1. Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial machinery, the forklift industry stands at a transformative juncture, primarily propelled by the integration of AI. The purpose of this paper is to present a comprehensive analysis of the impact of AI on the forklift industry, particularly in the realms of logistics and procurement. It aims to explore how AI-driven technologies are reshaping the traditional operational frameworks within SMEs in this sector [
1,
2,
3]. The forklift market, a critical component of industrial operations, is segmented into four main categories: traditional forklifts, dominating the market with their internal combustion engines; electric forklifts, increasingly popular for their environmental friendliness and operational efficiency; automated forklifts, an emerging segment driven by advancements in AI and automation; and hybrid forklifts, a nascent category blending features of traditional and electric forklifts. Using a multifaceted approach that includes benchmarking and ABM models as well as the ESG-AI-BSC and McKinsey 7S frameworks, this study evaluates the multifarious effects of AI. The paper investigates how AI innovations in logistics and procurement are enhancing operational efficiencies and sustainability, while simultaneously disrupting traditional employment roles within the industry. A pivotal case study of an SME is conducted, scrutinizing its financial particularities and strategic frameworks [
4,
5]. The paper concludes with a forward-looking perspective on the socio-economic impact of AI-driven innovations in the forklift industry, highlighting a future where machines increasingly assume roles traditionally held by humans. This shift, while enhancing efficiency and precision, also brings into question the future role of human labor in the forklift industry, suggesting a paradigm shift where humans transition from operational roles to supervisory and strategic positions. This transition not only redefines job roles but also accentuates the need for new skill sets and adaptability in the face of AI-driven automation in the industrial machinery landscape.
Research objectives:
Identifying how AI can optimize logistics activities.
Determining the implications of AI on procurement procedures.
Analysis of the evolution of the forklift industry following the implementation of AI in the logistics and procurement sector.
Analysis of the socio-economic progress and risks of AI implementation in the forklift industry.
Highlighting the socio-economic impact of the BCFI.
Research hypotheses:
The impact of AI on SMEs logistics and procurement transformation and risks.
The evolution of the BCFI in the context of the AI-driven technological revolution.
Socio-economic implications of AI on the forklift industry with impact on job losses for forklift operators.
The implementation of AI in SMEs raises many questions and suspicions worldwide [
6], as they are the backbone of an economy and implement AI and Internet of things (IoT) [
7]. SMEs will be dependent on AI and may have some advantages in a global competition with large companies. All internal processes will be influenced by AI, and SMEs can have lower costs by purchasing only specialized AI modules in their field of activity [
3]. Risk management assessment of business processes and internal procedures of SMEs concerned with sustainable development can be streamlined with AI [
1].
The forklift industry is undergoing a significant transformation as it embraces the principles of Industry 4.0, using cyber-physical systems, IoT and AI. The forklift industry is one of the most mature industries in terms of adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. Almost 70% of forklift manufacturers are already using or planning to use Industry 4.0 technologies in their products and services. The use of IoT sensors and AI can reduce downtime by up to 20% and increase productivity by up to 15%. Industry 4.0 technologies are also being used to improve the safety of forklift operations. Companies are using AI to develop autonomous forklifts that can operate without human intervention. This could reduce the number of forklift accidents and significantly improve the efficiency and productivity of forklift operations [
8]. Socio-economic development through cost reduction will be achieved through: IoT sensors used to collect forklift performance data, 3D printing used to create custom forklift parts, and virtual reality used to train forklift operators [
9]. Romania's most relevant SME in the forklift industry has abandoned the production of diesel forklifts and produces only electric forklifts, promoting lithium-ion technology [
10]. Refurbishing logistics equipment is a cost-effective solution, with a fully refurbished electric forklift being almost as good as a new one. [
11].
AI ensures economic development at micro and macro level. The process of digital transformation in all areas also has implications for logistics, both in transport and warehousing [
12]. AI applications in logistics are related to efficient inventory tracking and automated goods handling at the warehouse level. In terms of transportation, it optimizes the distribution route planning process [
4]. Smart logistics is involved in all stages of logistics processes, ensuring their efficiency with the help of AI [
2]. AI increases the material handling safety, reduces operating costs of autonomous forklifts and increases warehouse productivity and efficiency [
13,
14]. Recognition of the location of pallets of goods transported within a warehouse, as well as the position and trajectory of a forklift during loading/unloading operations can be achieved using sensors [
15]. Although AI is already implemented in many areas, in procurement it is still in its infancy [
16]. In procurement, AI currently bids companies at list prices, while human interaction makes custom prices lower [
17]. AI will radically transform logistics and supply chain management, with effects on increasing unemployment [
18].
Effective management of a company depends on a close link between transformational leadership competencies, ESG and BSC [
5]. Circular economy and digitization improve sustainability and ESG performance through optimal use of resources to maximize socio-economic impact [
19]. The focus is on a company in Romania, an emerging country in full expansion characterized by high risk-high return (HR2) investment attraction capabilities with accessibility to foreign investors. Economic and political stability is ensured not only based on the principles applicable to developed markets, but also on informal and cultural mechanisms, impacted by AI. The role of informal institutions creates unique forms of business development and surprisingly, comes with unique coping mechanisms to deal with crisis and turbulence [
20,
21].
