1. Introduction
Since the knowledge of how diet and diseases are related, the primary role of diet passed from supplying daily metabolic requirements to the use of the food itself as a way to promote health and reduce the risk of diseases [
1]. However, although consumers are now more interested in nutrition and health, diet-related diseases, especially obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and metabolic syndrome, are still a concern [
2]. Before such a scenario, a market niche focused on developing foods that could prevent diseases through bioactive substances from vegetables, fruits, and edible plants [
3]; those foods are term functional. Functional foods are naturally occurring or processed foods with health-promoting or disease-preventing properties beyond their traditional nutritional value [
4].
Microalgae are being seen as an innovative ingredient to produce functional foods due to their high nutritional value (vitamins, proteins, polysaccharides, minerals, enzymes, and fibers) and content in bioactive compounds such as peptides, polyphenols, essential amino acids, mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids, carotenoids and phycocyanins [
5] with properties as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antimicrobial compounds [
6]. Several studies have demonstrated that the inclusion of microalgae in food improved the nutritional value and their content of bioactive substances such as antioxidants [
7,
8,
9], which are important to prevent oxidative damage upon cells caused by oxidative stress, a state in which oxidation exceeds the antioxidant systems in the body secondary to a loss of the balance between them, causing hazardous effects upon the body [
10].
Arthrospira platensis (Ap) is a filamentous cyanobacterium of great biotechnological and nutritional importance that has been used successfully in developing food commodities, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics [
11]. Its inclusion in foods has shown increases in not only the nutritional value (especially proteins) but also their content in bioactive substances [
7] such antioxidants, water-soluble pigment-protein complexes (phycocyanin), carotenoids, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase) [
12].
A. platensis possesses GRAS status (Generally Recognized as Safe) by the FDA and is intended for 0.5-3 g per serving in a wide range of food matrixes, including noodles and pasta [
13].
Pasta, a staple food of worldwide consumption, has an affordable price, popularity, palatability, and good nutritional characteristics. Hence, pasta represents a good vehicle for the inclusion of nutriments, a consideration also supported by the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) [
14]. Previous studies dealing with the inclusion of
Arthrospira platensis in pasta reported increased nutritional value (especially protein) [
15], improved textural properties [
16] and enhanced antioxidant capacity [
17,
18]
Probiotics are another ideal example of functional ingredients since many food products today are becoming functional [
19]. Usually, dairy products have been adopted as the most popular vehicle of probiotics in products such as yogurts, fermented milk, and cheese [
20]. Milk fat enhances the viability of probiotics and their acid-bile tolerance [
21]. Therefore, dairy foods are used as carriers of probiotics mainly due to their pH, buffering capacity, and fat content, which creates extra protection for probiotics when undergoing gastrointestinal tract and enhances their maintenance [
22]. Buffering capacity and pH are significant factors influencing the survival of probiotics and their potential probiotic effects during gastric transit [
23]. Buffering capacity refers to the characteristic of food that resists changes in pH. It is a remarkable aspect to consider in gastric digestion since it will impact the physiochemical breakdown of food [
24].
There is an increasing interest in developing non-dairy probiotic foods for consumers with allergies like lactose intolerance or those who prefer low-cholesterol products. However, traditional and economic dynamics influence this context, sometimes making the employment of dairy products not feasible, making it necessary to supply them in other culturally compatible ways [
25]. Several studies have demonstrated that some non-dairy products also possess buffer capacity, and they can be considered feasible food carriers, like cereal-based products, vegetables, meat, fish products, fruit and fruit juices, and miscellaneous [
21].
The most common probiotic microorganisms used are
Bifidobacterium and
Lactobacillus [
26] and several approaches have been considered to increase their viability [
27]. However, these microorganisms do not always apply to alimentary matrixes requiring thermal processing or cooking. Spore-former lactic acid bacteria (SFLAB) have been presented as a way to produce probiotic food that can be heat-treated or cooked without losing its beneficial properties [
28].
Bacillus coagulans GBI 30 6068 is a probiotic strain with multiple health benefits such as reduction of gastrointestinal symptoms [
29], improvement of irritable bowel syndrome symptoms [
30], and in combination with prebiotics (fermentable substrates) shown improvements in dysbiosis [
31], intestinal gas symptoms, rheumatoid arthritis, improve the immune response to viral infections of the respiratory tract [
32] and enhances the digestion of proteins and carbohydrates like lactose and fructose [
33].
Previous studies have successfully used
B. coagulans GBI 30 6068 in the development of probiotic pasta formulations, showing that the microorganism is capable of withstanding pasta-making process conditions and cooking process and remain viable in enough quantity to be considered a probiotic food, without affecting primary pasta properties, texture or flavor [
32,
33,
34]. However, there is no information regarding a pasta formulation added with
A. platensis and
B. coagulans. For that, the development of this pasta could be of interest since many studies have indicated that
A. platensis can be used as a fermentable substrate [
35,
36], supporting the cell count and viability of microorganisms in probiotic foods [
37,
38] and increasing the content of bioactive substances with antioxidant properties and overall the nutritional value of foods Therefore, this study aimed to develop an artisanal soft wheat flour pasta with egg added with
A. platensis and
B. coagulans and to evaluate the effects on the nutritional value, antioxidant capacity, pigment content, color, probiotic viability, buffering capacity and textural properties of pasta.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pasta Formulation and Nutritional Value
Pasta formulations were made by mixing standard white wheat flour (69.83%), water (18.16%), egg yolk (11.31%) and salt (0.70%) with a) 5% of B. coagulans BC30 GBI 6068 (1x1013 CFU/g) freeze-dried (Bc pasta). b) 5% of a commercially available product of Arthrospira platensis dried biomass (Ap pasta) and c) both B. coagulans and A. platensis in the previously mentioned percentages (Bc+Ap pasta). A pasta formulation without A. platensis and without B. coagulans were used as control. The resultant doughs were kneaded for 10 min, rested for 90 min at room temperature (22°C), and processed using an Italian pasta hand press of 15 cm (Vencort, model: 349003) into tagliatelle-shaped pasta strips with dimensions of 100x5x1mm. Pasta strips were left to dry for 48 h at room temperature and used for the subsequent analyses on proteins (method 46-12.01; AOAC), fats (method 2003.06-2006; AOAC), carbohydrates (by difference), fiber (method 978.10; AOAC), moisture (method 948.12; AOAC) and ash (method 08-01.01; AOAC). Caloric value was calculated using the Atwater system by multiplying each macronutrient content by 4, 9, and 4 kcal for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, respectively. Furthermore, portions of uncooked and cooked pasta [10 g boiled in 200 mL of distilled water for 8 min (time for “al dente” term)], after cooking the pasta were freeze-dried for further analysis.
