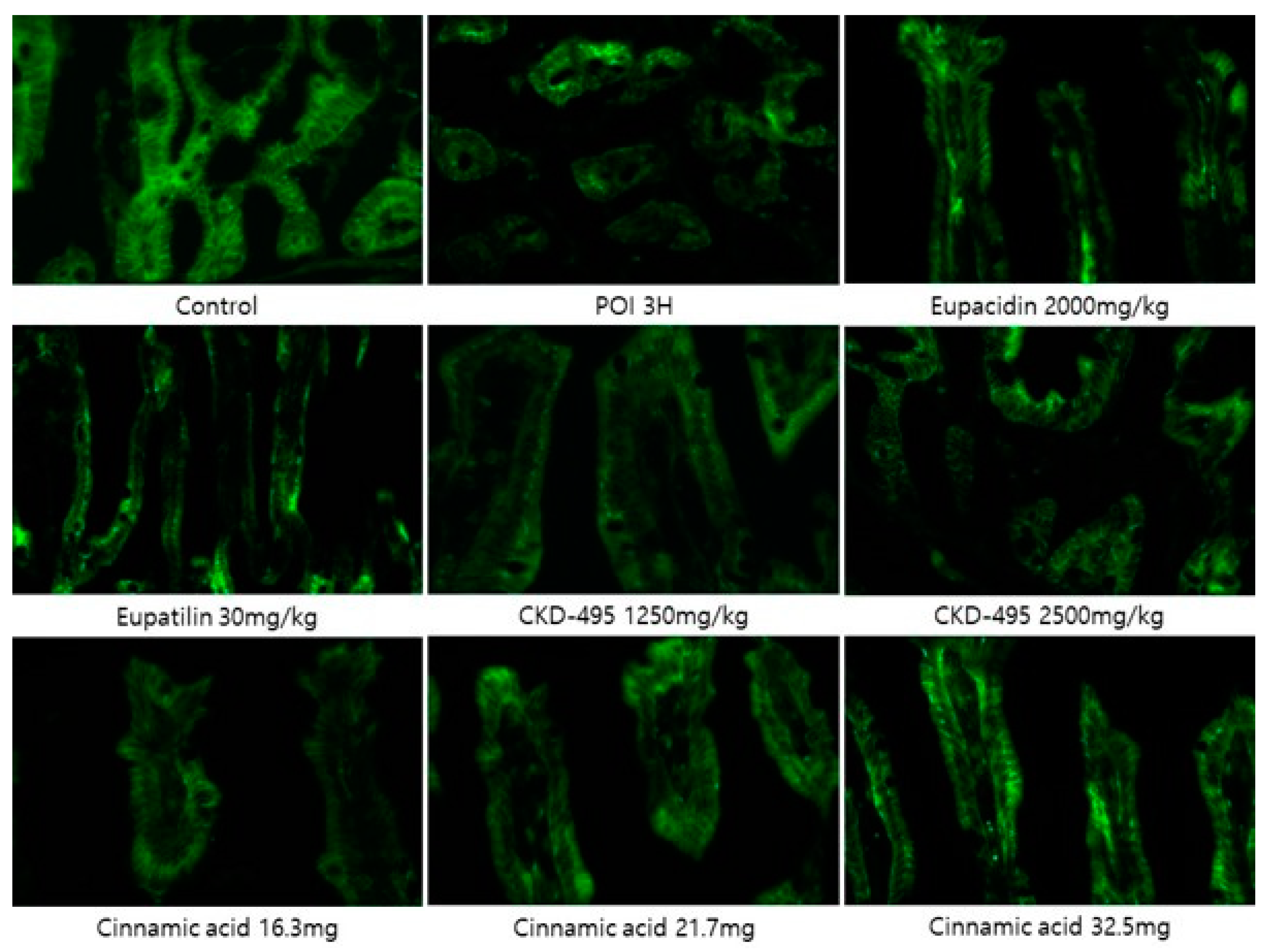
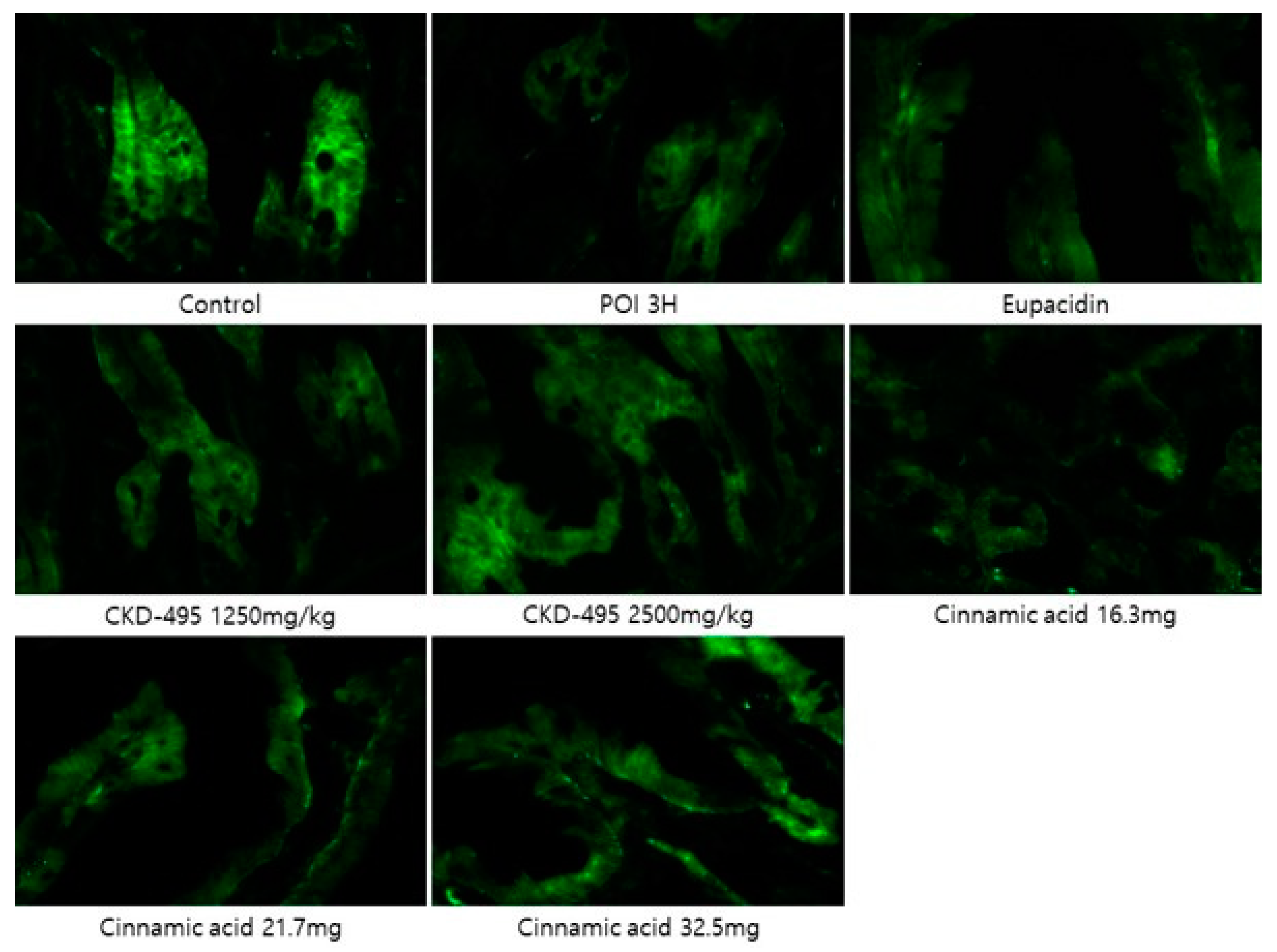
Expression levels of the tight junction proteins claudin-1 and claudin-2 were measured by analyzing immunofluorescence-stained tissue slide images of the ileum (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). We also used a semi-quantitative approach to analyze the slide images using a program to quantify the degree of expression. The results of each group were expressed as the percent change from the mean of the control group, but no significant differences were found between the groups (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). (*Claudin-1 and claudin-2 staining in the CKD-495 1675 mg/kg group and claudin-2 staining in the eupatilin group could not be performed due to sample issues)
4. Discussion
This study demonstrates that pre-administration of CKD-495, eupacidin, eupatilin, and cinnamic acid significantly reduces intestinal permeability and leukocyte infiltration in a guinea pig model of postoperative ileus (POI). These findings suggest that these compounds may serve as effective prophylactic treatments for POI, potentially improving postoperative outcomes.