The McKinsey 7S and BSC models are complementary, with the BSC being a more up-to-date model that can even improve the McKinsey 7S framework in terms of process effectiveness and organizational risk strategies [
22]. Increasing customer satisfaction is achieved with the help of the ABM method by improving internal processes, reducing resource consumption and product costs by eliminating activities that do not generate added value [
23].
2. Materials and Methods
The first phase of the research focused on interviews conducted in June 2024 with seven managers of a benchmarked company in the forklift industry (BCFI). After filtering the data obtained from these interviews, as well as from scientific papers in the forklift industry, we will be able to highlight the benefits and risks of the implications of AI for the logistics and procurement sector. To improve the efficiency and productivity of forklift operations by focusing on the specific activities involved in forklift use, we will apply the ABM methodology. Profitability will be analyzed through the lens of strengths and weaknesses and the recovery of loss-making activities will be followed through a better use of resources to reduce costs. A benchmarking plan will be implemented regarding effective planning of activities, collection of valid information, analysis of development opportunities and adoption of optimal decisions. The interest of this benchmarking methodology is to establish a standardized approach for evaluating and comparing the performance of forklift manufacturers and operators worldwide. This methodology will provide a comprehensive framework for assessing various aspects of forklift performance, including efficiency, productivity, risks, safety, and sustainability. The implications of AI on ESG and BSC (learning and growth, business processes, customers and finance) models will be highlighted. The learning and growth, business processes and customers components will be analyzed using the benchmarking methodology, while the financial component will be analyzed using the ABM methodology. We will implement a McKinsey 7S framework to highlight the organization’s effectiveness in terms of organizational structure, sustainable strategies, quality management systems, superior employee skills, managerial style, staff motivation and shared values promoted. Will be explored the interrelationships among the various financial aspects of the BCFI for a more nuanced understanding (
Table 1).
3. Results
By examining the multifaceted impact of AI through interviews with seven managers of a pioneering forklift company, this paper underscores the transformative potential and complexities of AI, offering a nuanced perspective that goes beyond mere technological advancements (
Table 2). The BCFI in focus has been at the forefront of integrating AI into its operations and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in material handling and logistics through: autonomous navigation, where AI algorithms enable forklifts to navigate complex warehouse environments autonomously, reducing the need for human intervention; predictive maintenance, where machine learning models predict equipment failures, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime; real-time analytics, where AI-driven analytics provide insights into operational efficiency, enabling data-driven decision-making [
4,
10,
11,
13,
14,
15,
21].
McKinsey 7S framework of the BCFI can be used to assess the state of the organization, to identify areas for improvement and to develop a change strategy to improve the organization’s performance [
22]:
Structure: has a decentralized organizational structure, has regional offices that are responsible for local operations, is responsive to the needs of customers.
Strategies: has a strategy to be a leader in the forklift industry, focuses on innovation and efficiency, is offering high quality products and services at an affordable price, has a distribution network that enables it to reach customers.
Systems: has a quality management system that ensures that its products meet the highest standards, has an innovation system that enables it to constantly launch new and improved products.
Skills: has a strong knowledge and skills base, invests in research and development to stay abreast of the latest trends in the forklift industry.
Style: has an organizational culture style that is customer-oriented, encourages employees to be friendly and proactive with customers.
Staff: has a talented and dedicated management team, invests in the development of its employees, provide opportunities to learn and grow.
Shared values: has a set of shared values that guide the company's organizational culture such as quality, efficiency and customer orientation.
Based on the McKinsey 7S framework the following recommendations can be made for the BCFI: continue to invest in AI-powered innovation and development, expand the distribution network with AI and invest in AI-powered employee training.