2.2. Preparation of Extracts for Antioxidant Capacity Assays
One gram of each freeze-dried paste was milled in a blender and added to assay tubes with 9 mL of methanol. Then, it was vortexed for 1 min, sonicated for 30 min at 30°C (Sonicator VWR model: 150D), and finally centrifuged (Eppendorf model 5804R) at 7563 g for 5 min at 20 °C. Aliquots of the resultant supernatants were transferred to microtubes and stored in dark and cold conditions (-80°C) until their use.
2.3. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
The TPC was determined using the rigorous methodology of López-Martínez
et al. [
39]. Briefly, 20 µL of the extract was mixed with 20 µL of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (Sigma-Aldrich®) and left to react for 5 min. After that, 20 µL of 0.01 M Na
2CO
3 was added and left to react for another 5 min, and finally, 125 µL of distilled water was added. The absorbance was measured at 790 nm using a microplate reader (Multiskan GO, Thermo Fisher Scientific). The TPC was calculated from linear regression using a gallic acid solution (0-1500 mg/L) and expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalents per gram of sample in dry weight (mg GAE/gdw).
2.4. Antioxidant Capacity
2.4.1. ABTS (2,2-Azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) Assay
The ABTS assay was done according to Buenrostro-Figueroa
et al. [
40]. Briefly, the ABTS free radical (ABTS
•+) was obtained by mixing 5 mL of 7 mM ABTS with 2.5 mL of 2 mM K
2S
2O
8 and subsequently incubated at room temperature for 12 h without. To prepare ABTS•+ solution, the mixture was diluted with ethanol until obtaining an absorbance of 0.70 at 734 nm was obtained. The assay was performed in a 96-well microplate, in which 10 µL of the sample was mixed with 190 µL of the ABTS
•+ and left to react for 1 min. Then, the absorbance was recorded at 734 nm using methanol as a blank in a microplate reader (Multiskan GO, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Finland). Antioxidant capacity was obtained by linear regression using a calibration curve of Trolox (0-800 µmol) and expressed as µmol of Trolox equivalents per gram of sample in dry weight (µmol TE/gdw).
2.4.2. FRAP (Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Capacity) Assay
FRAP reagent was prepared by combining 25 mL of 0.3 M acetate buffer (pH 3.6), 2.5 mL of 10 mM TPTZ (Sigma-Aldrich®) in 40 mM HCl, and 2.5 mL of 20 mM ferric chloride. This mixture was incubated for 20 min at 37°C before use. In a 96-well microplate, 6 µL of the extract was added with 18 µL of distilled water and 180 µL of FRAP reagent. The absorbance was measured at 593 nm (Multiskan GO, Thermo Fisher Scientific) using methanol as a blank, ensuring the accuracy of the results. The antioxidant power was determined by linear regression using Iron (II) sulphate heptahydrate solutions (0-3000 µmol) and expressed as µmol of Fe
+2 per gram of dried weight (µmolFe
+2 /gdw) [
42].
2.5. Pigments Determination
Adapting the methodology of Braniša
et al. [
43] to microplate, the content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total carotenoids were determined. Briefly, 0.5 g of milled sample was added with 5 mL of acetone (100%) in assay tubes, followed by a sonication (Sonicator VWR model: 150D) of 3 min, and subsequently centrifugated at 7563 g for 10 min (20°C). The resultant supernatants were stored in amber microtubes at -80°C until their use. In a 96-well microplate, 200 µL of each extract was added and the absorbance was measured in a microplate reader (Multiskan GO, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 662, 645 and 470 nm for chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total carotenoids, respectively. Acetone (100%) was used as blank. For the estimation of each pigment content, the equations of [
44] were used (eq. 1-3), and the results were expressed as milligrams/100 g of dry weight (dw).
2.6. Textural Profile Analysis (TPA)
The TPA was performed according to Milde
et al. [
45] using a texturometer TA. XTplus (Stable Micro Systems Ltd., London, United Kingdom) and texture exponent lite version 4.0.130.0 (Stable Micro Systems Ltd; 2007) software. The pasta was cooked as mentioned before (considering the AACCI Method 66-50.01, 2000). Three measurements were performed in each formulation. The TPA analysis was carried out in pasta strips of 4 cm in length, which were subjected to two compression cycles, using a 75 mm diameter flat-ended cylindrical probe. The test configuration was programmed to a speed of 0.5 mm/s, the pre-test speed was 1 mm/s, and the compression distance was 75% of the original size. From the force-distance curve from pasta, were determined the firmness (g), adhesiveness (g x sec), springiness (%), gumminess (g), chewiness (g), Cohesiveness (g), and resilience (%).
2.7. Buffer Capacity
Buffer capacity was evaluated using the methodology of Mennah-Govela
et al. [
24]. For this, pasta (100 g) was cooked in 200 mL of distilled water for 8 min (enough for the “al dente” term), then the pasta was drained and pureed with a blender. Twenty grams of pureed pasta were placed in beakers of enough length to allow the entrance of the pH lector tip (Thermo scientific ORION STAR A211). The initial pH was measured and recorded in 3 locations, then aliquots of 0.5-1 mL of HCl 0.16 M were added and mixed with the sample. After adding each HCl aliquot and mixing, the pH was measured again in three locations until reaching a final pH of 1.5. All pureed samples were measured in triplicate.
2.8. B. coagulans GBI-30 Count
Ten grams of pasta in 90 mL of phosphate buffer solution (PBS) were homogenized (Seward Stomacher 400) at 230 rpm for 30 sec, and serial decimal dilutions were made. Each dilution was heat-treated in a water bath at 75°C for 30 min. Finally, 1 mL of each dilution was spread-plated on GYE agar and incubated at 37°C for 48-72h. Typical B. coagulans colonies were counted and calculated as CFU/mL.
2.9. Colorimetric Analysis of Pasta
The color of raw and cooked samples was measured using a colorimeter (KONICA MINOLTA CM-600d), and a commercially available semolina pasta was used as a reference. For this, 100 g of pasta was milled in a blender until it became a powder. The milled sample was placed in a white recipient, covering all recipient surfaces (a powder layer of 2 mm of thickness). The lecture tube of the colorimeter was placed above the powdered paste, and then the colorimeter emitted a beam of light. Yellowness index was calculated according to Belahcen 2022 [
72].
