Submitted:
01 August 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms and Characteristics of CPPs
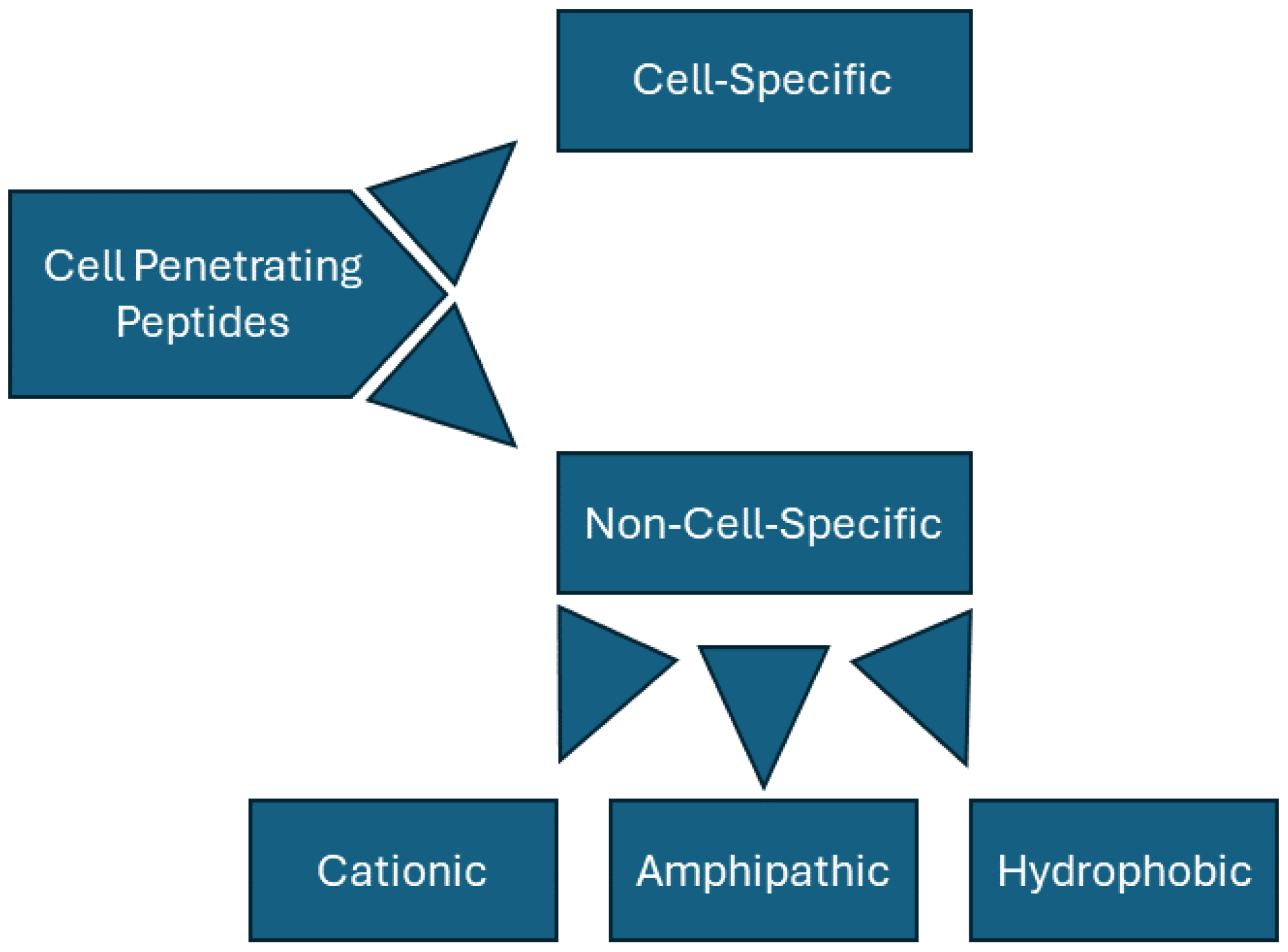
2.1. Classification of CPPs
2.2. CPP Transduction
2.3. Cell-Specific CPPs
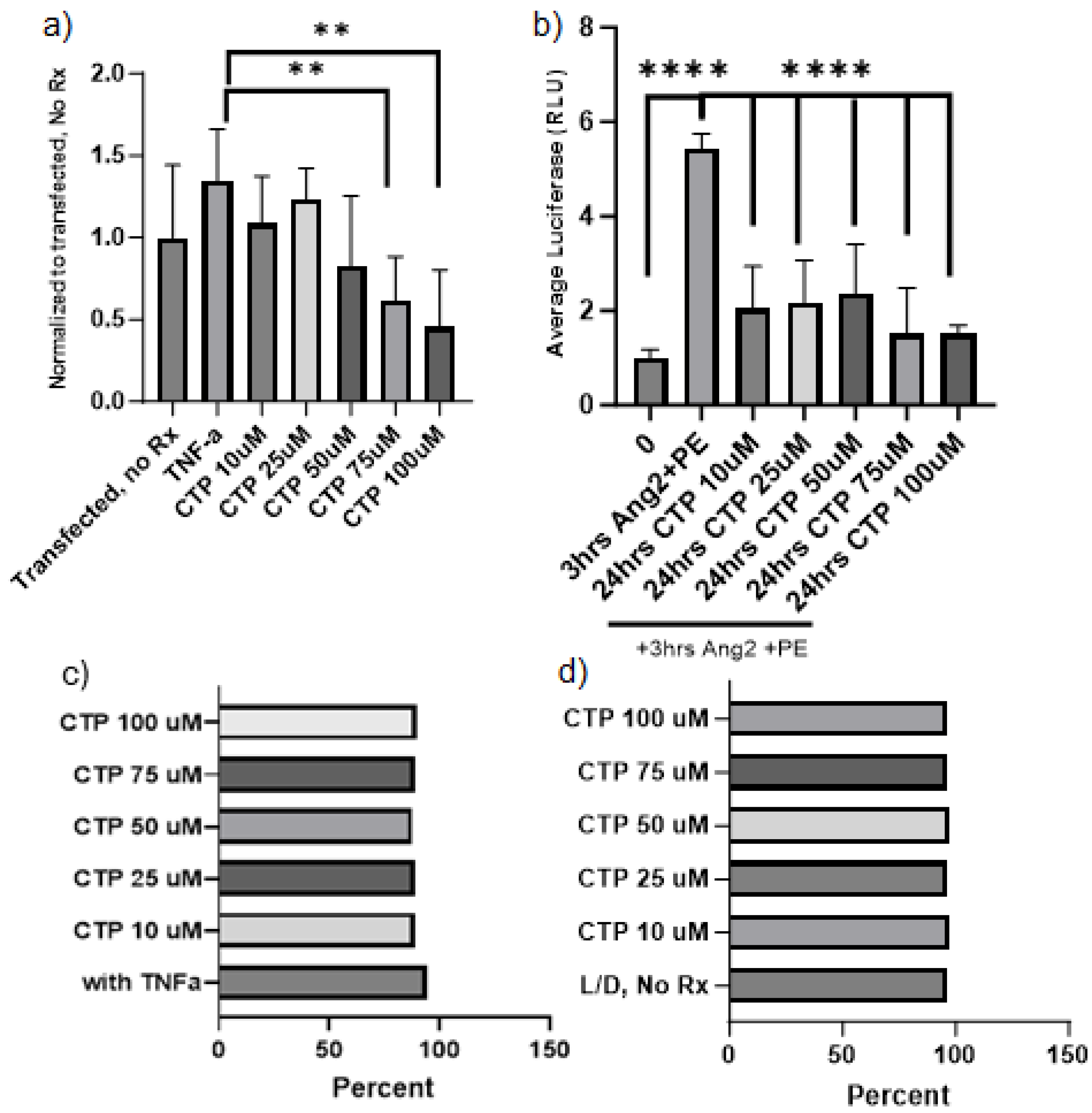
3. Biological Effects and Therapeutic Implications
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, R.E.; Zahid, M. Cell Penetrating Peptides, Novel Vectors for Gene Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.; Loewenstein, P.M. Autonomous functional domains of chemically synthesized human immunodeficiency virus tat trans-activator protein. Cell 1988, 55, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, A.D.; Pabo, C.O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell 1988, 55, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Joliot, A.H.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 10444–10450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawell, S.; Seery, J.; Daikh, Y.; Moore, C.; Chen, L.L.; Pepinsky, B.; Barsoum, J. Tat-mediated delivery of heterologous proteins into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarze, S.R.; Ho, A.; Vocero-Akbani, A.; Dowdy, S.F. In vivo protein transduction: delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse. Science 1999, 285, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, B.G.; Hornillos, V.; Luque-Ortega, J.R.; Abengozar, M.A.; Amat-Guerri, F.; Acuna, A.U.; Rivas, L.; Andreu, D. A BODIPY-embedding miltefosine analog linked to cell-penetrating Tat(48-60) peptide favors intracellular delivery and visualization of the antiparasitic drug. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Weber, B.; Yurko, R.; Islam, K.; Agrawal, V.; Lopuszynski, J.; Yagi, H.; Salama, G. Cardiomyocyte-Targeting Peptide to Deliver Amiodarone. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Yang, X.Z.; Du, X.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, F.J.; Dong, Y.; Li, P.F. Enhancing tumor-specific intracellular delivering efficiency of cell-penetrating peptide by fusion with a peptide targeting to EGFR. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, E.; Santos, D.; Huygens, C.; Peeters, P.; Van den Brande, S.; Wynant, N.; Vanden Broeck, J. The Study of Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Deliver dsRNA and siRNA by Feeding in the Desert Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insects 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Tanaka, M.; Oba, M. siRNA delivery using amphipathic cell-penetrating peptides into human hepatoma cells. Bioorg Med Chem 2020, 28, 115402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Duan, X.; Pan, H.; Akk, A.; Sandell, L.J.; Wickline, S.A.; Rai, M.F.; Pham, C.T.N. Development of a peptide-siRNA nanocomplex targeting NF- kappaB for efficient cartilage delivery. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falato, L.; Gestin, M.; Langel, U. Cell-Penetrating Peptides Delivering siRNAs: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol 2021, 2282, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayake, P.V.; Gunathunge, B.G.; Wimalasiri, P.N.; Karunaratne, D.N.; Ranatunga, R.J. Trends in the Binding of Cell Penetrating Peptides to siRNA: A Molecular Docking Study. J Biophys 2017, 2017, 1059216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanova, J.; Hejtmankova, A.; Zackova Suchanova, J.; Sauerova, P.; Forstova, J.; Hubalek Kalbacova, M.; Spanielova, H. Influence of cell-penetrating peptides on the activity and stability of virus-based nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 2020, 576, 119008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyakov, V.; Sharma, V.; Dahlheimer, J.L.; Pica, C.M.; Luker, G.D.