3.1. The Implications of AI in the Forklift Industry
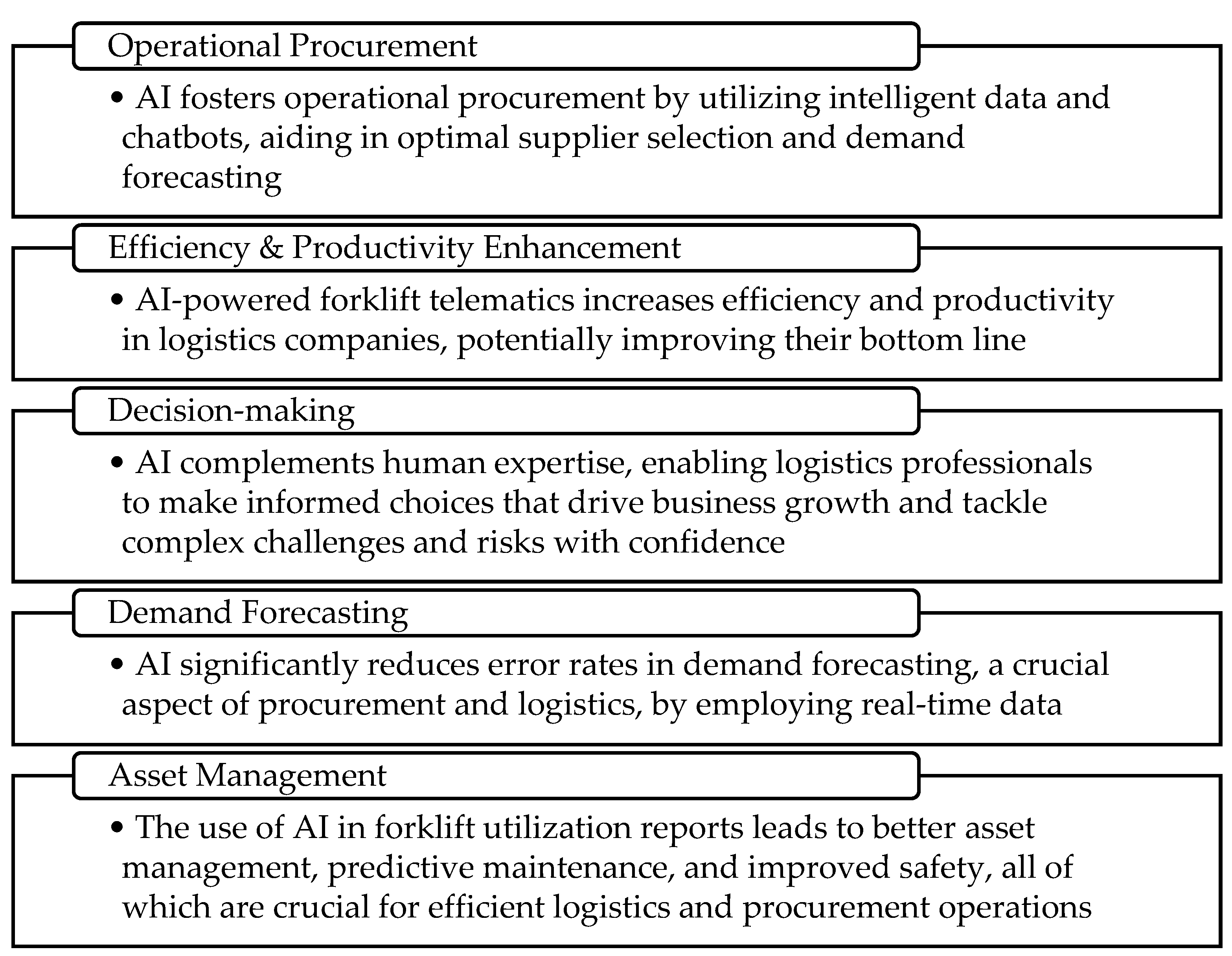
In the high-stakes world of forklift sales and logistics, where every move must be precise, efficiency is paramount. For SMEs in this industry, adapting to the whirlwind advancements of AI is no longer an option, it's a necessity [
1,
2,
3,
7,
20]. We will embark on a journey through the clever incorporation of AI, revealing how it is transforming logistics and procurement [
4,
12,
16]. We have a bustling warehouse with forklifts pirouetting gracefully through a maze of stacked pallets. Traditionally, logistics in this industry were akin to a clumsy waltz, but AI has brought forth efficiency. AI-powered predictive maintenance ensures forklifts never miss a step, predicting when they need attention, saving both time and money. AI provides real-time monitoring, tracking the forklift's every move so operators can intervene when necessary. AI's data analysis capabilities are a game-changer. It doesn't just point out inefficiencies, it elegantly waltzes through mountains of data to reveal patterns and trends, suggesting ways to optimize warehouse layouts, streamline routes, and reduce unnecessary footsteps [
2,
4,
8,
12,
13,
15]. When it comes to acquiring forklifts and equipment, the procurement process used to resemble a complex puzzle [
17]. Companies had to juggle various suppliers, negotiate prices, and keep an eye on inventory levels, often leading to an intricate ballet of paperwork and phone calls. AI, however, transforms this into a procurement ballet, where every move is choreographed to perfection. AI-driven procurement software can tap into a world of suppliers, compare prices, and even predict future costs, ensuring that the company gets the best deal without missing a beat [
16]. The days of painstakingly managing inventory are over, replaced by a performance where AI tracks usage patterns and orders new equipment seamlessly, all while staying within budget. The proliferation of AI in the forklift industry heralds transformative shifts [
9]. While the challenges are manifold, ranging from labor concerns to ethical dilemmas, the opportunities for increased efficiency and innovation are profound [
6]. The logistics and procurement departments stand to gain tremendously but must also adapt to a landscape where data-driven decision-making and automation become integral to operations [
4,
12]. Therefore, a strategic, well-considered approach to AI integration is imperative for harnessing its full potential while mitigating associated risks (
Figure 1).
