1. Introduction
Breastmilk, considered the golden standard for infant nutrition, plays the vital role of modulating the gut microbiome of newborns in a health-determining way that influences their well-being early on and later in life. The presence of bioactive components and microorganisms in human breast milk distinguishes it from powdered formula, These components play a crucial role by developing the gut microbiome and immunity of the newborns. Therefore, any fluctuations that may arise, for instance, mixed-feeding, solely formula feeding, antibiotic or probiotic consumption, contribute to positive or negative gut community development deviations from the “golden standard” feeding. The potentially probiotic microflora of breastmilk manifests different characteristics depending on many factors, the majority of which related to the individuality of the donors, their lifestyle and geographical location.
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have accumulated scientific and commercial popularity during the last decades due to their beneficial presence in the microbiota of the human body, specifically the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). The metabolic advantages of many probiotic strains, along with their protective capabilities against infection agents, have been the focus of a number of scientific studies, especially when it comes to the neonates.
The presence and persistence of these potentially beneficial bacteria in the infant’s gut depend on a number of factors, including the mother’s microbiota, mode of delivery, type of feeding, intake of probiotics or antibiotics, geographic and other characteristics. The inoculation of the neonate begins before birth, as shown by studies proving the existence of bacteria in the amniotic fluid, placenta and meconium [
1]. The type of birth is considered crucial for the infant’s initial GIT colonization due to the different bacteria acquired during birth: the characteristic of the mother’s skin microbiota in Caesarian Section (CS) or the vaginal microbiota during spontaneous natural delivery. The dominance of
Bifidobacterium,
Bacteroides and
Lactobacillaceae, along with higher variability is well represented in vaginally born infants, whereas lower diversity,
Staphylococcus,
Streptococcus and
Clostridium are attributed to Caesarian delivery [
2]. Not only does the transfer of beneficial microorganisms during the vaginal birth differ from CS-delivery, but also some immune-stimulatory factors, such as interleukin 18 (IL-18) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), are also absent in the Caesarian babies [
3].
Breastfeeding influences the gut ecosystem tremendously by providing the neonate with the most appropriate selection of nutrients for the growing organism. Ma et al. [
4] prove the beneficial microbiological qualities of the human milk compared to the infant formula and display the nutritional capacity of breast milk to not only deliver the needed elements, but also to formulate a healthy GIT microbiological profile. The modulation of an infant immune system increasingly depends on the probiotic potential of the representatives in the gut. The commensal bacteria balance the Th1/Th2 response, enhance the anti-inflammatory response [
5], affect the production of sIgA antibodies and play a significant part in the development of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue [
6]. Neonatal antibiotic prescription is one of the most prominent causers of dysbiosis [
7], which is related to necrotizing enterocolitis, inflammatory diseases and obesity [
8]. Neonates who have been on antibiotics show lower amounts of commensal microflora, such as members of the genera
Bifidobacterium and
Bacteroides [
9,
10,
11],
Firmicutes, along with higher
Proteobacteria [
12] and
Enterobacteriaceae [
13] resulting in microbiological deficiency. On the other hand, infant probiotic intake predisposes positive alternations in the gut microbiota and immune responses [
14], as well as mother’s probiotic supplementation [
15]. Other circumstances, such as pre-term pregnancy and prolonged hospitalization induce variation in the gut microbiota orchestration in newborns. They are related to use of antibiotics, physiological immaturity, lower birth weight, along with the breastfeeding difficulty, characteristic of a pre-term pregnancy contribute to
Enterobacteriaceae and
Clostridium domination of the GIT, related to intestine disorder development, for instance, necrotizing enterocolitis [
6,
16,
17]. The enormous variety of factors that affect the infant gut inoculation and maturation assemble a complex system that require further scientific research.
Since breast milk, the main nutritious source of neonates, was evidenced as a non-sterile fluid, two hypotheses on the origin of human milk microbiota emerged: the hypothesis of the retrograde flow and the one of the entero-mammary pathway [
7]. The retrograde flow represents the potential of bacterial transfer from the oral cavity of a breastfed neonate to the mammary duct system of the mother [
18]. Moossavi et al. [
19] support this theory by demonstrating the microbiological differences between breastfeeding and feeding pumped milk, finding increased numbers of
Vellionelaceae and
Actinobacteria members in the milk of directly breastfeeding mothers. The bacteria entero-mammary route suggests that non-pathogenic bacterial cells penetrate dendritic cells and macrophages in the GIT of the mother, which subjects them to transfer to the mammary gland via the lymph nodes [
6]. Jimenez et al. [
20] verified this hypothesis by supplementing breastfeeding women with
Lactobacillus salivarius CECT5713 and
Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714. After the 30-day oral intake of the supplementation, these strains were isolated from the milk of six out of ten women. Similar increase of the supplemented strains was surveilled in the study of Abrahamsson et al. [
21], which resulted in higher colony forming units (CFU) of
Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 in the colostrum of mothers after a 4-week intake of this strain during the last month of pregnancy. Numerous studies confirm or refute these theories, nonetheless, many individual factors significantly influence each case of mother-infant microbiota transmission.