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Novel Tat-peptide chelates for direct transduction of technetium-99m and rhenium into human cells for imaging and radiotherapy. Bioconjug Chem 2000, 11, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Cai, H.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wu, X.; Shen, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. Biodistribution and evaluation of (131) I-labeled neuropilin-binding peptide for targeted tumor imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2016, 11, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avula, U.M.; Yoon, H.K.; Lee, C.H.; Kaur, K.; Ramirez, R.J.; Takemoto, Y.; Ennis, S.R.; Morady, F.; Herron, T.; Berenfeld, O.; et al. Cell-selective arrhythmia ablation for photomodulation of heart rhythm. Sci Transl Med 2015, 7, 311ra172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Firdaus, F.; Azuar, A.; Khalil, Z.G.; Marasini, N.; Capon, R.J.; Hussein, W.M.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. Cell-Penetrating Peptides-Based Liposomal Delivery System Enhanced Immunogenicity of Peptide-Based Vaccine against Group A Streptococcus. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.J.; Wang, W.J.; Jia, Z.Y. Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Modified Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Rictor siRNA for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther 2021, 15, 4961–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wu, B.; Fan, H.; Hou, J.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Meng, S. PTD-fused p53 as a potential antiviral agent directly suppresses HBV transcription and expression. Antiviral Res 2016, 127, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Ruoslahti, E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 1998, 279, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, P.A.; Mitchell, D.J.; Pattabiraman, K.; Pelkey, E.T.; Steinman, L.; Rothbard, J.B. The design, synthesis, and evaluation of molecules that enable or enhance cellular uptake: peptoid molecular transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 13003–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, J.C.; Shen, H.; Watkins, S.C.; Cheng, T.; Robbins, P.D. Efficiency of protein transduction is cell type-dependent and is enhanced by dextran sulfate. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 30208–30218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.J.; Kim, D.T.; Steinman, L.; Fathman, C.G.; Rothbard, J.B. Polyarginine enters cells more efficiently than other polycationic homopolymers. J Pept Res 2000, 56, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Mai, J.; Lu, X.; Robbins, P.D. Characterization of a class of cationic peptides able to facilitate efficient protein transduction in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther 2000, 2, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soomets, U.; Lindgren, M.; Gallet, X.; Hallbrink, M.; Elmquist, A.; Balaspiri, L.; Zorko, M.; Pooga, M.; Brasseur, R.; Langel, U. Deletion analogues of transportan. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000, 1467, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Horikoshi, K.; Fujita, M.; Hirano, M.; Miyamoto, M.; Yokoo, H.; Demizu, Y. Development of Hydrophobic Cell-Penetrating Stapled Peptides as Drug Carriers. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Oba, M.; Misawa, T.; Tanaka, M.; Hattori, T.; Naito, M.; Kurihara, M.; Demizu, Y. A Helix-Stabilized Cell-Penetrating Peptide as an Intracellular Delivery Tool. Chembiochem 2016, 17, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, L.K.; Baumruck, A.C.; Zhdanova, H.; Tietze, A.A. Challenges and Perspectives in Chemical Synthesis of Highly Hydrophobic Peptides. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Cespi, M.; Palmieri, G.F.; Mason, A.J.; Lam, J.K. Incorporation of a Nuclear Localization Signal in pH Responsive LAH4-L1 Peptide Enhances Transfection and Nuclear Uptake of Plasmid DNA. Mol Pharm 2016, 13, 3141–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.I.; Moazzam, M.; Stueber, R.; Park, S.E.; Cho, Y.; Malik, N.U.A.; Tiwari, R.K. Applications of amphipathic and cationic cyclic cell-penetrating peptides: Significant therapeutic delivery tool. Peptides 2021, 141, 170542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, I.D.; Goasdoue, N.; Correia, I.; Aubry, S.; Galanth, C.; Sagan, S.; Lavielle, S.; Chassaing, G. Membrane interaction and perturbation mechanisms induced by two cationic cell penetrating peptides with distinct charge distribution. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1780, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruseska, I.; Zimmer, A. Internalization mechanisms of cell-penetrating peptides. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2020, 11, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooga, M.; Hallbrink, M.; Zorko, M.; Langel, U. Cell penetration by transportan. FASEB J 1998, 12, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Ishino, M.; Loewenstein, P.M. Mutational analysis of HIV-1 Tat minimal domain peptides: identification of trans-dominant mutants that suppress HIV-LTR-driven gene expression. Cell 1989, 58, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorko, M.; Langel, U. Cell-Penetrating Peptides. Methods Mol Biol 2022, 2383, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, G.; Muscat, S.; Rebella, M.; Morbiducci, U.; Audenino, A.; Danani, A.; Deriu, M.A. Cell penetrating peptide modulation of membrane biomechanics by Molecular dynamics. J Biomech 2018, 73, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Morishita, T.; Aburai, K.; Ito, D.; Imura, T.; Sakai, K.; Abe, M.; Nakase, I.; Futaki, S.; Sakai, H. Direct entry of cell-penetrating peptide can be controlled by maneuvering the membrane curvature. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.D.; Jiao, C.Y.; Aubry, S.; Aussedat, B.; Burlina, F.; Chassaing, G.; Sagan, S. Cell biology meets biophysics to unveil the different mechanisms of penetratin internalization in cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010, 1798, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimizu, S.; Watanabe, H.; Maeda, H.; Hamasaki, K.; Ikegami, K.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Kinoshita, R.; Nishida, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ishima, Y.; et al. Cell-penetrating mechanism of intracellular targeting albumin: Contribution of macropinocytosis induction and endosomal escape. J Control Release 2019, 304, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.P.; Melikov, K.; Brooks, H.; Prevot, P.; Lebleu, B.; Chernomordik, L.V. Cellular uptake of unconjugated TAT peptide involves clathrin-dependent endocytosis and heparan sulfate receptors. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 15300–15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Kuwata, K.; Chiba, J.; Hatanaka, Y.; Nakase, I.; Futaki, S. Syndecan-4 Is a Receptor for Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis of Arginine-Rich Cell-Penetrating Peptides. Bioconjug Chem 2016, 27, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, M.; Xing, H.; Yang, T.; Cai, C.; Zhao, X.; Wei, M.; Yu, J.; Ding, P. Intracellular distribution and internalization pathways of guanidinylated bioresponsive poly(amido amine)s in gene delivery. Asian J Pharm Sci 2018, 13, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; de la Torre, B.G.; Andreu, D.; Santos, N.C. Kinetic uptake profiles of cell penetrating peptides in lymphocytes and monocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013, 1830, 4554–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Liu, C. Highly Efficient Delivery of Functional Cargoes by a Novel Cell-Penetrating Peptide Derived from SP140-Like Protein. Bioconjug Chem 2016, 27, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.Y.; Raines, R.T. Mechanism of ribonuclease A endocytosis: analogies to cell-penetrating peptides. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8374–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.J.; Tian, D.M.; Fu, L.; Jin, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Ye, Y.B.; Wang, X.B.; Xu, X.J.; Tang, C.; et al. Elastin-Derived VGVAPG Fragment Decorated Cell-Penetrating Peptide with Improved Gene Delivery Efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, H.; Cao, W.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qi, X.; Luo, D.; Chen, C. Transcytosis mechanisms of cell-penetrating peptides: Cation-independent CC12 and cationic penetratin. J Pept Sci 2022, 28, e3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Phillips, B.E.; Albers, S.M.; Giannoukakis, N.; Watkins, S.C.; Robbins, P.D. Identification of a cardiac specific protein transduction domain by in vivo biopanning using a M13 phage peptide display library in mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamarthy, S.P.; Jia, L.; Kovacs, J.R.; Anderson, K.R.; Shen, H.; Firestine, S.M.; Meng, W.S. Gene delivery to dendritic cells facilitated by a tumor necrosis factor alpha-competing peptide. Mol Immunol 2004, 41, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Adachi, Y.; Komoike, Y.; Kamada, Y.; Koyama, R.; Fukuda, Y.; Kadotani, A.; Asami, T.; Sakamoto, J.I. Novel DOCK2-selective inhibitory peptide that suppresses B-cell line migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017, 483, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.K.; Bertera, S.; Bottino, R.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Mai, J.C.; Mi, Z.; Trucco, M.; Robbins, P.D. Protection of islets by in situ peptide-mediated transduction of the Ikappa B kinase inhibitor Nemo-binding domain peptide. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 9862–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahagun, D.A.; Lopuszynski, J.B.; Feldman, K.S.; Pogodzinski, N.; Zahid, M. Toxicity Studies of Cardiac-Targeting Peptide Reveal a Robust Safety Profile. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilk, K.; Mahlapuu, R.; Soomets, U.; Langel, U. Analysis of in vitro toxicity of five cell-penetrating peptides by metabolic profiling. Toxicology 2009, 265, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhorutsenko, J.; Oskolkov, N.; Arukuusk, P.; Kurrikoff, K.; Eriste, E.; Copolovici, D.M.; Langel, U. Cell-penetrating peptides, PepFects, show no evidence of toxicity and immunogenicity in vitro and in vivo. Bioconjug Chem 2011, 22, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saar, K.; Lindgren, M.; Hansen, M.; Eiriksdottir, E.; Jiang, Y.; Rosenthal-Aizman, K.; Sassian, M.; Langel, U. Cell-penetrating peptides: a comparative membrane toxicity study. Anal Biochem 2005, 345, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.G.; Sayers, E.J.; He, L.; Narayan, R.; Williams, T.L.; Mills, E.M.; Allemann, R.K.; Luk, L.Y.P.; Jones, A.T.; Tsai, Y.H. Cell-penetrating peptide sequence and modification dependent uptake and subcellular distribution of green florescent protein in different cell lines. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Milech, N.; Juraja, S.M.; Cunningham, P.T.; Stone, S.R.; Francis, R.W.; Anastasas, M.; Hall, C.M.; Heinrich, T.; Bogdawa, H.M.; et al. A platform for discovery of functional cell-penetrating peptides for efficient multi-cargo intracellular delivery. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Welte, S.; Mader, O.; Duchardt, F.; Fischer, R.; Hufnagel, H.; Scheurich, P.; Brock, R. Cationic cell-penetrating peptides interfere with TNF signalling by induction of TNF receptor internalization. J Cell Sci 2005, 118, 3339–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, J.H.; Jan, M.S.; Lin, Y.L.; Lin, C. Interactions between octaarginine and U-937 human macrophages: global gene expression profiling, superoxide anion content, and cytokine production. J Control Release 2009, 139, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letoha, T.; Kusz, E.; Papai, G.; Szabolcs, A.; Kaszaki, J.; Varga, I.; Takacs, T.; Penke, B.; Duda, E. In vitro and in vivo nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitory effects of the cell-penetrating penetratin peptide. Mol Pharmacol 2006, 69, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Xing, W.; Yu, J.; Yan, J.L.; et al. A cell-penetrating peptide suppresses inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. Mol Ther 2011, 19, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiandomenico, A.; Veach, R.A.; Zienkiewicz, J.; Moore, D.J.; Wylezinski, L.S.; Hutchens, M.A.; Hawiger, J. The “genomic storm” induced by bacterial endotoxin is calmed by a nuclear transport modifier that attenuates localized and systemic inflammation. PLoS One 2014, 9, e110183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zienkiewicz, J.; Armitage, A.; Hawiger, J. Targeting nuclear import shuttles, importins/karyopherins alpha by a peptide mimicking the NFkappaB1/p50 nuclear localization sequence. J Am Heart Assoc 2013, 2, e000386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Major, A.S.; Zienkiewicz, J.; Gabriel, C.L.; Veach, R.A.; Moore, D.J.; Collins, R.D.; Hawiger, J. Nuclear transport modulation reduces hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, and fatty liver. J Am Heart Assoc 2013, 2, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.Z.; Wei, G.; Lu, W. Cell-permeable NF-kappaB inhibitor-conjugated liposomes for treatment of glioma. J Control Release 2018, 289, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Seo, Y.N.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, C.P. The cell-penetrating peptide domain from human heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) has anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012, 419, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.S.; Wu, Y.R.; Fang, S.L.; Tsai, J.J.; Lin, H.K.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, T.Y.; Chang, M.D. Cell Penetrating Peptide Derived from Human Eosinophil Cationic Protein Decreases Airway Allergic Inflammation. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.J.; Liao, E.C.; Sheu, M.L.; Chang, D.T.; Tsai, J.J. Cell-penetrating peptide derived from human eosinophil cationic protein inhibits mite allergen Der p 2 induced inflammasome activation. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Tian, Y.; Qu, S.