The forklift industry is at a pivotal juncture with the advent of AI and autonomous mobile robot systems. The transformation is primarily seen in logistics and material handling facets, where autonomous forklifts are gaining traction due to the numerous benefits they offer including addressing labor shortages, enhancing safety, and boosting efficiency. Autonomous forklifts mitigate the physical demands associated with the risks of manual material transportation. The labor shortages in the warehousing sector have propelled the adoption of autonomous forklifts, bridging the labor gap and reducing dependency on human labor. These machines work continuously, enhancing warehouse throughput [
13]. They free up employees for other value-adding tasks, improving overall productivity and reducing workplace injuries. The inclusion of sophisticated sensor systems and real-time adaptive algorithms ensure safe operation in diverse environments, which is crucial in large warehouses and manufacturing facilities. The transition to autonomous forklifts also brings challenges [
8,
9,
18]. The integration with existing automation equipment and software, such as warehouse management systems, necessitates compatibility, interoperability, and ongoing support from solution providers. Ensuring safe operation while carrying heavy payloads and navigating around obstacles requires advanced sensor systems and real-time adaptive algorithms [
4,
14,
15].
3.2. Socio-Economic Perspectives of the Forklift Industry
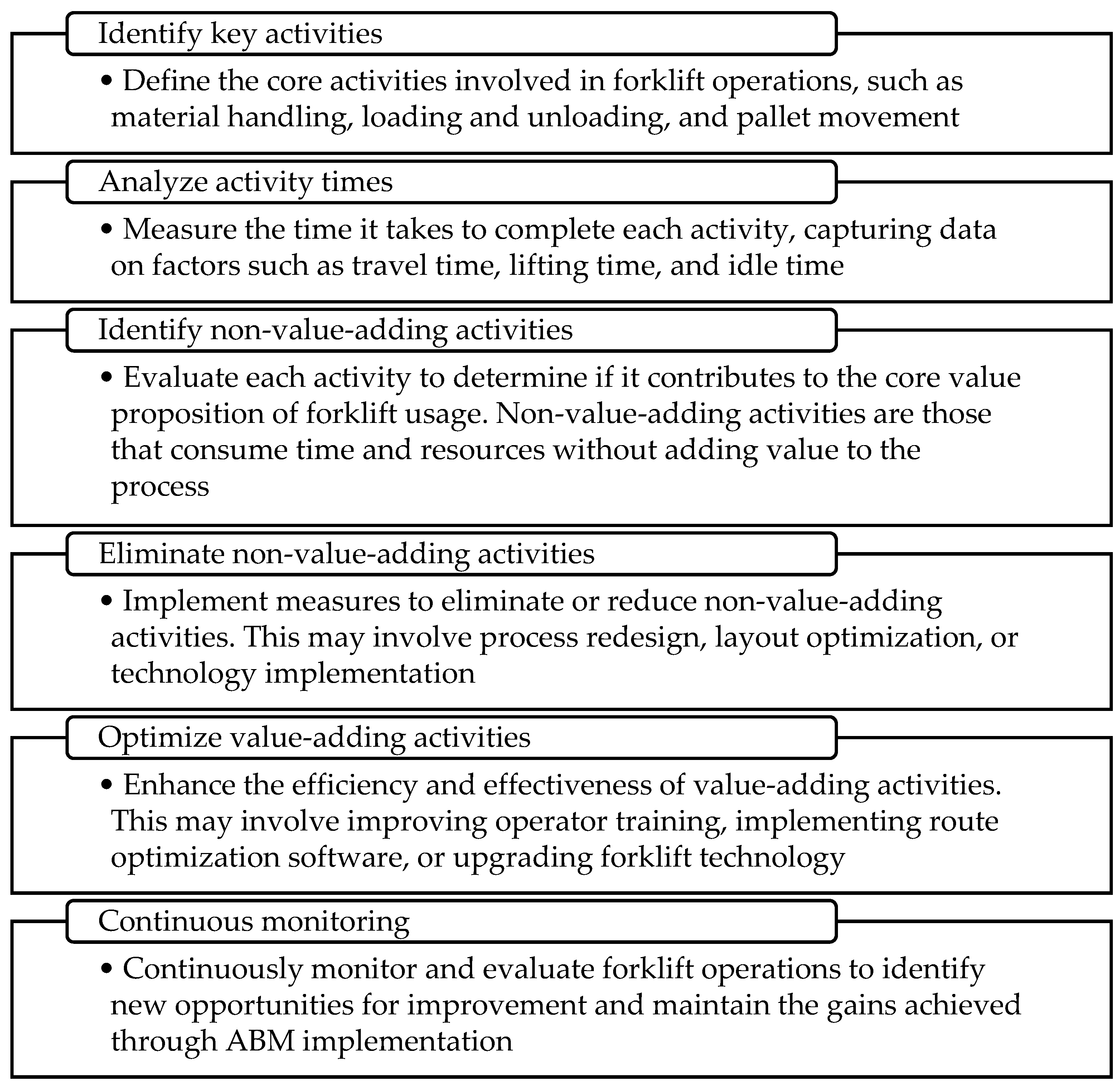
The ABM methodology aims to identify and eliminate non-value-adding activities that waste time and resources, thereby streamlining workflows and optimizing forklift usage (
Figure 2). Can be applied to various aspects of forklift operations in the forklift industry including warehouse operations, manufacturing facilities and distribution centers. By implementing an ABM, forklift operators can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, risks reduction, productivity, and cost-effectiveness, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge in the industry [
23].