2.10. Statistical Analysis
All samples were analyzed in triplicate and expressed as a mean (n=3) ± standard deviation. Statistics analyses were performed using SAS software (SAS 9.0). In case of nutritional value, a one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) followed by a Tukey test (p<0.05) was made. Regarding antioxidant capacity assays, pigment content, color measurements, and TPA, raw and cooked pastas were analyzed separately. A one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey test (p<0.05) was used to measure the differences between the raw pasta in the previously mentioned parameters, and another one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey test (p<0.05) to measure the differences between the cooked ones.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutritional Value
Pasta represents an important food in human nutrition due to its high content of complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index and some proteins. Previous reports dealing with the addition of
A. platensis to pasta have found enhancements in the nutritional value directly proportional to the addition of the microalgae, although with high variability [
15,
16,
18]. The nutritional values of pasta samples are shown in
Table 1.
Significant changes between pasta formulations were observed in protein, carbohydrate and fat content (p<0.05). The protein content of all samples showed statistically significant increases in the order of Bc, Ap, and Bc+Ap, in contrast to the control. The Bc formulation showed an increase in protein content of 19.02%, followed by Ap pasta with 19.65%. Finally, the Bc+Ap pasta showed a higher protein increase of 30.61% compared to the control, indicating that both A. platensis and B. coagulans positively impacted the protein content.
It is well known that
A. platensis has a high protein content, but more information about this needs to be provided on
B. coagulans. Regarding the increase in proteins produced by adding
B. coagulans found here, two previous studies deal with adding
B. coagulans in pasta [
32,
34]. However, these studies did not perform a proximal analysis on this parameter to determine if the addition of
B. coagulans has any effect on the protein content. Nonetheless, other studies have stated that bacterial spores possess a coat mainly made of proteins, representing 50-80% of the total spore protein [
46]. Thus, the protein increase evidenced here by the addition of
B. coagulans is probably attributed to spore coat proteins, but more studies must be carried out to confirm this.
According to the FDA, the recommended daily value (%DV) of proteins based on a diet of 2000 kcal is 50g, categorizing foods as high in proteins when they contain at least 20% of the %DV per serving. Bc+Ap pasta, in a portion of two ounces, contributes 16.35% to the daily recommended value of proteins. This pasta provides a significant portion of protein needs and offers additional benefits and the potential beneficial effects of B. coagulans on digestive and gut health. On the other hand, the carbohydrate content showed a statistically significant tendency to decrease, especially for Bc+Ap pasta. Other parameters, such as the fat content, caloric value, fiber, ash, and moisture, did not show an effect attributable to adding B. coagulans or A. platensis.
Although other studies have shown that
A. platensis produces increases in proteins, fats, carbohydrates, fiber, and ashes [
16,
18,
47], in this study, just the protein parameter was increased statistically significantly. In contrast, the other parameters did not show a change related to adding the microalga. Regarding these findings, Lemes
et al. [
16] stated that the nutritional profile of
A. platensis is highly dependent on factors such as the strain used, growth media, and freshness. Thus, this can explain the differences in the nutritional profile of pasta added with
A. platensis reported in the literature and the formulations developed here.
3.2. TPC (Total Phenolic Content)
The TPC of the samples is shown in
Table 2. All samples added with
B. coagulans (Bc and Bc+Ap) presented significantly reduced TPC than the non-added
B. coagulans samples, except cooked Bc pasta, which, although presented lowered TPC, was not significantly different from the cooked control (p<0.05). The Bc pasta showed a significant decrease in TPC values in uncooked at 23.28% in contrast to the control pasta. Interestingly, after the cooking process, Bc pasta recovered almost the same value on TPC as the control pasta with no difference (p<0.05) among them (43.50 and 41.95 mg GAE/g for control and Bc pasta, respectively).
The addition of A. platensis resulted in significant increases in the TPC. Uncooked and cooked Ap pasta showed increases of 9.64 and 28.34%, respectively, in contrast to uncooked and cooked control. Contrastingly to the uncooked control, the uncooked Bc+Ap pasta showed a decrease in TPC of 11.41% but a significative increase after cooking of 14.22 compared to the cooked control. On the other hand, the TPC of uncooked and cooked Bc+Ap pasta was 19.20 and 11% lower than uncooked and cooked Ap pasta (47.18 and 55.83 mg GAE/g, respectively). Nonetheless, when comparing both Bc+Ap and Ap cooked samples (as occurred with control and Bc cooked pasta), the Bc+Ap pasta recovered some of its TPC values after cooking and remained near the values obtained by the AP pasta. However, it was significantly (p<0.05) lower than the Ap sample.
Other studies dealing with adding
A. platensis in pasta have reported increases in the TPC of 0.16-1.31 and 1.23 mg GAE/g for 5%
A. platensis uncooked and cooked pasta, respectively, in contrast to controls [
18,
47]. The results presented here showed increased 4.15 and 12.33 mg/g for uncooked and cooked 5%
A. platensis pasta. This later gain could be due to the increment tendency of the cooked pasta to rehydrate during the extraction of the bioactive compounds, releasing more of its internal components to the media in contrast to the uncooked pasta. Furthermore, as was discussed previously, the high susceptibility of
A. platensis to cultivation variables, freshness, and the strain used can explain the high variability in the bioactive compound profile among the different commercially available
A. platensis products, explaining the differences in the TPC and antioxidant capacity of the different products added with
A. platensis reported on the literature. According to Park
et al. [
48], the variables involved during mass production, the drying process, food processing techniques, and storage conditions can affect the content of pigments, TPC and antioxidant capacity of
A. platensis powders.
3.2.1. Antioxidant Capacity
ABTS (2,2-Azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) assay
The results of the ABTS assay are shown in
Table 2. Adding of
A. platensis resulted in a significant increase in the antioxidant capacity of samples respect to the control and Bc pasta (p<0.05). Uncooked pasta added with
A. platensis showed an increased antioxidant capacity of 90.41% and 116.70% for Ap and Bc+Ap formulations in contrast to control and Bc pasta, respectively. Nonetheless, in the uncooked Bc+Ap sample, a synergic effect appears, increasing in a significant way (p<0.05) the antioxidant capacity of the sample by 11.70% in contrast to Ap pasta (17.69 µmol TE/g).
