Submitted:
02 August 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Areal and Data Processing
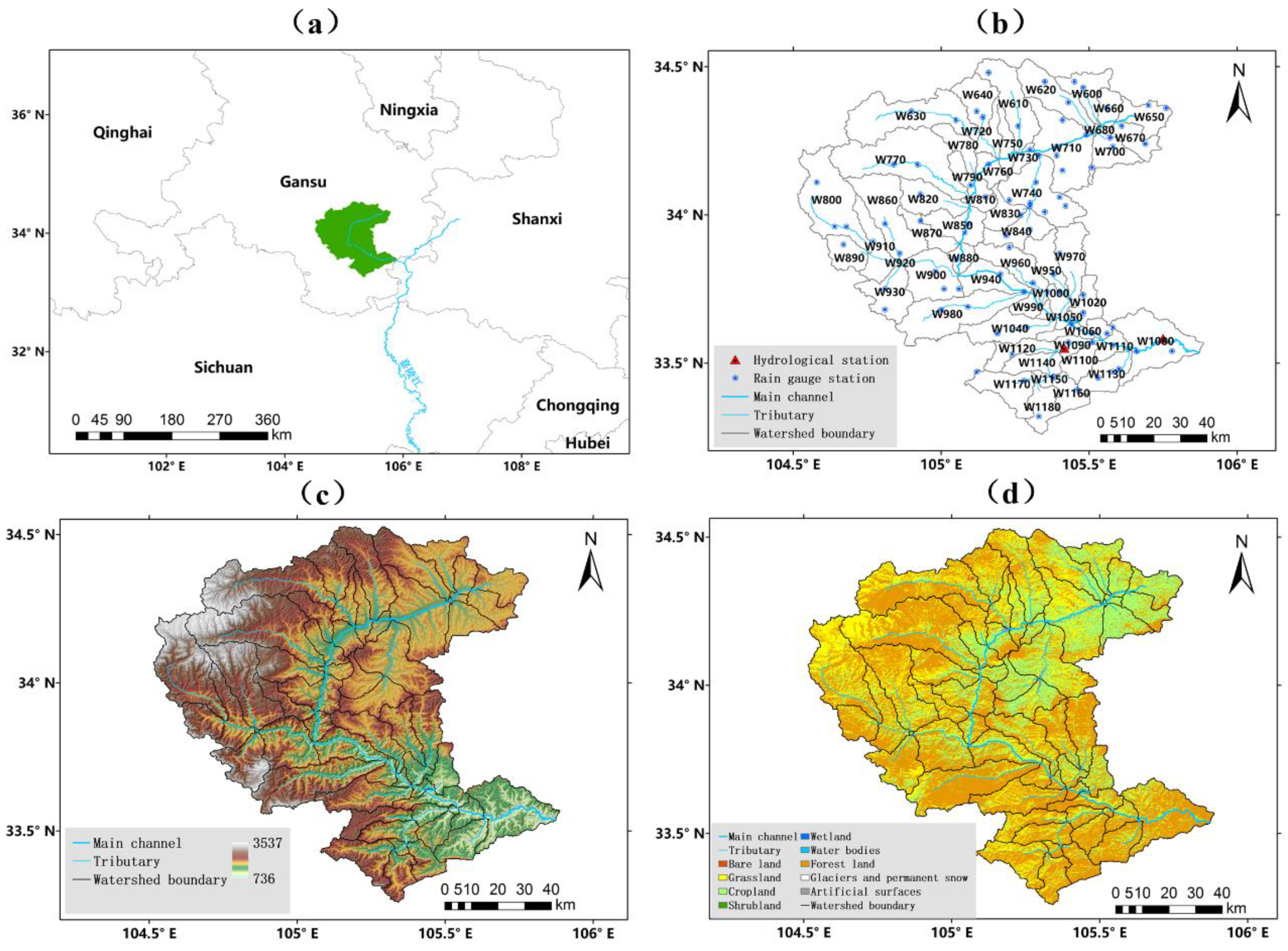
2.1. Study Areal Introduction
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
3. HEC-HMS Model and Methods
3.1. HEC-HMS Model Introduction
3.2. Parameter Calibration Method
3.3. Model Accuracy Evaluation
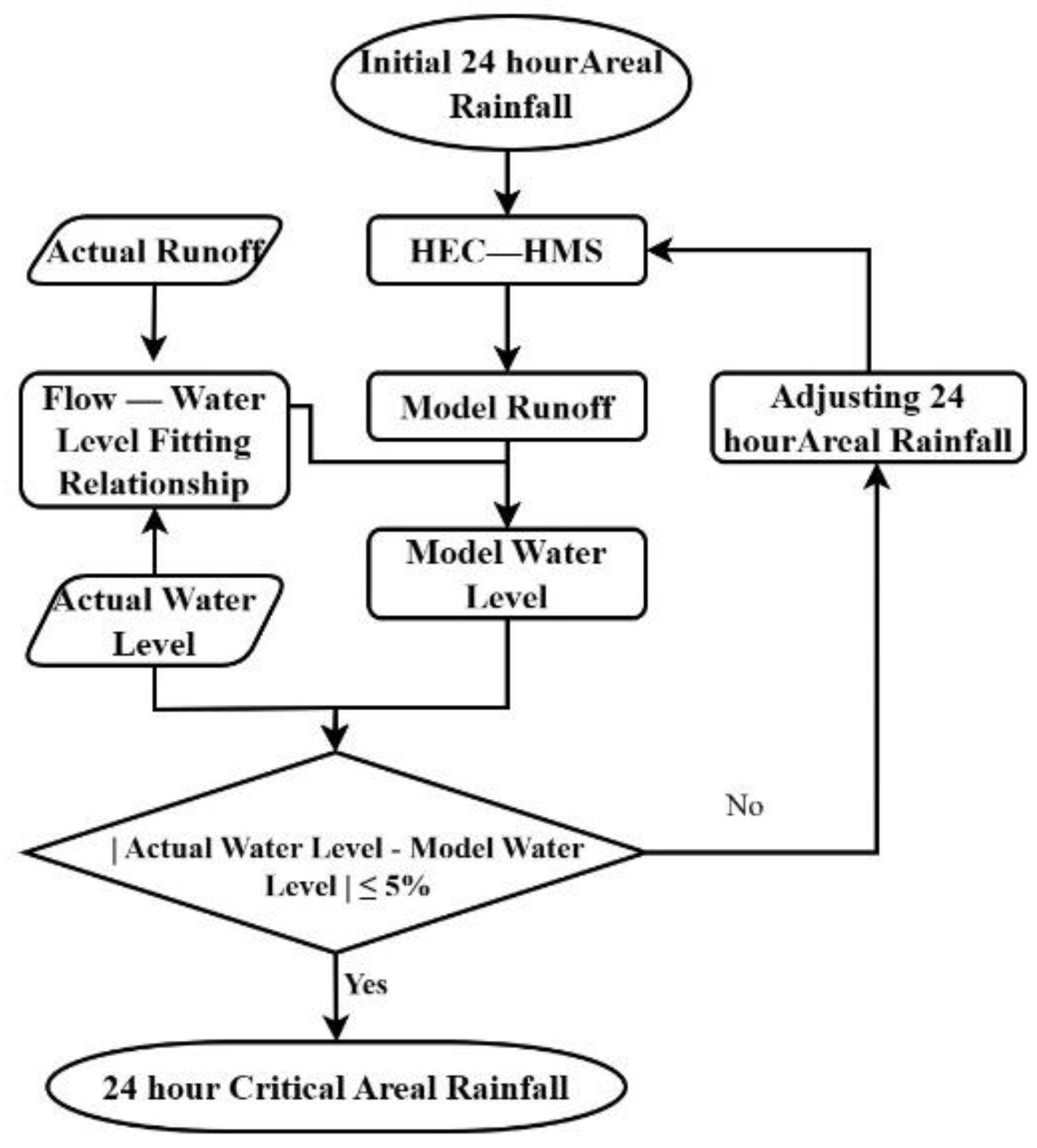
3.4. Critical Areal Rainfall Calculation
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Parameter Calibration Results
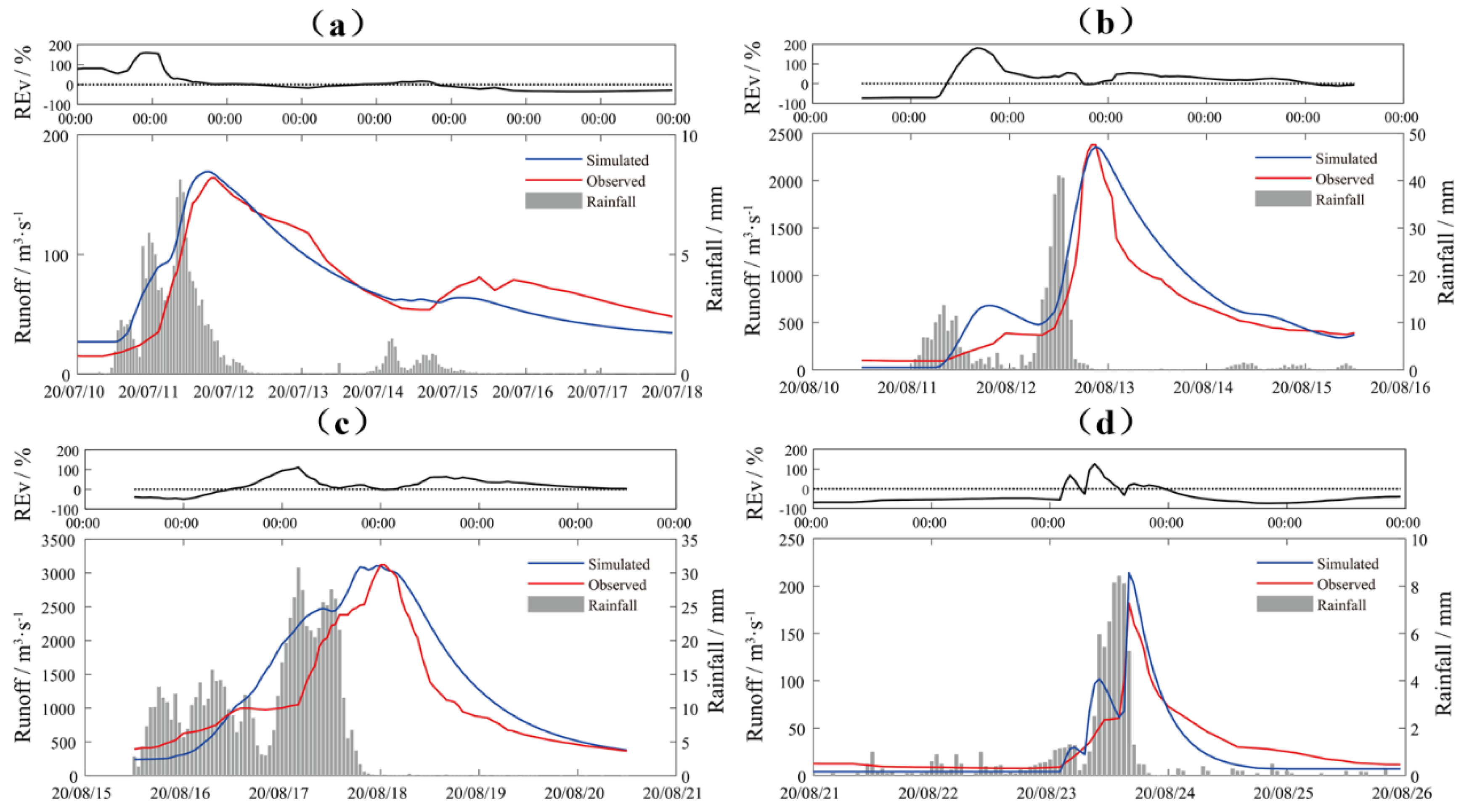
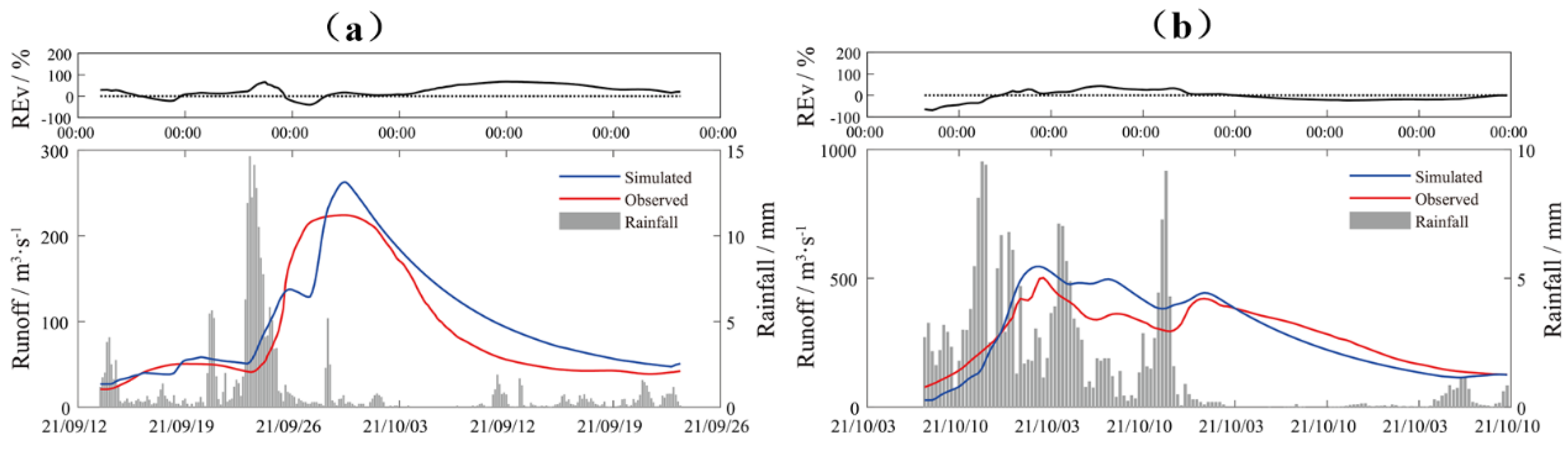
4.2. Model Evaluation and Analysis
5. Critical Areal Rainfall Calculation
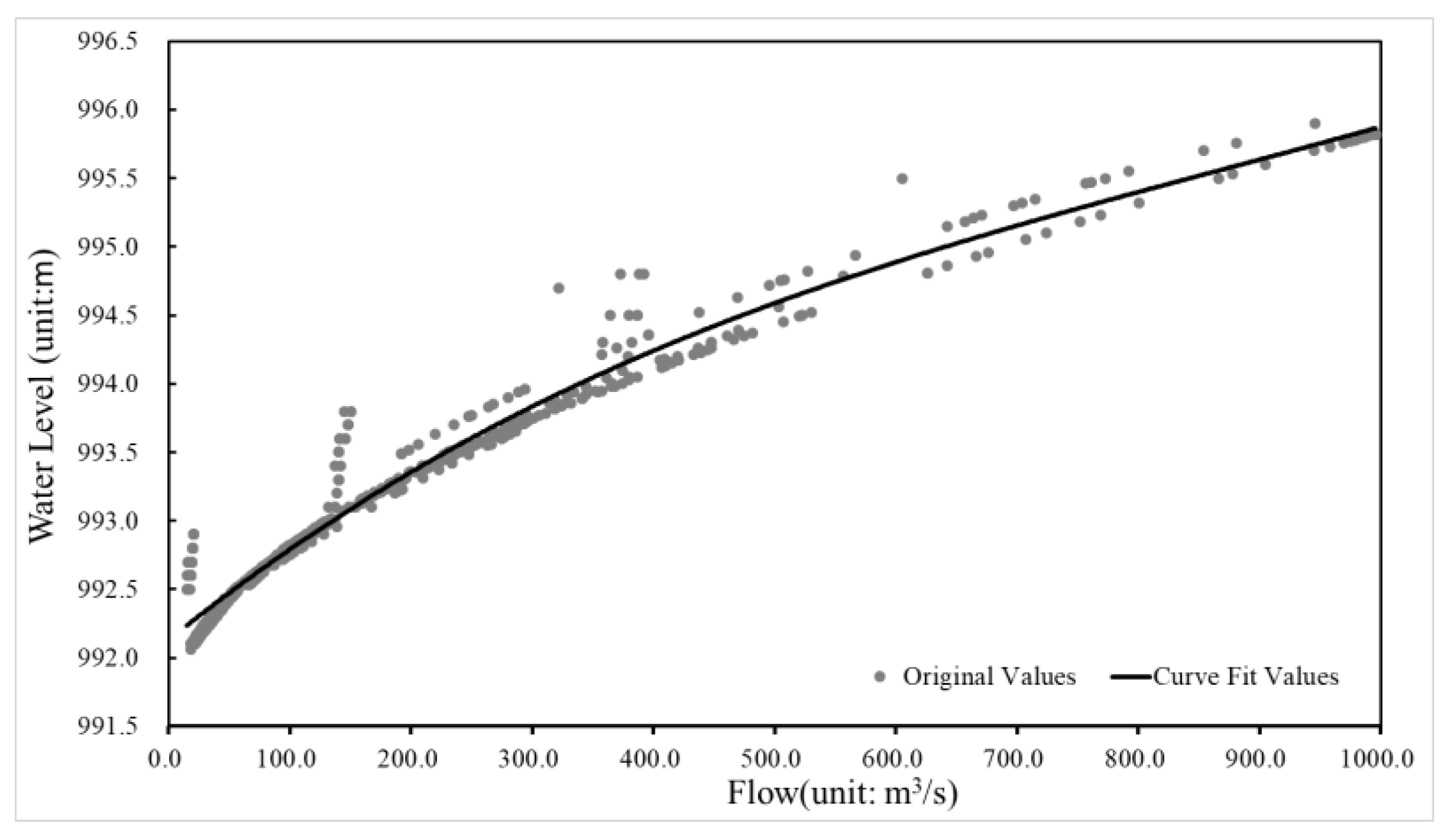