A scientific benchmarking methodology for the forklift industry worldwide is applicable to all types of forklifts, including electric, internal combustion engine, and propane-powered forklifts. It can be used to evaluate the performance of forklift manufacturers, operators and rental companies (
Table 3). Provides a standardized approach for evaluating and comparing the performance of forklifts worldwide. It can be used to identify areas for improvement, promote the adoption of best practices, and drive innovation in the forklift industry. By continuously benchmarking performance, the forklift industry can enhance efficiency, productivity, safety, and sustainability. Benchmarking compares the performance of different forklift manufacturers and operators based on the analyzed data. This comparison should reveal areas of strength and weakness for each entity. This can be done using various methods such as: performance matrices, radar charts and ranking systems [
8].
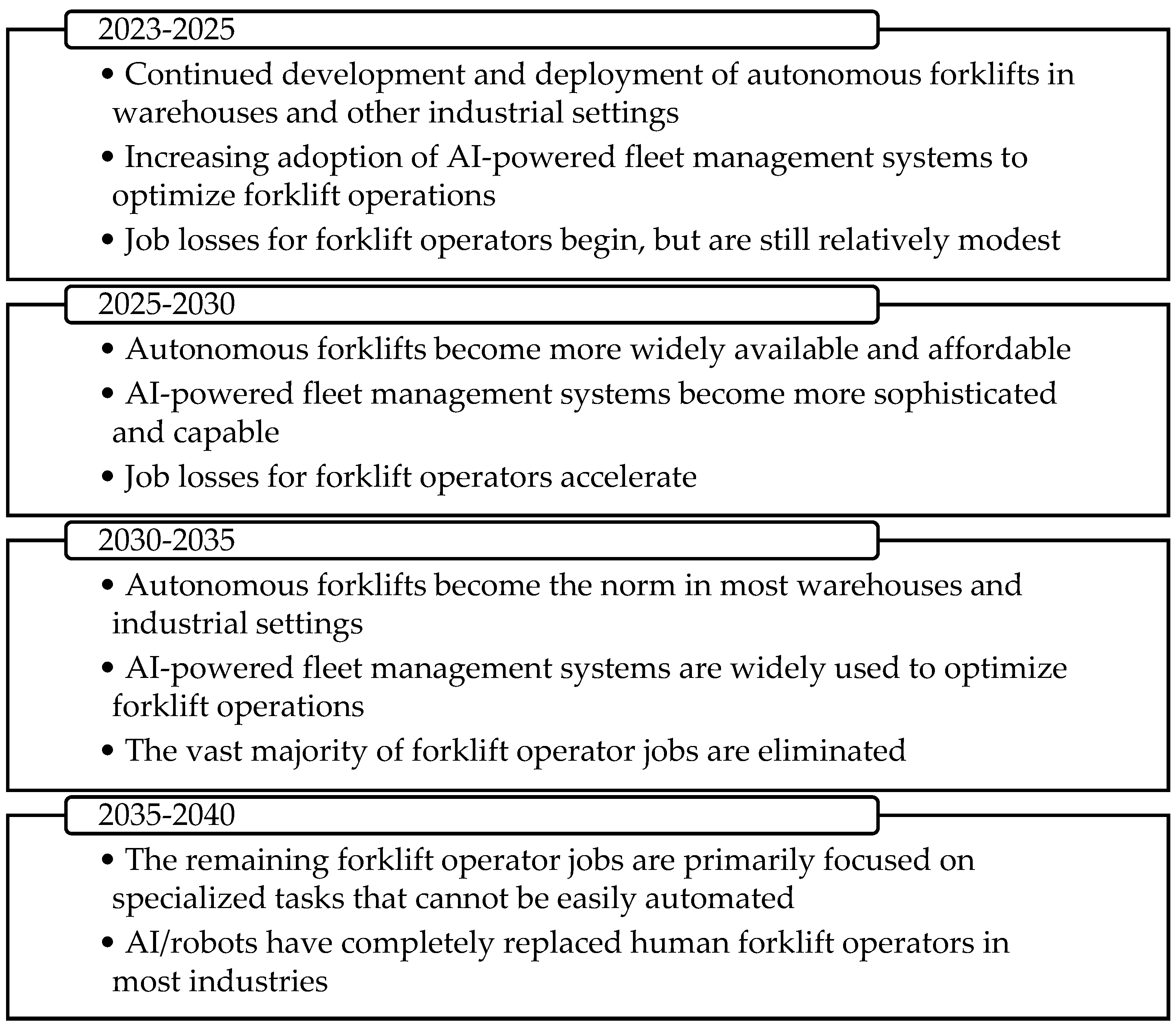
The loss of forklift operator jobs to AI/robots is likely to have several social and economic consequences (
Figure 3). For example, it could lead to increased unemployment, displacement of workers, and a decline in wages for other types of jobs in the logistics and manufacturing industries. It is important to think about these consequences and develop policies to mitigate them as we transition to a more automated future [
2,
4,
18].