This finding, which suggests that
B. coagulans can produced some organic acids or other antioxidant molecules using
A. platensis as a fermentable substrate during the rest time of doughs since the Bc pasta did not show this effect. Although the exact temporal order for spore germination has not been determined in bacterial spores, the germination process (and the steps involved) is generally triggered by the presence of nutrients, amino acids, sugars, and nucleosides [
49]. This could suggest an increased spore response to a media rich in amino acids, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and salts provided by adding
A. platensis into pasta. Previous studies have evidenced that
A. platensis can be used as a fermentable substrate for lactic acid bacteria, increasing their cell count, viability, and nutritional quality of fermented products [
35]. This suggestion of organic molecules derived from the interaction between
A. platensis and
B. coagulans is also supported by the results of cooked samples. When comparing Ap and Bc+Ap cooked pasta, these organic compounds responsible for the increase of antioxidant capacity in uncooked Bc+Ap sample are degraded, causing the antioxidant capacity of both samples to remain at similar levels of 14.01 and 13.63 µmol TE/g for Ap and Bc+Ap respectively. However, both samples evidenced antioxidant capacity degradation after the cooking process, showing respective reductions of 20.80% and 31.02% for Ap and Bc+Ap samples, but remaining 59.93% and 55.59% higher than cooked control.
On the other hand, control and Bc pasta presented slight differences after the cooking process with minimal changes in their respective antioxidant capacity in uncooked treatment. A decrease of 5.70% was evidenced for control pasta and an increase of 1.42% for Bc pasta but did not result in any statistically significant change in antioxidant capacity (p < 0.05).
Similar results on the antioxidant capacity by ABTS of probiotic pasta made with
B. coagulans were obtained by Fares
et al. [
32]. The authors compared the antioxidant capacity of three formulations: the first one consisting of durum wheat Vendetta hulled up to 4.5%; the second one durum wheat Vendetta hulled up to 4.5% (78.5%) mixed and homogenized with 18% of enriched barley flour (11% b-glucan) and 3.5% of vital gluten powder; and the third one consisting of this last formulation but with 1% of
B. coagulans GBI-30, 6086 (10.3 log CFU/g). The authors found a significant (p < 0.05) increase of 33% in the antioxidant capacity of the probiotic pasta in contrast to the second. After cooking, the antioxidant capacity of the three samples remained at similar levels without significant changes. At this moment, this is the only study that assessed the antioxidant capacity by ABTS (with a similar methodology as the one used here) of pasta added with
B. coagulans after and before cooking, obtaining a similar synergic effect as the showed here. However, the authors did not attribute this increase to any synergic effect of the microorganism and the pasta components.
At this moment, there are no more previous studies assessing the antioxidant capacity of pasta added with A. platensis or with B. coagulans to compare for reference values regarding the findings presented here by ABTS assay. Hence, the information presented here could be helpful for further analyses of antioxidant capacity measurement by ABTS on similar formulations.
3.2.2. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
FRAP assay results are shown in
Table 2. Contrary to the ABTS assay, adding
B. coagulans caused a significant reduction (p<0.05) in the ferric reducing antioxidant power capacity of uncooked and cooked samples in contrast to pasta without the microorganism. Uncooked Bc pasta showed a significantly lower value on ferric reducing antioxidant power of 25.38% less than control pasta (13.67 µmol Fe+2/g). After cooking, although both control and Bc pasta lost some of their original ferric reducing antioxidant power (17.33% and 44.01%, respectively), the Bc pasta obtained the lowest value (5.71 µmol Fe+2/g).
Regarding pasta added with A. platensis and B. coagulans, a similar effect was caused by B. coagulans addition. In this case, the synergic effect between A. platensis and B. coagulans observed previously in the ABTS assay is not shown here. The Bc+Ap sample showed lowered ferric reducing antioxidant power in uncooked (21%) and cooked (15.10%) in contrast to Ap pasta (21.61 and 14.77 µmol Fe+2/g for uncooked and cooked Ap pasta, respectively). However, both Ap and Bc+Ap samples obtained higher values of ferric reducing antioxidant power capacity in uncooked (58.08 and 67.35%) and cooked (30.70 and 119.43%) in contrast to control and Bc pasta, respectively, whose obtained values were 13.67 and 10.20 µmol Fe+2/g for uncooked and, 11.30 and 5.71 µmol Fe+2/g for cooked control and Bc pasta respectively.
Previous studies assessing FRAP values on
A. platensis added pasta vary to a great extent from 2.52-11.3 µmol/g and 2.96-31.4 µmol/g for uncooked control and 5%
A. platensis added pasta, respectively [
18,
47]. Regarding cooked pasta, values of 9.45 and 26.81 µmol/g for control and 5%
A. platensis have been reported [
18]. Therefore, the results presented here are in the range of the FRAP values reported in the literature.
3.2.3. Spectrophotometric Estimation of Pigment Content
Arthrospira platensis is a natural source of pigments with recognized health benefits and antioxidant properties such as chlorophylls, carotenoids, and phycocyanin (blue pigment) to which the strong antioxidant properties of
A. platensis are attributed [
50]. The pigment content provided by adding
A. platensis to pasta is shown in
Table 3.
The addition of A. platensis led to a unique enrichment of the pasta with pigments such as chlorophylls and carotenoids. The uncooked Ap pasta demonstrated a content of 5.16 and 1.5 mg of chlorophyll a+b and total carotenoids, respectively. However, the cooked Ap pasta exhibited a significant increase in all pigment content, with a 117.44 and 36.66% rise for chlorophyll a+b and total carotenoids, respectively.
The increase in pigment content after the cooking is probably attributed to the structural damage on
A. platensis induced by the cooking process, releasing more of its internal components to the media. In addition, the cooking process produced a weakened gluten network of pasta by the swelling of starch granules [
51], producing a brittle pasta more permeable to the extraction media than uncooked pasta. Experimentally, cooked pasta where prone to rehydrate easily and faster than uncooked samples, resulting in an increased release of the bioactive compounds contained in them to the extraction media.
Surprisingly, the addition of B. coagulans to pasta (Bc+Ap) caused a significant modification in the content of all pigments. In contrast to uncooked Ap pasta, the uncooked Bc+Ap pasta showed significant initial reductions of 15.70% and 8.66% for chlorophyll a+b and total carotenoids respectively. Furthermore, when comparing cooked Ap pasta with cooked Bc+Ap pasta also significant reductions (p < 0.05) of 40.10 and 42.92% were noticed for chlorophyll a+b and total carotenoids respectively. On the other hand, the increases in chlorophyll a+b and total carotenoids evidenced by Ap pasta after cooking were different for Bc+Ap pasta. Instead, an increase of 54.48% and a reduction of 14.60% were found for chlorophyll a+b and total carotenoids respectively in Bc+Ap pasta.