Geographic location is proven to be another determinant of dominating microbiota in newborns. Several regions have already published information regarding the distinctive characteristics of its population, especially in respect to probiotic microbiota [
18,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27]. Rod-shaped, Gram-positive lactobacilli were found on many occasions in human milk and infant fecal samples, moreover, different locations report dissimilar dominating species of
Lactobacillaceae representatives that are perhaps, in one way or another, attributed to the local population lifestyle bias.
The lack of scientific data regarding the probiotic microbiota of breast milk and infant feces, characteristic of Bulgarian population brought about the base interest of the present study. Therefore, samples were collected from Bulgarian volunteers, breastfeeding mothers and their neonates. Basic information regarding any supplementation intake was requested, along with details about the pregnancy, birth mode, gender of the baby, etc. The samples were processed according to the requirements of lactic acid bacteria and the isolated strains were identified by the MALDI-TOF system. Dušková et al. [
28] reported that the MALDI-TOF MS method has a higher success rate (93%) than the polymerase chain reaction method (77%) inidentifying
Lactobacillus species at the species level [
29]. It can be concluded from many results in the literature that the MALDI-TOF MS method is applicable and accurate. Treven et a., [
30] characterized human milk microbiota (HMM) with 16S rRNA gene amplicon next-generation sequencing and cultivation/matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI-TOF-MS identification approaches. They analyzed 31 human milk samples from Slovenian mothers and showed that cultivation/MALDI-TOF MS was a suitable tool for culture-dependent determination of HMM. More than 200 Lactobacillus spectra are already available in the MALDI Biotyper (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) database and therefore is frequently used in the analysis of lactic acid bacteria from milk and dairy products [
28,
31,
32,
33,
34].
Numerous study groups [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42] have demonstrated the effectiveness of RAPD-PCR for identifying inter-species and intra-species diversity of newly found isolates. This approach requires unsophisticated execution, while the sample handing is simple and expeditious, and the results provide crucial information about the genetic variability in a group of species. Considering the lack of profound genetic information regarding the isolated strains, we proceeded with this methodology that additionally expanded our knowledge in relation to the inter-species variety in the samples from our cohort.
The goals of the current study were the identification and characterization of cultivable lactobacilli strains isolated from mature human breast milk and infant feces from Bulgarian cohort for the first time. In addition, we aimed to evaluate the suitability of RAPD analysis for monitoring the strain diversity among the established dominant bacterial population. The published research from Bulgaria on the composition of the human breast milk microbiota and infant feces microbiota, are extremely limited and such investigation will open novel perspectives in the field of reported differences in the composition of core microbiota of the mentioned niches depending on geographic location.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
All the studies involving human participants were reviewed according to the Declaration of Helsinki and complied with all rules of bioethics. All the procedures concerning sample collection and analyses were approved by the Ethics commission of Sofia University “St. Kliment Ohridski” (approval: №93-И-8≠1/24.01.2023/№93-I-8≠1/24.01.2023). The participants/donors provided their written informed consent to participate in our study. We handled all the samples and personal data anonymously and published the results using unique codes. Mature breast milk and fecal samples were collected from fourteen healthy mothers from Sofia region and their infants up to the first month after delivery. They donated one sample between 3-4 weeks from the beginning of the lactation period.
The following information was collected by the subjects: mode of delivery, infant’s type of feeding (exclusive breastfeeding, mixed feeding or only formula feeding), mother’s antibiotic and probiotic intake during pregnancy and lactation period and infant antibiotic and probiotic supplementation etc. (
Table S1).
2.2. Sample Processing
Donors were supplied with sterile tubes for human milk and fecal collection tubes with spoon and screw cap and before sample collection, mothers were given written instructions for standardization of the sampling process. Proper milk samples were obtained through the following protocol: (1) the nipple is washed thoroughly with soap and water; (2) the first few drops of milk were discarded; (3) 30 ml were collected in the respective collection tube, (4) samples were stored at 4⁰C (not more than 24 hours) until the transport to the laboratory. The protocol for fecal sample gathering was as follows: (1) fecal material (at least 2-3 grams) was collected from the diaper with the special spoon of the respective collection tube; (2) samples were stored at 4⁰C (not more than 24 hours) until delivery to the laboratory.
In the current study we used samples from fourteen independent tandem pairs mother-newborn. The samples from three of them were provided by the Human Milk Bank, Sofia, Bulgaria and 11 samples were from volunteer mothers.
2.3. Isolation of Bacterial Strains and Identification by MALDI-TOF-MS
Standard laboratory protocols were implemented for isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from human breast milk (HBM) and fecal samples. Nine ml of De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) broth medium (Oxoid Ltd. Hampdhire, England) supplemented with 0.05% L-cysteine was inoculated with 1 ml of fresh human breast milk or 200 mg of infant feces and cultivated for 48 h at 37⁰C in anaerobic conditions. All the samples were enriched in MRS broth up to 24 hours after the sampling time. Afterwards, appropriate ten-fold dilutions were plated on MRS agar (Oxoid) supplemented with vancomycin (10 mg/L). The petri dishes were incubated under anaerobic conditions (GasPak™ EZ Anaerobe Sachets, Becton, Dickinson Company, NJ, USA) at 37 °C for 48–72 h. Representative numbers of colonies randomly picked from assayed medium were purified by streaking on the new dishes with MRS agar media. The colonies were selected according to their morphological characteristics (colour, colony size, shape etc.). The pure isolates were tested for their Gram reaction, catalase activity. After a microscopic examination of the cell morphology of the isolates, only rod-shaped ones were used for further analysis. Gram-positive, catalase-negative colonies with rod-shaped cells, were selected as presumptive LAB and were stored at -20oC in MRS liquid medium, supplemented with 25% (v/v) of glycerol.