4. Discussion
The integration of AI into different industries is an inexorable trend, fundamentally transforming traditional operational paradigms [
6]. The forklift industry, an essential component of logistics and procurement, is not exempt from this metamorphosis [
2,
4,
16]. As we delve into the challenges and opportunities presented by AI in this realm, it is essential to take a nuanced view, considering both the technological advancements and the ethical, economic, and labor implications they entail (
Table 4).
Efficient logistics and procurement are correlated in several ways: cost-efficiency, where better procurement strategies can lead to cost savings that can be invested in improving logistical capabilities; time management, where efficient logistics can speed up the procurement cycle, thereby reducing lead times; quality control, where both departments are crucial in maintaining the quality of goods, from sourcing to delivery; regulatory compliance, where effective logistics can help in easier compliance with international trade regulations, a task often initiated during the procurement stage [
12,
16,
17].
In SMEs, procurement and logistics often share a symbiotic relationship. Efficient procurement is futile without effective logistics, and vice versa. Leveraging data analytics for procurement, adopting green logistics, and focusing on supply chain resilience are imperatives [
12,
16,
20]. As we move towards a more globalized and digitized world, the challenges and opportunities for SMEs in the industrial machinery sector will proliferate in global supply chain disruptions, technological advancements and sustainability [
3,
7]. Logistics and procurement departments serve as the linchpin for SMEs dealing with industrial machinery. These departments are not merely cost centers but strategic units that can significantly influence a company's competitive edge. Improving logistics performance is crucial for economic growth and global competitiveness. Inefficient logistics can increase the risks and costs of trading and reduce global integration. Procurement in industrial machinery businesses is often a complex affair involving multiple stakeholders, from suppliers and manufacturers to transporters and regulatory bodies. Medium-sized businesses often find themselves in a goldilocks situation, not too big to enjoy economies of scale in procurement and logistics, and not too small to ignore the complexities these processes entail [
1,
3,
7,
12,
16].
The ESG-AI-BSC is a new and innovative proprietary framework well suited for forklift manufacturers and vendors improving their ESG performance with AI. The model consists of the following components: an ESG strategy, that defines the company's ESG objectives; an ESG measurement, that collects ESG data and information; an ESG analysis, that analyses ESG data and information to identify trends and opportunities; an ESG action, that implements measures to improve ESG performance. AI can be integrated into each of these components to improve model efficiency and accuracy. AI can be used to automate ESG data collection and analysis, identify ESG trends and opportunities that might be difficult for people to see and generate ESG reports that are more informative and easier to understand. The ESG-AI-BSC framework is a powerful tool that can be used to improve ESG performance in energy efficiency of forklifts, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from forklift trucks, work safety for forklift operators and social responsibility of the company towards employees, communities and the environment [
5,
19,
22]. By integrating AI into the model, companies can automate tasks, identify trends and opportunities, and generate more informative reports.
The proliferation of AI has been a game-changer across various industries, and the forklift industry is no exception, exploring the transformative role of AI in a BCFI committed to technological innovation [
10,
11]. The socio-economic implications of integrating AI into the forklift industry are examining both the opportunities and challenges that arise: employment dynamics, where AI-driven forklifts promise operational efficiency and a looming concern about job displacement; environmental sustainability, where electric and hybrid forklifts powered by AI algorithms optimize energy usage, contributing to sustainability goals and reducing its carbon footprint; market competitiveness, where the adoption of AI has given the company a competitive edge, allowing it to offer value-added services to its clients; regulatory compliance, where AI enables better compliance with safety and environmental regulations, reducing the risk of legal repercussions and enhancing social responsibility. The integration of AI into the forklift industry is not merely a technological evolution; it is a socio-economic revolution [
9]. The BCFI exemplifies how AI can be harnessed for operational excellence while also addressing socio-economic challenges [
10,
11]. This transformation is not without its risks and complexities, necessitating a balanced approach that considers ethical, social, and economic factors: ethical AI framework, where an ethical governance framework for AI implementation should be established; upskilling programs, where companies should invest in employee training to mitigate job displacement; stakeholder engagement, where open dialogue with stakeholders, including employees, regulators, and the community, is crucial for responsible AI adoption [
18].
In the realm of industrial equipment, the BCFI reigns supreme and its commitment to the digital era is second to none. With a keen eye on the future, has embraced digitalization with open arms. The company has invested heavily in research and development, and its products are now equipped with cutting-edge technology that makes them more efficient, productive, and sustainable than ever before. One of the most impressive aspects of the digital transformation is its focus on customer-centricity, developing several digital solutions that are designed to help customers optimize their operations, and meet their unique needs. The IoT platform provides real-time data on forklift performance, battery levels, and maintenance schedules. This data can be used to improve fleet utilization, reduce downtime and risks, and extend the lifespan of forklifts. The BCFI is a shining example of how an industrial company can successfully adapt to the digital era. The company's focus on innovation, customer-centricity, and sustainability is ensuring that it remains at the forefront of the industry for many years to come [
10,
11].