Although there are just a few studies assessing the pigment content regarding chlorophylls and total carotenoids in foods added with
A. platensis [
52,
53,
54] to compare for reference values, the results and addition percentages assessed here are similar just to those reported by Tańska
et al. [
53] who developed corn extrudates with several percentages of
A. platensis by using extrusion-cooking process. The authors found chlorophyll values of 6.2 and 12.6 mg/100g for corn extrudates added at 4 and 6%, respectively. Therefore, the value of 11.22 mg/100g for chlorophyll obtained by cooked pasta added at 5% fits between the range of the values reported by these authors. Nonetheless, regarding carotenoid content, there are no reference values in similar percentages of the addition of
A. platensis as assessed here.
3.3. Probiotic viability
Probiotics are defined as “live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host”. However, to exert their beneficial properties, probiotics have to be administered at least at the “minimum therapeutic” level, reached when supplied at 10
6 CFU/g of viable cells [
55]. While
Lactobacillus and
bifibacterium species have been typically used as probiotics and have shown remarkable probiotic activities, their survival is commonly low, ranging from 1-15% or even lower in some strains [
26]. These low survival rates pose significant challenges to the viability of probiotics, especially considering the harsh conditions, they undergo from manufacturing methods, storage, and shipping conditions, as well as the normal physiological conditions (acidic environment of stomach and bile salts when they are consumed) these are some aspects responsible for their low viability [
28]. However, probiotic spore forming bacteria, with their ability to withstand the effects of food and feed processing [
56], offer a promising solution. Their spore former ability brings them the capacity to withstand harsh conditions in contrast to vegetative cells [
57]. The results of the viability assay of the pasta added with
B. coagulans, a probiotic spore forming bacteria, are shown in
Table 4.
The viability of B. coagulans behaved differently in the presence of A. platensis. Although the initial concentration of added B. coagulans was 13 log CFU/g, the number of colonies on agar plates showed for Bc pasta a count of 5.19 log CFU/g on average, whereas when B. coagulans was in combination with A. platensis an increased response was evidenced, showing a count of 7 log CFU/g. Reductions of 7.81 and 6 log were evidenced by comparing the initial concentration of B. coagulans in the freeze-dried (13 log CFU/g) and the final concentration on raw pasta by the results of the agar plating for Bc and Bc+Ap pasta, respectively without significative changes on the B. coagulans counts after the cooking process (8 minutes).
The differences between the counts of
B. coagulans on Bc and Bc+Ap pasta is probably attributed to the compounds contained on
A. platensis. According to Løvdal
et al. [
58] bacterial dormant spores of bacillus can be induced to germinate by nutrients as amino acids, purine nucleosides, sugars, ions and combination of these. Hence, although Bc+Ap pasta had higher count of CFU/g on the agar plates in contrast to Bc pasta, both formulations contained the same amount of CFU/g but more spores were triggered to germinate by the presence of the previously mentioned compounds that are also present in
A. platensis in contrast to Bc pasta.
Previous studies on probiotic pasta with
B. coagulans have shown the high viability of this microorganism to withstand the making and cooking process and remain viable in enough quantities to be considered a probiotic food (>1x10
6). Fares
et al. [
32] developed probiotic pasta with 1% of
B. coagulans freeze-dried (10 log CFU/g). The authors obtained a concentration of 8 log CFU/g when
B. coagulans was mixed with wheat flour and a final concentration of 7 log CFU/g on raw pasta. Furthermore, the authors assessed the effect of cooking on the counts of
B. coagulans colonies. They found reductions of 0.43 and 0.62 log CFU/g after cooking for 5 and 7 minutes, respectively, in contrast to raw pasta (7.34 log CFU/g). A deeper analysis of the changes in
B. coagulans CFU counts during the pasta-making process is described in the study of Konuray & Erginkaya [
34]. The authors added
B. coagulans to wheat flour until they obtained an approximately 8.62 log CFU/g concentration. Subsequently, they measured the concentration after the formation of the dough, extrusion, drying and even after six months of storage, finding minimal reductions of 0.12, 0.01, 0.19 and 0.96 log CFU/g, respectively. These findings evidence the high viability of this microorganism in producing probiotic pasta products without detrimental effects on its CFU count even in 6 months of storage.
The results in this study, shown by Bc+Ap pasta regarding bacterial count and viability after the cooking process, are in agreement with those of the previously mentioned authors, who got counts of 8-7 log CFU/g on raw pasta and 7 log CFU/g on cooked pasta. These counts represent enough quantities of CFU per gram to confer the potential health benefits associated with probiotic foods.
3.4. Buffer Capacity
The buffering capacity is an important parameter to increase the survival of probiotics. Typically, dairy products, (mainly the fermented ones) are used as vehicles (also known as carriers) to carry probiotics due to characteristics and requirements such as low-temperature needs (4°C-8°C), limited shelf life (15-25 days), their richness in the necessary nutrients to promote the growth of the probiotic microorganisms, and the easy availability of the necessary guidelines for the use of probiotics in dairy products [
59]. However, the main aspect that makes dairy products the preferred vehicle for the delivery of probiotics is their buffer capacity [
22], which is attributed to their content of protein and minerals (calcium, citrate, phosphate, and lactate) [
60].
Buffering capacity refers to the ability of a substance to resist changes in pH [
24]. The relationship between buffer capacity and probiotic viability relies on the capacity of the food to slow down the velocity at which food changes its pH. Hence, the greater the buffer capacity is, the more gastric acid concentration and time are needed to change the pH of the food. This delay in the time required to change the pH can be visualized as a less drastic change in the pH; this means that the changes in the food are more gradual and, therefore, less stressful and lethal for probiotic microorganisms. Buffering capacity is essential from the point of view of digestion and storage/shelf life.
Since the gastrointestinal passage is a harsh environment characterized by high gastric acidity, oxygen stress is induced by ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) released from mucosal surfaces, bile salt stress, and osmotic stress, among other factors. The nature of the food when it is added probiotics becomes a vital factor regulating its further colonization in the gastrointestinal tract, and aid probiotic bacteria by buffering the stomach's acidic environment and supporting its viability alone or by adding other functional ingredients which can improve this capacity [
61].