We used a matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass analysis (MALDI-TOF-MS) for direct identification of 68 preliminary selected pure isolates. A single overnight bacterial colony from each isolate were picked and transferred onto a polished steel MSP 96 target plate (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA, USA). The samples were covered with 1 µL of 70% formic acid and left to air-dry. Deposited samples were overlaid with 1 µL of a saturated-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (HCCA) matrix solution (Bruker Daltonics). Unidentified strains were resubmitted using the extended protocol. Mass spectra were acquired using the microflex LT mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics) and analyzed with the research-use-only (RUO) software workflow and reference library MBT v. 4.1.100.
2.4. 16. S rRNA Gene Sequencing.
Individual colonies from the selected newly isolated and identified by MALDI-TOF strains (
Table S4) as well as some marked as no reliable identification according to score values, were cultivated overnight in MRS broth. From each sample DNA was extracted with Quick-DNA™ Fungal/Bacterial Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research Corp., CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA samples were subjected to Sanger sequencing. For amplification of 16S rRNA genes primers 27F AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG and 1492R TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT were applied. PCR amplification were performed in a 25 μL volume, included 50-70 ng of isolated genomic DNA, 1 µL of each primer with a concentration of 10 µM and 12.5 µL of Supreme NZYTaq II 2x Green Master Mix (NZYtech, Lda, Lisboa, Portugal). The PCR program comprises: denaturation 95ºC for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94ºC for 30 sec, 50ºC for 30 sec and 72ºC for 85 sec, with the final extension of 7 min at 72ºC. The resulting PCR products (1500 bp) were purified using Agarose-out DNA Purfication Kit (EURx, Gdansk, Poland), according to the manufacturer’s instructions and directly sequenced by Macrogen Inc. (Netherlands) on an automatic sequencer (Applied Biosystems Inc., Foster City, CA, USA) with the di-deoxy termination procedure in both directions using the universal primers 27F and 1492R.). We used Vector NTI v. 10 software package the obtained sequences were assembled and manually edited. They were deposited in the GenBank of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database under accession numbers from PQ008844 to PQ008869.
All retrieved sequences were used for construction of phylogenetic tree, applying Neighbour-Joining method, Mega 6.0 program. The tree was constructed with 16S-rDNA nucleotide sequences and nearest high homology sequences, obtained after Blast search in the NCBI database.
2.5. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA-PCR and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (RAPD-PCR)
RAPD-PCR with single arbitrary primers was used for the molecular characterization of identified dominant bacterial group as well as to assess the presence of genetic variation within the group.
Strains belonging to species
L. rhamnosus (n=12),
L. paracasei (n=2) and one
Lactobacillus zeae (
Table S5) were genetically characterized by RAPD-PCR analysis. For this purpose, PCR amplification reactions were performed in a 25 μL volume, included 50-70 ng of isolated genomic DNA, 1 µL of each primer with a concentration of 10 µM and 12.5 µL of Supreme NZYTaq II 2x Green Master Mix (NZYtech, Lda, Lisboa, Portugal). All RAPD-PCR primers and reaction conditions are listed in
Table S2. All PCR reactions were performed with a C1000 Touch Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., USA). The obtained amplification products and DNA Ladder (peqGOLD 100 bp DNA Ladder Plus, VWR Int., Leuven, Belgium) were separated by electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel in 1xTBE buffer and stained with GelGreen™ Nucleic Acid Gel Stain (Biotium, CA, USA). The gels were documented by ChemiDoc
TM Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., USA). The type strains
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus ATCC 53103 and
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei ATCC 334 were used as comparative controls to verify the primer
specificity (Table S5). At least two independent amplification reactions were performed for each primer.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Human Breast Milk and Infant Feces
A total of 68 isolates were obtained from fourteen pairs of mothers and their newborns, corresponding to the initial characteristics of lactobacilli as the object of primary interest in this study. The macro- and micromorphology of the strains were estimated by plate counting on MRS agar.
Most bacterial colonies appear
white or translucent, generally round and smooth. Colonies with different morphologies were purified by streaking on new MRS agar plates. Microscope observations of the cell morphology of the isolates showed that the majority of them were represented by short rods or rods polymorphic in size, occurring singly or in short chains. All isolates that were rod-shaped, lacking catalase activity and
Gram positive were chosen for further characterization by MALDI-TOF-MS analyses. The obtained MALDI-TOF MS profiles were compared to the reference spectra of the BioTyper database and their similarity was expressed by score values. The colour code illustrate the matching of the experimental MALDI-TOF MS profile of tested strain and the reference MALDI-TOF MS profiles of the BioTyper database. The green, yellow and red colour indicate the meaning of the score value and its interpretation as high-confidence (2-3), low-confidence (1.70–1.99) and no organism identification, respectively. In total, five different genera of LAB including
Lacticaseibacillus, Limosilactibacillus, Lactiplantibacillus, Levilactobacillus, Lactobacillus and eight different species belonging to the mentioned genus
: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Limosilactibacillus reuteri, Limosilactibacillus fermentum, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Levilactobacillus brevis,
Lactobacillus gasseri, Lactobacillus zeae were identified. The 68 LAB colonies (29 from breast milk and 39 from infant feces, respectively) were identified by MALDI-TOF MS. The isolates were identified with a score value between 1.73 and 2.51 (
Table S3). 42 of them (61,8%) with score ≥ 2.0, 14 (20.6%) with score ≥ 1,9 and 12 isolates (17.6%) with score ≥ 1,7 (
Table S3).