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Fu, Y. Protective effect of TM6 on LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Kumari, T.; Gupta, A.; Akhtar, S.; Verma, R.D.; Ghosh, J.K. Identification of a 10-mer peptide from the death domain of MyD88 which attenuates inflammation and insulin resistance and improves glucose metabolism. Biochem J 2024, 481, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallespi, M.G.; Fernandez, J.R.; Torrens, I.; Garcia, I.; Garay, H.; Mendoza, O.; Granadillo, M.; Falcon, V.; Acevedo, B.; Ubieta, R.; et al. Identification of a novel antitumor peptide based on the screening of an Ala-library derived from the LALF(32-51) region. J Pept Sci 2010, 16, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghero, H.; Fernandez Masso, J.R.; Astrada, S.; Guerra Vallespi, M.; Bollati-Fogolin, M. The Anticancer Peptide CIGB-552 Exerts Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Angiogenic Effects through COMMD1. Molecules 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallespi, M.G.; Mestre, B.; Marrero, M.A.; Uranga, R.; Rey, D.; Lugiollo, M.; Betancourt, M.; Silva, K.; Corrales, D.; Lamadrid, Y.; et al. A first-in-class, first-in-human, phase I trial of CIGB-552, a synthetic peptide targeting COMMD1 to inhibit the oncogenic activity of NF-kappaB in patients with advanced solid tumors. Int J Cancer 2021, 149, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orange, J.S.; May, M.J. Cell penetrating peptide inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappa B. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008, 65, 3564–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Qiao, Y.; Xue, L.; Xu, S.; Zhang, N. Targeted and MMP-2/9 responsive peptides for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Pharm 2019, 569, 118625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanemaru, Y.; Momiki, Y.; Matsuura, S.; Horikawa, T.; Gohda, J.; Inoue, J.; Okamoto, Y.; Fujita, M.; Otsuka, M. An artificial copper complex incorporating a cell-penetrating peptide inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2011, 59, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Meng, C.; Xia, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, K.; Gao, X.; et al. Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugated Au Nanoclusters Selectively Suppress Refractory Lymphoma Cells via Targeting Both Canonical and Noncanonical NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. Bioconjug Chem 2023, 34, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, Z.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Rahmatiyamchi, M.; Movassaghpour, A.A.; Alipour, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; Sadeghi, Z.; Dariushnejad, H.; Zarghami, N. Molecular target therapy of AKT and NF-kB signaling pathways and multidrug resistance by specific cell penetrating inhibitor peptides in HL-60 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014, 15, 4353–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Yum, S.; Yoo, H.J.; Kang, S.; Yoon, J.H.; Min, D.; Kim, Y.M.; Jung, Y. Colon-targeted cell-permeable NFkappaB inhibitory peptide is orally active against experimental colitis. Mol Pharm 2012, 9, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urata, M.; Kokabu, S.; Matsubara, T.; Sugiyama, G.; Nakatomi, C.; Takeuchi, H.; Hirata-Tsuchiya, S.; Aoki, K.; Tamura, Y.; Moriyama, Y.; et al. A peptide that blocks the interaction of NF-kappaB p65 subunit with Smad4 enhances BMP2-induced osteogenesis. J Cell Physiol 2018, 233, 7356–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bismarck, P.; Winoto-Morbach, S.; Herzberg, M.; Uhlig, U.; Schutze, S.; Lucius, R.; Krause, M.F. IKK NBD peptide inhibits LPS induced pulmonary inflammation and alters sphingolipid metabolism in a murine model. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2012, 25, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.K.; Patra, M.C.; Shin, H.J.; Gui, X.; Achek, A.; Panneerselvam, S.; Kim, D.J.; Song, S.J.; Hong, R.; Kim, K.S.; et al. A cell-penetrating peptide blocks Toll-like receptor-mediated downstream signaling and ameliorates autoimmune and inflammatory diseases in mice. Exp Mol Med 2019, 51, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Kim, D.S.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Morgan, K.A.; Adams, D.B.; Wang, H. Cell-Permeable Peptide Blocks TLR4 Signaling and Improves Islet Allograft Survival. Cell Transplant 2016, 25, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsen, K.E.; Zhang, B.; Skjesol, A.; Ryan, L.; Vagle, H.; Boe, M.H.; Orning, P.; Kim, H.; Bakke, S.S.; Elamurugan, K.; et al. Peptide derived from SLAMF1 prevents TLR4-mediated inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Life Sci Alliance 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, C.T.; Wang, Y.; Shan, J.; Kinyanjui, M.W.; Villeneuve, A.; Michael, H.; Fixman, E.D. Inhibition of experimental allergic airways disease by local application of a cell-penetrating dominant-negative STAT-6 peptide. J Immunol 2007, 179, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shan, J.; Fixman, E.; McCusker, C. Effective treatment of experimental ragweed-induced asthma with STAT-6-IP, a topically delivered cell-penetrating peptide. Clin Exp Allergy 2011, 41, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Lu, X.; Mi, Z.; Robbins, P.D. Cationic and tissue-specific protein transduction domains identification, characterization, and therapeutic application. Adv Genet 2010, 69, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Feldman, K.S.; Garcia-Borrero, G.; Feinstein, T.N.; Pogodzinski, N.; Xu, X.; Yurko, R.; Czachowski, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Mason, N.S.; et al. Cardiac Targeting Peptide, a Novel Cardiac Vector: Studies in Bio-Distribution, Imaging Application, and Mechanism of Transduction. Biomolecules 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahagun, D.; Zahid, M. Cardiac-Targeting Peptide: From Discovery to Applications. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurko, R.; Islam, K.; Weber, B.; Salama, G.; Zahid, M. Conjugation of amiodarone to a novel cardiomyocyte cell penetrating peptide for potential targeted delivery to the heart. Front Chem 2023, 11, 1220573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manno, C.S.; Pierce, G.F.; Arruda, V.R.; Glader, B.; Ragni, M.; Rasko, J.J.; Ozelo, M.C.; Hoots, K.; Blatt, P.; Konkle, B.; et al. Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat Med 2006, 12, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D. Lethal immunotoxicity in high-dose systemic AAV therapy. Mol Ther 2023, 31, 3123–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinderer, C.; Katz, N.; Buza, E.L.; Dyer, C.; Goode, T.; Bell, P.; Richman, L.K.; Wilson, J.M. Severe Toxicity in Nonhuman Primates and Piglets Following High-Dose Intravenous Administration of an Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Expressing Human SMN. Hum Gene Ther 2018, 29, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, E.; Argiro, A.; Hong, K.; Adler, E. Gene therapy vector-related myocarditis. Int J Cardiol 2024, 398, 131617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, L.; Gambhir, Y.; Bennett, J.; Stedman, H.H. Broader Implications of Progressive Liver Dysfunction and Lethal Sepsis in Two Boys following Systemic High-Dose AAV. Mol Ther 2020, 28, 1753–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