The study of Mennah-Govela
et al. [
60] indicated that the buffering capacity depends on the food's composition; this means content in proteins and their content in amino acids such as aspartic and glutamic acid, organic acids, initial pH, and other food ingredients, additives as well as food particle size (an increased superficial area also increase buffer capacity). Furthermore, the authors indicated that fat and carbohydrates negatively affect buffer capacity, preventing acid reactions with proteins by interfering with the diffusion of H+ or impacting reactions of H+ with those compounds with inherent buffering capacity.
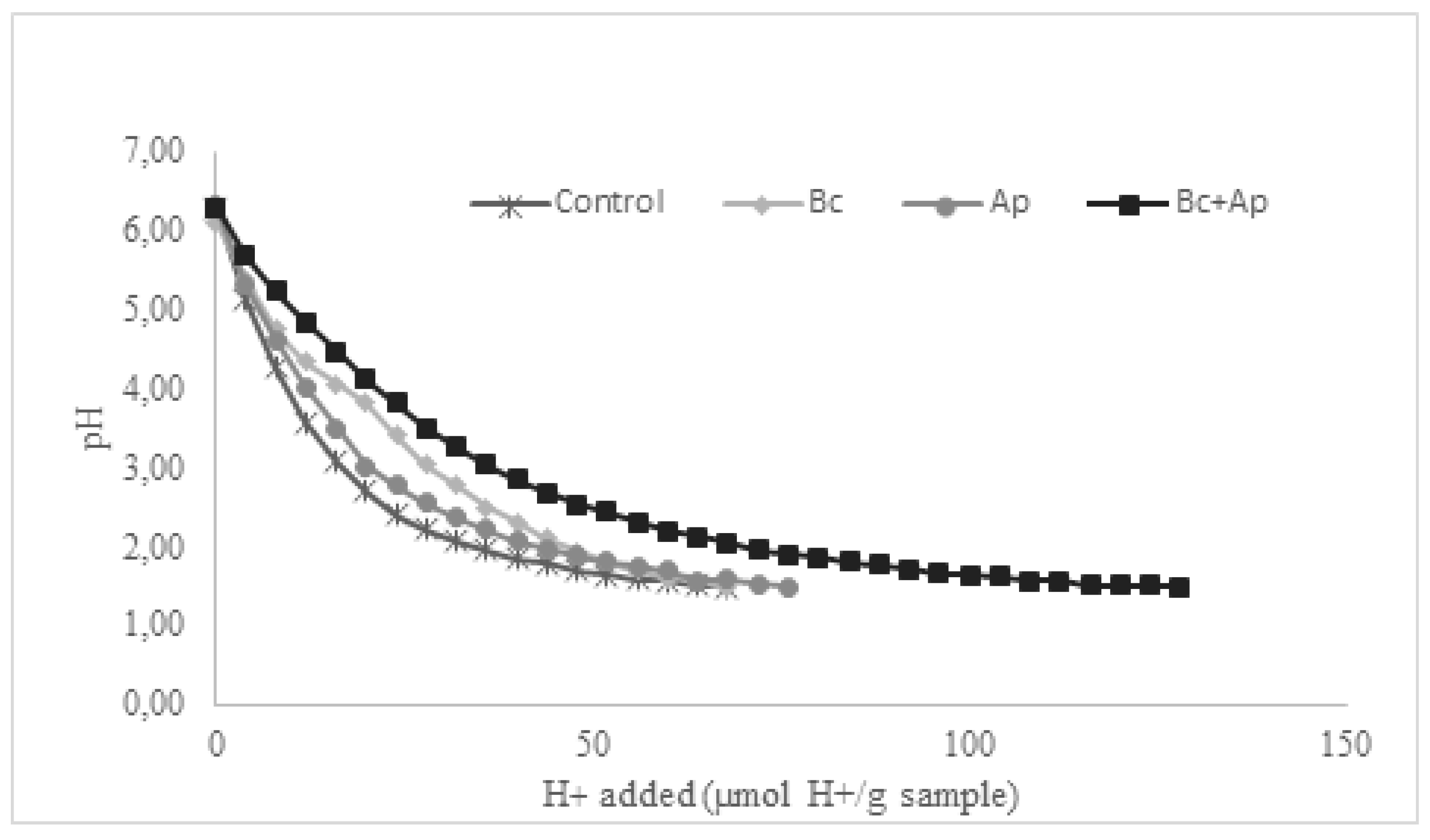
The acid-titration curves and buffering capacity of the pasta, as well as the macronutrients that affect the buffering capacity obtained from the nutritional analysis, are shown in
Figure 1 and Table 5, respectively. All samples had similar pH values at the beginning (6.27, 6.10, 6.30, and 6.28 for control, Bc, Ap, and Bc+Ap samples, respectively). However, the behavior during acid titration was different. The lowest buffer capacity was shown by control pasta, followed by Bc, Ap, and finally, Bc+Ap formulation, which obtained the highest value of the assay. Adding
B. coagulans (Bc pasta) resulted in an increased buffer capacity of 3.30% in contrast to control pasta. In comparison, adding
A. platensis (Ap pasta) an increase of 11.30%. Surprisingly, the combination of both
A. platensis and
B. coagulans resulted in an enhanced buffer capacity than
A. platensis or
B. coagulans alone, reaching a value of 87.84% in contrast to the control.
The differences between the formulations can be explained by their composition according to the information previously discussed. The control pasta obtained the lowest buffering capacity, attributable to the reduced protein content and increased fat and carbohydrate content. On the other hand, Bc pasta increased its buffer capacity by 3.3% in contrast to the control, probably attributable to its increase in proteins (by the nitrogen introduced by the microorganism addition) and reduced fat and carbohydrate content.
A slight increase in the buffer capacity is shown in the Ap pasta, clearly attributable to the enrichment of the pasta with the protein content
A. platensis. According to the nutritional analysis carried out by several studies glutamic and aspartic acid are two of the most abundant amino acids found in this cyanobacterium [
62,
63], information which is also in agreement with the nutritional value of the product used for the development of the pasta in this work.
On the other hand, when A. platensis and B. coagulans were mixed into the pasta (Bc+Ap), the buffering capacity rose higher than the values obtained by A. platensis or B. coagulans alone, suggesting a kind of synergic effect.
Although the study of Mennah-Govela
et al. [
24] showed the importance of low content of fat for improving buffering capacity in gastric conditions, the study of Tompkins
et al. [
64] gives a broad assessment of the impact of fat content on the viability of probiotic microorganisms. Between their experiments, the authors assessed
in vitro the effect of the buffering capacity of the food on the survival of probiotic bacteria (
Lactobacillus helveticus R0052,
Lactobacillus rhamnosus R0011,
Bifidobacterium longum R0175 and
Saccharomyces cerevisiae boulardii) during gastrointestinal transit. They found that even small percentages of fat (1% w/w) greatly impacted the number of viable bacteria reaching the duodenum, suggesting a protective effect by fat and proteins against bile and pancreatic enzymes. The authors indicated that regarding the viability of probiotics, fat was first important, followed by proteins. However, the carrier must provide both in a correct ratio to ensure probiotic viability.