The results obtained by MALDI-TOF showed that the dominating species was L. rhamnosus, found in five HBM samples and five fecal samples and representing up to 34% of all isolates. The second most abundant species was L. fermentum, constituting 26% of the isolated strains and found in two breast milk samples and five fecal ones. L. paracasei and L. reuteri followed, each corresponding to 15% of the detected species. L. paracasei was isolated from two breast milk samples and four fecal samples while L. reuteri from one HBM and three from feces. L. plantarum was detected in two HBM probes and one fecal, L. gasseri in only one breast milk sample. Although single strains, the presence of a species L. brevis and L. zeae was found. They were both isolated only from HBM samples (Fig. S1).
The presence of valuable ingredients in breast milk, including beneficial microbiota, depends on multiple factors, mainly maternal lifestyle, conditions, geography [
22], etc. The microbial characteristics of infant gut microbiota that, even though originating during pregnancy, are defined by another set of factors, such as birth mode, gestational age, hospital environment, and the occurrence of formula feeding [
43]. However, the most significant impact on the neonate trophic and metabolic characteristics [
6], immune system development, and infection susceptibility is owed to the breastfeeding manners.
Staphylococci, Streptococci, Corynebacteria, Propionibacteria, and some lactic acid bacteria a
re among the traditionally reported bacteria [6,44,45] in human breast milk. The probiotic microflora of breast milk has been of great scientific interest during the recent years, its origin, distribution and transmission from the mother to the child, along with the different species, strains and their metabolic profile, which determines their potentially beneficial functions [6].
Geographical location plays a pivotal role in microbiota proportions and has been the main factor among many researches [18,22,23,25–27]. Ding et al.
(2019) demonstrate the prevailing tendency of L. reuteri and L. gasseri in breast milk among Chinese population by sampling 89 healthy women from 11 different regions [23]. L. gasseri was also documented as the most frequently found species in human milk and neonate feces from the previous Lactobacillus genus in Spain [18,26] and Ireland [46]. Albesharat et al.
[45] report L. plantarum, L. fermentum and L. brevis
as the main Lactobacillaceae representatives not only in Syrian breast milk, but also infant and mother’s feces, as well as local fermented foods. In Germany and Austria, the dominating lactobacilli species were found to be L. salivarius, followed by L. fermentum, according to Soto et al.
[24]. Over 30% of the isolates in our study belonged to the L. rhamnosus species, a finding suggesting that this species is potentially the main representative of culturable Bulgarian breast milk lactic acid microbiota. Lack of previously reported data on this matter additionally reinforces the significance of the obtained results, but also underlines the need for further work in the field. The only data published so far concerning the investigation of LAB with origin from human breast milk in Bulgaria were from Mollova et al.
They studied genomic and phenotypic aspects of the L. plantarum PU3 strain that showed potential as a probiotic agent
[47].
L. fermentum was the second most encountered isolate in human milk and neonate feces, a result also manifested in the works of Albesharat et al.
[45] and Soto et al.
[24]. Moreover, the prevalence of L. rhamnosus among other lactobacilli in the infant fecal samples, followed by the L. fermentum representatives was also observed by Ahrné et al. [
48] in Swedish children before weaning.
Mitsou et al.
(2008) reported predominance of L. rhamnosus in stool samples of healthy Greek neonates, and L. paracasei as the third most abundant lactobacilli representative [25]. Nikolopoulou et al.
(2021) investigated breast milk samples collected from 100 healthy women in Greece. Twenty-six (26) samples were colostrum and seventy-four (74) mature breast milk. The presence of the genus Lactobacillus was identified in the 46.2% of colostrum and 24.3% of mature breast milk
[49].
Eventually, different geographic regions display unique microbiological profiles, probably related to lifestyle, climate, customs, or genetics. However, notable factor for the reported results is the individuality of the participants in similar studies, and the normal deviations that occur in the microbiota of a particular donor. Therefore, the number of subjects is determining for announcing the most accurate information.
Recently, a correlation between the infant’s and adults’ gut microbiome has been reported, indicating that the infant’s gut is initially colonized by bacteria originating from either breast milk or the environment [
50].