The main findings of this research relate to highlighting the industrial revolution driven by AI with implications in the forklift industry, logistics and procurement. The advantages of this research lie in the case study of BCFI using the interview method with seven managers and the McKinsey 7S framework, as well as the analysis of the forklift industry using ABM and benchmarking methods and the ESG-AI-BSC innovation framework. As managerial implications we can highlight the revolution generated by AI in all sectors of activity, most existing tasks can be taken over by AI and managers can focus in the future on areas that generate high added value. The limitations of this research lie in the limitations of the forklift industry, AI, logistics and procurement, and the limitations of the research methods used. These limitations will be overcome by future research on the implications of AI in other industries and fields, increasing safety, reducing risks, as well as the use of other research methods.
5. Conclusions
The forklift industry stands on the cusp of a transformative era, poised to be reshaped by the inexorable march of digitalization and AI. We can envision a timeline where, within the next decade, the integration of AI will not merely be an add-on but will constitute the core of material handling operations. Industry 4.0 technologies are transforming the forklift industry, helping to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety, and creating new opportunities for innovation and growth. In the short term, AI is set to enhance the capabilities of forklifts, making them more efficient, safer, and capable of predictive maintenance. This intelligence will be incremental, initially focusing on navigation and pallet handling in complex environments. By the mid-term, within five to ten years, fully autonomous forklifts are likely to be mainstream in large warehouses, driven by an industry-wide push towards greater productivity and the reduction of human error and risks. The long-term impact, extending beyond ten years, will see AI's role evolving from autonomous operations to strategic logistics management. Forklifts will communicate with each other and with an integrated supply chain management system, optimizing workflows in real-time. The data collected by AI will feed into broader economic models, allowing for predictive analytics that can anticipate market shifts and adjust operations accordingly. These changes will not be without their challenges and risks. Workforce displacement and the need for new skill sets will require thoughtful management and retraining programs. There will also be heightened concerns around data security and the ethical use of AI. The overall trajectory is towards a more efficient, safe, and intelligent forklift industry, one that is seamlessly integrated into the digital fabric of the 21st century.
As AI sweeps onto the stage of SMEs, logistics and procurement take on an entirely new rhythm. The days of clumsy missteps are over, replaced by a business in harmony with the ever-changing demands of the industry. As for the forklifts, they may not have gained the ability to tango, but with AI, they've become stars. The digitization of the forklift industry through AI is not a matter of if, but when. The transformation will be a phased journey rather than a sudden shift, with significant positive impacts on productivity, safety, and operational intelligence. The industry must navigate this transition with foresight, adapting to the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. As we embrace this new digital era, the forklift industry is set to become a paragon of technological integration in the realm of industrial machinery. The forklift industry is the unsung hero of warehouses, the knight in shining armor for pallets, and the nemesis of the traditional workforce in a paradoxical world where the quest for efficiency and profit is making forklifts smarter and humans, well, redundant. Forklifts were the loyal steeds of warehouse workers, obediently lifting and transporting goods under human guidance. In the era of AI, these forklifts started getting an "education," learning to navigate, sort, and even "think" for themselves. Suddenly, they didn't need a human to hold their "hand" (or wheel, in this case).
Factories and warehouses are not philanthropic entities; they're in it for the money. And what's more profitable than cutting down on human error, coffee breaks, and sick leaves? AI-powered forklifts that work round the clock without so much as a yawn, resulting in soaring profits and plummeting employment. As forklifts get smarter, the humans who once operated them are facing an existential crisis. They are not just losing their jobs, they are losing them to their own "teammates". It's like training a pet to fetch the newspaper, only to find out it is also reading the stock market section and advising you on investments. The cruel irony is that the very efficiency that makes AI-driven forklifts so appealing is what makes human workers dispensable. It's a classic case of being too good at your job, only the "you" in this scenario has wires and sensors instead of flesh and bones. On one path, we have unprecedented efficiency and profitability; on the other, a workforce grappling with obsolescence. It's high time industries realized that while machines can replace tasks, they can't replace human ingenuity (yet). In the end, the forklift industry's tale is a cautionary one. Be careful what you wish for, especially if it involves making your job easier. You might just innovate yourself out of it. We have a short, snappy look at the forklift industry's job displacement saga, where the wheels of progress are both lifting and tipping the scales. In the grand finale of our AI-driven performance, forklift SMEs not only survive, they thrive. They have become masters of logistics and procurement, thanks to the innovative use of AI.