The high resistance of
B. coagulans to harsh gastric conditions has been recognized by several studies and has been defined to vary in a strain-dependent way. Nonetheless, the study of Majeed
et al. [
65] assessed the survival of spores of
B. coagulans MTCC 5856 to gastric acid, and although they did not find significant differences in the spore count at pH of 3-8 in contrast to the initial spore count (10 log
10 spores/g) up to 4h, a decrease of 0.9 and 2.1 log 10 reduction was evidenced at a pH of 1.5 in 1 and 4 hours respectively. Although there is information about the effect of gastric conditions at several acidic pH levels for
B. coagulans GBI 30 6068 cells showing reductions between 16% to 33.33% at pH values of 3 to 1 respectively from an original count of 6 log CFU/mL [
34]. At this moment there is no similar information regarding the gastric acid resistance of
B. coagulans GBI 30 6068 spores at several acidic pH values as was done in the study of [
65]. However, since the Bc+Ap pasta obtained good buffering capacity, the gradient of pH change should be lesser, and therefore, enhanced viability may be expected, but further analysis in
-vitro mimicking full gastrointestinal conditions is needed to assess this effect and impact on
B. coagulans viability. This finding could be relevant as a way to keep the integrity of most of these spores along with the harsh conditions of the digestion process, to increase the number of intact spores reaching the duodenum, defined as the active site where the spore germination occurs [
26].
3.5. Textural Profile Analysis (TPA)
The result of the TPA is shown in
Table 6.
Hardness parameter increased by adding
A. platensis and
B. coagulans and the combination of both, in contrast, to control in raw and cooked pasta. For raw pasta, the most significant increase in hardness was shown by the addition of
B. coagulans(72.69%), followed by Ap pasta (32.03%), and finally the combination of both in pasta Bc+Ap (17.15%). Cooked pasta tended to increase hardness compared to raw pasta, with the highest value obtained by the Bc+Ap sample (59.32%). These results suggest a superior improvement in the cooked pasta structure compared to all other cooked formulations. According to Ogawa & Adachi [
66], hardness is a parameter governed by the strength of the gluten network. Therefore, combining
A. platensis and
B. coagulans improved the gluten network structure, enhancing its strength.
Chewiness (product of hardness, cohesiveness, and springiness) and gumminess (product of hardness and cohesiveness) are related parameters referred to as the necessary energy to be applied to disintegrate a pasta fragment and be swallowed subsequently. In this case, these parameters were also significantly affected by adding A. platensis and B. coagulans. In raw pasta, the highest chewiness value was obtained by Ap pasta, reaching an increase of 32.71%, followed by Bc pasta with 3.58%, and finally Bc+Ap pasta with a reduced chewiness value of 36.57% in contrast to the control. However, all cooked pasta enhanced their chewiness, compared to the control, reaching values of 31.63%, 58.93, and 57.25% for Bc, Ap, and Bc+Ap, respectively.
Regarding gumminess, raw pasta showed increases of 57.57, 30.88, and 24.68% for Bc, Ap, and Bc+Ap, respectively, in contrast to the control. In pasta cooked, the highest value in gumminess was obtained by Ap pasta at 59.07%, followed by Bc+Ap at 47.29%, and Bc at 19.52%.
In general, pasta must meet the consumer´s requirements, meaning that the product must retain its color, have a smooth surface, and be firm and elastic [
67]. All cooked pasta developed here showed increased firmness (Hardness), chewiness, and gumminess compared to control pasta. The main factor behind the improvement of hardness and, thus, its related parameters is the increase in proteins attributable to the addition of
A. platensis. According to Sozer
et al. [
68], firmness and adhesiveness are the most critical textural parameters in cooked pasta quality. The protein fraction, in particular, mainly influences the firmness of pasta and tolerance to overcooking. The authors found that spaghetti with reduced protein content absorbed more water, resulting in high stickiness and low firmness. Therefore, the enhancement of the hardness of pasta is due to the contribution of proteins from
A. platensis to the pasta gluten network. Zouari
et al. [
17] obtained similar results and found increased firmness in cooked semolina pasta added with 2%
A. platensis. The authors attributed this enhancement to the embedding of gelatinizing starch granules in a gluten network with the coexistence of microalgal proteins provided by this cyanobacterium. Effect that can be explained by the stipulated by Nilusha et al. [
14] the authors stated that a gluten network is formed when glutenin and gliadin are exposed to water, and when pasta is cooked, two events determining pasta properties can occur. According to the authors, a uniform and compact gluten network with swelled starch granules is formed when pasta is cooked. However, a physical competition between the coagulation of proteins and starch swelling occurs. If the protein coagulations are predominant during cooking time, then the starch granules are trapped in an alveoli-like system, enhancing the firmness of pasta. The contrary occurs when starch hydration wins, resulting in pasta with non-abrasiveness and typically stickiness.
3.5.1. Colorimetric Analysis
The colorimetric analysis of pasta is shown in
Table 7.
The use of Ap in pasta formulations caused an enrichment of mainly dark-green pigments such as chlorophyll and others such as blue pigments (phycocyanins) and yellow-orange pigments (carotenoids and lycopene), among others. Pasta added with Ap showed significant changes in L* (lightness), a* (- red to green +), and b* (- yellow to blue +) values attributable to their content in pigments. On the other hand, adding B. coagulans to pasta did not cause visually appreciable changes in pasta color regarding control and commercial control.
After cooking, pasta added with Ap showed increased redness color, probably due to the content of yellow-red pigments such as carotenoids and lycopene. Those pigments are more thermally stable in contrast to chlorophyll, suggesting a change in the chlorophyll color dominancy after cooking. Furthermore, the yellow index (an indicator of yellowness) was highly increased in pasta after cooking, which could be attributable to the prevalence of yellow pigments such as carotenoids. The changes induced by Ap addition, therefore, resulted in relative changes in the color of pasta, bringing them an attractive green color.