In our study similar dynamics of Lactobacillaceae microbiota is displayed in Bulgarian human breast milk and neonate fecal samples, whilst more than 50% of all of the detected species were found in both samples of the tandem pairs mother-child. For instance, L. fermentum was discovered in probes El (BM) and El (F), as well as Y (BM) and Y (F). In the same manner, M (BM) and M (F), N (BM) and N (F), KV (BM) and KV (F), all contained isolates of L. rhamnosus. The strains of L. paracasei followed the same principle by being presented in M (BM) and M (F), KV (BM) and KV (F). L. plantarum was isolated from tandem pair Sv. This microbial succession from mother’s milk to the infant’s gut exemplifies the notability of breastfeeding and its crucial role in gut microbiota development in infants (Table S6). However, Zhang et al.
(2020) report lack of correlation between lactobacilli isolated from breast milk and infant feces in their research [27]. We also detected some strains isolated only from HBM or feces. In our study, we revealed for the first time the core lactobacilli microbiota of breast milk of healthy Bulgarian mothers as well as the core lactobacilli microbiota isolated from infant feces. We found out that the dominant LAB in the both type of tested samples (HBM and feces) were L. rhamnosus, L. fermentum, L. paracasei and L. reuteri. Moreover, we isolated L. plantarum and L. gasseri from HBM and L. plantarum, L. zeae and L. brevis from feces according to MALDI-TOF MS identification, even though they represented small percentages of the total amount of the identified species. Various factors such as mother’s life style, lactation period, residential location may contribute to the presence of those species in the tested samples.
In fine, we succeed to identify six species from HBM and seven species from feces. Interestingly, despite the diversity of species, combination of not more than two species from the different samples was isolated.
There are two main hypothesis regarding the origin of breast milk microbiota, the retrograde flow of bacteria during breastfeeding and the entero-mammary pathway, which states that the breast milk bacteria source is the mother’s gut microbiota [35]. In the current study, both hypotheses provide a tendency of accuracy considering the cases, in which presence of one strain in both a breast milk and a stool sample was surveilled. Therefore, no conclusion on the breastmilk microbiota origin could be provided. Additional experimental work, including mother fecal samples for reference, along with more participants for increased factuality would shed light on the accuracy of these hypothesis. In their study, Martín et al. [18] reported lack of strain similarity between human milk and breast skin or neonate fecal L. gasseri isolates, and suggested that the vast majority of lactic acid bacteria in the breast milk have an endogenous origin. No resemblance between infant fecal LAB and vaginal isolates from the respective mothers was observed, which raised the question whether mother vaginal microbiome impacts the naturally born neonate gut microbiota [18]. In contrast, Martin et al. [51] demonstrated cases of strain homogeneity of L. gasseri, L. fermentum, L. salivarius and other lactobacilli in breastmilk-infant fecal samples. The data displayed in our study corresponded to the similar findings. For that reason, our study additionally confirms the existing transfer of potentially probiotic microbiota from breast milk to the neonate gut.
3.2. 16 S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing
In order to confirm the obtained results by MALDI-TOF and to get more profound information regarding the abundance of LAB in Bulgarian human breast milk and neonate fecal samples, 26 isolates were selected for the proceeding 16S rDNA sequencing (
Table S4). The strains were chosen based on sample type (almost identical number of strains originating from milk and fecal samples), presence of the species in both subjects in a mother-infant tandem pair, for example, M1-1, M1F-2, KV1-1, KV1F-4, KV1F-5, N1-1, N1F-2, El1-2, El1F-3, Sv1-1, Sv2F-1 Some strains found only in one member of the tandem pair were also included in the sequencing analysis (Zdr, Iv, Hr, L1, 40/2, Y1F). These isolates were used to reveal potentially individual differences among donors, like Zdr1F-1 and Y1F-3, both belonging to
L. fermentum. In the same principle, we selected the
L. rhamnosus isolates L1-1, Hr1F-1 and 40/2F-1. Also, we sequenced some isolates with the same origin in order to determine the presence of potential species diversity (1/24-1 and 1/24-2, Iv1-1 and Iv1-2) in a single sample. Lastly, the only representatives of
L. gasseri (1/24-1, 1/24-2)
, L. brevis and
L. zeae, (5/24F-1 and 40/2F-2, respectively) were incorporated because of their non-repetitiveness and exclusivity.
The PCR amplification resulted in PCR products in approximately 1500 bp. For the identification and phylogenetic determination the obtained sequences [52] and their retrieved nearest relatives from BLASTn search into the GenBank standard database non-re-dundant-nr/nt were used. Thе obtained results identified 26 different sequences, which identities varied from 99,56 % (21 sequnces) to 100 % (3 sequences). Only two had a lower indetities of about 99,30 %.