Both eupatilin and eupacidin were effective in preventing increases in intestinal permeability and inflammation in the POI animal model. Eupatilin, the active component of eupacidin, has been previously demonstrated to exert potent anti-inflammatory effects in various models. Notably, a prior study conducted in rats showed that eupatilin dose-dependently suppressed the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and subsequent production of nitric oxide (NO), a key mediator in inflammatory responses. [
15] This suppression was accompanied by a decrease in nuclear factor (NF)-κB-dependent inflammatory mediators and pro-inflammatory cytokines, including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6. [
16] Given that eupacidin contains eupatilin as its principal active ingredient, it is not surprising that the effects of these two treatments were similar in our study. Both eupatilin and eupacidin significantly inhibited the increases in intestinal permeability and inflammation induced by POI, as evidenced by reduced leukocyte infiltration. The comparison between the eupatilin and eupacidin treatment groups revealed no statistically significant differences in their efficacy, suggesting that the therapeutic effects of eupacidin in this model can be largely attributed to its eupatilin content. These findings align with previous studies and further support the potential of eupatilin as a key anti-inflammatory agent in the management of POI.
CKD-495 was recently recognized for its safety and efficacy in a Phase III clinical trial, where it demonstrated a significant ability to improve gastric mucosal lesions in patients with acute and chronic gastritis. [
9] Following its successful trial outcomes, CKD-495 has been released as a commercial product, expanding its potential applications. In the current study, CKD-495, alongside its key active component, cinnamic acid, effectively inhibited POI-induced increases in intestinal permeability and inflammation across all tested doses in an animal model. The similar mean values observed between the CKD-495 and cinnamic acid treatment groups suggest that cinnamic acid is the primary contributor to these protective effects. Despite varying the doses of CKD-495 and cinnamic acid, no significant differences in intestinal permeability were detected between the different dosage groups, indicating a lack of dose-dependency within the tested range. The absence of a significant difference between the lowest dose (1250 mg/kg of CKD-495 and 16.3 mg/kg of cinnamic acid) and the control group suggests that even the minimal dose used in this study was sufficient to prevent the POI-induced increase in intestinal permeability.
Moreover, increasing the dosage did not result in further reductions in permeability beyond what was observed in the normal control group, implying that the therapeutic ceiling for these compounds might have been reached at the lower doses. This finding is crucial for informing dosing strategies in future clinical studies, as it suggests that lower doses of CKD-495 and cinnamic acid may be adequate for achieving the desired therapeutic effects, potentially minimizing the risk of side effects associated with higher doses. Future research should focus on validating these results in human studies and exploring the long-term efficacy and safety of these dosing strategies. Additionally, exploring the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of CKD-495 and cinnamic acid could provide deeper insights into optimizing their clinical use.
Previous studies by our group have demonstrated that the increased permeability of the intestinal wall following surgical manipulation is accompanied by intestinal wall inflammation. [
17,
18] Therefore, it is reasonable to conclude that modulating this increased permeability would be beneficial in preventing the development of POI. In this study, eupacidin, eupatilin, CKD-495, and cinnamic acid were all effective in preventing the increase in intestinal permeability and inflammation in the POI guinea pig model when administered preoperatively. Thus, all four agents used in this study have the potential to inhibit the development of POI if administered preoperatively.
We measured the expression of the representative tight junction (TJ) proteins, claudin-1 and claudin-2, which are critical in maintaining the intestinal barrier while regulating the permeability of ions, water, and nutrients. [
19] Since previous studies have suggested that changes in the expression of claudin-1, claudin-2, and other TJ proteins may affect the development of POI, we hypothesized that similar changes would occur in our POI group compared to the control group, and that pre-administration of the drug would inhibit the development of POI. [
17] However, no significant differences in TJ protein expression were observed between the control and POI groups in this experiment, nor among the drug treatment groups. The difference between our study and previous studies could be attributed to the timing of tissue harvest; while prior research harvested tissues six hours after POI-inducing procedures, our study harvested tissues three hours post-procedure. This shorter time frame may not have allowed sufficient time for detectable changes in TJ protein expression to manifest. The three-hour time point was selected based on previous animal studies showing that ileal contraction decreases most significantly three hours after surgery. However, this time point may not be optimal for detecting changes in TJ protein expression related to POI development. [
18]