5.1. Water level-Flow Relationship Fitting
5.2. 24 Hour Critical Areal Rainfall
6. Conclusion and Discussion
6.1. Conclusion
6.2. Discussion
Funding
References
- Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, D.W.; Hu, J.W. Dynamic critical rainfall-based torrential flood early warning for medium-small rivers. Journal of Beijing Normal University ( Natural Science) 2010, 46, 317–321. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.X.; Wang, R.M.; Huang, Q.; Xiang, J.Y.; Qin, G.H. Advances on Flood Forecasting of Small-Medium Rivers [J]. Journal of China Hydrology 2020, 40, 16–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schreider, S.Y.; Jakeman, A.J.; Letcher, R.A.; Nathan, R.J.; Beavis, S.G. Detecting changes in streamflow response to changes in non-climatic catchment conditions: farm dam development in the Murray-Darling basin. Australia [J]. Journal of Hydrology 2002, 262, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhan, F.Z.; Ye, Y. Study on Relationship between Flood and Precipitation Concentration Degree in Time and Space in Medium- and Small-sized River Basins[J]. Journal of China Hydrology 2009, 29, 14–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Marchi, L.; Borga, M.; Preciso, E.; Gaume, E. Characterisation of selected extreme flash floods in Europe and implications for flood risk management[J]. Journal of Hydrology 2010, 394, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q. Hydrologic response in a humid steeo mountainous watershed in the west of China: A case study of Longxihe watershed in Sichuan[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University. 2014. (In Chinese).
- Meresa, H. Modelling of river flow in ungauged catchment using remote sensing data: Application of the empirical (SCS-CN), artifcial neural network (ANN) and hydrological model (HEC-HMS). Model Earth Sys Environ 2019, 5, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Harlan, R.L. Blueprint for a physically-based, digitally-simulated hydrologic response model[J]. Journal of Hydrology 1969, 9, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, C.E.; Hope, A.S.; Loaiciga, H.A. Distributed hydrological modelling in California semi-arid shrublands: MIKE SHE model calibration and uncertainty estimation[J]. Journal of Hydrology 2006, 317, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W. SWAT: MODEL USE, CALIBRATION, AND VALIDATION[J]. Transactions of the Asabe 2012, 55, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.J. Rainfall-runoff modeling: the primer [M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.Y.; Li, H.X. Predicting surface runoff from catchmentto large region [J]. Advances in Meteorology 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.X. Hydrological Models[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017. (In Chinese).