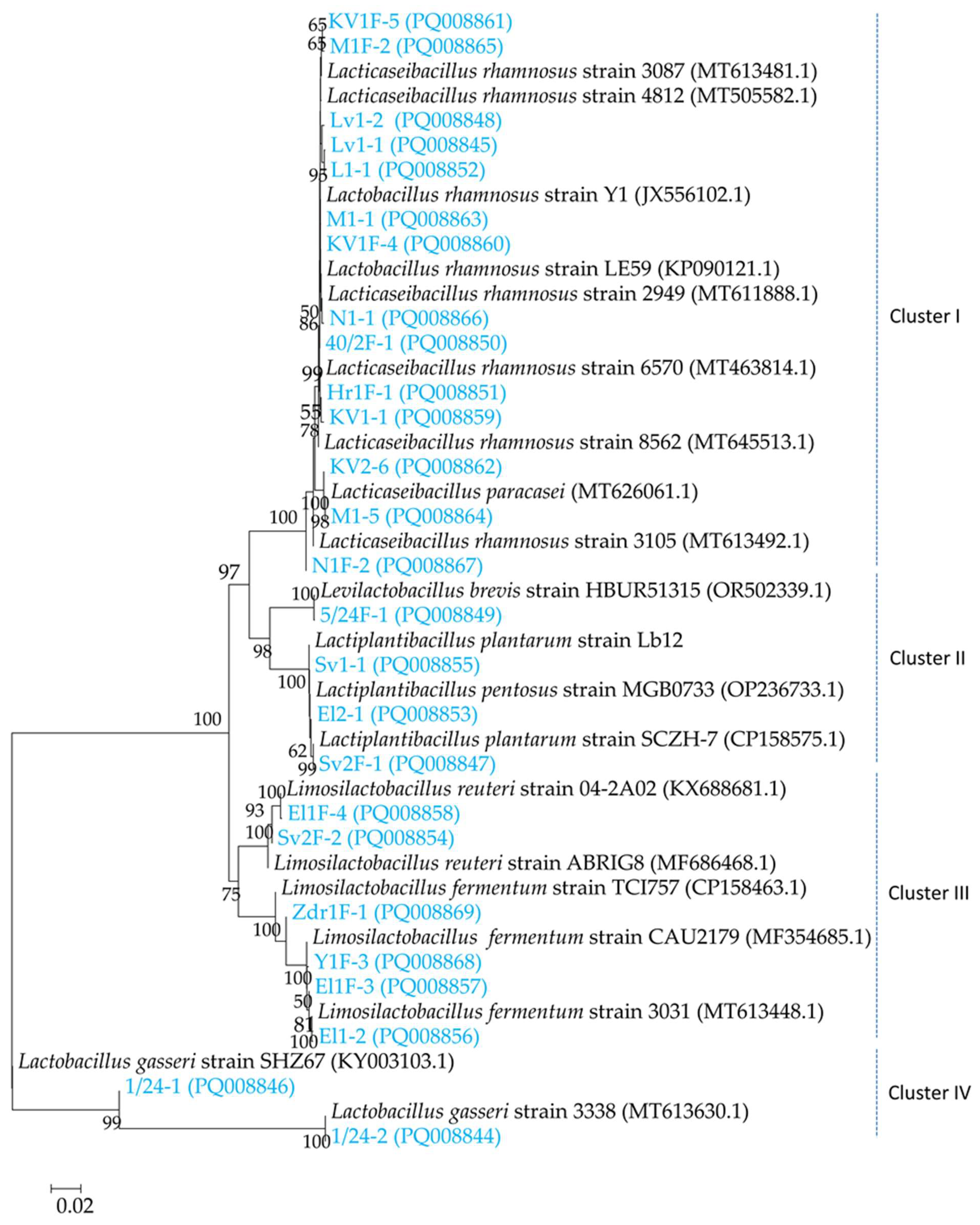
To strengthen the MALDI-TOF data, we performed the identification of 26 selected strains by 16S rDNA sequencing. The combined results from MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the 26 obtained sequences belonged to the 5 genera,
Lacticaseibacillus, Lactobacillus, Limosilactibacillus, Lactiplanplantibacillus and
Levilactobacillus. In the same time, the phylogenetic tree showed presence of four clusters: the first cluster (Cluster I), consisted of 12 different
L. rhamnosus strains and two
L. paracasei strains. The second cluster (Cluster II) was divided into two subclusters, which contained 1 strain
L. brevis and 2 strains
L. plantarum and 1 strain L. pentosus (strain El2-1; Notably, MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry identified El2-1 as
L. plantarum with score value of 2.02). A third cluster (Cluster III) was formed also with two subclusters, including 2 strains
L. reuteri and 4 strains
L. fermentum. Cluster IV included 2 strains of
L. gasseri. MALDI-TOF MS identification also showed the presence of strain
L. zeae (40/2F-2) but 16S rDNA sequencing did not confirm it. The score value of MALDI-TOF MS identification of the strain was 2.06 and the second-best match was
L. rhamnosus with score 1.90. We supposed that MALDI-TOF MS may generate too similar spectra for
L. zeae and
L. rhamnosus as 16S rDNA studies have shown that these two species are closely related within the
L. casei group [
53].
The applied approach by 16S rDNA sequencing and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in this study support the idea of rich intragenic diversity in the samples with domination of the Lacticaseibacillus genus.
Figure 1.
Neigbour—joining phylogenetic tree, of 26 LAB strains based on 16S rDNA gene sequences.
Figure 1.
Neigbour—joining phylogenetic tree, of 26 LAB strains based on 16S rDNA gene sequences.