This study has several limitations. First, to accommodate multiple groups, the number of guinea pigs per group was reduced. This limitation may have contributed to some results showing a trend towards significance without reaching statistical significance. For example, although we observed a statistically significant decrease in intestinal mucosal permeability in the case of eupatilin, the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration was not statistically significant, likely due to the limited sample size. Second, we were unable to determine the optimal doses of cinnamic acid and CKD-495. All tested doses of cinnamic acid and CKD-495 inhibited increases in intestinal barrier permeability and inflammation to a similar degree, without statistically significant differences between doses. While the lowest dose of CKD-495 (1250 mg/kg) and cinnamic acid (16.3 mg/kg) appeared sufficient, further studies are required to determine the most effective dose for clinical application.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, increased intestinal permeability and inflammation are critical factors in the pathogenesis of POI. This study demonstrates that eupacidin, eupatilin, CKD-495, and cinnamic acid have protective effects against these pathological changes. Therefore, these four compounds represent promising therapeutic agents for the prevention and treatment of POI.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Park. and MJ.Kim.; methodology, H.Park.; software, Z.Hussain. and YJ.Lee.; validation, H.Park.; formal analysis, MJ.Kim.; investigation, Z.Hussain. and YJ.Lee.; resources, Z.Hussain. and YJ.Lee.; data curation, Z.Hussain., YJ.Lee. and MJ.Kim.; writing—original draft preparation, MJ.Kim.; writing—review and editing, H.Park.; visualization, Z.Hussain. and MJ.Kim.; supervision, H.Park.; project administration, H.Park. and MJ.Kim ; funding acquisition, H.Park. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by research grants from Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The funding agencies had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and received approval from the Institutional Review Board of Gangnam Severance Hospital, South Korea (IRB number 2019-0156). All enrolled participants gave written informed consent.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Khawaja, Z.H.; Gendia, A.; Adnan, N.; Ahmed, J. Prevention and management of postoperative ileus: A review of current practice. Cureus 2022, 14, e22652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tevis, S.E.; Carchman, E.H.; Foley, E.F.; Harms, B.A.; Heise, C.P.; Kennedy, G.D. Postoperative ileus—more than just prolonged length of stay? Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2015, 19, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgeirsson, T.; El-Badawi, K.I.; Mahmood, A.; Barletta, J.; Luchtefeld, M.; Senagore, A.J. Postoperative ileus: It costs more than you expect. J Am Coll Surg 2010, 210, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venara, A.; Neunlist, M.; Slim, K.; Barbieux, J.; Colas, P.A.; Hamy, A.; Meurette, G. Postoperative ileus: Pathophysiology, incidence, and prevention. J. Visc. Surg. 2016, 153, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, E.H.; Passaro, E.P., Jr. Postoperative ileus. Dig Dis Sci 1990, 35, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, C.I.; Milne, T.G.E.; Seo, S.H.B.; Chapman, S.J.; Vather, R.; Bissett, I.P.; O’Grady, G. Post-operative ileus: Definitions, mechanisms and controversies. ANZ J. Surg. 2022, 92, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.J.; Shin, C.Y.; Oh, T.Y.; Sohn, U.D. The protective effect of eupatilin on indomethacin-induced cell damage in cultured feline ileal smooth muscle cells: Involvement of ho-1 and erk. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nageen, B.; Sarfraz, I.; Rasul, A.; Hussain, G.; Rukhsar, F.; Irshad, S.; Riaz, A.; Selamoglu, Z.; Ali, M. Eupatilin: A natural pharmacologically active flavone compound with its wide range applications. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, S.K.; Chun, H.J.; Song, G.A.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, T.N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ckd-495 in acute and chronic gastritis: A phase iii superiority clinical trial. Medicine 2023, 102, e35926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, L.S.M.; Li, Y.; Kam, S.-L.; Wang, H.; Wong, E.Y.L.; Ooi, V.E.C. Antimicrobial activities of cinnamon oil and cinnamaldehyde from the chinese medicinal herb cinnamomum cassia blume. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2006, 34, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sova, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of cinnamic acid derivatives. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, P.; Baltas, M.; Bedos-Belval, F. Cinnamic acid derivatives as anticancer agents-a review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1672–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwizhi, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Cinnamic acid derivatives and their biological efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, D.S.; Lee, O.Y.; Lee, K.N.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S. The effect of da-6034 on intestinal permeability in an indomethacin-induced small intestinal injury model. Gut Liver 2016, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-J.; Lee, S.; Chae, J.-R.; Lee, H.-S.; Jun, C.-D.; Kim, S.-H. Eupatilin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inflammatory mediators in macrophages. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-G.; Kim, K.-W.; Li, J.; Lee, D.Y.; Yoon, D.; Jeong, J.T.; Kim, G.-S.; Oh, H.; An, R.-B.; Kim, Y.-C. Anti-inflammatory components isolated from atractylodes macrocephala in lps-induced raw264.7 macrophages and bv2 microglial cells. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Hussain, Z.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, H. Altered intestinal permeability and drug repositioning in a post-operative ileus guinea pig model. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Hussain, Z.; Huh, C.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, H. Inflammation, impaired motility, and permeability in a guinea pig model of postoperative ileus. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: Implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).