To analyze the evolution of the forklift industry due to the implementation of AI in the logistics and procurement sector, we researched scientific papers in this field. The result was that in the future, we will have autonomous equipment inside warehouses, and transport planning and decisions on choosing the best suppliers will be made with the help of AI. Interviews with seven BCFI managers revealed that optimizing logistics and procurement procedures in technology SMEs with AI will lead to cost savings, risks reduction, refurbishment of logistics equipment and implementation of efficient logistics and procurement systems. We used ABM, benchmarking and the ESG-AI-BSC framework methodologies to analyze the socio-economic progress of AI implementation in the forklift industry. The result was cost and management optimization while implementing the highest standards of environmental, social responsibility and corporate governance. To highlight the socio-economic impact of BCFI, interviews with the seven managers were processed and a McKinsey 7S framework was implemented. It emerged that the company has the potential to become the market leader in the autonomous forklifts industry, which will no longer use forklift operators, if it invests in research-development-innovation, employee training and expands its distribution network.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.G. and Z.T.; methodology, A.S.G. and M.B.; software, M.A.M. and I.R.P.; validation, A.S.G. and Z.T.; formal analysis, Z.T. and I.R.P.; investigation, A.S.G. and Z.T.; resources, A.S.G. and M.B.; data curation, A.S.G. and M.A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.G. and Z.T.; writing—review and editing, Z.T. and M.B.; visualization, Z.T. and I.R.P.; supervision, A.S.G. and M.B.; project administration, Z.T. and M.A.M.; funding acquisition, M.A.M. and I.R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to BCFI managers wish to remain anonymous.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acknowledgments
We thank the BCFI managers for their cooperation during the interviews.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Žigienė, G.; Rybakovas, E.; Alzbutas, R. Artificial intelligence based commercial risk management framework for SMEs. Sustainability 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woschank, M.; Rauch, E.; Zsifkovits, H. A review of further directions for artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in smart logistics. Sustainability 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Pardo, C. Artificial intelligence and SMEs: How can B2B SMEs leverage AI platforms to integrate AI technologies? Industrial Marketing Management 2022, 107, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xie, F. Cognitive and artificial intelligence system for logistics industry. International Journal of Innovative Computing and Applications 2020, 11, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguanwongs, C.; Kritjaroen, T. The influence of transformational leadership on organization performance. International Journal of Professional Business Review 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baabdullah, A.M.; Alalwan, A.A.; Slade, E.L.; Raman, R.; Khatatneh, K.F. SMEs and artificial intelligence (AI): Antecedents and consequences of AI-based B2B practices. Industrial Marketing Management 2021, 98, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.B.; Bøgh, S. Artificial intelligence and internet of things in small and medium-sized enterprises: A survey. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2021, 58, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, T.; Jo, W.; Kim, J.; Shin, J.; Han, D.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, Y. Multispectral benchmark dataset and baseline for forklift collision avoidance. Sensors 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Wen, Y. Research on application of forklift dispatching intelligence in industrial intelligence. International Symposium on Computer Technology and Application 2022, 1, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, Z.; Puiu, I.R.; Wang, S.S.; Vrǎjitoru, E.S.; Boșcoianu, M. Dynamic capabilities and high quality standards in S.C. Jungheinrich Romania S.R.L. Zenodo 2022, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, Z.; Puiu, I.R.; Wang, S.S.; Vrǎjitoru, E.S.; Boșcoianu, M. Electric forklift trucks refurbishment at S. C. Jungheinrich Reconditionare Romania S.R.L. Zenodo 2022, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilin, V.; Simić, D.; Saulić, N. Logistics industry 4.0: challenges and opportunities. 4th Logistics International Conference 2019, 293-301. https://logic.sf.bg.ac.rs/wp-content/uploads/LOGIC_2019_ID_33.pdf.
- Downie, B.; Gyöngyösi, M.; Kuehl, C. Artificial intelligence in materials handling: How machine learning tools boost warehouse safety, productivity and cost-effectiveness. Journal of Supply Chain Management, Logistics and Procurement 2021, 4, 6–16. https://www.ingentaconnect.com/contentone/hsp/jscm/2021/00000004/00000001/art00002. [CrossRef]
- Motroni, A.; Buffi, A.; Nepa, P.; Pesi, M.; Congi, A. An action classification method for forklift monitoring in industry 4.0 scenarios. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motroni, A.; Buffi, A.; Nepa, P. Forklift tracking: industry 4.0 implementation in large-scale warehouses through uwb sensor fusion. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, M.; Caniato, F.; Moretto, A.; Ronchi, S. The role of artificial intelligence in the procurement process: State of the art and research agenda. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management 2023, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Li, M.; Zhang, S. AI and Procurement. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management 2021, 24, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey Jr., R.G.; Chowdhury, S.; Davis-Sramek, B.; Giannakis, M.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial intelligence in logistics and supply chain management: A primer and roadmap for research. Journal of Business Logistics 2023, 44, 532–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, Y.A.; Kannan, D.; Govindan, K.; Hasibuan, Z.A. Circular economy e-business model portfolio development for e-business applications: Impacts on ESG and sustainability performance. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dencker, J.C.; Bacq, S.; Gruber, M.; Haas, M. Reconceptualizing Necessity Entrepreneurship: A Contextualized Framework of Entrepreneurial Processes Under the Condition of Basic Needs. Academy of Management 2021, 46, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatovcev, I.; Ireland, R.D.; Stahl, G.K. Contextualizing Management Research: An Open Systems Perspective. Journal of Management Studies 2022, 59, 1036–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.S. How the balanced scorecard complements the McKinsey 7-S model. Strategy & Leadership 2005, 33, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleosakul, K.; Smutkupt, S. Applying Activity-Based Costing and Activity-Based Management Methods to Estimate Manufacturing Costs and Activities. Journal of Supply Chain Management 2018, 12, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).