3.3. Strain Diversity of L. rhamnosus (Cluster I Strain Group)
RAPD is a useful tool for generating genomic information of newly isolated strains. This technique uses a single short (around 10 bases in length) primer [
39] that randomly hybridizes to a location of DNA, which gets amplified and after electrophoretic separation produces a fingerprint profile, utilized in demonstrating genetic variability between two or more isolates [
36]. In their study, Mahenthiralingam et al. (2009) thoroughly investigate the discriminative ability and the reproducibility of the RAPD-PCR by performing RAPD fingerprinting using a set of 100 primers. Even though this method was noted for its low reproducibility [
40], the obtained results demonstrate high reproducibility, proper clustering of
L. casei and
L. acidophilus group representatives, and clear differentiation between genetically distant strains of LAB and different members of the same cluster [
38]. Many genetic variability determining methods were compared in the study of Jarotski et al. (2020), with PCR-RAPD being described by the authors as one of high differential strength. They tested the distinguishing properties of four RAPD primers and discovered that 80A_RAPD, 80B_RAPD_M13 and 80C_RAPD_OPT-14 effectively differentiate between 30 lactobacilli strains, belonging to the
L. casei group [
37]. These and other researches [40, 41] proving the capacity of RAPD-PCR analysis for genetic variability detection determined its implementation in the following study of genetic diversity of species belonging to the
L. casei group.
L. casei group includes species of
L. rhamnosus,
L. paracasei and
L. casei that possess certain metabolic, morphological and genetic similarities making their differentiation complicated [
37]. Therefore, we proceeded with differentiation between the isolates positioned in Cluster I in the neighbor joining phylogenic tree.
Fifteen strains, belonging to cluster I and two type strains
L. paracasei ATCC 334 and
L. rhamnosus ATCC 53103 were subjected to RAPD-PCR analysis in order to define any strain diversity or similarity within the established dominant bacterial group. The genetic fingerprinting was performed by using four short-length single primers RAPD-04, 80A_RAPD, 80B_RAPD_M13 and 80C_RAPD_OPT-14 described in
Table S2. Primer RAPD-04 was selected for its superior discriminative power to five other RAPD primers (opp-07, opp-08, opp-09, opp-14, RAPD-06) (data not shown). On the other hand, primers 80A_RAPD, 80B_RAPD_M13 and 80C_RAPD_OPT-14 were appointed based on literature data [37, 41].
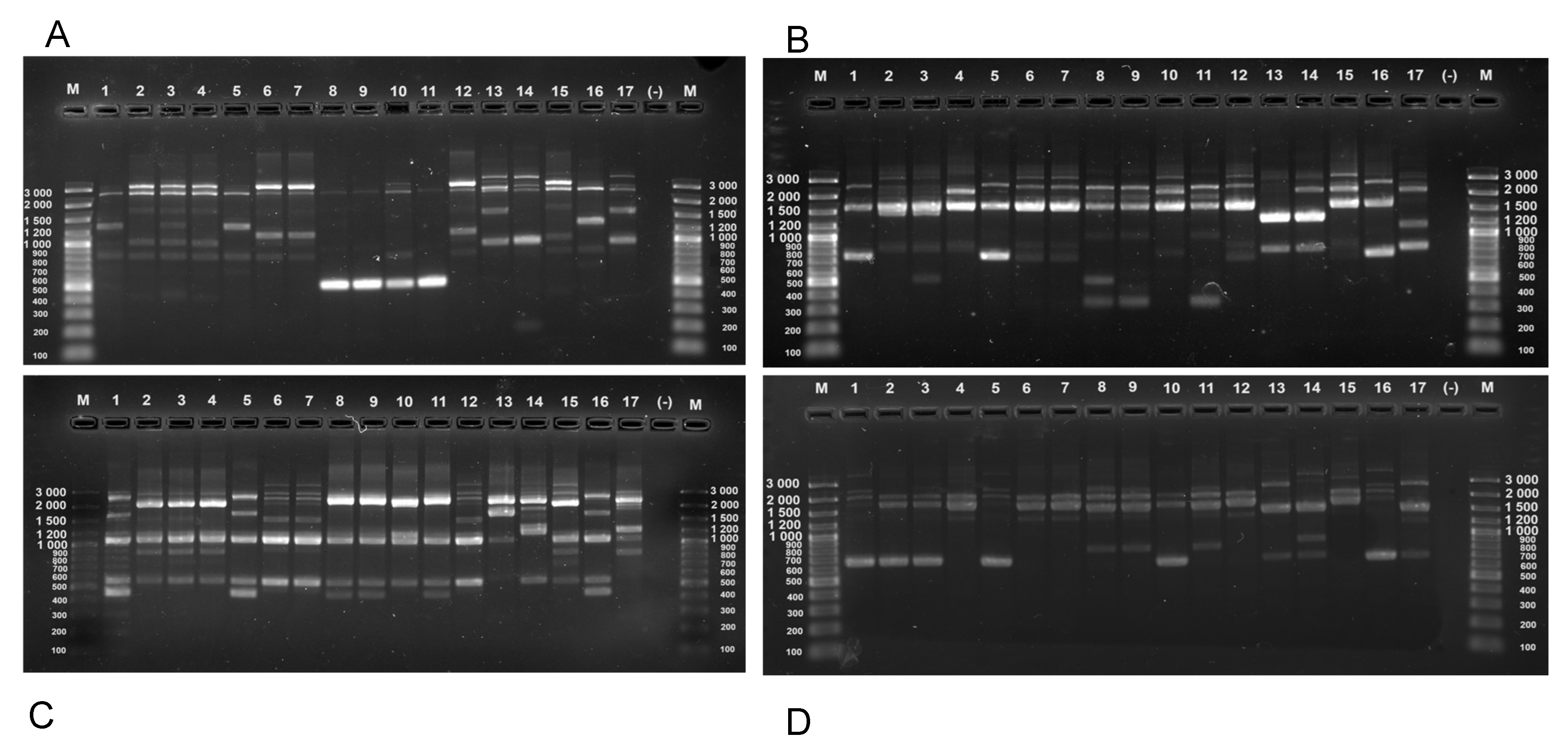
The obtained fingerprinting profiles of the strains from cluster I manifested genetic variations as well as similarities, not only between isolates originating from one tandem pair mother-child, but also from different donors and sample types (
Figure 2). With regard to primer RAPD-04, for example, the isolates were divided into five genotypes. Strains Iv1-2, L1-1, and N1F-2 (lanes 2, 4, and 15, respectively) were not only from different breast milk samples, but also exhibited the same fingerprinting profile as strain KV1F-4 (lane 6). Strain Iv1-1 (lane 3) possessed a slightly different profile from the first group because there was one additional band between 1200 and 1500 bp. The third group consisting of three strains KV1F-4 (lane 6), N1-1 (lane 7) KV1-1 (lane 12) also exhibited the same fingerprinting profile as the first group but with one exception. There was a band shifted from 1000 bp to around 1200 bp. The similarity between strain KV1F-4 (lane 6) and strain KV1-1 (lane 12) could be explained by the fact that they belong to one tandem pair mother-child. Likewise, strains 40/2F-1 (lane 8), 40/2F-2 (lane 9), KV1F-5 (lane 10) and Hr1F-1 (lane 11) displayed identical profiles, even though they were isolated from different donors, they were all of fecal origin. Isolates M1F-2 (lane 1) and M1-1 (lane 5) were resembling one another, and were most closely related to the type strain