3.5.2. Effect of B. coagulans Addition on Antioxidant Capacity of Pasta
Regarding TPC and antioxidant capacity assays, adding B. coagulans caused significant reductions in the TPC and FRAP values of uncooked and cooked pasta. Still, a synergism in the ABTS assay was evidenced in the Bc+Ap pasta. Uncooked Bc+Ap pasta showed 19.20% less TPC and 21% less FRAP values but a significative increase of 11.70% in the ABTS compared to uncooked Ap pasta. After cooking, Bc+Ap pasta showed 11 and 15.10% less TPC and FRAP values, respectively, but just a 2.71% difference regarding the ABTS assay in contrast to cooked Ap pasta. Nonetheless, cooked Bc+Ap pasta showed 14.22, 10.88, and 55.60% more TPC, FRAP, and ABTS values than cooked control pasta.
This significative pattern of reduction in the TPC and FRAP but not significant for ABTS induced by B. coagulans could be due to interference produced by the bacterial spores. Currently, no previous reports assess the effects caused by B. coagulans on the antioxidant capacity of pasta samples added with A. platensis by ABTS, FRAP, and TPC, and neither makes its impact on pigment content in similar foods. However, previous reports can be valuable given the need for more information in the actual literature regarding the phenomenon presented here.
The study of Gerhardt and Black [
69] using dormant spores of Bacillus cereus strain terminalis demonstrated that bacterial spores could uptake chemical compounds from media based on their charge, molecular weight, and lipophilicity. No physiological specificity towards those compounds of importance to the spore (metabolizable compounds or those needed for germination) was evidenced. The authors suggested that these substances are introduced inside the spore rather than through superficial adsorption.
Although there is no information regarding this effect on
B. coagulans spores, if it is the case, since
A. platensis is highly dense in compounds, among them proteins, amino acids, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and pigments, it isn't easy to assess which one of them is being uptake by the spores and the mechanisms involved. Possibly, molecules of low molecular weight and lipophilicity should be targeted as the preferred candidates, as indicated by Gerhardt and Black [
69]. Furthermore, it is considered that the charge of the molecule is important. Still, it also changes when immersed in an acidic or alkali media, where antioxidant capacity assays are performed since this determines whether a molecule is attracted or repelled.
Regarding the charge of the compounds, Douglas [
70], assessing by electrophoresis the mobility of bacterial spores of
B. subtilis at different pH levels, suggested that dormant spores possess a surface covered by amino and carboxyl groups. The author suggested that at a low pH, these groups exist as -COOH and -NH3+, at neutral pH as -COO- and -NH3+, and at basic pH as -COO- and -NH2. Hence, it is suggested that at low pH, the spore surface tends to ionize, producing a positive net charge; at neutral pH, the spore surface behaves as zwitterion (net charge equals 0) with affinity to adsorbs anions; and the contrary effect to low pH should occur in basic conditions. Hence, depending on the pH media conditions, different molecules can be targeted to be uptaken by the bacterial spores.
Nonetheless, in the antioxidant capacity assays, the oxidizing/reductant agent must be free to interact with the antioxidants of
A. platensis. Still, since each antioxidant capacity assay was carried out at a different pH, an interference was probably produced by the bacterial spore in the pH function. As was discussed previously, the effect induced by the superficial charges of the spore by amino and carboxyl groups could be having a considerable impact during the performing of the TPC and antioxidant capacity assays, probably affecting the interaction between the oxidizing or reductant agents with the antioxidants of
A. platensis, since the spore coat is mainly made of proteins, representing the 50-80 % of the total protein content of the spore [
46].
Other studies have shown that bacterial spores of
B. subtilis were able to adsorb purified antigens and were able to induce specific and protective immune responses in mucosal immunized mice, suggesting a combination of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions between spores and antigens to drive the adsorption that was not dependent on specific spore coat components but rather on the negatively charged and hydrophobic surface of the spore [
71].
The study of Sirec
et al. [
71] assessed the adsorption of β-galactosidase (β-Gal) of
Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius on wild-type spores of
Bacillus subtilis and mutant strains lacking a single or several spore coat proteins. They found that the normal bacterial spores could adsorb β-Gal strictly depending on the pH of the adsorption buffer. The authors found that acidic environments of 3.5 and 4.0 were proper to adsorb more units of β-Gal than higher pH levels of 4.5. However, they also found that mutant strains lacking a single or several spore coat proteins had altered adsorption efficiency, indicating the physicochemical properties of the spore surface as responsible for the interaction with the enzyme assessed in their work. Nonetheless, they suggested that electrostatic forces could be taking place and be related to the adsorption capacity of the spores. Still, regarding enzymes assessed in their work, the process is not predominantly driven by electrostatic interactions with the spore. It is out of the scope of this work to determine the interaction between
B. coagulans spores and the TPC and antioxidant capacity assays. However, based on the previously discussed studies, it is suggested that the phenomenon responsible for the modifications to the antioxidant capacity of pasta added with
B. coagulans is probably induced by the resultant charges on the spore surface depending on the pH of the media from the antioxidant capacity assay. Therefore, based on the suggested by Douglas [
70] and Sirec
et al. [
71], the pH of the media could be influencing the interaction of the spore with other surrounding molecules depending on the charge of the spore conditioned by the pH of the media, i.e., interfering with the electron donor or acceptor capacity between the oxidant or reductant agent and the antioxidants contained in
A. platensis.
All pigments showed a reduction in their content when
B. coagulans was present in pasta but to different extents. This effect on the reduction of the pigments could be explained considering the statement by Gerhardt & Black [
69], where the molecular weight and lipophilicity of pigments could show affinity to spores. Nonetheless, more studies assessing this interference/absorption phenomenon are needed to understand the fundamental nature of the process involved.
This is the first work assessing the changes a probiotic microorganism induces regarding nutritional value, TPC, antioxidant capacity, pigment content, TPA, buffering capacity, probiotic viability, and colorimetry. Therefore, the methodologies, information, and findings presented here could be helpful for further analysis of similar probiotic foods as a reference guide to measuring the impacts of adding spore former probiotic microorganisms and the changes induced not only from the nutritional point of view but also from the textural and functional properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.-G. and J.J.B.-F.; methodology, A.I.G.-M., E.O.-R., H.K.S.-H., and P-G.-P.; formal analysis, L.N.M.-C., D.R.S.-A, J.J.B.-F. and M.A.-G.; investigation, M.A.-G.; data curation, L.N.M.-C., D.R.S.-A, and J.J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.I.G.-M.; writing—review and editing, L.N.M.-C., D.R.S.-A, J.J.B.-F. and M.A.-G.; funding acquisition, M.A.-G.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.