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H. Improving flood forecasting capability of physically based distributed hydrological models by parameter optimization. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2016, 20, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Regionalising rainfall-runoff modelling for predicting daily runoff: Comparing gridded spatial proximity and gridded integrated similarity approaches against their lumped counterparts [J]. Journal of Hydrology 2017, 550, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, Q.; Huang, F.; Xu, H.; Cluckie, I. Liuxihe model and its modeling to river basin flood. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 2011, 16, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, B.; Mousavi, S.J. , Abbaspour K C. Automatic calibration of HEC-HMS using single-objective and multi-objective PSO algorithms[J]. Hydrological processes 2013, 27, 4028–4042. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. Nakakita, E. Kim, S.; Yamaguchi, K. Improving the accuracy of flood forecasting with transpositions of ensemble NWP rainfall fields considering orographic effects[J]. Journal of Hydrology 2016, 539, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Research on design flood of small watershed in semi-arid loess gully region based on HEC-HMS model[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018. (In Chinese).
- Bournaski, E.; Iliev, R.; Kirilov, L. HEC-HMS modelling of rainstorm in a catchment. The mesta case study[J]. Comptes Rendus de L’Academie Bulgare des Sciences 2009, 62, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Olang, L.O.; Fürst, J. Effects of land cover change on flood peak discharges and runoff volumes: model estimates for the Nyando River Basin, Kenya. Hydrological Processes 2011, 25, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Tang, C.; Tang, H.X. Conflux Process of Debris flow in Shuida Gully Using HEC-HMS Model[J]. Mountain Research 2015, 03, 318–325. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.W. Confluence process of debris flow in Shuidaogou based on HEC-HMS[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2016. (In Chinese).
- Gumindoga, W.; Rwasoka, D.T.; Nhapi, I.; Dube, T. Ungauged runoff simulation in Upper Manyame Catchment, Zimbabwe: Application of the HEC-HMS model[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 2017, 100, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z.X.; Dai, X.Y.; Hu, Z.L. Assessing sub-daily rainstorm variability and its effects on flood processes in the Yangtze River Delta region[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal/Journal des Sciences Hydrologiques, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Labate, A. Martino D, et al. Comparing different infiltration methods of the HEC-HMS model: the case study of the Mésima Torrent (Southern Italy)[J]. Land Degradation Development 2017, 28, 294–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafati, A.; Khazaei, M.R.; Nashwan, M.S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Shahid, S. Assessing the uncertainty associated with flood features due to variability of rainfall and hydrological parameters[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayarathne, D.B.; Coulibaly, P. Identification of hydrological models for operational flood forecasting in St. John's, Newfoundland, Canada[J].Elsevier 2020. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.L.; Fu, L.; Gao, Q.Y. Research on Rainfall Threshold of Flash Flood Based on HEC-HMS Model [J]. Yellow River 2019, 41, 22–27+31. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Na, L.; Zhang, B. Applicability of the distributed hydrological model of HEC-HMS in a small watershed of the Loess Plateau area[J]. Journal of Beijing ForestryUniversity 2009, 31, 52–57. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X. Application of HEC-HMS Parameter Regionalization in Small Watershed of Hilly Area[J]. Water Resources Management 2021, 35, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.H.; Zheng, X.Q.; Chen, P.; Zhao, X.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Shen, Y. An Investigation into Sub-Basin Rainfall Losses in Different Underlying Surface Conditions Using HEC-HMS: A Case Study of a Loess Hilly Region in Gedong Basin in the Western Shanxi Province of China[J]. Water 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. The Application of HEC-HMS in Mountain Torrents Simulation of Northern Small Watershed[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science 2019, 252, 052060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.Y. Simulation of watershed flood critical rainfall value using HEC-HMS Hydrological Model[J]. China Flood & Drought Management, 2021, 31, 49–55. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.H.; Ding, R.; Huang, E.; Luo, M.; Zheng, H.W. Research on flood warning of Tongkou River basin based on HEC-HMS model[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering 2021, 52, 80–89. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.Y.; Miao, J.Q.; Yao, X.Y.; Deng, Z.Y.; Liu, W.M. A Study on Characteristics of Distribution of Rainstorm andFlood Disastersin Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology 2006, 21, 27–31. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, W.B.; Sha, H.E. Cause of two heavy rainfall causing massive mudslidein Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography 2018, 41, 443–448. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Huang, W.B.; Li, A.T.; Yang, X.M.; Li, Q.; Bian, H.W. Fine meteorological risk early warning forecast of main geological disasters in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography 2023, 46, 1443–1452. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.D. Variation characteristics and influencing factors of water runoff in the Western Han Dynasty from 1960 to 2020[D]. Lanzhou University, 2022. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.X.; Lv, Y.B. Investigation and analysis of “20200812” rainstorm flood in Pingluo River Basin [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Quick Report 2021, 42, 8–11+20. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C. Analysis of Runoff Evolution Characteristics and Response to Climate Change in the Upper Reaches of the XiHan River[J]. Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology 2022, 58, 7–10+24. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Liu, M.; Wan, F. Calculation of critical rainfall for small-watershed flash floods based on the HEC-HMS hydrological model[J]. Water Resources Management 2019, 33, 2555–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Kjeldsen, T.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H. A comparison of two event-based flood models (ReFH-rainfall runoff model and HEC-HMS) at two Korean catchments, Bukil and Jeungpyeong[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Dong, X.H.; Bo, H.J. Research on Influence of Objective Function on HEC-HMS Model Parameter Calibration[J]. Water Resources and Power 2010, 28, 17–19. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of china. GB/T 22482-2008. (https://std.samr.gov.cn/gb/search/gbDetailed?id=71F772D761A6D3A7E05397BE0A0AB82A). 0539.
- Zhang, G.C. Rainstorm Flood Forecast and Risk Assessment[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2012: 19-33. (in Chinese).
- Li, X.X. Application of HEC-HMS hydrological modeling system principle and method[M]. Beijing: China Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, 2015. (in Chinese).
- Yu, Z.B. Principles and Applications of Distributed Hydrological Science in Watersheds [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese).
- Liang, R. Application of HEC-HMS in the Beizhangdian Watershed[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese).
| Simulation Period | Flood Event Number | Start-End Time (YYYYMMDDHHMM) |
Basin Average Areal Rainfall (mm) | Peak Flow (m³‧s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration Period | 20200711 | 202007100000―202007172300 | 3.4 | 164.0 |
| 20200812 | 202008101200―202008151200 | 11.2 | 2380.0 | |
| 20200817 | 202008151200―202008201200 | 15.1 | 3120.0 | |
| 20200823 | 202008210000―202008252300 | 3.7 | 182.0 | |
| Validation Period | 20210919 | 202109151000―202109290600 | 5.7 | 224.2 |
| 20211004 | 202110031500―202110092300 | 4.1 | 501.7 |
| /(mm) | Direct Runoff Storage Coefficient K/(h) |
Base Flow Index Decay Constant k/(h) |
Channel Routing Lag Time τ/(h) |
Channel Storage Coefficient R/(h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.72 |
| Period | Flood Event Number | /(%) | /(h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /(m³‧s-1) | /(m³‧s-1) | /(%) | |||||
| Calibration Period | 20200711 | 164.0 | 169.3 | 3.23 | 3.75 | -1 | 0.775 |
| 20200812 | 2380.0 | 2358.1 | -0.92 | 19.07 | 1 | 0.736 | |
| 20200817 | 3120.0 | 3104.8 | -0.49 | 18.72 | -1 | 0.758 | |
| 20200823 | 182.0 | 214.0 | 17.58 | 18.10 | 0 | 0.771 | |
| Validation Period | 20210919 | 224.2 | 262.7 | 17.17 | 15.77 | -1 | 0.826 |
| 20211004 | 501.7 | 545.9 | 8.81 | 13.16 | -1 | 0.748 | |
| Average | 7.56 | 14.76 | -0.5 | 0.769 |
| Station Name | Station ID | Warning Stage (m) | Guaranteed Stage (m) | Warning Flow (m³) | Guaranteed Flow (m³) | Warning Areal Rainfall (mm) | Guaranteed Areal Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pingluo | 60705400 | 1095.1 | 1097.3 | 128.2 | 371.9 | 108.1 | 230.8 |
| Tanjiaba | 60704800 | 996.23 | 997.8 | 1224.5 | 2125.4 | 128.5 | 184.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