L. rhamnosus ATCC 53103 (lane 16). We observed that the two
L. paracasei representatives, KV2-6 (lane 13) and M1-5 (lane 14) formed different profiles. They differed from one another by a band formed between 1500 and 2000 bp, present in KV2-6. The same band was in the profile of type strain
L. paracasei ATCC 334 also. The current data signified not only microbial, but also strain analogy between different subjects in the current cohort.
The fingerprinting profiles of L. rhamnosus strains were grouped almost identically when using primers RAPD-04 and RAPD 80 A, with two exceptions. Strain Iv1-1 (lane 3) was group together with strains Iv1-2, L1-1, and N1F-2 (lanes 2, 4, and 15, respectively). Also, strain KV1F-5 (lane 10) showed certain variation from 40/2F-1 (lane 8), 40/2F-2 (lane 9), and Hr1F-1 (lane 11), as the band at 400 bp was absent, whereas one band between 1000 bp and 1200 bp appeared, so it generated an individual profile. All other RAPD groups were the same. In fine, primer RAPD 80 A generated four genotypes. In regards to primer 80B_RAPD_M13, it formed almost completely different clustering between strains beside the observed similarity of the previous RAPD-PCR primers. Strains Iv1-2 (lane 2), Iv1-1 (lane 3) and KV1F-5 (lane 10) were also almost identical to the type strain but they were missing the band between 2000 and 3000 bp and showed one around 1900 bp. Isolates L1-1 (lane 4), KV1F-4 (lane 6), N1-1 (lane 7) and KV1-1 (lane 12) were more or less comparable to the N1F-2 (lane 15), which additionally confirms the taxonomical closeness between the identified strains in our cohort. Primer 80C_RAPD_OPT-14 displayed the most heterogenic fingerprinting profiles among the four RAPD-PCR primers. Isolates Iv1-2 (lane 2), Iv1-1 (lane 3) were almost identical, however, additional band was surveilled at 600 bp in lane 3. Strains KV1F-4 (lane 6), N1-1 (lane 7), KV1F-5 (lane 10), KV1-1 (lane 12) and N1F-2 (lane 15), exhibited similarity in their fingerprinting profiles, in the same manner as 40/2F-1 (lane 8), 40/2F-2 (lane 9), and Hr1F-1 (lane 11), except for the band around 600 bp in strain 40/2F-1. PCR-RAPD approach clearly defined the taxonomical relation and the strain diversity between the isolates from the samples in our cohort. The type strain L. rhamnosus (lane 16) and strains M1F-2 (lane 1) and M1-1 (lane 5) were grouped with identical fingerprints, nevertheless of the tested RAPD-PCR primers. On the other hand, the two L. paracasei (lanes 13 and 14), and the type strain (line 17), also showed different RAPD profiles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.R.; methodology, I.R., Z.U., and P.M.; Validation, I.R., A.A., Z.U., and P.M.; investigation, I.R., A.A., H.H., S.I., V.M., V.Y. I.Z. and D.D.; resources, T.N., T.G., P.H., M.T., M.R. and T.B.; writing—original draft preparation A.A. and I.R.; writing—review and editing, I.R., Z.U., and P.M.; software, I.R., and K.S.; supervision, I.R.; project administration, I.R.; All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.